Factoring Trinomials of the Form
|
|
|
- Cameron Carter
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 4 6B: Factoring Trinomials of the Form A x 2 + Bx + C where A > 1 by The AC and Factor By Grouping Method Easy Trinomials: 1 x 2 + Bx + C The last section covered the topic of factoring second degree trinomials that had 1x 2 as the first term. These trinomials looked like 1x 2 ± bx ± c. The factoring technique used in that section did not require multiple steps and many students develop their skills to the level where they can factor these trinomials in their head. For this reason we call these type of trinomials "Easy Trinomials" as in "easy to factor." Hard Trinomials: Hard Trinomials have a first term of Ax 2 where A > 1. A x 2 + Bx + C where A > 1 Examples of Hard Trinomials 6x 2 25x + 4 5x 2 16x x 2 + x 6 15x 2 x 6 Students are taught many different techniques to factor Hard Trinomials: Factoring by Grouping, The AC method, trying all the possible factors FOIL, The Box Method, and many others. A search of the internet and u tube will reveal many methods. Each of these techniques require 3 or 4 written steps. The amount of work required to factor these trinomials is why we call them "Hard Trinomials" The best technique is the one you know and are good at. If you already know a method to factor these polynomials and are good at it then continue to use that technique. If you do not know a technique then the one that follows may be considered. It is as easy as any of the other choices, and seems to be one the easiest methods for many students to learn. It seems every technique for factoring Hard Trinomials has a name. This method will be called Factoring Hard Trinomials by The AC and Factor By Grouping Method Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
2 The AC and Factor By Grouping Method to factor A x 2 + Bx + C where C is positive Example 1 Factor: 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Factor: 3x 2 + 7x + 2 3x 2 and the 2 + 6x 2 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to + 6x 2 and add to + 7x + 6x and + 1x Replace the 9x in 2x x x + 1x 2x x 2 + 6x + 1x x 2 + 6x + 1x + 2 Factor a GCF of 3x out of the first two terms and Factor a GCF of 1 out of the last two terms 3x (x + 2 ) + 1(x + 2 ) Factor a GCF of ( x + 2 ) out of the two terms ( x + 2 ) ( 3x + 1) Factor: 3x 2 + 7x + 2 (x + 2) (3x +1) Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
3 Example 2 Factor: 2x 2 9x +10 2x 2 and the x 2 2x 2 9x +10 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to + 20x 2 and add to 9x 5x and 4x Replace the 9x in 2x 2 9x x 4x 2x x 2 5x 4x x 2 5x 4x + 10 Factor a GCF of x out of the first two terms and Factor a GCF of 2 out of the last two terms x (2x 5 ) 2 (2x 5 ) Factor a GCF of ( 2x 5 ) out of the two terms ( 2x 5 ) ( x 2) Factor: 2x 2 9x +10 (2x 5) (x 2) Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
4 Example 3 Factor: 12x 2 11x x 2 and the x 2 12x 2 11x + 2 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to + 24x 2 and add to 11x 8x and 3x Replace the 11x in 12x 2 11x + 2 8x 3x 12x x 2 8x 3x x 2 8x 3x + 2 Factor a GCF of 4x out of the first two terms and Factor a GCF of 1 out of the last two terms 4x (3x 2 ) 1 (3x 2 ) Factor a GCF of ( 3x 2 ) out of the two terms ( 3x 2 ) ( 4x 1) Factor: 12x 2 11x + 2 (3x 2) (4x 1) Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
5 to factor Ax 2 ± Bx C where C is Negitive Example 4 Factor: 6x 2 7x 3 6x 2 and the 3 18x 2 6x 2 7x 3 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to 18x 2 and subtract to 7x 9x and + 2x Replace the 7x in 6x 2 7x 3 9x + 2x 6x 2 3 6x 2 9x + 2x 3 6x 2 9x + 2x 3 Factor a GCF of 3x out of the first two terms and Factor a GCF of + 1 out of the last two terms 3x (2x 3 ) + 1 (2x 3 ) Factor a GCF of ( 3x 2 ) out of the two terms ( 2x 3 ) ( 3x + 1) Factor: 6x 2 7x 3 (2x 3) (3x +1) Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
6 to factor Ax 2 ± Bx C where C is Negitive Example 5 Factor: 12x 2 + 5x 2 12x 2 and the 2 24x 2 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to 24x 2 and subtract to + 5x + 8x and 3x Replace the + 5x in 12x 2 + 5x 2 + 8x 3x 12x x 2 + 8x 3x 2 12x 2 + 8x 3x 2 Factor a GCF of 4x out of the first two terms and Factor a GCF of 1 out of the last two terms 4x (3x + 2 ) 1 (3x + 2 ) Factor a GCF of ( 3x + 2 ) out of the two terms ( 3x + 2 ) ( 4x 1) Factor: 12x 2 + 5x 2 (3x + 2) (4 x 1) Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
7 to factor Ax 2 ± Bx C where C is Negitive Example 6 Factor: 8x 2 10x 3 8x 2 and the 3 24x 2 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to 24x 2 and subtract to 10x 12x and + 2x Replace the 10x in 8x 2 10x 3 12x + 2x 8x 2 3 8x 2 12x + 2x 3 8x 2 12x + 2x 3 Factor a GCF of 4x out of the first two terms and Factor a GCF of + 1 out of the last two terms 4x (2x 3 ) + 1 (2x 3 ) Factor a GCF of ( 3x 2 ) out of the two terms ( 2x 3 ) ( 4x + 1) Factor: 8x 2 10x 3 (2x 3) (4x +1) Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
