7/22/2011. Breast MRI: Pulse Sequences, Acquisition Protocols, and Analysis. Objectives. Challenges in DCE Breast Imaging
|
|
|
- Godwin Hector Preston
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Breast MRI: Pulse Sequences, Acquisition Protocols, and Analysis Objectives Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Review background of MRI breast cancer imaging 2. Present technical challenges of breast MRI 3. Discuss typical pulse sequences 4. Describe typical image acquisition protocols 5. ACR requirements for pulse sequences and protocols 6. Discuss new approaches to image review and analysis Dynamic Contrast Enhanced (DCE) MRI of the Breast Scientific Background for Current Breast MRI Protocols Kuhl, et.al. Radiology 1999; 211: Continuous (likely benign) Kuhl, et. al. Radiology 1999; 211: Suspicious (plateau) 2005 Highly Suspicious (washout) Importance of Both Lesion Enhancement and the Enhancement Pattern Kuhl, et.al. Radiology 1999; 211: Challenges in DCE Breast Imaging Degree of Enhancement Alone: Sensitivity: 91% Specificity: 37% i.e. high false positive rate Accuracy: 58% Both Enhancement and Curve Type Sensitivity: 91% Specificity: 83% Accuracy: 86% Group size: 266 cases, 101 cancers Recent study finds that false-positive rate falls following initial baseline study: 13% to 5.6% 1) Enhancing lesions result from Gd contrast agent leaking from poorly formed blood vessels within and around the malignant tumor. 2) The contrast agent shortens the T1 of the lesion relative to the surrounding normal tissues and thus may be detected as bright regions on T1-weighted images, provided there is adequate signal-to-noise (SNR). 3) The breast has significant adipose (fatty) tissues, also with short T1, thus a significant background: fat-suppression or subtraction is essential. 4) High 3D spatial resolution for small-lesion detection and shape assessment. 5) Enhancement patterns are critical to differentiation of benign and malignant masses, high temporal resolution is also essential. 6) Full simultaneous coverage of both breasts: comparison and disease extent 7) Image artifacts must be minimized: motion (cardiac and breathing), out-ofvolume wrap and non-uniform fat-suppression. Unfortunately: SNR, spatial resolution, volume coverage and imaging time all compete with one other and artifact free images may be difficult to obtain. An MR pulse sequence that can meet all of these technical requirements is a significant challenge. 1
2 Fat Suppression (FS) to Minimize Lesion Background Signal DCE T1-weighted images without fat suppression must utilize image subtraction to minimize background. Pre-Contrast No fat-suppressions Early Post-Contrast Later Post-Contrast T1-weighted 3DGRE without FS (pre-contrast) Pre-contrast T1-weighted 3DGRE with FS Wash-out Phase Early Post - Pre Late Post - Pre Post-contrast T1-weighted 3DGRE with FS Subtraction of Post Pre FS Approaches to Fat Suppression Frequency Selective Fat Suppression 1) Short TI inversion recovery (STIR) sequences: (Acquire at null-point of fat T1 recovery, M z = 0) 2) Sequences with frequency selective pre-pulses: (FATSat, CHEMSat, CHESS, PRESat) 3) Combined frequency selective and inversion i recovery: SPIR (Spectral Presaturation with Inversion Recovery) SPAIR (Spectral Adiabatic Inversion Recovery) 4) Phase-cycling: 3.5 ppm difference in precessional frequency (Dixon method, in-phase/out-of-phase of fat and water signal using selected echo times in gradient-echo sequences.) 5) Highly water-selective binomial RF excitation ( e.g ) RODEO* (Rotating Delivery of Excitation Off Resonance) *Harms,SE, et al Radiology 187: (1994) 6) Subtraction of pre-contrast images from post-contrast images 1) Sequence pre-pulse at resonant frequency of fat with pulse bandwidth set for appropriate volume coverage 2) Nominal fat frequency located at 3.5 ppm below water frequency 3) Important to have homogeneous B 0 field 4) B 0 field will by affected by magnetic susceptibility of patient: Importance of good auto-shimming. For: 1.5T = (64 X 10 6 Hz) X 3.5 pp/10 6 ~ 220 Hz For: 3T ~ 440 Hz Frequency-Selective Fat Suppression Pre-pulse 1) A 90 0 pulse centered at the fat frequency re-orients the fat protons into the transverse plane, in phase. The spoiling gradients are then used to destroy (crush or scramble) the coherence of the transverse magnetization to ensure that fat does not contribute to the signal or 2) a SPAIR pre-pulse that is a inverting pulse followed by a spoiler gradient. What spatial resolution and SNR is required? Fat-Sat pre-pulse RF excitation Basically, the answer is the best you can get and still maintain the necessary SNR and temporal sampling. RF Slice Select gradient Gradient Echo ACR established guidelines: 1) < 1.0mm X 1.0mm in-plane pixel size 2) < 3 mm slice thickness (with no slice-gap) 3) not too grainy G sl G ro Spoiler gradients Read Out G pe gradients Comparison: 1.25 X 1.25 mm pixel vs 0.6 X 0.8 pixels 1) Correctly upgraded BIRADS scores in 13 of 26 cancers 2) Correctly down-graded 10 of 28 benign lesions 2
