Artificial Bone Models Extremities and Joints
|
|
|
- Charlene Mills
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SE T Somso Modelle Artificial Bone Models Extremities and Joints MARCUS SOMMER SOMSO MODELLE SEI riedrich-rueckert-straße 54, D Coburg Phone , ax [email protected], Internet:
2 ANATOMY 14 Extremities and Joints THE HUMAN OOT - A MARVEL COM AND 19 MUSCLES NS 1 NORMAL OOT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the anatomical structure and the distal end of tibia. In one piece. Length (Pternion-Akropodion): 24 cm., height: 13 cm., width: 26 cm., depth: 10 cm., weight: 450 g NS 2 LAT OOT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the anatomical structure and the distal end of tibia. In one piece. Height: 13 cm., width: 26 cm., depth: 9 cm., weight: 450 g NS 9 MUSCLES O THE OOT Natural size, in SOMSO- Plast. Showing the network of nerves and vessels, the layers of the muscles of the sole of the foot are removable (M. flexor digitorum brevis, M. quadratus plantae, M. extensor digitorum longus, Tendo calcaneus (Achillis), M. abductor digiti minimi, M. flexor hallucis brevis, M. adductor hallucis (caput obliquum) and M. abductor hallucis), ligamentous apparatus is shown. Altogether in 9 parts. On a stand with base. Height: 18 cm., width: 33 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 1.1 kg NS 3 ARCHED OOT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the anatomical structure and the distal end of tibia. In one piece. Height: 16 cm., width: 24 cm., depth: 10 cm., weight: 450 g NS 7 NORMAL OOT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the surface muscles. In one piece. On a stand with base. Height: 29 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 17.5 cm., weight: 600 g NS 4 CLUB OOT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The model had been developed in cooperation with Dr. Urs Schneider, Tübingen. Showing the pathological anatomy of the foot and distal tibia. Height: 13 cm., width: 20,5 cm., depth: 10,5 cm., weight: 410 g NS 8 NORMAL OOT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Sagittal section through the inside of the foot. Showing the surface muscles at the right half of the foot. In one piece. On a stand with base. Height: 28 cm., width: 29 cm., depth: 17.5 cm., weight: 98
3 SEIT PRISING 26 BONES, 107 LIGAMENTS Nature is our Model Somso Modelle This leaflet is an overworked extract from our complete catalogue A 74. On page you will find the extremities and joints and on page the artificial bone preparations are shown. Our models are protected by copyright by Marcus Sommer, SOMSO Modelle. Duplication and reprinting in any form by any method, whether digital or conventional processes, are prohibited. NS 5 HALLUX VALGUS MODEL In cooperation with Dr. Urs Schneider, Tübingen Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The purchased hallux valgus model is a frequent orthopaedic clinical picture as an accompanying aspect of splay feet or pes phanovalgus. On the one hand the model shows the "first ray" pathology with abduction of the first metatarsal bone, adduction and pronation of the proximal phalanx as well as the facultative flexed distal phalanx. On the other hand the significance of the pathological muscle pull for the ethiology and therapy of the deformity is shown. The role of a pathological muscle pull direction in the progression of the hallux valgus can be studied as an example for many other deformities. Height: 13 cm., width: 25 cm., depth: 10 cm., weight: 430 g NS 10 MUSCLES O THE LEG WITH BASE O PELVIS A little under natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the most important blood vessels and nerves in the left leg. The following muscles are removable: the greater gluteal muscle, tensor muscle of the broad fascia, sartorius muscle, straight muscle of the femur, semimembranous muscle, semitendinous muscle, biceps muscle of the femur, digitorum longus muscle, triceps muscle of the calf. Separates altogether in 10 parts. Standing upright, revolving on a stand with base. Height: 108 cm., width: 39 cm., depth: 26 cm., weight: 5 kg 99
4 ANATOMY 14 Extremities and Joints ARM AND LEG MODELS SHOW THE A BONES, TENDONS, JOINTS AND BLOO NS 13 MUSCLES O THE HAND WITH BASE O ORE-ARM Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Aponeurosis of the inner hand with the superficial muscles removable in layers (Mm. lumbricales, M. abductor pollicis brevis, M. abductor digiti minimi und M. flexor digiti minimi brevis). Showing the network of blood vessels and nerves as well as ligamentous apparatus. Altogether in 5 parts. On a stand with base. Height: 34 cm., width: 14 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 500 g ADVANCED NOTICE NS 13/1 SURGICAL HAND MODEL This model has been developed in cooperation with Dr. Niels Benatar, Braunschweig. Natural size, in SOMSO plast, dismantlable and made up of 6 parts. NS 15 MUSCLES O THE ARM WITH SHOULDER GIRDLE Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the network of blood vessels and nerves in the right arm. The following muscles are removable: deltoid muscle, lateral head of the triceps muscle of the arm, short and long extensor muscle of the radial wrist with brachioradial muscle, round pronator muscle - flexor muscle of the radial wrist - long palmar muscle, superficial flexor muscle of the fingers. Altogether in 6 parts. Standing upright and revolving on a stand with base. Height: 105 cm., width: 39 cm., depth: 26 cm., weight: 4.6 kg The colouring corresponds with the natural colours of the muscles, tendons, vessels and nerves during a empty blood operation carried out on the hand. Typical disease changes such as the carpal tunnel syndrome, snapping finger and the dupuytrens's contracture can be shown and demonstrated on this model. On stand with plinth. In preparation. 100
5 SEIT NATOMY O THE MUSCLES, D VESSELS Nature is our Model Somso Modelle The advantages of SOMSO functional models NS 17 SHOULDER JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. With ligaments and synovial capsule. In one piece. On a stand with base. Height: 23 cm., width: 19 cm., depth: 19 cm., weight: 500 g NS 20 HIP JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the ligaments. In one piece. On a base. Height: 28 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 600 g NS 18 ELBOW JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the ligaments. In one piece. On a base. Height: 21 cm., width: 13 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 200 g NS 19 KNEE JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the ligaments and menisci. In one piece. On a base. Height: 24 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 14 cm., weight: 300 g 1. Authentic reproduction of the articular anatomy 2. Top quality, tough and durable flexible plastic for the ligaments 3. Use of screw connections wherever possible 4. Practical to handle by removal from the stand 5. Key on base 6. 5-year warranty NS 50 UNCTIONAL MODEL O THE KNEE JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The following movements are possible: flexion, extension, inner and outer rotation. On a base. Height: 34 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 1 kg 101
