Algebra 2 PreAP. Name Period
|
|
|
- Roger Glenn
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Algebra 2 PreAP Name Period IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS!!! We understand that students come to Algebra II with different strengths and needs. For this reason, students have options for completing the packet and getting assistance! Students should try to answer all the questions if possible; you must show all work. Students must answer a minimum of 85 out of 101 questions to receive full credit. So, if you really can t answer certain questions, students may write the word pass on up to 16 questions without penalty. (The purpose of this option is to allow students to show what they know on certain concepts while informing the teacher of concepts that may need to be reviewed with students after school starts). Khan Academy video tutorials may be very helpful to you. HISD has aligned Khan Academy with Algebra I, are available by clicking this link: Need face-to-face help with packet? Come to WHS on August 9 th between 9-12pm! WHS Algebra II teachers will be on hand to give you assistance! There will be a test over this material on or before September 6, Finally, honor and integrity is at the heart of a Westside Wolf! Smart wolves never cheat. You are only hurting yourself by attempting to copy someone else s work. This packet is to help you be ready for Algebra II, and help your teachers know what you can do. All existing and new students who are enrolled at WHS on or before August 17 th, must submit their summer packet to their math teacher no later than Friday, August 30, Students who enrolled at Westside High School on or after August 19 th, must submit their summer packet within two weeks of their enrollment date at Westside. Now! Get Ready, Get Set, and Do Your Best!
2 Solving Equations Addition Property of Equality For any numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a + c = b +c. Subtraction Property of Equality For any numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a c = b c. Multiplication Property of Equality For any numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then ac = bc. Division Property of Equality For any numbers a, b, and c, with c 0, if a = b, then a = b. c c Example 1 Solve: 3 ½ p = 1 ½ 7 2 p = p p = Check: 3 ½ 7 = 1 ½ = Original equation Rewrite each mixed number as an improper fraction Multiply each side by the reciprocal of 7/2. Simplify Substitute solution for variable Rewrite each mixed number as an improper fraction Left Hand Side = Right Hand Side LHS = RHS correct Example 2 Solve: -5n = 60 Original equation -5n = 60 Divide both sides by -5 or -5-5 multiply both sides by -1/5 n = -12 Simplify Check: -5 (-12) = 60 Substitute solution for variable 60 = 60 Left Hand Side = Right Hand Side LHS = RHS correct Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side To solve an equation with the same variable on each side, first use the Addition or the Subtraction Property of Equality to write an equivalent equation that has the variable on just one side of the equation. Then use the Multiplication or Division Property of Equality to solve the equation. Example 1 Solve: 5y 8 = 3 y y 8 3y = 3 y y 2y 8 = 12 2y = y = 20 2y = y = 10 Check: 5y 8 = 3 y (10) 8 = 3(10) = = 42 LHS = RHS correct Example 2 Solve: -11 3y = 8y y + 3y = 8y y -11 = 11y = 11y = 11y -12 = 11y = y = y Check: -11 3y = 8y = = = = LHS = RHS correct Example 3 Solve: 4 (2a 1) = -10 (a 5 ) 8a 4 = -10a a a = -10 a a 18a 4 = a = a = 54 18a = a = 3 Check: 4 (2a 1) = -10 (a 5 ) 4 (2(3) 1) = -10 (3 5 ) 4 ( 6 1 ) = -10(-2) 4 (5) = = 20 LHS = RHS correct
3 Exercises: Solve each equation. Then check your solution = y 8 2. w ½ = = b h = m = p = h = ½ m = t = b = 5b y 2 y = 3y x + 2 = 2x n 8 = 3n x = 2.1 x s = 8.8s ½ b + 4 = 1 8 b ¾ k 5 = ¼ k p = 4p 1 3
