California Eastern Laboratories
|
|
|
- Morgan Dickerson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 California Eastern Laboratories AN1026 1/f Noise Characteristics Influencing Phase Noise APPLICATION NOTE Abstract In applications such as VCO s where 1/f noise is one of the major contributors to phase noise, the device with the best 1/f noise will yield the best phase noise. To better understand how 1/f noise changes with bias and from device to device, the 1/f noise of two different bipolar devices were measured and compared. Nonlinear models were developed and the predicted and measured 1/f noise spectrums compared. In addition, how manufacturers quantify 1/f for simulation purposes is evaluated to provide the designer who is new to noise simulation with better insight into what the 1/f coefficient and exponent mean, and how the values effect the 1/f noise simulations. I. Introduction The phase noise of an oscillator, quantified by its short term frequency stability, determines a system s ability to separate adjacent channels. With the significant increase in portable, wireless traffic, better frequency stability is required. Phase noise becomes an important consideration. Choosing the appropriate topology for a low phase noise source is important, as is the choice of resonator and coupling network [1]. Many articles exist on how to design an oscillator for low phase noise by selecting the appropriate topology, resonator and coupling network[2]. This article focuses on the important characteristics for device evaluation and selection. II. Oscillator Phase Noise Phase perturbations due to random noise in the oscillator result in a random shift of the oscillator frequency. These random frequency variations are caused by thermal noise, shot noise, and flicker noise. Thermal noise is a function of the temperature, bandwidth and resistance, shot noise is a function of the DC bias current, and flicker noise is a function of the active device characteristics. Single sideband phase noise is defined as the noise power in a 1-Hz bandwidth at some offset frequency from the carrier, Fosc, and has the units of dbc/hz, Figure 1. Fosc Figure 1. Single sideband phase noise 1 Hz Oscillator phase noise has two components: phase noise resulting from direct upconversion of white noise and 1/f noise, and phase noise resulting from the changing phase of the noise sources modulating the oscillation frequency, freq. The composite oscillator phase noise spectrum consists of the white noise and 1/f noise directly upconverted around the carrier, and the phase modulated noise spectrum. The frequency noise in the frequency domain is converted to phase noise in the frequency domain by multiplying by 1/f 2. The white noise spectra, f 0, then contributes 1/f 2 and the 1/f noise spectra contributes 1/f 3, see Table 1. Noise Source Phase Noise Spectrum Upconverted freq white noise white noise 1/f 2 1/f noise 1/f noise 1/f 3 Table 1. Noise sources and their phase noise spectrum
2 For a low Q oscillator where the half-bandwidth frequency, fo/2q, is greater than the flicker corner frequency, fc, the oscillator phase noise characteristics will be determined by the white noise, 1/f 2, and the flicker noise, 1/f 3, Figure 2. SSB Phase Noise (dbc/hz) f -3 flicker FM f -2 white FM fc 1k 10k fo/2q 100k Baseband offset Frequency (Hz) Figure 2. Baseband noise spectrum for fc<fo/2q, Low Q. For a high Q oscillator where the halfbandwith frequency, fo/2q, is less than the flicker corner frequency, f c, the oscillator phase noise characteristics will be determined by the frequency modulated flicker noise, 1/f -3, and the upconverted 1/f noise, Figure 3. Flicker noise in BJTs is also known as 1/f noise because of the 1/f slope characteristics of the noise spectra. This noise is caused mainly by traps associated with contamination and crystal defects in the emitter-base depletion layer. These traps capture and release carriers in a random fashion. The time constants associated with the process produce a noise signal at low frequencies. The flicker noise spectral density is given by: S(f)df = (KF)IB AF df / Fc (1) where: KF = flicker noise constant AF = flicker noise exponent IB = DC base current Fc = flicker noise corner frequency A. Noise Test Setup The test setup to measure 1/f noise is shown in Figure 4. The 50 ohm terminations insure amplifier stability at higher frequencies. The entire test setup is contained in an EMI shielded box. The supply voltages, VBB and VCC are provided by batteries to eliminate 60 Hz noise. Vcc SSB Phase Noise (dbc/hz) f -3 flicker FM f -1 fo/2q k 10k Baseband offset Frequency (Hz) III. 1/f Measurements 100k Figure 3. Baseband noise spectrum for fc>fo/2q, High Q. 1/f measurements are performed to obtain the flicker noise frequency spectra and determine the flicker corner frequency. From this spectra, the simulation coefficient KF and the simulation exponent AF necessary for modeling the 1/f noise spectra can be determined. VBB LPF 50 Figure 4. 1/f Noise Test Setup LPF 50 FET Test Setup CPU/ Printer The measured 1/f noise spectrum for the at Vce = 3V, Ic=12mA is shown in Figure 5. The measured flicker corner frequency, Fmeas = 5.6kHz, is determined by noting the intersection of the 1/f noise spectrum and the white noise spectrum. This intersection is where the measured flicker noise power and the white noise power are equal.