6 ANATOMY 14 Extremities and Joints SOMSO UNCTIONAL MODELS ALLOW NATURAL LOCOMOTIVE PROCESSES NS 52 UNCTIONAL MODEL O THE ELBOW JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The following movements are possible: extension and flexion of the upper arm and forearm, rotation movement of the radius. Pronation and supination. Removable from stand with base. Height: 41 cm., width: 19 cm., depth: 22 cm., weight: 650 g NS 51 UNCTIONAL MODEL O THE HIP JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The following movements are possible: raising of the thigh (anteversion), retracting of the thigh (retroversion), lifting up of the thigh to the side (abduction), inner and outer rotation. Removable from stand with base. Height: 35 cm., width: 20 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 1.25 kg NS 53 UNCTIONAL MODEL O THE SHOULDER JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The following movements are possible: raising of the arm (abduction), swinging of the arm (anteversion), back swinging of the arm (retroversion), inner and outer rotation. Removable from stand with base. Height: 26 cm., width: 19 cm., depth: 22 cm., weight: 650 g 102
7 A DETAILED PRESENTATION O Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT Bending movements of the toe joints NS 54 UNCTIONAL MODEL O THE ANKLE JOINTS Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The following movements are possible: up and down movement of the foot (flexion and extension) and rotations (inwards and outwards turning of the foot). Removable from stand with base. Length (Pternion-Akropodion): 25.2 cm. Height: 25 cm., width: 28 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 900 g NS 54/1 UNCTIONAL MODEL O THE TARSUS Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The model had been developed in cooperation with Dr. Urs Schneider, Tübingen. The shifting of the individual tarsal bones during the transition from a normal position to inversion and eversion in an unstrained foot can be semiquantitatively recognized. The purpose of this is to provide an insight into the movement patterns of the foot under phsiological and pathological circumstances. On stand with base. Height: 28 cm., length: 28 cm., depth: 16.5 cm., weight: 1.2 kg Showing the carpal canal NS 55 UNCTIONAL MODEL O THE HAND AND INGER JOINTS Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The following movements are possible: flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, opposition and reposition of the thumb, dorsal and palmar flexion, radial abduction and ulnar abduction of the hand. Removable from stand with base. Length (Stylion-Daktylion III): 19.8 cm. Height: 36 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 19 cm., weight: 400 g 103
8 ANATOMY 14 Extremities and Joints THE SECTIONS O JOINT IN SOMSO-PLAST, DOCUMENTED IN A SERIES O MODELS NS 43 - NS 48. CASTS ROM NATURAL BONE SECTIONS WITH TOPOGRAPHY O MUSCLES, LIGAMENTS, VESSELS AND NERVES. EACH WITH EXPLANATION ON THE BASE PLATE. UNDER REMOVABLE TRANSPARENT COVER NS 43 SECTION THROUGH THE KNEE JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Sagittal section. In one piece. Height: 26 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 4 cm., weight: 800 g NS 44 SECTION THROUGH THE HIP JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. rontal section. In one piece. Height: 26 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 4 cm., weight: 900 g NS 21 ANKLE JOINTS WITH LIGAMENTS Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Consisting of the bones of the foot and the distal ends of tibia and fibula with ligamentous apparatus. Length (Pternion- Akropodion): 21.5 cm. In one piece. On a stand with base. Height: 38 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 400 g NS 45 SECTION THROUGH THE HAND Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Sagittal section. In one piece. Height: 26 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 4 cm., weight: 800 g NS 46 SECTION THROUGH THE ELBOW Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Sagittal section. In one piece. Height: 26 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 4 cm., weight: 800 g NS 21/1 JOINTS O HAND AND INGERS WITH LIGAMENTS Natural size, in SOM- SO-Plast. Consisting of the distal ends of ulna and radius, the carpal bones, metacarpal bones and the finger bones in connection with the ligamentous apparatus. In one piece, on a stand with base. Length (Stylion-Daktylion III): 16.8 cm. Height: 34 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 650 g NS 37 LIGAMENTS O THE ANKLE WITH OPEN TALONAVI- CULAR JOINT To show the deep-set ligaments. Modeled after nature. In SOMSO-Plast. Separates into 2 parts. Height: 14 cm., width: 14.5 cm., depth: 7.5 cm., weight: 400 g NS 47 SECTION THROUGH A NORMAL OOT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Sagittal section. In one piece. Height: 26 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 4 cm., weight: 800 g NS 48 SECTION THROUGH THE SHOULDER JOINT Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. rontal section. In one piece. Height: 26 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 4 cm., weight: 900 g. SEIT The»Somso Sun«is the registered trademark for more than 1000 anatomy, zoology and botany models. The Symbol of high quality, state of the art teaching aids. 104
9 Over 1,000 anatomical, zoological and botanical models Applying to nearly every one of these models is the SOMSO SUN, the instantly recognisable and world famous registered trade mark. To produce the teaching aids for studying anatomy, zoology and botany the company has a quite simple, but demanding philosophy: Nature is Our Model. SOMSO - a full five-year guarantee SOMSO SEIT GUARANTEE 5 YEARS No other manufacturer in this field offers a full five-year warranty - on nearly all models - that covers both durability and workmanship. A family-run firm founded in 1876 SOMSO SUN, the symbol of quality SOMSO was founded in Sonneberg, Thuringia more than 125 years ago. Since then, SOMSO MODELLE have proved to be the benchmark to which others aspire, recognised by the most discerning experts as the ultimate for teaching aids and scientific demonstration. or the Sommer family this is the motivation that drives them to contribute now, and in the future, to training and teaching in the service of science. The company has been owned and managed by five generations of the Sommer family since it was first established in Nature is Our Model Each and every model in the range demonstrates SOMSO s commitment to the highest standards of scientific accuracy and artistry. rom concept through prototype to limited or series production, only specialist scientists, model makers and technicians are employed to produce the highest quality models, accurate down to the finest detail. SOMSO MODELLE - subject to stringent quality controls SOMSO s primary concern is for quality. Quality that passes the tests for scientific accuracy, paintwork, function, durability and materials. Genuine SOMSO MODELLE reflect these quality criteria, and their base material is virtually unbreakable SOMSO-PLAST. The Sommer family The family members are personally responsible for the production of every model, and the guaranteed quality of their products. Hand assembly and finishing by German craftsmen SOMSO MODELLE are produced only in Sonneberg or Coburg - nowhere else - by highly qualified and skilled craftsmen. Some components are now machinemade, but all models are assembled and painted entirely by hand so that each is a unique work of art. World-wide appreciation from the science and teaching professions and from museums SOMSO MODELLE are indispensable for practical teaching of general biology in schools. The Nature is Our Model range is superbly instructive, particularly in accuracy, quality and colour, enabling students to experience nature in an incomparable, hands-on manner. Appropriately proportioned SOMSO MODELLE are in use in science laboratories and lecture halls of universities and colleges throughout the world, making an important contribution to the efficient instruction of trainee doctors and nurses. or many decades, SOMSO MODELLE have been permanently displayed in private collections and public museums, and are of unique interest to specialists and lay visitors alike.
