The Bracket Method: there is a simple way to learn algebra
|
|
|
- Nathan Heath
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 No More Double Signs Page 1
2 No more double signs A +, or - sign can mean many things; create a list of words for both signs: + : positive, plus, add, - : negative, subtract, minus, Circle all double signs and replace with one sign, then punch the problem in your calculator exactly as you see it! TI-83 The colored buttons on your calculator are math operations (add and subtract). Use these buttons only! Do not touch the negative sign if you want to add or subtract! 1: : Add Subtract What happens when the first number is -? You must tell the calculator the starting point is negative! The only time you use the negative sign when adding or subtracting is to tell the calculator the first number is negative. TI-83 The negative (-) button is only used to tell the calculator the starting point of an addition or subtraction problem is negative. If the first number is negative, use this button. 3: : : : : : Negative The Big Ugly (TBU): No More Double Signs Page 2
3 No More Double Signs Everything in math is either positive or negative; the sign of the number tells you both: (1) if it is positive or negative; and (2) to add or subtract when combining. No more or A number is either + or! Write the following real life scenarios as a mathematical expression with one sign in front of each number 1: balance of your checking account is $134 2: write a check for $103 3: the temperature drops by 16 degrees, then falls another 6 degrees. 4: you sell $350 at a garage sale 5: you lose 5 points on an exam for not writing your name, but you got the extra credit right for 2 extra points 6: 60 students left the concert early. 23 students came in late. 7: the fence has to be 7 feet longer A little tougher remember one sign for each number! 9: Starting temperature is 67 degrees; the temperature rises 15 degrees at noon, then goes up 8 more degrees by dinner time; the temperature then drops 19 degrees at sundown, and decreases another 5 during the night. b: What is the final temperature? 10: The business account had a starting balance of $1340. You write a check for $245; then you take $160 out at an ATM; then you make a deposit for $378; finally, you write another check for $29. b) What is the final balance? Speak Geek Expression: numbers and/or variables put together in a mathematical sentence with + or signs (no equal sign). No More Double Signs Page 3
4 No more double signs Find the Mistakes: 1: : : Speak Geek Commutative Property: Do you see the Co in the word Commutative? Remember Co - change order. It says you can change the order of an addition (or subtraction) problem, without changing the order. Prove the Commutative property by going through the following examples. a & b are the same problem, just a different order. Put both in the calculator; see if you get the same answer. 4a: a: a: b: b: b: Now that you know the Commutative Property works: find the mistakes; why don t these problems work? 7a: a: a: b: b: b: Fraction Time: Get rid of double signs; Use your calculator to find the answer; put the answer as a fraction. 10: : TBU: TI-83 A fraction is a division problem in disguise. To enter a fraction, simply type the top number,, and the bottom number. To be safe, put all fractions inside (); do not put the operation sign inside the () example: (3 5) (5 7) 1: [Math] Don t worry about simplifying or reducing your answers, the calculator can do that: Press [Math], [1], [Enter]. You should be able to change any answer from decimal to fraction with the press of 3 buttons: Math, one, enter. 2: [1] 3: [Enter] No More Double Signs Page 4
5 How to Bracket Page 5
6 How to Bracket Bracketing Terms: the first step to the bracket method is to be able to bracket the terms in an expression What is the rule for bracketing: Bracket the following expressions 1: 5x 2 6(3x) + 5y(8x) : -6x(4y) 7x(2y-7t) + 6z 8(5) + 19(-t) 3: -2(5x) + 6(2x-7+8y) + 9(3)(-7) 4: 6x2(4x) 2(5y)(-6)(-9y) 6t 7t : y (5)(-8x)(6y) - 8t(-6x)(3y4) 4(-7x) (-x) Don t panic, stick with your rules! 6: x 8 7x (2!)(6x 5y) 7: 5x 7y 6x 2 + sin 6x cos(3x 9) TBU: -6(5x) + 6x(6y)(-6) (4x +5-7y) 8(4)(-6) + 5x 6(-x)(-y) + 4 6(-8) 2 + 9x(-3x)(-6x) How well have you trained your eyes? Without bracketing, write the number terms in each expression? 8: 5x(-40) 7(-3) (3x-4) (3-6y) 9: 4(3x)(4y)(-5z) 2(3) (53y) 2(-5) 10: -6(3x)(-6y) 6x 6(4x-7) - 6(7) 11: -5x(7y)(-6) 2x 2 + 5(-3x-2y 2 ) x(5y) + (-t) Speak Geek Term: a part of a mathematical expression or equation separated by + or signs. How to Bracket Page 6
7 How to Mash Page 7
8 Multiplication = Mash potatoes In algebra, the easiest operation is multiplication. Just put it all the signs, numbers, letters in one pile (like your uncle s mash potato plate at thanksgiving: potato s, butter, peas, carrots, etc.), Multiply each term 1: 4(3x)(6y) 3: 7x(7y)(5t)(2) 4: 6(2x)(5)(2t)(10) 5: x(y)(t)(z) 6: 2(x)(5)(2y) Don t forget about signs? (In multiplication and division, every 2 negative signs is equal to a positive!) Even # of signs = Odd # of signs = Multiply each term: (1) signs; (2) numbers; (3) letters 7: -3(4x)(7y)(-5t) 8: 4t(6y)(-5)(-8z) 9: -6(-4x)(-7y)(5t)(10z) 10: 4(-3x)(12y)(-4)(-9z) 11: -(2)(3x)(-7y)(-10)(-8t) 12: -x(y)(-z)(t) 13): -6.8x(2.3y)(-7.1z) 14: 2.5(-6.8x)(6.25y)(-6.5t) 15: -(3.4x)(8.4y)(-9.2t)(-4) TBU: 3 5 7x y 5t t ( 8z) Math Geeks Only: 16: Is 5(4)(-6)(-10) the same as -6(5)(-10)(4)? 17: What property allows you to change the order and keep the same answer? (ahem change order) How to Mash Page 8
