AP Biology TEST #4 - Chapters 09, 10, REVIEW SHEET
|
|
|
- Isabel Holland
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NAME: AP Biology TEST #4 - Chapters 09, 10, REVIEW SHEET 1. Which of the following is true of mitosis? A) The chromosome number in the resulting cells is halved. B) DNA replication is completed prior to the beginning of this phase. C) The chromosome number of the resulting cells is the same as that of the parent cell. D) Both b and c 2. Which of the following is true of meiosis? A) The chromosome number in the resulting cells is halved. B) DNA replication occurs before meiosis I and meiosis II. C) The homologs do not pair during prophase I. D) The chromosome number of the resulting cells is the same as that of the parent cell. 3. Which of the following is true of kinetochores on mitotic chromosomes? A) They are located at the centromere of each chromosome. B) They are the sites where microtubules attach to separate the chromosomes. C) They are organized so that there is one per sister chromatid. D) All of the above 4. Which of the following is true of the mitotic spindle? A) It is composed of actin and myosin microfilaments. B) It is composed of kinetochores at the metaphase plate. C) It is composed of microtubules, which help separate the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. D) It originates only at the centrioles in the centrosomes. 5. Imagine that there is a mutation in the Cdk2 gene such that its gene product is nonfunctional. What kind of effect would this mutation have on a mature red blood cell? A) The cell would be unable to replicate its DNA. B) The cell would not be able to enter G1. C) The cell would be unable to reproduce itself. D) There would be no effect, because mature red blood cells do not enter the cell cycle. Page 1
2 6. Imagine that there is a mutation in the Cdk2 gene such that its gene product is nonfunctional. What kind of effect would this mutation have on a mammalian white blood cell? A) The cell would be unable to replicate its DNA. B) The cell would be unable to enter G1. C) The cell would be unable to reproduce itself. D) Both a and c 7. Which of the following is true of chromatids? A) They are replicated chromosomes still joined together at the centromere. B) They are identical in mitotic chromosomes. C) They are identical in meiotic chromosomes. D) Both a and b 8. Chromosome movement during anaphase is the result of A) the molecular motors at the kinetochores that move the chromosomes toward the poles. B) molecular motors at the centrosome that pull the microtubules toward the poles. C) shortening of the microtubules at the centrosome that pull the chromosomes toward the poles. D) Both a and c 9. The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction is A) asexual reproduction only occurs in bacteria, and sexual reproduction occurs in plants and animals. B) asexual reproduction results in an organism that is identical to the parent, whereas sexual reproduction results in an organism that is not identical to either parent. C) asexual reproduction results from the fusion of two gametes; sexual reproduction produces clones of the parent organism. D) asexual reproduction only occurs in haplontic organisms, and sexual reproduction occurs only in diplontic organisms. 10. A chromatid is A) one of the pairs of homologous chromosomes. B) a homologous chromosome. C) a newly replicated bacterial chromosome. D) one half of a newly replicated eukaryotic chromosome. Page 2
3 11. In the beginning of Chapter 10, hemophilia is mentioned as a trait carried by the mother and passed to her sons. What is the pattern of inheritance for this trait? A) Hemophilia is an allele carried on one of the mother's autosomal chromosomes. B) Hemophilia is an allele carried on the Y chromosome because more males have this genetic disorder than females. C) Hemophilia is an allele carried on the X chromosome and can be directly inherited by the son from the father or the mother. D) Hemophilia is carried on the X chromosome and can only be inherited by the son if the mother is a carrier. 12. Originally, genetic inheritance was thought to be a function of the blending of traits from the two parents. Which exception to Mendel's rules is an example of blending? A) Polygenic inheritance B) Incomplete dominance C) Codominance D) Pleiotropism 13. True-breeding plants A) produce the same offspring when crossed for many generations. B) result from a monohybrid cross. C) result from a dihybrid cross. D) result from crossing over during prophase I of meiosis. 14. What is the probability that a cross between a true-breeding pea plant with spherical seeds and a true-breeding pea plant with wrinkled seeds will produce F1 progeny with spherical seeds? A) 1/2 B) 1/4 C) 0 D) What is the pattern of inheritance for a rare recessive allele? A) Every affected person has an affected parent. B) Unaffected parents can produce children who are affected. C) Unaffected mothers have affected sons and daughters who are carriers. D) None of the above 16. What is the pattern of inheritance for a rare dominant allele? A) Every affected person has an affected parent. B) Unaffected parents can produce children who are affected. C) Unaffected mothers have affected sons and daughters who are carriers. D) None of the above Page 3