10 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models NATURAL BONE STRUCTURE IS THE OR SOMSO ARTIICIAL BONE PREPA Subdivision for artificial bone preparations: Bone structure 139 Cranium models and single skull bones Skeletons Skeleton parts and single bones oot skeleton Hand skeleton 129 Spinal columns (whole or sections) , Skeleton-muscle models Skeleton-vessel models Intervertebral disc models Alphabetical list (for numerical list, see price list): QS 2 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Removable vault, the lower jaw is movable and modelled to show the roots of the teeth and their network of vessels. Base of the skull and roof with markings in colour of the venous sinus of the dura mater of the brain and the arteries. Separates into 3 parts. Length: 17.5 cm., width: 14.1 cm., size: 51.2 cm., weight: 800 g Arm muscle model Arm skeleton 126 Atlas 127 Axis 127 Auditory ossicles 115 Base of the skull 111 Bauchene Skull Bone collection Bone structure 139 Cervical vertebra 127 Cervical vertebral column 132 Child s skull 112 Clavicle 125 Collection case 127 Compartment box 127 Demonstration skull 113 Disarticulated skeleton Dust-proof box 112 emale pelvis 126 emale skeleton emur 125 etal skull 112 oot skeleton Hand skeleton 129 Hernia of intervertebral disc 137 Human skull Human skeleton Hyoid bone 112 Innominate 126 Intervertebral disc model 137 Leg skeleton 126 Lower arm 126 Lower leg 126 Lumbar vertebra 127 Lumbar spinal column Male human skeleton Male pelvis 126 Muscle function 139 Pelvic skeleton 126 Sacrum 124 Scapula 125 Skull model Spinal column Storage box 117 Temporal bone 115 Thoracic vertebra 127 Thoracic spinal column 130 Upper arm 125 Vertebra 127 Vertebrae collection 127 Vertebral column QS 2/1 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 2, but with notation and explanation in English and Latin. Separates into 3 parts. Weight: 800 g 110
11 ESSENTIAL YARDSTICK RATIONS Nature is our Model SEIT Somso Modelle QS 7/T ARTIICIAL TRANSPARENT HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Removable vault, lower jaw movable. Life-like reproduction of the bony structure. Separates into 3 parts. Weight: 800 g QS 7/E ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Removable vault, lower jaw movable. Separates into 3 parts. Length: 17.5 cm., width: 14.1 cm., size 51.2 cm., weight: 800 g QS 7/1 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 7, but with notation and explanation in English and Latin. Separates into 3 parts. Weight: 800 g Illustration of the skullbase from below. The structure of the bones is identical to the models QS 2, QS 2/1, QS 7 and QS 7/1 QS 7 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Removable vault, lower jaw movable. Life-like reproduction of the bony skull. Separates into 3 parts. Length cm., width: 14,1 cm., size: 51.2 cm., weight: 800 g QS 7/2 ARTIICIAL BASE O THE SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Designed for medical students' studies. In one piece. Length: 17.5 cm., width: 14.1 cm., size: 51.2 cm., weight: 530 g 111
12 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE HUMAN CRANIUM CLASSICALLY LAST DETAIL QS 3 ARTIICIAL SKULL O A NEWBORN Modeled according to nature, in SOMSO-Plast. Upper and lower jaw are open. Altogether in 2 parts. Length: 12.1 cm., width: 9.6 cm., size: 33.9 cm., weight: 180 g QS 3/3 ARTIICIAL SKULL O A ETUS Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. In one piece. Length: 10.5 cm., width: 8.5 cm., size: 29.7 cm., weight: 130 g QS 3/2 ARTIICIAL SKULL O CHILD (ABOUT 6 YEARS OLD) Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Lower jaw movable. Upper and lower jaw are open to show the emergent second dentition. Altogether 2 parts. Length: 16 cm., width: 11.5 cm., size: 44 cm., weight: 380 g QS 7/3 ARTIICIAL HYOID BONE Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. In one piece. On a stand with base. Height: 13 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 130 g QS 8 TRANSPARENT DUSTPROO COVER Suitable for the artificial human skulls. Height: 21 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 19 cm., weight: 600 g QS 7/5 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 7/1, but showing the areas of origin and insertion of the most important muscles of the head. Separates into 3 parts. Length: 17.5 cm., width: 14.1 cm., size: 51.2 cm., weight: 800 g QS 7/6-1 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL, EMALE QS 7/6 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL, EMALE Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Removable vault, lower jaw movable. Lifelike reproduction of the bony structure. Separates into 3 parts. Length: 18.3 cm., width: 12.8 cm., size: 50.8 cm., weight: 700 g Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 7/6, but with notation. Explanation in English and Latin. Separates into 3 parts. Weight: 700 g QS 1 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. With closed vault, lower jaw removable. Separates into 2 parts. Weight: 700 g 112
13 SEIT PREPARED RIGHT DOWN TO THE Nature is our Model Somso Modelle QS 8/10 ARTIICIAL SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, made of SOMSO-Plast. Designed to be separated into 10 parts. Design as QS 8/11, but without representation of the blood vessels and nerves. Weight: 1 kg QS 8/11 ARTIICIAL DEMONSTRATION SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, made of SOMSO-Plast. With representation of the blood vessels and nerves (N. trigeminus and N. opticus etc.). Designed to be separated into 10 parts as follows: 1. Cranium with coloured vessels and blood supply of the hard meninx 2. Base of the skull, sectioned through median line into two halves 3. Nasal septum detachable. The paranasal sinuses and turbinate bones are shown 4. The frontal sinus can be opened 5. The maxillary sinus can be opened 6. The right temporal bone can be taken out and opened. Representation of the bony labyrinths, the semicircular canals, the eardrum and the chain of auditory ossicles. A radial mastoidectomy is shown on the left temporal bone. 7. Detachable lower jaw and roots of the teeth are exposed (flap). Complete set of teeth Length: 18 cm., width: 13.1 cm., size: 50.4 cm., weight: 1 kg QS 8/11-S ARTIICIAL DEMONSTRATION SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 8/11, but with notation. Key in English and Latin. Weight: 1 kg 113
14 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models COMPLEX CRANIAL ANATOMY - 14 P QS 8/2 14-PIECE MODEL O THE SKULL Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. The model is constructed from 14 individual parts, which can easily be dismantled and put back together by way of interconnecting plugs. The sphenoid bone, occipital bone and the two temporal bones form the basis of the skull; the two parietal bones and the frontal bone attach to the anterior of the sphenoid bone. The facial part of the skull is then completed through attachment of the right and left maxilla, each of which also includes the lacrimal, nasal and palatine bones. acial and cranial bones are connected to each other on each side by the zygomatic bone, which in the model is a separate element that can be individually removed. The mandible is fixed into sockets on either side of the skull through a hinge-joint. Weight: 700 g 114
15 ART STEP BY STEP SEPARATION Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT QS 69 THE THREE AUDITORY OSSICLES Cast from natural specimen 1 : 1, in SOM- SO-Plast. Malleus, incus and stapes mounted under "Plexiglas" cover, removable. On a base plate. Height: 3 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 80 g QS 69/1 THE THREE AUDITORY OSSICLES Natural cast 1 : 1, in SOMSO-Plast. Malleus, Incus and Stapes mounted in natural position under "Plexiglas cover". Can be removed, on stand. Height: 3 cm., width: 12 cm., length: 12 cm., weight 80 g. QS 8/51 ARTIICIAL TEMPORAL BONE Natural cast, in OMSO-Plast. In one part. On stand with base. Height: 17 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 150 g QS 70 ARTIICIAL BONY LABYRINTH Cast from natural specimen 1:1, in SOM- SO-Plast. The labyrinth is mounted under "Plexiglas" cover, removable. On a base plate. Height: 3 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 80 g QS 70/1 THE THREE AUDITORY OSSICLES WITH BONY LABYRINTH Natural cast 1 : 1, in SOMSO-Plast. Under "Plexiglas cover". Can be removed, on stand. Height: 3 cm., width: 12 cm., length: 12 cm., weight 80 g QS 8/53 ARTIICIAL TEMPORAL BONE Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. The opened tympanic cavity shows the tympanic membrane, the three auditory ossicles, the cochlea and the semicircular canals. Separates into 2 parts. On a stand with base. Height: 17 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 150 g QS 8/3 14-PIECE MODEL O THE HUMAN SKULL Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. The same model as QS 8/2, but in colour. Here, the individual bones are identified by different colours. This version of the model eases learning of the shape and size of the individual bones and thereby assists in the understanding of the mosaic-like structure of the human skull. Weight: 700 g QS 8/4 TRANSPARENT CASE Hinged and made out of transparent synthetic material. Suitable for SOMSO skulls. Weight: 900 g 115