8 Some Trinomials DO NOt Factor (DNF) Many trinomials cannot be factored. We write DOES NOt Factor or Prime or DNF if that is the case. Example 7 Factor: 3x 2 + 2x + 4 3x 2 and the x 2 3x 2 + 2x + 4 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to + 12x 2 and add to +2 x there are no numbers that work so the hard trinomial Does Not Factor DNF Factor: 3x 2 + 2x + 4 Does not Factor DNF Prime The GCF must be taken out first before factoring the hard trinomial Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
9 To factor any polynomial completely you should factor the GCF out FIRST if the polynomial has a GCF. If the polynomial remaining inside the parentheses is a trinomial that can be factored then the complete factored answer is the product of the GCF and the factored trinomial. Example 8 Factor: 6x 2 26x + 8 Factor out the GCF of 2 ( ) 2 3x 2 13x + 4 now factor the hard trinominal 3x 2 13x + 4 3x 2 and the x 2 3x 2 13x + 4 Step 2: Find 2 terms that multiply to + 12x 2 and add to 13x 12x and 1x Replace the 13x in 3x 2 13x x 1x 3x x 2 12x 1x + 4 3x 2 12x 1x + 4 Factor a GCF of 3x out of the first two terms and Factor a GCF of 1 out of the last two terms 3x (x 4 ) 1 (x 4 ) Factor a GCF of ( x 4 ) out of the two terms ( x 4 ) ( 3x - 1) ( ) we factored out a 2 as the GCF of 6x 2 26x x 2 13x + 4 so the final factored answer is 2(x 4)(3x 1) Math 120 Section 4 6B Page Eitel
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring
 Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials
 Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring
 1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
Factoring Guidelines. Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms. 2008 Shirley Radai
 Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
expression is written horizontally. The Last terms ((2)( 4)) because they are the last terms of the two polynomials. This is called the FOIL method.
 A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c
 Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions
 Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions The first method we will discuss, in solving polynomial equations, is the method of FACTORING. Before we jump into this process, you need to have some concept of what
Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions The first method we will discuss, in solving polynomial equations, is the method of FACTORING. Before we jump into this process, you need to have some concept of what
6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping
 386 CHAPTER 6 Factoring and Applications 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
386 CHAPTER 6 Factoring and Applications 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
In algebra, factor by rewriting a polynomial as a product of lower-degree polynomials
 Algebra 2 Notes SOL AII.1 Factoring Polynomials Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Factoring Review Factor: rewrite a number or expression as a product of primes; e.g. 6 = 2 3 In algebra, factor by rewriting
Algebra 2 Notes SOL AII.1 Factoring Polynomials Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Factoring Review Factor: rewrite a number or expression as a product of primes; e.g. 6 = 2 3 In algebra, factor by rewriting
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring a Polynomial Expression Factoring a polynomial is expressing the polynomial as a product of two or more factors. Simply stated, it is somewhat the reverse process of multiplying. To factor polynomials,
Factoring a Polynomial Expression Factoring a polynomial is expressing the polynomial as a product of two or more factors. Simply stated, it is somewhat the reverse process of multiplying. To factor polynomials,
Factoring Methods. Example 1: 2x + 2 2 * x + 2 * 1 2(x + 1)
 Factoring Methods When you are trying to factor a polynomial, there are three general steps you want to follow: 1. See if there is a Greatest Common Factor 2. See if you can Factor by Grouping 3. See if
Factoring Methods When you are trying to factor a polynomial, there are three general steps you want to follow: 1. See if there is a Greatest Common Factor 2. See if you can Factor by Grouping 3. See if
Factoring and Applications
 Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Name Intro to Algebra 2. Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring
 Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
5 means to write it as a product something times something instead of a sum something plus something plus something.