9 Bracket and Mash Each term (bracket) is a potential multiplication (mash) group. After you bracket, mash each term. Bracket and then mash each term separately (signs, numbers, letters) 1: 4(3x) - 4(-5x)(2y) - 3(4y) 2: -5x(4y)(2) 5(-2x) + 7(3t)(-5x) 3: 3(-5) + 3x(-7y) - 3(-x)(y)(-t) 4: -(4)(-5) 5(-2x)(-7) + 4(-6x)(y) 5: -(-4x) + (-6)(-5t)(7z) x(-y)(-z) 6: 7(3) 4(-8x) + 4x(2y) 6(-8t) 7: x 4t(6)(3) 6 + 2x(-6) 8: -6(-4)(-5)(7) (2x)(3y)(-6y)3 9: -(-1)(-1)(-5) + 3x(-3z) + 5(-y) 10: 3.2(-6.5) + 4x(-5.7)(-2.1) 3.6z(-4.5t) 11: -12(7x)(-15y) 5(-19)(6t) (-12x)(-25) 12: -t (-x)(-t)(-y) (v)(-z)(-t) x(z) TBU: 3 5 x 7y x 4 7 t + 5.6t 5x 2 5 y 7.2t y 6 5 t x y How to Mash Page 9
10 Part I: No more double signs you know what to do! Mixed Review 1: : : : Part II: Bracket the following terms don t do the math, just see how many terms there are! 5: 5(2x) 7(-3) + x(y)(-z) 6: sin32 14(x) + 4cos(3x) 2(3)(4) 7: 3 4 4x x x (y) 8: 4 (7-2x) (x)(2y) + 17(4) 2x3 + 16(-x 2 )(x) 3 Part III: Mash the following terms 9: 2(-3x)(-6y) 10: -(-3x)(4y)(-7z) 11: -2(-x)(-7)(-y) 12: 7(-6y)(5x)(-t) 13: 3 5y 2 t ( 3 x) 14: -(-x)(-y)(-t)(-z) Part IV: Bracket terms; mash each term. 15: 2(-4) + 4x(-6y) - 3(-x)(5)(-t) 16: -(3)(-5) 2(-3x)(-5) + 3(-6x)(y) 17: -(-4x) + (-3)(-2t)(7z) x(-2)(-z) 18: 5(4) (-8z) + 4x(2y) 3(-7t) How to Mash Page 10
11 How to Distribute (Pizza Delivery) Page 11
12 How to Distribute (Pizza Delivery) Page 12
13 Distribute: the second type of multiplication Write M (mash) or D (distribute) above each term then do it! 1: 6(3x)(-5) 2: 7(5x + 7) 3: 7(x + 9) 4: -5(6 x + 7y) 5: -(6x)(+7) 6: -(7 5x) 7: 5(4x)(7y)(6z) 8: 3(5x-8y+9) Distribute each problem (draw those arrows if you are not sure!) 9: 6( 4x + 8) 10: -5(7 + 3t) 11: -7(6 8x) 12: 2y( -7 4x) 13: - ( 5x 8) 14: 5(t x) 15: -5(2x y + 5) 16: (6 5x + 7y) TBU1: -2xy(6t 9 + 4z u) TBU2: 3 4 (5x 1 3 y z) How to Distribute (Pizza Delivery) Page 13
14 Part I: No more double signs you know what to do! Mixed Review 1: : : : Part II: Bracket the following terms don t do the math, just see how many terms there are! 5: 3(-2x) 5(-2) + x(3y)(-4) 6: 32(7!) (2x) + tan(3x) 2!(3)(4) 7: x + x 2 4 (y) 3 8: (y -2x) (-x 2 )(-18x) 3 - (5x)(3y) + 17(4) 2x 3 (5x) Part III: Bracket terms; mash each term 9: 2(5x) - 4(-x)(2y) - 8(5y) 10: 6(-2x) - 5x(4y)(2) + (4t)(-7x) 11: -(-7) - 2(-x)(y)(-7) + 3x(-7y) 12: -(3)(-2)(7)(v) 5(-2x)(-7t)(-w) + 4(-6x)(y)+(2) Part IV:. Mash or Distribute the following terms 13: 6(3x)(-5) 14: 7(5x + 7) 15: -(4x 2 5x 8) 16: 2 3 (1 x 1 ) 17: -(-4x)(-7)(-6y) 18: -5(6 x + 7y) 2 3 How to Distribute (Pizza Delivery) Page 14
15 PEMD: The Bracket Way Page 15
16 Bracket and Identify Find Terms (Bracket), then write M (mash) or D (distribute) or S (solo) above the bracket; do not do the math! 1: 4(2x) 3(2 +6y) 2: -2(5y) + 4(2)(5) 3(2x) 3: -3(4-5x) 2(4y) + 2(3t)(-z) 4: 5(3x-6y) 4(-5)(-3) 4(t) 5: -(4x)(-5) (5y 7) 6: -3(2x) 4(5 3y) 4w + 2(3xy 5t) Put it all together now: bracket, decide and label each term (M, D or S); do the math one term at a time! 7: 4y + 7(3x 8) 8: 5x + 6y(3x) 7y(-3) 9: 7 3y(-4)(-7) + 4(5x) 10: 5x + 3(5y 6t) : -(-3x)(-8) (5y 10) 12: -3t(2z) (4x - 8) + (-8y) 13: -(x)(-y)(-t) + cos(90) 3x(2t) 14: 3 4 5x 2 3 x 4 7 y + 3x(5 6 t) 15: 3 2x 3y 7x 2 5 y ( t) 16: 3x y 17z 4x 1 3 6y x( 9t) TBU: 3x 5 7y y 6t + 3t 7y z 4x 5 8 y t x 1 2 z ( 3 4 ) PEMD: The Bracket Way Page 16
17 Algebra Multiplication how good are you? Part I: Bracket terms; don t do the math; just label each term M, D or S. 1: 5x(-5) (-3)(-5) 7y(3x 10) 2: 4!(-7y) -.387(2x) 4cosx 3: 7 4(3x 12) + 8 7y 4: x 2 (2y 3 8) 2 (4)sin x Part II: Mash or Distribute each term 5: -(3x 5) 6: -(4x)(-5) 7: 2(4x)(+7)(-8) 8: -2(7 x) Part III: Find the mistakes! 9: 5(3x) 7y (4t 8) 10: 6 + 4(4x 8y) 15x 7y -4t x 8y 11: 5x 7x(3t) + 4 (2)(-x) 12: -(3x 7y) 3 + (3t 8z) 2x + 3t + 8x -3x -7y -9y +24z Part IV: Put it all together now: bracket, decide and label each term with (M or D or S), and do the math one term at a time. 13: 6(3x) + 5(3y 17) (-6)(-3v) 14: -(-6)(-5x) 7 + 3(4y 8z) 15: -5(2y) 9x(-7y)(-2) 8(-3) 16: 6(4 7x) 2y (7t 9z) 3(-2x)(-z)(-t) PEMD: The Bracket Way Page 17
18 Basic Exponents Page 18
19 What About Exponents? Speak Geek Exponent: math notation used to show repeat multiplication (mashing) of numbers or variables (ie. xxx=x 3 ) Expanded Notation: writing terms without the use of exponents (ie. xxxyy instead of x 3 y 2 ) Alphabetical Order: it doesn t really matter, but mathematicians do prefer you write variables in alphabetical order Mash and write the answers in expanded notation (the long way) 1: 2x(3x)(-5x) 2: -4x(2y)(-3x) 3: -x(4x)(2t)(-5x) 4: -2x(3t)(4x)(-10t)(-t) Part b: Now, in the box below, rewrite your answer using exponents (exponential notation) Distribute and write the answers in expanded notation 5: 3x(2x + 5y) 6: -2y(6x 5xy) 7: -xy(2x + 4y 2xy) 8) x(x y + 2xy) Part b: Now below your expanded answer, write the answer using exponents Put it all together: find terms, mash or distribute; use exponents if necessary 9: 2x(-3x) - (2y)(3y)(-4y) + 3x(2x)(-5x) 10: -3(2x)(-x) + 3(-5y)(-6y) (-2y)(3x) 11: 3x(2 4x) + 3(2y)(-3y) x(xy) 12: 2xy(3y 4x) 5y(y)(-y) 13: -(2x)(-5x)(-y) + 5y(3x)(-2y) 14: 3(4x)(5x) 5y(2y)(-10y) + 6(2)(-10) TBU: 2 3 x 4x 5 4 3x x 7 8 x 8 9 y + 2y 2 5 y + 4xy 4 3 (6xy)(8t) Basic Exponents Page 19
