Electrical Circuits I Lecture 1
|
|
|
- Egbert Rice
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrical Circuits I Lecture <Dr Ahmed El-Shenawy>
2 Course Contents Basic dc circuit elements, series and parallel Networks Ohm's law and Kirchoff's laws Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Source Transformation Method Superposition Theory Thevenin's Theorem and Norton Theorem Maximum Power Transfer Alternating current Fundamentals and AC generation MS value, average value, form factor and crisp factor Phasor concept elation between voltage and current in resistor, capacitor and inductor esponse of L and C circuits Sinusoidal response of LC circuit Series esonance
3 Introduction Electrical systems pervade our lives; they are found in home, school, workplaces, factories, and transportation vehicles-everywhere. A circuit model is used to connect our visualization to our analysis of a physical system. The challenge is to develop models that will predict the physical behaviour of real components accurately and result in mathematical equations that can be solved.
4 Basic Electrical Quantities Basic quantities: current, voltage and power. Electric Circuits I Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy Electric current: Electric current in a wire is defined as the net amount of charge that passes through the wire per unit time, and is measured in amperes (A). where i dq dt i = current in amperes q = charge in coulombs t = time in sec. Ampere = Coulomb per second (C/s) Current in circuits physically realized by movement of electrons. Direction of current must be specified by an arrow.
5 By convention, current direction defined as flow of positive charge. Note that positive charge is not flowing physically. Electrons have negative charge. They move in the opposite direction of current. electron motion positive current direction In general, current can be an arbitrary function of time. Constant current is called direct current (DC). Current that can be represented as a sinusoidal function of time (or in some contexts a sum of sinusoids) is called alternating current (AC).
6 Voltage Voltage is the energy absorbed or expended as a unit charge moves from one point to the other. Analogous to pressure in hydraulic system. Sometimes called potential difference. Can be created by a separation of charge. Is a measure of the potential between two points. Voltage pushes charge in one direction.
7 We use polarity (+ and on batteries) to indicates which direction the charge is being pushed Voltage is the energy required to move a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V) v d dq where v = voltage in volts ω = energy in Joules q = charge in coulombs i + v - A Circuit Element B
8 Voltage ~ Pressure Electric Current ~ Water Current Sponge ~ esistance
9 Electrical Power Time rate of expending or absorbing energy and is measured by Watts. p p d dt d dq dq dt vi where p = power in watts ω = energy in Joules t = time in seconds q = charge in coulombs i = current in apperes v = voltage in volts By convention Circuit elements that absorb power have a positive value of p. Circuit elements that produce power have a negative value of p.
10 Active elements Elements of electrical circuits Active elements are the elements that can generate energy or power, such as voltage and current sources. Ideally, a voltage source produces V s volts regardless of the current absorbed or produced by the connected device. Ideally, a current source produces I s amps regardless of the current in the connected device. In a particular circuit, there can be active elements that absorb power for example, a battery being charged.
11 Passive elements passive elements are the elements that can not generate energy, such as resistors, capacitors and inductors. resistors The ability of a material to resist (impede, obstruct) the flow charge is called its resistivity. It is represented by the letter. A resistor is a circuit element that dissipates electrical energy (usually as heat) eal-world devices that are modeled by resistors: incandescent light bulbs, heating elements, long wires esistance is measured in Ohms (Ω) esistor is indicated by the symbol
12 esistance of a wire depends on some factors like as length (L), crosssectional area (A) and resistivity of material (ρ). L A Where ρ resistivity in Ω.m L length in m A cross-section area in m The conductance (G) of a pure resistor is the reciprocal of its resistance. The unit of conductance is the siemens (S) or mho ( ). G Ω
13 Ohm s Law Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference or voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them. The mathematical equation that describes this relationship is: i v where v is the potential difference measured across the resistance in units of volts; i is the current through the resistance in units of amperes and is the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms.
