Dorsal scapular nerve Long thoracic nerve Nerve to subclavius Suprascapular nerve. The Clavicle. Branches
|
|
|
- Angelina Shields
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Courses of Nerves and Vessels in the Upper Limb STRUCTURE OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS, and the consequences of injuries thereto Branches: Posterior cord = 5 branches Lateral cord = 3 branches Medial cord = 5 branches Thoracodorsal nerve Upper and lower subscapular nerves Supraclavicular branches Dorsal scapular nerve Long thoracic nerve Nerve to subclavius Suprascapular nerve The Clavicle Branches Cords Divisions Trunks Roots Medial pectoral nerve Medial brachial cutaneous Medial antebrachial cutaneous Three little trivial nerves Injuries of the Brachial Plexus: Superior parts: C5, C6: Erb-Duchenne Palsy - caused by an increased angle between neck and shoulder, eg. falling on your head. - Causes Waiter s Tip position, where the limb hangs limp in a medially rotated position - Deltoid, biceps, brachialis and brachioradialis are paralysed. Lateral arm loses sensation Compression of the Cords Anterior divisions supply flexors Posterior divisions supply extensors - Caused by prolonged hyperabduction, eg. painting the ceiling; cords get pinched between coracoid process and pectoralis minor tendon - Causes pain radiating down the arm, hand numbness, hand weakness, and erythema Inferior parts: C8, T1: Klumpke Paralysis - caused when the arm is suddenly pulled superiorly, eg. when you grab something while falling vertically down - short muscles of the hand are affected, and you get a claw hand
2 RELATIONSHIPS OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS Medial Scalene Anterior Scalene ROOTS enter the neck between the bodies of the Anterior Scalene and the Medial Scalene muscles TRUNKS enter the apex of axilla throught the cervicoaxillary canal DIVISIONS form behind the clavicle, in the cervicoaxillary canal Subclavian artery 1 st rib CORDS Form around the second part of the axillary artery, and are named according to their position in relation to it. Axillary nerve Which curves upward to innervate the Deltoid and Teres Minor muscles Posterior circumflex humeral artery Quadrangular space Posterior cord Lateral cord Medial cord Clavicle Axillary artery: second part Radial nerve Profunda Brachii: Deep Artery of the arm Lateral Triangular Space Musculocutaneous nerve Which pierces the coracobrachialis around here, and innervates the anterior compartment of the arm Ulnar nerve Which lies medial to the brachial artery Median nerve Which continues down the arm lateral to the brachial artery Brachial artery
3 SUPPLY DISTRIBUTION OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS Lateral cord Lateral pectoral nerve MUSCULOCUTANEOUS NERVE Pectoralis major Anterior compartment of the arm: Biceps, coracobrachialis, brachialis Skin over the lateral forearm, once it becomes cutaneous in the cubital fossa MEDIAN NERVE Anterior compartment of the forearm: EXCEPT for the ulnar part of flexor digitorum profundis Thenar muscles: EXCEPT adductor pollicis and the deep part of flexor pollicis brevis First and second lumbricals Medial cord Posterior cord Lateral cord: lateral pectoral nerve MUSCULOCUTANEOUS NERVE lateral root of MEDIAN NERVE o Medial cord forms Medial cutaneous nerve of arm Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm Medial pectoral nerve ULNAR NERVE Upper subscapular nerve medial root of MEDIAN NERVE medial pectoral nerve medial cutaneous nerve of arm Teres minor medial cutaneous nerve of forearm ULNAR NERVE Lower subscapular nerve AXILLARY NERVE Skin on the medial surface of arm up to the elbow Skin on the medial surface of forearm up to the elbow Pectoralis minor and sternocostal part of pectoralis major Intrinsic muscles of the hand, EXCEPT 1 st and 2 nd lumbricals and three of the thenar muscles Flexor carpi ulnaris Ulnar half of the flexor digitorum profundis to the pinky and ring fingers Superior half of subscapularis Inferior half of subscapularis AND teres major Glenohumeral joint Deltoid Skin over the deltoid RADIAL NERVE o o Thoracodorsal nerve o o Posterior cord forms: Long Thoracic nerve ALL MUSCLES IN THE POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT OF THE ARM AND FOREARM Ski over posterior and inferolateral forearm Some of the dorsum of the hand Latissimus Dorsi Serratus anterior Supraclavicular branches Dorsal scapular nerve Nerve to subclavius Suprascapular nerve Rhomboids; levator scapulae Subclavius and sternoclavicular joint Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Glenohumeral joint