20 What About Exponents? Write the following expanded answers in exponential form 1: 7xx 2 x 3 2: -42y 3 xy 2 x 5 3: -x 4 x 2 txt 3 y 2 4: -2xy 3 t 4 xt 3 t 2 y Math Geeks Only: What property allows you to re-arrange 5x 3 yxy 2 into 5xx 3 yy 2? (hint: change order?!) Mash and write the answers in expanded notation (the long way) 1: 2x(3x)(-5x 2 ) 2: -4x 3 (2y)(-3x 2 ) 3: -x(4x 3 )(2t)(-5x) 4: -2x(3t 2 )(4x 2 )(-10t)(-t 3 ) Part b: Now, below your expanded answer, write the answer using exponents Distribute and write the answers in expanded notation 5: 3x(2x 3 + 5y) 6: -3y 2 (6x 5xy) 7: -xy 2 (2x + 4y 2x 3 y) 8: x(x 2 y + 2x 3 y) Part b: Now below your expanded answer, write the answer using exponents Put it all together: bracket, mash or distribute; use exponents if necessary 9: 2x(-3x) - (2y)(3y)(-4y) + 3x(2x)(-5x) 10: -3(2x)(-x) + 3x(-5y)(-6y) x(-2y)(3x) 11: 3x(2x 4y) + 3(2y)(-3y) x(2xy) 12: 2x(3 4x) 5y(2y)(-y) 13: -(2x)(-5x)(-y) + 5(3y)(-2y) 3(2x)(-5) 14: 3(4x)(5x) 5y(2y)(-10y) + 6(2)(-10) Basic Exponents Page 20
21 The Challenge The problems below are considered tough! If you can handle these, you officially have algebra skills! 1: 5x(3x) 4(x 7) (-8)(-y) 2: 4 5(4x 8y) (x)(3x)(-x) 3: 5y(3x 4y) 4xy(5x) + 6y(-y)(2y) 4: 5x 3 (-3x 2 ) 2x(5x 2 7y 2 ) + y 2 (4y 3 ) 5: -x(-x 2 )(-x 3 ) + x 2 (y 2 ) (x 2 y 2 ) 6: -2xy(4x 2 ) + 2xy(3x 4y) 4x 2 (5x 3 ) 7: 2x 3 (3x) 4y 2 (3y 4x) - 5x 3 8: -(-3x 2 )(x 4 ) 5(4x 7y) 6 + (3x)(-2x 2 )(3y) 9: 3x 2 y 3 (5x 2 7y 3 ) + x 3 y(5xy 2 7xy) 10: 2x(-2y) 4x 2 (x 2-5x) xy(-x 3 )(-y 2 ) 11: 2 5 x 15x2 1 3 y2 9y 21y 3 12: 2 3 x 4x 3 5 x2 1 3 y2 ( y3 ) TBU: ( 3x) 5x 3x 2 5x x 6x2 7y x2 y xy2 3 4 x(5 8 x3 9y) Basic Exponents Page 21
22 Clean-up: Combine Like Terms Page 22
23 Clean-up: Combine Like Terms Page 23
24 Combine = Clean-up Learn how to identify like terms: use underlines, double underlines, and circle constants (regular numbers). 1: 5t 7y + 4-8t 12t + 8x 2: 3x + 6x 2-7xy - 18x x 17xy 3: 4xy 7x xy 2 + 8xy x + 3x 2 y 4: 3x 5y 3x 2 6x 3 + x 7x x 3 5: : 5t 7t t t 3 5 6t 2 + 9t 3 6 7: 6x 3x 2 10xy +8x 2 y 6xy 2 + 6x 2 8x 3 + x 2 7xy + 15x 2 y -3x 2 y xy x +2x 3 Clean these up...combine the following expressions 8: 7x 12x + 8x 20x + 11x 9: 3y + 11y + 8y + 20y 40y 10: 3t 2 + 9t 2-4t 2 21t 2 + 6t 2 11: -8x 5 + 9x 5 3x 5 x 5 +8x 5 12: -101x + 56x 68x -71x -211x + 57x 13: 15y + 9y -12y + y 5y Cleaning up (combining) is all about adding or subtracting; the sign tells you what to do. 14: 5x - 6x + 8x + 9y + 18y 7y 15: -9y + 7x 13x + 18y + 9x -21y 5x 16: 8x 5x 2 11x 2 + 7x - 17x 2 + 8x 17: 12x 15y y 17 9y + 10x - 5 Speak Geek Coefficient: a number in front of a variable Constant: a number by itself (no variables): a regular number (all constants/regular numbers are like terms) Like Terms: terms where the non-coefficient parts (the stuff after the front number) are the same Clean-up: Combine Like Terms Page 24
25 Combine = Clean-up Clean-up the mess: Identify a term, find all of them, and combine (add or subtract depending on the sign) 1: Answer: 2: Answer: 3: Answer: Clean-up: Combine Like Terms Page 25
26 Combine = Clean-up Clean-up the mess: Identify a term, find all of them, and combine (add or subtract depending on the sign) 1: Answer: 2: Answer: Now that you have seen the worst, try some basic problems: do the same thing! 3: -5x + 17y xy - 3y 11x + 8xy : 4x 2 5x 3 + 9xy 10x xy 2 2x 2 y + 25xy 14x 2 y xy 2 5: Clean-up: Combine Like Terms Page 26
27 Combining Like Terms (Clean-up) Math Geeks Only: If xx = x 2, then why is x+x not x 2? Find the Mistakes 1: 4x 5x x 2 11x + 3x 2-7 2: 6x + 18y y y + 8x - 9-4x - 11x x + 35y + 13 Identify and combine (clean-up) 3: 3x 5y +6x y 84x -17 4: 5x 2 7x 8x 2-18x + 34x 2 17x 2 5: 5x + x x 4x x + 5x : 16x + 14 xy 5y 8xy 7y y 2 - xy 7: : 6x 3 4x x x x 2 + 8x : x + xy y + 4xy 4y + x + xy 3x 6y 10: 3x 2 4xy 2 + 7y 2 7x 2 y 9y xy TBU1: 3 4 x 1 2 x x 2 3 x TBU2: y 1 4 y2 1 6 y + y 1 3 y y2 Clean-up: Combine Like Terms Page 27
28 Simplify: The Bracket Way Page 28
29 Simplify = Bracket Find the Mistakes 1: 5x 3(5 8x) + 3(-4) 2: 7 + 3(6x 2) - 5x 5x x (6x 2) x x x - 25 Simplify: (1) Bracket terms, (2) Mash, Distribute (or Solo) each term, (3) Clean-up 3: 17 5(3x 8) 4: 5x + 2(-4) 7x(-5) : 20(-2x) 7(-8) + 2x 3(-7) 6: 5(2x - 8) 4(9x - 5) 7: -3(4) (3x 6) (-4x) 8: 5x 7(-2x)(-5) 2(x 4) 9: 3(4x 2 5x -8) 2x 2 4(3x) - (-2) 10: -(-4)(-3y) + 3x -2(-4x -7y) + 5(-4y) TBU: 7(3x)(-7) 4x 6(-3)(-1) - (4x 8y + 7) + 14y x(-5) 8(-3y + 8x) (- 7)(-6) x y Simplify: The Bracket Way Page 29
30 The Challenge (Part II) If you can simplify these you can simplify anything! Remember: (1) find terms, (2) Mash or Distribute each term, (3) Clean-up (combine) 1: 5x(2x) 5(3x 2 7x - 8) + (-7) 2: -2(-3x 3 ) 2x(-5x) 6x 2 + 5x(-2x)(-7x) 3: 2(x 3 18x 2 + 9x 34) (x 3 8x 2 14x - 21) 4: 5(2x 6y) (4x)(-3y) 7(-2x) + x(3y) (-x) 5: x(x) 2(3x 2 7x 9) 3(2x) : -(-6x 3 ) + 18x 2 2x 2 (-5x) x(x 5) 7: 5(-2y) 7y(4y 8) 9 +2(7y) (-4y 2 ) 8: 2xy(3x 8y) 3x(-4y 2 ) x(9x)(-3y) + 7y(-2xy) 9: x(x 3 9x 2 + 4x 21) 2x(x 2 4x) 2(-11) 10: 3 8 x 4x 5x x2 3x ( 7) TBU: -4x 2 (3x 2 ) 7x 3 (-5) x(x 3 6x 2 10) x(-4x)(-7x) + 18x 2 (-x) + 5x 3 (-7x) 6x(18 7x x2 + 5x 3 ) Simplify: The Bracket Way Page 30
31 Solving: Junk & Divide Page 31
32 Solving: Junk & Divide Page 32
33 Solving: Junk & Divide Page 33
34 Solving Equations: Junk & Divide Speak Geek Equation: when one mathematical expression is set equal to another. Solving Basic Rules: 1. Draw the 2. Work on the 3. Whatever you do to one side of the wall, Draw the wall; put an * above the junk (do not solve!) 1: 7x 27 = 76 2: 35 = x 3: 16 8x = 123 4: -352 = 21x + 7 5: 4x - 7π = 237 6: 71 = 2 3 7x 7: 9x 4 = 78 8: 6 + 7x = Now go back (1-8) and show how you would get rid of the junk (do not dive yet, that is next) Solve: Put it all together now Junk & Divide 9: 17 9x = 71 10: -5x 35 = : 89 = 4x : -57 = x 13: 12 7x = : 13x + 78 = : 171 = 5 5.2x 16: 17 x = 58 17: 5x = 16 Solving: Junk & Divide Page 34