4 19. -3(x + 5) = 3(x - 1) 20. 2(7 + 3t) = -t 21. 3(a + 1) 5 = 3a 2 Solving Equations and Formulas Solve for variables: sometimes you may want to solve an equation such as V = lwh for one of its variables. For example, if you know the values of V, w, and h, then the equation l = V is more useful for finding the value of l. wh Example 1 Solve 2x 4 y = 8 for y. 2x 4y = 8 2x 4y 2x = 8 2x -4y = 8 2x -4y = 8 2x -4-4 y = 8-2x or 2x Example 2 Solve 3m n = km 8 3m n = km 8 3m n km = km 8 km 3m n km = -8 3m n km + n = -8 + n 3m km = -8 + n m (3 k ) = -8 + n m (3 k ) = -8 + n 3 k 3 k m = -8 + n, or n 8 3 k 3 k Exercises: Solve each equation or formula for the variable specified. Since division by 0 is undefined, 3 k 0, or k ax b = c for x x + 1 = y for x 24. (x + f) + 2 = j for x 25. xy + z = 9 for y 26. x( 4 k ) = p for k 27. 7x + 3y = m for y 28. xy + xz = 6 + a for x 4
5 Describe Number Patterns Write Equations: Sometimes a pattern can lead to a general rule that can be written as an equation. Example: Suppose you purchased a number of packages of blank CDs. If each package contains 3 CDs, you could make a chart to show the relationship between the number of packages of compact disks and the number of disks purchased. Use x for the number of packages and y for the number of compact disks. Make a table of ordered pairs for several points of the graph. Number of packages Number of CDs The difference in the x values is 1, and the difference in the y values is 3. This pattern shows that y is always three times x. This suggests the relation y = 3x. Since the relation is also a function, we can write the equation in functional notation as f(x) = 3x. Exercises: 29. Write an equation for the function in functional notation. Then complete the table. x y Write an equation for the function in functional notation. Then complete the table. Example 1 x y Write an equation in functional notation. 32. Write an equation in functional notation. 5
6 Equations of Linear Function Standard Form Slope-Intercept Form Point-Slope Form Ax + By = C y = mx + b, where m is the given slope and b is the y-intercept y- y 1 = m (x x 1 ), where m is the given slope and (x 1, y 1 ) is the given point Example 1: Write an equation of a line in standard form whose slope is -4 and whose y-intercept is 3. y = mx + b y = -4x x +4x 4x + y = 3 Example 2: Graph 3x 4y = 8 3x 4y = 8 Original equation -4y = - 3x + 8 Subtract 3x from each side -4y = - 3x + 8 Divide each side by y = ¾ x 2 Simplify The y-intercept of y = 3/4x 2 is -2 and the slope is ¾. So graph the point (0, -2). From this point, move up 3 units and right 4 units. Draw a line passing through both points. Exercises: Write an equation of the line in Standard Form with the given information. 33. Slope: 8, y-intercept Slope: -2, point (5, 3) 35. Slope: -1, y-intercept -7 Write an equation of the line in Standard Form in each graph Graph each equation x y = x + y = x + y = -1 6
7 Graphing Systems of Equations Solve by Graphing One method of solving a system of equations is to graph the equations on the same coordinate plane. Example: Graph each system of equations. Then determine whether the system has no solution, one solution, or infinitely many solutions. If the system has one solution, name it. a. x + y = 2 x y = 4 The graphs intersect. Therefore, there is one solution. The point (3, -1) seems to lie on both lines. Check this estimate by replacing x with 3 and y with -1 in each equation. x + y = (-1) = 2 x y = 4 3 (-1) = or 4 The solution is (3,-1). b. y = 2x + 1 2y = 4x + 2 The graphs coincide. Therefore there are infinitely many solutions. Exercises: Graph each system of equations. Then determine whether the system has no solution, one solution, or infinitely many solutions. If the system has one solution, name it. 42. y = x = y = ½ x 3x y = -1 2x + y = 1 x + y = x + y = x + 2y = y = -4x + 4 2x y = -2 3x + 2y = -4 y = -2x + 2 7
8 Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution Example 1: use substitution to solve they system of equations. y = 2x 4x y = -4 Substitute 2x for y in the second equation. 4x y = -4 second equation 4x 2x = -4 y = 2x 2x = -4 combine like terms x = -2 Divide each side by 2 and simplify. Use y = 2x to find the value of y. y = 2x First equation y = 2(-2) x = -2 y = -4 simplify The solution is (-2,-4). Example 2: Solve for one variable, then substitute. x + 3y = 7 2x 4y = -6 Solve the first equation for x since the coefficient of x is 1. x + 3y = 7 First equation x + 3y 3y = 7 3y Subtract 3y from each side x = 7 3y Simplify Find the value of y by substituting 7 3y for x in the second equation. 2x 4y = -6 Second equation 2(7-3y) 4y = -6 x = 7 3y 14-6 y 4y = -6 Distributive Property 14-10y = -6 Combine like terms y 14 = Subtract 14 from each side. -10y = -20 Simplify. y = 2 Divide each side by -10 and simplify. Use y = 2 to find the value of x. x = 7-3y x = 7 3(2) x = 1 The solution is (1, 2). Exercises: Use substitution to solve each system of equations. If the system does not have exactly one solution, state whether it has no solution or infinitely many solutions. 48. y = 4x 49. x = 2y 50. x = 2y - 3 3x y = 1 y = x 2 x = 2y + 4 8
