THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
|
|
|
- Timothy Watkins
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic animations and illustrations, microscopic imaging, expert commentary, and footage of the body in motion to provide a thorough overview of the amazing human machine. The series includes: Cells, Tissues, and Skin The Immune System Human Development and the Reproductive System The Respiratory System The Circulatory System The Skeletal and Muscular Systems Digestion and Nutrition The Endocrine System The Nervous System and the Senses Topics Chapter 1: Movers and Shakers The program begins with an overview of the skeletal and muscular systems, listing five basic functions of the bones and five of the muscles. Also covered: The differences between an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton; and between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Chapter 2: Bones and the Skeleton This section outlines the four classifications of bones: long, short, flat, and irregular. The terms axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton are introduced. Copyright
2 Chapter 3: The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton is now described in detail: the skull (and its parts), and the main sections of the vertebral column cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, and coccyx. Also covered: True, false, and floating ribs; fused and unfused vertebrae. Chapter 4: The Appendicular Skeleton The four segments of the appendicular skeleton are reviewed in this section. Clearly labeled animations depict the bones of the pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, and upper and lower limbs. Also covered: flat feet, or fallen arches. Chapter 5: Joints and Soft Tissues This section spells out the different ways in which fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial, and bony joints attach bones to one another. Shots of athletes and weight lifters illustrate a discussion of the six types of synovial joint. Chapter 6: Skeletal Muscles Here viewers learn the five categories of skeletal muscle, and how agonist, antagonist, and synergist muscles work together to provide movement. The point is made that muscles do more than heavy lifting they are also responsible for a variety of processes including facial expressions and speech. Also covered: Ligaments and tendons; fixators, flexors, and extensors. Chapter 7: Bone Composition and Repair Now the narrator gives an in-depth description of the complex structure of bones, reminding viewers that bones are living tissue. Along with a discussion of the blood vessels, nerves, and cavities, animations portray the various bone membranes and their function. The four types of bone cell, and how they work together when bone repair is necessary, are also explored. Chapter 8: Muscle Cells and Tissues We now know that muscles work by contracting here we learn exactly how sarcomeres within muscle fiber cause them to contract. Animations illustrate the detailed anatomy of a muscle cell, getting all the way down to the molecular level with a discussion of myofilaments, myosin, and actin. Also covered: The types of connective tissue within the muscle; the role of somatic motor neurons and ATP in muscle movement. Copyright
3 Learning Objectives Students will learn Five basic functions of the body s 206 bones Five basic functions of the muscles, including the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles The four categories of bones and the five categories of skeletal muscles The parts of the axial skeleton, including the different types of ribs The four segments of the appendicular skeleton, including the names of the bones in each segment The four categories of joints based on their mode of attachment, and the six subcategories of synovial joints The difference between muscles, tendons, and ligaments The movements of agonist, antagonist, and synergist muscles The structure of the bone, including its four types of cells, and how they repair damaged bone The structure of the muscle, including its cells and connective tissues The molecular actions that occur within muscles, causing them to move Vocabulary ATP: Adenosine triphosphate, a molecule that stores and transfers energy used by the cells. actin: A protein found in the cells, its myofilaments act with myosin heads to cause muscles to move. agonist muscles: Muscles that exerts the majority of force, aided by synergist muscles. antagonist muscles: Muscles that pull in the opposite direction of agonist muscles. appendicular skeleton: The part of the skeleton that includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs, the pectoral girdle, and the pelvic girdle. It is attached to the axial skeleton, and protects the digestive and reproductive organs. axial skeleton: The part of the skeleton that includes the skull, the bones of the inner ear, the hyoid bone of the throat, the spinal column, and the bony thorax. ball and socket joint: A type of synovial joint that allows for movement in many directions (e.g., the joining of arms to shoulders and legs to hips). Copyright
