SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698
|
|
|
- Kory Fleming
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28,
2 VERSION HISTORY Version Section Summary of Change 1.0 Final Document ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 2 of 11
3 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Overview of Imaging Requirements Imaging Qualification Imaging Equipment 2.2 DWI Phantom Test 2.3 DWI Test Scans 2.4 DW MRI Learning Module 2.5 Qualification Review and Notification 2.6 Changes to Qualified Scanner(s) and/or Breast Coil 3.0 Standardized Breast MRI Imagine Schedule 3.2 Imaging Procedure Exam Preparations DWI Acquisition Protocol DWI Reproducibility Scan 4.0 Management of Image Data Storage of Image Data 4.2 Submission of Image Data to Core Lab De identification of Images Image Transmittal Worksheet (ITW) 5.0 Quality Control Study Imaging 5.2 DWI Phantom Tests Standardized I SPY 2 and ACRIN 6698 MRI Acquisition Parameters (Table 4).. 11 Please refer to the ACRIN 6698 web page for the current versions of all study documents, DW MRI Qualification Form DWI Phantom Test Instructions Image Transmittal Worksheet (ITW) Imaging Equipment Update Form ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 3 of 11
4 1.0 OVERVIEW OF IMAGING REQUIREMENTS DWI Qualification MRI/DWI Time Points Reproducibility DWI Standardized QC Submit prior to ACRIN 6698 study enrollment (for each scanner): DWI Qualification Form DWI Phantom QC Testing 2 DWI Test Scans 6698 DW MRI Learning Module Perform per standardized I SPY 2/ACRIN 6698 acquisition protocol MRI 1: Pre treatment (prior to randomization) MRI 2: Early treatment (end of paclitaxel cycle 3, prior to cycle 4) MRI 3: Inter regimen (at least 1 day after paclitaxel, prior to AC) MRI 4: Pre surgery (at least 2 3 weeks after AC, prior to surgery) Perform per standardized ACRIN 6698 acquisition protocol MRI 1: Preferred time point (select sites and patients only) MRI 2: If not performed at MRI 1 DWI Phantom QC Testing performed every 6 months 2.0 IMAGING QUALIFICATION Participation in the I SPY2 trial and ACRIN 6698 sub study requires that all sites adhere to a standardized MR imaging protocol. The use of standard imaging guidelines is an essential component of clinical trials in which imaging plays a central role in the research endpoints. This is of particular importance in multicenter trials where equipment, personnel, and imaging acquisition protocols can vary significantly. Thus, the use of standardized imaging guidelines helps control the inter and intra site variability inherent in multicenter imaging trials. To participate in the ACRIN 6698 sub study, I SPY 2 sites will be required to perform phantom QC testing and submit at least 2 DWI test scans acquired using the multi b value DWI sequence provided below in Section 3. Sites must pass the qualification requirements for at least one scanner prior to accrual to ACRIN The purpose of the imaging qualification process is to help ensure trial imaging is of high quality and performed per the trial standardized acquisition protocol. Suboptimal image quality and/or imaging not performed per the trial standardized protocol can result in exclusion of the imaging exam(s) and/or the entire case from analysis. Therefore, routine QC and adherence to the I SPY 2 and ACRIN 6698 image acquisition protocol are of great importance. 2.1 Imaging Equipment Consistent with I SPY 2, the required imaging equipment includes: at least one 1.5T or 3T whole body MRI scanner a dedicated breast radiofrequency coil Sites are required to identify at least one 1.5T or 3T MR scanner for imaging of ACRIN 6698 study patients. An ACRIN 6698 DW MRI Qualification Form is required for each ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 4 of 11
5 scanner to be used for study imaging. In choosing which scanner(s) to qualify, please note that it is preferred (best practice) that all study imaging for a given patient be performed on the same scanner. When this is not possible, all imaging for a given patient must be performed using the same scanner configuration (manufacturer, field strength, model, and breast coil model). 2.2 DWI Phantom Test DWI phantom tests are required for each scanner to be used for study imaging. Upon receipt of the ACRIN 6698 Protocol Specific Application (PSA), a pair of DWI phantoms will be delivered to the site for system testing. These ice water based phantoms, by utilizing a medium with a known diffusion coefficient and temperature control, provide a standardized/harmonized method for DWI QC testing. The DWI Phantom Test Instructions, detailing phantom preparation and scan instructions, is available for download from the ACRIN 6698 web site, For image submission instructions, refer to section 4.2 below. 2.3 DWI Test Scans Two clinical DWI test scans are required for each scanner to be used for study imaging. The DWI test scans should be acquired per the 4 b value DWI acquisition protocol provided in Section 3, but only after receiving ACRIN approval of the DWI phantom test. The test scans can be performed on current I SPY 2 patients or volunteers. Refer to Section 4.2 for image submission instructions. 2.4 DWI Learning Module As part of the site qualification process, sites will be asked to identify a lead/research MRI technologist to oversee the study related imaging activities. This technologist is required to complete a study specific DWI learning module. The learning module will provide an overview of the 6698 imaging requirements as well as provide information regarding image quality issues specific to DWI. Though not required, all MRI technologists working with 6698 study participants are urged to complete the learning module. 2.5 Qualification Review and Notification The DWI data from both the QC and clinical test scans will be evaluated for general image quality (e.g. artifacts, distortion, signal to noise) and compliance with the standardized DWI acquisition protocol. Upon approval of the DWI phantom tests, ACRIN will notify sites via to move forward with the required test scans. If the test scans are approved, ACRIN will a scanner specific qualification notification/report. If the test scans are not approved, the required technical corrections will be communicated (by and/or phone) and another test scan, with the required corrections, should be submitted for review. Approval of the test scan(s) is mandatory prior to a site registering a participant onto the ACRIN 6698 trial. 2.6 Changes to Qualified Scanner(s) and/or Breast Coil Changes in the scanner or breast coil used to image I SPY 2 and/or ACRIN 6698 study patients should be reported immediately to the ACRIN Core Lab using the Imaging ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 5 of 11
