CATEGORY I TYPE OF INTERFACE Interfaces that the equipment asynchronously multiplexes into (or demultiplexes from) higher speed signals
|
|
|
- Gerald Lindsey
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TAN-048 AP NOTE HOW THE JITTER TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF THE XRT71D00 DS3/E3/STS-1 JITTER ATTENUATOR IC COMPARES WITH THE JITTER TRANSFER CHARACTERISTIC REQUIREMENTS OF BELLCORE GR-499- CORE 1
2 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this Applications Note is two-fold. 1. To present the Jitter Transfer Characteristics of the XRT71D00 device, for DS3 Applications, and 2. To illustrate how these Jitter Transfer Characteristics compare with the Category II Interface to Category II Interface Jitter Transfer Characteristics requirements per (for DS3 applications). JITTER TRANSFER CHARACTERISTIC REQUIREMENT FOR DS3 APPLICATIONS For DS3 Applications, specifies Jitter Transfer Characteristic requirements for three combinations of interfaces/configurations. Category II Type of Interface to Category I Type of Interface (e.g., for an M13 MUX application, this configuration relates the input Jitter, within an input DS3 signal, to the resulting output jitter, within an output DS1 signal). Category I Type of Interface to Category I Type of Interface (e.g., this configuration would typically involve jitter across a Multiplexer/De-Multiplexer pair). Category II Type of Interface to Category II Type of Interface (e.g., this configuration would typically involve jitter within a Repeater/Regenerator application). For completeness, the Bellcore definition of each of the Category I and Category II types of interfaces are presented below. CATEGORY I TYPE OF INTERFACE Interfaces that the equipment asynchronously multiplexes into (or demultiplexes from) higher speed signals Examples of Category I Type of Interface Low speed interfaces to Multiplexers (e.g., the DS1 interface to an M13 MUX). Low speed interfaces to Add-Drop MUXes and, Low speed interfaces to Digital Cross Connect Systems (DCS) 2
3 CATEGORY II TYPE OF INTERFACE Interfaces for signals that do one of the following. Regenerates Demultiplexes into (or is created by) lower speed signals. Synchronously multiplexes into (or demultiplexes from) higher speed signals. Examples of Category II Type of Interface Regenerators High Speed interfaces to Multiplexers (e.g., the DS3 interface to an M13 MUX). High Speed interfaces to Add-Drop MUXes and/ High Speed interfaces to Digital Cross Connect Systems (DCS) Jitter Transfer Characteristics Requirements (Summary) As mentioned above, specifies the Jitter Transfer Characteristic requirements for the following Interface Configurations. Category II Type of Interface to Category I Type of Interface (e.g., for an M13 MUX application, this configuration relates the input Jitter, within an input DS3 signal, to the resulting output jitter, within an output DS1 signal). Category I Type of Interface to Category I Type of Interface (e.g., this configuration would typically involve jitter across a Multiplexer/De-Multiplexer pair). Category II Type of Interface to Category II Type of Interface (e.g., this configuration would typically involve jitter within a Repeater/Regenerator application). Out of each of these Category Interface/Configurations, the only one that will be discussed in this document is the Category II Type of Interface to Category II Type of Interface Jitter Transfer Characteristic requirements. Each of the remaining Category Interface/Configurations involve determining the Jitter Transfer Characteristics across other circuitry, such as Multiplexer/De-Multiplexer pairs, Digital Cross-Connect System, and Add-Drop-MUXes. Since the intent of this document is to discuss Jitter Characteristics of LIU and the XRT71D00 devices, discussions of these remaining Category Interface/Configurations are beyond the scope of this document. The Jitter Transfer Characteristic Requirement for a Category II to Category II type of Interface (in DS3 applications) is plotted below in Figure 1. 3
4 0.1dB Slope = -20dB/Decade Jitter Gain (db) kHz 596kHz Jitter Frequency, Hz Figure 1, Illustration of the Jitter Transfer Characteristic requirements for Category II to Category II Type of Interfaces (e.g., DS3 Repeater/Regenerator Applications). Figure 1 indicates that (for a Category II to Category II Type of Interface/Configuration), the maximum Jitter Gain (over all frequencies above 10Hz) is 0.1dB. Further, this curve indicates that a 20dB/decade roll-off, in the Jitter Gain must begin at frequencies of 59.6kHz or less. 4
5 JITTER TRANSFER CHARACTERISTIC MEASUREMENTS OF THE XRT71D00 DEVICE Jitter Transfer Characteristics measurements of the XRT71D00 (for DS3 applications) have been recorded and are tabulated below in Table 1. Please note that measurements were taken for whenever the input jitter amplitude is small (e.g., 1UIpp) and large (e.g., 10 UIpp). Further, these measurements were also made for the two different settings of the BWS (Bandwidth Select) input pin. Table 1, The Jitter Transfer Characteristics of the XRT71D00 device, for DS3 Applications BWS Setting Low High Low High Input Jitter (UI-pp) 1 UI 1 UI 10 UI 10 UI Jitter Frequency (Hz) Jitter Gain (db) Jitter Gain (db) Jitter Gain (db) Jitter Gain (db) > NOTE: This data was taken via the XRT71D00/XRT7300 Evaluation Board. Hence, this data reflects the Jitter Transfer Characteristics of the composite solution consisting of both the XRT7300 LIU IC and the XRT71D00 Jitter Attenuator IC. Table 1 indicates that when the BWS input pin is low, then the -3dB Frequency of the Jitter Transfer Characteristic curve occurs at around 30Hz. Further, this table also 5
6 indicates that when the BWS input pin is high, then the -3dB Frequency of the Jitter Transfer Characteristic curve occurs at around 100 Hz. Figure 2 presents a plot of each of the Jitter Transfer Curves, listed in Table 1. Jitter Transfer Characteristics of the XRT71D00 Jitter Attenuator IC, DS3 Applications Jitter Gain, db Jitter Transfer, BW S = Low, Input Jitter = 1UI-pp Jitter Transfer, BWS = High, Input Jitter = 1UI-pp Jitter Transfer, BW S = Low, Input Jitter = 10UI-pp Jitter Transfer, BWS = High, Input Jitter = 10UI-pp Jitter Frequency, Hz Figure 2, Plot of the Jitter Transfer Characteristics of the XRT71D00 Jitter Attenuator IC, for DS3 Applications. TEST CONDITIONS a. Tests performed with the Wandel & Goltermann ANT20, on the XRT7300/XRT71D00 Evaluation Board. b. Test Pattern used: Unframed 2^23-1 PRBS Pattern. c. Transmit Output of W&G ANT20 Tester = DSX-3 6
