PCB 4023 Cell Biology. Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs
|
|
|
- Leo Cannon
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
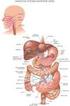
1 PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them, simply highlight and copy the address and paste it into the address box of your browser Preparation assignment (to be completed before lab: 1) Kerr (1999) Chapter 13. Gastrointestinal Tract (pp ) 2) Kerr (1999) Chapter 14: Liver, Gall Bladder, Pancreas (pp ) Web resources: N.B. Again, you may wish to examine the Stomach and Intestine and Liver, Gall Bladder and Pancreas modules (review & quizzes) at the University of Florida College of Medicine histology tutorial. As before, these modules may contain information that is not covered in this course and you will not be held responsible for any information presented there. However, you may wish to consider using them as additional preparation and/or review. The URL is as follows: Know of any other web sites pertaining to the integument and its derivatives that you have found helpful or interesting? me the link at and let me know what and why you found it informative and/or interesting Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs This week we continue our examination of organology. As noted previously, time does not permit an examination of all the organ systems found in craniates, nor is it necessary. Once identification of the basic tissues has been accomplished, one can identify organs by learning and recognizing their unique combination and arrangement of specific tissues and/or cells. Nowhere is this principal better illustrated than in the alimentary canal where the same four tissue layers are found throughout, yet each portion is unique and easily distinguished. This week, in deference to the physician wannabe s who always seem to hold a [to my mind unhealthy] fascination with the guts, we ll examine the histology of the alimentary canal and two of its [tasty] accessory organs, the liver and pancreas. I. Alimentary Canal figure: 3K
2 The alimentary canal is a hollow muscular tube that begins at the caudal end of the pharynx or oropharynx and is made up of the esophagus, stomach, intestines, and, in most craniates, the cloaca (except in meta- and eu-therian mammals where the large intestine terminates in a (dedicated) anus). Each region exhibits a common plan or organization, specifically a hollow tube with walls composed of four layers. The innermost layer is the mucosa (mucous membrane) which consists of a lining epithelium and a thin layer of smooth muscle (the ) separated by the loose connective tissue. The consists of a vascularized layer of loose connective tissue; it also contains nerve plexi (Meisnner s) of the enteric nervous system (ENS). External to this is the composed of circular and longitudinal sheets of smooth muscle. [N.B. In histological sections, the orientation of the muscle fibers may not appear purely circular or longitudinal due to variation in the plane of sectioning.] The surface layer is the adventitia, a fibrous connective tissue. If the organ is intraperitoneal, then the adventitia is covered with a mesothelium and is referred to as a serosa. The esophagus is a distensable tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach. In mammals the mucosa is a stratified squamous epithelium to resist the abrasions of the passing bolus. [The presence or degree of keratinization varies between species and correlates with the abrasiveness of the diet.] Secretions from mucous glands in the mucosa or assist in the passage of the bolus by peristaltic contractions of the muscularis externa. Interestingly; the proximal, like the adjacent pharynx, is skeletal rather than smooth muscle. figure 3K13.24 The stomach is an expanded region of the alimentary canal, its expansion facilitated by folds known as rugae which open in an accordion-like fashion to accommodate a meal. The stomach is the site of mechanical, acid and enzyme digestion as well as the site of limited absorption (water, salts, vitamins, ethanol, caffeine, etc.). The mucosa consists of columnar mucous epithelial cells which line both the surface and indentations known as gastric pits.. The gastric pits lead to the branched, tubular gastric glands which also contain the acid-secreting parietal cells and enzyme-secreting chief cells. figure 3K13-25 The mucosa of the intestines differs substantially from the stomach. Instead of pits, the opposite holds with thousands of villi projecting into the lumen from the wall, increasing the 2
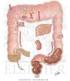
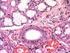
3 surface area. Within the villi are arterioles, venules and lacteals, specialized lymphatic vessels that absorb long-chain fats. The lining epithelium is comprised of (1) columnar enterocytes (absorptive) which are covered with hundreds to thousands of microvilli and (2) secretory goblet cells. Mucous secretions from the goblet cells protect the epithelial lining from digestive agents and serve as a lubricant to facilitate passage of the food. At the base of the wall are the intestinal glands (crypts of Lieberkühn) which are sunken into the mucosa and are the source of digestive enzymes. In many craniates the intestine is divided into two major regions, small and large. The small intestine is of smaller diameter (hence its name) but of greater length than the latter is divided into three successive and histologically distinct parts (from proximal to distal): duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum receives chyme from