16 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE DISMANTABLE SKULL MODEL A ALSO AVAIABLE IN 18 PIECES AND M QS 8/ PIECES MODEL O THE SKULL Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast, after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. The model comprises 18 elements corresponding to the natural bones. Apart from the cranium (frontal, parietal, occipital and sphenoid bones), the bones of the viscero cranium (ethmoid bone, vomer, palatine bone, zygomatic bone, maxilla and mandible) and the inferior nasal concha can be removed and reassembled to form the complete skull. Weight: 640 g QS 8/2C+M 14-PIECES MODEL O THE SKULL WITH MUSCLES O MASTICA- TION AND CERVICAL VERTEBRAL, COLUMN AND HYOID BONE Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast, after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. As QS 8/2, but with the 4 muscles of mastication and cervical vertebral, column and hyoid bone. Weight: kg Moreover the skull (18-pieces) with muscles of mastication, cervical vertebral column and hyoid bone is available under article number QS 8/218C+M and the coloured versions areavailable with article number QS 8/3C+M (14-pieces skull) as well as QS 8/318C+M (18-pieces skull). QS 8/ PIECES MODEL O THE SKULL Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast, after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. The model comprises 18 elements corresponding to the natural bones. Weight: 640 g 116
17 TER PROESSOR ROHEN NOW USCLES O MASTICATION Nature is our Model SEIT Somso Modelle see back titles QS 8/6 ALX CEREBRI Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast, after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen.The 14 or 18 piece skull model can also be supplied with a transparent plastic falx cereberi with tentorium cerebelli. Weight: 66 g QS 8/3M 14-PIECES MODEL O THE SKULL WITH MUSCLES O MASTICATION Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast, after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. Version as QS 8/3 but with the 4 masticatory muscles. Weight: 715 g QS 8/3C 14-PIECES MODEL O THE SKULL WITH CERVICAL VERTEBRAL COLUMN AND HYOID BONE Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast, after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. Version as QS 8/3 but with cervical vertebral column and hyoid bone. Weight kg The 18-pieces model of the skull with muscles of mastication has the article number QS 8/318M. Lower jaw with the 4 muscles of mastication QS 8/218M 18-PIECES MODEL O THE SKULL WITH MUSCLES O MASTICATION Natural size, made from SOMSO-Plast, after Prof. Dr. Dr. J. W. Rohen, Department of Anatomy, University of Erlangen. Version as QS 8/218 but with the 4 masticatory muscles. Weight: 715 g The 14-pieces model of the skull with muscles of mastication has the article number QS 8/2M. QS 8/1 METAL STAND WITH BASE Suitable for the SOMSO skull models. Height: 19 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 300 g; Illustration of the stand with the skull model see QS 8/3C 117
18 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE EXPLODED ARTIICIAL SKULL - Detail - Os occipitale Detail - Joint stand Detail - Taking apart and putting back the individual bones QS 9 ARTIICIAL BAUCHENE SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Natural representation of bone structure in all anatomical details. All the bones are mounted on a plastic base corresponding to the shape of the skull, and can be removed from this base: frontal, pariecal (2), temporal (2), zygomatic (2), nasal (2), occipital, Maxilla (2) with lacrimal (2), inferior nasal concha (2) and palatine (2), Vomer, ethmoid, sphenoid, Mandible. Particularly suitable for demonstrations as a result of a joint stand. Separates into 22 parts. Height: 40 cm., width: 26 cm., depth: 39 cm., weight: 1.9 kg 118
19 THE ART O BONE PREPARATION Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT QS 9/5 ARTIICIAL BAUCHENE SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. The same model as QS 9, but coloured. Height: 40 cm., width: 26 cm., depth: 39 cm., weight: 1.9 kg QS 9/1 ARTIICIAL BAUCHENE SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Unmounted in a case, altogether 22 parts. Height: 12 cm., width: 42 cm., depth: 30 cm., weight: 3 kg QS 9/2 ARTIICIAL BAUCHENE SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. Unmounted, each bone individually packed in a suitable transparent box, altogether 22 parts. Weight: 2.2 kg. Illustration of the individual bones see QS 9/1 QS 9/3 ARTIICIAL BAUCHENE SKULL O AN ADULT Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast. All bones loose and unmounted in plastic sacks included in a carton, altogether 22 parts. Weight: 550 g. Illustration of the individual bones see QS 9/1 Illustration of the individuell bones QS 9/1, QS 9/2 and QS 9/3 QS 9/4 TRANSPARENT STORAGE CASE itting to unmounted single bones of the bauchene skull. Height: 12 cm., width: 42 cm., depth: 30 cm., weight: 2.4 kg 119
20 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE HUMAN SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE The height and dimensions comply with the Central European average. Maximum cranium circumference: emale = 50.8 cm., male = 51.2 cm. Cranium length (Glabella-Ophistocranion line): emale = 18.3 cm., male = 17.5 cm. Cranium width (Euryon distance): emale = 12.8 cm., male = 14.1 cm. Hand skeleton length (Stylion-Dactylion III): emale = 18 cm., male = 19 cm. Detail Hyoid bone oot skeleton length (Pternion-Acropodion): emale = 22.2 cm., male = 25 cm. QS 10 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing life-size all the anatomical details of the bone structure. Skull with removable vault and mandible. Joints mounted and movable, upper and lower extremities removable. The right and left foot can be detached from the leg. Mounted upright on a stand. With a dustproof cover. Height: 179 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 10 kg Detail Thorax bone from the top The assembly of SOMSO skeletons is anatomically correct, functional and practice-orientated. QS 10/1 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10, but with rollers on the base of the stand. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 10.4 kg QS 10/E ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON (without ill.) Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing lifesize all the anatomical details of the bone structure. Skull with removable vault and mandible. Joints mounted and movable, upper and lower extremities removable, except of the hands and feet. Mounted upright with rollers on the base of the stand. With a dustproof cover. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 10 kg Male Skeleton QS 10 Detail Wrist bone Detail Tarsus bone 120
21 SEIT SOMSO PROGRAMME Nature is our Model Somso Modelle Detail QS 10/2 Muscular function QS 10/2 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10, but on one arm the flexible muscles of the upper arm are reproduced. By bending or stretching the arm the flexion or extension of the muscles can be shown. Schematic working model. Height: 179 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 10.1 kg QS 10/3 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10, but with hook for hanging at the skull (without stand). Height: 170 cm., width: 38 cm., depth: 28 cm., weight: 8.8 kg QS 10/4 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10/3, but with stand for hanging and base. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 11.5 kg Detail QS 10/3, QS 10/10, QS 10/11 Hook for hanging Detail - Stand for hanging QS 10/4 QS 10/12 QS 10/13 QS 10/13GA QS 10/14 Rollers on the base of the stand (5 arms) The artificial skeletons are articulated standing or suspended, rigid or articulated, with muscular attachments, numbering, articular ligaments or muscle function, according to the customer s requirements. QS 10/7 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a female adult, in SOMSO-Plast. Life-like representation of bone structure with full anatomical detail. Skull with removable vault and mandible. Joints movable, upper and lower limbs removable. Both right and left foot can be detached from the leg. Mounted upright on stand. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 171 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 10.4 kg QS 10/8 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a female adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10/7, but with rollers on the base of the stand. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 171 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 10.7 kg QS 10/10 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a female adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10/7 but with hook for hanging on the skull (without stand). Height: 171 cm., width: 39 cm., depth: 28 cm., weight: 8.5 kg emale Skeleton QS 10/7 121