7 CONCLUSIONS: The test results, presented in Table 1 and Figure 2 indicate the following. a. The peak gain of the Jitter Transfer Characteristics never exceeds 0.1dB. b. The -3dB Frequency of the XRT71D00 device (for each of the various combinations of BWS and FSS settings) is all considerably less than 59.6kHz. As a consequence, the Jitter Transfer Characteristics of the XRT71D00 device is compliant with the Jitter Transfer Characteristic requirements, per Bellcore GR-499- CORE (for a Category II to Category II type of Interface DS3 Applications). 7
8 8
TAN-030 Application Note Performance Characteristics of the XRT7300 Device for DS3 Applications Rev. 1.00
 APPLICATION NOTE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE XRT7300 DEVICE FOR DS3 APPLICATIONS 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 2.0 TRANSMIT OUTPUT PULSE TEMPLATE MEASUREMENTS
APPLICATION NOTE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE XRT7300 DEVICE FOR DS3 APPLICATIONS 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 2.0 TRANSMIT OUTPUT PULSE TEMPLATE MEASUREMENTS
ANT-20, ANT-20E Advanced Network Tester PDH MUX/DEMUX
 ANT-20, ANT-20E Advanced Network Tester BN 3035/90.30 to 90.31 Drop & Insert BN 3035/90.20 in combination with 4 Software Version 7.20 Operating Manual BN 3035/98.23 Please direct all enquiries to your
ANT-20, ANT-20E Advanced Network Tester BN 3035/90.30 to 90.31 Drop & Insert BN 3035/90.20 in combination with 4 Software Version 7.20 Operating Manual BN 3035/98.23 Please direct all enquiries to your
Application Note. Line Card Redundancy Design With the XRT83SL38 T1/E1 SH/LH LIU ICs
 Application Note Design With the XRT83SL38 T1/E1 SH/LH LIU ICs Revision 1.3 1 REDUNDANCY APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION Telecommunication system design requires signal integrity and reliability. When a T1/E1
Application Note Design With the XRT83SL38 T1/E1 SH/LH LIU ICs Revision 1.3 1 REDUNDANCY APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION Telecommunication system design requires signal integrity and reliability. When a T1/E1
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.825 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (03/2000) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS Digital networks Quality
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.825 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (03/2000) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS Digital networks Quality
DigiPoints Volume 1. Student Workbook. Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology
 Growing Capacity Through Technology Page 5. 1 DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology Summary This module covers the North American Digital Hierarchy (NADH), the European Digital
Growing Capacity Through Technology Page 5. 1 DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology Summary This module covers the North American Digital Hierarchy (NADH), the European Digital
LAB 12: ACTIVE FILTERS
 A. INTRODUCTION LAB 12: ACTIVE FILTERS After last week s encounter with op- amps we will use them to build active filters. B. ABOUT FILTERS An electric filter is a frequency-selecting circuit designed
A. INTRODUCTION LAB 12: ACTIVE FILTERS After last week s encounter with op- amps we will use them to build active filters. B. ABOUT FILTERS An electric filter is a frequency-selecting circuit designed
Sol: Optical range from λ 1 to λ 1 +Δλ contains bandwidth
 1. Use Figure 3.47 and Figure 3.50 to explain why the bandwidth of twisted-wire pairs and coaxial cable decreases with distance. Figure 3.47 figure 3.50 sol: The bandwidth is the range of frequencies where
1. Use Figure 3.47 and Figure 3.50 to explain why the bandwidth of twisted-wire pairs and coaxial cable decreases with distance. Figure 3.47 figure 3.50 sol: The bandwidth is the range of frequencies where
Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier
 Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier 12.1: Introduction to Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are very high gain dc coupled amplifiers with differential inputs; they are used
Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier 12.1: Introduction to Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are very high gain dc coupled amplifiers with differential inputs; they are used
DS26303 OCTAL 3.3V T1/E1/J1 SHORT HAUL LIU PRODUCT BRIEF
 DS26303 OCTAL 3.3V T1/E1/J1 SHORT HAUL LIU PRODUCT BRIEF www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Eight complete E1, T1, or J1 short haul LIUs Independent E1 or T1 or J1 selections for each of the LIU s in non-hardware
DS26303 OCTAL 3.3V T1/E1/J1 SHORT HAUL LIU PRODUCT BRIEF www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Eight complete E1, T1, or J1 short haul LIUs Independent E1 or T1 or J1 selections for each of the LIU s in non-hardware
Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1
 Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Note Bandwidth utilization is the wise use of
Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Note Bandwidth utilization is the wise use of
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
(Refer Slide Time: 2:10)
 Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-12 Multiplexer Applications-1 Hello and welcome to today s lecture on multiplexer
Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-12 Multiplexer Applications-1 Hello and welcome to today s lecture on multiplexer
TECHNICAL TBR 12 BASIS for December 1993 REGULATION
 TECHNICAL TBR 12 BASIS for December 1993 REGULATION Source: ETSI TC-BT Reference: DTBR/BT-02036 ICS: 33.040.40 Key words: ONP, leased lines, D2048U Business Telecommunications (BT); Open Network Provision
TECHNICAL TBR 12 BASIS for December 1993 REGULATION Source: ETSI TC-BT Reference: DTBR/BT-02036 ICS: 33.040.40 Key words: ONP, leased lines, D2048U Business Telecommunications (BT); Open Network Provision
TUTORIAL FOR CHAPTER 8
 TUTORIAL FOR CHAPTER 8 PROBLEM 1) The informaiton in four analog signals is to be multiplexed and transmitted over a telephone channel that has a 400 to 3100 Hz bandpass. Each of the analog baseband signals
TUTORIAL FOR CHAPTER 8 PROBLEM 1) The informaiton in four analog signals is to be multiplexed and transmitted over a telephone channel that has a 400 to 3100 Hz bandpass. Each of the analog baseband signals
Multiplexing. Multiplexing is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single physical medium.