35 Solve: Junk & Divide 1: -17x = : x = : 54.5 = x 4: 1235 = 123x 86 5: 1 x = 0 6: 67 12x = -782 These are so easy, they are tough (sometimes you only do junk, and sometimes you skip right to divide)!? Speak Geek One Step Equations: equations which can be solved in one mathematical step. 7: 5x = 876 8: x = 91 9: -17 = -4x 10: -346 = 89 + x 11: - x = : x 13 = -21 Don t panic, they re only fractions (remember to use parenthesis) junk and divide! 13: 5x 2 3 = 28 14: x = 34 15: 174 = x 16: 6 = 3 8 x : 5 9 x 27 3 = 34 18: 46 7 = 1 4 x Solving: Junk & Divide Page 35
36 Simplify and Solve Bracket, Junk & Divide 1: 7 + 2(3x 8) = 123 2: 5x 2(3x) 18(-4) = 231 3: 4(-2) 6(3x 8) + 8(-3x) = : -5x 4(x 8) = : 1056 = 4(-2x) 18(3) 7 6: -78 = 7(2) 3(4x 8) + 2(-5x) 7: -(3x 8) x (-7x) = : 78 = 17 2(x - 8) + 5(-7x) (-5)(-8) TBU: (5x)(-17)(-4) (12x 2 6) 5x 4(5 x) (-2)(-8)(-3x) + 2(3x)(-7) + 4(3x 2 7x +9) = Solving: Junk & Divide Page 36
37 X s on Both Sides make one disappear, junk & divide 1: 5x 19 = x 2: x = x 3: 24 8x = x 4: 34 18x = x 5: 8x + 19 = -6x 23 6: -16x + 31 = -7x : x = 25.4x : 5.26x = : x = 40 8x These are strange think about which x you want to disappear!? 10: x = 6x 11: -78 7x = -12x 12: 15x = x 13: -19x = -7x : x = x 15: x = 19x Hmmm?16: 6x 8 = x Hmmm?17: 21 7x = -7x + 21 Solving: Junk & Divide Page 37
38 The Challenge (Part III) If you can solve these you can solve anything! 1: 6 + 2(3x 8) = 7x -9 2: -3(x 8) = -4(5x 7) 3: -4(-3) (6x 8) + 7 = 5x 18 4: 7x 8(-5x) + 7 = 17 5x 5: 5(2x) 17(-2) = 2(7x 8) 6: -(-5) 4(2x 8) = 3x 7(-2) + 8x 7: 4x 2(-3x) + 2(5) = 7 3(2x 8) 9x 8: 4(3x + 21) = 5x 7x + 15x 9: 5(-2)(3) (4x 9) 4(-7) = 3(-2) -3(4)(-5x) 9 10: 2(-4) x 2(3) = 8 + 8x x 11: 3 4 2x 8 = 2 3 6x 14( 3) 12: x 3 8 = 1 2 4x ( 2 21 ) Solving: Junk & Divide Page 38
39 Solving for Letters Speak Geek Implicit Formulas: solving a formula for another variable When solving for formulas, nothing changes (except the answers are ugly looking). Identify what you are trying to solve for; get rid of the junk; divide. 1: solve for x: 5x t = 4g 2: solve for t: 4g 7t = cy 3: solve for v: 3tv = 35g 4: solve for g: 16t 2 5g = F 5: Solve for r: 6πrh = 156 6: solve for h: fm gh = 38t 7: solve for v: 6t 2 7t 5vh = 324 8: solve for g: 7y 6t 8g = 56 9: solve for r: 7d 3πrh = -72g One of the most common things you will do in algebra is to solve for y (get y alone!). 10: y + 4x = 7 11: 5x - y = 18 12: 5x + 8y = 21 13: 2x 7y = : 7y 4x 8 = 18 15: 15 = 5x 3y Solving: Junk & Divide Page 39
40 Adding to your repertoire Junk & Divide can be used to solve most any type of linear algebraic equation. However, once you get good at this method, there are certain methods you should learn to make solving faster or easier! 1) Cross Multiplication: used anytime you have fractions set equal to each other. 2) Dot Method, or IHF (I hate fractions), or GCF (this is the official geek name: it stands for greatest common factor): used when you have a lot of fractions in an equation, and you just want to get rid of them! 3) Graph the equation and find the intersect: every equation can be solved this way. 4) Two Sticks, Two Equations: used to solve absolute value problems. 5) The Inverse of Square is Square Root: Used to solve x 2 or x problems Solving: Junk & Divide Page 40
0.8 Rational Expressions and Equations
 96 Prerequisites 0.8 Rational Expressions and Equations We now turn our attention to rational expressions - that is, algebraic fractions - and equations which contain them. The reader is encouraged to
96 Prerequisites 0.8 Rational Expressions and Equations We now turn our attention to rational expressions - that is, algebraic fractions - and equations which contain them. The reader is encouraged to
SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS
 40 (8-8) Chapter 8 Powers and Roots 8. SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS In this section Using the Product Rule Rationalizing the Denominator Simplified Form of a Square Root In Section 8. you learned to simplify
40 (8-8) Chapter 8 Powers and Roots 8. SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS In this section Using the Product Rule Rationalizing the Denominator Simplified Form of a Square Root In Section 8. you learned to simplify
A positive exponent means repeated multiplication. A negative exponent means the opposite of repeated multiplication, which is repeated
 Eponents Dealing with positive and negative eponents and simplifying epressions dealing with them is simply a matter of remembering what the definition of an eponent is. division. A positive eponent means
Eponents Dealing with positive and negative eponents and simplifying epressions dealing with them is simply a matter of remembering what the definition of an eponent is. division. A positive eponent means
FINDING THE LEAST COMMON DENOMINATOR
 0 (7 18) Chapter 7 Rational Expressions GETTING MORE INVOLVED 7. Discussion. Evaluate each expression. a) One-half of 1 b) One-third of c) One-half of x d) One-half of x 7. Exploration. Let R 6 x x 0 x
0 (7 18) Chapter 7 Rational Expressions GETTING MORE INVOLVED 7. Discussion. Evaluate each expression. a) One-half of 1 b) One-third of c) One-half of x d) One-half of x 7. Exploration. Let R 6 x x 0 x
Exponents. Exponents tell us how many times to multiply a base number by itself.