3 K 5.6 KHz 10K 100K Bv(f) [dbv/hz] vs. f[hz] Figure 5. 1/f measurement for the at Vce=3V, Ic=12 ma To determine the intrinsic base flicker noise corner, F bn, requires solving the following equation [3]: F bn = F meas [1 + 1/β + 2V th G in /IB] (2) where: F bn = intrinsic base flicker noise corner F meas = measured flicker corner β = collector-base current gain V th = thermal voltage = kt/q G in = external input conductance IB = DC base biasing current The equation for the intrinsic base flicker corner modifies the measured flicker corner to account for the input conductance, base current, and DC current gain of the device. The formula for F bn is valid providing the measured output noise characteristics are dominated by the base flicker and base shot noise sources. The design of the test setup and selection of biasing circuitry is chosen to insure these conditions. B. Calculating AF and KF Measuring the flicker corner frequency at two different base currents provides two different flicker corner values. Using equation (3) twice, once for each IB and F bn value provides two equations and two unknowns, resulting in a solution for AF and KF. F bn = (KF)IB (AF-1) / 2q (3) The resulting expressions for AF and KF are: AF = log(f1) - log(f2) + Z (4) Z Z = log (IB1) - log (IB2) Calculated AF and KF values resulting from 1/f measurements for the NE68519 and the are provided in Table 2. NE68519 Ic VCE=1V VCE=3V VCE=1V VCE=3V (ma) AF KF AF KF AF KF AF KF K Table 2. AF and KF for the NE68519 and the (KF values are times ) C. Bias Dependency Next we examine the bias dependency of the flicker corner frequency for the same two NEC devices. The base voltage was varied to obtain the collector currents shown in Table 3. The flicker corner frequency, F bn, was determined at VCE=1V and VCE=3V as shown in Table 3 and Figure 6. Fbn (KHz) Ic NE68519 (ma) Vce=1V Vce=3V Vce=1V Vce=3V Table 3. F bn versus bias - NE68519, Fbn (KHz) Ic (ma) NE68519 Figure 6a. F bn at VCE=1V for the NE68519 and the KF = 10 (log (F bn ) + log (IB) (AF)log (IB)) (5)
4 Fbn (KHz) Ic (ma) NE Figure 6b. F bn at VCE=3V for the NE68519 and the K 100 1K 10K 5V (f) [dbv/hz] vs. f (Hz) 100K The flicker corner frequencies for the two devices are within 3% at the lower bias of Vce=1V and Ic=5mA; F bn = 5.8kHz for the NE68519 and Fbn=5.6kHz for the. At higher biases, the has lower 1/f noise. As the bias voltage increases from 1V to 3V with a constant collector current Ic=20mA, the amplitude of the 1/f slope is unchanged but the amplitude of the white noise floor increases due to the increase in thermal noise voltage as shown in Figure 7a. The higher noise floor results in a lower 1/f corner frequency of 11.8kHz at Vce=3V. At Vce=1V the 1/f corner frequency is 16kHz Figure 7b. 1/f measurement with Vce constant, Vce=3V, and Ic=5mA aand 10mA for the NE68519 IV. 1/f Noise Simulation A nonlinear model was developed for the NE68519 and the. The simulation schematic and the variable values for the are shown in Figures 8a and 8b. The simulator used is the LIBRA TM harmonic balance simulator by HP/EESOF [4]. The test bench is shown in Figure 8c. Note that AF=1.26 and KF=2.6e-14 to provide flicker noise simulation. Simulated 1/f noise for the at Vce=3V, Ic=10mA is shown in Figure 9. A. simulated versus measured V 1 V Measured 1/f noise spectra at Vce=3V, Ic=12mA, Figure 5, was compared to simulated 1/f noise at Vce=3V, Ic=10mA, Figure 9. Although the collector currents were 20% different, the 1/f corner frequencies - measured vs model - were within 10% of each other. The white noise floor was -149dB (measured) compared to -151dB (model) resulting in a 1.32% difference. The 1MHz noise amplitude was -131dB (measured compared to -132dB (modeled), a difference of only 0.76%. B. Modeling 1/f noise with AF and KF K 10K 100K 9V(f) [dbv/hz] vs. f[hz] Figure 7a. 1/f measurement with IC constant, Ic=20mA and Vce=1V and 3V for the NE68519 As the bias current increases from 5mA to 10mA and the bias voltage stays constant at Vce=3V, the 1/f spectrum amplitude increases proportionally with increases in base current, and the shot noise component of the white noise floor increases proportionally with increasing base current, Figure 7b. Most commercial simulators set AF and KF to default values of 1.0 and 0 respectively. Inspection of equation (1) shows that if KF = 0, the flicker noise spectral density will also be 0, resulting in the presence of white noise only. Examining figure 10c with KF=1e-13 shows the 1/f spectra approaching the white noise spectra. Figures 10a and 10b model the 1/f spectra changes as KF and AF are varied. Note that the Y- intercept of the 1/f spectra increases proportionally to KF, as expected from equation (1). The Y-intercept of the 1/f spectra decreases more rapidly with increases in AF. Equation (2) verifies this to be the case with the 1/f spectral density decreasing exponentially with increases in AF, since IB is less than unity.
5 Lc L = Lc AMMETER AMM1 Co RES C = RL R = 2000 TEMP = TEMP2 PORT P2 port = 2 PORT P1 port = 1 Ci_g C= RES AMMETER Rbb AMM2 R = rbb TEMP = TEMP2 Ccb C = Ccb Lb L = Lb BJT BJT1 AREA = 1 MODEL = NE688 chip model MODE = nonlinear Ccc C = Ccc La L = DCVS SRCc - DC = 23 Cc1 C = DCVS SRC1 _ DC = 5.48 Le L = Le BJTM NE688 chip model IS = is BR = br BF = bf NR = nr NF = nf VAR = var VAF = vaf IKR = ikr IKF = ikf ISC = isc ISE = ise NC = nc NE = ne RB = rb IRB = irb RBM = rbm RE = re RC = rc CJE = cje VJE = vje MJE = mje TF = tf XTF = xtf VTF = vtf ITF = itf PTF = 0 CJC = cjc VJC = vjc MJC = mjc XCJC = xcjc TR = tr CJS = 0 VJS = 0.75 MJ5 = 0 XTB = 0 EG = 1.11 XT = 3 KF = kf AF = af FC = fc TYPE = type NK = 0.50 TNOM = 27 FFE = 1 KB = 0 AB = 1 FB = 1 ISS = 0 NS = 1 Figure 8a. Simulation Schematic UNITS UNITS_DEFAULT FREQ=GHz RES=0hm COND=S =nh =pf LNG=mil TIME=psec Var Eqn ANG=deg POWER=dBm VOLT=V CUR=mA DIST=mi DATA TEMP TEMP_DEFAULT TEMP=27 DATA TEMP TEMP2 TEMP=0 DATA DATA DATA DATA RREF RREF_DEFAULT R=50 TAND TAND_DEFAULT TAND=0 SIGMA SIGMA_DEFAULT SIGMA=0 PERM PERM_DEFAULT MUR=1 TANM=0 VAR _VAR is=3.80e-16 bf= nf=1.00 vaf=28 ikf=0.60 ise=3.80e 15 ne=1.49 br=12.28 nr=1.10 var=3.50 ikr=0.06 isc=3.50e-16 nc=1.62 rb=6.14 irb=1.00e-03 rbm=3.50 re=0.40 rc=4.20 cje=7.96e-13 vje=0.71 mje=0.38 tf=1.10e-11 xtf=0.36 vtf=0.65 itf=0.61 ptf=50 cjc=5.49e-13 vjc=0.65 mjc=0.48 xcjc=0.56 tr=3.20e-11 fc=0.75 kf=2.60e-14 cf=1.26 Ccb=0.24 Cce=0.27 Lb=0.72 Lc=0.51 Le=0.19 rbb=50000 NE688_chip_model PARAMETERS AND BONDING PARASITICS DATE: 10/2/96 PROJECT NAME: LIBRA DEFAULT FILE: 68800_def Figure 8b. nonlinear model parameter values 68800_noise_sch X1 FREQUENCY FPLAN value = ESWEEP 1.00e e VNOISEQ VNOISEQ1 PORT = 2 OUTPUT EQUATION OUT EQN OUTEQN v_noise_out = 20* log(vnoiseq1) Figure 8c. test bench