3 What determines adequate temporal sampling? Enhancement Pattern for Focal Invasive Cancers (Type III Enhancement Curve) Adequate Temporal Sampling is Essential for Correct Enhancement Curve Classification Type III Type III MR Signal Time-to-peak enhancement ~ 1-3 minutes Type II? (Minutes after contrast agent injection) Temporal Sampling rate of >2 minutes (may be marginal for confident classification) Temporal Sampling rate of 1 minute (accurate curve classification) Gadoliniun Contrast Agent: Rate and Volume 1) For accurate timing and consistency, power injector preferred 2) 0.1 mmol/kg (Typically, ml volume) 3) Rate ~ 2 ml/s, w/saline flush MR Compatible Power Injectors Rapid temporal sampling with 3D pulse sequences may require parallel imaging with multi-element coils. Example of image acquisiton time with a bi-lateral 16- channel coil with parallel-imaging acceleration factor of 5.6. Note: May need to contact vendor representative for some of this information. Acquistiton time = TR X slice phase matrix X in-plane phase matrix X NSA Parallel Imaging Undersampling (Acceleration) Factors (SENSE, SMASH, GRAPPA...) Example: FOV = 250 mm, Matrix = 356 X 356 X 200 (SENSE) TE/TR/φ = 3.2 ms/6.5 ms/10 0 In-plane phase matrix = 356 (0.7mm X 0.7mm) Slice phase matrix = 200 (1.25 mm slice thickness) SPAIR (Spectrally selective Adiabatic IR) Fat-suppression Acq. Time = sec X 200 X (phase) X 2.0 (slice) = 83 sec Image contrast is determined by when the center of k- space is acquired, one k y step each TR interval. Thus, the center of k-space (k y =0, k x =0) should be timed to coincide with the arrival of the Gd contrast agent. Center - contrast se-encoding steps phas The center of k-space occurs when the zero-strength phase-encoding gradients are applied. For 3D phase encoding is applied in two directions: slice and in-plane phase. (0,0) Sequential k-space acquisition Contrast Injection Scan Delay k-space center occurs at middle of scan Total Acquisition Time Read-out gradient Periphery - resolution Contrast Injection starts at k-space center (filled center to periphery) Mezrich R, A Perspective on k- Space: Radiology 1995; 195: Paschal CB and Morris HD: k-space in the Clinic, JMRI 19(2) (2004) Scan Delay Acquisition Time (ACR: Delay + Acquistion Time 4 minutes) Spiral or centric-elliptical (phase and slice) center-out for 3D k-space acquisition 3
4 RF T1 Weighted 3D Fat Suppressed Gradient Echo Sequence (sequential, spiral or 3D elliptical k space filling) Fat suppression Pre pulse (e.g. SPAIR) α Slab selective RF pulse ( ) TE (1-3 ms) TR (4-6 ms) Gradient Echo Fat Suppression pulse RF Slab Select α RF pulse 3D Fat Sat Balanced Steady state Free Precession (b SSFP) Sequence (No spoiling: T1/T2 Weighted) Gradient Echo G sl SPAIR Spoiler (partition/slice) G sl (partition/slice) G ro Read Out G ro Read Out Rewinding gradients G pe In plane G pe In plane Centric-elliptic (phase and slice) Sequential (e.g. bottom-to-top) Spoiler or Crusher gradients eliminate residual transverse magnetization and mimimizes T2 weighting. Sequences will run several un recorded cycles to establish equilibrium prior to acquisition. Transverse magnetization is retained Vendor supplied 3D Fat-suppressed T1-W GE Sequences (Most 3D sequences will use centric k-space filling.) Left MIP General Electric Philips Siemens Aurora Hitachi Toshiba VIBRANT (Volume Image Breast Assessment) THRIVE (T1 High-Res Isotropic Vol Excitation) VIEWS (fl3d, 3D-FLASH) RODEO (AuroraEdge, 3DGRE) TIGRE (fast STIR, FIR) RADIANCE (FFE_3D2.5_quick) DCE pre-contrast Non-uniform fat suppression Early post-contrast Enhancing lesion Right MIP Typical Sequence Timing Parameters for T1-weighting: TE/TR/φ 1-3 ms/4-6 ms/ Acquisition time: 1-3 minutes ACR: 4 minutes (sum of scan delay and single series time) T2 (fat-suppression) Subtraction: post-pre 3D Flash TE/TR/φ = 1.6 ms/4.4 ms/15 0 Slice thickness (DCE) = 1.0 mm TA = 86 sec FOV = 300X300 mm Matrix = 448 X 448 Pixel size = 0.7 X 0.7 mm Typical Breast MRI Protocol (Image acquisiton time ~15-20 minutes) ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May ) Scout Images (~1 minute) 2) Pre-contrast (~5-7 minutes) i. T1-weighted no-fat suppression (fat/glandular morphology) ii. T2-weighted with fat suppression (bright fluid for cysts) iii. High-resolution, 3D T1-weighted fat-suppressed gradient-echo echo sequence (pre-contrast baseline image of identifying enhancing lesions) 3) Post-contrast (3-5 volume acquisitions ~ 10 minutes) Dynamic multi-phase 3D T1-weighted fat-suppressed GE sequence (Note: Pre-contrast and post-contrast images must have identical image paramaters to allow subtraction.) 4) Analysis i. Subtraction of pre-contrast and post-contrast images (identify enhancing lesions) ii. Dynamic contrast curve evaluation (enhancement pattern assessment) iii. Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP) images of subtracted images (vascular bed assessment) 4