 Intermediate algebra Class notes Factoring Introduction (section 6.1) Recall we factor 10 as 5. Factoring something means to think of it as a product! Factors versus terms: terms: things we are adding
Intermediate algebra Class notes Factoring Introduction (section 6.1) Recall we factor 10 as 5. Factoring something means to think of it as a product! Factors versus terms: terms: things we are adding
NSM100 Introduction to Algebra Chapter 5 Notes Factoring
 Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced
 Instructor! Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced Last week we looked at greatest common factors and the basics of factoring out the GCF. In this second activity, we will discuss factoring more difficult
Instructor! Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced Last week we looked at greatest common factors and the basics of factoring out the GCF. In this second activity, we will discuss factoring more difficult
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:.
 MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
( ) FACTORING. x In this polynomial the only variable in common to all is x.
 FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
Factoring. Factoring Monomials Monomials can often be factored in more than one way.
 Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Factoring Flow Chart
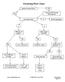 Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
15.1 Factoring Polynomials
 LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
Algebra 2 PreAP. Name Period
 Algebra 2 PreAP Name Period IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS!!! We understand that students come to Algebra II with different strengths and needs. For this reason, students have options for completing
Algebra 2 PreAP Name Period IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS!!! We understand that students come to Algebra II with different strengths and needs. For this reason, students have options for completing
Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder).
 Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
AIP Factoring Practice/Help
 The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
6.3 FACTORING ax 2 bx c WITH a 1
 290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
 Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method
 6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
A Systematic Approach to Factoring
 A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
Factors and Products
 CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
CHAPTER 7: FACTORING POLYNOMIALS
 CHAPTER 7: FACTORING POLYNOMIALS FACTOR (noun) An of two or more quantities which form a product when multiplied together. 1 can be rewritten as 3*, where 3 and are FACTORS of 1. FACTOR (verb) - To factor
CHAPTER 7: FACTORING POLYNOMIALS FACTOR (noun) An of two or more quantities which form a product when multiplied together. 1 can be rewritten as 3*, where 3 and are FACTORS of 1. FACTOR (verb) - To factor
2x 2x 2 8x. Now, let s work backwards to FACTOR. We begin by placing the terms of the polynomial inside the cells of the box. 2x 2
 Activity 23 Math 40 Factoring using the BOX Team Name (optional): Your Name: Partner(s): 1. (2.) Task 1: Factoring out the greatest common factor Mini Lecture: Factoring polynomials is our focus now. Factoring
Activity 23 Math 40 Factoring using the BOX Team Name (optional): Your Name: Partner(s): 1. (2.) Task 1: Factoring out the greatest common factor Mini Lecture: Factoring polynomials is our focus now. Factoring
FACTORING ax 2 bx c. Factoring Trinomials with Leading Coefficient 1
 5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any.
 Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Student Activity
 Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Student Activity Materials: Algebra Tiles (student set) Worksheet: Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Algebra Tiles: Each algebra tile kits should contain
Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Student Activity Materials: Algebra Tiles (student set) Worksheet: Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Algebra Tiles: Each algebra tile kits should contain
A. Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor.
 DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - FACTORING POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you!
DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - FACTORING POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you!
This unit has primarily been about quadratics, and parabolas. Answer the following questions to aid yourselves in creating your own study guide.