 Multiplexing Multiplexing is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single physical medium. The following two factors in data communications lead to
Multiplexing Multiplexing is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single physical medium. The following two factors in data communications lead to
2.488Gbps/2.667Gbps Clock and Data Recovery with Limiting Amplifier
 查 询 供 应 商 捷 多 邦, 专 业 PCB 打 样 工 厂,24 小 时 加 急 出 货 9-27; Rev ; 4/3 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 2.488Gbps/2.667Gbps Clock and General Description The is a compact, dual-rate clock and data recovery with limiting
查 询 供 应 商 捷 多 邦, 专 业 PCB 打 样 工 厂,24 小 时 加 急 出 货 9-27; Rev ; 4/3 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 2.488Gbps/2.667Gbps Clock and General Description The is a compact, dual-rate clock and data recovery with limiting
Timing Errors and Jitter
 Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
The Calculation of G rms
 The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
TECHNICAL TBR 14 BASIS for April 1994 REGULATION
 TECHNICAL TBR 14 BASIS for April 1994 REGULATION Source: ETSI TC-BTC Reference: DTBR/BTC-02038 ICS: 33.040.40 Key words: ONP, leased line Business TeleCommunications (BTC); 64 kbit/s digital unrestricted
TECHNICAL TBR 14 BASIS for April 1994 REGULATION Source: ETSI TC-BTC Reference: DTBR/BTC-02038 ICS: 33.040.40 Key words: ONP, leased line Business TeleCommunications (BTC); 64 kbit/s digital unrestricted
DataSMART 554 & 558 T1/FT1 Plug-in DSU/CSUs Page 1 of 8. T1/FT1 Single-port Plug-in DSU/CSUs
 554 & 558 T1/FT1 Plug-in DSU/CSUs Page 1 of 8 = PDF Leased Line Economical T1 Internet Access Central Site T1 Management T1/FT1 Single-port Plug-in DSU/CSUs Key Features Specifications Ordering Information
554 & 558 T1/FT1 Plug-in DSU/CSUs Page 1 of 8 = PDF Leased Line Economical T1 Internet Access Central Site T1 Management T1/FT1 Single-port Plug-in DSU/CSUs Key Features Specifications Ordering Information
DS2186. Transmit Line Interface FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT
 DS2186 Transmit Line Interface FEATURES Line interface for T1 (1.544 MHz) and CEPT (2.048 MHz) primary rate networks PIN ASSIGNMENT TAIS 1 20 LCLK On chip transmit LBO (line build out) and line drivers
DS2186 Transmit Line Interface FEATURES Line interface for T1 (1.544 MHz) and CEPT (2.048 MHz) primary rate networks PIN ASSIGNMENT TAIS 1 20 LCLK On chip transmit LBO (line build out) and line drivers
Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis
 Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
The Phase Modulator In NBFM Voice Communication Systems
 The Phase Modulator In NBFM Voice Communication Systems Virgil Leenerts 8 March 5 The phase modulator has been a point of discussion as to why it is used and not a frequency modulator in what are called
The Phase Modulator In NBFM Voice Communication Systems Virgil Leenerts 8 March 5 The phase modulator has been a point of discussion as to why it is used and not a frequency modulator in what are called
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. EE105 Lab Experiments
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE15 Lab Experiments Bode Plot Tutorial Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Bode Plots Basics
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE15 Lab Experiments Bode Plot Tutorial Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Bode Plots Basics
Chapter 4 T1 Interface Card
 Chapter 4 T1 Interface Card GENERAL This chapter describes DTE interface options that may be required if application requirements change. It also describes software configuration for the T1 interface card.
Chapter 4 T1 Interface Card GENERAL This chapter describes DTE interface options that may be required if application requirements change. It also describes software configuration for the T1 interface card.
Lecture 12 Transport Networks (SONET) and circuit-switched networks
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 1 Transport Networks (SONET) and circuit-switched networks Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 005 Transport Networks and SONET/SDH In most cases
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 1 Transport Networks (SONET) and circuit-switched networks Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 005 Transport Networks and SONET/SDH In most cases
Propagation Channel Emulator ECP_V3
 Navigation simulators Propagation Channel Emulator ECP_V3 1 Product Description The ECP (Propagation Channel Emulator V3) synthesizes the principal phenomena of propagation occurring on RF signal links
Navigation simulators Propagation Channel Emulator ECP_V3 1 Product Description The ECP (Propagation Channel Emulator V3) synthesizes the principal phenomena of propagation occurring on RF signal links
DS2187 Receive Line Interface
 Receive Line Interface www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Line interface for T1 (1.544 MHz) and CEPT (2.048 MHz) primary rate networks Extracts clock and data from twisted pair or coax Meets requirements of PUB
Receive Line Interface www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Line interface for T1 (1.544 MHz) and CEPT (2.048 MHz) primary rate networks Extracts clock and data from twisted pair or coax Meets requirements of PUB
It explains the differences between the Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy and the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy.