14 Two elements are in series if the current that flows through one must also flow through the other. Series If we wish to replace the two series resistors with a single equivalent resistor whose voltage-current relationship is the same, the equivalent resistor has a value given by eq
15 For N resistors in series, the equivalent resistor has a value given by: eq 3 eq 3 N
16 Consider two resistors in series with a voltage v across them: v v v v v v v i Voltage division:
17 esistors in Parallel When the terminals of two or more circuit elements are connected to the same two nodes, the circuit elements are said to be in parallel. If we wish to replace the two parallel resistors with a single equivalent resistor whose voltage-current relationship is the same, the equivalent resistor has a value given by eq
18 Consider two resistors in parallel with a voltage v across them: i i i i + - v i Current division: i i
Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models
 EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
Lecture Notes: ECS 203 Basic Electrical Engineering Semester 1/2010. Dr.Prapun Suksompong 1 June 16, 2010
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Lecture Notes: ECS 203 Basic Electrical Engineering Semester 1/2010 Dr.Prapun
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Lecture Notes: ECS 203 Basic Electrical Engineering Semester 1/2010 Dr.Prapun
Electronics. Basic Concepts. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç GÖREN Yrd. Doç. Dr. Levent ÇETİN
 Electronics Basic Concepts Electric charge Ordinary matter is made up of atoms which have positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons surrounding them. Charge is quantized as the subtraction
Electronics Basic Concepts Electric charge Ordinary matter is made up of atoms which have positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons surrounding them. Charge is quantized as the subtraction
1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives
 Real Analog Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Circuit Analysis Fundamentals 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter, we introduce all fundamental concepts associated with circuit analysis. Electrical
Real Analog Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Circuit Analysis Fundamentals 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter, we introduce all fundamental concepts associated with circuit analysis. Electrical
Chapter 1. Fundamental Electrical Concepts
 Chapter 1 Fundamental Electrical Concepts Charge, current, voltage, power circuits, nodes, branches Branch and node voltages, Kirchhoff Laws Basic circuit elements, combinations 01 fundamental 1 1.3 Electrical
Chapter 1 Fundamental Electrical Concepts Charge, current, voltage, power circuits, nodes, branches Branch and node voltages, Kirchhoff Laws Basic circuit elements, combinations 01 fundamental 1 1.3 Electrical
Preamble. Kirchoff Voltage Law (KVL) Series Resistors. In this section of my lectures we will be. resistor arrangements; series and
 Preamble Series and Parallel Circuits Physics, 8th Edition Custom Edition Cutnell & Johnson Chapter 0.6-0.8, 0.0 Pages 60-68, 69-6 n this section of my lectures we will be developing the two common types
Preamble Series and Parallel Circuits Physics, 8th Edition Custom Edition Cutnell & Johnson Chapter 0.6-0.8, 0.0 Pages 60-68, 69-6 n this section of my lectures we will be developing the two common types
W03 Analysis of DC Circuits. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 W03 Analysis of DC Circuits Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors and
W03 Analysis of DC Circuits Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors and
Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection
 Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection Object To study the properties of series and parallel connection. Apparatus 1. DC circuit training system 2. Set of wires. 3. DC Power supply 4. Digital A.V.O.
Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection Object To study the properties of series and parallel connection. Apparatus 1. DC circuit training system 2. Set of wires. 3. DC Power supply 4. Digital A.V.O.
Student Exploration: Circuits
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Circuits Vocabulary: ammeter, circuit, current, ohmmeter, Ohm s law, parallel circuit, resistance, resistor, series circuit, voltage Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Circuits Vocabulary: ammeter, circuit, current, ohmmeter, Ohm s law, parallel circuit, resistance, resistor, series circuit, voltage Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
7. What is the current in a circuit if 15 coulombs of electric charge move past a given point in 3 seconds? (1) 5 A (3) 18 A (2) 12 A (4) 45 A
 1. Compared to the number of free electrons in a conductor, the number of free electrons in an insulator of the same volume is less the same greater 2. Most metals are good electrical conductors because
1. Compared to the number of free electrons in a conductor, the number of free electrons in an insulator of the same volume is less the same greater 2. Most metals are good electrical conductors because
802307 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEER. Tarek M. Abdolkader
 802307 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEER Tarek M. Abdolkader KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA Ministry of Higher Education Umm Al-Qura University College of Engineering and Islamic Architecture Electrical
802307 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEER Tarek M. Abdolkader KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA Ministry of Higher Education Umm Al-Qura University College of Engineering and Islamic Architecture Electrical
= (0.400 A) (4.80 V) = 1.92 W = (0.400 A) (7.20 V) = 2.88 W
 Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Last time : energy storage elements capacitor.