the stomach, digestive enzymes from the exocrine portion of the pancreas, and bile from the liver. The secretions of the duodenal (Brunner s) glands within the serve to neutralize the hydrochloride acid of the stomach. The jejunum has the most extensive villi and generally lacks Brunner s glands and lymphatic nodules. In contrast, the of the ileum is rich in aggregated lymphoid follicles (Peyer s patches). The small intestine is the major site of nutrient absorption (amino acids, carbohydrates, and fatty acids). The large intestine is named for its large diameter and it passes to the cloaca or anus. It s mucosa is rich in goblet cells and its enterocytes absorb water and metabolic ions. II. Accessory organs The accessory organs of the digestive tract arise as diverticuli or outpocketings of the endoderm from the developing gut tube into the adjacent mesenchyme (splanchnic mesoderm). These include the liver, gall bladder and pancreas. figure: 3K13-39 The liver is typically the second largest organ in craniates (after the skin) and serves a variety of functions (carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism, detoxification, bile production, etc.). Despite this diversity of functions, its histological appearance is remarkably uniform. The liver is composed of sheets of hepatocytes separated by blood sinuses (sinusoids) which carries blood from the nutrient-rich hepatic portal vein and oxygen-rich hepatic arteries. The products of liver metabolism are released to the central veins and 3
4 conducted to the caval venous system. Bile is transported to the small intestine by a series of canaliculi and ducts. figure: 3K15-11 The pancreas actually arises from two diverticuli (dorsal and ventral) that may or may not fuse together during subsequent development. The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine components. The exocrine cells form acinar glands that dump their enzymatic secretions ( pancreatic juice ) to a duct system terminating in the duodenum. Embedded among the acinar glands are clusters of endocrine glands called pancreatic islets (isles of Langerhans). While at least four major cell types are known (alpha (producing glucagon), beta (producing insulin), delta (producing somatostain), and pancreatic polypeptide cells ), they can not be distinguished in H&E stained sections. Lab Assignment: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Work through the following sections using your atlas as a guide. Make sure to answer the questions (marked by? ) at the end of the lab; these will be evaluated when you turn in your handout next week. A list of structures which will form the basis for next week s quiz is given at the end of the handout. To learn how to identify the structures, write down criteria which will assist you in your identification (e.g., simple squamous epithelium: single layer, flat cells with flattened nuclei). Your text is a good source for such material as well as your own observations. Some students find it helpful to make rough sketches of the structure to assist in their learning. N.B. Due to [unprogrammed] slide death, your slide box may not contain the required slide. If this is the case, notify an instructor and they will provide a replacement or suggest an alternative. If you end up borrowing a slide from one of your colleagues, please don t forget to return it to them. I. Digestive tract A. Esophagus trachea and esophagus: 93W4875 mucosa (mucous membrane) stratified squamous epithelium mucous glands (variable; can be within mucosa) adventitia 4
5 B, Stomach (gaster) stomach, fundus: HK 6-23 mucosa rugae gastric pits simple columnar epithelium (surface mucous cells) gastric glands parietal (oxyntic) - predominately apical chief (zyogenic) - predominately basal serosa C. Small Intestine small intestine: HK 7-24; 93W4526 (duodenum only) mucosa (simple column epithelium) villi enterocytes goblet cells crypts of Lieberkühn adventitia or serosa Be able to distinguish the three parts of the small intestine: duodenum - l duodenal (Brunner s) glands jejunum - tall villi; scarcity of Brunner s glands and lymphoid follicles ileum - aggregated lymphoid follicles (Peyer s patches) in D. Enteric nervous system The enteric nervous system (ENS) is not directly connected to the central nervous system and thus is considered distinct from the autonomic nervous system (ANS). It modifies local gut behavior (e.g., peristalsis, secretion, epithelial proliferation, etc.). Although it can act independently of the ANS, parasympathetic fibers from cranial nerve X (CN X; vagus) and the sacrum and sympathetic fibers from abdominal ganglia terminates on ganglia of the ENS and influence their behavior. Small ganglia of the ENS can be observed in the (Meissner s plexus ) and between the layers of the muscularis externa (Auerbach s plexus ). Auerbach s plexus: 93W3675 Auerbach s plexus - between inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of the muscularis externa Meissner s plexus - l 5
6 E. Large Intestine (colon) colon: 93W4542 mucosa enterocytes goblet cells crypts of Lieberkühn adventitia II. Accessory organs of the digestive tract A. Liver liver: H3230 (extras available); HK 10-2; 93W4567 (pig; clearest structure) liver lobule central vein portal triad hepatic arteriole portal venule bile duct canaliculi hepatocytes sinusoids B. Pancreas pancreas: H3130 (extras available); HK 9-2 (extras available); also look for portions of the pancreas on 93W4526 (duodenum) acinar glands (exocrine) ducts connective tissue septa pancreatic islets (isles of Langerhans; endocrine) IV. Questions (Due the following lab)? What three layers form the mucosa (mucous membrane) of the alimentary tract? What type(s) of tissue(s) forms each?? What tissues can be found within the?? What tissues is often found between the inner and outer layers of the?? What is the difference between an adventitia and a serosa in the alimentary tract?? What two types of muscle are found in the of the esophagus? 6