22 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models SOMSO ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETO SEVERAL VERSIONS QS 10/6 QS 10/9 QS 10/
23 NS AVAILABLE IN Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT QS 10/6 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10, but on the right side presentation of the articular ligaments on the knee, the hip, the elbow and on the shoulder. Demonstration of the natural movements true to exact anatomy. Mounted upright on stand with rollers. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 11.2 kg QS 10/9 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. Upper limbs including the shoulder girdle can be removed. The lower limbs can also be removed and moreover both right and left foot can be separated from the leg. The right side shows all the muscles from head to foot with their areas of origin and onset in colour (origin = red, onset = blue). On the left side the single bones are numbered (more than 500 numbers). Mounted upright on a stand. With rollers on the base of the stand. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 10.4 kg QS 10/6 + 9 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON* Natural cast of a male adult skeleton made of SOMSO-Plast. On the right side of the body the bones are numbered and the articular ligaments shown on the knee, hip, elbow and shoulder. Demonstration of natural movements anatomically accurate. The points of origin and attachment of the most important muscles from head to foot are marked in colour on the left side of the body (origin red, attachment blue). Erect on stand with rollers. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 11.2 kg QS 10/11 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10/9, but with hook for hanging on the skull (without stand). Height: 170 cm., width: 38 cm., depth: 28 cm., weight: 8.8 kg * The skeleton QS 10/6+9 is also available with wrist and ankle joint ligaments under the order no. QS 10/6+9 L. (or details see illustration of models NS 54 and NS 55 on page 103). The models QS 10/12 and QS 10/14 can be delivered with a new, improved stand which makes the complete model even more stable. QS 10/13 GA QS 10/13 GA ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON, EMALE Version as QS 10/13 but with extended stand and holding facility for the ala of the illium, movable thoracic cage and telescopic chest support, weight: 11 kg Detail QS 10/13 GA QS 10/12 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON (without ill.) Natural cast of the bones of a male adult. As QS 10, but with movable vertebral column and stand for hanging with rollers. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 170 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 11 kg QS 10/13 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON (without ill.) Natural cast of the bones of a female adult. As QS 10/7, but with movable vertebral column and stand for hanging with rollers. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 171 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 11 kg QS 10/14 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON (without ill.) Natural cast of the bones of a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 10, but with movable vertebral column and spinal cord with nerve endings and with stand for hanging with rollers. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 171 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 11.5 kg 123
24 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE 206 BONES O HUMAN SKELETO SOME ARTICULATED All the individual bones are also available to choice as left or right bones and can be ordered with the suffix R or L, e.g. QS 18-R scapula, right. QS 40/2 DISARTICULATED QS 17 (choose from C1 - L5) QS 17 C1- C7 HUMAN SKELETON Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO- Plast. With the exception of the skull (removable vault and mandible) all the bones are disarticulated. Stored in box in plastic bags. Height: 26 cm., width: 50 cm., depth: 31 cm., weight: 8.75 kg QS 40/70 QS 17/3 QS 19 QS 18 QS 19/2 QS 19/8 QS 19/9 QS 17 Th1- Th12 QS 41/2 DISARTICULATED HUMAN HAL- SKELETON QS 17/23 QS 19/3 QS 17 L1- L5 Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO- Plast. With the exception of the skull (with removable vault and mandible) all the bones are disarticulated. Stored in box in plastic bags. Height: 26 cm., width: 50 cm., depth: 31 cm., weight: 5.5 kg QS 16/3 QS 16/1 QS 17/22 QS 17/31 C2- C7 QS 71 THIGH WITH S/P - PROSTHESIS QS 16/4 QS 19/7 QS 19/20 QS 19/5 QS 17/31 Th1- Th12 About half natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Two models for demonstration showing the S/P - Prosthesis in the ML- and AP-area opened. Separates altogether into 4 parts. Height: 6 cm., width: 31 cm., depth: 18.5 cm., weight: 170 g QS 19/6 QS 17/31 L1-L5 QS 19/10 QS 19/1 QS 19/4 QS 41/2 QS 40/2 QS 17/31 (choose from C2 - L5 ) 124
25 N - SEPARATE OR WITH Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT QS 16/1 INNOMINATE Weight: 390 g QS 16/3 SACRUM Weight: 270 g QS 16/4 COCCYX Weight: 6 g QS 17 VERTEBRA Choose from cervical, thoracic or lumbar vertebra. Weight: cervical vertebra 20 g, thoracic vertebra 25 g, lumbar vertebra 60 g QS 17/3 HYOID BONE Weight: 4 g QS 17/22 RIB (COSTA) Alternatively rib. Weight: g. QS 40/3 BOX WITH COMPARTMENTS for QS 40/1, QS 40/2, QS 41/1 or QS 41/2. Height: 19 cm., width: 63 cm., depth: 41 cm., weight: 3.4 kg QS 17/23 STERNUM Weight: 220 g QS 17/31 DISC Choose from cervical, thoracic or lumbar disc. Weight: 2-17 g. QS 18 SCAPULA Weight: 110 g QS 19 CLAVICLE Weight: 40 g QS 19/1 EMUR Weight: 670 g QS 19/2 HUMERUS Weight: 270 g QS 19/3 ULNA AND RADIUS Weight: 160 g QS 19/4 TIBIA AND IBULA Weight: 460 g QS 19/5 TIBIA Weight: 390 g QS 19/6 IBULA Weight: 70 g QS 19/7 PATELLA Weight: 30 g QS 19/8 ULNA Weight: 80 g QS 19/9 RADIUS Weight: 80 g QS 19/10 BONES O OOT Weight: 320 g QS 19/20 BONES O HAND Weight: 110 g QS 40/70 SKULL WITH REMOVABLE VAULT AND MANDIBLE (Without suspension hole) 3 parts, weight: 800 g QS 41/1 QS 40/1 QS 40/1 UNMOUNTED HUMAN SKELETON Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. With the exception of the skull (with removable vault and mandible), and one hand and one foot all the bones are disarticulated. Stored in box in plastic bags. Height: 26 cm., width: 50 cm., depth: 31 cm., weight: 8.75 kg QS 41/1 UNMOUNTED HUMAN HAL-SKELETON Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. With the exception of the skull (with removable vault and mandible) the hand and foot all the bones are disarticulated. Stored in box in plastic bags. Height: 26 cm., width: 50 cm., depth: 31 cm., weight: 5.5 kg QS 10/12 T ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKELETON, TRANSPARENT Natural cast of the bonesof a male adult, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing life-size all the anatomical details of the bone structure. Skull with removable vault and mandible. Joints mounted and movable, upper and lower extremities removable. The right and left foot can be detached from the leg. Mounted upright on a stand. With movable vertebral column and stand for hanging with rollers. Height: 180 cm. (skeleton 171 cm.), width: 55 cm., depth: 55 cm., weight: 11 kg All the artificial extremities are available to choice in transparent version and can be ordered with the suffix T. 125
26 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE HUMAN SKELETAL SYSTEM. AN LEXIBLE OR PAINTED MODELS QS 42 COLLECTION O TYPICAL HUMAN BONES Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Consisting of skull (mounted), scapula, clavicle, humerus, forearm-bone, carpal bone, bones of the index, each three right and left ribs, one cervical, one thoracic, and one lumbar vertebra, one pelvic bone - coccyx, each one thigh and one leg bone, tarsal bone and bone of big toe. Stored in box in plastic bags. Height: 26 cm., width: 50 cm., depth: 31 cm., weight: 3.2 kg QS 14 SKELE- TON O THE ARM WITH SHOULDER GIRDLE Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO- Plast. Mounted and movable. Length: 88 cm., weight: 660 g QS 16 SKELETON O MALE PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Consisting of the two innominates, sacrum, coccyx, fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae with discs and symphysis. Mounted. Weight: 1.2 kg QS 26 SKELETON O EMALE PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Consisting of the two innominates, sacrum, coccyx, 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae with discs and symphysis. Mounted. Weight: 1.1 kg QS 13 SKELETON O THE LOWER EXTREMITY WITH INNOMINATE Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. Mounted and movable. Length: 100 cm., weight: 1.85 kg QS 27 SKELETON O EMALE PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. With head of femur and mounted on a stand with base. Height: 36 cm., width: 39 cm., depth: 26 cm., weight: 2.5 kg QS 27/1 SKELETON O EMALE PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 27 but without stand and base. Weight: 1.6 kg (without illustration) 126