6 Equipment Update Form (download from The addition of a new scanner or breast coil for study imaging will require full scanner qualification. Software and/or hardware upgrades to already qualified scanners will be reviewed by the ACRIN Imaging Core Lab to determine whether additional QC testing or test scans will be required. In either case, use of a new scanner/breast coil or software/hardware upgrades, sites should consult ACRIN prior to scanning study patients. 3.0 STANDARDIZED BREAST MRI Because acquisition protocols can vary significantly across institutions both the I SPY 2 and ACRIN 6698 studies make use of a standardized MR acquisition protocol. All breast MRI scans performed on ACRIN 6698 study patients should be performed per the I SPY 2 acquisition protocol with the exception of the DWI scan, which should be performed using the 4 b value DWI acquisition protocol provided below instead of the two b value I SPY 2 DWI acquisition protocol. Contact the ACRIN Imaging Core Laboratory with any questions regarding the imaging protocol. 3.1 Imaging Schedule All I SPY 2 and ACRIN 6698 imaging should be performed at the following time points, as defined in the I SPY 2 protocol. Figure 1. Schema MRI DWI Reproducibility DWI (If patient consented) MRI DWI Reproducibility DWI (If patient consented and not acquired with MRI 1) MRI DWI MRI DWI ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 6 of 11
7 3.2 Imaging Procedure As identified by the I SPY 2 protocol, the standardized MRI protocol includes a bilateral pre contrast T2 weighted sequence, a pre contrast diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) sequence, a pre contrast T1 weighted sequence, and a T1 weighted dynamic contrastenhanced (DCE) sequence. For I SPY 2 patients also enrolled to ACRIN 6698 the DWI sequence will be acquired using a diffusion weighted spin echo echo planar imaging (DW SE EPI) sequence with 4 b values. When setting up this acquisition protocol for the first time (e.g. for the qualification test scans) the protocol should be saved to the scanner s protocol menu under an easily recognizable name, such as ISPY2 or ACRIN 6698; this will help avoid future confusion about which imaging protocol to select. Please note that some facilities limit access to the system s protocol menu so this may require special user permissions Exam Preparations All MRI exams of the same patient must be performed on an ACRIN qualified scanner, using the same scanner (best practice) or the same scanner configuration (manufacturer, field strength, model, and breast coil model), and using the same contrast agent brand. Patients should be scanned prone and centered to the table. Place an intravenous catheter in the arm or hand prior to the start of imaging for contrast injection. Sites should adhere to standard clinical guidelines for the safe administration of contrast media (such as pre testing and contrast history). Please use universal MRI safety precautions DWI Acquisition Protocol The DWI scan must be acquired prior to the DCE sequence using a diffusionweighted spin echo echo planar imaging (DW SE EPI) sequence. Axial orientation Diffusion gradients in three orthogonal directions to measure isotropic ADC Parallel imaging (reduction factor > 2) Fat suppression utilizing the optimal technique (SPAIR, STIR, etc.) for the MRI scanner being used 4 b values: 0, 100, 600 and 800 s/mm 2 Acquire the maximum number of slices that can be acquired during a single acquisition (typically slices). Coverage should be adjusted to keep the scan within a single acquisition to minimize scan time and motion artifacts. Total scan duration for the DWI sequence should be 4 6 minutes; for multi bvalue acquisition, should be on the order of 5 minutes. The required imaging sequences are outlined below in Table 2. Refer to Table 4 (on page 11) for detailed acquisition parameters. ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 7 of 11
8 Table 2. Acquisition Sequences: I SPY 2 / ACRIN 6698 MRI Protocol Localizer/Scout Pre contrast T2 weighted fast spin echo (FSE) or STIR Pre contrast DWI (DW SE EPI) Pre contrast 3D T1 weighted gradient echo (GE) 1 Post contrast dynamic multi phase 3D T1 weighted GE (DCE) 1 1 Pre and post contrast T1 weighted sequences MUST have identical image parameters to allow subtraction/maps. Transmit and receive gain settings should remain constant. Pre contrast T1 images should be checked prior to contrast injection to confirm acceptable fat suppression DWI Reproducibility Scan A subset of patients (approximately 60) will undergo a reproducibility DWI scan with MRI 1 (preferred) or MRI 2. For participating patients, two T2 (for DWI planning) and DWI sequences are to be acquired prior to injection of contrast for the DCE sequence. To simulate performance of an entirely distinct DW MRI exam, completely remove the patient from the scan table after the first DWI sequence, re position the patient on the table and re landmark, acquire a new localizer (scout), then acquire a full MRI exam per the standardized I SPY 2/ACRIN 6698 acquisition protocol. DO NOT end the exam session after the first DWI sequence as this will cause multiple exams to be created with the same accession number, which can complicate the image submission process. Rather, all sequences should be acquired within a single exam session. The required imaging sequences are outlined below in Table 3. Refer to Table 4 (on page 11) for detailed acquisition parameters. Table 3. Acquisition Sequences: DWI Reproducibility Sub Study Localizer/Scout Pre contrast T2 weighted fast spin echo (FSE) or STIR Pre contrast DWI (DW SE EPI) Remove patient from MRI scanner but DO NOT exit exam session Reposition patient in MRI scanner and start new series (same exam session) Localizer/Scout Pre contrast T2 weighted fast spin echo (FSE) or STIR Pre contrast DWI (DW SE EPI) Pre contrast 3D T1 weighted gradient echo (GE) 1 Post contrast dynamic multi phase 3D T1 weighted GE (DCE) 1 1 Pre and post contrast T1 weighted sequences MUST have identical image parameters to allow subtraction/maps. Transmit and receive gain settings should remain constant. Pre contrast T1 images should be checked prior to contrast injection to confirm acceptable fat suppression. ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 8 of 11