7 ? In what tissue layer (i.e., mucosa,, muscularix externa, adventitia) are the esophageal glands found? What type of glands are these and what is the function of their secretion?? What are the major functions of the stomach?? What is the purpose of the mucous secretions by the surface epithelia of the stomach?? How can you distinguish histologically the parietal and chief cells within gastric glands (i.e., describe their histological appearance)? What is the major secretion of each? How do they interact to perform a common function?? Which cells of the gastric gland secret the hormone gastrin?? How can you distinguish (differentiate) histologically the three regions of the small intestine (i.e., duodenum, jejunum, ileum)?? What are the major functions of the duodenum? The jejunum? The ileum?? Why are duodenal (Brunner s) glands found primarily in the proximal portion of the small intestine?? What morphological feature found on the apical surface of entoerocytes suggests it is an absorptive cell?? Who was Lieberkühn? In what organs will you find his crypts?? Who was Langerhans and where are his Isles? Where are his cells?? Who was Peyer? Where are his patches? What are they?? Why are the ganglion cells of Meissner and Auerbach incorrectly described as plexi? [Hint: look up the definition of plexus in a good medical dictionary.]? What are the major functions of the large intestine?? How can the large and small intestine be distinguished histologically?? What are the thre components of a liver lobule?? What are the three components of a portal triad?? What is the function of bile salts? Describe their activity.? What is the function of bile pigments? Describe their activity.? If alcohol (ethanol) is metabolized in the liver (into acetaldehyde and acetate), how is it that the amount of alcohol consumed can be assayed in the urine and breath?? What is the unique feature of the structure of the pancreatic acini that differentiates it from all other exocrine glands?? What enzyme in the duodenum activates the enzymes of the pancreatic juice? Why is it necessary for the pancreatic enzymes to remain inactivated in the pancreas? 7
8 ? Why aren t the many enzymes of the pancreatic juice and the bile of the liver delivered to the stomach, rather than the duodenum?? What are the four cell types found in the pancreatic isles? What hormone(s) does each produce and what is its function. V. Quiz: Be prepared to identify the following structures on next week s quiz. Esophagus mucosa (mucous membrane) stratified squamous epithelium mucous glands (variable; can be within mucosa) adventitia Stomach (gaster) Small Intestine mucosa rugae gastric pits gastric glands parietal cells chief cells serosa mucosa (simple column epithelium) villi enterocytes goblet cells intestinal glands (crypts of Lieberkühn) adventitia or serosa Be able to distinguish the three parts of the small intestine: duodenum, jejunum, ileum Enteric nervous system Auerbach s plexus Meissner s plexus Large Intestine (colon) mucosa 8
9 enterocytes goblet cells intestinal glands (crypts of Lieberkühn) adventitia Liver liver lobule central vein portal triad hepatic arteriole portal venule bile duct hepatocytes sinusoids Pancreas acinar glands (exocrine) ducts connective tissue septa pancreatic islets (isles of Langerhans) 9
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
Small & Large Intestines
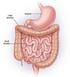 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Digestive System Digestive Tract
 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
SEER Training Modules
 http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
26. Digestive System
 26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Functions of the digestive system
 Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestive tract. Accessory organs. Digestive System Overview
 Digestive System Digestive System The process of chemically and physically breaking down foods into simpler forms that can be absorbed is called digestion. The digestive system can be divided into two
Digestive System Digestive System The process of chemically and physically breaking down foods into simpler forms that can be absorbed is called digestion. The digestive system can be divided into two
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15
 Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System
 General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE
 CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes The Gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Continuing Education Independent Study Series
 Continuing Education Independent Study Series Professional Development Manager Association of Surgical Technologists Englewood, Colorado Association of Surgical Technologists Publication made possible
Continuing Education Independent Study Series Professional Development Manager Association of Surgical Technologists Englewood, Colorado Association of Surgical Technologists Publication made possible
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Digestive system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Overview of the Digestive System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46506 1 Overview of the Digestive System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46506 1 Overview of the Digestive System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
