BIOL 3244: Human Anatomy SI Mock Exam: Exam 1 Ian Stewart
|
|
|
- Lawrence Osborne
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOL 3244: Human Anatomy SI Mock Exam: Exam 1 Ian Stewart Name Select the best answer for each question. 1. The reticular layer of the dermis is made up of what kind of connective tissue? A. Dense irregular connective tissue B. Reticular connective tissue C. Loose connective tissue D. Areolar connective tissue E. Dense elastic connective tissue 2. The joints between the central incisors and the alveolar margins of the maxillae are: 1. Fibrous articulations 3. Synarhtrotic 2. Gomphoses 4. Amphiarthrotic 3. You are working in an urgent care clinic and a parent comes in with their child. The child is complaining of pain in their distal antebrachium, and you notice some swelling around the child s wrist. The parent explains that the child had fallen, and you begin to suspect that the child has fractured their radius. What kind of fracture would you expect to see in an X-ray? A. Comminuted B. Complete C. Simple D. Greenstick 4. All of the following structures are sensory receptors in the dermis except: A. Merkel cells B. Free nerve endings C. Pacinian corpuscles D. Meissner s corpuscles E. Ruffini endings 1
2 5. The vermiform appendix, located in the right lower quadrant, is relative to the stomach. 1. Contralateral 2. Superior 3. Inferior 4. Ipsilateral 6. Microvilli can be found on the apical poles of epithelial cells in: A. Small intestine B. Proximal convoluted tubule in the kidney C. Stomach D. Both A and B E. All of the above 7. In the epiphyseal plate, the largest chondrocytes can be found in the: A. Ossification zone B. Resorption zone C. Hypertrophic zone D. Proliferative zone E. Reserve zone 8. Which of the following is an intracapsular ligament of the knee? A. Anterior cruciate ligament B. Lateral collateral ligament C. Medial collateral ligament D. Oblique popliteal ligament E. Arcuate popliteal ligament 9. Osteoclasts: A. Are uninucleated cells. B. Will be responsible for the deposition of new bony matrix. C. Will decrease serum calcium levels. D. Are not important for remodeling bone.. 2
3 10. All of the following bones are carpals except for: A. Trapezium B. Capitate C. Cuboid D. Triquetral E. All of the above are carpals. 11. Which of the following are components of the basement membrane? 1. Reticular lamina 3. Basal lamina 2. Lamina propria 4. Basal pole 12. Melanocytes produce: A. Melatonin B. Melanin C. Keratin D. Collagen E. Elastin 13. In a quadrupedal organism (or, say, your foot), the positional term dorsal is analogous to: A. Posterior B. Inferior C. Superior D. Anterior E. Ventral 14. The acromion is a major feature of the: A. Mandible B. Clavicle C. Scapula D. Sternum E. Humerus 3
4 15. Symphyses include: 1. Symphysis pubis 2. Medial and lateral menisci of the knee 3. Intervertebral discs 4. Sternoclavicular joint 16. The major complication associated with femoral fractures is fat embolism, where adipose tissue enters the bloodstream and occludes a blood vessel distal (i.e., away from) to the site of the fracture in the thigh. The fat that embolizes comes from what part of the femur? A. Diaphysis B. Metaphysis C. Medullary cavity D. Epiphysis 17. Stratum germinativum: A. Consists of the stratum basale and the stratum spinosum B. Is composed of cells capable of mitotic activity C. Contains cells that are anchored to one another with desmosomes D. Has a primarily squamous cellular morphology E. All of the above are characteristics of the stratum germinativum. 18. The bony process you are currently (hopefully?) sitting on is the: A. Iliac tuberosity B. Pubic tubercle C. Ischial tuberosity D. Ischial tubercle E. Ischium 19. The term coxal refers to: A. Buttocks and the posterior aspect of the pelvic girdle (but not the sacrum or coccyx) B. Groin C. The area between the external genitals and the anus D. Coccyx E. Lateral aspect of the pelvic girdle 4
5 20. The slide on the right is a biopsy of elastic cartilage. Where would you find this kind of tissue? A. Costochondral joints B. Epiglottis C. Brachiocephalic artery D. Pubic symphysis E. Tendon of quadriceps femoris 21. The Haversian system consists of which of the following? 1. Central canal 2. Lacuna(e) 3. Lamella(e) 4. Osteocyte(s) 22. Regarding ceruminous glands, all of the following are true except: A. Produce cerumen, a waxy substance to keep the tympanic membrane pliable B. Are found within the dermis of the skin in the external auditory canal C. The glands use an apocrine secretion mechanism D. Act to (theoretically) keep insects out of your external ear E. All of the above are true. 23. Which of the following is an accessory structure in a synovial joint? A. Synovial membrane B. Capsular ligaments C. Fibrous capsule D. Articular cartilage E. Synovial fluid 5