 TECHNICAL TUTORIAL Subject: SDH Date: October, 00 Prepared by: John Rumsey SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy. Introduction. The Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH). The Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
TECHNICAL TUTORIAL Subject: SDH Date: October, 00 Prepared by: John Rumsey SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy. Introduction. The Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH). The Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
1+1 PROTECTION WITHOUT RELAYS USING IDT82V2044/48/48L & IDT82V2054/58/58L HITLESS PROTECTION SWITCHING
 1+1 PROTECTION WITHOUT RELAYS USING IDT82V2044/48/48L & IDT82V2054/58/58L APPLICATION NOTE AN-357 1.0 INTRODUCTION In today's highly competitive market, high quality of service, QOS, and reliability is
1+1 PROTECTION WITHOUT RELAYS USING IDT82V2044/48/48L & IDT82V2054/58/58L APPLICATION NOTE AN-357 1.0 INTRODUCTION In today's highly competitive market, high quality of service, QOS, and reliability is
DS-3 Technology and Testing Overview
 DS-3 Technology and Testing Overview Presented by Moti Shacham for Cincinnati Bell Technical Training Symposium September 12-14, 2000 Tel: 770-246-9662 Fax: 770-246-9733 www.telesync.com 1 OC-48/STM-16
DS-3 Technology and Testing Overview Presented by Moti Shacham for Cincinnati Bell Technical Training Symposium September 12-14, 2000 Tel: 770-246-9662 Fax: 770-246-9733 www.telesync.com 1 OC-48/STM-16
TCOM 370 NOTES 99-6 VOICE DIGITIZATION AND VOICE/DATA INTEGRATION
 TCOM 370 NOTES 99-6 VOICE DIGITIZATION AND VOICE/DATA INTEGRATION (Please read appropriate parts of Section 2.5.2 in book) 1. VOICE DIGITIZATION IN THE PSTN The frequencies contained in telephone-quality
TCOM 370 NOTES 99-6 VOICE DIGITIZATION AND VOICE/DATA INTEGRATION (Please read appropriate parts of Section 2.5.2 in book) 1. VOICE DIGITIZATION IN THE PSTN The frequencies contained in telephone-quality
MT9043 T1/E1 System Synchronizer
 T1/E1 System Synchronizer Features Supports AT&T TR62411 and Bellcore GR-1244- CORE, Stratum 4 Enhanced and Stratum 4 timing for DS1 interfaces Supports ETSI ETS 300 011, TBR 4, TBR 12 and TBR 13 timing
T1/E1 System Synchronizer Features Supports AT&T TR62411 and Bellcore GR-1244- CORE, Stratum 4 Enhanced and Stratum 4 timing for DS1 interfaces Supports ETSI ETS 300 011, TBR 4, TBR 12 and TBR 13 timing
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators
 Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
DigiPoints Volume 1. Student Workbook. Module 4 Bandwidth Management
 Bandwidth Management Page 4.1 DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 4 Bandwidth Management Summary This module will cover Time Division Multiplexing (TDM). TDM technology allows many users to access a particular
Bandwidth Management Page 4.1 DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 4 Bandwidth Management Summary This module will cover Time Division Multiplexing (TDM). TDM technology allows many users to access a particular
PART 3 - Access Services Original Page 1 SECTION 31 - Synchronous Broadband Network Services (SBNS) ACCESS SERVICE
 PART 3 - Access Services Original Page 1 31. Synchronous Broadband Network Services 31.1 Service Description-General Synchronous Broadband Network Services (SBNS) are a family of optional special access
PART 3 - Access Services Original Page 1 31. Synchronous Broadband Network Services 31.1 Service Description-General Synchronous Broadband Network Services (SBNS) are a family of optional special access
Wideband Driver Amplifiers
 The driver amplifier is a wideband, 1 khz to 4 GHz amplifier intended for use in broadband microwave and high data rate systems. The is a 3-stage high output power modulator driver amplifier that can provide
The driver amplifier is a wideband, 1 khz to 4 GHz amplifier intended for use in broadband microwave and high data rate systems. The is a 3-stage high output power modulator driver amplifier that can provide
DCM555 - Data Communications Lab 8 Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Part 1 - T1/DS1 Signals
 DCM555 - Data Communications Lab 8 Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Part 1 - T1/DS1 Signals Name: St. #: Section: (Note: Show all of your calculations, express your answer to the appropriate number of
DCM555 - Data Communications Lab 8 Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Part 1 - T1/DS1 Signals Name: St. #: Section: (Note: Show all of your calculations, express your answer to the appropriate number of
)454 6 ")43 0%2 3%#/.$ $50,%8 -/$%- 34!.$!2$):%$ &/2 53% ). 4(% '%.%2!, 37)4#(%$ 4%,%0(/.%.%47/2+ $!4! #/--5.)#!4)/. /6%2 4(% 4%,%0(/.%.
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION )454 6 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU $!4! #/5.)#!4)/. /6%2 4(% 4%,%0(/.%.%47/2+ ")43 0%2 3%#/.$ $50,%8 /$% 34!.$!2$):%$ &/2 53% ). 4(% '%.%2!, 37)4#(%$
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION )454 6 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU $!4! #/5.)#!4)/. /6%2 4(% 4%,%0(/.%.%47/2+ ")43 0%2 3%#/.$ $50,%8 /$% 34!.$!2$):%$ &/2 53% ). 4(% '%.%2!, 37)4#(%$
W a d i a D i g i t a l
 Wadia Decoding Computer Overview A Definition What is a Decoding Computer? The Wadia Decoding Computer is a small form factor digital-to-analog converter with digital pre-amplifier capabilities. It is
Wadia Decoding Computer Overview A Definition What is a Decoding Computer? The Wadia Decoding Computer is a small form factor digital-to-analog converter with digital pre-amplifier capabilities. It is
Physical Layer, Part 2 Digital Transmissions and Multiplexing
 Physical Layer, Part 2 Digital Transmissions and Multiplexing These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable
Physical Layer, Part 2 Digital Transmissions and Multiplexing These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable
AN-837 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
What Does Communication (or Telecommunication) Mean?