5 ACR Accreditation Pulse Sequence Requirements Analysis of DCE images: CAD programs may improve consistency of breast MRI interpretation Breast MR Imaging: Computer Aided Evaluation Program for Discriminating Benign from Malignant Lesions, Williams TC, DeMartini WB, Partridge SC, Peacodk S and Lehman CD, Radiology: Vol 244 (1), pp (2007) Acquisition time 4 minutes (delay + time to acquire a single image volume) CAD program attempt to automatically identifies lesion by: 1)Enhancement threshold 2)Persistence of enhancement 3)Initial peak enhancement Output from comercially available analysis program with automatic color-coding of wash-out curve category. Future: Kinetic Modeling for estimating Tumor extravasation rate constant: K trans Extravascular-extracellular volume fraction: V e DCE kinetic modeling for assessing breast cancer therapy response. Conclusions Pretherapy Postchemo Current imaging protocols for breast cancer assessment rely upon dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MRI to provide clearly detectable lesion enhancement as well as an accurate characterization of the lesion enhancement pattern. To meet these clinical i l requirements, the technical elements for breast MRI are: 1)A dedicated breast-coil array to provide high SNR images and simultaneous coverage of both breasts. 2)Fat-suppressed, T1-weighted 3D multi-phase gradient echo sequences with high in-plane spatial resolution (< 1mm X 1mm), thin slices (< 3mm) and good temporal resolution (~ 90sec) made possible by using parallel imaging. 3)Post-processing capability should provide post-contrast injection subtraction images, multi-phase time-intensity curves and maximum intensity projection (MIP) for 3D viewing and vascular maps. 5
6 Bi lateral Multi channel Breast Coil 6
7/16/2010. Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI. Objectives. ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010
 Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
MRI SEQUENCES. 1 Gradient Echo Sequence
 5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
GE 3.0T NPW,TRF,FAST,F R NPW,TRF,FAST,F R
 GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time
 Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698
 SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio
 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 12: Spin Echo
 Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
Breast MRI Quality Control
 Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics Educational Objectives Discuss the importance of breast MRI quality control (QC). Provide an overview of the new ACR Breast MRI Accreditation
Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics Educational Objectives Discuss the importance of breast MRI quality control (QC). Provide an overview of the new ACR Breast MRI Accreditation
3/30/2013. Disclosure. Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization. MRI, 35 year ago. MRI Today. Outlines
 http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
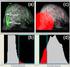 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T
 32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T Thomas Benner Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T Thomas Benner Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols
 MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols Structural scans SIEMENS MAGNETOM ConnectomA syngo MR D11 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Default\AAHScout_64 TA:0:14 PAT:3 Voxel size:1.6 1.6 1.6 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :fl
MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols Structural scans SIEMENS MAGNETOM ConnectomA syngo MR D11 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Default\AAHScout_64 TA:0:14 PAT:3 Voxel size:1.6 1.6 1.6 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :fl
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
ParaVision 6. Innovation with Integrity. The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research.
 ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
Overview. Optimizing MRI Protocols. Image Contrast. Morphology & Physiology. User Selectable Parameters. Tissue Parameters
 Overview Optimizing MRI Protocols Clinical Practice & Compromises Geoffrey D. Clarke, Radiology Department University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Pulse timing parameters for adjusting
Overview Optimizing MRI Protocols Clinical Practice & Compromises Geoffrey D. Clarke, Radiology Department University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Pulse timing parameters for adjusting
Cirrus 0.2T. MRI for Everyone. North America, Asia, Europe. contact: [email protected]
 Cirrus 0.2T MRI for Everyone North America, Asia, Europe contact: [email protected] MRI-TECH inc. Cirrus MRI system for all your needs: Low costs Low maintenance High quality Open geometry Imaging of
Cirrus 0.2T MRI for Everyone North America, Asia, Europe contact: [email protected] MRI-TECH inc. Cirrus MRI system for all your needs: Low costs Low maintenance High quality Open geometry Imaging of
Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications)
 Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications) Excelart Vantage Magnet Configuration: Ultra-short-bore Strength (or W x H): 1.5 T Homogeneity, ppm V-RMS: Dimensions of maximum
Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications) Excelart Vantage Magnet Configuration: Ultra-short-bore Strength (or W x H): 1.5 T Homogeneity, ppm V-RMS: Dimensions of maximum
THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI. Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider
 THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider Departments of *Radiology, *Electrical Engineering, and Psychology University
THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider Departments of *Radiology, *Electrical Engineering, and Psychology University
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials. Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA
 Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Sustaining a High-Quality Breast MRI Practice
 Sustaining a High-Quality Breast MRI Practice Christoph Lee, MD, MSHS Associate Professor of Radiology Adjunct Associate Professor, Health Services University of Washington September 11, 2015 Overview
Sustaining a High-Quality Breast MRI Practice Christoph Lee, MD, MSHS Associate Professor of Radiology Adjunct Associate Professor, Health Services University of Washington September 11, 2015 Overview
Kap 8 Image quality, signal, contrast and noise
 4/5/ FYS-KJM 474 contrast SNR MR-teori og medisinsk diagnostikk Kap 8 Image qualit, signal, contrast and noise resolution vailable MRparameters speed Main source of noise in MRI: Noise generated within
4/5/ FYS-KJM 474 contrast SNR MR-teori og medisinsk diagnostikk Kap 8 Image qualit, signal, contrast and noise resolution vailable MRparameters speed Main source of noise in MRI: Noise generated within
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know
 Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London [email protected] CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London [email protected] CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Table 11: Pros and Cons of 1.5 T MRI vs. 3.0 T MRI; Safety and Technical Issues, and Clinical Applications
 Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
How To Grow With An Mri
 Growth with Body MRI Body MRI H.-Hartziekenhuis Lier 40 oz/d tussen 8 en 21 uur 3-5 body mri/d Aparte protocols voor leverletsels / pancreas, mrcp rectum, ovarium, cervix / uterus, pelvimetrie anus / fistula
Growth with Body MRI Body MRI H.-Hartziekenhuis Lier 40 oz/d tussen 8 en 21 uur 3-5 body mri/d Aparte protocols voor leverletsels / pancreas, mrcp rectum, ovarium, cervix / uterus, pelvimetrie anus / fistula
MRI Physics for Radiologists
 Alfred L. Horowitz MRI Physics for Radiologists A Visual Approach Second Edition With 94 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Alfred
Alfred L. Horowitz MRI Physics for Radiologists A Visual Approach Second Edition With 94 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Alfred
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the brain: Report of AAPM MR Task Group #9
 Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the brain: Report of AAPM MR Task Group #9 Dick J. Drost a) Nuclear Medicine and MRI Department, St. Joseph s Health Centre, London, Ontario N6A 4L6, Canada William
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the brain: Report of AAPM MR Task Group #9 Dick J. Drost a) Nuclear Medicine and MRI Department, St. Joseph s Health Centre, London, Ontario N6A 4L6, Canada William
Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica. E. Pagani, M. Filippi
 Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica E. Pagani, M. Filippi DW-MRI DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED MRI Principles Diffusion results from a microspic random motion known as Brownian motion THE RANDOM WALK How
Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica E. Pagani, M. Filippi DW-MRI DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED MRI Principles Diffusion results from a microspic random motion known as Brownian motion THE RANDOM WALK How
Medical Imaging. MRI Instrumentation, Data Acquisition, Image Reconstruction. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology, NYU School of Medicine
 G16.4426/EL5823/BE6203 Medical Imaging MRI Instrumentation, Data Acquisition, Image Reconstruction Riccardo Lattanzi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology, NYU School of Medicine Department
G16.4426/EL5823/BE6203 Medical Imaging MRI Instrumentation, Data Acquisition, Image Reconstruction Riccardo Lattanzi, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology, NYU School of Medicine Department
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Achieving High Resolution and Controlling
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Achieving High Resolution and Controlling
Spectral Adiabatic Inversion Recovery (SPAIR) MR imaging of the Abdomen
 Spectral Adiabatic Inversion Recovery (SPAIR) MR imaging of the Abdomen Thomas C. Lauenstein Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology, University Hospital Essen, Germany
Spectral Adiabatic Inversion Recovery (SPAIR) MR imaging of the Abdomen Thomas C. Lauenstein Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology, University Hospital Essen, Germany
Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance
 Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Contents: Jorge Jovicich [email protected] I) Historical Background II) An MR experiment - Overview - Can we scan the subject? - The subject goes into the magnet -
Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Contents: Jorge Jovicich [email protected] I) Historical Background II) An MR experiment - Overview - Can we scan the subject? - The subject goes into the magnet -
ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 63. 41 ~ 49, 2000 ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS ERIKO SHIBAHARA 1, HIROSHI FUKATSU
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 63. 41 ~ 49, 2000 ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS ERIKO SHIBAHARA 1, HIROSHI FUKATSU
THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY
 THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY The Widest Wide Bore in the Industry 74cm Oval Bore Provides a comfortable and spacious environment around the patient WIT Monitor Allows technologist to review and
THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY The Widest Wide Bore in the Industry 74cm Oval Bore Provides a comfortable and spacious environment around the patient WIT Monitor Allows technologist to review and
Generation and Detection of NMR Signals
 Generation and Detection of NMR Signals Hanudatta S. Atreya NMR Research Centre Indian Institute of Science NMR Spectroscopy Spin (I)=1/2h B 0 Energy 0 = B 0 Classical picture (B 0 ) Quantum Mechanical
Generation and Detection of NMR Signals Hanudatta S. Atreya NMR Research Centre Indian Institute of Science NMR Spectroscopy Spin (I)=1/2h B 0 Energy 0 = B 0 Classical picture (B 0 ) Quantum Mechanical
Etude POPART'MUS MRI Component
 TECHNICAL SURVEY Dear Investigators, This document is a Technical Survey which provides the teams of THERALYS and of the Pierre Wertheimer Neurological Hospital of Lyon with an overview of your site s
TECHNICAL SURVEY Dear Investigators, This document is a Technical Survey which provides the teams of THERALYS and of the Pierre Wertheimer Neurological Hospital of Lyon with an overview of your site s
PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience
 20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
Breast MRI: Imaging and Intervention. Jaroslaw Nicholas Tkacz, M. D.