6 68800_mod_noise10_tb v_noise_out 68800_noise OUT EQN Re Measured Model -132 db db KHz 6.3 KHz Frequency KHz VCE = 3 V IC = 10 ma Figure 9. 1/F noise simulation for the at Vce= 3V, Ic=10 ma AF = 1 AF = Frequency KHz AF = 1 to 2, KF = 5e-13 Vce = 3V Ic = 10ma Figure 10a. Effect of varying AF from 1 to 2 with KF=5e KF = 20e-13 KF = 10e-13 KF = 5e-13 Model Measured KF = 2e-13 KF = 1e db -149 db 0.1 Frequency KHz AF = 1, KF = 1e-13 to 2e-12 Ic = 10mA Figure 10b. Effect of varying KF from 1e-13 to 20-e-13 with AF= KF = 20e-13 KF = 10e-13 KF = 5e-13 KF = 2e-13 KF = 1e Frequency KHz AF = 1.6, Vce = 3V, KF = 1e-13 to 2e-12 Ic = 10mA Figure 10c. Effect of varying KF from 1e-13 to 20-e-13 with AF=1.6 CONCLUSIONS 1. Using the test setup and measurement techniques described, 1/f noise can be measured. 2. Using an accurate nonlinear model, 1/f noise simulations agree closely to measured data. 3. As Vce increases, the flicker corner increases as the white noise increases, but the magnitude of the 1/f noise is constant. 4. As base current increases, the flicker corner frequency increases with the magnitude of the 1/f noise and the increased shot noise current. 5. 1/f noise increases linearly as KF increases and decreases with increases in AF for IB less than 1.0 amp, as is expected from equation (1). REFERENCES [1] Roger Muat, Choosing devices for quiet oscillators, Microwave & RF, August 1984, pp [2] Grant Moulton, Dig for the roots of oscillator noise, Microwave & RF, pp , April [3] Julio Costa et al, Extracting 1/f Noise Coefficients for BJT s, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Vol. 41, No.11, pp , Nov [4] Simulating Noise in Nonlinear Circuits Using the HP Microwave and RF Design Systems, HP Product note , c California Eastern Laboratories Exclusive Agents for NEC RF, Microwave and Optoelectronic semiconductor products in the U.S. and Canada 4590 Patrick Henry Drive, Santa Clara, CA Telephone FAX Telex 34/6393 Internet: Information and data presented here is subject to change without notice. California Eastern Laboratories assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuits described herein and makes no representations or warranties, expressed or implied, that such circuits are free from patent infingement. California Eastern Laboratories 02/04/2003
New Models Simulate RF Circuits
 New Models Simulate RF Circuits Its no news to those who simulate that the accuracy of SPICE is directly related to the accuracy of the models. What may be news is that simulation of high frequency circuits
New Models Simulate RF Circuits Its no news to those who simulate that the accuracy of SPICE is directly related to the accuracy of the models. What may be news is that simulation of high frequency circuits
VCO Phase noise. Characterizing Phase Noise
 VCO Phase noise Characterizing Phase Noise The term phase noise is widely used for describing short term random frequency fluctuations of a signal. Frequency stability is a measure of the degree to which
VCO Phase noise Characterizing Phase Noise The term phase noise is widely used for describing short term random frequency fluctuations of a signal. Frequency stability is a measure of the degree to which
DATA SHEET. BFG540W BFG540W/X; BFG540W/XR NPN 9 GHz wideband transistor DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product specification Supersedes data of 1997 Dec 04
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET BFGW BFGW/X; BFGW/XR Supersedes data of 997 Dec May 3 BFGW BFGW/X; BFGW/XR FEATURES MARKING High power gain Low noise figure High transition frequency Gold metallization
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET BFGW BFGW/X; BFGW/XR Supersedes data of 997 Dec May 3 BFGW BFGW/X; BFGW/XR FEATURES MARKING High power gain Low noise figure High transition frequency Gold metallization
Transistor Models. ampel
 Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Using Texas Instruments Spice Models in PSpice
 Application Report SLOA070 September 2001 Using Texas Instruments Spice Models in PSpice Bruce Carter ABSTRACT Texas Instruments provides Spice models for operational amplifiers. These Spice models, however,
Application Report SLOA070 September 2001 Using Texas Instruments Spice Models in PSpice Bruce Carter ABSTRACT Texas Instruments provides Spice models for operational amplifiers. These Spice models, however,
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor
 The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
California Eastern Laboratories AN1023 Converting GaAs FET Models For Different Nonlinear Simulators
 California Eastern Laboratories AN1023 Converting GaAs FET Models For Different Nonlinear Simulators APPLICATION NOTE INTRODUCTION This paper addresses the issues involved in converting GaAs models for
California Eastern Laboratories AN1023 Converting GaAs FET Models For Different Nonlinear Simulators APPLICATION NOTE INTRODUCTION This paper addresses the issues involved in converting GaAs models for
Making Accurate Voltage Noise and Current Noise Measurements on Operational Amplifiers Down to 0.1Hz
 Author: Don LaFontaine Making Accurate Voltage Noise and Current Noise Measurements on Operational Amplifiers Down to 0.1Hz Abstract Making accurate voltage and current noise measurements on op amps in
Author: Don LaFontaine Making Accurate Voltage Noise and Current Noise Measurements on Operational Amplifiers Down to 0.1Hz Abstract Making accurate voltage and current noise measurements on op amps in
Optimizing VCO PLL Evaluations & PLL Synthesizer Designs
 Optimizing VCO PLL Evaluations & PLL Synthesizer Designs Today s mobile communications systems demand higher communication quality, higher data rates, higher operation, and more channels per unit bandwidth.
Optimizing VCO PLL Evaluations & PLL Synthesizer Designs Today s mobile communications systems demand higher communication quality, higher data rates, higher operation, and more channels per unit bandwidth.
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
 LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
The front end of the receiver performs the frequency translation, channel selection and amplification of the signal.