 COLLEGE ALGEBRA UNIT 2 WRITING ASSIGNMENT This unit has primarily been about quadratics, and parabolas. Answer the following questions to aid yourselves in creating your own study guide. 1) What is the
COLLEGE ALGEBRA UNIT 2 WRITING ASSIGNMENT This unit has primarily been about quadratics, and parabolas. Answer the following questions to aid yourselves in creating your own study guide. 1) What is the
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations
 Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet
 Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
4.4 Factoring ax 2 + bx + c
 4.4 Factoring ax 2 + bx + c From the last section, we now know a trinomial should factor as two binomials. With this in mind, we need to look at how to factor a trinomial when the leading coefficient is
4.4 Factoring ax 2 + bx + c From the last section, we now know a trinomial should factor as two binomials. With this in mind, we need to look at how to factor a trinomial when the leading coefficient is
FOIL FACTORING. Factoring is merely undoing the FOIL method. Let s look at an example: Take the polynomial x²+4x+4.
 FOIL FACTORING Factoring is merely undoing the FOIL method. Let s look at an example: Take the polynomial x²+4x+4. First we take the 3 rd term (in this case 4) and find the factors of it. 4=1x4 4=2x2 Now
FOIL FACTORING Factoring is merely undoing the FOIL method. Let s look at an example: Take the polynomial x²+4x+4. First we take the 3 rd term (in this case 4) and find the factors of it. 4=1x4 4=2x2 Now
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials
 Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
7-6. Choosing a Factoring Model. Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable IN T RO DUC E T EACH. Standards for Mathematical Content
 7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
Gouvernement du Québec Ministère de l Éducation, 2004 04-00813 ISBN 2-550-43545-1
 Gouvernement du Québec Ministère de l Éducation, 004 04-00813 ISBN -550-43545-1 Legal deposit Bibliothèque nationale du Québec, 004 1. INTRODUCTION This Definition of the Domain for Summative Evaluation
Gouvernement du Québec Ministère de l Éducation, 004 04-00813 ISBN -550-43545-1 Legal deposit Bibliothèque nationale du Québec, 004 1. INTRODUCTION This Definition of the Domain for Summative Evaluation
When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property and take out the GCF.
 Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
1.3 Algebraic Expressions
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
FACTORING ax 2 bx c WITH a 1
 296 (6 20) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.4 FACTORING a 2 b c WITH a 1 In this section The ac Method Trial and Error Factoring Completely In Section 6.3 we factored trinomials with a leading coefficient of 1. In
296 (6 20) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.4 FACTORING a 2 b c WITH a 1 In this section The ac Method Trial and Error Factoring Completely In Section 6.3 we factored trinomials with a leading coefficient of 1. In
MATH 108 REVIEW TOPIC 10 Quadratic Equations. B. Solving Quadratics by Completing the Square
 Math 108 T10-Review Topic 10 Page 1 MATH 108 REVIEW TOPIC 10 Quadratic Equations I. Finding Roots of a Quadratic Equation A. Factoring B. Quadratic Formula C. Taking Roots II. III. Guidelines for Finding
Math 108 T10-Review Topic 10 Page 1 MATH 108 REVIEW TOPIC 10 Quadratic Equations I. Finding Roots of a Quadratic Equation A. Factoring B. Quadratic Formula C. Taking Roots II. III. Guidelines for Finding
Pre-Calculus II Factoring and Operations on Polynomials
 Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING
 POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping
 296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
x 4-1 = (x²)² - (1)² = (x² + 1) (x² - 1) = (x² + 1) (x - 1) (x + 1)
 Factoring Polynomials EXAMPLES STEP 1 : Greatest Common Factor GCF Factor out the greatest common factor. 6x³ + 12x²y = 6x² (x + 2y) 5x - 5 = 5 (x - 1) 7x² + 2y² = 1 (7x² + 2y²) 2x (x - 3) - (x - 3) =
Factoring Polynomials EXAMPLES STEP 1 : Greatest Common Factor GCF Factor out the greatest common factor. 6x³ + 12x²y = 6x² (x + 2y) 5x - 5 = 5 (x - 1) 7x² + 2y² = 1 (7x² + 2y²) 2x (x - 3) - (x - 3) =
Sect 6.7 - Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Rule
 Sect 6.7 - Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Rule 116 Concept #1: Definition of a Quadratic Equation A quadratic equation is an equation that can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 (referred