27 EXTENSIVE RANGE O RIGID, Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT QS 17/1 IRST AND SECOND CERVICAL VERTEBRAE (Atlas and axis). Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Mounted and removable. Weight: 40 g QS 17/2 COLLECTION O VERTEBRAE Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Atlas, axis, cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae hanging loosely on a nylon thread. Weight: 140 g QS 54 CASE WITH COLLECTION "VERTEBRAE AND SPINAL CORD" Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast, consisting of: 1. lumbar vertebra, 2. thoracic vertebra, 3. cervical vertebra, 4. atlas, 5. axis, 6. cervical vertebra with spinal cord and nerve endings, with explanation, 7. intervertebral disc. The models are in a transparent box with compartments. Height: 7 cm., width: 32 cm., depth: 18.5 cm., weight: 800 g QS 17 VERTEBRA Choose from cervical, thoracic or lumbar vertebra. Weight: cervical vertebra 20 g, thoracic vertebra 25 g, lumbar vertebra 60 g QS 56 ATLAS AND AXIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Mounted on a stand so that the pivot of the head can be demonstrated. Height: 12 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 130 g QS 57 ATLAS, AXIS AND SQUA- MOUS PART O THE OCCIPITAL BONE Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO- Plast. The pivot of the head in connection with the skull-bone can be demonstrated. On a stand with base. Height: 15 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 17 cm., weight: 210 g 127
28 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE 26 BONES O THE OOT-ELEME RIGID OR LEXIBLE ARTICULATION QS 22 SKELETON O THE OOT (RIGID ARTICULATION) Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. With distal ends of tibia and fibula.rigid articulation. With numbering. Weight: 440 g QS 24 SKELETON O THE OOT (WIRE ARTICULATION) Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 22, but without distal ends of tibia and fibula. Rigid articulation. Weight: 320 g (without illustration) QS 23 SKELETON O THE OOT (ELASTIC ARTICULATION) Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. With distal ends of tibia and fibula. lexibly articulated to show the change in position of the bones with a spread or flat foot. With numbering. Weight: 440 QS 22/2 SKELETON O THE OOT, RIGHT (RIGID) Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. With distal ends of tibia and fibula, modelled true to nature, medial and lateral ray of the foot and the articular surfaces are shown in colour. Separates into 2 parts. Weight: 400 g QS 25 SKELETON O THE OOT (ELASTIC ARTICULATION) Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 23, but without distal ends of tibia and fibula. Weight: 320 g. (Without ill.). QS 22/1 SKELETON O THE OOT (RIGID) Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. With distal ends of tibia and fibula, modelled true to nature and in one piece. Weight: 400 g QS 22/4 SKELETON O THE OOT, RIGHT (MOVABLE JOINT MECHANISMS AND COLOUR) Life-size, made of SOMSO-Plast, with lower leg attachment. Demonstration model for foot movements. The individual bone elements are distinguished by colour to facilitate familiarization with the parts of the foot. In one piece. Weight: 400 g oot skeleton length QS 22 - QS 25 (Pternion-Acropodion): 25 cm. 128
29 NTS O LOCOMOTION - Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT QS 22/5 SKELETON O THE OOT, RIGHT (MOVABLE JOINTS) Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Model demonstrating the moving function of the foot. Showing the ankle joints, the tarsal bones, the metatarso-phalangeal joints and the toe joints. In one piece. Weight: 400 g QS 31/5 SKELETON O THE HAND (MOVABLE JOINTS) Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast, model demonstrating the hand's capability of movement. In one piece. Weight: 200 g With due consideration to the technical possibilities the artificial foot or hand skeletons are available to order assembled and articulated on nylon such as, for example, QS 22-N foot skeleton or QS 31-N hand skeleton both articulated on nylon. QS 24-N SKELETON O THE OOT (ARTICULATION ON NYLON) Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Without base of tibia. Weight: 320 g. QS 31/1 SKELETON O HAND WITH BASE O OREARM (WIRE ARTICULATION) Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO- Plast. Mounted. With numbering. Weight: 165 g QS 31/4 HAND SKELETON, RIGHT (MOVABLE JOINT MECHANISMS AND COLOUR) Life-size, made of SOMSO-Plast, distal ends of radius and ulna. Demonstration model for hand movements. The individual bone elements are distinguished by colour to facilitate familiarisation with the parts of the hand. In one piece. Weight: 200 g QS 31/7 HAND SKELETON WITH OREARM CONNECTION (LEXIBLE ARTICULATION) Natural casting. In SOMSO-Plast. lexibly articulated. With numbering. Weight: 165 g (without illustration). Hand skeleton length QS 31/1 - QS 31/7 (Stylion-Dactylion III): 19 cm. QS 31/2 SKELETON O HAND WITH BASE O OREARM (RIGID) Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast, modelled true to nature, in one piece. Weight: 200 g 129
30 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models SOMSO LEXIBLE SPINAL COLUMNS, WITH DURABLE UNCTIONAL TECHN All spinal columns, with the exception of the QS 21/2, can be supplied to order with skull, thoracic cage and femur stumps and can be supplied with the origins of muscles. Vertebral column dimensions C 1 70 cm Coccyx QS 20 VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS QS 15 VERTE- BRAL COLUMN Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. Consisting of occipital bone, cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae with sacrum and coccyx. Rigid articulation. Weight: 1.6 kg Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Consisting of occipital bone, cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum and coccyx and innominates. Rigid articulation. Weight: 2.6 kg QS 21 VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 20 but mounted and flexible. Designed for chiropractic demonstrations. Weight: 2.2 kg Demonstration of wrong position with SOMSOvertebral column 1. lat back 2. Hollow back 3. Round back QS 21/1 VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. Articulated and flexible, showing the arteria vertebralis, the spinal cord, the spinal nerves leaving it and the connected ganglion cells. Consisting of occipital bone, cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum and coccyx and innominates. Especially suitable for the demonstration of the curvature of healthy and pathological vertebral columns. Weight: 2.3 kg 130
31 COMBINE ACCURATE ANATOMY OLOGY Nature is our Model SEIT Somso Modelle QS 21/3 VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 21/1 but with stand for hanging. Weight: 3.6 kg With due consideration to the technical possibilities the artificial vertebral columns are available to order assembled and threaded on nylon such as, for example, QS 15-N vertebral column articulated on nylon. QS 21/2 VERTE- BRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 21/1, but the pelvis (axle of the femur joint) is articulated so that it is either flexible or fixed in the upright position. On a stand and base. Weight: 3.8 kg QS 21/5 VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. As QS 21/4 but with stand for hanging. Weight: 3.6 kg QS 15-N VERTEBRAL COLUMN (ARTICULATION ON NYLON) Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. As QS 15, but articulated on nylon. Weight: 1.2 kg QS 21/4 VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. Articulated and flexible, showing the arteria vertebralis, the spinal cord, the spinal nerves leaving it and the connected ganglion cells. With prolapse of the intervertebral disc and laminectomy. Weight: 2.3 kg 131