9 4.0 MANAGEMENT OF IMAGE DATA 4.1 Storage of Image Data Sites are expected to keep all study data, including study imaging, for at least 7 years after the trial closes. 4.2 Submission of Image Data to Core Lab All I SPY 2 and ACRIN 6698 imaging should be submitted to the ACRIN Imaging Core Lab via TRIAD within 48 hours of acquisition. Developed by the American College of Radiology, TRIAD provides a secure, web based method of transferring and managing image data. For questions related to TRIAD contact TRIAD Support by phone at or TRIAD [email protected]. Additionally, the TRIAD Installation Guide and TRIAD Users Guide can be found online at Imaging for patients enrolled to both the I SPY 2 and ACRIN 6698 trials should be submitted via TRIAD under the ACRIN 6698 trial. I SPY 2 patients not enrolled to ACRIN 6698 should continue to be submitted via TRIAD under the I SPY 2 trial De identification of Images Sites are urged not to employ the use of other de identification software before uploading the images to TRIAD as these applications are typically not developed for research purposes and may remove data pertinent to the research. TRIAD removes patient information and replaces it with site and study specific identifiers provided by and at the site. The implementation of TRIAD anonymization is based on DICOM Supplement 142: Clinical Trial De Identification Profiles, ftp://medical.nema.org/medical/dicom/final/sup142_ft.pdf Image Transmittal Worksheet (ITW) An ACRIN 6698 ITW must be submitted for all imaging at the time of image submission. The ITW should be completed in full and submitted via to ACRIN [email protected]. All current study documents can be found on the ACRIN 6698 web site, QUALITY CONTROL (QC) 5.1 Study Imaging Sites are expected to acquire the MRI exams per the standardized MR acquisition protocol and review all imaging at the time of acquisition for basic image quality and compliance with the standardized acquisition protocol. MR technologists with any questions/concerns regarding image quality of the study MR, as performed, should consult their study radiologist(s) prior to the patient leaving to determine whether the exam should be repeated. ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 9 of 11
10 Upon receipt of the images at ACRIN, a QC review will be conducted by a qualified ACRIN Imaging Technologist (ACRIN IT). The QC review includes checking for: [a] missing images/sequences, [b] appropriate level of de identification, [c] complete anatomical coverage of the breast parenchyma, [d] absence of image artifacts, [e] scanner compliance (performed on qualified scanner, performed on same scanner or same scanner configuration), and [f] compliance with acquisition parameters. Missing or discrepant image data will be communicated to the site by the ACRIN IT via a Z5 Data Query. Queries will be ed to the responsible site personnel for resolution. Sites are expected to resolve data queries expeditiously. Queries not resolved within 7 business days will be categorized as overdue data. All study imaging will undergo an additional quality review as part of the central review and image analysis process conducted by the UCSF Breast MRI Research Laboratory. 5.2 DWI Phantom Test For each qualified scanner, sites are required to conduct DWI phantom tests every 6 months using the same phantom and testing procedures used for the qualification testing. The DWI Phantom Test Instructions is available for download from the ACRIN 6698 web site, The purpose of the phantom test is to provide a standardized, quantitative process to confirm ongoing MRI system performance in acquisition of diffusion weighted (DW) images of the breast. ACRIN will identify a testing schedule for each site based on the approval date of the site qualification testing. All phantom imaging should be submitted to the ACRIN core lab via TRIAD under the ACRIN 6698 study (versus I SPY 2). ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 10 of 11
11 Table 4. Standardized I SPY 2 and ACRIN 6698 MRI Acquisition Parameters Parameter T2 weighted DWI T1 weighted Sequence type FSE or STIR DW SE EPI GE 2D or 3D sequence 2D 2D 3D Slice orientation Axial or sagittal Axial Axial Laterality Bilateral Bilateral Bilateral Frequency direction A/P A/P A/P Phase direction R/L (axial) R/L R/L S/I (sagittal) FOV frequency mm (axial) mm (a) mm mm (sagittal) FOV phase mm (axial) mm (a) mm mm (sagittal) Matrix frequency (acquired) Matrix phase (acquired) Reconstruction Matrix 512 x x x 512 In plane resolution 1.4 mm mm 1.4 mm Fat suppression Active fat sat recommended Active fat sat Active fat sat recommended TR ms > 4,000 ms 4 10 ms TE ms (STIR 70 ms) Minimum (50 100ms) Minimum (fat/water in phase preferable) Echo Train Length 16 N/A N/A TI (STIR sequence) 170 ms (1.5T) N/A N/A 230 ms (3.0T) Flip Angle 90 degrees 90 degrees degrees Readout Bandwidth N/A N/A Maximum (per pixel) b values N/A 0, 100, 600, 800 s/mm 2 N/A Slice thickness (acquired) 4 mm 4 5 mm 2.5 mm # of slices Variable; complete bilateral coverage Variable; bilateral coverage; adjust to keep 60; complete bilateral coverage w/in single acquisition Slice Gap 1.0 mm No gap No gap Parallel imaging factor 2 >2 2 # of excitations/averages 2 >2 2 k space ordering N/A N/A k to +k standard, non centric Sequence acquisition time 7 minutes 4 6 minutes (multi b seq ~ 5 min) 80 sec scan time 100 sec Total post contrast imaging duration N/A N/A 8 minutes following injection (a) Adjust up to 400 mm to accommodate for large body habitus if necessary. ACRIN 6698 Site Imaging Manual, Version 1.0 Page 11 of 11
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Etude POPART'MUS MRI Component
 TECHNICAL SURVEY Dear Investigators, This document is a Technical Survey which provides the teams of THERALYS and of the Pierre Wertheimer Neurological Hospital of Lyon with an overview of your site s
TECHNICAL SURVEY Dear Investigators, This document is a Technical Survey which provides the teams of THERALYS and of the Pierre Wertheimer Neurological Hospital of Lyon with an overview of your site s
32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T
 32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T Thomas Benner Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T Thomas Benner Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time
 Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Breast MRI Quality Control
 Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics Educational Objectives Discuss the importance of breast MRI quality control (QC). Provide an overview of the new ACR Breast MRI Accreditation
Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics Educational Objectives Discuss the importance of breast MRI quality control (QC). Provide an overview of the new ACR Breast MRI Accreditation
GE 3.0T NPW,TRF,FAST,F R NPW,TRF,FAST,F R
 GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 12: Spin Echo
 Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications)
 Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications) Excelart Vantage Magnet Configuration: Ultra-short-bore Strength (or W x H): 1.5 T Homogeneity, ppm V-RMS: Dimensions of maximum
Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications) Excelart Vantage Magnet Configuration: Ultra-short-bore Strength (or W x H): 1.5 T Homogeneity, ppm V-RMS: Dimensions of maximum
Current Industry Neuroimaging Experience in Clinical Trials Jerome Barakos, M.D.