4 bony joint: The joint between bones that have fused together naturally (e.g., in the sacrum and coccyx). bony thorax: Also called the rib cage or thoracic cage, it consists of the sternum, ribs, and the twelve thoracic vertebrae. carpal bones: The eight bones of the wrist. cartilaginous joint: A joint held together by cartilage (e.g., the joint between the first rib and the sternum). This type of joint is more movable than a fibrous joint, but less movable than a synovial joint. cervical vertebrae: The top seven bones of the spinal column, these are the smallest, weakest, and lightest. circular muscle: Also known as a sphincter muscle, it is a muscle that forms a ring around various body openings, such as the lips and eyelids. clavicle: Collarbone. coccyx: Also called the tailbone, it is made up of four fused vertebrae. The coccyx is part of the pelvic girdle. condyloid joint: Also called an ellipsoid joint, a type of synovial joint that allows bones to move in two directions, such as the wrist joint. convergent muscle: A muscle that is shaped like a fan, such as the muscle of the upper front chest (commonly called pecs ). costal cartilage: The elastic material connecting the sternum with the ends of the ribs. endoskeleton: A skeleton inside the body of larger organisms such as humans. endosteum: The membrane lining the inner surface of bones. epimysium: The sheath of connective tissue that surrounds and holds muscles together. exoskeleton: A rigid layer that insects and crustaceans have on the outside of their bodies to provide strength and allow for movement. Copyright
5 extensor muscles: Muscles that allow for extending or stretching a body part. false ribs: The five ribs beneath the true ribs; the first three false ribs connect to the cartilage of the rib above it instead of to the sternum; the bottom two false ribs are called floating ribs. fascicles: Bundles of muscle fibers within a muscle. The individual muscle fibers within the fascicles are surrounded by a connective tissue called endomysium; the fascicles are surrounded by the perimysium; groups of fascicles are surrounded by the epimysium. femur: The bone in the leg extending from the pelvis to the knee. fibrous joint: A joint held together by the collagen fibers of ligaments. Fibrous joints are immovable (e.g., the sutures between the bones of the skull). fibula: The smaller of the two bones extending from the knee to the ankle. fixator muscles: Muscles that prevent the bone from moving in an unwanted direction. flexor muscles: Muscles controlling the movement of joints by bending. floating ribs: The two bottom-most ribs. The back of these ribs attach to the spine, and not to the sternum or cartilage as the other ribs do. fusiform muscle: A muscle that is thicker in the middle and tapered on both ends, such as the biceps. gliding joint: A type of synovial joint that allows bones to move in only one direction by sliding past each other. hinge joint: A type of synovial joint that allows bones to move in only one direction, such as knuckles and elbows. humerus: The single long bone of the upper arm. involuntary muscles: Muscles that control our vital functions automatically, such as those involved with breathing and digestion. irregular bones: Bones, such as the vertebrae and hip bones, that don t fit into the other three categories of bones. Copyright
6 joint: The place where two bones connect. Joints of the human body are classified by how much freedom of movement they permit, and/or by their mode of attachment (fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial). ligament: A band of tissue that connects bones to other bones. lumbar vertebrae: The five sturdy bones of the lower part of the spinal column, they carry most of the weight of the upper body. mandible: Also called the jawbone, it is the part of the skull that holds the lower teeth. maxilla: Also known as the upper jaw bone, it is the part of the skull that holds the upper teeth. medullary cavity: A large cavity in the center of bones; the medullary cavity contains the bone marrow. metacarpals: The five bones of the palm. metatarsals: The bones of the feet. muscle: A tissue that produces movement in the body through contraction. myofilaments: Threadlike filaments of proteins within the muscles. A combination of thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments make up sarcomeres, responsible for muscle contraction. myosin: A protein found in the cells, it plays a key role in causing muscles to move. myosin head: The head of a myosin molecule, it works with actin myofilaments to cause muscular movement. osteoblast: A type of cell from which bone is formed. osteoclast: One of the four types of cells that make up bones, it removes excess bone during bone repair. osteocyte: One of the four types of cells that make up bones. When a bone breaks, osteocytes communicate this to other bone cells so that repair can begin. osteogenic cell: A stem cell that is one of the four types of cells that make up bones. Copyright