 Many receivers must be capable of handling a very wide range of signal powers at the input while still producing the correct output. This must be done in the presence of noise and interference which occasionally
Many receivers must be capable of handling a very wide range of signal powers at the input while still producing the correct output. This must be done in the presence of noise and interference which occasionally
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers
 BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES
 200 WOOD AVENUE, MIDDLESEX, NJ 08846 PHONE (732) 469-9510 FAX (732) 469-0418 MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES MTN-107 TEST SETUP FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF X-MOD, CTB, AND CSO USING A MEAN SQUARE CIRCUIT AS A DETECTOR
200 WOOD AVENUE, MIDDLESEX, NJ 08846 PHONE (732) 469-9510 FAX (732) 469-0418 MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES MTN-107 TEST SETUP FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF X-MOD, CTB, AND CSO USING A MEAN SQUARE CIRCUIT AS A DETECTOR
How PLL Performances Affect Wireless Systems
 May 2010 Issue: Tutorial Phase Locked Loop Systems Design for Wireless Infrastructure Applications Use of linear models of phase noise analysis in a closed loop to predict the baseline performance of various
May 2010 Issue: Tutorial Phase Locked Loop Systems Design for Wireless Infrastructure Applications Use of linear models of phase noise analysis in a closed loop to predict the baseline performance of various
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference (selectivity, images and distortion) Large dynamic range
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference (selectivity, images and distortion) Large dynamic range
LM1596 LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator
 LM1596 LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator General Description The LM1596 LM1496 are doubled balanced modulator-demodulators which produce an output voltage proportional to the product of an input (signal)
LM1596 LM1496 Balanced Modulator-Demodulator General Description The LM1596 LM1496 are doubled balanced modulator-demodulators which produce an output voltage proportional to the product of an input (signal)
Application Note SAW-Components
 Application Note SAW-Components Principles of SAWR-stabilized oscillators and transmitters. App: Note #1 This application note describes the physical principle of SAW-stabilized oscillator. Oscillator
Application Note SAW-Components Principles of SAWR-stabilized oscillators and transmitters. App: Note #1 This application note describes the physical principle of SAW-stabilized oscillator. Oscillator
Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
INTELLIGENT INTERACTIVE SYNTHESIZER SURFACE MOUNT MODEL: MFSH615712-100
 SURFACE MOUNT MODEL: MFSH6572 65-72 MHz FEATURES: Small Size, Surface Mount (.6" x.6") Low Phase Noise Standard Programming Interface Ultra Wide Tuning Range Lead Free - RoHS Compliant Patented REL-PRO
SURFACE MOUNT MODEL: MFSH6572 65-72 MHz FEATURES: Small Size, Surface Mount (.6" x.6") Low Phase Noise Standard Programming Interface Ultra Wide Tuning Range Lead Free - RoHS Compliant Patented REL-PRO
BJT Ebers-Moll Model and SPICE MOSFET model
 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
APN1009: A Varactor Controlled Phase Shifter for PCS Base Station Applications
 APPLICATION NOTE APN1009: A Varactor Controlled Phase Shifter for PCS Base Station Applications Introduction Power amplifiers in today s base stations use compensation techniques to reduce distortion.
APPLICATION NOTE APN1009: A Varactor Controlled Phase Shifter for PCS Base Station Applications Introduction Power amplifiers in today s base stations use compensation techniques to reduce distortion.
LOW POWER FM TRANSMITTER SYSTEM
 Order this document by MC28/D MC28 is a onechip FM transmitter subsystem designed for cordless telephone and FM communication equipment. It includes a microphone amplifier, voltage controlled oscillator
Order this document by MC28/D MC28 is a onechip FM transmitter subsystem designed for cordless telephone and FM communication equipment. It includes a microphone amplifier, voltage controlled oscillator
CONDUCTED EMISSION MEASUREMENT OF A CELL PHONE PROCESSOR MODULE
 Progress In Electromagnetics esearch C, Vol. 42, 191 203, 2013 CONDUCTED EMISSION MEASUEMENT OF A CELL PHONE POCESSO MODULE Fayu Wan *, Junxiang Ge, and Mengxiang Qu Nanjing University of Information Science
Progress In Electromagnetics esearch C, Vol. 42, 191 203, 2013 CONDUCTED EMISSION MEASUEMENT OF A CELL PHONE POCESSO MODULE Fayu Wan *, Junxiang Ge, and Mengxiang Qu Nanjing University of Information Science
TS321 Low Power Single Operational Amplifier
 SOT-25 Pin Definition: 1. Input + 2. Ground 3. Input - 4. Output 5. Vcc General Description The TS321 brings performance and economy to low power systems. With high unity gain frequency and a guaranteed
SOT-25 Pin Definition: 1. Input + 2. Ground 3. Input - 4. Output 5. Vcc General Description The TS321 brings performance and economy to low power systems. With high unity gain frequency and a guaranteed
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators
 Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
S-Band Low Noise Amplifier Using the ATF-10136. Application Note G004
 S-Band Low Noise Amplifier Using the ATF-10136 Application Note G004 Introduction This application note documents the results of using the ATF-10136 in low noise amplifier applications at S band. The ATF-10136
S-Band Low Noise Amplifier Using the ATF-10136 Application Note G004 Introduction This application note documents the results of using the ATF-10136 in low noise amplifier applications at S band. The ATF-10136
RF Network Analyzer Basics
 RF Network Analyzer Basics A tutorial, information and overview about the basics of the RF Network Analyzer. What is a Network Analyzer and how to use them, to include the Scalar Network Analyzer (SNA),
RF Network Analyzer Basics A tutorial, information and overview about the basics of the RF Network Analyzer. What is a Network Analyzer and how to use them, to include the Scalar Network Analyzer (SNA),
LM566C Voltage Controlled Oscillator
 LM566C Voltage Controlled Oscillator General Description The LM566CN is a general purpose voltage controlled oscillator which may be used to generate square and triangular waves the frequency of which
LM566C Voltage Controlled Oscillator General Description The LM566CN is a general purpose voltage controlled oscillator which may be used to generate square and triangular waves the frequency of which
Tx/Rx A high-performance FM receiver for audio and digital applicatons