 Exponents Exponents tell us how many times to multiply a base number by itself. Exponential form: 5 4 exponent base number Expanded form: 5 5 5 5 25 5 5 125 5 625 To use a calculator: put in the base number,
Exponents Exponents tell us how many times to multiply a base number by itself. Exponential form: 5 4 exponent base number Expanded form: 5 5 5 5 25 5 5 125 5 625 To use a calculator: put in the base number,
Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section
 Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section What is algebra? Operations with algebraic terms Mathematical properties of real numbers Order of operations What is Algebra? Algebra is
Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section What is algebra? Operations with algebraic terms Mathematical properties of real numbers Order of operations What is Algebra? Algebra is
2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction:
 2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction: As is usually the case when learning a new concept in mathematics, the new concept is the reverse of the previous one. Remember how you first learned
2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction: As is usually the case when learning a new concept in mathematics, the new concept is the reverse of the previous one. Remember how you first learned
Algebraic expressions are a combination of numbers and variables. Here are examples of some basic algebraic expressions.
 Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
1.6 The Order of Operations
 1.6 The Order of Operations Contents: Operations Grouping Symbols The Order of Operations Exponents and Negative Numbers Negative Square Roots Square Root of a Negative Number Order of Operations and Negative
1.6 The Order of Operations Contents: Operations Grouping Symbols The Order of Operations Exponents and Negative Numbers Negative Square Roots Square Root of a Negative Number Order of Operations and Negative
Year 9 set 1 Mathematics notes, to accompany the 9H book.
 Part 1: Year 9 set 1 Mathematics notes, to accompany the 9H book. equations 1. (p.1), 1.6 (p. 44), 4.6 (p.196) sequences 3. (p.115) Pupils use the Elmwood Press Essential Maths book by David Raymer (9H
Part 1: Year 9 set 1 Mathematics notes, to accompany the 9H book. equations 1. (p.1), 1.6 (p. 44), 4.6 (p.196) sequences 3. (p.115) Pupils use the Elmwood Press Essential Maths book by David Raymer (9H
Polynomials and Factoring. Unit Lesson Plan
 Polynomials and Factoring Unit Lesson Plan By: David Harris University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Math 410 Dr. Thomas, M D. 2 Abstract This paper will discuss, and give, lesson plans for all the topics
Polynomials and Factoring Unit Lesson Plan By: David Harris University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Math 410 Dr. Thomas, M D. 2 Abstract This paper will discuss, and give, lesson plans for all the topics
CAHSEE on Target UC Davis, School and University Partnerships
 UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
 3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
MATH 10034 Fundamental Mathematics IV
 MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
COLLEGE ALGEBRA. Paul Dawkins
 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iv Preliminaries... Introduction... Integer Exponents... Rational Exponents... 9 Real Exponents...5 Radicals...6 Polynomials...5
COLLEGE ALGEBRA Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... iii Outline... iv Preliminaries... Introduction... Integer Exponents... Rational Exponents... 9 Real Exponents...5 Radicals...6 Polynomials...5
A Quick Algebra Review
 1. Simplifying Epressions. Solving Equations 3. Problem Solving 4. Inequalities 5. Absolute Values 6. Linear Equations 7. Systems of Equations 8. Laws of Eponents 9. Quadratics 10. Rationals 11. Radicals
1. Simplifying Epressions. Solving Equations 3. Problem Solving 4. Inequalities 5. Absolute Values 6. Linear Equations 7. Systems of Equations 8. Laws of Eponents 9. Quadratics 10. Rationals 11. Radicals
Order of Operations More Essential Practice
 Order of Operations More Essential Practice We will be simplifying expressions using the order of operations in this section. Automatic Skill: Order of operations needs to become an automatic skill. Failure
Order of Operations More Essential Practice We will be simplifying expressions using the order of operations in this section. Automatic Skill: Order of operations needs to become an automatic skill. Failure
Operations with positive and negative numbers - see first chapter below. Rules related to working with fractions - see second chapter below
 INTRODUCTION If you are uncomfortable with the math required to solve the word problems in this class, we strongly encourage you to take a day to look through the following links and notes. Some of them
INTRODUCTION If you are uncomfortable with the math required to solve the word problems in this class, we strongly encourage you to take a day to look through the following links and notes. Some of them
Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals
 8. Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals Objective: Multiply and divide radicals using the product and quotient rules of radicals. Multiplying radicals is very simple if the index on all the radicals
8. Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals Objective: Multiply and divide radicals using the product and quotient rules of radicals. Multiplying radicals is very simple if the index on all the radicals
SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS
 Tallahassee Community College 5 SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS In arithmetic, you learned that a fraction is in simplest form if the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of the numerator and the denominator is
Tallahassee Community College 5 SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS In arithmetic, you learned that a fraction is in simplest form if the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of the numerator and the denominator is
If A is divided by B the result is 2/3. If B is divided by C the result is 4/7. What is the result if A is divided by C?
 Problem 3 If A is divided by B the result is 2/3. If B is divided by C the result is 4/7. What is the result if A is divided by C? Suggested Questions to ask students about Problem 3 The key to this question
Problem 3 If A is divided by B the result is 2/3. If B is divided by C the result is 4/7. What is the result if A is divided by C? Suggested Questions to ask students about Problem 3 The key to this question
SAT Math Facts & Formulas Review Quiz
 Test your knowledge of SAT math facts, formulas, and vocabulary with the following quiz. Some questions are more challenging, just like a few of the questions that you ll encounter on the SAT; these questions
Test your knowledge of SAT math facts, formulas, and vocabulary with the following quiz. Some questions are more challenging, just like a few of the questions that you ll encounter on the SAT; these questions
Mathematics Placement
 Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
All the examples in this worksheet and all the answers to questions are available as answer sheets or videos.
 BIRKBECK MATHS SUPPORT www.mathsupport.wordpress.com Numbers 3 In this section we will look at - improper fractions and mixed fractions - multiplying and dividing fractions - what decimals mean and exponents
BIRKBECK MATHS SUPPORT www.mathsupport.wordpress.com Numbers 3 In this section we will look at - improper fractions and mixed fractions - multiplying and dividing fractions - what decimals mean and exponents
5 means to write it as a product something times something instead of a sum something plus something plus something.
 Intermediate algebra Class notes Factoring Introduction (section 6.1) Recall we factor 10 as 5. Factoring something means to think of it as a product! Factors versus terms: terms: things we are adding
Intermediate algebra Class notes Factoring Introduction (section 6.1) Recall we factor 10 as 5. Factoring something means to think of it as a product! Factors versus terms: terms: things we are adding
Negative Integer Exponents
 7.7 Negative Integer Exponents 7.7 OBJECTIVES. Define the zero exponent 2. Use the definition of a negative exponent to simplify an expression 3. Use the properties of exponents to simplify expressions
7.7 Negative Integer Exponents 7.7 OBJECTIVES. Define the zero exponent 2. Use the definition of a negative exponent to simplify an expression 3. Use the properties of exponents to simplify expressions
Section 1.5 Exponents, Square Roots, and the Order of Operations
 Section 1.5 Exponents, Square Roots, and the Order of Operations Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Identify perfect squares.
Section 1.5 Exponents, Square Roots, and the Order of Operations Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Identify perfect squares.