Sect 6.7 - Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Rule 116 Concept #1: Definition of a Quadratic Equation A quadratic equation is an equation that can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 (referred
6.4 Special Factoring Rules
 6.4 Special Factoring Rules OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor a sum of cubes. By reversing the rules for multiplication
6.4 Special Factoring Rules OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor a sum of cubes. By reversing the rules for multiplication
Factoring - Factoring Special Products
 6.5 Factoring - Factoring Special Products Objective: Identify and factor special products including a difference of squares, perfect squares, and sum and difference of cubes. When factoring there are
6.5 Factoring - Factoring Special Products Objective: Identify and factor special products including a difference of squares, perfect squares, and sum and difference of cubes. When factoring there are
Factoring a Difference of Two Squares. Factoring a Difference of Two Squares
 284 (6 8) Chapter 6 Factoring 87. Tomato soup. The amount of metal S (in square inches) that it takes to make a can for tomato soup is a function of the radius r and height h: S 2 r 2 2 rh a) Rewrite this
284 (6 8) Chapter 6 Factoring 87. Tomato soup. The amount of metal S (in square inches) that it takes to make a can for tomato soup is a function of the radius r and height h: S 2 r 2 2 rh a) Rewrite this
SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
 (Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
(Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives. Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers.
 Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: - Beginning Algebra CREDITS: 4 (Lec 4 / Lab 0) PREREQUISITES: MATH 0920: Fundamental Mathematics with a grade of C or better, Placement Exam,
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: - Beginning Algebra CREDITS: 4 (Lec 4 / Lab 0) PREREQUISITES: MATH 0920: Fundamental Mathematics with a grade of C or better, Placement Exam,
Simplification Problems to Prepare for Calculus
 Simplification Problems to Prepare for Calculus In calculus, you will encounter some long epressions that will require strong factoring skills. This section is designed to help you develop those skills.
Simplification Problems to Prepare for Calculus In calculus, you will encounter some long epressions that will require strong factoring skills. This section is designed to help you develop those skills.
By reversing the rules for multiplication of binomials from Section 4.6, we get rules for factoring polynomials in certain forms.
 SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
EAP/GWL Rev. 1/2011 Page 1 of 5. Factoring a polynomial is the process of writing it as the product of two or more polynomial factors.
 EAP/GWL Rev. 1/2011 Page 1 of 5 Factoring a polynomial is the process of writing it as the product of two or more polynomial factors. Example: Set the factors of a polynomial equation (as opposed to an
EAP/GWL Rev. 1/2011 Page 1 of 5 Factoring a polynomial is the process of writing it as the product of two or more polynomial factors. Example: Set the factors of a polynomial equation (as opposed to an
COLLEGE ALGEBRA 10 TH EDITION LIAL HORNSBY SCHNEIDER 1.1-1
 10 TH EDITION COLLEGE ALGEBRA LIAL HORNSBY SCHNEIDER 1.1-1 1.1 Linear Equations Basic Terminology of Equations Solving Linear Equations Identities 1.1-2 Equations An equation is a statement that two expressions
10 TH EDITION COLLEGE ALGEBRA LIAL HORNSBY SCHNEIDER 1.1-1 1.1 Linear Equations Basic Terminology of Equations Solving Linear Equations Identities 1.1-2 Equations An equation is a statement that two expressions
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions
 6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS BY THE NEW TRANSFORMING METHOD (By Nghi H Nguyen Updated Oct 28, 2014))
 SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS BY THE NEW TRANSFORMING METHOD (By Nghi H Nguyen Updated Oct 28, 2014)) There are so far 8 most common methods to solve quadratic equations in standard form ax² + bx + c = 0.
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS BY THE NEW TRANSFORMING METHOD (By Nghi H Nguyen Updated Oct 28, 2014)) There are so far 8 most common methods to solve quadratic equations in standard form ax² + bx + c = 0.
Florida Math 0028. Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper
 Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
a. You can t do the simple trick of finding two integers that multiply to give 6 and add to give 5 because the a (a = 4) is not equal to one.