 Current Industry Neuroimaging Experience in Clinical Trials Jerome Barakos, M.D. Melbourne Australia March 28, 2012 Synarc Experience and Expertise Largest imaging service provider dedicated to clinical
Current Industry Neuroimaging Experience in Clinical Trials Jerome Barakos, M.D. Melbourne Australia March 28, 2012 Synarc Experience and Expertise Largest imaging service provider dedicated to clinical
Configuration and Use of the MR Knee Dot Engine
 Configuration and Use of the MR Knee Dot Engine Kai Reiter (RT); Sebastian Auer (RT) Radiology Herne, Herne, Germany 1 42 MAGNETOM Flash 3/2011 www.siemens.com/magnetom-world We are a radiological joint
Configuration and Use of the MR Knee Dot Engine Kai Reiter (RT); Sebastian Auer (RT) Radiology Herne, Herne, Germany 1 42 MAGNETOM Flash 3/2011 www.siemens.com/magnetom-world We are a radiological joint
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio
 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols
 MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols Structural scans SIEMENS MAGNETOM ConnectomA syngo MR D11 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Default\AAHScout_64 TA:0:14 PAT:3 Voxel size:1.6 1.6 1.6 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :fl
MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols Structural scans SIEMENS MAGNETOM ConnectomA syngo MR D11 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Default\AAHScout_64 TA:0:14 PAT:3 Voxel size:1.6 1.6 1.6 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :fl
MRI SEQUENCES. 1 Gradient Echo Sequence
 5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT
 GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT Formal requirements and procedures OVERVIEW This document is intended to help a principle investigator set up a research project using magnetic resonance imaging
GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT Formal requirements and procedures OVERVIEW This document is intended to help a principle investigator set up a research project using magnetic resonance imaging
Cirrus 0.2T. MRI for Everyone. North America, Asia, Europe. contact: [email protected]
 Cirrus 0.2T MRI for Everyone North America, Asia, Europe contact: [email protected] MRI-TECH inc. Cirrus MRI system for all your needs: Low costs Low maintenance High quality Open geometry Imaging of
Cirrus 0.2T MRI for Everyone North America, Asia, Europe contact: [email protected] MRI-TECH inc. Cirrus MRI system for all your needs: Low costs Low maintenance High quality Open geometry Imaging of
ParaVision 6. Innovation with Integrity. The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research.
 ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
SMRT Student Scope Submission
 SMRT Student Scope Submission Title and Author Title: Massive Disk Herniation of the Thoracic Vertebrae Author: Tamara N. Lewis E-mail: [email protected] Phone: (404)963-2304 Expected date of graduation:
SMRT Student Scope Submission Title and Author Title: Massive Disk Herniation of the Thoracic Vertebrae Author: Tamara N. Lewis E-mail: [email protected] Phone: (404)963-2304 Expected date of graduation:
Kap 8 Image quality, signal, contrast and noise
 4/5/ FYS-KJM 474 contrast SNR MR-teori og medisinsk diagnostikk Kap 8 Image qualit, signal, contrast and noise resolution vailable MRparameters speed Main source of noise in MRI: Noise generated within
4/5/ FYS-KJM 474 contrast SNR MR-teori og medisinsk diagnostikk Kap 8 Image qualit, signal, contrast and noise resolution vailable MRparameters speed Main source of noise in MRI: Noise generated within
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials. Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA
 Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
DWI Case Study - QIBA PDF- MRI Technical Committee. What is IMI?