9 Elimination Using Addition and Subtraction Elimination Using Addition: In systems of equations in which the coefficients of the x or y terms are additive inverses, solve the system by adding the equations. Because one of the variables is eliminated, this method is called elimination. Example 1: Use addition to solve the system of equations x 3y = 7 3x + 3y = 9 Write the equations in column form and add to eliminate y. x 3y = 7 (+) 3x+ 3y = 9 4x = 16 4x = x = 4 Substitute 4 for x either equation and solve for y. 4x 3 y = 7 4 3y 4 = 7 4-3y = y = -1 The solution is (4, -1). Example 2: The sum of two numbers is 70 and their difference is 24. Find the numbers. Let x represent one number and y represent the other number. x + y = 70 (+) x y = 24 2x = 94 2x = x = 47 Substitute 47 for x in either equation y = y 47 = y = 23 The numbers are 47 and 23. Exercises: Use elimination to solve each system of equations. 51. x + y = m 3n = a b = -9 x y = 2 m + 3n = -11-3a 2b = 0 9
10 Multiplying a Polynomial by a Monomial Product of Monomial and Polynomial: The Distributive Property can be used to multiply a polynomial by a monomial. You can multiply horizontally or vertically. Sometimes multiplying results in like terms. The products can be simplified by combining like terms. Example 1: Find -3x 2 (4x 2 + 6x 8). -3x 2 (4x 2 + 6x 8) = -3x 2 (4x 2 ) + (-3x 2 )(6x)-(-3x 2 )(8) = -12x 4 + (-18x 3 ) (-24x 2 ) = -12x 4-18x x 2 Example 2: Simplify -2(4x 2 + 5x) x (x 2 + 6x) -2(4x 2 + 5x) x (x 2 + 6x) = -2(4x 2 ) + (-2)(5x) + (-x)(x 2 ) + (-x)(6x) = -8x 2 + (-10x) + (-x 3 ) + (-6x 2 ) = (-x 3 ) + [ -8x 2 + (-6x 2 )] + (-10x) = -x 3 14x 2 10x Exercises: Find each product. 54. x(5x + x 2 ) 55. x (4x 2 + 3x + 2) xy(2y + 4x 2 ) g (g 2-2g +2 ) 58. 3x (x 4 + x 3 +x 2 ) x (2x 3-2x + 3) Factoring Using the Greatest Common Factor Example 1: Use GCF to factor 12mn + 80m 2 Find the GCF of 12mn and 80m 2 12mn = m n 80 m 2 = m m GCF = 2 2 m or 4m Write each term as the product of the GCF and its remaining factors. 12mn + 80m 2 = 4m (3 n) + 4m (2 2 5 m) = 4m (3n) + 4m (20m) = 4m (3n + 20 m) 12mn + 80m 2 = 4m (3n + 20 m) Example 2: Factor 6ax + 3ay + 2bx + by by grouping. 6ax + 3ay + 2bx + by = (6ax + 3ay) + (2bx + by) = 3a (2x + y) + b (2x + y) = (3a + b)( 2x + y) Check using the FOIL method. (3a + b )(2x + y) = 3a(2x) + (3a)(y) + (b)(2x) + (b)(y) = 6ax + 3ay + 2bx + by Exercises: Factor each polynomial x + 48 y mn 2 + m 2 n 6n 62. q 4 18q q 63. 9x 2 3x 64. 4m + 6n 8mn s 3 15s c 3 42c 5 49c p 2 11p p y 3 28y 2 + y 10
11 Multiplying Polynomials Multiply Binomials: To multiply two binomials, you can apply the Distributive Property twice. You can use FOIL (First, Outer, Inner and Last) method. Example 1: Find (x + 3)(x 4) (x + 3)(x 4) = x (x 4) + 3 (x 4) = (x)(x) + x (-4) + 3(x) + 3(-4) = x 2 4x + 3x 12 = x 2 x 12 Example 2: Find (x 2) (x + 5) using FOIL method. (x 2) (x + 5) First Outer Inner Last = (x)(x) + (x)(5) +(-2) (x) +(-2)(5) = x 2 + 5x + (-2x) 10 = x 2 + 3x 10 Exercises: Find each product. 69. (x + 2)(x + 3) 70. (x 4)(x +1) 71. (x 6)(x 2) 72. (p 4)(p + 2) 73. (y + 5)(y + 2) 74. (2x 1)(x + 5) 75. (3n 4)(3n 4) 76. (8m 2 )(8m + 2) 77. (k + 4)(5k 1 ) 11
12 Factoring Trinomials: x 2 +bx +c Factor x 2 +bx +c : To factor a trinomial of the form x 2 +bx +c, find two integers m and n, whose sum is equal to b and whose product is equal to c. Example 1: Factor each trinomial. a. x 2 + 7x + 10 In this trinomial, b = 7 and c = 10. Factors of 10 Sum of Factors 1, , 5 7 x 2 + 7x + 10 = (x + 5)(x + 2) b. x 2-8x + 7 In this trinomial, b = -8 and c = 7. Notice that m + n is negative and mn is positive, so m and n are both negative. Since -7 + (-1) = -8 and (-7)(-1) = 7, m = -7 and n = -1. x 2 8x + 7 = (x 7)(x 1) Example 2: Factor x 2 + 6x 16 In this trinomial, b = 6 and c = -16. This means m + n is positive and mn is negative. Make a list of the factors of -16, where one factor of each pair is positive. Factors of -16 Sum of Factors 1, , , , 8 6 Therefore, m = -2 and n = 8. x 2 + 6x 16 = (x 2)(x + 8) Exercises: Factor each trinomial. 78. x 2 + 4x m m r 2 3r x 2 x x 2 4x x 2 22x c 2 4c p 2 16p x + x x 2 + 6x a 2 + 8a y 2 7y x 2 2x y 2 +14y m 2 + 9m