 FACTORING TRINOMIALS USING THE AC METHOD. Factoring trinomial epressions in one unknown is an important skill necessary to eventually solve quadratic equations. Trinomial epressions are of the form a 2
FACTORING TRINOMIALS USING THE AC METHOD. Factoring trinomial epressions in one unknown is an important skill necessary to eventually solve quadratic equations. Trinomial epressions are of the form a 2
Using the ac Method to Factor
 4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
In the above, the number 19 is an example of a number because its only positive factors are one and itself.
 Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
Introduction Assignment
 PRE-CALCULUS 11 Introduction Assignment Welcome to PREC 11! This assignment will help you review some topics from a previous math course and introduce you to some of the topics that you ll be studying
PRE-CALCULUS 11 Introduction Assignment Welcome to PREC 11! This assignment will help you review some topics from a previous math course and introduce you to some of the topics that you ll be studying
Polynomials and Factoring
 7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
Brunswick High School has reinstated a summer math curriculum for students Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2 for the 2014-2015 school year.
 Brunswick High School has reinstated a summer math curriculum for students Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2 for the 2014-2015 school year. Goal The goal of the summer math program is to help students
Brunswick High School has reinstated a summer math curriculum for students Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2 for the 2014-2015 school year. Goal The goal of the summer math program is to help students
FACTOR POLYNOMIALS by SPLITTING
 FACTOR POLYNOMIALS by SPLITTING THE IDEA FACTOR POLYNOMIALS by SPLITTING The idea is to split the middle term into two pieces. Say the polynomial looks like c + bx + ax 2. Further more suppose the DL METHOD
FACTOR POLYNOMIALS by SPLITTING THE IDEA FACTOR POLYNOMIALS by SPLITTING The idea is to split the middle term into two pieces. Say the polynomial looks like c + bx + ax 2. Further more suppose the DL METHOD
THE SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ON COURSE OUTLINE
 THE SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ON COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: College Preparatory Mathematics Code No.: Mth 92-5 Semester: Two Program: College Entrance - Native Author:
THE SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ON COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: College Preparatory Mathematics Code No.: Mth 92-5 Semester: Two Program: College Entrance - Native Author:
4.1. COMPLEX NUMBERS
 4.1. COMPLEX NUMBERS What You Should Learn Use the imaginary unit i to write complex numbers. Add, subtract, and multiply complex numbers. Use complex conjugates to write the quotient of two complex numbers
4.1. COMPLEX NUMBERS What You Should Learn Use the imaginary unit i to write complex numbers. Add, subtract, and multiply complex numbers. Use complex conjugates to write the quotient of two complex numbers
Algebra Cheat Sheets
 Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
How To Factor By Gcf In Algebra 1.5
 7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
Wentzville School District Algebra 1: Unit 8 Stage 1 Desired Results
 Wentzville School District Algebra 1: Unit 8 Stage 1 Desired Results Unit Title: Quadratic Expressions & Equations Course: Algebra I Unit 8 - Quadratic Expressions & Equations Brief Summary of Unit: At
Wentzville School District Algebra 1: Unit 8 Stage 1 Desired Results Unit Title: Quadratic Expressions & Equations Course: Algebra I Unit 8 - Quadratic Expressions & Equations Brief Summary of Unit: At
Factoring - Grouping
 6.2 Factoring - Grouping Objective: Factor polynomials with four terms using grouping. The first thing we will always do when factoring is try to factor out a GCF. This GCF is often a monomial like in
6.2 Factoring - Grouping Objective: Factor polynomials with four terms using grouping. The first thing we will always do when factoring is try to factor out a GCF. This GCF is often a monomial like in
Adding and Subtracting Fractions. 1. The denominator of a fraction names the fraction. It tells you how many equal parts something is divided into.