4 17. What is the pattern of inheritance for a sex-linked allele? A) Every affected person has an affected parent. B) Unaffected parents can produce children who are affected. C) Unaffected mothers have affected sons and daughters who are carriers. D) None of the above 18. Sex determination in humans and Drosophila is similar because A) females are hemizygous. B) males have one X chromosome and females have two X chromosomes. C) all males from both species always have one Y chromosome D) the ratio of X chromosomes to sets of autosomes determines maleness or femaleness. 19. Linked genes are genes that A) assort independently. B) segregate equally in the gametes during meiosis. C) always contribute the same trait to the zygote. D) are found on the same chromosome. E) recombine during mitosis. 20. Cytoplasmic inheritance A) results from polygenic nuclear traits. B) is the result of gametes contributing equal amounts of cytoplasm to the zygote. C) is determined by genes on DNA molecules in mitochondria and chloroplasts. D) follows Mendel's law of segregation. 21. Epistasis is A) the degree a particular genotype is expressed in an individual. B) the proportion of individuals within a group with a particular genotype that show the expected phenotype. C) when a heterozygotic individual expresses an intermediate phenotype of the parents. D) when one gene masks the expression of another gene. 22. A test cross A) is used to determine if an organism that is displaying a dominant trait is heterozygous or homozygous for that trait. B) is used to determine if an organism that is displaying a recessive trait is heterozygous or homozygous for that trait. C) results in the F2 generation having a phenotypic ratio of 3/4 dominant to 1/4 recessive. D) results in the same alleles being transferred from generation to generation. Page 4
5 23. An individual has a karyotype that is XX but is phenotypically male. What could explain this result? A) The Y chromosome was not visible in the karyotype. B) Sex determination is determined by the autosomes and not the X chromosomes. C) A translocation has occurred placing the SRY gene on one of the X chromosomes. D) The DAX I protein is overproduced. 24. Cell differentiation is a result of A) the loss of particular genes from the nucleus of the differentiated cell. B) the differential expression of genes that are responsive to environmental signals. C) early embryonic cells remaining totipotent in the mature organism. D) mutations in genes that control the synthesis of DNA. 25. genes are involved in the development of the anterior posterior axis in both humans and insects. A) Developmental plasticity B) Heterochrony C) Hox D) All of the above 26. A totipotent cell is a cell A) whose developmental fate has been decided. B) that has differentiated into a specialized tissue. C) that is expressing morphogens to form a particular structure. D) whose developmental potential is extremely broad. 27. An important difference between a sperm and an egg is A) their size. B) the amount of cytoplasm they contain. C) whether or not they are motile. D) All of the above 28. Which of the following statements about fertilization is false? A) The egg permits several sperm to enter it. B) The plasma membranes of sperm and egg fuse. C) The egg is activated and stimulated to begin development. D) Species-specific recognition occurs between egg and sperm. Page 5
6 29. The sperm and the egg make different contributions to the zygote. Which statement about their contributions is false? A) The sperm contributes most of the organelles. B) The egg contributes most of the cytoplasm. C) Both the sperm and the egg contribute a haploid nucleus. D) All of the above 30. What is the order of the germ layers from the inside to the outside? A) Mesoderm, ectoderm, endoderm B) Endoderm, ectoderm, mesoderm C) Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm D) Endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm 31. How does cytokinesis differ in animal and plant cells? 32. Describe two ways that the genetic diversity of organisms is increased during meiosis. 33. Draw a pedigree for three generations in which the grandfather has red green color blindness and his daughter is a carrier. This daughter has four sons. Predict how many of the sons will be color-blind. 34. Draw a sample pedigree with three generations in which the paternal grandfather has a rare dominant autosomal trait. What is the probability that one of his children will have the disease? That one of his grandchildren will have the disease? 35. Draw a sample pedigree with three generations in which the maternal grandmother and paternal grandfather are carriers of a rare recessive autosomal trait. What is the probability that one of their children will be carriers of this trait? What is the probability that the grandchild with these grandparents would have the disease? 36. You are a genetics counselor who is working with a 21-year-old pregnant woman who has just discovered that her father has Huntington's chorea, a rare dominant autosomal trait. This disease usually develops in middle-aged individuals, so people carrying this trait do not find out they have this genetic disorder until midlife. What are the chances that the child she is carrying will develop Huntington's chorea? (Assume that her husband's family has no history of Huntington's chorea.) What is the chance that she has Huntington's chorea? Page 6