 DWI Case Study - QIBA PDF- MRI Technical Committee QIBA Annual Meeting May 21, 2014 What is IMI? The Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) is the world s largest biomedical /healthcare public-private initiative
DWI Case Study - QIBA PDF- MRI Technical Committee QIBA Annual Meeting May 21, 2014 What is IMI? The Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) is the world s largest biomedical /healthcare public-private initiative
3/30/2013. Disclosure. Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization. MRI, 35 year ago. MRI Today. Outlines
 http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
The Importance of Following the PROTOCOL in Clinical Trials
 The Importance of Following the PROTOCOL in Clinical Trials Presentation Objectives: Upon completion of this presentation, participants will be able to: Describe the following terms: Protocol, Protocol
The Importance of Following the PROTOCOL in Clinical Trials Presentation Objectives: Upon completion of this presentation, participants will be able to: Describe the following terms: Protocol, Protocol
Table 11: Pros and Cons of 1.5 T MRI vs. 3.0 T MRI; Safety and Technical Issues, and Clinical Applications
 Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
7/16/2010. Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI. Objectives. ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010
 Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
Prepublication Requirements
 Issued Prepublication Requirements The Joint Commission has approved the following revisions for prepublication. While revised requirements are published in the semiannual updates to the print manuals
Issued Prepublication Requirements The Joint Commission has approved the following revisions for prepublication. While revised requirements are published in the semiannual updates to the print manuals
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
SWABIK Project. Software Tools for DICOM Media Exchange in Clinical Research: the. SWABIK Project
 Software Tools for DICOM Media Exchange in Clinical Research: the SWABIK Project Software Tools for DICOM Media Exchange in Clinical Research: the SWABIK Project O. ElGazzar 1, M. Onken 1, M. Eichelberg
Software Tools for DICOM Media Exchange in Clinical Research: the SWABIK Project Software Tools for DICOM Media Exchange in Clinical Research: the SWABIK Project O. ElGazzar 1, M. Onken 1, M. Eichelberg
MR Imaging of Peritoneal Malignancy Russell N. Low, MD
 MR Imaging of Peritoneal Malignancy Russell N. Low, MD From: Sharp and Children's MRI Center and Sharp HealthCare, 7901 Frost Street, San Diego, California, 92123. Phone: (858) 939-3600. Email: [email protected]
MR Imaging of Peritoneal Malignancy Russell N. Low, MD From: Sharp and Children's MRI Center and Sharp HealthCare, 7901 Frost Street, San Diego, California, 92123. Phone: (858) 939-3600. Email: [email protected]
Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update
 Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update Paul Kinahan, Robert Doot Imaging Research Laboratory Department of Radiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA Supported by RSNA Quantitative
Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update Paul Kinahan, Robert Doot Imaging Research Laboratory Department of Radiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA Supported by RSNA Quantitative
Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance
 Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Contents: Jorge Jovicich [email protected] I) Historical Background II) An MR experiment - Overview - Can we scan the subject? - The subject goes into the magnet -
Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Contents: Jorge Jovicich [email protected] I) Historical Background II) An MR experiment - Overview - Can we scan the subject? - The subject goes into the magnet -
UMHS-PUHSC JOINT INSTITUTE
 Imaging Biomarkers for Staging and Assessing Response to Therapy in Multiple Myeloma Qian Dong, MD. Radiology University of Michigan Wei Guo, MD. Orthopedic Oncology Peking University Second Hospital Team
Imaging Biomarkers for Staging and Assessing Response to Therapy in Multiple Myeloma Qian Dong, MD. Radiology University of Michigan Wei Guo, MD. Orthopedic Oncology Peking University Second Hospital Team
Unwarping Echo Planar Images Using CMTK 1 Release 1.2
 Unwarping Echo Planar Images Using CMTK 1 Release 1.2 Torsten Rohlfing October 1, 2012 Neuroscience Program, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA Abstract This document describes the workflow for unwarping
Unwarping Echo Planar Images Using CMTK 1 Release 1.2 Torsten Rohlfing October 1, 2012 Neuroscience Program, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA Abstract This document describes the workflow for unwarping
MRI QA Technologist s Tests
 AAPM 55th Annual Meeting MRI QA Technologist s Tests Guang Jia, PhD Associate Professor Department of Physics Louisiana State University Background Outline QC importance Technologist s role QC test tips
AAPM 55th Annual Meeting MRI QA Technologist s Tests Guang Jia, PhD Associate Professor Department of Physics Louisiana State University Background Outline QC importance Technologist s role QC test tips
MRI DATA PROCESSING. Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira. Introduction
 MRI DATA PROCESSING Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a clinical exam that is safe to the patient. Nevertheless, it s very important to attend
MRI DATA PROCESSING Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a clinical exam that is safe to the patient. Nevertheless, it s very important to attend
PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience
 20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
What s new in Trendsetting Applications?