Part 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities: Simplifying and Solving
 Section 7 Algebraic Manipulations and Solving Part 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities: Simplifying and Solving Before launching into the mathematics, let s take a moment to talk about the words
Section 7 Algebraic Manipulations and Solving Part 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities: Simplifying and Solving Before launching into the mathematics, let s take a moment to talk about the words
Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons. Stanley Ocken. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013
 Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons Prof. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013 An important feature of the following Beamer slide presentations is that you, the reader, move
Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons Prof. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013 An important feature of the following Beamer slide presentations is that you, the reader, move
This is a square root. The number under the radical is 9. (An asterisk * means multiply.)
 Page of Review of Radical Expressions and Equations Skills involving radicals can be divided into the following groups: Evaluate square roots or higher order roots. Simplify radical expressions. Rationalize
Page of Review of Radical Expressions and Equations Skills involving radicals can be divided into the following groups: Evaluate square roots or higher order roots. Simplify radical expressions. Rationalize
Determine If An Equation Represents a Function
 Question : What is a linear function? The term linear function consists of two parts: linear and function. To understand what these terms mean together, we must first understand what a function is. The
Question : What is a linear function? The term linear function consists of two parts: linear and function. To understand what these terms mean together, we must first understand what a function is. The
MTN Learn. Mathematics. Grade 10. radio support notes
 MTN Learn Mathematics Grade 10 radio support notes Contents INTRODUCTION... GETTING THE MOST FROM MINDSET LEARN XTRA RADIO REVISION... 3 BROADAST SCHEDULE... 4 ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS... 5 EXPONENTS... 9
MTN Learn Mathematics Grade 10 radio support notes Contents INTRODUCTION... GETTING THE MOST FROM MINDSET LEARN XTRA RADIO REVISION... 3 BROADAST SCHEDULE... 4 ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS... 5 EXPONENTS... 9
Algebra Cheat Sheets
 Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced
 Instructor! Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced Last week we looked at greatest common factors and the basics of factoring out the GCF. In this second activity, we will discuss factoring more difficult
Instructor! Math 25 Activity 6: Factoring Advanced Last week we looked at greatest common factors and the basics of factoring out the GCF. In this second activity, we will discuss factoring more difficult
Factoring - Greatest Common Factor
 6.1 Factoring - Greatest Common Factor Objective: Find the greatest common factor of a polynomial and factor it out of the expression. The opposite of multiplying polynomials together is factoring polynomials.
6.1 Factoring - Greatest Common Factor Objective: Find the greatest common factor of a polynomial and factor it out of the expression. The opposite of multiplying polynomials together is factoring polynomials.
Method To Solve Linear, Polynomial, or Absolute Value Inequalities:
 Solving Inequalities An inequality is the result of replacing the = sign in an equation with ,, or. For example, 3x 2 < 7 is a linear inequality. We call it linear because if the < were replaced with
Solving Inequalities An inequality is the result of replacing the = sign in an equation with ,, or. For example, 3x 2 < 7 is a linear inequality. We call it linear because if the < were replaced with
x 2 + y 2 = 1 y 1 = x 2 + 2x y = x 2 + 2x + 1
 Implicit Functions Defining Implicit Functions Up until now in this course, we have only talked about functions, which assign to every real number x in their domain exactly one real number f(x). The graphs
Implicit Functions Defining Implicit Functions Up until now in this course, we have only talked about functions, which assign to every real number x in their domain exactly one real number f(x). The graphs
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials
 Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Balancing Chemical Equations
 Balancing Chemical Equations A mathematical equation is simply a sentence that states that two expressions are equal. One or both of the expressions will contain a variable whose value must be determined
Balancing Chemical Equations A mathematical equation is simply a sentence that states that two expressions are equal. One or both of the expressions will contain a variable whose value must be determined
Week 13 Trigonometric Form of Complex Numbers
 Week Trigonometric Form of Complex Numbers Overview In this week of the course, which is the last week if you are not going to take calculus, we will look at how Trigonometry can sometimes help in working
Week Trigonometric Form of Complex Numbers Overview In this week of the course, which is the last week if you are not going to take calculus, we will look at how Trigonometry can sometimes help in working
Unit 7 The Number System: Multiplying and Dividing Integers
 Unit 7 The Number System: Multiplying and Dividing Integers Introduction In this unit, students will multiply and divide integers, and multiply positive and negative fractions by integers. Students will
Unit 7 The Number System: Multiplying and Dividing Integers Introduction In this unit, students will multiply and divide integers, and multiply positive and negative fractions by integers. Students will
Exponents, Radicals, and Scientific Notation
 General Exponent Rules: Exponents, Radicals, and Scientific Notation x m x n = x m+n Example 1: x 5 x = x 5+ = x 7 (x m ) n = x mn Example : (x 5 ) = x 5 = x 10 (x m y n ) p = x mp y np Example : (x) =
General Exponent Rules: Exponents, Radicals, and Scientific Notation x m x n = x m+n Example 1: x 5 x = x 5+ = x 7 (x m ) n = x mn Example : (x 5 ) = x 5 = x 10 (x m y n ) p = x mp y np Example : (x) =
ACCUPLACER. Testing & Study Guide. Prepared by the Admissions Office Staff and General Education Faculty Draft: January 2011
 ACCUPLACER Testing & Study Guide Prepared by the Admissions Office Staff and General Education Faculty Draft: January 2011 Thank you to Johnston Community College staff for giving permission to revise
ACCUPLACER Testing & Study Guide Prepared by the Admissions Office Staff and General Education Faculty Draft: January 2011 Thank you to Johnston Community College staff for giving permission to revise
Radicals - Rational Exponents
 8. Radicals - Rational Exponents Objective: Convert between radical notation and exponential notation and simplify expressions with rational exponents using the properties of exponents. When we simplify
8. Radicals - Rational Exponents Objective: Convert between radical notation and exponential notation and simplify expressions with rational exponents using the properties of exponents. When we simplify
Overview. Observations. Activities. Chapter 3: Linear Functions Linear Functions: Slope-Intercept Form
 Name Date Linear Functions: Slope-Intercept Form Student Worksheet Overview The Overview introduces the topics covered in Observations and Activities. Scroll through the Overview using " (! to review,
Name Date Linear Functions: Slope-Intercept Form Student Worksheet Overview The Overview introduces the topics covered in Observations and Activities. Scroll through the Overview using " (! to review,
Quick Reference ebook
 This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
MATH 13150: Freshman Seminar Unit 10
 MATH 13150: Freshman Seminar Unit 10 1. Relatively prime numbers and Euler s function In this chapter, we are going to discuss when two numbers are relatively prime, and learn how to count the numbers
MATH 13150: Freshman Seminar Unit 10 1. Relatively prime numbers and Euler s function In this chapter, we are going to discuss when two numbers are relatively prime, and learn how to count the numbers
Rational Exponents. Squaring both sides of the equation yields. and to be consistent, we must have
 8.6 Rational Exponents 8.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Define rational exponents 2. Simplify expressions containing rational exponents 3. Use a calculator to estimate the value of an expression containing rational exponents
8.6 Rational Exponents 8.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Define rational exponents 2. Simplify expressions containing rational exponents 3. Use a calculator to estimate the value of an expression containing rational exponents
Systems of Equations Involving Circles and Lines
 Name: Systems of Equations Involving Circles and Lines Date: In this lesson, we will be solving two new types of Systems of Equations. Systems of Equations Involving a Circle and a Line Solving a system
Name: Systems of Equations Involving Circles and Lines Date: In this lesson, we will be solving two new types of Systems of Equations. Systems of Equations Involving a Circle and a Line Solving a system
Rules of Exponents. Math at Work: Motorcycle Customization OUTLINE CHAPTER
 Rules of Exponents CHAPTER 5 Math at Work: Motorcycle Customization OUTLINE Study Strategies: Taking Math Tests 5. Basic Rules of Exponents Part A: The Product Rule and Power Rules Part B: Combining the
Rules of Exponents CHAPTER 5 Math at Work: Motorcycle Customization OUTLINE Study Strategies: Taking Math Tests 5. Basic Rules of Exponents Part A: The Product Rule and Power Rules Part B: Combining the
1) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-1) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-1)(2) =
 Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION OF REAL NUMBERS In this section we will complete the study of the four basic operations with real numbers.