13 Factoring Trinomials: ax 2 +bx +c Factor ax 2 +bx +c : To factor a trinomial of the form ax 2 +bx +c, find two integers m and n, whose sum is equal to b and whose product is equal to ac. If there are no integers that satisfy these requirements, the polynomial is called a prime polynomial. Example 1: Factor 2x 2 +15x +18. In this example, a = 2, b =15, and c = 18. You need to find two numbers whose sum is 15 and whose product is 2 18 or 36. Make a list of the factors of 36 and look for the pair of factors whose sum is 15. Factors of 36 Sum of Factors 1, , , Use the pattern ax 2 +mx + nx +c with a= 2, m= 3, n = 12 and c = 18. 2x 2 +15x +18 = 2x 2 +3x + 12x +18 = (2x 2 +3x) + (12x +18) = x(2x + 3) + 6(2x + 3) = (x + 6) (2x + 3) Example 2: Factor 3x 2 3x 18 Note that the GCF of the terms 3x 2, 3x, and 18 is 3. First factor out this GCF. 3x 2 3x 18 = 3(x 2 x 6). Now factor x 2 x 6. Since a = 1, find the two factors of -6 whose sum is -1. Factors of -6 Sum of Factors 1, , 6 5-2, 3 1 2, -3-1 Now use the pattern (x + m) (x + n) with m = 2 and n = -3. x 2 x 6 = (x + 2) (x 3) The complete factorization is 3x 2 3x 18 = 3(x + 2) (x 3). Exercises: Factor each trinomial, if possible. If the trinomial cannot be factored using integers, write prime x 2 3x m 2 8m r 2 8r x 2 + 5x x 2 + 2x x 2 27x a 2 +5a y 2 + 9x c 2 +19c 21 13
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring
 1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
expression is written horizontally. The Last terms ((2)( 4)) because they are the last terms of the two polynomials. This is called the FOIL method.
 A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
Algebra Cheat Sheets
 Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards
 Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Brunswick High School has reinstated a summer math curriculum for students Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2 for the 2014-2015 school year.
 Brunswick High School has reinstated a summer math curriculum for students Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2 for the 2014-2015 school year. Goal The goal of the summer math program is to help students
Brunswick High School has reinstated a summer math curriculum for students Algebra 1, Geometry, and Algebra 2 for the 2014-2015 school year. Goal The goal of the summer math program is to help students
Vocabulary Words and Definitions for Algebra
 Name: Period: Vocabulary Words and s for Algebra Absolute Value Additive Inverse Algebraic Expression Ascending Order Associative Property Axis of Symmetry Base Binomial Coefficient Combine Like Terms
Name: Period: Vocabulary Words and s for Algebra Absolute Value Additive Inverse Algebraic Expression Ascending Order Associative Property Axis of Symmetry Base Binomial Coefficient Combine Like Terms
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
 Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
NSM100 Introduction to Algebra Chapter 5 Notes Factoring
 Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Mathematics Placement
 Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
Name Intro to Algebra 2. Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring
 Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials
 Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: - Beginning Algebra CREDITS: 4 (Lec 4 / Lab 0) PREREQUISITES: MATH 0920: Fundamental Mathematics with a grade of C or better, Placement Exam,
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: - Beginning Algebra CREDITS: 4 (Lec 4 / Lab 0) PREREQUISITES: MATH 0920: Fundamental Mathematics with a grade of C or better, Placement Exam,
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring
 Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
Algebraic expressions are a combination of numbers and variables. Here are examples of some basic algebraic expressions.
 Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives. Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers.
 Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Factoring and Solving by Factoring, chapter 6 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
EQUATIONS and INEQUALITIES
 EQUATIONS and INEQUALITIES Linear Equations and Slope 1. Slope a. Calculate the slope of a line given two points b. Calculate the slope of a line parallel to a given line. c. Calculate the slope of a line
EQUATIONS and INEQUALITIES Linear Equations and Slope 1. Slope a. Calculate the slope of a line given two points b. Calculate the slope of a line parallel to a given line. c. Calculate the slope of a line
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS
 MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
What are the place values to the left of the decimal point and their associated powers of ten?
 The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in geometry and algebra. (Everything
The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in geometry and algebra. (Everything
Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder).
 Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials
 Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Florida Math for College Readiness
 Core Florida Math for College Readiness Florida Math for College Readiness provides a fourth-year math curriculum focused on developing the mastery of skills identified as critical to postsecondary readiness
Core Florida Math for College Readiness Florida Math for College Readiness provides a fourth-year math curriculum focused on developing the mastery of skills identified as critical to postsecondary readiness
Higher Education Math Placement
 Higher Education Math Placement Placement Assessment Problem Types 1. Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Decimals 1.1 Operations with Whole Numbers Addition with carry Subtraction with borrowing Multiplication
Higher Education Math Placement Placement Assessment Problem Types 1. Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Decimals 1.1 Operations with Whole Numbers Addition with carry Subtraction with borrowing Multiplication
Section 1.1 Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines
 Section. Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines Slope The measure of the steepness of a line is called the slope of the line. It is the amount of change in y, the rise, divided by the amount of
Section. Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines Slope The measure of the steepness of a line is called the slope of the line. It is the amount of change in y, the rise, divided by the amount of
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions
 6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
Florida Math 0028. Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper
 Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
( ) FACTORING. x In this polynomial the only variable in common to all is x.
 FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions
 Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions The first method we will discuss, in solving polynomial equations, is the method of FACTORING. Before we jump into this process, you need to have some concept of what
Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions The first method we will discuss, in solving polynomial equations, is the method of FACTORING. Before we jump into this process, you need to have some concept of what
A. Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor.
 DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - FACTORING POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you!
DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - FACTORING POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you!
Polynomials. Key Terms. quadratic equation parabola conjugates trinomial. polynomial coefficient degree monomial binomial GCF
 Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any.
 Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
What does the number m in y = mx + b measure? To find out, suppose (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) are two points on the graph of y = mx + b.
 PRIMARY CONTENT MODULE Algebra - Linear Equations & Inequalities T-37/H-37 What does the number m in y = mx + b measure? To find out, suppose (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) are two points on the graph of
PRIMARY CONTENT MODULE Algebra - Linear Equations & Inequalities T-37/H-37 What does the number m in y = mx + b measure? To find out, suppose (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) are two points on the graph of
Factoring Flow Chart
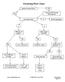 Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring a Polynomial Expression Factoring a polynomial is expressing the polynomial as a product of two or more factors. Simply stated, it is somewhat the reverse process of multiplying. To factor polynomials,
Factoring a Polynomial Expression Factoring a polynomial is expressing the polynomial as a product of two or more factors. Simply stated, it is somewhat the reverse process of multiplying. To factor polynomials,
By reversing the rules for multiplication of binomials from Section 4.6, we get rules for factoring polynomials in certain forms.
 SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
ALGEBRA 2: 4.1 Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Goal Graph quadratic functions. VOCABULARY Quadratic function A function that can be written in the standard form y = ax 2 + bx+ c where a 0 Parabola
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING
 POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
The Point-Slope Form
 7. The Point-Slope Form 7. OBJECTIVES 1. Given a point and a slope, find the graph of a line. Given a point and the slope, find the equation of a line. Given two points, find the equation of a line y Slope
7. The Point-Slope Form 7. OBJECTIVES 1. Given a point and a slope, find the graph of a line. Given a point and the slope, find the equation of a line. Given two points, find the equation of a line y Slope
Factoring. Factoring Monomials Monomials can often be factored in more than one way.
 Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method
 6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
15.1 Factoring Polynomials
 LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet
 Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
SPECIAL PRODUCTS AND FACTORS
 CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
ALGEBRA I (Created 2014) Amherst County Public Schools
 ALGEBRA I (Created 2014) Amherst County Public Schools The 2009 Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework is a companion document to the 2009 Mathematics Standards of Learning and amplifies
ALGEBRA I (Created 2014) Amherst County Public Schools The 2009 Mathematics Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework is a companion document to the 2009 Mathematics Standards of Learning and amplifies
In algebra, factor by rewriting a polynomial as a product of lower-degree polynomials
 Algebra 2 Notes SOL AII.1 Factoring Polynomials Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Factoring Review Factor: rewrite a number or expression as a product of primes; e.g. 6 = 2 3 In algebra, factor by rewriting
Algebra 2 Notes SOL AII.1 Factoring Polynomials Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Factoring Review Factor: rewrite a number or expression as a product of primes; e.g. 6 = 2 3 In algebra, factor by rewriting
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
CRLS Mathematics Department Algebra I Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide
 Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide page 1 of 14 Quarter I start (CP & HN) 170 96 Unit 1: Number Sense and Operations 24 11 Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test Operating with Real Numbers: How are
Curriculum Map/Pacing Guide page 1 of 14 Quarter I start (CP & HN) 170 96 Unit 1: Number Sense and Operations 24 11 Totals Always Include 2 blocks for Review & Test Operating with Real Numbers: How are
5 means to write it as a product something times something instead of a sum something plus something plus something.
 Intermediate algebra Class notes Factoring Introduction (section 6.1) Recall we factor 10 as 5. Factoring something means to think of it as a product! Factors versus terms: terms: things we are adding
Intermediate algebra Class notes Factoring Introduction (section 6.1) Recall we factor 10 as 5. Factoring something means to think of it as a product! Factors versus terms: terms: things we are adding
Slope-Intercept Form of a Linear Equation Examples
 Slope-Intercept Form of a Linear Equation Examples. In the figure at the right, AB passes through points A(0, b) and B(x, y). Notice that b is the y-intercept of AB. Suppose you want to find an equation
Slope-Intercept Form of a Linear Equation Examples. In the figure at the right, AB passes through points A(0, b) and B(x, y). Notice that b is the y-intercept of AB. Suppose you want to find an equation
MATH 095, College Prep Mathematics: Unit Coverage Pre-algebra topics (arithmetic skills) offered through BSE (Basic Skills Education)
 MATH 095, College Prep Mathematics: Unit Coverage Pre-algebra topics (arithmetic skills) offered through BSE (Basic Skills Education) Accurately add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, integers,
MATH 095, College Prep Mathematics: Unit Coverage Pre-algebra topics (arithmetic skills) offered through BSE (Basic Skills Education) Accurately add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, integers,
Linear Equations. Find the domain and the range of the following set. {(4,5), (7,8), (-1,3), (3,3), (2,-3)}
 Linear Equations Domain and Range Domain refers to the set of possible values of the x-component of a point in the form (x,y). Range refers to the set of possible values of the y-component of a point in
Linear Equations Domain and Range Domain refers to the set of possible values of the x-component of a point in the form (x,y). Range refers to the set of possible values of the y-component of a point in
FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c
 Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
SUNY ECC. ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop. Algebra Skills
 SUNY ECC ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop Algebra Skills Gail A. Butler Ph.D. Evaluating Algebraic Epressions Substitute the value (#) in place of the letter (variable). Follow order of operations!!! E)
SUNY ECC ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop Algebra Skills Gail A. Butler Ph.D. Evaluating Algebraic Epressions Substitute the value (#) in place of the letter (variable). Follow order of operations!!! E)
A Systematic Approach to Factoring
 A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
1.3 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1.3 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use slope to graph linear equations in two variables. Find the slope of a line given two points
1.3 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Use slope to graph linear equations in two variables. Find the slope of a line given two points
Factoring Polynomials
 UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
Using the ac Method to Factor
 4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
Big Bend Community College. Beginning Algebra MPC 095. Lab Notebook
 Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:.
 MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
FACTORING ax 2 bx c. Factoring Trinomials with Leading Coefficient 1
 5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
Students will be able to simplify and evaluate numerical and variable expressions using appropriate properties and order of operations.