 What s new in Trendsetting Applications? Leading. With MAGNETOM. Answers for life. What s new in trendsetting applications? Growth with Body MRI FREEZEit 2 Quiet Suite Advanced WARP 1,3 DotGO 1 MyoMaps
What s new in Trendsetting Applications? Leading. With MAGNETOM. Answers for life. What s new in trendsetting applications? Growth with Body MRI FREEZEit 2 Quiet Suite Advanced WARP 1,3 DotGO 1 MyoMaps
CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM. Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH
 CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH CT Patient comes out... Patient goes in... Big Black Box Radiology
CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH CT Patient comes out... Patient goes in... Big Black Box Radiology
The smart approach to digital MRI
 Philips Healthcare is part of Royal Philips Electronics How to reach us: www.philips.com/healthcare [email protected] Product information: www.philips.com/smartpathtodstream The smart approach to
Philips Healthcare is part of Royal Philips Electronics How to reach us: www.philips.com/healthcare [email protected] Product information: www.philips.com/smartpathtodstream The smart approach to
2/28/2011. MIPPA overview and CMS requirements. CT accreditation. Today s agenda. About MIPPA. Computed Tomography
 Today s agenda Computed Tomography Presented by: Dina Hernandez, BSRT, RT (R), CT, QM Krista Bush, RT, MBA Leonard Lucey, JD ACR Quality & Safety MIPPA overview and CMS requirements CT accreditation How
Today s agenda Computed Tomography Presented by: Dina Hernandez, BSRT, RT (R), CT, QM Krista Bush, RT, MBA Leonard Lucey, JD ACR Quality & Safety MIPPA overview and CMS requirements CT accreditation How
PET and PET/CT in Clinical Trials
 PET and PET/CT in Clinical Trials Nathan C. Hall, M.D., Ph.D. The Ohio State University Medical Center CALGB Imaging Core Lab CALGB Imaging Committee Outline Introduction to PET Positron Emitter Physics
PET and PET/CT in Clinical Trials Nathan C. Hall, M.D., Ph.D. The Ohio State University Medical Center CALGB Imaging Core Lab CALGB Imaging Committee Outline Introduction to PET Positron Emitter Physics
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
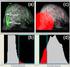 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica. E. Pagani, M. Filippi
 Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica E. Pagani, M. Filippi DW-MRI DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED MRI Principles Diffusion results from a microspic random motion known as Brownian motion THE RANDOM WALK How
Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica E. Pagani, M. Filippi DW-MRI DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED MRI Principles Diffusion results from a microspic random motion known as Brownian motion THE RANDOM WALK How
INTRODUCTION. A. Purpose
 New York State Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Radiation Protection Guide for Radiation Safety/Quality Assurance Programs Computed Radiography INTRODUCTION A. Purpose This guide describes
New York State Department of Health Bureau of Environmental Radiation Protection Guide for Radiation Safety/Quality Assurance Programs Computed Radiography INTRODUCTION A. Purpose This guide describes
7/22/2011. Breast MRI: Pulse Sequences, Acquisition Protocols, and Analysis. Objectives. Challenges in DCE Breast Imaging
 Breast MRI: Pulse Sequences, Acquisition Protocols, and Analysis Objectives Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 1. Review background of MRI breast cancer imaging 2. Present
Breast MRI: Pulse Sequences, Acquisition Protocols, and Analysis Objectives Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 1. Review background of MRI breast cancer imaging 2. Present
RF Coils... They ve Come a Long, Long Way
 GE Healthcare MR Field Notes The sensitivity area relates to the diameter of the coil. By Increasing coil size, the area of sensitivity also increases. But as with most MR princicloser a coil s position
GE Healthcare MR Field Notes The sensitivity area relates to the diameter of the coil. By Increasing coil size, the area of sensitivity also increases. But as with most MR princicloser a coil s position
Phantom Test Guidance
 Phantom Test Guidance for the ACR MRI Accreditation Program The American College of Radiology 1891 Preston White Dr Reston, VA 20191-4397 www.acr.org Contents 0.0 INTRODUCTION............................................................................
Phantom Test Guidance for the ACR MRI Accreditation Program The American College of Radiology 1891 Preston White Dr Reston, VA 20191-4397 www.acr.org Contents 0.0 INTRODUCTION............................................................................
Advanced MRI methods in diagnostics of spinal cord pathology
 Advanced MRI methods in diagnostics of spinal cord pathology Stanisław Kwieciński Department of Magnetic Resonance MR IMAGING LAB MRI /MRS IN BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH ON HUMANS AND ANIMAL MODELS IN VIVO Equipment:
Advanced MRI methods in diagnostics of spinal cord pathology Stanisław Kwieciński Department of Magnetic Resonance MR IMAGING LAB MRI /MRS IN BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH ON HUMANS AND ANIMAL MODELS IN VIVO Equipment:
ADNI 2 Alzheimer s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 3T MRI Technical Procedures Manual
 1 V1. 01_31_2011 ADNI 2 Alzheimer s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 3T MRI Technical Procedures Manual 2 Table of Contents I. Contact Information...4 II. ADNI2 3T Study Overview..5 III. Site Qualification..7
1 V1. 01_31_2011 ADNI 2 Alzheimer s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 3T MRI Technical Procedures Manual 2 Table of Contents I. Contact Information...4 II. ADNI2 3T Study Overview..5 III. Site Qualification..7
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 PRIMARY CERTIFICATION DIDACTIC AND CLINICAL COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS EFFECTIVE JANUARY 2014 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet
PRIMARY CERTIFICATION DIDACTIC AND CLINICAL COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS EFFECTIVE JANUARY 2014 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program. 2011-2012 Assessment Report
 Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2011-2012 Assessment Report I. Introduction II. III. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program Mission
Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program 2011-2012 Assessment Report I. Introduction II. III. Mission, Objectives, and Student Learning Outcomes a. Radiologic Science Degree Completion Program Mission
COST AID ASL post- processing Workshop
 COST AID ASL post- processing Workshop This workshop runs thought the post- processing of ASL data using tools from the FMRIB Software Library (www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk.uk/fsl), we will primarily focus on the
COST AID ASL post- processing Workshop This workshop runs thought the post- processing of ASL data using tools from the FMRIB Software Library (www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk.uk/fsl), we will primarily focus on the
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts
 Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Update on MQSA and ACR Mammography Accreditation
 MQSA - Who s Who Update on MQSA and ACR Mammography Accreditation The Law: Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) The Regulator: US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Pamela L. Platt, BSRT(R)(M)(CV)
MQSA - Who s Who Update on MQSA and ACR Mammography Accreditation The Law: Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) The Regulator: US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Pamela L. Platt, BSRT(R)(M)(CV)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 31 (2013) 1439 1444 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Magnetic Resonance Imaging journal homepage: www.mrijournal.com Technical notes Evaluation of MRI issues for an
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 31 (2013) 1439 1444 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Magnetic Resonance Imaging journal homepage: www.mrijournal.com Technical notes Evaluation of MRI issues for an
THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY
 THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY The Widest Wide Bore in the Industry 74cm Oval Bore Provides a comfortable and spacious environment around the patient WIT Monitor Allows technologist to review and
THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY The Widest Wide Bore in the Industry 74cm Oval Bore Provides a comfortable and spacious environment around the patient WIT Monitor Allows technologist to review and
In vivo stem cell tracking in the myocardium of small laboratory animals: Feasibility and acquisition strategies on clinical magnetic resonance
 In vivo stem cell tracking in the myocardium of small laboratory animals: Feasibility and acquisition strategies on clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems Piotr A. Wielopolski Erasmus MC Department
In vivo stem cell tracking in the myocardium of small laboratory animals: Feasibility and acquisition strategies on clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems Piotr A. Wielopolski Erasmus MC Department
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know
 Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London [email protected] CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London [email protected] CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Overview. Optimizing MRI Protocols. Image Contrast. Morphology & Physiology. User Selectable Parameters. Tissue Parameters
 Overview Optimizing MRI Protocols Clinical Practice & Compromises Geoffrey D. Clarke, Radiology Department University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Pulse timing parameters for adjusting
Overview Optimizing MRI Protocols Clinical Practice & Compromises Geoffrey D. Clarke, Radiology Department University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Pulse timing parameters for adjusting
NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
Embedded Systems in Healthcare. Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008
 Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
MRI Physics for Radiologists
 Alfred L. Horowitz MRI Physics for Radiologists A Visual Approach Second Edition With 94 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Alfred
Alfred L. Horowitz MRI Physics for Radiologists A Visual Approach Second Edition With 94 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Alfred
LONI IMAGE & DATA ARCHIVE USER MANUAL
 IMAGE & DATA ARCHIVE USER MANUAL Laboratory of Neuro Imaging Dr. Arthur W. Toga, Director June 2013 INTRODUCTION The LONI (IDA) is a user-friendly environment to archive, search, share, track and disseminate
IMAGE & DATA ARCHIVE USER MANUAL Laboratory of Neuro Imaging Dr. Arthur W. Toga, Director June 2013 INTRODUCTION The LONI (IDA) is a user-friendly environment to archive, search, share, track and disseminate
FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety
 FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety Loren A. Zaremba, Ph.D. Center for Devices and Radiological Health Food and Drug Administration Outline I. Introduction II. Static Magnetic Field
FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety Loren A. Zaremba, Ph.D. Center for Devices and Radiological Health Food and Drug Administration Outline I. Introduction II. Static Magnetic Field
MRI Technical Operations Manual. Final Version 7.0 20.January.2015
 MRI Technical Operations Manual Final Version 7.0 20.January.2015 2 Table of Contents 1 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging... 3 1.1 MRI Acquisition Procedures... 3 1.2 MRI Local Read Requirement (Baseline
MRI Technical Operations Manual Final Version 7.0 20.January.2015 2 Table of Contents 1 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging... 3 1.1 MRI Acquisition Procedures... 3 1.2 MRI Local Read Requirement (Baseline
MRI Department Goals. Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam. Lecture Topics
 Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam [email protected] Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam [email protected] Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs
 Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
A software tool for Quality Assurance of Computed / Digital Radiography (CR/DR) systems
 A software tool for Quality Assurance of Computed / Digital Radiography (CR/DR) systems Nikunj Desai a and Daniel J Valentino a,b a icr Company Inc, 2580 West 237th Street, Torrance, CA 90505, USA b Department
A software tool for Quality Assurance of Computed / Digital Radiography (CR/DR) systems Nikunj Desai a and Daniel J Valentino a,b a icr Company Inc, 2580 West 237th Street, Torrance, CA 90505, USA b Department
An Overview of Digital Imaging Systems for Radiography and Fluoroscopy
 An Overview of Digital Imaging Systems for Radiography and Fluoroscopy Michael Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Outline Introduction Imaging Considerations Receptor Properties General
An Overview of Digital Imaging Systems for Radiography and Fluoroscopy Michael Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Outline Introduction Imaging Considerations Receptor Properties General
Investigation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Effects when Using Bone Conduction Implants
 Investigation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Effects when Using Bone Conduction Implants Master of Science Thesis in Biomedical Engineering, MPBME Karl-Johan Fredén Jansson Department of Signals and Systems
Investigation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Effects when Using Bone Conduction Implants Master of Science Thesis in Biomedical Engineering, MPBME Karl-Johan Fredén Jansson Department of Signals and Systems
The in-house dedicated Vet MRI. Vet -MR
 Vet-MR The in-house dedicated Vet MRI Vet -MR Welcome to the world of Vet-MR The Innovation in imaging Pets: > Why Vet-MR > Vet-MR: the reasons for success > Easy MRI With more than twenty years of experience
Vet-MR The in-house dedicated Vet MRI Vet -MR Welcome to the world of Vet-MR The Innovation in imaging Pets: > Why Vet-MR > Vet-MR: the reasons for success > Easy MRI With more than twenty years of experience
University of California San Francisco, CA, USA 4 Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, San Francisco, CA, USA