 1.4 Multiplication and (1-25) 25 In this section Multiplication of Real Numbers Division by Zero helpful hint The product of two numbers with like signs is positive, but the product of three numbers with
1.4 Multiplication and (1-25) 25 In this section Multiplication of Real Numbers Division by Zero helpful hint The product of two numbers with like signs is positive, but the product of three numbers with
Exponents and Radicals
 Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
A.2. Exponents and Radicals. Integer Exponents. What you should learn. Exponential Notation. Why you should learn it. Properties of Exponents
 Appendix A. Exponents and Radicals A11 A. Exponents and Radicals What you should learn Use properties of exponents. Use scientific notation to represent real numbers. Use properties of radicals. Simplify
Appendix A. Exponents and Radicals A11 A. Exponents and Radicals What you should learn Use properties of exponents. Use scientific notation to represent real numbers. Use properties of radicals. Simplify
Direct Translation is the process of translating English words and phrases into numbers, mathematical symbols, expressions, and equations.
 Section 1 Mathematics has a language all its own. In order to be able to solve many types of word problems, we need to be able to translate the English Language into Math Language. is the process of translating
Section 1 Mathematics has a language all its own. In order to be able to solve many types of word problems, we need to be able to translate the English Language into Math Language. is the process of translating
Definition 8.1 Two inequalities are equivalent if they have the same solution set. Add or Subtract the same value on both sides of the inequality.
 8 Inequalities Concepts: Equivalent Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Inequalities Absolute Value Inequalities (Sections 4.6 and 1.1) 8.1 Equivalent Inequalities Definition 8.1 Two inequalities are equivalent
8 Inequalities Concepts: Equivalent Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Inequalities Absolute Value Inequalities (Sections 4.6 and 1.1) 8.1 Equivalent Inequalities Definition 8.1 Two inequalities are equivalent
3.2. Solving quadratic equations. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes. Learning Style
 Solving quadratic equations 3.2 Introduction A quadratic equation is one which can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a, b and c are numbers and x is the unknown whose value(s) we wish to find.
Solving quadratic equations 3.2 Introduction A quadratic equation is one which can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a, b and c are numbers and x is the unknown whose value(s) we wish to find.
SUNY ECC. ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop. Algebra Skills
 SUNY ECC ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop Algebra Skills Gail A. Butler Ph.D. Evaluating Algebraic Epressions Substitute the value (#) in place of the letter (variable). Follow order of operations!!! E)
SUNY ECC ACCUPLACER Preparation Workshop Algebra Skills Gail A. Butler Ph.D. Evaluating Algebraic Epressions Substitute the value (#) in place of the letter (variable). Follow order of operations!!! E)
Section 1. Finding Common Terms
 Worksheet 2.1 Factors of Algebraic Expressions Section 1 Finding Common Terms In worksheet 1.2 we talked about factors of whole numbers. Remember, if a b = ab then a is a factor of ab and b is a factor
Worksheet 2.1 Factors of Algebraic Expressions Section 1 Finding Common Terms In worksheet 1.2 we talked about factors of whole numbers. Remember, if a b = ab then a is a factor of ab and b is a factor
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING
 POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING BASIC ALGEBRA
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING BASIC ALGEBRA TUTORIAL 1 ALGEBRAIC LAWS This tutorial is useful to anyone studying engineering. It uses the principle of learning by example. On completion of this tutorial
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING BASIC ALGEBRA TUTORIAL 1 ALGEBRAIC LAWS This tutorial is useful to anyone studying engineering. It uses the principle of learning by example. On completion of this tutorial
Graphing Parabolas With Microsoft Excel
 Graphing Parabolas With Microsoft Excel Mr. Clausen Algebra 2 California State Standard for Algebra 2 #10.0: Students graph quadratic functions and determine the maxima, minima, and zeros of the function.
Graphing Parabolas With Microsoft Excel Mr. Clausen Algebra 2 California State Standard for Algebra 2 #10.0: Students graph quadratic functions and determine the maxima, minima, and zeros of the function.
Chapter 7 - Roots, Radicals, and Complex Numbers
 Math 233 - Spring 2009 Chapter 7 - Roots, Radicals, and Complex Numbers 7.1 Roots and Radicals 7.1.1 Notation and Terminology In the expression x the is called the radical sign. The expression under the
Math 233 - Spring 2009 Chapter 7 - Roots, Radicals, and Complex Numbers 7.1 Roots and Radicals 7.1.1 Notation and Terminology In the expression x the is called the radical sign. The expression under the
ALGEBRA REVIEW LEARNING SKILLS CENTER. Exponents & Radicals
 ALGEBRA REVIEW LEARNING SKILLS CENTER The "Review Series in Algebra" is taught at the beginning of each quarter by the staff of the Learning Skills Center at UC Davis. This workshop is intended to be an
ALGEBRA REVIEW LEARNING SKILLS CENTER The "Review Series in Algebra" is taught at the beginning of each quarter by the staff of the Learning Skills Center at UC Davis. This workshop is intended to be an
Maths Workshop for Parents 2. Fractions and Algebra
 Maths Workshop for Parents 2 Fractions and Algebra What is a fraction? A fraction is a part of a whole. There are two numbers to every fraction: 2 7 Numerator Denominator 2 7 This is a proper (or common)
Maths Workshop for Parents 2 Fractions and Algebra What is a fraction? A fraction is a part of a whole. There are two numbers to every fraction: 2 7 Numerator Denominator 2 7 This is a proper (or common)
Session 29 Scientific Notation and Laws of Exponents. If you have ever taken a Chemistry class, you may have encountered the following numbers:
 Session 9 Scientific Notation and Laws of Exponents If you have ever taken a Chemistry class, you may have encountered the following numbers: There are approximately 60,4,79,00,000,000,000,000 molecules
Session 9 Scientific Notation and Laws of Exponents If you have ever taken a Chemistry class, you may have encountered the following numbers: There are approximately 60,4,79,00,000,000,000,000 molecules
Lagrange Interpolation is a method of fitting an equation to a set of points that functions well when there are few points given.
 Polynomials (Ch.1) Study Guide by BS, JL, AZ, CC, SH, HL Lagrange Interpolation is a method of fitting an equation to a set of points that functions well when there are few points given. Sasha s method
Polynomials (Ch.1) Study Guide by BS, JL, AZ, CC, SH, HL Lagrange Interpolation is a method of fitting an equation to a set of points that functions well when there are few points given. Sasha s method
Graphing Calculator Workshops
 Graphing Calculator Workshops For the TI-83/84 Classic Operating System & For the TI-84 New Operating System (MathPrint) LEARNING CENTER Overview Workshop I Learn the general layout of the calculator Graphing
Graphing Calculator Workshops For the TI-83/84 Classic Operating System & For the TI-84 New Operating System (MathPrint) LEARNING CENTER Overview Workshop I Learn the general layout of the calculator Graphing
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring
 1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
THE TRANSPOSING METHOD IN SOLVING LINEAR EQUATIONS (Basic Step to improve math skills of high school students) (by Nghi H. Nguyen Jan 06, 2015)
 THE TRANSPOSING METHOD IN SOLVING LINEAR EQUATIONS (Basic Step to improve math skills of high school students) (by Nghi H. Nguyen Jan 06, 2015) Most of the immigrant students who first began learning Algebra
THE TRANSPOSING METHOD IN SOLVING LINEAR EQUATIONS (Basic Step to improve math skills of high school students) (by Nghi H. Nguyen Jan 06, 2015) Most of the immigrant students who first began learning Algebra
Calculate Highest Common Factors(HCFs) & Least Common Multiples(LCMs) NA1
 Calculate Highest Common Factors(HCFs) & Least Common Multiples(LCMs) NA1 What are the multiples of 5? The multiples are in the five times table What are the factors of 90? Each of these is a pair of factors.