4 Course of the Median Nerve Forms from the MEDIAL and LATERAL cords of the brachial plexus Runs lateral to the brachial artery Sits on top of the coracobrachialis muscle Coracobrachialis Crosses anteriorly over the brachial artery when it encounters the brachialis muscle Then, runs medial to the brachial artery Brachialis Runs under the biceps into the cubital fossa Biceps Cubital fossa Gives a branch to the elbow joint; THERE ARE NO OTHER BRANCHES ABOVE THE ELBOW Gives branches to the anterior compartment muscles of the forearm Gives rise to the ANTERIOR INTEROSSEOUS NERVE Interosseous membrane The ANTERIOR INTEROSSEOUS NERVE Runs between the flexor digitorum profundis and the flexor pollicis longus, on top of the interosseous membrane, until it hit pronator quadratus. Flexor pollicis longus Palmar cutaneous branch to the skin of the palm Enters the arm between the heads of pronator teres Travels down the forearm between the two flexor digitorum muscles Flexor digitorum profundis Flexor digitorum superficialis Becomes superficial at the wrist Flexor Retinaculum Recurrent branch to the thenar muscles Supplies the 1 st and 2 nd lumbrical muscles
5 Course of the Radial Nerve Starts as the direct continuation of the posterior cord Runs posterior to the brachial artery, On top of the long head of the triceps Gives branches to innervate the long head and the lateral head of tripceps brachii BEFORE it crosses the humerus Crosses the humerus in the RADIAL GROOVE with the deep artery of the arm Inside the radial groove, behind the triceps, it gives rise to the posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm and the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm, which pierce the lateral head of the triceps The branch to the medial head of the triceps also branches off behind the humerus Triceps Brachii, long head Brachial artery Deep artery of the arm After crossing the humerus, it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum and descends between the brachialis and the brachioradialis Lateral intermuscular septum Brachioradialis At the level of the lateral condyle, in the cubital fossa, it divides into the deep and the superficial branches BRACHIALIS RADIAL NERVE LESIONS Fracture of the HUMERUS: wrist drop due to extensor paralysis, as well as a loss of sensation on the dorsum of the hand Damage to the DEEP BRANCH: Inability to extend the thumb and to extend the MCP joints of the digits- but NO SENSORY LOSS Damage o the superficial branch usually only results in a tiny area of anaesthesia because of the overlap in median and ulnar nerve territories The SUPERFICIAL BRANCH runs under brachioradialis all the way down the arm The DEEP BRANCH pierces the supinator Still Brachioradialis Supinator Beyond the supinator, the DEEP BRANCH becomes the POSTERIOR INTEROSSEOUS NERVE The SUPERFICIAL BRANCH Eventually becomes superficial when it emerges from beneath brachioradialis, crosses the roof of the anatomical snuffbox, and innervates the dorsal skin of the hand the POSTERIOR INTEROSSEOUS NERVE winds laterally behind the radius and enters the posterior compartment of the forearm In the posterior compartment, it runs along the interosseous membrane to innervate the extensor muscles
6 Course of the Ulnar Nerve Arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus Runs medial to the brachial artery Superior ulnar collateral artery Medial intermuscular septum Together with the superior ulnar collateral artery, it pierces the medial intermuscular septum - around the middle of the humerus and then continues down the arm on top of the medial head of triceps brachii Triceps brachii: medial head Travels behind the medial epicondyle, where it is superficial and vulnerable ( funny bone ) Gives a branch to the elbow joint Enters the arm between the two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor carpi ulnaris Gives branches to innervate the two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris the Palmar Cutaneous Branch of the ulnar nerve arises midway along the arm, and travels under the antebrachial fascia directly above the ulnar artery Then, travels down the arm between the flexor carpi ulnaris and the flexor digitorum profundis FCU Gives a branch to innervate the ulnar 2 digits worth of flexor digitorum profundis the Palmar Cutaneous Branch pierces the antebrachial fascia in the distal third of the arm and innervates the skin of the ulnar half of the palm Antebrachial fascia Ulnar artery Pisiform Hook of Hamate Travels on the radial side of the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon Crosses under the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon together with the ulnar artery at the level of the wrist Passes between the hook of hamate and the pisiform (in Guyons canal) to enter the hand