6 24. The primary curvatures of the vertebral column: 1. Includes the lumbar and cervical curvature 2. Includes the thoracic and sacral curvatures 3. Are formed after birth 4. Are formed in utero 25. The following membranes are all epithelial except: A. Mucous B. Serous C. Synovial D. Cutaneous E. All of the above are epithelial membranes. 26. Functions of the skeleton include all of the following except: A. Primary center of hematopoiesis in the adult B. Primary storage center and source of calcium and phosphate C. Site for deposition and sequestration of strontium and other heavy metals D. Protection of the central nervous system E. Protection of the small intestine 27. Which of the following statements about anatomical position is incorrect? A. The palms face medially. B. The body is erect. C. The eyes face forward. D. The feet are parallel. E. The arms are at the sides of the body. 28. The only articulation between the pectoral girdle and the axial skeleton is the: A. Acromioclavicular joint B. Croacoclavicular joint C. Sternoclavicular joint D. Glenohumeral joint E. Acromiohumeral joint 6
7 29. Periosteum: 1. Is anchored to the bone via Sharpey s fibers 2. Is composed of dense irregular connective tissue 3. Consists of two layers, an outer fibrous layer and an inner osteogenic layer 4. Covers trabeculae in spongy bone 30. Goblet cells can be found interspersed with the epithelium of the respiratory tree, which is. A. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium B. Simple ciliated columnar epithelium C. Simple columnar epithelium D. Stratified ciliated columnar epithelium E. Stratified columnar epithelium 31. The additional layer of cells present in the palms and soles is: A. Stratum basale B. Stratum spinosum C. Stratum granulosum D. Stratum lucidum E. Stratum corneum 32. In intramembranous ossification, all of the following are true except: A. Ossification centers form in a hyaline cartilage template. B. Osteoblasts deposit osteoid, which through some unknown, hand-waving magic, becomes calcified into bone. C. The initial bone formed in this method has architecture similar to spongy bone. D. Osteoblasts and osteocytes will produce vascular endothelial growth factor to encourage the development of blood vessels in the newly forming bone. E. The spongy bone will be remodeled into compact bone. 33. The spleen and other lymphoid organs are good examples of what kind of connective tissue? A. Areolar connective tissue B. Dense irregular connective tissue C. Dense regular connective tissue D. Reticular connective tissue E. Adipose connective tissue 7
8 34. False ribs: 1. Articulate directly with the sternum 2. Includes the floating ribs 3. Are ribs 1 through 7 4. Are ribs 8 through Which of the following statements about the knee is correct? A. The knee is a single, synovial joint hinge joint. B. The knee includes articulations between the femur and the fibula. C. The knee has 5 reinforcing ligaments. D. The knee is not a major weight-bearing joint. E. The knee is the largest joint in the human body. 36. A gland that employs an apocrine secretion mechanism is: A. Goblet cells in the respiratory mucosa B. Sudoriferous glands in the palms C. Sebaceous glands D. Mammary glands 37. Cell types found in the stratum basale of the epidermis include all of the following except: A. Leiberkuhn cells B. Melanocytes C. Keratinocytes D. Langerhans cells E. Merkel cells 38. Features of endochondral ossification include all of the following except: A. The formation of a bone collar around the primary ossification center. B. Secondary ossification centers form in the proximal and distal epiphyses. C. Remodeling of the bone in the center of the diaphysis will form the medullary cavity. D. Appositional growth occurs at the epiphyseal plate. E. Bones formed through endochondral ossification start with a hyaline cartilage template. 8