 Last time : energy storage elements capacitor. Charge on plates Energy stored in the form of electric field Passive sign convention Vlt Voltage drop across real capacitor can not change abruptly because
Last time : energy storage elements capacitor. Charge on plates Energy stored in the form of electric field Passive sign convention Vlt Voltage drop across real capacitor can not change abruptly because
Chapter 11. Inductors ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Three phase circuits
 Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
2 A bank account for electricity II: flows and taxes
 PHYS 189 Lecture problems outline Feb 3, 2014 Resistors and Circuits Having introduced capacitors, we now expand our focus to another very important component of a circuit resistors. This entails more
PHYS 189 Lecture problems outline Feb 3, 2014 Resistors and Circuits Having introduced capacitors, we now expand our focus to another very important component of a circuit resistors. This entails more
Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum
 WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
People s Physics Book
 The Big Ideas: The name electric current is given to the phenomenon that occurs when an electric field moves down a wire at close to the speed of light. Voltage is the electrical energy density (energy
The Big Ideas: The name electric current is given to the phenomenon that occurs when an electric field moves down a wire at close to the speed of light. Voltage is the electrical energy density (energy
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods
 Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Chapter 5. Parallel Circuits ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 5 Parallel Circuits Objectives Identify a parallel circuit Determine the voltage across each parallel branch Apply Kirchhoff s current law Determine total parallel resistance Apply Ohm s law in
Chapter 5 Parallel Circuits Objectives Identify a parallel circuit Determine the voltage across each parallel branch Apply Kirchhoff s current law Determine total parallel resistance Apply Ohm s law in
Voltage, Current, and Resistance
 Voltage, Current, and Resistance This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Voltage, Current, and Resistance This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
PS-6.2 Explain the factors that determine potential and kinetic energy and the transformation of one to the other.
 PS-6.1 Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy,
PS-6.1 Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy,
Diodes have an arrow showing the direction of the flow.
 The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
ES250: Electrical Science. HW7: Energy Storage Elements
 ES250: Electrical Science HW7: Energy Storage Elements Introduction This chapter introduces two more circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor whose elements laws involve integration or differentiation;
ES250: Electrical Science HW7: Energy Storage Elements Introduction This chapter introduces two more circuit elements, the capacitor and the inductor whose elements laws involve integration or differentiation;
Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force. Young and Freedman Chapter 25
 Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force Young and Freedman Chapter 25 Electric Current: Analogy, water flowing in a pipe H 2 0 gallons/minute Flow Rate is the NET amount of water passing through a
Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force Young and Freedman Chapter 25 Electric Current: Analogy, water flowing in a pipe H 2 0 gallons/minute Flow Rate is the NET amount of water passing through a
SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES, COMERCIAL LTDA.
 Pocket book of Electrical Engineering Formulas Content 1. Elementary Algebra and Geometry 1. Fundamental Properties (real numbers) 1 2. Exponents 2 3. Fractional Exponents 2 4. Irrational Exponents 2 5.
Pocket book of Electrical Engineering Formulas Content 1. Elementary Algebra and Geometry 1. Fundamental Properties (real numbers) 1 2. Exponents 2 3. Fractional Exponents 2 4. Irrational Exponents 2 5.