 Disrupted Brain Connectivity in Alzheimer s Disease: Effects of Network Thresholding Madelaine Daianu 1, Emily L. Dennis 1, Neda Jahanshad 1, Talia M. Nir 1, Arthur W. Toga 1, Clifford R. Jack, Jr. 2,
Disrupted Brain Connectivity in Alzheimer s Disease: Effects of Network Thresholding Madelaine Daianu 1, Emily L. Dennis 1, Neda Jahanshad 1, Talia M. Nir 1, Arthur W. Toga 1, Clifford R. Jack, Jr. 2,
Software Packages The following data analysis software packages will be showcased:
 Analyze This! Practicalities of fmri and Diffusion Data Analysis Data Download Instructions Weekday Educational Course, ISMRM 23 rd Annual Meeting and Exhibition Tuesday 2 nd June 2015, 10:00-12:00, Room
Analyze This! Practicalities of fmri and Diffusion Data Analysis Data Download Instructions Weekday Educational Course, ISMRM 23 rd Annual Meeting and Exhibition Tuesday 2 nd June 2015, 10:00-12:00, Room
Interfacing Fuji CR in a DICOM Network Environment
 Interfacing Fuji CR in a DICOM Network Environment Wayne T. DeJarnette, Ph.D., Valmore Albrecht, RT, Alan Orth, RT, Jon Sayer, M.S. DeJarnette Research Systems, Inc. 401 Washington Avenue Towson, MD 21204
Interfacing Fuji CR in a DICOM Network Environment Wayne T. DeJarnette, Ph.D., Valmore Albrecht, RT, Alan Orth, RT, Jon Sayer, M.S. DeJarnette Research Systems, Inc. 401 Washington Avenue Towson, MD 21204
How To Improve Your Ct Image Quality
 Translating Protocols Between Scanner Manufacturer and Model Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
Translating Protocols Between Scanner Manufacturer and Model Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL
 Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Making Multiple Code Reading Easy. Webinar
 Making Multiple Code Reading Easy Webinar Today s Agenda Introduction How DataMan Makes Multiple Code Reading Easy Multiple Code Reading Applications Product Demonstration Videos Q&A 2 Introduction Introduction
Making Multiple Code Reading Easy Webinar Today s Agenda Introduction How DataMan Makes Multiple Code Reading Easy Multiple Code Reading Applications Product Demonstration Videos Q&A 2 Introduction Introduction
TISSUE MIMICKING GEL QUALITY LE PHANTOM SERIES DESIGN. performance the ultrasound labs ofand. icking material has the same attenuation mim-
 QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest
 Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
University of Minnesota Center for Magnetic Resonance Research Standard Operating Procedure Human System Magnet Operator Training
 University of Minnesota Center for Magnetic Resonance Research Standard Operating Procedure Human System Magnet Operator Training SOP Number / Version: SOP001 / Version 1 Approval Date: Implementation
University of Minnesota Center for Magnetic Resonance Research Standard Operating Procedure Human System Magnet Operator Training SOP Number / Version: SOP001 / Version 1 Approval Date: Implementation
Data. microcat +SPECT
 Data microcat +SPECT microcat at a Glance Designed to meet the throughput, resolution and image quality requirements of academic and pharmaceutical research, the Siemens microcat sets the standard for
Data microcat +SPECT microcat at a Glance Designed to meet the throughput, resolution and image quality requirements of academic and pharmaceutical research, the Siemens microcat sets the standard for
High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves
 Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1199 1205 (1999) High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves Michael H. Buonocore* and David C. Zhu Ghost artifacts in echoplanar imaging (EPI) arise
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1199 1205 (1999) High Spatial Resolution EPI Using an Odd Number of Interleaves Michael H. Buonocore* and David C. Zhu Ghost artifacts in echoplanar imaging (EPI) arise
LONI De-Identification Policy
 The following defines how different file formats are de-identified with LONI tools. Each metadata attribute of each file can have the following operations performed: Operation keep Remove Replace Description
The following defines how different file formats are de-identified with LONI tools. Each metadata attribute of each file can have the following operations performed: Operation keep Remove Replace Description
Revenue Cycle Management: It Takes a Village. Problem Statement
 Revenue Cycle Management: It Takes a Village AHRA 38 th Annual Meeting August 24, 2010 Patricia R. Blank, Executive Vice President, InSight Imaging Nancy Walker, Executive Director, RCM, Insight Imaging
Revenue Cycle Management: It Takes a Village AHRA 38 th Annual Meeting August 24, 2010 Patricia R. Blank, Executive Vice President, InSight Imaging Nancy Walker, Executive Director, RCM, Insight Imaging
Cone Beam Reconstruction Jiang Hsieh, Ph.D.
 Cone Beam Reconstruction Jiang Hsieh, Ph.D. Applied Science Laboratory, GE Healthcare Technologies 1 Image Generation Reconstruction of images from projections. textbook reconstruction advanced acquisition
Cone Beam Reconstruction Jiang Hsieh, Ph.D. Applied Science Laboratory, GE Healthcare Technologies 1 Image Generation Reconstruction of images from projections. textbook reconstruction advanced acquisition
THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI. Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider
 THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider Departments of *Radiology, *Electrical Engineering, and Psychology University
THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider Departments of *Radiology, *Electrical Engineering, and Psychology University
DICOM Correction Item
 Correction Number DICOM Correction Item CP-626 Log Summary: Type of Modification Clarification Rationale for Correction Name of Standard PS 3.3 2004 + Sup 83 The description of pixel spacing related attributes
Correction Number DICOM Correction Item CP-626 Log Summary: Type of Modification Clarification Rationale for Correction Name of Standard PS 3.3 2004 + Sup 83 The description of pixel spacing related attributes
WHERE IN THE WORLD JILL LIPOTI?
 WHERE IN THE WORLD IS JILL LIPOTI? HELLO FROM NEW JERSEY CRCPD - National Symposium on Fusion Imaging and Multimodalities February 18-20, 2004 Kansas City, Missouri New Jersey s Requirements As They Pertain
WHERE IN THE WORLD IS JILL LIPOTI? HELLO FROM NEW JERSEY CRCPD - National Symposium on Fusion Imaging and Multimodalities February 18-20, 2004 Kansas City, Missouri New Jersey s Requirements As They Pertain
runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging SECOND EDITION Scott A. HuetteS Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Allen W. Song Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Gregory McCarthy
runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging SECOND EDITION Scott A. HuetteS Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Allen W. Song Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Gregory McCarthy
MDCT Technology. Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington
 MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
MDCT Technology Kalpana M. Kanal, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Washington Seattle, Washington ACMP Annual Meeting 2008 - Seattle, WA Educational Objectives Historical