7 Arteries of the Arm The AXILLARY ARTERY begins at the border of the 1 st rib as a continuation of the subclavian artery The FIRST PART stretches between the 1 st rib and the medial border of pectoralis minor. It has only one branch the superior thoracic artery The SECOND PART lies under the pectoralis minor; it has 2 branches: - The Thoracoacromial artery - The Lateral Thoracic artery The THIRD PART stretches from the lateral border of pectoralis minor to the inferior border of Teres Major; it has 3 branches: - The Anterior circumflex humeral artery - The Posteror circumflex humeral artery - The Subscapular artery Axillary nerve Posterior - circumflex humeral artery Travels through the quadrangular space together with the axillary nerve. It s the larger of the two. Anterior circumflex humeral artery Passes laterally deep to the coracobrachialis and the biceps brachii Profunda Brachii- deep artery of the arm Passes through the lateral triangular space (with the radial nerve) into the posterior compartment of the arm. It is the largest branch of the Brachial artery Under the bicipital aponeurosis, the brachial artery divides into the Radial and Ulnar arteries Subclavian artery First rib Superior thoracic artery Thoracoacromial artery Which pierces the costocoracoid membrane deep to the clavicular head of pectoralis major Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor Lateral Thoracic artery Which follows the lateral border of pectoralis minor onto the chest wall Circumflex scapular artery Teres Major Passes dorsally between subscapularis and teres major to supply the dorsum of the scapula Thoracodorsal artery Goes to the inferior angle of the scapula, Triceps brachii supplies mainly the latissimus dorsi Intermuscular septum Subscapular artery The branch with the greatest diameter but the Biceps brachii shortest length; soon divides into the thoracodorsal and the circumflex scapular arteries BRACHIAL ARTERY Travels from the edge of Teres Major to the cubital fossa, on top of the medial intermuscular septum. Has 3 main branches: Deep artery of the arm Superior ulnar collateral artery which accompanies the ulnar nerve down the arm Inferior ulnar collateral artery which arises 5cm proximal to the elbow crease, and anastomoses with the recurrent branches of the ulnar artery Radial Artery Travels down the arm under the brachioradialis, along with the radial nerve. Lies lateral to the flexor carpi radialis tendon. Gives a recurrent branch. Flexor carpi radialis tendon Brachioradialis The Radial Artery winds around dorsally, crosses the floor of the anatomical snuffbox and pierces the 1 st dorsal interossei to enter the palm between the two heads of adductor pollicis. Ulnar Artery Gives some recurrent branches, and then travels down the arm under the superficial muscles of the forearm (deep to the pronator teres, palmaris longus, and flexor digitorum superficialis) Common interosseous artery is very short, because it bifurcates immediately Anterior interosseous artery travels down the arm along the interosseous membrane, and when it reaches pronator quadratus, it pierces the interosseous membrane and becomes dorsal (where it joins the dorsal carpal arch) Posterior interosseous artery travels down the arm along the interosseous membrane, and anastomoses with the anterior interosseous artery when they meet. Superficial group of forearm flexors Palmar carpal arch: anastomosis of the palmar carpal branches of the ulnar and radial arteries Dorsal carpal arch: anastomosis of the dorsal carpal branches of the ulnar and radial arteries Deep palmar arch: the more proximal arch - A continuation of the radial artery Superficial palmar arch: the more distal arch - A continuation of the ulnar artery
8 Arterial Anastomosis around the Scapula Thyrocervical artery Suprascapular artery Subclavian artery Subscapular artery Dorsal scapular artery Which is also the deep branch of the transverse cervical artery Thoracodorsal artery Circumflex scapular artery This point is labored because: If the axillary artery is cut or ligated, an adequate collateral blood supply will arrive to the arm via the dorsal scapular artery, and its anastomosis with the circumflex scapular artery. However, if the axillary artery is ligated BELOW the third part of the axillary artery, there will not be any collaterals, and the arm will become ischaemic.