 Breast MRI: Imaging and Intervention Jaroslaw Nicholas Tkacz, M. D. Purpose To examine the typical morphologic, enhancement and kinetic features of breast lesions on MR Imaging and determine the role of
Breast MRI: Imaging and Intervention Jaroslaw Nicholas Tkacz, M. D. Purpose To examine the typical morphologic, enhancement and kinetic features of breast lesions on MR Imaging and determine the role of
University Children s Hospital Basel
 Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
REVIEW. Magnetic Resonance: An Introduction to Ultrashort TE (UTE) Imaging
 REVIEW Magnetic Resonance: An Introduction to Ultrashort TE (UTE) Imaging Matthew D. Robson, PhD, Peter D. Gatehouse, DPhil, Mark Bydder, PhD, and Graeme M. Bydder, MB, ChB Abstract: The background underpinning
REVIEW Magnetic Resonance: An Introduction to Ultrashort TE (UTE) Imaging Matthew D. Robson, PhD, Peter D. Gatehouse, DPhil, Mark Bydder, PhD, and Graeme M. Bydder, MB, ChB Abstract: The background underpinning
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
MR Imaging of Peritoneal Malignancy Russell N. Low, MD
 MR Imaging of Peritoneal Malignancy Russell N. Low, MD From: Sharp and Children's MRI Center and Sharp HealthCare, 7901 Frost Street, San Diego, California, 92123. Phone: (858) 939-3600. Email: [email protected]
MR Imaging of Peritoneal Malignancy Russell N. Low, MD From: Sharp and Children's MRI Center and Sharp HealthCare, 7901 Frost Street, San Diego, California, 92123. Phone: (858) 939-3600. Email: [email protected]
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT
 GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT Formal requirements and procedures OVERVIEW This document is intended to help a principle investigator set up a research project using magnetic resonance imaging
GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT Formal requirements and procedures OVERVIEW This document is intended to help a principle investigator set up a research project using magnetic resonance imaging
MRI QA Technologist s Tests
 AAPM 55th Annual Meeting MRI QA Technologist s Tests Guang Jia, PhD Associate Professor Department of Physics Louisiana State University Background Outline QC importance Technologist s role QC test tips
AAPM 55th Annual Meeting MRI QA Technologist s Tests Guang Jia, PhD Associate Professor Department of Physics Louisiana State University Background Outline QC importance Technologist s role QC test tips
In vivo stem cell tracking in the myocardium of small laboratory animals: Feasibility and acquisition strategies on clinical magnetic resonance
 In vivo stem cell tracking in the myocardium of small laboratory animals: Feasibility and acquisition strategies on clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems Piotr A. Wielopolski Erasmus MC Department
In vivo stem cell tracking in the myocardium of small laboratory animals: Feasibility and acquisition strategies on clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems Piotr A. Wielopolski Erasmus MC Department
COST AID ASL post- processing Workshop
 COST AID ASL post- processing Workshop This workshop runs thought the post- processing of ASL data using tools from the FMRIB Software Library (www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk.uk/fsl), we will primarily focus on the
COST AID ASL post- processing Workshop This workshop runs thought the post- processing of ASL data using tools from the FMRIB Software Library (www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk.uk/fsl), we will primarily focus on the
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging
 Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Glossary of MRI Terms
 Glossary of MRI Terms A Absorption mode. Component of the MR signal that yields a symmetric, positive-valued line shape. Acceleration factor. The multiplicative term by which faster imaging pulse sequences
Glossary of MRI Terms A Absorption mode. Component of the MR signal that yields a symmetric, positive-valued line shape. Acceleration factor. The multiplicative term by which faster imaging pulse sequences
REVIEW. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 00:00 00 (2014)
 REVIEW Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 00:00 00 (2014) Recommended Implementation of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI for Clinical Applications: A Consensus of the ISMRM Perfusion Study Group and the
REVIEW Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 00:00 00 (2014) Recommended Implementation of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI for Clinical Applications: A Consensus of the ISMRM Perfusion Study Group and the
It takes two to connect the dots in MRI.