 What Does Communication (or Telecommunication) Mean? The term communication (or telecommunication) means the transfer of some form of information from one place (known as the source of information) to
What Does Communication (or Telecommunication) Mean? The term communication (or telecommunication) means the transfer of some form of information from one place (known as the source of information) to
CHAPTER 8 MULTIPLEXING
 CHAPTER MULTIPLEXING 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS.1 Multiplexing is cost-effective because the higher the data rate, the more cost-effective the transmission facility.. Interference is avoided under frequency
CHAPTER MULTIPLEXING 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS.1 Multiplexing is cost-effective because the higher the data rate, the more cost-effective the transmission facility.. Interference is avoided under frequency
Clock Data Recovery Design Techniques for E1/T1 Based on Direct Digital Synthesis Author: Paolo Novellini and Giovanni Guasti
 Application Note: Virtex and Spartan FPGA Families XAPP868 (v1.0) January 29, 2008 Clock Data ecovery Design Techniques for E1/T1 Based on Direct Digital Synthesis Author: Paolo Novellini and Giovanni
Application Note: Virtex and Spartan FPGA Families XAPP868 (v1.0) January 29, 2008 Clock Data ecovery Design Techniques for E1/T1 Based on Direct Digital Synthesis Author: Paolo Novellini and Giovanni
Engineering Sciences 22 Systems Summer 2004
 Engineering Sciences 22 Systems Summer 24 BODE PLOTS A Bode plot is a standard format for plotting frequency response of LTI systems. Becoming familiar with this format is useful because: 1. It is a standard
Engineering Sciences 22 Systems Summer 24 BODE PLOTS A Bode plot is a standard format for plotting frequency response of LTI systems. Becoming familiar with this format is useful because: 1. It is a standard
TUBE-TECH HLT 2A Stereo High- and Low shelving, T- filter & Low- and High cut
 TUBE-TECH HLT 2A Stereo High- and Low shelving, T- filter & Low- and High cut Description: The TUBE-TECH HLT 2A is a stereo unit, featuring low and high cut filters, low and high shelving filters and a
TUBE-TECH HLT 2A Stereo High- and Low shelving, T- filter & Low- and High cut Description: The TUBE-TECH HLT 2A is a stereo unit, featuring low and high cut filters, low and high shelving filters and a
Spike-Based Sensing and Processing: What are spikes good for? John G. Harris Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept
 Spike-Based Sensing and Processing: What are spikes good for? John G. Harris Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept ONR NEURO-SILICON WORKSHOP, AUG 1-2, 2006 Take Home Messages Introduce integrate-and-fire
Spike-Based Sensing and Processing: What are spikes good for? John G. Harris Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept ONR NEURO-SILICON WORKSHOP, AUG 1-2, 2006 Take Home Messages Introduce integrate-and-fire
Using Pre-Emphasis and Equalization with Stratix GX
 Introduction White Paper Using Pre-Emphasis and Equalization with Stratix GX New high speed serial interfaces provide a major benefit to designers looking to provide greater data bandwidth across the backplanes
Introduction White Paper Using Pre-Emphasis and Equalization with Stratix GX New high speed serial interfaces provide a major benefit to designers looking to provide greater data bandwidth across the backplanes
GSM Testers for Rent and Sale
 GSM Testers for Rent and Sale ^ Introduction... 2 4202S Mobile Service Tester GSM Module Tester... 3 4107S Mobil Phone Tester... 4 Sales and rent information... 6 GSM tester for sale and to rent Page 1
GSM Testers for Rent and Sale ^ Introduction... 2 4202S Mobile Service Tester GSM Module Tester... 3 4107S Mobil Phone Tester... 4 Sales and rent information... 6 GSM tester for sale and to rent Page 1
Communications. www.exar.com. SONET/SDH Multi-Ch/Multi-Rate Framer+Serdes Mappers + Framers Transceivers/CDR
 Communications SONET/SDH Multi-Ch/Multi-Rate Framer+Serdes Mappers + Framers Transceivers/CDR PDH E1 LIUs T1/E1/J1 LIUs Framer + LIUs Combos BITS Solutions T3/E3 LIUs T3/E3 Framers T3/E3 Combos T/E Timing
Communications SONET/SDH Multi-Ch/Multi-Rate Framer+Serdes Mappers + Framers Transceivers/CDR PDH E1 LIUs T1/E1/J1 LIUs Framer + LIUs Combos BITS Solutions T3/E3 LIUs T3/E3 Framers T3/E3 Combos T/E Timing
Pericom PCI Express 1.0 & PCI Express 2.0 Advanced Clock Solutions
 Pericom PCI Express 1.0 & PCI Express 2.0 Advanced Clock Solutions PCI Express Bus In Today s Market PCI Express, or PCIe, is a relatively new serial pointto-point bus in PCs. It was introduced as an AGP
Pericom PCI Express 1.0 & PCI Express 2.0 Advanced Clock Solutions PCI Express Bus In Today s Market PCI Express, or PCIe, is a relatively new serial pointto-point bus in PCs. It was introduced as an AGP
Chapter 4: Passive Analog Signal Processing
 hapter 4: Passive Analog Signal Processing In this chapter we introduce filters and signal transmission theory. Filters are essential components of most analog circuits and are used to remove unwanted
hapter 4: Passive Analog Signal Processing In this chapter we introduce filters and signal transmission theory. Filters are essential components of most analog circuits and are used to remove unwanted
Solution. (Chapters 5-6-7-8) Dr. Hasan Qunoo. The Islamic University of Gaza. Faculty of Engineering. Computer Engineering Department
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Data Communications ECOM 4314 Solution (Chapters 5-6-7-8) Dr. Hasan Qunoo Eng. Wafaa Audah Eng. Waleed Mousa 1. A cable
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Data Communications ECOM 4314 Solution (Chapters 5-6-7-8) Dr. Hasan Qunoo Eng. Wafaa Audah Eng. Waleed Mousa 1. A cable
CLOCK AND SYNCHRONIZATION IN SYSTEM 6000
 By Christian G. Frandsen Introduction This document will discuss the clock, synchronization and interface design of TC System 6000 and deal with several of the factors that must be considered when using
By Christian G. Frandsen Introduction This document will discuss the clock, synchronization and interface design of TC System 6000 and deal with several of the factors that must be considered when using
PCI Express Transmitter PLL Testing A Comparison of Methods. Primer