9 39. Mesenchyme will differentiate into which of the following adult cell types? A. Erythrocytes B. Adipocytes C. Osteoclasts D. Fibroblasts E. All of the above are derived from mesenchyme. 40. Functions of the skin include: A. Thermoregulation B. Sensation of tactile stimuli C. Protection from ultraviolet light D. Synthesis of vitamin D E. All of the above are functions of skin. 41. In neuroanatomy, rostral and caudal refer to and, respectively. A. Towards the belly, towards the back B. Towards the forehead, towards the tail C. Towards the forehead, towards the spinal cord or back of skull D. Towards the front, towards the back 42. Trepanation, an ancient (and frankly barbaric) practice of drilling holes into the head to allow bad spirits to escape from the brain, was a common treatment for various mental disorders. Which bone(s) would be a good site (i.e., what bones are flat enough) to perform a trepanation procedure? 1. Parietal 3. Temporal 2. Mandible 4. Sphenoid D. All of them! Drilling holes into someone s head is bad. (Hint: not the answer!) E. None of them? (Shame on you.) 43. Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium can be found in all of the locations below except: A. Vaginal canal B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Rectum E. All of the above have nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. 9
10 44. Red marrow is found in which of the following bones? A. Proximal epiphysis of the humerus B. Ilium C. Proximal epiphysis of the tibia D. Both A and B E. All of the above 45. Of the following statements about epithelium, which is false? A. Epithelium is innervated, but vascular. B. Epithelium has a high regenerative rate, and high cellularity. C. Epithelial cells demonstrate polarity. D. Epithelium is innervated, but avascular. E. All epithelium is anchored to areolar connective tissue through a basement membrane. 46. An example of a temporary synchondrosis is the: A. Epiphyseal plates in long bones B. The costal cartilage between rib 1 and the manubrium C. The lambdoid suture D. Intervertebral discs 47. Which of the following bones is not appendicular? A. Ilium B. Clavicle C. Scapula D. Sacrum E. Ischium 48. The hypodermis: A. Is primarily dense regular connective tissue. B. Anchors the epidermis to underlying structures, including muscles and bones. C. Helps maintain body temperature by altering the diameter of cutaneous blood vessels. D. Is also referred to as deep fascia and helps compartmentalize muscle groups. E. Serves as a primary storage site for lipids. 49. The lamellae that surround the Haversian canal in an osteon are the: A. Circumferential lamellae B. Centrifugal lamellae C. Concentric lamellae D. Interstitial lamellae E. Circumduction lamellae 10
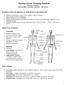
11 50. The major components of the extracellular matrix of connective tissue includes: 1. Ground substance 2. Collagen fibers 3. Reticular fibers 4. Elastin fibers 51. In osteoarthritis, the articular cartilage on the articular surfaces of the bones in a synovial joint is broken down and erodes, allowing for spicules of bone to come through the articular cartilage and grind against the other bone in the articulation. If this were to affect the glenohumeral joint, then the and the would end up grinding together, causing the characteristic pain associated with osteoarthritis. A. Scapula and humerus B. Glenoid tubercle and humerus C. Head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity D. Glenoid fossa and humerus E. Scapula and the head of the humerus Matching: Match the following terms to the appropriate label in the diagram. Each term will only be used one time. There are more terms than answers. A. Acromial B. Antebrachial C. Antecubital D. Brachial E. Crural F. Facial G. Orbital H. Patellar I. Peroneal J. Popliteal K. Scapular L. Sural M. Zygomatic G Orbital 53. C Antecubital 54. E Crural 55. A Acromial 56. J - Popliteal 11
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY
 SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Function of Bones. Bone Tissue and Bones BONE CLASSIFICATION. Long Bones Gross Anatomy. Lab Activity 1 - Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
 Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY
 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
E. Blood cells production. Blood cells are produced within the cavities of bones.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
BONES AND BONE TISSUE
 BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
OBJECTIVE: List and describe the functions of the skeletal system. D. Storage depot for minerals and homeostasis
 Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE. Chapter 6. Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
CHAPTER 5: TISSUES. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Location: air sacs of lungs; nephrons of kidney; lining of circulatory system, lymphatic vessels, & ventral body cavity
 Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3)
 Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM. 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200)