7 Answer Key 1. D 2. A 3. D 4. C 5. D 6. D 7. D 8. D 9. B 10. D 11. D 12. B 13. A 14. D 15. B 16. A 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. C 21. D 22. A 23. C 24. B 25. C 26. D 27. D 28. A 29. A 30. D 31. In animal cells, cytokinesis results from the interaction of actin filaments and myosin, which causes the cell membrane to pinch in and divide the cytoplasm into two cells. In plant cells, a cell plate forms between the newly segregated chromosomes, and Golgi vesicles fuse at that site to form the new cell membranes. Cell wall components are then secreted between the plasma membranes to complete cytokinesis. 32. Genetic diversity is increased during crossing over of prophase I of meiosis so that each gamete has chromosomes with different combinations of alleles. During meiosis, each homologous chromosome is randomly segregated to one of the two poles, resulting 2 23 different possible combinations of homologous chromosomes per gamete. 33. See Figure 10.24, generations II, III, and IV. One-half of her sons could be color-blind. 34. See Figure 10.10A. One-half of his children could get the disease; one-fourth of his grandchildren could get the disease. 35. See Figure 10.10B, generations III, and IV. One-half of the children of these grandparents could be carriers. One-sixteenth of the children could have the disease. Page 7
8 36. She has a 50 percent chance that she will develop Huntington's chorea. Because the trait is an autosomal dominant allele, one-half of her father's gametes will contain the homologous chromosome carrying that allele and one-half of his gametes will contain the homologous chromosome that carries the wild-type allele. If she received the Huntington's allele, her child has a 50 percent chance of receiving this allele from her. The product rule is used to predict the probability that her child will inherit the Huntington's allele: 1/2 (the probability that she has the Huntington's allele) 1/2 (the probability her child will inherit this allele from her) = 1/4 (the probability her child has the allele). Her child has a 25 percent chance of carrying the Hunting ton's chorea allele and thus of developing the disease. She has a 50 percent chance of carrying the Huntington's chorea allele. Page 8
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
 CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
5. The cells of a multicellular organism, other than gametes and the germ cells from which it develops, are known as
 1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
www.njctl.org PSI Biology Mitosis & Meiosis
 Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis
 The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells
 Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes?
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis
 Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
List, describe, diagram, and identify the stages of meiosis.
 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Meiosis is a special form of cell division.
 Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Heredity. Sarah crosses a homozygous white flower and a homozygous purple flower. The cross results in all purple flowers.
 Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
The correct answer is c A. Answer a is incorrect. The white-eye gene must be recessive since heterozygous females have red eyes.
 1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Chapter 3. Cell Division. Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.
 Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
If and when cancer cells stop dividing, they do so at random points, not at the normal checkpoints in the cell cycle.
 Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis
 BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Heredity Grade Ten
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Name: 4. A typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross is a) 9:1 b) 3:4 c) 9:3:3:1 d) 1:2:1:2:1 e) 6:3:3:6
 Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
7A The Origin of Modern Genetics
 Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance
 Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
17. A testcross A.is used to determine if an organism that is displaying a recessive trait is heterozygous or homozygous for that trait. B.
 ch04 Student: 1. Which of the following does not inactivate an X chromosome? A. Mammals B. Drosophila C. C. elegans D. Humans 2. Who originally identified a highly condensed structure in the interphase
ch04 Student: 1. Which of the following does not inactivate an X chromosome? A. Mammals B. Drosophila C. C. elegans D. Humans 2. Who originally identified a highly condensed structure in the interphase
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Reproduction Growth and development Tissue removal Example
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Reproduction Growth and development Tissue removal Example
Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis
 Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction In this workshop you will examine how cells divide, including how they partition their genetic material (DNA) between the two resulting
Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction In this workshop you will examine how cells divide, including how they partition their genetic material (DNA) between the two resulting
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis
 Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA
 Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Bio 101 Section 001: Practice Questions for First Exam
 Do the Practice Exam under exam conditions. Time yourself! MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. The substrate fits in the of an enzyme: (A) allosteric site (B) active site (C) reaction groove (D) Golgi body (E) inhibitor
Do the Practice Exam under exam conditions. Time yourself! MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. The substrate fits in the of an enzyme: (A) allosteric site (B) active site (C) reaction groove (D) Golgi body (E) inhibitor
CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE
 SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2
 Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
Test Two Study Guide