 PCI Express Transmitter PLL Testing A Comparison of Methods Primer Primer Table of Contents Abstract...3 Spectrum Analyzer Method...4 Oscilloscope Method...6 Bit Error Rate Tester (BERT) Method...6 Clock
PCI Express Transmitter PLL Testing A Comparison of Methods Primer Primer Table of Contents Abstract...3 Spectrum Analyzer Method...4 Oscilloscope Method...6 Bit Error Rate Tester (BERT) Method...6 Clock
SDI SDI SDI. Frame Synchronizer. Figure 1. Typical Example of a Professional Broadcast Video
 TIMING AND SYNCHRONIZATION IN BROADCAST VIDEO 1. Introduction Digitization of video signals has been common practice in broadcast video for many years. Early digital video was commonly encoded on a -bit
TIMING AND SYNCHRONIZATION IN BROADCAST VIDEO 1. Introduction Digitization of video signals has been common practice in broadcast video for many years. Early digital video was commonly encoded on a -bit
The Effect of Network Cabling on Bit Error Rate Performance. By Paul Kish NORDX/CDT
 The Effect of Network Cabling on Bit Error Rate Performance By Paul Kish NORDX/CDT Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Probability of Causing Errors... 3 Noise Sources Contributing to Errors... 4 Bit Error
The Effect of Network Cabling on Bit Error Rate Performance By Paul Kish NORDX/CDT Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Probability of Causing Errors... 3 Noise Sources Contributing to Errors... 4 Bit Error
VCO Phase noise. Characterizing Phase Noise
 VCO Phase noise Characterizing Phase Noise The term phase noise is widely used for describing short term random frequency fluctuations of a signal. Frequency stability is a measure of the degree to which
VCO Phase noise Characterizing Phase Noise The term phase noise is widely used for describing short term random frequency fluctuations of a signal. Frequency stability is a measure of the degree to which
SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR EFFECTIVE VIBRATION ANALYSIS
 SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR EFFECTIVE VIBRATION ANALYSIS Dennis H. Shreve IRD Mechanalysis, Inc Columbus, Ohio November 1995 ABSTRACT Effective vibration analysis first begins with acquiring an accurate time-varying
SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR EFFECTIVE VIBRATION ANALYSIS Dennis H. Shreve IRD Mechanalysis, Inc Columbus, Ohio November 1995 ABSTRACT Effective vibration analysis first begins with acquiring an accurate time-varying
How To Power A Powerline System On A Cell Phone Or Ipad Or Ipa Computer (For A Cell)
 Digital Loop Carrier System 12:1 Multi-Line System 12 lines over a single twisted pair: Expand customer service to a range of up to 100,000 ft. without the expense of installing new copper G The 12:1 Multi-Line
Digital Loop Carrier System 12:1 Multi-Line System 12 lines over a single twisted pair: Expand customer service to a range of up to 100,000 ft. without the expense of installing new copper G The 12:1 Multi-Line
DigiPoints Volume 1. Leader Guide. Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology
 Growing Capacity Through Technology Page 5. i DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology Summary In Module 4, TDM was introduced and explained. The technology focus was on T1, the
Growing Capacity Through Technology Page 5. i DigiPoints Volume 1 Module 5 Growing Capacity Through Technology Summary In Module 4, TDM was introduced and explained. The technology focus was on T1, the
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP - 1-1 Introduction In this lab you will use software reconfigurable RF hardware from National
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev LAB 1 - Introduction to USRP - 1-1 Introduction In this lab you will use software reconfigurable RF hardware from National
Chapter 6 PLL and Clock Generator
 Chapter 6 PLL and Clock Generator The DSP56300 core features a Phase Locked Loop (PLL) clock generator in its central processing module. The PLL allows the processor to operate at a high internal clock
Chapter 6 PLL and Clock Generator The DSP56300 core features a Phase Locked Loop (PLL) clock generator in its central processing module. The PLL allows the processor to operate at a high internal clock
Frequency Response of Filters
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
PIEZO FILTERS INTRODUCTION
 For more than two decades, ceramic filter technology has been instrumental in the proliferation of solid state electronics. A view of the future reveals that even greater expectations will be placed on
For more than two decades, ceramic filter technology has been instrumental in the proliferation of solid state electronics. A view of the future reveals that even greater expectations will be placed on
AT&T Private Line Service OC-192 SERVICE DESCRIPTION AND INTERFACE SPECIFICATION
 TR 54079 Data Communications AT&T Private Line Service OC-192 SERVICE DESCRIPTION AND INTERFACE SPECIFICATION Issue 1.0 September 1999 AT&T 1999 Printed in USA ii NOTICE This Technical Reference is published
TR 54079 Data Communications AT&T Private Line Service OC-192 SERVICE DESCRIPTION AND INTERFACE SPECIFICATION Issue 1.0 September 1999 AT&T 1999 Printed in USA ii NOTICE This Technical Reference is published
Chap 4 Circuit-Switching Networks
 hap 4 ircuit-switching Networks Provide dedicated circuits between users Example: 1. telephone network: provides 64Kbps circuits for voice signals 64Kbps=8 k samples/sec * 8 bits/sample 2. transport network:
hap 4 ircuit-switching Networks Provide dedicated circuits between users Example: 1. telephone network: provides 64Kbps circuits for voice signals 64Kbps=8 k samples/sec * 8 bits/sample 2. transport network:
Selecting the Optimum PCI Express Clock Source
 Selecting the Optimum PCI Express Clock Source PCI Express () is a serial point-to-point interconnect standard developed by the Component Interconnect Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG). lthough originally
Selecting the Optimum PCI Express Clock Source PCI Express () is a serial point-to-point interconnect standard developed by the Component Interconnect Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG). lthough originally
Objective. To design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors.