 Tx/Rx A high-performance FM receiver for audio and digital applicatons This receiver design offers high sensitivity and low distortion for today s demanding high-signal environments. By Wayne C. Ryder
Tx/Rx A high-performance FM receiver for audio and digital applicatons This receiver design offers high sensitivity and low distortion for today s demanding high-signal environments. By Wayne C. Ryder
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED
 Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v.113 Frequency Divider Operation
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v.113 Frequency Divider Operation
Understanding Noise Figure
 Understanding Noise Figure Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul One of the most frequently discussed forms of noise is known as Thermal Noise. Thermal noise is a random fluctuation in
Understanding Noise Figure Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul One of the most frequently discussed forms of noise is known as Thermal Noise. Thermal noise is a random fluctuation in
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design
 Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
Features. Applications. Description. Blockdiagram. K-LC1a RADAR TRANSCEIVER. Datasheet
 Features 24 GHz K-band miniature transceiver 180MHz sweep FM input (n.a. for K-LC1a_V2) Dual 4 patch antenna Single balanced mixer with 50MHz bandwidth Beam aperture 80 /34 15dBm EIRP output power 25x25mm
Features 24 GHz K-band miniature transceiver 180MHz sweep FM input (n.a. for K-LC1a_V2) Dual 4 patch antenna Single balanced mixer with 50MHz bandwidth Beam aperture 80 /34 15dBm EIRP output power 25x25mm
7-41 POWER FACTOR CORRECTION
 POWER FTOR CORRECTION INTRODUCTION Modern electronic equipment can create noise that will cause problems with other equipment on the same supply system. To reduce system disturbances it is therefore essential
POWER FTOR CORRECTION INTRODUCTION Modern electronic equipment can create noise that will cause problems with other equipment on the same supply system. To reduce system disturbances it is therefore essential
PECL and LVDS Low Phase Noise VCXO (for 65-130MHz Fund Xtal) XIN XOUT N/C N/C CTRL VCON (0,0) OESEL (Pad #25) 1 (default)
 Reserved BUF BUF 62 mil OESEL^ Reserved Reserved PL520-30 FEATURES 65MHz to 130MHz Fundamental Mode Crystals. Output range (no PLL): 65MHz 130MHz (3.3V). 65MHz 105MHz (2.5V). Low Injection Power for crystal
Reserved BUF BUF 62 mil OESEL^ Reserved Reserved PL520-30 FEATURES 65MHz to 130MHz Fundamental Mode Crystals. Output range (no PLL): 65MHz 130MHz (3.3V). 65MHz 105MHz (2.5V). Low Injection Power for crystal
Using ADS to simulate Noise Figure
 Using ADS to simulate Noise Figure ADS can be used to design low noise amplifiers much in the same way you have already used it for MAG or MSG designs. Noise circles and available gain circles are the
Using ADS to simulate Noise Figure ADS can be used to design low noise amplifiers much in the same way you have already used it for MAG or MSG designs. Noise circles and available gain circles are the
Wide Bandwidth, Fast Settling Difet OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 Wide Bandwidth, Fast Settling Difet OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES HIGH GAIN-BANDWIDTH: 35MHz LOW INPUT NOISE: 1nV/ Hz HIGH SLEW RATE: V/µs FAST SETTLING: 24ns to.1% FET INPUT: I B = 5pA max HIGH OUTPUT
Wide Bandwidth, Fast Settling Difet OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES HIGH GAIN-BANDWIDTH: 35MHz LOW INPUT NOISE: 1nV/ Hz HIGH SLEW RATE: V/µs FAST SETTLING: 24ns to.1% FET INPUT: I B = 5pA max HIGH OUTPUT
Analog Optical Isolators VACTROLS
 Analog Optical Isolators VACTROLS What Are Analog Optical Isolators? PerkinElmer Optoelectronics has been a leading manufacturer of analog optical isolators for over twenty years and makes a broad range
Analog Optical Isolators VACTROLS What Are Analog Optical Isolators? PerkinElmer Optoelectronics has been a leading manufacturer of analog optical isolators for over twenty years and makes a broad range
S-parameter Simulation and Optimization
 S-parameter Simulation and Optimization Slide 5-1 S-parameters are Ratios Usually given in db as 20 log of the voltage ratios of the waves at the ports: incident, reflected, or transmitted. S-parameter
S-parameter Simulation and Optimization Slide 5-1 S-parameters are Ratios Usually given in db as 20 log of the voltage ratios of the waves at the ports: incident, reflected, or transmitted. S-parameter
Silicon Schottky Barrier Diode Bondable Chips and Beam Leads
 DATA SHEET Silicon Schottky Barrier Diode Bondable Chips and Beam Leads Applications Detectors Mixers Features Available in both P-type and N-type low barrier designs Low 1/f noise Large bond pad chip
DATA SHEET Silicon Schottky Barrier Diode Bondable Chips and Beam Leads Applications Detectors Mixers Features Available in both P-type and N-type low barrier designs Low 1/f noise Large bond pad chip
LM833 LOW NOISE DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 LOW NOISE DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER LOW VOLTAGE NOISE: 4.5nV/ Hz HIGH GAIN BANDWIDTH PRODUCT: 15MHz HIGH SLEW RATE: 7V/µs LOW DISTORTION:.2% EXCELLENT FREQUENCY STABILITY ESD PROTECTION 2kV DESCRIPTION
LOW NOISE DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER LOW VOLTAGE NOISE: 4.5nV/ Hz HIGH GAIN BANDWIDTH PRODUCT: 15MHz HIGH SLEW RATE: 7V/µs LOW DISTORTION:.2% EXCELLENT FREQUENCY STABILITY ESD PROTECTION 2kV DESCRIPTION
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B3 - Using nonlinearity» Tuned amplifier» Frequency multiplier» Gain compressor» Adding feedback AY 2015-16 15/03/2016-1 ATLCE
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B3 - Using nonlinearity» Tuned amplifier» Frequency multiplier» Gain compressor» Adding feedback AY 2015-16 15/03/2016-1 ATLCE
PIN CONFIGURATION FEATURES ORDERING INFORMATION ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS. D, F, N Packages
 DESCRIPTION The µa71 is a high performance operational amplifier with high open-loop gain, internal compensation, high common mode range and exceptional temperature stability. The µa71 is short-circuit-protected
DESCRIPTION The µa71 is a high performance operational amplifier with high open-loop gain, internal compensation, high common mode range and exceptional temperature stability. The µa71 is short-circuit-protected
Optimizing IP3 and ACPR Measurements
 Optimizing IP3 and ACPR Measurements Table of Contents 1. Overview... 2 2. Theory of Intermodulation Distortion... 2 3. Optimizing IP3 Measurements... 4 4. Theory of Adjacent Channel Power Ratio... 9 5.
Optimizing IP3 and ACPR Measurements Table of Contents 1. Overview... 2 2. Theory of Intermodulation Distortion... 2 3. Optimizing IP3 Measurements... 4 4. Theory of Adjacent Channel Power Ratio... 9 5.