Analysis of a single-loop circuit using the KVL method
 Analysis of a single-loop circuit using the KVL method Figure 1 is our circuit to analyze. We shall attempt to determine the current through each element, the voltage across each element, and the power
Analysis of a single-loop circuit using the KVL method Figure 1 is our circuit to analyze. We shall attempt to determine the current through each element, the voltage across each element, and the power
AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules
 Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Energy in Electrical Systems. Overview
 Energy in Electrical Systems Overview How can Potential Energy be stored in electrical systems? Battery Stored as chemical energy then transformed to electrical energy on usage Water behind a dam Water
Energy in Electrical Systems Overview How can Potential Energy be stored in electrical systems? Battery Stored as chemical energy then transformed to electrical energy on usage Water behind a dam Water
Simon Nemsadze. BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Theory and Practice
 The Georgian Technical University The Department of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Simon Nemsadze BASC ELECTCAL ENGNEENG Theory and Practice TBLS 04 A course in basic electrical engineering is
The Georgian Technical University The Department of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Simon Nemsadze BASC ELECTCAL ENGNEENG Theory and Practice TBLS 04 A course in basic electrical engineering is
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits
 Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7. Introduction...7-7. Electromotive Force...7-3 7.3 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...7-5 7.4 Kirchhoff s Circuit Rules...7-7 7.5 Voltage-Current Measurements...7-9
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7. Introduction...7-7. Electromotive Force...7-3 7.3 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...7-5 7.4 Kirchhoff s Circuit Rules...7-7 7.5 Voltage-Current Measurements...7-9
101 BASICS SERIES LEARNING MODULE 2: FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICITY. Cutler-Hammer
 101 BASICS SERIES LEARNING MODULE 2: FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICITY Cutler-Hammer WELCOME Welcome to Module 2, Fundamentals of Electricity. This module will cover the fundamentals of electricity in a practical
101 BASICS SERIES LEARNING MODULE 2: FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICITY Cutler-Hammer WELCOME Welcome to Module 2, Fundamentals of Electricity. This module will cover the fundamentals of electricity in a practical
CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESISTANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESI STANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE P R E A M B L E This problem is adapted from an on-line knowledge enhancement module for a PGCE programme. It is used to cover
CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESI STANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE P R E A M B L E This problem is adapted from an on-line knowledge enhancement module for a PGCE programme. It is used to cover
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Chapter 13: Electric Circuits
 Chapter 13: Electric Circuits 1. A household circuit rated at 120 Volts is protected by a fuse rated at 15 amps. What is the maximum number of 100 watt light bulbs which can be lit simultaneously in parallel
Chapter 13: Electric Circuits 1. A household circuit rated at 120 Volts is protected by a fuse rated at 15 amps. What is the maximum number of 100 watt light bulbs which can be lit simultaneously in parallel
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS. Electrical Circuits
 Electrical Circuits A complete path, or circuit, is needed before voltage can cause a current flow through resistances to perform work. There are several types of circuits, but all require the same basic
Electrical Circuits A complete path, or circuit, is needed before voltage can cause a current flow through resistances to perform work. There are several types of circuits, but all require the same basic
FB-DC3 Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits
 CREST Foundation Electrical Engineering: DC Electric Circuits Kuphaldt FB-DC3 Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits Contents 1. What are "series" and "parallel"? 2. Simple series circuits 3.
CREST Foundation Electrical Engineering: DC Electric Circuits Kuphaldt FB-DC3 Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits Contents 1. What are "series" and "parallel"? 2. Simple series circuits 3.
Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits
 Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits PREPARED BY IAT Curriculum Unit August 2008 Institute of Applied Technology, 2008 ATE310- Electrical Fundamentals 2 Module 3 Parallel Circuits Module
Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits PREPARED BY IAT Curriculum Unit August 2008 Institute of Applied Technology, 2008 ATE310- Electrical Fundamentals 2 Module 3 Parallel Circuits Module
Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007
 [ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
[ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
Chapter 1 Basic Electric Circuit Concepts
 Chapter 1 Basic Electric Circuit Concepts 1 BASIC CONCEPTS LEARNING GOALS System of Units: The SI standard system Systeme International unit (=International System of Units) ( 法 ) 國 際 單 位 制 Basic Quantities:
Chapter 1 Basic Electric Circuit Concepts 1 BASIC CONCEPTS LEARNING GOALS System of Units: The SI standard system Systeme International unit (=International System of Units) ( 法 ) 國 際 單 位 制 Basic Quantities:
Coupled Inductors. Introducing Coupled Inductors
 Coupled Inductors From power distribution across large distances to radio transmissions, coupled inductors are used extensively in electrical applications. Their properties allow for increasing or decreasing
Coupled Inductors From power distribution across large distances to radio transmissions, coupled inductors are used extensively in electrical applications. Their properties allow for increasing or decreasing
13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571
 13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571 Key Concepts: 5. Connecting loads in series and parallel affects the current, potential difference, and total resistance. - Using your knowledge of
13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571 Key Concepts: 5. Connecting loads in series and parallel affects the current, potential difference, and total resistance. - Using your knowledge of
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits
 Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits The configuration of circuit elements clearly affects the behaviour of a circuit. Resistors connected in series or in parallel are very common in a circuit and act
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits The configuration of circuit elements clearly affects the behaviour of a circuit. Resistors connected in series or in parallel are very common in a circuit and act
First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering)
 Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Introduction to Electricity & Magnetism. Dr Lisa Jardine-Wright Cavendish Laboratory
 Introduction to Electricity & Magnetism Dr Lisa Jardine-Wright Cavendish Laboratory Examples of uses of electricity Christmas lights Cars Electronic devices Human body Electricity? Electricity is the presence
Introduction to Electricity & Magnetism Dr Lisa Jardine-Wright Cavendish Laboratory Examples of uses of electricity Christmas lights Cars Electronic devices Human body Electricity? Electricity is the presence
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel
 Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
PHYSICAL METHODS, INSTRUMENTS AND MEASUREMENTS - Measurements Of Electrical Quantities - Ján Šaliga MEASUREMENTS OF ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES
 MEASUREMENTS OF ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES Ján Šaliga Department of Electronics and Multimedia Telecommunication, Technical University of Košice, Košice, Slovak Republic Keywords: basic electrical quantities,
MEASUREMENTS OF ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES Ján Šaliga Department of Electronics and Multimedia Telecommunication, Technical University of Košice, Košice, Slovak Republic Keywords: basic electrical quantities,
Aircraft Electrical System
 Chapter 9 Aircraft Electrical System Introduction The satisfactory performance of any modern aircraft depends to a very great degree on the continuing reliability of electrical systems and subsystems.
Chapter 9 Aircraft Electrical System Introduction The satisfactory performance of any modern aircraft depends to a very great degree on the continuing reliability of electrical systems and subsystems.
Energy, Work, and Power
 Energy, Work, and Power This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Energy, Work, and Power This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, California State University, Sacramento
 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, California State University, Sacramento Engr 17 Introductory Circuit Analysis, graded, 3 units Instructor: Tatro - Spring 2016 Section 2, Call No. 30289,
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, California State University, Sacramento Engr 17 Introductory Circuit Analysis, graded, 3 units Instructor: Tatro - Spring 2016 Section 2, Call No. 30289,
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Series Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006. Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com
 Tristan s Guide to: Solving Series Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Series Circuits. A Series circuit, in my opinion, is the simplest circuit
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Series Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Series Circuits. A Series circuit, in my opinion, is the simplest circuit
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 2 Grundlagen der Elektrotechnik 2
 Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 2 Grundlagen der Elektrotechnik 2 Chapter: Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis / Netzwerkanalyse bei harmonischer Erregung Michael E. Auer Source of figures: Alexander/Sadiku:
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 2 Grundlagen der Elektrotechnik 2 Chapter: Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis / Netzwerkanalyse bei harmonischer Erregung Michael E. Auer Source of figures: Alexander/Sadiku:
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
 Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) I. Charge (current flow) conservation law (the Kirchhoff s Current law) Pipe Pipe Pipe 3 Total volume of water per second flowing through pipe = total volume of water per