II. General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
The Digestive System
 16 The Digestive System FOCUS: The function of the digestive system is to take in food, break it down into smaller compounds, and absorb those compounds so that the body can use them. This process provides
16 The Digestive System FOCUS: The function of the digestive system is to take in food, break it down into smaller compounds, and absorb those compounds so that the body can use them. This process provides
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
The Digestive System
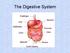 The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI)
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI) I. A tube traveling through the body
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI) I. A tube traveling through the body
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
h. Large intestine 3
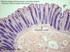 (1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
(1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit
 Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46496 1 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m46496 1 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
Classifications of animals: ruminant vs non-ruminant carnivore: meat-eating herbivore: plant-eating omnivore: both meat and plant-eating
 Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Digestive System Module 5: The Small and Large Intestines
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49292 1 Digestive System Module 5: The Small and Large Intestines Donna Browne Based on The Small and Large Intestines by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
OpenStax-CNX module: m49292 1 Digestive System Module 5: The Small and Large Intestines Donna Browne Based on The Small and Large Intestines by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Study Guide Digestive System
 Study Guide Digestive System 1. Digestion is breakdown of complex food molecules like starch into smaller molecules like glucose that can pass through the cell membranes of intestine and get absorbed into
Study Guide Digestive System 1. Digestion is breakdown of complex food molecules like starch into smaller molecules like glucose that can pass through the cell membranes of intestine and get absorbed into
Chapter 22: Digestive System
 Chapter 22: Digestive System Converts food into raw materials necessary for cell maintenance and growth Digestive System: Main Divisions of Digestive System: 1) Alimentary Canal (gastrointestinal tract)
Chapter 22: Digestive System Converts food into raw materials necessary for cell maintenance and growth Digestive System: Main Divisions of Digestive System: 1) Alimentary Canal (gastrointestinal tract)
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
The Digestive System
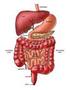 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
Physiology of Digestive system II
 Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion.
 CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
Digestion in the small and Large Intestines
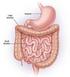 9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012
 Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
23.4 Digestive System
 23.4 Digestive System The Pancreas & Pancreatic Regulation Regulation of Bile Secretions The Small Intestine The Large Intestine Pancreas Location Mostly retroperitoneal Deep to greater curvature of stomach
23.4 Digestive System The Pancreas & Pancreatic Regulation Regulation of Bile Secretions The Small Intestine The Large Intestine Pancreas Location Mostly retroperitoneal Deep to greater curvature of stomach
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
Digestion. Processing of food Types. Mechanical (physical) Chemical. Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix. Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis
 Digestive System Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases Ingestion
Digestive System Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases Ingestion
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
The Digestive System. - teeth, tongue, gall bladder, and glands (salivary glands, liver, pancreas).
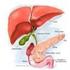 The Digestive System I. Overview A. Organs of the digestive system. 1. Alimentary canal (GI Tract): - continuous muscular tube, open at both ends. - digests food, absorbs digested fragments. 2. Accessory
The Digestive System I. Overview A. Organs of the digestive system. 1. Alimentary canal (GI Tract): - continuous muscular tube, open at both ends. - digests food, absorbs digested fragments. 2. Accessory
The Digestive System. The organ system that processes food, extracts nutrients from it, and eliminates the residue.
 The Digestive System The organ system that processes food, extracts nutrients from it, and eliminates the residue. Digestive System The digestive system allows your body to obtain substances required to
The Digestive System The organ system that processes food, extracts nutrients from it, and eliminates the residue. Digestive System The digestive system allows your body to obtain substances required to
Digestive System. Student Learning Objectives: Structures to be studied: Introduction
 Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