 Test Two Study Guide 1. Describe what is happening inside a cell during the following phases (pictures may help but try to use words): Interphase: : Consists of G1 / S / G2. Growing stage, cell doubles
Test Two Study Guide 1. Describe what is happening inside a cell during the following phases (pictures may help but try to use words): Interphase: : Consists of G1 / S / G2. Growing stage, cell doubles
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257
 CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE. Section B: Sex Chromosomes
 CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE Section B: Sex Chromosomes 1. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism 2. Sex-linked genes have unique patterns of inheritance 1. The chromosomal
somatic cell egg genotype gamete polar body phenotype homologous chromosome trait dominant autosome genetics recessive
 CHAPTER 6 MEIOSIS AND MENDEL Vocabulary Practice somatic cell egg genotype gamete polar body phenotype homologous chromosome trait dominant autosome genetics recessive CHAPTER 6 Meiosis and Mendel sex
CHAPTER 6 MEIOSIS AND MENDEL Vocabulary Practice somatic cell egg genotype gamete polar body phenotype homologous chromosome trait dominant autosome genetics recessive CHAPTER 6 Meiosis and Mendel sex
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3
 Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
MCAS Biology. Review Packet
 MCAS Biology Review Packet 1 Name Class Date 1. Define organic. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2. All living things are made up of 6 essential elements: SPONCH. Name the six elements of life. S N P C O H 3. Elements
MCAS Biology Review Packet 1 Name Class Date 1. Define organic. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2. All living things are made up of 6 essential elements: SPONCH. Name the six elements of life. S N P C O H 3. Elements
Practice Problems 4. (a) 19. (b) 36. (c) 17
 Chapter 10 Practice Problems Practice Problems 4 1. The diploid chromosome number in a variety of chrysanthemum is 18. What would you call varieties with the following chromosome numbers? (a) 19 (b) 36
Chapter 10 Practice Problems Practice Problems 4 1. The diploid chromosome number in a variety of chrysanthemum is 18. What would you call varieties with the following chromosome numbers? (a) 19 (b) 36
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles. Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully
 Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions. Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions!
 AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
From DNA to Protein
 Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Cellular Reproduction
 9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype.
 SECTION 7.1 CHROMOSOMES AND PHENOTYPE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation
SECTION 7.1 CHROMOSOMES AND PHENOTYPE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation
Chapter 3. Chapter Outline. Chapter Outline 9/11/10. Heredity and Evolu4on
 Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele.
 Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
Sexual Reproduction. and Meiosis. Sexual Reproduction
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 12 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Concept Outline 12.1 Meiosis produces haploid cells from diploid cells. Discovery of Reduction Division. Sexual reproduction does not increase chromosome number because
12 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Concept Outline 12.1 Meiosis produces haploid cells from diploid cells. Discovery of Reduction Division. Sexual reproduction does not increase chromosome number because
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction
 Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
The Somatic Cell Cycle
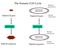 The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
I. Genes found on the same chromosome = linked genes
 Genetic recombination in Eukaryotes: crossing over, part 1 I. Genes found on the same chromosome = linked genes II. III. Linkage and crossing over Crossing over & chromosome mapping I. Genes found on the
Genetic recombination in Eukaryotes: crossing over, part 1 I. Genes found on the same chromosome = linked genes II. III. Linkage and crossing over Crossing over & chromosome mapping I. Genes found on the
CELL DIVISION. STAGES OF MITOTIC DIVISION (Diag. C1)
 1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis
 K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
BioBoot Camp Genetics
 BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses
 B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
Genetics 1. Defective enzyme that does not make melanin. Very pale skin and hair color (albino)
 Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
5 GENETIC LINKAGE AND MAPPING
 5 GENETIC LINKAGE AND MAPPING 5.1 Genetic Linkage So far, we have considered traits that are affected by one or two genes, and if there are two genes, we have assumed that they assort independently. However,
5 GENETIC LINKAGE AND MAPPING 5.1 Genetic Linkage So far, we have considered traits that are affected by one or two genes, and if there are two genes, we have assumed that they assort independently. However,
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009
 MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance. Ch. 3
 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Ch. 3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND SEX CHROMOSOMES! The chromosome theory of inheritance describes how the transmission of chromosomes account for the Mendelian
A and B are not absolutely linked. They could be far enough apart on the chromosome that they assort independently.