7 osteogenic layer: The layer of bone membrane that forms new bone cells. parallel muscle: A muscle that tends to be equally wide throughout its length, such as a thigh muscle. patella: Also called the kneecap, it is the bone that protects the knee joint. pectoral girdle: In humans, the clavicle and scapula. It connects the arms to the axial skeleton. pelvic girdle: Also called the pelvis, it consists of the bones that cradle the internal organs (the ilium, ischium, pubis, coccyx, and sacrum). The pelvic girdle connects the lower appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton. pennate muscle: A muscle shaped like a feather, such as a calf muscle. periosteum: The membrane lining the outer surface of bones. phalanges: Any of the fourteen bones of the thumb and fingers, or of the fourteen bones of the toes. pivot joint: A type of synovial joint that allows for movement in many directions, such as the head rotating on the neck. pubis: The front part of the hip bones. The pubis is part of the pelvic girdle. radius: One of the two bones in the forearm. sacrum: The lowest section of the spine, it is made up of five fused vertebrae and is the point of attachment for the hips and the pelvis. The sacrum is part of the pelvic girdle. saddle joint: A type of synovial joint that allows bones to move in two directions, such as the joints between the thumbs and metacarpals. sarcomeres: Bundles of myofilaments within muscle cells that cause muscles to contract, thus causing the muscles to move. scapula: Also called a shoulder blade, it is either of two flat bones forming the back of the shoulder. soft tissue: A type of tissue that surrounds, supports, and connects structures and organs. Muscles, tendons, and ligaments are examples of soft tissue. Copyright
8 spinal cord: The bundle of nerve tissue extending from the brain stem through the spinal column. sternum: Also called the breastbone, it it the part of the skeleton that protects the heart and lungs. sutures: The lines that form the meeting point of the plate-like bones of the cranium. synergist muscle: A muscle that aids the agonist muscle in movement. synovial joint: Joints connected via a fluid-filled sac-like pad (e.g., knee joints). Synovial joints are more movable than fibrous or cartilaginous joints, and are the most common type in the human body. Synovial joints are classified by their structure: pivot, ball and socket, hinge, gliding, saddle, or condyloid. tarsal bones: The bones of the ankle. tendon: A fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones. thoracic vertebrae: The group of twelve bones in the spinal column to which the ribs are attached. thorax: Also called the chest, in humans it is the region between the neck and the diaphragm. tibia: Also called the shin bone, it is the larger of the two bones extending from the knee to the ankle. true ribs: The first seven ribs on each side that attach directly to the sternum through costal cartilage. ulna: One of the bones in the forearm. vertebra (plural is vertebrae or vertebras): Any of the bones or cartilaginous segments of the spinal column. vertebral column: Also called the backbone, spinal column, or spine, it consists of 33 vertebrae that surround and protect the spinal cord and support the head and the body. The vertebrae are classified as cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. voluntary muscles: Muscles that we can consciously control, such as those of the arms and legs. Copyright
9 Student Projects Starting with a depiction of the human skeleton, label each bone, and identify which are classified as long, short, flat, and irregular. Include whether the bone belongs to the axial or the appendicular skeleton. [This can be done as individual student assignments, or as a class. Another way to do this as a class is to print out a list of the major bones, then challenge students to correctly label a skeleton.] Do the activity above, substituting the muscular system for the skeletal system. Shooting hoops, fixing a snack, using a cell phone what parts of the skeletal and muscular systems are involved in these activities? Pick an activity, then list as many bones, muscles, and joints as you can think of that are involved. (Don t forget eyeblinks, laughing, how your legs and feet are positioned when sitting in a chair, etc.) Sections 7 and 8 of the program provided detailed information about the structure of bones and of muscle cells. Review one of these chapters, then illustrate how the bones cells team up to repair a break OR how molecules within muscles are responsible for movement. Work in any media you choose, from straight written report, to soap opera melodrama, visual art, or flash animation. Playing the investigative journalist, choose one of the following headlines (or write one of your own) as the start of a hard-hitting, fact-filled news report to present to the class. Functional Fitness vs Weight Training: Which Should You Choose? Soft Drinks Will Dissolve Your Bones! Warns Mom Biomechatronics: Exploring the Latest in Prosthetic Limbs Joint Pain Remedies: What Works and What Doesn t Fact or fiction? Using the library and Internet, find the answers to the following questions. Then, write a brief report that also incorporates what you ve learned in the film (such as the names of joints and muscles). Present the questions as a quiz to the rest of the class. Does it really take more muscles to frown than to smile? What causes the popping sound when cracking your knuckles? Does stretching before exercise help prevent injury? Is No pain, no gain a good rule of thumb for fitness training? What is osteoporosis, and who is at risk for it? Are calcium supplements and/or antacids the best way to avoid this disease? To avoid bone breakage? Can older bones actually be strengthened, or can this be done only when young? Report to the class on this, citing actual statistics whenever possible. Copyright
10 Quiz 1. Among other important functions, the bones also. a) create blood cells b) aid in human communication c) both a and b d) none of the above 2. Besides allowing us to move, the muscles. a) aid in balance b) generate heat to maintain body temperate c) both a and b d) none of the above 3. The 206 bones of the human body are classified into the following groups:. a) long, short, flat, and irregular b) long, short, and mid-sized c) rounded and flat d) axial and coaxial 4. The axial skeleton is connected to the appendicular skeleton via the. a) pectoral girdle and pelvic girdle b) pectoral girdle c) pelvic girdle d) nerves of the spinal cord 5. The ribs are part of the. a) cervical vertebrae b) thoracic vertebrae c) appendicular skeleton d) axial skeleton Copyright
11 6. The bones of the arms and legs are part of the. a) axial skeleton b) appendicular skeleton c) metacarpals d) metatarsals 7. The phalanges are bones of the. a) fingers b) toes c) neither of these d) both a and b 8. True or False? The joints of the pectoral girdle are rigid, preventing movement in an unwanted direction. 9. Joints are classified into four major categories: cartilaginous, bony, synovial, or. a) costal b) fibrous c) condyloid d) irregular 10. The is an example of a synovial joint. a) suture of the skull b) knee c) rib-to-sternum connection d) fused vertebrae of the sacrum 11. A muscle is a tissue that produces movement in the body, while a is a fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones. a) fusiform b) hinge joint c) ligament d) tendon i Copyright
12 12. Muscles that aid the movement of the agonist are called muscles. a) antagonist b) voluntary c) flexor d) synergist 13. When a bone breaks,. a) the cells at the edge of the broken pieces die off, forming scar tissue b) new bone tissue is generated, completing repair within 4 to 6 weeks c) blood leaks into the area and a repair team of cells comes in to fix the damage d) a potentially dangerous hematoma may form 14. The is the hollow center of the bone that contains the marrow. a) medullary cavity b) Haversian canal c) endoskeleton d) maxillary cavity 15. A muscle fascicle is a. a) bundle of myofilaments b) bundle of muscle fibers c) type of connective tissue d) muscle cell 16. Which of the following is a part of how muscles contract? a) The elastic myofilaments pull on Z disks, prompting the motor neurons to signal the muscles to contract. b) The actin myofilaments absorb the myosin heads, causing the sarcomere to shorten. c) Motor neurons trigger a chain of events that causes an interactive ratcheting process between the sarcomeres heads and the myosin myofilaments, causing the actin filaments to shorten. d) Motor neurons trigger a chain of events that causes an interactive ratcheting process between myosin molecules heads and actin myofilaments, causing the sarcomere to shorten. i Copyright
13 Answers to Quiz 1. c) both a and b 2. c) both a and b 3. a) long, short, flat, and irregular 4. a) pectoral girdle and pelvic girdle 5. d) axial skeleton 6. b) appendicular skeleton 7. d) both a and b 8. False. These joints are loose, allowing arms and shoulders a wide range of motion. 9. b) fibrous 10. b) knee 11. d) tendon 12. d) synergist 13. c) blood leaks into the area and a repair team of cells comes in to fix the damage 14. a) medullary cavity 15. b) bundle of muscle fibers 16. d) Motor neurons trigger a chain of events, fueled by ATP, that causes an interactive ratcheting process between myosin molecules heads and actin myofilaments, causing the sarcomere to shorten. Please send comments, questions, and feedback to [email protected]. i Copyright
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Observing Vertebrate Skeletons
 Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
The Search for the Missing Bones
 The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Brunswick School Department: Grades 11-12. Essential Understandings
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
BONE BINGO. Blood Production Red and white blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, a substance found inside the larger bones of the body.
 BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND
 SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
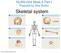 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller [email protected] Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller [email protected] Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510
 Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Mobility and Exercise for Health and Social Care
 Unit 32: Mobility and Exercise for Health and Social Care Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose R/600/8987 BTEC National This unit aims to enable learners to
Unit 32: Mobility and Exercise for Health and Social Care Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose R/600/8987 BTEC National This unit aims to enable learners to
II. Third Grade, Human Body 2004 Colorado Summer Writing Institute 1
 HUMAN BODY Grade Level or Special Area: Third Grade Written by: Vicki Menefee, Louisville Elementary School, Louisville, CO Length of Unit: Seven lessons (seven days, one day = 45 minutes) not including
HUMAN BODY Grade Level or Special Area: Third Grade Written by: Vicki Menefee, Louisville Elementary School, Louisville, CO Length of Unit: Seven lessons (seven days, one day = 45 minutes) not including
COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES
 CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
SHOULDER PULL DOWNS. To learn efficient use of the shoulder blades and arms while maintaining a neutral spine position.
 SHOULDER INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your shoulder exercise program The exercises in the program are designed to improve your shoulder mobility, posture and the control of the muscles in your neck and shoulder
SHOULDER INTRODUCT ION Welcome to your shoulder exercise program The exercises in the program are designed to improve your shoulder mobility, posture and the control of the muscles in your neck and shoulder
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education. Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh
 Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
Systems of the Human Body
 . s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
. s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques
 Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
MELT Mini Map For Motorcyclists
 MELT Mini Map For Motorcyclists The MELT Self-Treatment Tools needed for this monthʼs Mini Map can be found online at store.meltmethod.com. Depending on which tools you have on hand, you can start with
MELT Mini Map For Motorcyclists The MELT Self-Treatment Tools needed for this monthʼs Mini Map can be found online at store.meltmethod.com. Depending on which tools you have on hand, you can start with
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
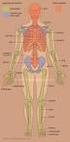 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES
 RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
S.M.A.R.T.box. Skeletal System The Infrastructure Teacher s Guide CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP. Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers
 CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Skeletal System The Infrastructure Teacher s Guide 33118 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher s
CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Skeletal System The Infrastructure Teacher s Guide 33118 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher s
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Locating Common Bones*
 4H1656 4ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ACTIVITY Locating Common Bones* Skill Level: 4Beginner to advanced Life Skills: 4Communication, critical thinking, decision-making and teamwork Setting: 4Room with chairs arranged
4H1656 4ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ACTIVITY Locating Common Bones* Skill Level: 4Beginner to advanced Life Skills: 4Communication, critical thinking, decision-making and teamwork Setting: 4Room with chairs arranged
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
How To Stretch Your Body
 Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
ANSWER KEY. Bones, Muscles, and Skin
 Bones, Muscles, and Skin Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. It must be able to grasp, lift, and release; it must be activated by a pulled cord or string; it must spring back when the cord is released. 2. The
Bones, Muscles, and Skin Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. It must be able to grasp, lift, and release; it must be activated by a pulled cord or string; it must spring back when the cord is released. 2. The
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
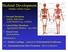 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation:
 EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
EHFA Assessment Strategy (EAD 03) Name of Training Organisation: Introduction European Health and Fitness Association (EHFA) Standards The following EHFA standards are currently available: Fitness Instructor
www.roylco.com EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton
 EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY www.roylco.com Canada: 30 Northland Road, Waterloo, Ontario, N2V 1Y1 USA: PO Box 13409 Anderson, SC 29624 No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton Teach students about human bone structure
EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY www.roylco.com Canada: 30 Northland Road, Waterloo, Ontario, N2V 1Y1 USA: PO Box 13409 Anderson, SC 29624 No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton Teach students about human bone structure
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
stretches and exercises
 stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
HealthStream Regulatory Script
 HealthStream Regulatory Script Back Safety Version: May 2007 Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Back Injury Lesson 3: Spinal Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 4: Safe Operation of the Spine Lesson 5: Preventive
HealthStream Regulatory Script Back Safety Version: May 2007 Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Back Injury Lesson 3: Spinal Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 4: Safe Operation of the Spine Lesson 5: Preventive
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
by Ellen Saltonstall and Dr. Loren Fishman
 10 Yoga Poses for Low Back Pain Prevention by Ellen Saltonstall and Dr. Loren Fishman Introduction This series of poses is designed to prevent future back pain and also to relieve back pain that you may
10 Yoga Poses for Low Back Pain Prevention by Ellen Saltonstall and Dr. Loren Fishman Introduction This series of poses is designed to prevent future back pain and also to relieve back pain that you may