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) I. Charge (current flow) conservation law (the Kirchhoff s Current law) Pipe Pipe Pipe 3 Total volume of water per second flowing through pipe = total volume of water per
Kirchhoff s Laws Physics Lab IX
 Kirchhoff s Laws Physics Lab IX Objective In the set of experiments, the theoretical relationships between the voltages and the currents in circuits containing several batteries and resistors in a network,
Kirchhoff s Laws Physics Lab IX Objective In the set of experiments, the theoretical relationships between the voltages and the currents in circuits containing several batteries and resistors in a network,
EE301 Lesson 14 Reading: 10.1-10.4, 10.11-10.12, 11.1-11.4 and 11.11-11.13
 CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS Learning Objectives EE301 Lesson 14 a. Define capacitance and state its symbol and unit of measurement. b. Predict the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. c. Analyze how
CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS Learning Objectives EE301 Lesson 14 a. Define capacitance and state its symbol and unit of measurement. b. Predict the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. c. Analyze how
Slide 1 / 26. Inductance. 2011 by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
THE BREADBOARD; DC POWER SUPPLY; RESISTANCE OF METERS; NODE VOLTAGES AND EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE; THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
 THE BREADBOARD; DC POWER SUPPLY; RESISTANCE OF METERS; NODE VOLTAGES AND EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE; THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT YOUR NAME LAB MEETING TIME Reference: C.W. Alexander and M.N.O Sadiku, Fundamentals
THE BREADBOARD; DC POWER SUPPLY; RESISTANCE OF METERS; NODE VOLTAGES AND EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE; THÉVENIN EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT YOUR NAME LAB MEETING TIME Reference: C.W. Alexander and M.N.O Sadiku, Fundamentals
Basic Principles of. Electricity. Basic Principles of Electricity. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department
 Basic Principles of Electricity METU by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU,
Basic Principles of Electricity METU by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU,
Fundamentals of Electronic Circuit Design. By Hongshen Ma
 Fundamentals of Electronic Circuit Design By Hongshen Ma Preface Why Study Electronics? Purely mechanical problems are often only a subset of larger multidomain problems faced by the designer. Particularly,
Fundamentals of Electronic Circuit Design By Hongshen Ma Preface Why Study Electronics? Purely mechanical problems are often only a subset of larger multidomain problems faced by the designer. Particularly,
Electronics Technology Fundamentals
 Lindem 11. jan 09 Electronics Technology Fundamentals Chapter 1 Principles of Electricity 1 1.1 The Starting Point Atomic Structure Atom smallest particle of matter that retains the physical characteristics
Lindem 11. jan 09 Electronics Technology Fundamentals Chapter 1 Principles of Electricity 1 1.1 The Starting Point Atomic Structure Atom smallest particle of matter that retains the physical characteristics
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
Parallel DC circuits
 Parallel DC circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Parallel DC circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Exercises on Voltage, Capacitance and Circuits. A d = (8.85 10 12 ) π(0.05)2 = 6.95 10 11 F
 Exercises on Voltage, Capacitance and Circuits Exercise 1.1 Instead of buying a capacitor, you decide to make one. Your capacitor consists of two circular metal plates, each with a radius of 5 cm. The
Exercises on Voltage, Capacitance and Circuits Exercise 1.1 Instead of buying a capacitor, you decide to make one. Your capacitor consists of two circular metal plates, each with a radius of 5 cm. The
BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. December 2011
 AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA
 PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
Chapter 7. DC Circuits
 Chapter 7 DC Circuits 7.1 Introduction... 7-3 Example 7.1.1: Junctions, branches and loops... 7-4 7.2 Electromotive Force... 7-5 7.3 Electrical Energy and Power... 7-9 7.4 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...
Chapter 7 DC Circuits 7.1 Introduction... 7-3 Example 7.1.1: Junctions, branches and loops... 7-4 7.2 Electromotive Force... 7-5 7.3 Electrical Energy and Power... 7-9 7.4 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...
First Order Circuits. EENG223 Circuit Theory I
 First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Series and Parallel Circuits Direct-Current Series Circuits A series circuit is a circuit in which the components are connected in a line, one after the other, like railroad cars on a single track. There
Series and Parallel Circuits Direct-Current Series Circuits A series circuit is a circuit in which the components are connected in a line, one after the other, like railroad cars on a single track. There
DEGREE: Bachelor's Degree in Industrial Electronics and Automation COURSE: 1º TERM: 2º WEEKLY PLANNING
 SESSION WEEK COURSE: Physics II DEGREE: Bachelor's Degree in Industrial Electronics and Automation COURSE: 1º TERM: 2º WEEKLY PLANNING DESCRIPTION GROUPS (mark ) Indicate YES/NO If the session needs 2