 It takes two to connect the dots in MRI. www.siemens.com/healthcare Tim+ Tim (Total imaging matrix) technology has made fast, flexible and accurate scans the rule, rather than the exception. But we know
It takes two to connect the dots in MRI. www.siemens.com/healthcare Tim+ Tim (Total imaging matrix) technology has made fast, flexible and accurate scans the rule, rather than the exception. But we know
Master s Program in Medical Physics. Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging V. Prof. Dr.
 1 12/9/2008 Page 1 Master s Program in Medical Physics Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging V Chair in Faculty of Medicine Mannheim University of Heidelberg Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer
1 12/9/2008 Page 1 Master s Program in Medical Physics Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging V Chair in Faculty of Medicine Mannheim University of Heidelberg Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer
Concepts for High-Resolution Low-Dose CT of the Breast
 RSNA 2012 Refresher Course 721B, Chicago, Nov. 30, 2012 Concepts for High-Resolution Low-Dose CT of the Breast Disclosures WAK is founder, shareholder and CEO of CT Imaging GmbH, Erlangen, Germany. Willi
RSNA 2012 Refresher Course 721B, Chicago, Nov. 30, 2012 Concepts for High-Resolution Low-Dose CT of the Breast Disclosures WAK is founder, shareholder and CEO of CT Imaging GmbH, Erlangen, Germany. Willi
Clinical applications of MRI in radiation therapy. Jatta Berberat, PhD Kantonsspital Aarau [email protected]
 Clinical applications of MRI in radiation therapy Jatta Berberat, PhD Kantonsspital Aarau [email protected] Background and introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging Relaxation mechanisms Imaging gradients
Clinical applications of MRI in radiation therapy Jatta Berberat, PhD Kantonsspital Aarau [email protected] Background and introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging Relaxation mechanisms Imaging gradients
Lecture 14. Point Spread Function (PSF)
 Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
RE: Invitation for Bid (IFB) No. Q14-32 Type of Service: Magnetic Resonance Imaging System, Maintenance Agreement and Mobile MRI Unit. Addendum No.
 VIA EMAIL DATE: June 16, 2014 TO: FROM: Prospective Proposers Maureen Crystal Director of Contracts RE: Invitation for Bid (IFB) No. Q14-32 Type of Service: Magnetic Resonance Imaging System, Maintenance
VIA EMAIL DATE: June 16, 2014 TO: FROM: Prospective Proposers Maureen Crystal Director of Contracts RE: Invitation for Bid (IFB) No. Q14-32 Type of Service: Magnetic Resonance Imaging System, Maintenance
VI. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS CONCERNING BREAST IMAGING AUDITS
 ACR BI-RADS ATLAS VI. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS CONCERNING BREAST IMAGING AUDITS American College of Radiology 55 ACR BI-RADS ATLAS A. All Breast Imaging Modalities 1. According to the BI-RADS Atlas,
ACR BI-RADS ATLAS VI. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS CONCERNING BREAST IMAGING AUDITS American College of Radiology 55 ACR BI-RADS ATLAS A. All Breast Imaging Modalities 1. According to the BI-RADS Atlas,
QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging SECOND EDITION Scott A. HuetteS Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Allen W. Song Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Gregory McCarthy
runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging SECOND EDITION Scott A. HuetteS Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Allen W. Song Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Gregory McCarthy
MRI Department Goals. Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam. Lecture Topics
 Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam [email protected] Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam [email protected] Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
Tetramethylsilane (TMS) Trimethylsilyl d 4. -propionic acid (TMSP) Dioxane. O - Na + Dimethylfura n. Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate. Sodium Maleate CH 3
 Practical Aspects of Quantitative NMR Experiments This discussion presumes that you already have an understanding of the basic theory of NMR. There are a number of issues that should be considered when
Practical Aspects of Quantitative NMR Experiments This discussion presumes that you already have an understanding of the basic theory of NMR. There are a number of issues that should be considered when
MRI SCANNERS: A BUYER S GUIDE
 09 MRI SCANNERS: A BUYER S GUIDE MRI SCANNERS: A BUYER S GUIDE D. Price, I. Delakis, C. Renaud and R. Dickinson Correspondence Centre for Evidence-based Purchasing 152C Skipton House 80 London Road London
09 MRI SCANNERS: A BUYER S GUIDE MRI SCANNERS: A BUYER S GUIDE D. Price, I. Delakis, C. Renaud and R. Dickinson Correspondence Centre for Evidence-based Purchasing 152C Skipton House 80 London Road London
Medical Image Processing on the GPU. Past, Present and Future. Anders Eklund, PhD Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute [email protected].