 Outcome 1: (Introduction to Algebra) Skills/Content 1. Simplify numerical expressions: a). Use order of operations b). Use exponents Students will be able to simplify and evaluate numerical and variable
Outcome 1: (Introduction to Algebra) Skills/Content 1. Simplify numerical expressions: a). Use order of operations b). Use exponents Students will be able to simplify and evaluate numerical and variable
Factoring and Applications
 Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III
 Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
Algebra 1 If you are okay with that placement then you have no further action to take Algebra 1 Portion of the Math Placement Test
 Dear Parents, Based on the results of the High School Placement Test (HSPT), your child should forecast to take Algebra 1 this fall. If you are okay with that placement then you have no further action
Dear Parents, Based on the results of the High School Placement Test (HSPT), your child should forecast to take Algebra 1 this fall. If you are okay with that placement then you have no further action
Polynomials and Factoring
 7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Warm Up. Write an equation given the slope and y-intercept. Write an equation of the line shown.
 Warm Up Write an equation given the slope and y-intercept Write an equation of the line shown. EXAMPLE 1 Write an equation given the slope and y-intercept From the graph, you can see that the slope is
Warm Up Write an equation given the slope and y-intercept Write an equation of the line shown. EXAMPLE 1 Write an equation given the slope and y-intercept From the graph, you can see that the slope is
Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced
 Instructor! Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced Last week we looked at greatest common factors and the basics of factoring out the GCF. In this second activity, we will discuss factoring more difficult
Instructor! Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced Last week we looked at greatest common factors and the basics of factoring out the GCF. In this second activity, we will discuss factoring more difficult
1.3 Algebraic Expressions
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR DSMA 0306 INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA. Semester Hours Credit: 3
 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR DSMA 0306 INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA Semester Hours Credit: 3 (This course is equivalent to DSMA 0301. The difference being that this course is offered only on those campuses
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR DSMA 0306 INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA Semester Hours Credit: 3 (This course is equivalent to DSMA 0301. The difference being that this course is offered only on those campuses
SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
 (Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
(Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
MATH 10034 Fundamental Mathematics IV
 MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
Review of Intermediate Algebra Content
 Review of Intermediate Algebra Content Table of Contents Page Factoring GCF and Trinomials of the Form + b + c... Factoring Trinomials of the Form a + b + c... Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials... 6
Review of Intermediate Algebra Content Table of Contents Page Factoring GCF and Trinomials of the Form + b + c... Factoring Trinomials of the Form a + b + c... Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials... 6
Polynomials and Quadratics
 Polynomials and Quadratics Want to be an environmental scientist? Better be ready to get your hands dirty!.1 Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials............703.2 They re Multiplying
Polynomials and Quadratics Want to be an environmental scientist? Better be ready to get your hands dirty!.1 Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials............703.2 They re Multiplying
CORRELATED TO THE SOUTH CAROLINA COLLEGE AND CAREER-READY FOUNDATIONS IN ALGEBRA
 We Can Early Learning Curriculum PreK Grades 8 12 INSIDE ALGEBRA, GRADES 8 12 CORRELATED TO THE SOUTH CAROLINA COLLEGE AND CAREER-READY FOUNDATIONS IN ALGEBRA April 2016 www.voyagersopris.com Mathematical
We Can Early Learning Curriculum PreK Grades 8 12 INSIDE ALGEBRA, GRADES 8 12 CORRELATED TO THE SOUTH CAROLINA COLLEGE AND CAREER-READY FOUNDATIONS IN ALGEBRA April 2016 www.voyagersopris.com Mathematical
Slope-Intercept Equation. Example
 1.4 Equations of Lines and Modeling Find the slope and the y intercept of a line given the equation y = mx + b, or f(x) = mx + b. Graph a linear equation using the slope and the y-intercept. Determine
1.4 Equations of Lines and Modeling Find the slope and the y intercept of a line given the equation y = mx + b, or f(x) = mx + b. Graph a linear equation using the slope and the y-intercept. Determine
Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c
 4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS
 278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
Factoring Special Polynomials
 6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
Factoring Trinomials of the Form
 Section 4 6B: Factoring Trinomials of the Form A x 2 + Bx + C where A > 1 by The AC and Factor By Grouping Method Easy Trinomials: 1 x 2 + Bx + C The last section covered the topic of factoring second
Section 4 6B: Factoring Trinomials of the Form A x 2 + Bx + C where A > 1 by The AC and Factor By Grouping Method Easy Trinomials: 1 x 2 + Bx + C The last section covered the topic of factoring second