9 Arterial Arches of the Hand Proper palmar digital arteries Common palmar digital arteries Arise from the superficial arch Palmar metacarpal arteries Arise from the deep arch Ulnar artery divides into the SUPERFICIAL and the DEEP Palmar arches Princeps Pollicis artery Anatomical snuffbox Guyons canal Superficial branch of the radial artery Joins the superficial palmar arch Dorsal branch of the radial artery Joins the deep palmar arch Ulnar Artery Enters the hand via Guyons canal, between the hook of hamate and the pisiform Branch to anterior interosseous artery Radial Artery Hooks around the scaphoid and trapezium and enters the palm between the 1 st and 2 nd metacarpals Dorsal digital arteries Perforating branches, which join the deep palmar arch Dorsal carpal arch Ulnar Artery Branch to anterior interosseous artery Radial Artery
10 Veins and lymphatic drainage patterns of the upper limb Piercing the costacoracoid membrane- part of the clavipectoral fascia Cephalic vein: - spends all of its time in subcutaneous tissues - drains the radial dorsum of hand Basilic vein: - is subcutaneous right up until the middle of the biceps; then it dives deep and runs parallel to the brachial artery - drains the ulnar dorsum of the hand both merge to form the axillary vein Piercing the brachial fascia Median cubital vein: - communicates between the two in the cubital fossa Antebrachial vein: - highly variable - begins at the dorsum of the thumb - sometimes divides into a median basilic vein, which joins the basilic vein, and a median cephalic vein, which joins the cephalic vein. o o DRAINAGE OF THE PALM PASSES INTO THE DORSUM OF THE HAND Vessels converge mainly on the basilic, but also the cephalic vein o Subclavian lymphatic trunk Apical axillary nodes nodes Humeral (lateral) nodes Basilic vein Cubital lymph nodes Deltopectoral nodes Basilic vein Ascend the arm next to the superficial veins Dorsum of hand palm cephalic vein The superficial lymphatics follow the superficial veins, mainly the basilic. Theis also the deep lymphatic system, which follows the deep veins, and this system of lymph vessels terminates at the humeral lymph nodes. The deep system drains all the joints tendons and nerves.
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
GROSS ANATOMY. Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs. Lecture Syllabus 2008
 GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
The Muscular System. Appendicular Musculature
 11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Anatomical Consideration and Brachial Plexus Anesthesia. Anatomy
 Brachial Plexus Anesthesia There are four approaches to the brachial plexus. These include the interscalene, supraclavicular, infraclavicular, and axillary approach. For the purposes of this lecture we
Brachial Plexus Anesthesia There are four approaches to the brachial plexus. These include the interscalene, supraclavicular, infraclavicular, and axillary approach. For the purposes of this lecture we
Muscles of the Forearm and Hand
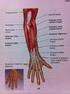 8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Brachial Plexopathy, an overview
 Brachial Plexopathy, an overview Learning Objectives: The brachial plexus is the network of nerves that originate from cervical and upper thoracic nerve roots and eventually terminate as the named nerves
Brachial Plexopathy, an overview Learning Objectives: The brachial plexus is the network of nerves that originate from cervical and upper thoracic nerve roots and eventually terminate as the named nerves
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
 TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis. Disclosures: None
 Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME
 EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
The Symptomatic Upper Extremity: An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis, Part 2
 Journal of the American Chiropractic Association May 1999 The Symptomatic Upper Extremity: An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis, Part 2 By David J. Schimp, DC, DACNB, DAAPM Dorsal scapular nerve entrapment:
Journal of the American Chiropractic Association May 1999 The Symptomatic Upper Extremity: An Algorithmic Approach to Diagnosis, Part 2 By David J. Schimp, DC, DACNB, DAAPM Dorsal scapular nerve entrapment:
Basic Concepts. Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG. Pathophysiology. Median Nerve. A Clinical Approach
 Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Upper Extremity Special Tests. Cervical Tests. TMJ Dysfunction
 Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
The material in this ebook also appears in the print version of this title: 0-07-148980-0.