 Medical Image Processing on the GPU Past, Present and Future Anders Eklund, PhD Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute [email protected] Outline Motivation why do we need GPUs? Past - how was GPU programming
Medical Image Processing on the GPU Past, Present and Future Anders Eklund, PhD Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute [email protected] Outline Motivation why do we need GPUs? Past - how was GPU programming
The smart approach to digital MRI
 Philips Healthcare is part of Royal Philips Electronics How to reach us: www.philips.com/healthcare [email protected] Product information: www.philips.com/smartpathtodstream The smart approach to
Philips Healthcare is part of Royal Philips Electronics How to reach us: www.philips.com/healthcare [email protected] Product information: www.philips.com/smartpathtodstream The smart approach to
High Field MRI: Technology, Applications, Safety, and Limitations. Brief overview of high-field MRI. The promise of high-field MRI
 High Field MRI: Technology, Applications, Safety, and Limitations R. Jason Stafford, Ph.D. Department of Imaging Physics The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Brief overview
High Field MRI: Technology, Applications, Safety, and Limitations R. Jason Stafford, Ph.D. Department of Imaging Physics The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Brief overview
Embedded Systems in Healthcare. Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008
 Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Technique and Safety of. by Pierluigi Castellone, Electronics Engineer Brain Products General Manager
 Technique and Safety of performing EEG/fMRI measurements by Pierluigi Castellone, Electronics Engineer Brain Products General Manager Contents of the presentation Why recording simultaneous EEG and fmri?
Technique and Safety of performing EEG/fMRI measurements by Pierluigi Castellone, Electronics Engineer Brain Products General Manager Contents of the presentation Why recording simultaneous EEG and fmri?
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
RF Coils... They ve Come a Long, Long Way
 GE Healthcare MR Field Notes The sensitivity area relates to the diameter of the coil. By Increasing coil size, the area of sensitivity also increases. But as with most MR princicloser a coil s position
GE Healthcare MR Field Notes The sensitivity area relates to the diameter of the coil. By Increasing coil size, the area of sensitivity also increases. But as with most MR princicloser a coil s position
MRI Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality Guide
 MRI Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality Guide Introduction Read this entire document carefully. This document provides guidance for interpreting physicians and technologists on the criteria evaluated
MRI Accreditation Program Clinical Image Quality Guide Introduction Read this entire document carefully. This document provides guidance for interpreting physicians and technologists on the criteria evaluated
Principles of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 Principles of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Martin A. Lindquist Department of Biostatistics; Johns Hopkins University Tor D. Wager Department of Psychology & Neuroscience; University of Colorado
1 Principles of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Martin A. Lindquist Department of Biostatistics; Johns Hopkins University Tor D. Wager Department of Psychology & Neuroscience; University of Colorado
NMR for Physical and Biological Scientists Thomas C. Pochapsky and Susan Sondej Pochapsky Table of Contents
 Preface Symbols and fundamental constants 1. What is spectroscopy? A semiclassical description of spectroscopy Damped harmonics Quantum oscillators The spectroscopic experiment Ensembles and coherence
Preface Symbols and fundamental constants 1. What is spectroscopy? A semiclassical description of spectroscopy Damped harmonics Quantum oscillators The spectroscopic experiment Ensembles and coherence
Secretin Enhanced Imaging of the Pancreas
 Secretin Enhanced Imaging of the Pancreas Pablo R. Ros, MD University Hospitals Case Medical Center Case Western Reserve University SCBT-MR Boston, MA October, 2012 [email protected] Disclosures
Secretin Enhanced Imaging of the Pancreas Pablo R. Ros, MD University Hospitals Case Medical Center Case Western Reserve University SCBT-MR Boston, MA October, 2012 [email protected] Disclosures
Phantom Test Guidance
 Phantom Test Guidance for the ACR MRI Accreditation Program The American College of Radiology 1891 Preston White Dr Reston, VA 20191-4397 www.acr.org Contents 0.0 INTRODUCTION............................................................................
Phantom Test Guidance for the ACR MRI Accreditation Program The American College of Radiology 1891 Preston White Dr Reston, VA 20191-4397 www.acr.org Contents 0.0 INTRODUCTION............................................................................