 ascode Amplifier Design. Objective. o design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors. Assignment description he cascode amplifier utilises the advantage of the common-emitter
ascode Amplifier Design. Objective. o design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors. Assignment description he cascode amplifier utilises the advantage of the common-emitter
Course 12 Synchronous transmission multiplexing systems used in digital telephone networks
 Course 12 Synchronous transmission multiplexing systems used in digital telephone networks o Disadvantages of the PDH transmission multiplexing system PDH: no unitary international standardization of the
Course 12 Synchronous transmission multiplexing systems used in digital telephone networks o Disadvantages of the PDH transmission multiplexing system PDH: no unitary international standardization of the
DVT913 TV CHANNEL CONVERTER
 Broadband Cable Networks 1(5) DVT913 TV CHANNEL CONVERTER General DVT913 is a TV Channel Converter for the DVX tend product family. It consists of an input down converter from to, a high selectivity part
Broadband Cable Networks 1(5) DVT913 TV CHANNEL CONVERTER General DVT913 is a TV Channel Converter for the DVX tend product family. It consists of an input down converter from to, a high selectivity part
Sheilded CATx Cable Characteristics
 Sheilded CATx Cable Characteristics Jack MacDougall & Hossein Shakiba AMS Systems Engineering & AMS Principal Engineer, February 2009 For more information on Gennum s ActiveConnect solutions please contact
Sheilded CATx Cable Characteristics Jack MacDougall & Hossein Shakiba AMS Systems Engineering & AMS Principal Engineer, February 2009 For more information on Gennum s ActiveConnect solutions please contact
FAST TUTORIALS FOR TIME-CHALLENGED TECHNICIANS
 Tech Notes from a Telephone Engineer FAST TUTORIALS FOR TIME-CHALLENGED TECHNICIANS DDS Description: DDS Digital Data Service Long held industry acronym for transporting digital data at rates of: 2.4kbps,
Tech Notes from a Telephone Engineer FAST TUTORIALS FOR TIME-CHALLENGED TECHNICIANS DDS Description: DDS Digital Data Service Long held industry acronym for transporting digital data at rates of: 2.4kbps,
Ultra640 SCSI Measured Data from Cables & Backplanes
 T10/01-224r0 Ultra640 SCSI Measured Data from Cables & Backplanes Russ Brown Maxtor Corporation Parallel SCSI Working Group 17 July 2001 Colorado Springs, CO Introduction The following presents some of
T10/01-224r0 Ultra640 SCSI Measured Data from Cables & Backplanes Russ Brown Maxtor Corporation Parallel SCSI Working Group 17 July 2001 Colorado Springs, CO Introduction The following presents some of
T1/E1/OC3 WAN PLL WITH DUAL
 T1/E1/OC3 WAN PLL WITH DUAL REFERENCE INPUTS IDT82V3012 FEATURES Supports AT&T TR62411 and Telcordia GR-1244-CORE Stratum 3, Stratum 4 Enhanced and Stratum 4 timing for DS1 interfaces Supports ITU-T G.813
T1/E1/OC3 WAN PLL WITH DUAL REFERENCE INPUTS IDT82V3012 FEATURES Supports AT&T TR62411 and Telcordia GR-1244-CORE Stratum 3, Stratum 4 Enhanced and Stratum 4 timing for DS1 interfaces Supports ITU-T G.813
Multiplexing on Wireline Telephone Systems
 Multiplexing on Wireline Telephone Systems Isha Batra, Divya Raheja Information Technology, Dronacharya College of Engineering Farrukh Nagar, Gurgaon, India ABSTRACT- This Paper Outlines a research multiplexing
Multiplexing on Wireline Telephone Systems Isha Batra, Divya Raheja Information Technology, Dronacharya College of Engineering Farrukh Nagar, Gurgaon, India ABSTRACT- This Paper Outlines a research multiplexing
ANALYZER BASICS WHAT IS AN FFT SPECTRUM ANALYZER? 2-1
 WHAT IS AN FFT SPECTRUM ANALYZER? ANALYZER BASICS The SR760 FFT Spectrum Analyzer takes a time varying input signal, like you would see on an oscilloscope trace, and computes its frequency spectrum. Fourier's
WHAT IS AN FFT SPECTRUM ANALYZER? ANALYZER BASICS The SR760 FFT Spectrum Analyzer takes a time varying input signal, like you would see on an oscilloscope trace, and computes its frequency spectrum. Fourier's
DATA SHEET. TDA1518BQ 24 W BTL or 2 x 12 watt stereo car radio power amplifier INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 July 1994 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is an integrated class-b output amplifier in a 13-lead single-in-line (SIL) plastic power package.
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 July 1994 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is an integrated class-b output amplifier in a 13-lead single-in-line (SIL) plastic power package.
Starlink 9003T1 T1/E1 Dig i tal Trans mis sion Sys tem
 Starlink 9003T1 T1/E1 Dig i tal Trans mis sion Sys tem A C ombining Moseley s unparalleled reputation for high quality RF aural Studio-Transmitter Links (STLs) with the performance and speed of today s
Starlink 9003T1 T1/E1 Dig i tal Trans mis sion Sys tem A C ombining Moseley s unparalleled reputation for high quality RF aural Studio-Transmitter Links (STLs) with the performance and speed of today s
Chapter 9: Controller design
 Chapter 9. Controller Design 9.1. Introduction 9.2. Effect of negative feedback on the network transfer functions 9.2.1. Feedback reduces the transfer function from disturbances to the output 9.2.2. Feedback
Chapter 9. Controller Design 9.1. Introduction 9.2. Effect of negative feedback on the network transfer functions 9.2.1. Feedback reduces the transfer function from disturbances to the output 9.2.2. Feedback
Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapter 6 Information Sources and Signals. Introduction
 Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapter 6 Information Sources and Signals Modified from the lecture slides of Lami Kaya (LKaya@ieee.org) for use CECS 474, Fall 2008. 2009 Pearson Education Inc., Upper
Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapter 6 Information Sources and Signals Modified from the lecture slides of Lami Kaya (LKaya@ieee.org) for use CECS 474, Fall 2008. 2009 Pearson Education Inc., Upper
5 in 1 DVB-T Transmitter & Dual Cast Agile Digital Transposer TV EQUIPMENT
 The VHF/UHF Dual cast Digital Transposers/ Digital Transmitters set new standards for ATV and DVB-T transposer and transmitter technology by combining top performance with an extensive number of features
The VHF/UHF Dual cast Digital Transposers/ Digital Transmitters set new standards for ATV and DVB-T transposer and transmitter technology by combining top performance with an extensive number of features
AN1200.04. Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: 902-928 MHz. FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: 902-928 MHz
 AN1200.04 Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: Copyright Semtech 2006 1 of 15 www.semtech.com 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents...2 1.1 Index of Figures...2 1.2 Index of Tables...2