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Protective Functions. Functions in Sensation. Functions in Excretion. Functions in Temperature Regulation
 Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science
 Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science INTERACTION OF SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS: Skeletal and Muscular systems works together to allow movement
Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science INTERACTION OF SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS: Skeletal and Muscular systems works together to allow movement
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Laboratory 3 Histology
 Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System. What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system?
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term.
 This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term. 1 Run for your lives!!! (Just Kidding) Matching - Anatomy or Physiology? A 1. Study of structure A. Anatomy 2. muscle actions B. Physiology 3. Brain Function
This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term. 1 Run for your lives!!! (Just Kidding) Matching - Anatomy or Physiology? A 1. Study of structure A. Anatomy 2. muscle actions B. Physiology 3. Brain Function
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CHAPTER5 INTRODUCTION COMPLETION: In the space(s) provided, write the word(s) that correctly complete(s) each statement. 1. The submicroscopic particles that make up all substances
Human Anatomy and Physiology CHAPTER5 INTRODUCTION COMPLETION: In the space(s) provided, write the word(s) that correctly complete(s) each statement. 1. The submicroscopic particles that make up all substances
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Bone Tissue Chapter 7
 Bone Tissue Chapter 7 Tissues and organs of the skeletal system Histology of osseous tissue Bone development Physiology of osseous tissue Bone disorders Bone Tissue Bone is alive and continuously changing.
Bone Tissue Chapter 7 Tissues and organs of the skeletal system Histology of osseous tissue Bone development Physiology of osseous tissue Bone disorders Bone Tissue Bone is alive and continuously changing.
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
relating to head, neck, and trunk 206 bones organized into structural framework Skeleton relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis
 Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 203 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Figure 6.1 Child Looking at Bones Bone is a living tissue. Unlike the bones of a fossil made inert by a process of
CHAPTER 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 203 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Figure 6.1 Child Looking at Bones Bone is a living tissue. Unlike the bones of a fossil made inert by a process of
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals
 Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals 6 Bones and skeletal system Contents Bones Introduction Classification of Bones Bone Structure Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Chemical Composition
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals 6 Bones and skeletal system Contents Bones Introduction Classification of Bones Bone Structure Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Chemical Composition
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN
 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SYLLABUS FOR COMMUNITY COLLEGES. Leslie Dawn Schulz, B.S. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SYLLABUS FOR COMMUNITY COLLEGES Leslie Dawn Schulz, B.S. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS May 2000 APPROVED: Gerard A O Donovan, Major
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SYLLABUS FOR COMMUNITY COLLEGES Leslie Dawn Schulz, B.S. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS May 2000 APPROVED: Gerard A O Donovan, Major
Brunswick School Department: Grades 11-12. Essential Understandings
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more
 BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues
 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues Cartilage Location and basic structure Found throughout adult body Ear and epiglottis Articular cartilages and costal cartilage Larynx, trachea, and nose Intervertebral discs,
6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues Cartilage Location and basic structure Found throughout adult body Ear and epiglottis Articular cartilages and costal cartilage Larynx, trachea, and nose Intervertebral discs,