Calculate Highest Common Factors(HCFs) & Least Common Multiples(LCMs) NA1 What are the multiples of 5? The multiples are in the five times table What are the factors of 90? Each of these is a pair of factors.
Algebra I Credit Recovery
 Algebra I Credit Recovery COURSE DESCRIPTION: The purpose of this course is to allow the student to gain mastery in working with and evaluating mathematical expressions, equations, graphs, and other topics,
Algebra I Credit Recovery COURSE DESCRIPTION: The purpose of this course is to allow the student to gain mastery in working with and evaluating mathematical expressions, equations, graphs, and other topics,
Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c
 4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
Factoring Flow Chart
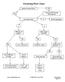 Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
What are the place values to the left of the decimal point and their associated powers of ten?
 The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in geometry and algebra. (Everything
The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in geometry and algebra. (Everything
Chapter 9. Systems of Linear Equations
 Chapter 9. Systems of Linear Equations 9.1. Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing KYOTE Standards: CR 21; CA 13 In this section we discuss how to solve systems of two linear equations in two variables
Chapter 9. Systems of Linear Equations 9.1. Solve Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing KYOTE Standards: CR 21; CA 13 In this section we discuss how to solve systems of two linear equations in two variables
Welcome to Basic Math Skills!
 Basic Math Skills Welcome to Basic Math Skills! Most students find the math sections to be the most difficult. Basic Math Skills was designed to give you a refresher on the basics of math. There are lots
Basic Math Skills Welcome to Basic Math Skills! Most students find the math sections to be the most difficult. Basic Math Skills was designed to give you a refresher on the basics of math. There are lots
SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
 (Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
(Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
Big Bend Community College. Beginning Algebra MPC 095. Lab Notebook
 Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
A Systematic Approach to Factoring
 A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives. Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers.
 Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Pre-Algebra Lecture 6
 Pre-Algebra Lecture 6 Today we will discuss Decimals and Percentages. Outline: 1. Decimals 2. Ordering Decimals 3. Rounding Decimals 4. Adding and subtracting Decimals 5. Multiplying and Dividing Decimals
Pre-Algebra Lecture 6 Today we will discuss Decimals and Percentages. Outline: 1. Decimals 2. Ordering Decimals 3. Rounding Decimals 4. Adding and subtracting Decimals 5. Multiplying and Dividing Decimals
Algebra I Teacher Notes Expressions, Equations, and Formulas Review
 Big Ideas Write and evaluate algebraic expressions Use expressions to write equations and inequalities Solve equations Represent functions as verbal rules, equations, tables and graphs Review these concepts
Big Ideas Write and evaluate algebraic expressions Use expressions to write equations and inequalities Solve equations Represent functions as verbal rules, equations, tables and graphs Review these concepts
MBA Jump Start Program
 MBA Jump Start Program Module 2: Mathematics Thomas Gilbert Mathematics Module Online Appendix: Basic Mathematical Concepts 2 1 The Number Spectrum Generally we depict numbers increasing from left to right
MBA Jump Start Program Module 2: Mathematics Thomas Gilbert Mathematics Module Online Appendix: Basic Mathematical Concepts 2 1 The Number Spectrum Generally we depict numbers increasing from left to right
Integers are positive and negative whole numbers, that is they are; {... 3, 2, 1,0,1,2,3...}. The dots mean they continue in that pattern.
 INTEGERS Integers are positive and negative whole numbers, that is they are; {... 3, 2, 1,0,1,2,3...}. The dots mean they continue in that pattern. Like all number sets, integers were invented to describe
INTEGERS Integers are positive and negative whole numbers, that is they are; {... 3, 2, 1,0,1,2,3...}. The dots mean they continue in that pattern. Like all number sets, integers were invented to describe
How do you compare numbers? On a number line, larger numbers are to the right and smaller numbers are to the left.
 The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems I
 RP7-1 Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems I Pages 46 48 Standards: 7.RP.A. Goals: Students will write equivalent statements for proportions by keeping track of the part and the whole, and by solving
RP7-1 Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems I Pages 46 48 Standards: 7.RP.A. Goals: Students will write equivalent statements for proportions by keeping track of the part and the whole, and by solving
Math 10C. Course: Polynomial Products and Factors. Unit of Study: Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address. Guiding Questions:
 Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
No Solution Equations Let s look at the following equation: 2 +3=2 +7
 5.4 Solving Equations with Infinite or No Solutions So far we have looked at equations where there is exactly one solution. It is possible to have more than solution in other types of equations that are
5.4 Solving Equations with Infinite or No Solutions So far we have looked at equations where there is exactly one solution. It is possible to have more than solution in other types of equations that are
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS
 MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
2 Integrating Both Sides
 2 Integrating Both Sides So far, the only general method we have for solving differential equations involves equations of the form y = f(x), where f(x) is any function of x. The solution to such an equation
2 Integrating Both Sides So far, the only general method we have for solving differential equations involves equations of the form y = f(x), where f(x) is any function of x. The solution to such an equation
Unit 1 Number Sense. In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions.
 Unit 1 Number Sense In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions. BLM Three Types of Percent Problems (p L-34) is a summary BLM for the material
Unit 1 Number Sense In this unit, students will study repeating decimals, percents, fractions, decimals, and proportions. BLM Three Types of Percent Problems (p L-34) is a summary BLM for the material
Florida Math 0028. Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper
 Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
(Refer Slide Time: 2:03)
 Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 11 Models of Industrial Control Devices and Systems (Contd.) Last time we were
Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 11 Models of Industrial Control Devices and Systems (Contd.) Last time we were
PREPARATION FOR MATH TESTING at CityLab Academy
 PREPARATION FOR MATH TESTING at CityLab Academy compiled by Gloria Vachino, M.S. Refresh your math skills with a MATH REVIEW and find out if you are ready for the math entrance test by taking a PRE-TEST
PREPARATION FOR MATH TESTING at CityLab Academy compiled by Gloria Vachino, M.S. Refresh your math skills with a MATH REVIEW and find out if you are ready for the math entrance test by taking a PRE-TEST
Factoring and Applications
 Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
1.2 Linear Equations and Rational Equations
 Linear Equations and Rational Equations Section Notes Page In this section, you will learn how to solve various linear and rational equations A linear equation will have an variable raised to a power of
Linear Equations and Rational Equations Section Notes Page In this section, you will learn how to solve various linear and rational equations A linear equation will have an variable raised to a power of
Pre-Algebra - Order of Operations
 0.3 Pre-Algebra - Order of Operations Objective: Evaluate expressions using the order of operations, including the use of absolute value. When simplifying expressions it is important that we simplify them
0.3 Pre-Algebra - Order of Operations Objective: Evaluate expressions using the order of operations, including the use of absolute value. When simplifying expressions it is important that we simplify them