Tutorial and Simulations for Micro-Cap IV
 ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II Tutorial and Simulations for Micro-Cap IV By Adam Zielinski (Posted at: http://wwwece.uvic.ca/~adam/) Version: August 22, 2002 ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II - Tutorial
ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II Tutorial and Simulations for Micro-Cap IV By Adam Zielinski (Posted at: http://wwwece.uvic.ca/~adam/) Version: August 22, 2002 ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II - Tutorial
Application Notes FREQUENCY LINEAR TUNING VARACTORS FREQUENCY LINEAR TUNING VARACTORS THE DEFINITION OF S (RELATIVE SENSITIVITY)
 FREQUENY LINEAR TUNING VARATORS FREQUENY LINEAR TUNING VARATORS For several decades variable capacitance diodes (varactors) have been used as tuning capacitors in high frequency circuits. Most of these
FREQUENY LINEAR TUNING VARATORS FREQUENY LINEAR TUNING VARATORS For several decades variable capacitance diodes (varactors) have been used as tuning capacitors in high frequency circuits. Most of these
Op Amp Circuit Collection
 Op Amp Circuit Collection Note: National Semiconductor recommends replacing 2N2920 and 2N3728 matched pairs with LM394 in all application circuits. Section 1 Basic Circuits Inverting Amplifier Difference
Op Amp Circuit Collection Note: National Semiconductor recommends replacing 2N2920 and 2N3728 matched pairs with LM394 in all application circuits. Section 1 Basic Circuits Inverting Amplifier Difference
Low Phase Noise XO (for HF Fund. and 3 rd O.T.) XIN XOUT N/C N/C OE CTRL N/C (0,0) Pad #9 OUTSEL
 Reserved BUF BUF 62 mil Reserved Reserved FEATURES 100MHz to 200MHz Fund. or 3 rd OT Crystal. Output range: 100 200MHz (no multiplication). Available outputs: PECL, or LVDS. OESEL/OECTRL for both PECL
Reserved BUF BUF 62 mil Reserved Reserved FEATURES 100MHz to 200MHz Fund. or 3 rd OT Crystal. Output range: 100 200MHz (no multiplication). Available outputs: PECL, or LVDS. OESEL/OECTRL for both PECL
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
XR-2206 Monolithic Function Generator
 ...the analog plus company TM XR-0 Monolithic Function Generator FEATURES Low-Sine Wave Distortion, 0.%, Typical Excellent Temperature Stability, 0ppm/ C, Typ. Wide Sweep Range, 000:, Typical Low-Supply
...the analog plus company TM XR-0 Monolithic Function Generator FEATURES Low-Sine Wave Distortion, 0.%, Typical Excellent Temperature Stability, 0ppm/ C, Typ. Wide Sweep Range, 000:, Typical Low-Supply
Agilent AN 1316 Optimizing Spectrum Analyzer Amplitude Accuracy
 Agilent AN 1316 Optimizing Spectrum Analyzer Amplitude Accuracy Application Note RF & Microwave Spectrum Analyzers Table of Contents 3 3 4 4 5 7 8 8 13 13 14 16 16 Introduction Absolute versus relative
Agilent AN 1316 Optimizing Spectrum Analyzer Amplitude Accuracy Application Note RF & Microwave Spectrum Analyzers Table of Contents 3 3 4 4 5 7 8 8 13 13 14 16 16 Introduction Absolute versus relative
LM381 LM381A Low Noise Dual Preamplifier
 LM381 LM381A Low Noise Dual Preamplifier General Description The LM381 LM381A is a dual preamplifier for the amplification of low level signals in applications requiring optimum noise performance Each
LM381 LM381A Low Noise Dual Preamplifier General Description The LM381 LM381A is a dual preamplifier for the amplification of low level signals in applications requiring optimum noise performance Each
DATA SHEET. TDA1543 Dual 16-bit DAC (economy version) (I 2 S input format) INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 February 1991 FEATURES Low distortion 16-bit dynamic range 4 oversampling possible Single 5 V power supply No external components required
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 February 1991 FEATURES Low distortion 16-bit dynamic range 4 oversampling possible Single 5 V power supply No external components required
Understand the effects of clock jitter and phase noise on sampled systems A s higher resolution data converters that can
 designfeature By Brad Brannon, Analog Devices Inc MUCH OF YOUR SYSTEM S PERFORMANCE DEPENDS ON JITTER SPECIFICATIONS, SO CAREFUL ASSESSMENT IS CRITICAL. Understand the effects of clock jitter and phase
designfeature By Brad Brannon, Analog Devices Inc MUCH OF YOUR SYSTEM S PERFORMANCE DEPENDS ON JITTER SPECIFICATIONS, SO CAREFUL ASSESSMENT IS CRITICAL. Understand the effects of clock jitter and phase
TL074 TL074A - TL074B
 A B LOW NOISE JFET QUAD OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS WIDE COMMONMODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT LOW NOISE e n = 15nV/ Hz (typ) OUTPUT SHORTCIRCUIT PROTECTION
A B LOW NOISE JFET QUAD OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS WIDE COMMONMODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT LOW NOISE e n = 15nV/ Hz (typ) OUTPUT SHORTCIRCUIT PROTECTION
Phase Noise Measurement Methods and Techniques
 Phase Noise Measurement Methods and Techniques Presented by: Kay Gheen, Agilent Technologies Introduction Extracting electronic signals from noise is a challenge for most electronics engineers. As engineers
Phase Noise Measurement Methods and Techniques Presented by: Kay Gheen, Agilent Technologies Introduction Extracting electronic signals from noise is a challenge for most electronics engineers. As engineers
Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor Technology (InGaP HBT) Broadband High Linearity Amplifier
 Freescale Semiconductor Technical Data Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor Technology (InGaP HBT) Broadband High Linearity Amplifier The is a general purpose amplifier that is input and output internally
Freescale Semiconductor Technical Data Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor Technology (InGaP HBT) Broadband High Linearity Amplifier The is a general purpose amplifier that is input and output internally
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
TS34119 Low Power Audio Amplifier
 SOP-8 DIP-8 Pin assignment: 1. CD 8. VO2 2. FC2 7. Gnd 3. FC1 6. Vcc 4. Vin 5. VO1 General Description The TS34119 is a low power audio amplifier, it integrated circuit intended (primarily) for telephone
SOP-8 DIP-8 Pin assignment: 1. CD 8. VO2 2. FC2 7. Gnd 3. FC1 6. Vcc 4. Vin 5. VO1 General Description The TS34119 is a low power audio amplifier, it integrated circuit intended (primarily) for telephone
Theory of Operation. Figure 1 illustrates a fan motor circuit used in an automobile application. The TPIC2101. 27.4 kω AREF.