32 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE SPINAL COLUMN IN SECTIONS: DEMONSTRATE, UNCTIONAL AND I QS 62 CERVICAL VERTE- BRAL COLUMN Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Articulated and flexible with spinal cord and nerve endings. On a stand with base. Height: 16 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 290 g QS 65 CERVICAL VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Articulated and flexible, with occipital bone, spinal cord with spinal bulb and nerve endings. Presentation of the vertebral artery with laminectomy on C 4. Removable on a stand with base. Height: 22 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 21 cm., weight: 500 g QS 21/6 VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH PELVIS Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. Articulated and flexible, showing the arteria vertebralis, the spinal cord, the spinal nerves leaving it and the connected ganglion cells. Cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae are shown in colour. With stand for hanging. Weight: 3.6 kg QS 63 THORACIC VER- TEBRAL COLUMN Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Articulated and flexible with spinal cord and nerve endings. On a stand and base. Height: 37 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 750 g 132
33 EASY TO HANDLE AND NSTRUCTIVE Nature is our Model SEIT Somso Modelle QS 58 THREE DORSAL VERTE- BRAE WITH DISCS Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Articulated and separable, on a stand with base. Height: 13 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 180 g QS 66/1 LUMBAR VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. As QS 66, but showing the spondylolysthesis. On a stand with base. Height: 36 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 1.2 kg QS 66 LUMBAR VERTE- BRAL COLUMN Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. With spinal cord and nerve endings. Shows hernia of dorsolateral intervertebral disc (prolapse of the pulpous nucleus). On a stand and base. Height: 37 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 750 g QS 64 LUMBAR VERTE- BRAL COLUMN Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO- Plast. Articulated and flexible, with spinal cord and nerve endings. On a stand and base. Height: 32 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 18 cm., weight: 1 kg QS 59 THREE LUMBAR VERTEBRAE WITH DISCS Cast from natural specimen, in SOM- SO-Plast. Articulated and separable, on a stand with base. Height: 14 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 14 cm., weight: 330 g 133
34 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models SOMSO MODELS O THE NERVES AND SCIENTIICALLY ACCURATE AND PRA QS 65/6 ARTIICIAL BASE O SKULL WITH ARTERIES Natural casting in SOMSO-Plast, consisting of base of skull, mandible and cervical vertebrae with nerves. Representation of cervical arteries with internal passage through the base of skull with emphasis on basilar artery with complete circle of Willisi. In one piece. Movable on stand with base. Height: 26 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 21 cm., weight: 1.2 kg QS 65/5 CERVICAL VERTEBRAL COLUMN WITH SHOULDER GIRDLE Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Showing the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus. On a stand with base. Height: 57 cm., width: 39 cm., depth: 30 cm., weight: 2.3 kg QS 66/3 MODEL O THE LUMBAR SPINAL COLUMN - WITHOUT INNERVATION Natural cast, in SOMSO-Plast after Prof. Dr. med. H. R. Henche of Rheinfelden. Presentation of the degenerative mutation on the pelvic bones and the lumbar spinal column compared to the most important disorders thereof. Can be dismantled in two sections. Supplied on a stand with base. Height: 39 cm., width: 22 cm., depth: 19 cm., weight: 1.35 kg 134
35 BLOOD VESSELS - AUTHENTIC, CTICAL Nature is our Model SEIT Somso Modelle QS 65/7 NEUROANATOMY HEAD MODEL Natural cast, made of SOMSO-Plast. The model is made of a Transparent Human Skull with Cervical Vertebral Column and the model of Brain separates into 8 parts with Indicated Cyto-architectural areas. Showing the cranial nerves and the arterial network of vessels. Separates altogether into 10 parts. On stand with base. Height: 29 cm., width: 18 cm., depth: 21 cm., weight. 2.2 kg 135
36 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models PATIENT EDUCATION WITH SOMSO QS 66/2 LUMBAR SPINAL COLUMN - WITH INNERVATION Natural cast in SOMSO-Plast after Prof. Dr. med. H. R. Henche of Rheinfelden. Presentation of the degenerative mutation on the pelvic bones and the lumbar spinal column compared to the most important disorders thereof. Representation of the innervation. Can be dismantled in two sections. Supplied on a stand with base. Height: 37 cm, width: 22 cm, depth: 19 cm, weight: 1.46 kg The anatomy of the lumbar spinal column The new SOMSO models of the lumbar spinal column QS 66/2 and QS 66/3 are lifelike, scientifically exact and practice-orientated. The lumbar part of the cord, epidural cavity, all of the nerve roots, the plexus lumbalis, plexus sacralis, plexus coccygeus and the sympathetic trunk ganglia are shown on a lifelike replica. Comparison of the most important disorders: Vertebral compression fracture Tumorous mutations Vertebral metastases Spondylosis and spondylarthrosis Morbus Baastrup Slipped disc Spondylarthritic osteophytes QS 66/4 OSTEOPOROSIS MODEL Natural cast made of SOMSO-Plast according to Prof. Dr. med. H. R. Henche of Rheinfelden. Comparison of an osteoporotic and a healthy lumbar vertebra. The vertebral bodies are divided frontally and can be opened by a hinged joint. Altogether 4 pieces. On base. Height: 8 cm., width: 21 cm., depth: 15 cm., weight: 0.26 kg 136
37 DISC MODELS Nature is our Model Somso Modelle SEIT QS 68/1 IRST LUMBAR VER- TEBRA WITH INTERVERTEBRAL DISCS AND DORSAL MUSCLES Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. The spinal cord with spinal nerves as well as the central and dorsolateral hernia of intervertebral disc (prolapse of the intervertebral disc) are shown. In one piece. Removable on a stand with base. Height: 16 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 230 g QS 68/3 CENTRAL AND DORSOLATERAL HERNIA O INTER- VERTEBRAL DISC Natural size, in SOM- SO-Plast. 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae with lumbar region of spinal cord and with the following changeable discs 1st normal, 2nd medial protrusion and 3rd lateral prolapse. Separates altogether into 5 parts. On a base. Height: 13 cm., width: 14 cm., depth: 15 cm., weight: 300 g QS 67 HERNIA O DORSOLATERAL INTERVERTEBRAL DISC Cast from natural specimen, in SOMSO-Plast. Prolapse of the pulpous nucleus on the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebra, compression of the nerve roots towards the wall of the intervertebral foramen, 4th lumbar vertebra and disc removable. Altogether 4 parts. On a stand with base. Height: 12 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 270 g QS 68 HERNIA O CENTRAL INTERVERTEBRAL DISC Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Prolapse of the pulpous nucleus, prolapse of the intervertebral disc on the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebra, compression of the dural sack with cauda equina caused by the hernia. 4th lumbar vertebra and disc removable. Altogether 4 parts. On a stand with base. Height: 12 cm., width: 12 cm., depth: 12 cm., weight: 270 g QS 68/8 MODEL O HERNIA O INTERVERTEBRAL DISC According to Dr. Lie. Natural size, in SOMOS-Plast. Presentation of normal anatomy in conjunction with pathological changes: I. Normal anatomy II. Anulus fibrosus according to Rumpert III. Medio-lateral nuclear prolapse IV. Medial prolapse, V. Spinal stenosis VI. L-4 vertebral spondylolysis Separates altogether into 10 parts. Height: 13 cm., width: 14 cm., 15 cm., weight: 500 g 137
38 ANATOMY 16 Artificial Bone Models THE MOST IMPORTANT MOVEMENTS AND ROTATING UNDERSTANDABLE QS 55/3 DEMONSTRATION MODEL O THE ARM MUSCLES Natural size, in SOMSO-Plast. Can be separated into 10 parts. The most important arm muscles can be assigned to their insertion and origin either individually or collectively. The muscle groups responsible for the bending and stretching movements and pronation and supination can be demonstrated. On a stand with a base. Height: 81 cm., width: 38 cm., depth: 38 cm., weight: 4.4 kg QS 55/3 is detachable as follows: M. biceps brachii M. triceps brachii M. brachialis M. brachioradialis M. supinator M. pronator teres M. pronator quadratus 138