 Tallahassee Community College Adding and Subtracting Fractions Important Ideas:. The denominator of a fraction names the fraction. It tells you how many equal parts something is divided into.. The numerator
Tallahassee Community College Adding and Subtracting Fractions Important Ideas:. The denominator of a fraction names the fraction. It tells you how many equal parts something is divided into.. The numerator
Factoring ax 2 + bx + c - Teacher Notes
 Southern Nevada Regional Professi onal D evel opment Program VOLUME 1, ISSUE 8 MAY 009 A N ewsletter from the Sec ondary Mathematic s Team Factoring ax + bx + c - Teacher Notes Here we look at sample teacher
Southern Nevada Regional Professi onal D evel opment Program VOLUME 1, ISSUE 8 MAY 009 A N ewsletter from the Sec ondary Mathematic s Team Factoring ax + bx + c - Teacher Notes Here we look at sample teacher
How To Factor By Grouping
 Lecture Notes Factoring by the AC-method page 1 Sample Problems 1. Completely factor each of the following. a) 4a 2 mn 15abm 2 6abmn + 10a 2 m 2 c) 162a + 162b 2ax 4 2bx 4 e) 3a 2 5a 2 b) a 2 x 3 b 2 x
Lecture Notes Factoring by the AC-method page 1 Sample Problems 1. Completely factor each of the following. a) 4a 2 mn 15abm 2 6abmn + 10a 2 m 2 c) 162a + 162b 2ax 4 2bx 4 e) 3a 2 5a 2 b) a 2 x 3 b 2 x
Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors
 Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors Brenda Meery Kaitlyn Spong Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) www.ck12.org Chapter 6. Factoring CHAPTER
Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors Brenda Meery Kaitlyn Spong Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) www.ck12.org Chapter 6. Factoring CHAPTER
Title: Factoring Trinomials Using the Trial-and-Error Method Class: Math 100 Author: Sharareh Masooman Instructions to tutor: Read instructions under
 Title: Factoring Trinomials Using the Trial-and-Error Method Class: Math 100 Author: Sharareh Masooman nstructions to tutor: Read instructions under Activity and follow all steps for each problem exactly
Title: Factoring Trinomials Using the Trial-and-Error Method Class: Math 100 Author: Sharareh Masooman nstructions to tutor: Read instructions under Activity and follow all steps for each problem exactly
ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you factor expressions of the form ax 2 + bx + c?
 LESSON 15.3 Factoring ax 2 + bx + c A.SSE.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you factor expressions of the form ax 2 + bx + c?
LESSON 15.3 Factoring ax 2 + bx + c A.SSE.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you factor expressions of the form ax 2 + bx + c?
SPECIAL PRODUCTS AND FACTORS
 CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
Determinants can be used to solve a linear system of equations using Cramer s Rule.
 2.6.2 Cramer s Rule Determinants can be used to solve a linear system of equations using Cramer s Rule. Cramer s Rule for Two Equations in Two Variables Given the system This system has the unique solution
2.6.2 Cramer s Rule Determinants can be used to solve a linear system of equations using Cramer s Rule. Cramer s Rule for Two Equations in Two Variables Given the system This system has the unique solution
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials 8A Factoring Methods 8-1 Factors and Greatest Common Factors Lab Model Factoring 8-2 Factoring by GCF Lab Model Factorization of Trinomials 8-3 Factoring x 2 + bx + c 8-4 Factoring
Factoring Polynomials 8A Factoring Methods 8-1 Factors and Greatest Common Factors Lab Model Factoring 8-2 Factoring by GCF Lab Model Factorization of Trinomials 8-3 Factoring x 2 + bx + c 8-4 Factoring
Factoring (pp. 1 of 4)
 Factoring (pp. 1 of 4) Algebra Review Try these items from middle school math. A) What numbers are the factors of 4? B) Write down the prime factorization of 7. C) 6 Simplify 48 using the greatest common
Factoring (pp. 1 of 4) Algebra Review Try these items from middle school math. A) What numbers are the factors of 4? B) Write down the prime factorization of 7. C) 6 Simplify 48 using the greatest common
Answers to Basic Algebra Review
 Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS
 278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
6.6 Factoring Strategy
 456 CHAPTER 6. FACTORING 6.6 Factoring Strategy When you are concentrating on factoring problems of a single type, after doing a few you tend to get into a rhythm, and the remainder of the exercises, because
456 CHAPTER 6. FACTORING 6.6 Factoring Strategy When you are concentrating on factoring problems of a single type, after doing a few you tend to get into a rhythm, and the remainder of the exercises, because
Factoring Polynomials
 UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
Mathematics Placement
 Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