 In many applications, a key design goal is to minimize variations in power delivered to a load as the supply voltage varies. This application brief describes a simple DC brush motor control circuit using
In many applications, a key design goal is to minimize variations in power delivered to a load as the supply voltage varies. This application brief describes a simple DC brush motor control circuit using
Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
BIASING OF CONSTANT CURRENT MMIC AMPLIFIERS (e.g., ERA SERIES) (AN-60-010)
 BIASING OF CONSTANT CURRENT MMIC AMPLIFIERS (e.g., ERA SERIES) (AN-60-010) Introduction The Mini-Circuits family of microwave monolithic integrated circuit (MMIC) Darlington amplifiers offers the RF designer
BIASING OF CONSTANT CURRENT MMIC AMPLIFIERS (e.g., ERA SERIES) (AN-60-010) Introduction The Mini-Circuits family of microwave monolithic integrated circuit (MMIC) Darlington amplifiers offers the RF designer
UA741. General-purpose single operational amplifier. Features. Applications. Description. N DIP8 (plastic package)
 General-purpose single operational amplifier Datasheet - production data N DIP8 (plastic package) D SO8 (plastic micropackage) Pin connections (top view) 1 - Offset null 1 2 - Inverting input 3 - Non-inverting
General-purpose single operational amplifier Datasheet - production data N DIP8 (plastic package) D SO8 (plastic micropackage) Pin connections (top view) 1 - Offset null 1 2 - Inverting input 3 - Non-inverting
AN-837 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
BJT Circuit Configurations
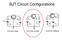 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
Features. Applications. Transmitter. Receiver. General Description MINIATURE MODULE. QM MODULATION OPTIMAL RANGE 1000m
 Features MINIATURE MODULE QM MODULATION OPTIMAL RANGE 1000m 433.05 434.79 ISM BAND 34 CHANNELS AVAILABLE SINGLE SUPPLY VOLTAGE Applications IN VEHICLE TELEMETRY SYSTEMS WIRELESS NETWORKING DOMESTIC AND
Features MINIATURE MODULE QM MODULATION OPTIMAL RANGE 1000m 433.05 434.79 ISM BAND 34 CHANNELS AVAILABLE SINGLE SUPPLY VOLTAGE Applications IN VEHICLE TELEMETRY SYSTEMS WIRELESS NETWORKING DOMESTIC AND
Bipolar Junction Transistor Basics
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
AP331A XX G - 7. Lead Free G : Green. Packaging (Note 2)
 Features General Description Wide supply Voltage range: 2.0V to 36V Single or dual supplies: ±1.0V to ±18V Very low supply current drain (0.4mA) independent of supply voltage Low input biasing current:
Features General Description Wide supply Voltage range: 2.0V to 36V Single or dual supplies: ±1.0V to ±18V Very low supply current drain (0.4mA) independent of supply voltage Low input biasing current:
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED
 Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK PLL & PLL with Integrated VCO Evaluation
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK PLL & PLL with Integrated VCO Evaluation
HP 8970B Option 020. Service Manual Supplement
 HP 8970B Option 020 Service Manual Supplement Service Manual Supplement HP 8970B Option 020 HP Part no. 08970-90115 Edition 1 May 1998 UNIX is a registered trademark of AT&T in the USA and other countries.
HP 8970B Option 020 Service Manual Supplement Service Manual Supplement HP 8970B Option 020 HP Part no. 08970-90115 Edition 1 May 1998 UNIX is a registered trademark of AT&T in the USA and other countries.
Application of network analyzer in measuring the performance functions of power supply
 J Indian Inst Sci, July Aug 2006, 86, 315 325 Indian Institute of Science Application of network analyzer in measuring the performance functions of power supply B SWAMINATHAN* AND V RAMANARAYANAN Power
J Indian Inst Sci, July Aug 2006, 86, 315 325 Indian Institute of Science Application of network analyzer in measuring the performance functions of power supply B SWAMINATHAN* AND V RAMANARAYANAN Power
Network Analyzer Operation
 Network Analyzer Operation 2004 ITTC Summer Lecture Series John Paden Purposes of a Network Analyzer Network analyzers are not about computer networks! Purposes of a Network Analyzer Measures S-parameters
Network Analyzer Operation 2004 ITTC Summer Lecture Series John Paden Purposes of a Network Analyzer Network analyzers are not about computer networks! Purposes of a Network Analyzer Measures S-parameters
Reading: HH Sections 4.11 4.13, 4.19 4.20 (pgs. 189-212, 222 224)
 6 OP AMPS II 6 Op Amps II In the previous lab, you explored several applications of op amps. In this exercise, you will look at some of their limitations. You will also examine the op amp integrator and
6 OP AMPS II 6 Op Amps II In the previous lab, you explored several applications of op amps. In this exercise, you will look at some of their limitations. You will also examine the op amp integrator and
Symbol Parameters Units Frequency Min. Typ. Max. 850 MHz 14.8 16.3 17.8
 Product Description Sirenza Microdevices SGC-689Z is a high performance SiGe HBT MMIC amplifier utilizing a Darlington configuration with a patented active-bias network. The active bias network provides
Product Description Sirenza Microdevices SGC-689Z is a high performance SiGe HBT MMIC amplifier utilizing a Darlington configuration with a patented active-bias network. The active bias network provides
TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL
 TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL The circuit of the basic two port network is shown on the right. Depending on the application, it may be used in a number of different ways to develop different
TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL The circuit of the basic two port network is shown on the right. Depending on the application, it may be used in a number of different ways to develop different
MUSES8920. High Quality Audio J-FET Input Dual Operational Amplifier - 1 -
 MUSES89 High Quality Audio J-FET Input Dual Operational Amplifier GENERAL DESCRIPTION The MUSES89 is a high quality Audio J-FET input dual operational amplifier. This is a mass production model of MUSES
MUSES89 High Quality Audio J-FET Input Dual Operational Amplifier GENERAL DESCRIPTION The MUSES89 is a high quality Audio J-FET input dual operational amplifier. This is a mass production model of MUSES
AVX EMI SOLUTIONS Ron Demcko, Fellow of AVX Corporation Chris Mello, Principal Engineer, AVX Corporation Brian Ward, Business Manager, AVX Corporation
 AVX EMI SOLUTIONS Ron Demcko, Fellow of AVX Corporation Chris Mello, Principal Engineer, AVX Corporation Brian Ward, Business Manager, AVX Corporation Abstract EMC compatibility is becoming a key design
AVX EMI SOLUTIONS Ron Demcko, Fellow of AVX Corporation Chris Mello, Principal Engineer, AVX Corporation Brian Ward, Business Manager, AVX Corporation Abstract EMC compatibility is becoming a key design
Local Oscillator for FM broadcast band 88-108 MHz
 Local Oscillator for FM broadcast band 88-108 MHz Wang Luhao Yan Shubo Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University 2012.05.15 Abstract In this project
Local Oscillator for FM broadcast band 88-108 MHz Wang Luhao Yan Shubo Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University 2012.05.15 Abstract In this project
Jeff Thomas Tom Holmes Terri Hightower. Learn RF Spectrum Analysis Basics
 Jeff Thomas Tom Holmes Terri Hightower Learn RF Spectrum Analysis Basics Learning Objectives Name the major measurement strengths of a swept-tuned spectrum analyzer Explain the importance of frequency
Jeff Thomas Tom Holmes Terri Hightower Learn RF Spectrum Analysis Basics Learning Objectives Name the major measurement strengths of a swept-tuned spectrum analyzer Explain the importance of frequency
www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description
Agilent AN 1315 Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range. Application Note
 Agilent AN 1315 Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note Table of Contents 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 6 7 7 7 7 9 10 10 11 11 12 12 13 13 14 15 1. Introduction What is dynamic range?