39 O THE ARM - LEXING, EXTENDING THANKS TO SOMSO MODELS Nature is our Model SEIT Somso Modelle QS 61 CONSTRUCTION O BONE Enlarged many times in SOMSO-Plast. Shown in a wedge segment from the compact part of a pipe bone. Shows Haversian lamellae, outer bone- and interstitial lamellae etx. In one piece. On a base. Height: 28 cm., width: 39 cm., depth: 26 cm., weight: 2.82 kg QS 55 MOVEMENTS O MUSCLES IN THE UPPER ARM Natural size, in SOMSO- Plast. The muscles of the upper arm are of an elastic material. By bending and stretching the arm the flexion and extension of the muscles can be shown. Weight: 740 g QS 55/2 MOVEMENT O MUSCLES IN THE UPPER ARM AND OREARM Natural size, in SOMSO- Plast. Showing the bending and stretching muscles of the upper arm and the rotator muscles of the forearm. By bending and stretching the arm, the flexion and extension as well as the movements around the rotary axis, the pronator and supinator muscles can be demonstrated. On a stand and base. Height: 83 cm., width: 45 cm., depth: 26 cm., weight: 2 kg QS 55/5 MODEL O THE ARM MUSCLES Natural size, in SOM- SO-Plast. Can be separated into 24 parts. All muscles can be traced to their point of attachment (blue) and their origin (red) both singly and in relation to each other. On stand with base. Height: 81 cm., width: 38 cm., depth: 38 cm., weight: 5.1 kg The demonstration model of the arm muscles is especially suitable for showing the location of the muscles in relation to each other, their points of origin and attachment to the bones and the shape of each muscle. 139
40 THE NEW MODELS: QS 7/7, QS 7/8-E, QS 7/9-E, QS 8/6 QS 7/7 ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL As QS 7, but without teeth (skull of an old man). Weight: 800 g illustration of the alx cerebri with a skull modell QS 8/6 ALX CEREBRI The 14 or 18 piece skull model can also be supplied with a transparent plastic falx cereberi with tentorium cerebelli. Marked on the falx cerebri is the position of the sinuses of the dura mater (Sinus durae matris) as well as of the Pacchioni granulations on the sinus sagittalis superior. The pathways of the venous blood and the cerebrospinal fluid can be clearly regognized. rontally the falx cerebri is fastened to the crista galli and superior at the parietal bone; the tentorium can be supported laterally by the pyramidal crest and anterior in the region of the sella turcica. However, it can be completely removed easily so that not only the structure of the dura duplications but also the position of the sinus (blue) of the dura mater can be clearly seen. Weight: 66 g QS 7/8-E ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Modeled according to nature, in SOM- SO-Plast. After removing the cranium, the base of the skull, sectioned through median line into two halves where the nasal septum (can be opened), the paranasal sinuses and turbinate bones are (partly) shown. The lower jaw is movable. Separates into 5 parts. Length: 17.5 cm., width: 14.1 cm., size: 51.2 cm., weight: 800 g QS 7/8-E total dissected QS 7/9-E partial dissected QS 7/9-E ARTIICIAL HUMAN SKULL Modeled according to nature, in SOM- SO-Plast. After removing the cranium, the base of the skull, sectioned through median line into two halves where the nasal septum (can be opened), the paranasal sinuses and turbinate bones are (partly) shown. The lower jaw is movable. The upper with the middle and the lower paranasal sinuses can be taken off. Separates into 9 parts. Length: 17.5 cm., width: 14.1 cm., size: 51.2 cm., weight: 800 g Special brochure A 79/4, Copyright by Marcus Sommer SOMSO MODELLE, April 2004 With the Compliments of:
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
BONE BINGO. Blood Production Red and white blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, a substance found inside the larger bones of the body.
 BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
Observing Vertebrate Skeletons
 Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES
 HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES 0003 0008 0005 0008 0009 0019 0001 0000 0000 0001 0003 0005 0008 0009 0019 MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK*
HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES 0003 0008 0005 0008 0009 0019 0001 0000 0000 0001 0003 0005 0008 0009 0019 MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK*
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND
 SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller [email protected] Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller [email protected] Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Structure and Function of the Hip
 Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine. head neck greater trochanter intertrochanteric line lesser trochanter
 Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
POLICY 2: DEATH AND PERMANENT DISABILITY
 POLICY 2: DEATH AND PERMANENT DISABILITY Article 1 - Death (as a result from any cause) 1.1. - Amount of indemnity The capital sum payable on the death of an Insured Person, shall be: 1. 25.000 USD in
POLICY 2: DEATH AND PERMANENT DISABILITY Article 1 - Death (as a result from any cause) 1.1. - Amount of indemnity The capital sum payable on the death of an Insured Person, shall be: 1. 25.000 USD in
The Muscular System. Appendicular Musculature
 11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation:
 EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Appendix A Partial Pick List of Injury and Sequelae Codes (ICD-10-CA)
 What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
Lower Extremities. Posterior Compartment of Thighs Knee Flexors
 Lower Extremities Lower extremities are adjusted to provide locomotion but, at the same time, carry the full body weight. The lower limb movement is transferred through the hip joint and pelvis onto the
Lower Extremities Lower extremities are adjusted to provide locomotion but, at the same time, carry the full body weight. The lower limb movement is transferred through the hip joint and pelvis onto the
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
www.roylco.com EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton
 EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY www.roylco.com Canada: 30 Northland Road, Waterloo, Ontario, N2V 1Y1 USA: PO Box 13409 Anderson, SC 29624 No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton Teach students about human bone structure
EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY www.roylco.com Canada: 30 Northland Road, Waterloo, Ontario, N2V 1Y1 USA: PO Box 13409 Anderson, SC 29624 No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton Teach students about human bone structure
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education. Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh
 Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Elbow & Forearm. Notes. Notes. Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics. Bones & Joints: Elbow & Forearm
 Elbow & Forearm Elbow & Forearm Notes Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics Notes Bones & Joints: The elbow joint is a combination of joints but common reference is usually to the articulation of the distal
Elbow & Forearm Elbow & Forearm Notes Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics Notes Bones & Joints: The elbow joint is a combination of joints but common reference is usually to the articulation of the distal
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
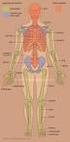 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Mobility and Exercise for Health and Social Care
 Unit 32: Mobility and Exercise for Health and Social Care Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose R/600/8987 BTEC National This unit aims to enable learners to
Unit 32: Mobility and Exercise for Health and Social Care Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose R/600/8987 BTEC National This unit aims to enable learners to
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
For better understanding human anatomy...
 Ruediger-Anatomy 1) Skeleton Models manufactured in Germany Ruediger-Anatomie is a traditionally family business from Germany with 20 employees. It was founded more than 40 years ago. We produce skeleton
Ruediger-Anatomy 1) Skeleton Models manufactured in Germany Ruediger-Anatomie is a traditionally family business from Germany with 20 employees. It was founded more than 40 years ago. We produce skeleton
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Anthropology 209: Forensic Anthropology Fall 2012
 Anthropology 209: Forensic Anthropology Fall 2012 Instructor: Adam Van Arsdale Lecture: PNW 117, Tu/Fr 9:50-11:00 Lab: SC 314, W 10:00-12:00 (1 hour) Office: PNE 348 Office Hours: Tuesday: 11-12, Friday:
Anthropology 209: Forensic Anthropology Fall 2012 Instructor: Adam Van Arsdale Lecture: PNW 117, Tu/Fr 9:50-11:00 Lab: SC 314, W 10:00-12:00 (1 hour) Office: PNE 348 Office Hours: Tuesday: 11-12, Friday:
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine James McCrossin MS ATC, CSCS Philadelphia Flyers April 23 rd, 2015
 American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine James McCrossin MS ATC, CSCS Philadelphia Flyers April 23 rd, 2015 Coming together is a beginning; keeping together is progress; working together is success.
American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine James McCrossin MS ATC, CSCS Philadelphia Flyers April 23 rd, 2015 Coming together is a beginning; keeping together is progress; working together is success.
The Search for the Missing Bones
 The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