AN1200.04 Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: Copyright Semtech 2006 1 of 15 www.semtech.com 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents...2 1.1 Index of Figures...2 1.2 Index of Tables...2
Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
 Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) Definition Synchronous optical network (SONET) is a standard for optical telecommunications transport formulated by the Exchange Carriers Standards Association (ECSA)
Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) Definition Synchronous optical network (SONET) is a standard for optical telecommunications transport formulated by the Exchange Carriers Standards Association (ECSA)
Successfully negotiating the PCI EXPRESS 2.0 Super Highway Towards Full Compliance
 Successfully negotiating the PCI EXPRESS 2.0 Super Highway Towards Full Compliance Page 1 Agenda Introduction PCIe 2.0 changes from 1.0a/1.1 Spec 5GT/s Challenges Error Correction Techniques Test tool
Successfully negotiating the PCI EXPRESS 2.0 Super Highway Towards Full Compliance Page 1 Agenda Introduction PCIe 2.0 changes from 1.0a/1.1 Spec 5GT/s Challenges Error Correction Techniques Test tool
EECC694 - Shaaban. Transmission Channel
 The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
Computer Networks II
 Computer Networks II SDH Giorgio Ventre COMICS LAB Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica Università di Napoli Federico II Nota di Copyright Quest insieme di trasparenze è stato ideato e realizzato
Computer Networks II SDH Giorgio Ventre COMICS LAB Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica Università di Napoli Federico II Nota di Copyright Quest insieme di trasparenze è stato ideato e realizzato
SDH and WDM: a look at the physical layer
 SDH and WDM: a look at the physical SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and
SDH and WDM: a look at the physical SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and
HDSL Basics. HDSL Basics. Introduction. HDSL Overview
 1 Introduction Providing T1 service is a competitive race, and High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line () is quickly emerging as the ideal solution to remain a step ahead. Currently touted as repeaterless
1 Introduction Providing T1 service is a competitive race, and High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line () is quickly emerging as the ideal solution to remain a step ahead. Currently touted as repeaterless
MICROPHONE SPECIFICATIONS EXPLAINED
 Application Note AN-1112 MICROPHONE SPECIFICATIONS EXPLAINED INTRODUCTION A MEMS microphone IC is unique among InvenSense, Inc., products in that its input is an acoustic pressure wave. For this reason,
Application Note AN-1112 MICROPHONE SPECIFICATIONS EXPLAINED INTRODUCTION A MEMS microphone IC is unique among InvenSense, Inc., products in that its input is an acoustic pressure wave. For this reason,
EMC Basics. Speaker : Alain Lafuente. Alain.lafuente@we-online.com
 EMC Basics Speaker : lain Lafuente lain.lafuente@we-online.com WHT IS EMC? 2 CE Marking With the formation of the single European market, standardization was required to remove technical barriers to trade.
EMC Basics Speaker : lain Lafuente lain.lafuente@we-online.com WHT IS EMC? 2 CE Marking With the formation of the single European market, standardization was required to remove technical barriers to trade.
Working with T3 and T1: Technology, Troubleshooting and Fault Location
 Working with T3 and T1: Technology, Troubleshooting and Fault Location Sunrise Telecom... A Step Ahead 1 Overview This handbook gives you an overview of T3 and T1 technology and equipment. It also shows
Working with T3 and T1: Technology, Troubleshooting and Fault Location Sunrise Telecom... A Step Ahead 1 Overview This handbook gives you an overview of T3 and T1 technology and equipment. It also shows
US-Key New generation of High performances Ultrasonic device
 US-Key New generation of High performances Ultrasonic device US-Key connected to a laptop computer US-Key Ultrasound device single channel Features USB2 High Speed connection Ultralow noise preamplifier
US-Key New generation of High performances Ultrasonic device US-Key connected to a laptop computer US-Key Ultrasound device single channel Features USB2 High Speed connection Ultralow noise preamplifier
Network Performance: Networks must be fast. What are the essential network performance metrics: bandwidth and latency
 Network Performance: Networks must be fast What are the essential network performance metrics: bandwidth and latency Transmission media AS systems Input'signal'f(t) Has'bandwidth'B System'with'H(-) Output'signal'g(t)
Network Performance: Networks must be fast What are the essential network performance metrics: bandwidth and latency Transmission media AS systems Input'signal'f(t) Has'bandwidth'B System'with'H(-) Output'signal'g(t)
V CC TOP VIEW. f SSO = 20MHz to 134MHz (DITHERED)
 19-013; Rev 1; 10/11 0MHz to 13MHz Spread-Spectrum General Description The is a spread-spectrum clock modulator IC that reduces EMI in high clock-frequency-based, digital electronic equipment. Using an
19-013; Rev 1; 10/11 0MHz to 13MHz Spread-Spectrum General Description The is a spread-spectrum clock modulator IC that reduces EMI in high clock-frequency-based, digital electronic equipment. Using an
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications
 Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
1. ANSI T1.102-1993 T1
 AN7 Application Note Measurement and Evaluation of Pulse Shapes in T1/E1 Transmission Systems By Roger Taylor Crystal Semiconductor Corporation P.O. Box 17847, Austin, TX 78760 (512) 445-7222 FAX: (512)
AN7 Application Note Measurement and Evaluation of Pulse Shapes in T1/E1 Transmission Systems By Roger Taylor Crystal Semiconductor Corporation P.O. Box 17847, Austin, TX 78760 (512) 445-7222 FAX: (512)
SDH and WDM A look at the physical layer
 SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and QoS provisioning - 1 Copyright This
SDH and WDM A look at the physical Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network management and QoS provisioning - 1 Copyright This
VCO K 0 /S K 0 is tho slope of the oscillator frequency to voltage characteristic in rads per sec. per volt.
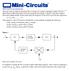 Phase locked loop fundamentals The basic form of a phase locked loop (PLL) consists of a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), a phase detector (PD), and a filter. In its more general form (Figure 1), the
Phase locked loop fundamentals The basic form of a phase locked loop (PLL) consists of a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), a phase detector (PD), and a filter. In its more general form (Figure 1), the