Agilent AN 1315 Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note Table of Contents 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 6 7 7 7 7 9 10 10 11 11 12 12 13 13 14 15 1. Introduction What is dynamic range?
TL084 TL084A - TL084B
 A B GENERAL PURPOSE JFET QUAD OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS WIDE COMMONMODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT OUTPUT SHORTCIRCUIT PROTECTION HIGH INPUT IMPEDANCE
A B GENERAL PURPOSE JFET QUAD OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS WIDE COMMONMODE (UP TO V + CC ) AND DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE LOW INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT OUTPUT SHORTCIRCUIT PROTECTION HIGH INPUT IMPEDANCE
In 3G/WCDMA mobile. IP2 and IP3 Nonlinearity Specifications for 3G/WCDMA Receivers 3G SPECIFICATIONS
 From June 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC IP and IP3 Nonlinearity Specifications for 3G/WCDMA Receivers By Chris W. Liu and Morten Damgaard Broadcom Corporation
From June 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC IP and IP3 Nonlinearity Specifications for 3G/WCDMA Receivers By Chris W. Liu and Morten Damgaard Broadcom Corporation
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong SAE 800
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
OMNIYIG. .5 TO 2 GHz, 1 TO 4 GHz, 6 to 18 GHz Thin Film YIG-TUNED OSCILLATORS OUTLINE DIMESIONS MOUNTING SURFACE GND +15V + TUNE - HTR HTR
 . TO Hz, 1 TO Hz, to 1 Hz Thin Film YITUNED OSCILLATORS Highly Reliable StateoftheArt ThinFilm Technology s. to 1 Hz oscillators employ thinfilm technology, coupled with aas FET transistors, and were designed
. TO Hz, 1 TO Hz, to 1 Hz Thin Film YITUNED OSCILLATORS Highly Reliable StateoftheArt ThinFilm Technology s. to 1 Hz oscillators employ thinfilm technology, coupled with aas FET transistors, and were designed
RF Communication System. EE 172 Systems Group Presentation
 RF Communication System EE 172 Systems Group Presentation RF System Outline Transmitter Components Receiver Components Noise Figure Link Budget Test Equipment System Success Design Remedy Transmitter Components
RF Communication System EE 172 Systems Group Presentation RF System Outline Transmitter Components Receiver Components Noise Figure Link Budget Test Equipment System Success Design Remedy Transmitter Components
HA-5104/883. Low Noise, High Performance, Quad Operational Amplifier. Features. Description. Applications. Ordering Information. Pinout.
 HA5104/883 April 2002 Features This Circuit is Processed in Accordance to MILSTD 883 and is Fully Conformant Under the Provisions of Paragraph 1.2.1. Low Input Noise Voltage Density at 1kHz. 6nV/ Hz (Max)
HA5104/883 April 2002 Features This Circuit is Processed in Accordance to MILSTD 883 and is Fully Conformant Under the Provisions of Paragraph 1.2.1. Low Input Noise Voltage Density at 1kHz. 6nV/ Hz (Max)
Four quadrant diode front end module for the Virgo Linear Alignment 3/ 30 mw, plus configuration
 NI K HEF NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR NUCLEAR AND HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS Four quadrant diode front end module for the Virgo Linear Alignment 3/ 30 mw, plus configuration Find the most recent files and related files
NI K HEF NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR NUCLEAR AND HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS Four quadrant diode front end module for the Virgo Linear Alignment 3/ 30 mw, plus configuration Find the most recent files and related files
Tire pressure monitoring
 Application Note AN601 Tire pressure monitoring 1 Purpose This document is intended to give hints on how to use the Intersema pressure sensors in a low cost tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS). 2 Introduction
Application Note AN601 Tire pressure monitoring 1 Purpose This document is intended to give hints on how to use the Intersema pressure sensors in a low cost tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS). 2 Introduction
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance
 Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Series AMLDL-Z Up to 1000mA LED Driver
 FEATURES: Click on Series name for product info on aimtec.com Series Up to ma LED Driver Models Single output Model Input Voltage (V) Step Down DC/DC LED driver Operating Temperature range 4ºC to 85ºC
FEATURES: Click on Series name for product info on aimtec.com Series Up to ma LED Driver Models Single output Model Input Voltage (V) Step Down DC/DC LED driver Operating Temperature range 4ºC to 85ºC
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 956 24-BIT DIFFERENTIAL ADC WITH I2C LTC2485 DESCRIPTION
 LTC2485 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 956 features the LTC2485, a 24-Bit high performance Σ analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The LTC2485 features 2ppm linearity, 0.5µV offset, and 600nV RMS noise.
LTC2485 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 956 features the LTC2485, a 24-Bit high performance Σ analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The LTC2485 features 2ppm linearity, 0.5µV offset, and 600nV RMS noise.
Since any real component also has loss due to the resistive component, the average power dissipated is 2 2R
 Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS IN ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies
 Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Equivalent Circuit. Operating Characteristics at Ta = 25 C, V CC = ±34V, R L = 8Ω, VG = 40dB, Rg = 600Ω, R L : non-inductive load STK4181V
 Ordering number: 2137B Thick Film Hybrid IC STK4181V AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply) (45W + 45W min, THD = 0.08%) Features Pin-compatible with the STK4102II series. The STK4101V series use the
Ordering number: 2137B Thick Film Hybrid IC STK4181V AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply) (45W + 45W min, THD = 0.08%) Features Pin-compatible with the STK4102II series. The STK4101V series use the
Understanding the Terms and Definitions of LDO Voltage Regulators
 Application Report SLVA79 - October 1999 Understanding the Terms and Definitions of ltage Regulators Bang S. Lee Mixed Signal Products ABSTRACT This report provides an understanding of the terms and definitions
Application Report SLVA79 - October 1999 Understanding the Terms and Definitions of ltage Regulators Bang S. Lee Mixed Signal Products ABSTRACT This report provides an understanding of the terms and definitions