 Case Files Anatomy Second Edition EUGENE C.TOY, MD The John S. Dunn, Senior Academic Chief and Program Director The Methodist Hospital-Houston Obstetrics and Gynecology Residency Program Houston,Texas
Case Files Anatomy Second Edition EUGENE C.TOY, MD The John S. Dunn, Senior Academic Chief and Program Director The Methodist Hospital-Houston Obstetrics and Gynecology Residency Program Houston,Texas
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
by joe muscolino body mechanics
 by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
Elbow & Forearm. Notes. Notes. Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics. Bones & Joints: Elbow & Forearm
 Elbow & Forearm Elbow & Forearm Notes Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics Notes Bones & Joints: The elbow joint is a combination of joints but common reference is usually to the articulation of the distal
Elbow & Forearm Elbow & Forearm Notes Lecture Slides - A.D.A.M. Lab Pics Notes Bones & Joints: The elbow joint is a combination of joints but common reference is usually to the articulation of the distal
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. II. Elbow
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines II. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines II. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Medical Report Checklist: Upper Extremities Peripheral Nerve Disorders Impairments (PND)
 http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain
 Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Scottish Adult Brachial Plexus Injury Service
 Scottish Adult Brachial Plexus Injury Service Information for Physiotherapists Scottish Adult Brachial Plexus Injury Service The Victoria Infirmary Langside Road, Glasgow G42 9TY BPI Service Administrator
Scottish Adult Brachial Plexus Injury Service Information for Physiotherapists Scottish Adult Brachial Plexus Injury Service The Victoria Infirmary Langside Road, Glasgow G42 9TY BPI Service Administrator
Upper limb injuries. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Pain in the limbs: May be classified under 4 headings: 1. Joint pain 2. Soft tissue pain 3. Neurogenic pain 4. Orthopaedic causes (fractures,
Upper limb injuries Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Pain in the limbs: May be classified under 4 headings: 1. Joint pain 2. Soft tissue pain 3. Neurogenic pain 4. Orthopaedic causes (fractures,
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys
 Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
Compression Neuropathies. Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM OMED 2013
 Compression Neuropathies Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM OMED 2013 Compression Neuropathies Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Spinal Accessory Nerve Upper/Lower Trunk Plexopathy Long Thoracic
Compression Neuropathies Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM OMED 2013 Compression Neuropathies Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Spinal Accessory Nerve Upper/Lower Trunk Plexopathy Long Thoracic
Coding for Difficult Tendon Repairs and Transfers. Current Procedural Terminology 2013 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved.
 Coding for Difficult Tendon Repairs and Transfers Rotator Cuff Repair 23420 February 2002 page 11 Code 23420 describes a repair of a complete shoulder (rotator) cuff avulsion, referring to the repair of
Coding for Difficult Tendon Repairs and Transfers Rotator Cuff Repair 23420 February 2002 page 11 Code 23420 describes a repair of a complete shoulder (rotator) cuff avulsion, referring to the repair of
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist
 http://www.pdratings.com/ AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist [L.C. 139.2 (J)-(2)&(3), (k)-(5), 4060(b)(1), 4062 (d)(2), 4068, 4620, 8 CCR WCAB 10606 & 8 CCR 9785] AMA Brachial
http://www.pdratings.com/ AMA Guides & California Code of Regulations P&S Report Checklist [L.C. 139.2 (J)-(2)&(3), (k)-(5), 4060(b)(1), 4062 (d)(2), 4068, 4620, 8 CCR WCAB 10606 & 8 CCR 9785] AMA Brachial
17 Forequarter Amputation
 Malawer Chapter 17 22/02/2001 08:32 Page 289 17 Forequarter Amputation Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW Forequarter amputation entails surgical removal of the entire upper extremity, scapula,
Malawer Chapter 17 22/02/2001 08:32 Page 289 17 Forequarter Amputation Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW Forequarter amputation entails surgical removal of the entire upper extremity, scapula,
Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand. Bony Anatomy. Objectives. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Objectives Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand Chapter 19 Identify and discuss the functional anatomy of the elbow and forearm Discuss the common injuries associated with these anatomical structures Bones Humerus
Objectives Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand Chapter 19 Identify and discuss the functional anatomy of the elbow and forearm Discuss the common injuries associated with these anatomical structures Bones Humerus
Boxing/Kickboxing Shoulder Injuries and Prevention
 Boxing/Kickboxing Shoulder Injuries and Prevention Dr. Paul Newhart, D.C. Kickboxing and boxing are an excellent workout regimen, as long as precautions are taken so as not to injure the shoulders, elbows
Boxing/Kickboxing Shoulder Injuries and Prevention Dr. Paul Newhart, D.C. Kickboxing and boxing are an excellent workout regimen, as long as precautions are taken so as not to injure the shoulders, elbows
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
Thank You for Your Support!
 Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed on the Internet with the goal of providing quality learning material at a low price to cover web operating expenses. This document is shareware,
Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed on the Internet with the goal of providing quality learning material at a low price to cover web operating expenses. This document is shareware,
Dimensional Massage Therapy Techniques for Soft-tissue Conditions of the Elbow and Radioulnar Joints, Hand and Wrist. AMTA National Convention
 Dimensional Massage Therapy Techniques for Soft-tissue Conditions of the Elbow and Radioulnar Joints, Hand and Wrist AMTA National Convention Date: Wednesday September 17, 2014 Place: Denver, CO By Nancy
Dimensional Massage Therapy Techniques for Soft-tissue Conditions of the Elbow and Radioulnar Joints, Hand and Wrist AMTA National Convention Date: Wednesday September 17, 2014 Place: Denver, CO By Nancy
Background Š Compression neuropathy: Nerve compression resulting in nerve dysfunction. Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments
 Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments Compression Neuropathies: Pathophysiology Scott P. Olvey, MD 1 2 Goals Understand peripheral nerve histology Understand the pathophysiology of peripheral nerve compression
Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapments Compression Neuropathies: Pathophysiology Scott P. Olvey, MD 1 2 Goals Understand peripheral nerve histology Understand the pathophysiology of peripheral nerve compression
Examination of the Elbow. Elbow Examination. Structures to Examine. Active Range of Motion. Active Range of Motion 8/22/2012
 Examination of the Elbow The elbow is a complex modified hinge joint The humero-ulnar joint is a hinge joint allowing flexion and extension The radio-ulnar joint allows for pronation and supination of
Examination of the Elbow The elbow is a complex modified hinge joint The humero-ulnar joint is a hinge joint allowing flexion and extension The radio-ulnar joint allows for pronation and supination of
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
7 Cubital Tunnel Release and Ulnar Nerve Transposition
 C H A P T E R 7 Cubital Tunnel Release and Ulnar Nerve Transposition Julia A. Kenniston and David R. Steinberg 70 Carpal tunnel syndrome is seen in 40% of patients with cubital tunnel syndrome. As it courses
C H A P T E R 7 Cubital Tunnel Release and Ulnar Nerve Transposition Julia A. Kenniston and David R. Steinberg 70 Carpal tunnel syndrome is seen in 40% of patients with cubital tunnel syndrome. As it courses
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks
 The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks Nikki Strauss Schroeder, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 4, 2013 Outline Surface Anatomy Hand Anatomy Exam Management of
The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks Nikki Strauss Schroeder, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 4, 2013 Outline Surface Anatomy Hand Anatomy Exam Management of
Shoulder Examination
 Shoulder Examination Summary Inspection Palpation Movement Special Tests Neurological examination Introduction Shoulder disorders are can be broadly classified into the following types: Pain Stiffness
Shoulder Examination Summary Inspection Palpation Movement Special Tests Neurological examination Introduction Shoulder disorders are can be broadly classified into the following types: Pain Stiffness
CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM
 Deep Tissue Massage CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 1 How to Complete this Program Thank you
Deep Tissue Massage CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 1 How to Complete this Program Thank you
Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone
 Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone In this article we wish to document some of the electrical stimulation techniques we use for the upper limb, primarily
Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone In this article we wish to document some of the electrical stimulation techniques we use for the upper limb, primarily
Whether a physician is
 ILLUSTRATIONS BY SCOT BODELL Hand and Wrist Injuries: Part I. Nonemergent Evaluation JAMES M. DANIELS II, M.D., M.P.H., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Quincy, Illinois ELVIN G. ZOOK,
ILLUSTRATIONS BY SCOT BODELL Hand and Wrist Injuries: Part I. Nonemergent Evaluation JAMES M. DANIELS II, M.D., M.P.H., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Quincy, Illinois ELVIN G. ZOOK,
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies
 Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
The Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand
 Elbow - Bones The Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Chapters 23 & 24 Humerus Distal end forms the medial & lateral condyles Lateral: capitulum Medial: trochlea Radius Ulna Sports Medicine II Elbow - Bones
Elbow - Bones The Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Chapters 23 & 24 Humerus Distal end forms the medial & lateral condyles Lateral: capitulum Medial: trochlea Radius Ulna Sports Medicine II Elbow - Bones
Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies. Second Edition
 Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition This page intentionally left blank Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition Ralph M. Buschbacher, MD Nathan D. Prahlow, MD Indiana University
Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition This page intentionally left blank Manual of Nerve Conduction Studies Second Edition Ralph M. Buschbacher, MD Nathan D. Prahlow, MD Indiana University
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle
 Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex
 Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex MALCOLM PEAT The shoulder complex, together with other joint and muscle mechanisms of the upper limb, primarily is concerned with the ability to place and control
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex MALCOLM PEAT The shoulder complex, together with other joint and muscle mechanisms of the upper limb, primarily is concerned with the ability to place and control
Rotator Cuff Tears in Football
 Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation.
 Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Injuries to Upper Limb
 Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
SPLINTING THE HAND WITH A PERIPHERAL-NERVE INJURY
 Chapter 34 SPLINTING THE HAND WITH A PERIPHERAL-NERVE INJURY Judy C. Colditz Splinting the hand with a peripheral-nerve injury is both easy and difficult. The ease of splinting results from the readily
Chapter 34 SPLINTING THE HAND WITH A PERIPHERAL-NERVE INJURY Judy C. Colditz Splinting the hand with a peripheral-nerve injury is both easy and difficult. The ease of splinting results from the readily
WRIST EXAMINATION. Look. Feel. Move. Special Tests
 WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
Name the muscle, A: (Action), O: (Origin), and I: (Insertion)
 FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
NOW PLAYING THE WRIST. David Costa, OTR/L October 20, 2007
 NOW PLAYING THE WRIST David Costa, OTR/L October 20, 2007 Starring Radius Ulna Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrum Trapezium Trapezoid Capitate Hamate Pisiform TFCC Transverse Carpal Ligament Scapholunate Ligament
NOW PLAYING THE WRIST David Costa, OTR/L October 20, 2007 Starring Radius Ulna Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrum Trapezium Trapezoid Capitate Hamate Pisiform TFCC Transverse Carpal Ligament Scapholunate Ligament
Deltoid Trapezius. Identify the muscle pair(s) that work together to produce the movements listed above.
 Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
 F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. I. Shoulder
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapment Syndromes in Sports: an Update
 HEAD, NECK, AND SPINE Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapment Syndromes in Sports: an Update Shane Cass, DO Abstract Peripheral nerve entrapment syndromes are difficult diagnoses to make. Symptoms are often vague
HEAD, NECK, AND SPINE Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapment Syndromes in Sports: an Update Shane Cass, DO Abstract Peripheral nerve entrapment syndromes are difficult diagnoses to make. Symptoms are often vague
Completing the Loop: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury. Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC
 : Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
Management of brachial plexus injuries
 Management of brachial plexus injuries G. BLAAUW 1,R.S.MUHLIG 2, and J. W. VREDEVELD 3 1 Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital, Maastricht, The Netherlands 2 Rehabilitation Out-Patient Clinic,
Management of brachial plexus injuries G. BLAAUW 1,R.S.MUHLIG 2, and J. W. VREDEVELD 3 1 Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital, Maastricht, The Netherlands 2 Rehabilitation Out-Patient Clinic,
During routine dissection of an 81-year-old male embalmed. The Axillary Arch: Anatomy and Suggested Clinical Manifestations
 The Axillary Arch: Anatomy and Suggested Clinical Manifestations A. Russell Smith, Jr, PT, EdD, OCS, FAAOMPT 1 John P. Cummings, PT, PhD 2 The purpose of this commentary is to describe bilateral anomalous
The Axillary Arch: Anatomy and Suggested Clinical Manifestations A. Russell Smith, Jr, PT, EdD, OCS, FAAOMPT 1 John P. Cummings, PT, PhD 2 The purpose of this commentary is to describe bilateral anomalous
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