 Name Section 7.014 Problem Set 5 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68-120 by 5:00pm on Friday
Name Section 7.014 Problem Set 5 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68-120 by 5:00pm on Friday
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1
 Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
Saffiyah Y. Manboard Biology Instructor Seagull Alternative High School Saffiyah.manboard@browardschools.com
 The Effect of Discovery Learning through Biotechnology on the Knowledge and Perception of Sickle Cell Anemia and It s Genetics on Lower Income Students Saffiyah Y. Manboard Biology Instructor Seagull Alternative
The Effect of Discovery Learning through Biotechnology on the Knowledge and Perception of Sickle Cell Anemia and It s Genetics on Lower Income Students Saffiyah Y. Manboard Biology Instructor Seagull Alternative
Gene Mapping Techniques
 Gene Mapping Techniques OBJECTIVES By the end of this session the student should be able to: Define genetic linkage and recombinant frequency State how genetic distance may be estimated State how restriction
Gene Mapping Techniques OBJECTIVES By the end of this session the student should be able to: Define genetic linkage and recombinant frequency State how genetic distance may be estimated State how restriction
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Terms: The following terms are presented in this lesson (shown in bold italics and on PowerPoint Slides 2 and 3):
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Cell Division and Mitosis DNA. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. 2. Meiosis occurs in the reproductive organs, producing four haploid sex cells.
 ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
the!sun!to!sugars.!this!is!called!! photosynthesis.!the!byproduct!of!those! Nucleus! sugars!is!our!oxygen.!
 Cytoplasm ANIMAL CELL Vacuoles Mitochondria Chromosomes GolgiApparatus Chloroplast+ TheChloroplastiswhatmakesthefood inthecell.they reonlyfoundinplant cellsandsomeprotists.everygreen plantyouseeisconvertingenergyfrom
Cytoplasm ANIMAL CELL Vacuoles Mitochondria Chromosomes GolgiApparatus Chloroplast+ TheChloroplastiswhatmakesthefood inthecell.they reonlyfoundinplant cellsandsomeprotists.everygreen plantyouseeisconvertingenergyfrom
Classify chromosomes in a karyotype according to size and centromere position. Identify metacentric, submetacentric and acrocentric chromosomes
 Mitosis, Meiosis and the Cell Cycle Prof. Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives By the end of the session the student shoud be able to: Define the meaning of chromosomes
Mitosis, Meiosis and the Cell Cycle Prof. Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives By the end of the session the student shoud be able to: Define the meaning of chromosomes
Genetics Part 1: Inheritance of Traits
 Genetics Part 1: Inheritance of Traits Genetics is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. Offspring usually show some traits of each parent. For a long time, scientists did not understand
Genetics Part 1: Inheritance of Traits Genetics is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. Offspring usually show some traits of each parent. For a long time, scientists did not understand
This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive.
 11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
BIO 184 Page 1 Spring 2013 NAME VERSION 1 EXAM 3: KEY. Instructions: PRINT your Name and Exam version Number on your Scantron
 BIO 184 Page 1 Spring 2013 EXAM 3: KEY Instructions: PRINT your Name and Exam version Number on your Scantron Example: PAULA SMITH, EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Write your name CLEARLY at the top of every page of
BIO 184 Page 1 Spring 2013 EXAM 3: KEY Instructions: PRINT your Name and Exam version Number on your Scantron Example: PAULA SMITH, EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Write your name CLEARLY at the top of every page of
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
Given these characteristics of life, which of the following objects is considered a living organism? W. X. Y. Z.
 Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
2 18. If a boy s father has haemophilia and his mother has one gene for haemophilia. What is the chance that the boy will inherit the disease? 1. 0% 2
 1 GENETICS 1. Mendel is considered to be lucky to discover the laws of inheritance because 1. He meticulously analyzed his data statistically 2. He maintained pedigree records of various generations he
1 GENETICS 1. Mendel is considered to be lucky to discover the laws of inheritance because 1. He meticulously analyzed his data statistically 2. He maintained pedigree records of various generations he
Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics. Chapter 4 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings 2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
 Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Pigmentation Gene and Albinism Fig. 3.14 Two Genes Fig. 3.15 The Inheritance of Human Traits Difficulties Long generation time
Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Pigmentation Gene and Albinism Fig. 3.14 Two Genes Fig. 3.15 The Inheritance of Human Traits Difficulties Long generation time
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES 1. Margaret has just learned that she has adult polycystic kidney disease. Her mother also has the disease, as did her maternal grandfather and his younger
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES 1. Margaret has just learned that she has adult polycystic kidney disease. Her mother also has the disease, as did her maternal grandfather and his younger
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Cells CHAPTER. 1.2.1 Prokaryotic Cells. 1.2.2 Eukaryotic Cells
 C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
Genetics Test Biology I
 Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