SESSION WEEK COURSE: Physics II DEGREE: Bachelor's Degree in Industrial Electronics and Automation COURSE: 1º TERM: 2º WEEKLY PLANNING DESCRIPTION GROUPS (mark ) Indicate YES/NO If the session needs 2
Power Factor Correction for Power Systems First Semester Report Spring Semester 2007
 Power Factor Correction for Power Systems First Semester Report Spring Semester 2007 by Pamela Ackerman Prepared to partially fulfill the requirements for EE401 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Power Factor Correction for Power Systems First Semester Report Spring Semester 2007 by Pamela Ackerman Prepared to partially fulfill the requirements for EE401 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
TECH TIP # 37 SOLVING SERIES/PARALLEL CIRCUITS THREE LAWS --- SERIES CIRCUITS LAW # 1 --- THE SAME CURRENT FLOWS THROUGH ALL PARTS OF THE CIRCUIT
 TECH TIP # 37 SOLVING SERIES/PARALLEL CIRCUITS Please study this Tech Tip along with assignment 4 in Basic Electricity. Parallel circuits differ from series circuits in that the current divides into a
TECH TIP # 37 SOLVING SERIES/PARALLEL CIRCUITS Please study this Tech Tip along with assignment 4 in Basic Electricity. Parallel circuits differ from series circuits in that the current divides into a
Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement. 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits. Experiment no 1
 Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law
 Experiment 2 31 Kuwait University Physics 107 Physics Department Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law Introduction In this experiment the relations among voltages, currents and resistances for
Experiment 2 31 Kuwait University Physics 107 Physics Department Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law Introduction In this experiment the relations among voltages, currents and resistances for
CHAPTER 28 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
DC Circuits (Combination of resistances)
 Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: DC Circuits (Combination of resistances) EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Circuits Experiment Board One Dcell Battery Wire leads Multimeter 100, 330, 1k resistors Purpose The purpose
Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: DC Circuits (Combination of resistances) EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Circuits Experiment Board One Dcell Battery Wire leads Multimeter 100, 330, 1k resistors Purpose The purpose
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
What is a multimeter?
 What is a multimeter? A multimeter is a devise used to measure voltage, resistance and current in electronics & electrical equipment It is also used to test continuity between to 2 points to verify if
What is a multimeter? A multimeter is a devise used to measure voltage, resistance and current in electronics & electrical equipment It is also used to test continuity between to 2 points to verify if
ÇANKAYA UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Architecture
 ÇANKAYA UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Course Definition Form This form should be used for both a new elective or compulsory course being proposed and curricula development processes
ÇANKAYA UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Course Definition Form This form should be used for both a new elective or compulsory course being proposed and curricula development processes
BJT AC Analysis. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents. Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49
 Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
How To Understand And Understand The Theory Of Electricity
 DIRECT CURRENT AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SYSTEMS N. Rajkumar, Research Fellow, Energy Systems Group, City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK Keywords: Electrical energy, direct current, alternating
DIRECT CURRENT AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SYSTEMS N. Rajkumar, Research Fellow, Energy Systems Group, City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK Keywords: Electrical energy, direct current, alternating
CURRENT ELECTRICITY - I
 CURRNT LCTRCTY - 1. lectric Current 2. Conventional Current 3. Drift elocity of electrons and current 4. Current Density 5. Ohm s Law 6. Resistance, Resistivity, Conductance & Conductivity 7. Temperature
CURRNT LCTRCTY - 1. lectric Current 2. Conventional Current 3. Drift elocity of electrons and current 4. Current Density 5. Ohm s Law 6. Resistance, Resistivity, Conductance & Conductivity 7. Temperature
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
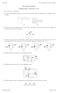 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Parallel Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006. Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com
 Tristan s Guide to: Solving Parallel Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Parallel Circuits. Parallel Circuits are a little bit more complicated
Tristan s Guide to: Solving Parallel Circuits. Version: 1.0 Written in 2006 Written By: Tristan Miller Tristan@CatherineNorth.com Parallel Circuits. Parallel Circuits are a little bit more complicated
Electrical Circuit Theory
 Electrical Circuit Theory Learning Objectives: 1. Review the basic electrical concepts of voltage, amperage, and resistance. 2. Review the components of a basic automotive electrical circuit. 3. Introduce