MRI DATA PROCESSING. Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira. Introduction
 MRI DATA PROCESSING Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a clinical exam that is safe to the patient. Nevertheless, it s very important to attend
MRI DATA PROCESSING Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a clinical exam that is safe to the patient. Nevertheless, it s very important to attend
Spatial Encoding Using Multiple rf Coils: SMASH Imaging and Parallel MRI
 SPATIAL ENCODING USING MULTIPLE RF COILS: SMASH IMAGING AND PARALLEL MRI 1 Spatial Encoding Using Multiple rf Coils: SMASH Imaging and Parallel MRI Daniel K. Sodickson Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
SPATIAL ENCODING USING MULTIPLE RF COILS: SMASH IMAGING AND PARALLEL MRI 1 Spatial Encoding Using Multiple rf Coils: SMASH Imaging and Parallel MRI Daniel K. Sodickson Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program. 2011-2012 Assessment Report
 Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2011-2012 Assessment Report I. Introduction II. III. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program Mission
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2011-2012 Assessment Report I. Introduction II. III. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program Mission
The Magnetic Resonance Imaging Examination
 The Magnetic Resonance Imaging Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Examination in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is to assess the knowledge and cognitive
The Magnetic Resonance Imaging Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Examination in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is to assess the knowledge and cognitive
LONI De-Identification Policy
 The following defines how different file formats are de-identified with LONI tools. Each metadata attribute of each file can have the following operations performed: Operation keep Remove Replace Description
The following defines how different file formats are de-identified with LONI tools. Each metadata attribute of each file can have the following operations performed: Operation keep Remove Replace Description
Fundamentals of Cone-Beam CT Imaging
 Fundamentals of Cone-Beam CT Imaging Marc Kachelrieß German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) Heidelberg, Germany www.dkfz.de Learning Objectives To understand the principles of volumetric image formation
Fundamentals of Cone-Beam CT Imaging Marc Kachelrieß German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) Heidelberg, Germany www.dkfz.de Learning Objectives To understand the principles of volumetric image formation
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging What are the uses of MRI? To begin, not only are there a variety of scanning methodologies available, but there are also a variety of MRI methodologies available which provide
Magnetic Resonance Imaging What are the uses of MRI? To begin, not only are there a variety of scanning methodologies available, but there are also a variety of MRI methodologies available which provide
Super-Resolution Reconstruction in MRI: Better Images Faster?
 Super-Resolution Reconstruction in MRI: Better Images Faster? Esben Plenge 1,, Dirk H. J. Poot 1, Monique Bernsen 2, Gyula Kotek 2, Gavin Houston 2, Piotr Wielopolski 2, Louise van der Weerd 3, Wiro J.
Super-Resolution Reconstruction in MRI: Better Images Faster? Esben Plenge 1,, Dirk H. J. Poot 1, Monique Bernsen 2, Gyula Kotek 2, Gavin Houston 2, Piotr Wielopolski 2, Louise van der Weerd 3, Wiro J.
FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety
 FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety Loren A. Zaremba, Ph.D. Center for Devices and Radiological Health Food and Drug Administration Outline I. Introduction II. Static Magnetic Field
FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety Loren A. Zaremba, Ph.D. Center for Devices and Radiological Health Food and Drug Administration Outline I. Introduction II. Static Magnetic Field
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem
 Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves
 Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1199 1205 (1999) High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves Michael H. Buonocore* and David C. Zhu Ghost artifacts in echoplanar imaging (EPI) arise
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1199 1205 (1999) High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves Michael H. Buonocore* and David C. Zhu Ghost artifacts in echoplanar imaging (EPI) arise
MDCT Technology. Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington
 MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
Real Time MRI guided Focal Laser Ablation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Real Time MRI guided Focal Laser Ablation Therapy for Prostate Cancer A/Prof Celi Varol and Dr Orit Raz Uro-Oncologist Nepean and Macquarie Hospital Trial at Macquarie University Hospital Ethics board
Real Time MRI guided Focal Laser Ablation Therapy for Prostate Cancer A/Prof Celi Varol and Dr Orit Raz Uro-Oncologist Nepean and Macquarie Hospital Trial at Macquarie University Hospital Ethics board
Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Utility of Resonance Assignments
 Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Basics of multidimensional NMR (2D NMR) 2D NOESY, COSY and TOCSY 2/23/15 Utility of Resonance Assignments Resonance Assignments: Assignment of frequency positions of resonances (peaks)
Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Basics of multidimensional NMR (2D NMR) 2D NOESY, COSY and TOCSY 2/23/15 Utility of Resonance Assignments Resonance Assignments: Assignment of frequency positions of resonances (peaks)
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Difficulties of T1 brain MRI segmentation techniques M S. Atkins *a, K. Siu a, B. Law a, J. Orchard a, W. Rosenbaum a a School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University ABSTRACT This paper looks at
Difficulties of T1 brain MRI segmentation techniques M S. Atkins *a, K. Siu a, B. Law a, J. Orchard a, W. Rosenbaum a a School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University ABSTRACT This paper looks at
Update: MRI in Multiple sclerosis
 Nyt indenfor MS ved MR Update: MRI in Multiple sclerosis Hartwig Roman Siebner Danish Research Centre for Magnetic Resonance (DRCMR) Copenhagen University Hospital Hvidovre Dansk Radiologisk Selskabs 10.
Nyt indenfor MS ved MR Update: MRI in Multiple sclerosis Hartwig Roman Siebner Danish Research Centre for Magnetic Resonance (DRCMR) Copenhagen University Hospital Hvidovre Dansk Radiologisk Selskabs 10.