CAHSEE on Target UC Davis, School and University Partnerships
 UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
Answers to Basic Algebra Review
 Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
A synonym is a word that has the same or almost the same definition of
 Slope-Intercept Form Determining the Rate of Change and y-intercept Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Graph lines using the slope and y-intercept. Calculate the y-intercept of a line when given
Slope-Intercept Form Determining the Rate of Change and y-intercept Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Graph lines using the slope and y-intercept. Calculate the y-intercept of a line when given
MATH 21. College Algebra 1 Lecture Notes
 MATH 21 College Algebra 1 Lecture Notes MATH 21 3.6 Factoring Review College Algebra 1 Factoring and Foiling 1. (a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2. 2. (a b) 2 = a 2 2ab + b 2. 3. (a + b)(a b) = a 2 b 2. 4. (a
MATH 21 College Algebra 1 Lecture Notes MATH 21 3.6 Factoring Review College Algebra 1 Factoring and Foiling 1. (a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2. 2. (a b) 2 = a 2 2ab + b 2. 3. (a + b)(a b) = a 2 b 2. 4. (a
Factoring Guidelines. Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms. 2008 Shirley Radai
 Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
6.3 FACTORING ax 2 bx c WITH a 1
 290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
Make sure you look at the reminders or examples before each set of problems to jog your memory! Solve
 Name Date Make sure you look at the reminders or examples before each set of problems to jog your memory! I. Solving Linear Equations 1. Eliminate parentheses. Combine like terms 3. Eliminate terms by
Name Date Make sure you look at the reminders or examples before each set of problems to jog your memory! I. Solving Linear Equations 1. Eliminate parentheses. Combine like terms 3. Eliminate terms by
Sect 6.1 - Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
 Sect 6.1 - Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping Our goal in this chapter is to solve non-linear equations by breaking them down into a series of linear equations that we can solve. To do this,
Sect 6.1 - Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping Our goal in this chapter is to solve non-linear equations by breaking them down into a series of linear equations that we can solve. To do this,
Math 10C. Course: Polynomial Products and Factors. Unit of Study: Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address. Guiding Questions:
 Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
ACCUPLACER. Testing & Study Guide. Prepared by the Admissions Office Staff and General Education Faculty Draft: January 2011
 ACCUPLACER Testing & Study Guide Prepared by the Admissions Office Staff and General Education Faculty Draft: January 2011 Thank you to Johnston Community College staff for giving permission to revise
ACCUPLACER Testing & Study Guide Prepared by the Admissions Office Staff and General Education Faculty Draft: January 2011 Thank you to Johnston Community College staff for giving permission to revise
6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping
 386 CHAPTER 6 Factoring and Applications 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
386 CHAPTER 6 Factoring and Applications 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
FACTORING POLYNOMIALS
 296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
Successful completion of Math 7 or Algebra Readiness along with teacher recommendation.
 MODESTO CITY SCHOOLS COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE:... Basic Algebra COURSE NUMBER:... RECOMMENDED GRADE LEVEL:... 8-11 ABILITY LEVEL:... Basic DURATION:... 1 year CREDIT:... 5.0 per semester MEETS GRADUATION
MODESTO CITY SCHOOLS COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE:... Basic Algebra COURSE NUMBER:... RECOMMENDED GRADE LEVEL:... 8-11 ABILITY LEVEL:... Basic DURATION:... 1 year CREDIT:... 5.0 per semester MEETS GRADUATION
When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property and take out the GCF.
 Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
Pre-Calculus II Factoring and Operations on Polynomials
 Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions 1 Created January 17, 2006
 MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions Created January 7, 2006 Math 092, Elementary Algebra, covers the mathematical content listed below. In order
MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions Created January 7, 2006 Math 092, Elementary Algebra, covers the mathematical content listed below. In order
Introduction Assignment
 PRE-CALCULUS 11 Introduction Assignment Welcome to PREC 11! This assignment will help you review some topics from a previous math course and introduce you to some of the topics that you ll be studying
PRE-CALCULUS 11 Introduction Assignment Welcome to PREC 11! This assignment will help you review some topics from a previous math course and introduce you to some of the topics that you ll be studying
Answer Key for California State Standards: Algebra I
 Algebra I: Symbolic reasoning and calculations with symbols are central in algebra. Through the study of algebra, a student develops an understanding of the symbolic language of mathematics and the sciences.
Algebra I: Symbolic reasoning and calculations with symbols are central in algebra. Through the study of algebra, a student develops an understanding of the symbolic language of mathematics and the sciences.