Electrical Circuit Theory Learning Objectives: 1. Review the basic electrical concepts of voltage, amperage, and resistance. 2. Review the components of a basic automotive electrical circuit. 3. Introduce
LAB2 Resistors, Simple Resistive Circuits in Series and Parallel Objective:
 LAB2 Resistors, Simple Resistive Circuits in Series and Parallel Objective: In this lab, you will become familiar with resistors and potentiometers and will learn how to measure resistance. You will also
LAB2 Resistors, Simple Resistive Circuits in Series and Parallel Objective: In this lab, you will become familiar with resistors and potentiometers and will learn how to measure resistance. You will also
How To Find The Current Of A Circuit
 The node voltage method Equivalent resistance Voltage / current dividers Source transformations Node voltages Mesh currents Superposition Not every circuit lends itself to short-cut methods. Sometimes
The node voltage method Equivalent resistance Voltage / current dividers Source transformations Node voltages Mesh currents Superposition Not every circuit lends itself to short-cut methods. Sometimes
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Pre-Laboratory Assignment Series and Parallel Circuits ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Laboratory updated 16 May 2011 1. Consider the following series circuit. Derive a formula to calculate voltages V 1, V 2,
Pre-Laboratory Assignment Series and Parallel Circuits ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Laboratory updated 16 May 2011 1. Consider the following series circuit. Derive a formula to calculate voltages V 1, V 2,
2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Terms and definitions
 .1 Introduction An important step in the procedure for solving any circuit problem consists first in selecting a number of independent branch currents as (known as loop currents or mesh currents) variables,
.1 Introduction An important step in the procedure for solving any circuit problem consists first in selecting a number of independent branch currents as (known as loop currents or mesh currents) variables,
Fig. 1 Analogue Multimeter Fig.2 Digital Multimeter
 ELECTRICAL INSTRUMENT AND MEASUREMENT Electrical measuring instruments are devices used to measure electrical quantities such as electric current, voltage, resistance, electrical power and energy. MULTIMETERS
ELECTRICAL INSTRUMENT AND MEASUREMENT Electrical measuring instruments are devices used to measure electrical quantities such as electric current, voltage, resistance, electrical power and energy. MULTIMETERS
Chapter 5. A Power Distribution System
 Chapter 5 A Power Distribution System K. Barry A. Williams, Principal Engineer, Hewlett Packard 5.1 Introduction The goal of a power distribution system is to have an impedence that is flat over frequency.
Chapter 5 A Power Distribution System K. Barry A. Williams, Principal Engineer, Hewlett Packard 5.1 Introduction The goal of a power distribution system is to have an impedence that is flat over frequency.
PHYSICS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits
 PHYSCS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits This experiment is designed to investigate the relationship between current and potential in simple series
PHYSCS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits This experiment is designed to investigate the relationship between current and potential in simple series
STUDY GUIDE: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM An atom is made of three
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM An atom is made of three
Current and Temperature Ratings
 Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
EE 221 Circuits II. Chapter 13 Magnetically Coupled Circuits
 EE Circuits II Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits 3. What is a transformer? 3. Mutual Inductance 3.3 Energy in a Coupled Circuit 3.4 inear Transformers 3.5 Ideal Transformers
EE Circuits II Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits 3. What is a transformer? 3. Mutual Inductance 3.3 Energy in a Coupled Circuit 3.4 inear Transformers 3.5 Ideal Transformers
Objectives. Electric Current
 Objectives Define electrical current as a rate. Describe what is measured by ammeters and voltmeters. Explain how to connect an ammeter and a voltmeter in an electrical circuit. Explain why electrons travel
Objectives Define electrical current as a rate. Describe what is measured by ammeters and voltmeters. Explain how to connect an ammeter and a voltmeter in an electrical circuit. Explain why electrons travel
Springs and Dampers. MCE371: Vibrations. Prof. Richter. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Handout 2 Fall 2011
 MCE371: Vibrations Prof. Richter Department of Mechanical Engineering Handout 2 Fall 2011 Spring Law : One End Fixed Ideal linear spring law: f = kx. What are the units of k? More generally: f = F(x) nonlinear
MCE371: Vibrations Prof. Richter Department of Mechanical Engineering Handout 2 Fall 2011 Spring Law : One End Fixed Ideal linear spring law: f = kx. What are the units of k? More generally: f = F(x) nonlinear
Voltage Drop (Single-Phase)
 Voltage Drop (Single-Phase) To Find: To Find Voltage Drop Formula: 2 x K x L x I V.D. = ------------------- C.M. Variables: C.M. = Circular Mill Area (Chapter 9, Table 8) To Find Voltage Drop Percentage
Voltage Drop (Single-Phase) To Find: To Find Voltage Drop Formula: 2 x K x L x I V.D. = ------------------- C.M. Variables: C.M. = Circular Mill Area (Chapter 9, Table 8) To Find Voltage Drop Percentage
