Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle
|
|
|
- Eugene Washington
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-1 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-2 Key Acromionprocess Glenoid Lateral bony fossa landmarks Inferior Medial border angle Bones Superior Spine of the angle scapula From Shoulder girdle (scapulothoracic) scapula moves on the rib cage joint motion occurs at sternoclavicular joint & to a lesser amount at the acromioclavicular joint Seeley RR, Stephens TD, Tate P; anatomy and physiology, ed 7, New York, 2006, McGraw-Hill McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-3 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-4 Sternoclavicular (SC) (multiaxial) arthrodial classification anteriorly 15 degrees with protraction posteriorly 15 degrees with retraction superiorly 45 degrees with elevation inferiorly 5 degrees with depression Sternoclavicular (SC) Ligamentous support anteriorly by the anterior SC ligament posteriorly by the posterior SC ligament costoclavicular & interclavicular ligaments provide stability against superior displacement McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-5 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved
2 Acromioclavicular (AC) arthrodial classification 20- to 30-degree total gliding & rotational motion accompanying other shoulder girdle & shoulder joint motions supported by Coracoclavicular ligaments Superior acromioclavicular ligament Inferior acromioclavicular ligament often injured McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-7 Scapulothoracic not a true synovial joint does not have regular synovial features movement depends on SC & AC joints which allows the scapula to move 25-degrees abduction-adduction 60-degrees upward-downward rotation 55-degrees elevation-depression supported dynamically by its muscles no ligamentous support McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-8 Focus on specific bony landmarks inferior angle glenoid fossa acromion process Shoulder girdle movements = scapula movements Abduction (protraction) scapula moves laterally away from spinal column Adduction (retraction) scapula moves medially toward spinal column McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 4-9 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Downward rotation returning inferior angle inferomedially toward spinal column & glenoid fossa to normal position Upward rotation turning glenoid fossa upward & moving inferior angle superolaterally away from spinal column Depression downward or inferior movement, as in returning to normal position Elevation upward or superior movement, as in shrugging shoulders McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved
3 Shoulder joint & shoulder girdle work together in carrying out upper extremity activities Shoulder girdle movement is not dependent upon the shoulder joint & its muscles Shoulder girdle muscles Stabilize scapula so the shoulder joint muscles will have a stable base from which to exert force for moving the humerus Contract to maintain scapula in a relatively static position during shoulder joint actions Contract to move shoulder girdle & to enhance movement of upper extremity when shoulder goes through extreme ranges of motion McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved For some shoulder girdle movements, scapula must rotate or tilt on its axis Lateral tilt (outward tilt) during abduction scapula rotates about its vertical axis resulting in posterior movement of medial border & anterior movement of lateral border Medial tilt (return from lateral tilt, inward tilt) during extreme adduction scapula rotates about its vertical axis resulting in anterior movement of medial border & posterior movement of lateral border Anterior tilt (upward tilt) rotational movement of scapula about frontal axis occurring during glenohumeral hyperextension superior border moving anteroinferiorly & inferior angle moving posterosuperiorly Posterior tilt (downward tilt) rotational movement of scapula about frontal axis occurring during glenohumeral hyperflexion superior border moving posteroinferiorly & inferior angle moving anterosuperiorly McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Synergy with muscles of glenohumeral joint As shoulder joint goes through more extreme ranges of motion, scapular muscles contract to move shoulder girdle so that its glenoid fossa will be in a more appropriate position from which the humerus can move Without the accompanying scapula movement humerus can only be raised into approximately 90 degrees of total shoulder abduction & flexion Synergy with muscles of glenohumeral joint This works through the appropriate muscles of both joints working in synergy to accomplish the desired action of the entire upper extremity Ex. to raise our hand out to the side laterally as high as possible, the serratus anterior & trapezius (middle & lower fibers) muscles upwardly rotate scapula as supraspinatus & deltoid initiate glenohumeral abduction This synergy between scapula & shoulder joint muscles enhances movement of entire upper extremity McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved
4 Shoulder Girdle Adduction Downward Rotation Elevation Depression Upward Rotation Abduction 5 girdle All Do muscles originate movements primarily on axial involved skeleton & in insert shoulder Essential scapula shoulder not attach and/or joint providing actions to clavicle humerus do not cause on Muscles the base such scapula as of support throwing, so it for can batting, shoulder serve dynamic & as blocking joint a stability relative activities of McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved involved girdle -upper, muscles primarily Rhomboid middle, movements in lower shoulder Shoulder -deep Girdle Muscles Levatorscapula Serratus Pectoralis deep anterior minor - Shoulder Girdle Muscles Location & action Anterior Pectoralis minor abduction, downward rotation, & depression Subclavius depression Posterior & laterally Serratus anterior abduction & upward rotation McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Shoulder Girdle Muscles Location & action Posterior Upper fibers elevation & extension of the head Middle fibers elevation, adduction, & upper rotation Lower fibers adduction, depression, & upper rotation Rhomboid adduction, downward rotation, & elevation Levator scapulae elevation McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Upper fibers: elevation of scapula, extension & rotation of head Middle fibers: elevation, upward rotation, & adduction Lower fibers: depression, adduction, & upward rotation muscle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved
5 Elevates the medial margin of the scapula Levator scapulae muscle Rhomboid muscles - major & minor Rhomboid major & minor muscles work together Adduction (retraction): draw scapula toward spinal column Downward rotation: from upward rotated position they draw scapula in downward rotation Elevation: slight upward movement accompanying adduction McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Serratus anterior muscle Abduction (protraction): draws medial border of scapula away from vertebrae Upward rotation: longer, lower fibers tend to draw inferior angle of scapula farther away from vertebrae, thus rotating scapula upward slightly Pectoralis minor muscle Abduction (protraction): draws scapula forward & tends to tilt lower border away from ribs Downward rotation: as it abducts, it draws scapula downward Depression: when scapula is rotated upward, it assists in depression McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Stabilization & protection of sternoclavicular joint Depression Abduction Subclavius muscle Scapula Abduction Scapula move laterally away from spinous processes without rotation EX. Push-up & bench press Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved
6 Return from abduction Occurs with retractions Middle Rhomboids Scapula Adduction Lateral & upward movement Middle Lower Serratus anterior Scapula Upward Rotation McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Scapula Downward Rotation Downward & Medial Movement Glenoid Fossa is rotated downward when downward movement of shoulder joint occurs EX. Lat Pulls - pulling wt. down Pectoralis Minor Rhomboid Scapula Elevation Lifting scapula without rotation in anatomic position Shoulder Shrug Levator Scapula Upper Rhomboid McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved Scapula Depression EX. Dip Lower Pectoralis Minor McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle
 The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex
 Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex MALCOLM PEAT The shoulder complex, together with other joint and muscle mechanisms of the upper limb, primarily is concerned with the ability to place and control
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex MALCOLM PEAT The shoulder complex, together with other joint and muscle mechanisms of the upper limb, primarily is concerned with the ability to place and control
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Shoulder
 X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Shoulder Anatomy 3 Bones Humerus Scapula Clavicle 3 Joints Glenohumeral Acromioclavicular Sternoclavicular 1 Articulation Scapulothoracic Anatomy Humerus
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Shoulder Anatomy 3 Bones Humerus Scapula Clavicle 3 Joints Glenohumeral Acromioclavicular Sternoclavicular 1 Articulation Scapulothoracic Anatomy Humerus
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears. Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
Shoulder MRI for Rotator Cuff Tears Conor Kleweno,, Harvard Medical School Year III Goals of Presentation Shoulder anatomy Function of rotator cuff MRI approach to diagnose cuff tear Anatomy on MRI images
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
SCAPULAR FRACTURES. Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading.
 SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
SCAPULAR FRACTURES Jai Relwani, Shoulder Fellow, Reading Shoulder Unit, Reading. Aims Anatomy Incidence/Importance Mechanism Classification Principles of treatment Specific variations Conclusion Anatomy
Shoulder Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation for Health & Fitness Professionals
 s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Shoulder Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation for Health & Fitness Professionals with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Functional Anatomy 3 2. Scapulohumeral
s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Shoulder Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation for Health & Fitness Professionals with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Functional Anatomy 3 2. Scapulohumeral
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. I. Shoulder
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Structure and Function of the Hip
 Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
I tro r duct c io i n t o Exercise Technique
 Introduction to Exercise Technique Is Exercise Technique Important? It is the actual technique used for a resistance training exercise that determines; The precise movement pattern the body will be attempting
Introduction to Exercise Technique Is Exercise Technique Important? It is the actual technique used for a resistance training exercise that determines; The precise movement pattern the body will be attempting
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Diagnosis of Acromioclavicular Joint Injuries
 PO Box 15 Rocky Hill, CT 06067 (860) 463-9003 [email protected] www.chirocredit.com ChiroCredit.com is proud to present a section from one of our continuing education programs: Physical Diagnosis
PO Box 15 Rocky Hill, CT 06067 (860) 463-9003 [email protected] www.chirocredit.com ChiroCredit.com is proud to present a section from one of our continuing education programs: Physical Diagnosis
Muscles of the Spinal Column. Chapter 12
 Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
BRIDGET LAWLOR, PH.TH RESISTANCE TRAINING INJURIES THE ROTATOR CUFF INJURY WATCH. the glenoid cavity to the neck of the humerus.
 Common resistance training injuries shouldn't have to be common. In this article we re looking at causes and prevention of resistance training injuries and taking a closer look at the shoulder joint, and
Common resistance training injuries shouldn't have to be common. In this article we re looking at causes and prevention of resistance training injuries and taking a closer look at the shoulder joint, and
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY
 REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
Shoulder Injuries. Why Bother? QAS Injury Prevalence. Screening Injury 29.2% 12 month cumulative injury prevalence. Dr Simon Locke
 Shoulder Injuries Dr Simon Locke Why Bother? Are shoulder and upper limb injuries common? Some anatomy What, where, what sports? How do they happen? Treatment, advances? QAS Injury Prevalence Screening
Shoulder Injuries Dr Simon Locke Why Bother? Are shoulder and upper limb injuries common? Some anatomy What, where, what sports? How do they happen? Treatment, advances? QAS Injury Prevalence Screening
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation.
 Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles and prevent scapular elevation. Stephanie Blum July 13 th, 2014 Flow Studios, Chicago, IL Page 1 of 19 Abstract It s important to recognize where your
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
MANAGEMENT OF SCAPULAR DYSKINESIA
 MANAGEMENT OF SCAPULAR DYSKINESIA supplement to Comprehensive Approach to the Management of Scapular Dyskinesia in the Overhead Throwing Athlete UPMC Rehab Grand Rounds Fall 2012 1A. Scapular Clock at
MANAGEMENT OF SCAPULAR DYSKINESIA supplement to Comprehensive Approach to the Management of Scapular Dyskinesia in the Overhead Throwing Athlete UPMC Rehab Grand Rounds Fall 2012 1A. Scapular Clock at
Completing the Loop: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury. Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC
 : Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Shoulder Examination
 Shoulder Examination Summary Inspection Palpation Movement Special Tests Neurological examination Introduction Shoulder disorders are can be broadly classified into the following types: Pain Stiffness
Shoulder Examination Summary Inspection Palpation Movement Special Tests Neurological examination Introduction Shoulder disorders are can be broadly classified into the following types: Pain Stiffness
Pittsburgh Pirates Shoulder & Arm Care Manual
 Pittsburgh Pirates Shoulder & Arm Care Manual Compliments of Glossary of Medical Terms commonly used in these programs: Abduction: Movement of any extremity away from the midline of the body. (Example:
Pittsburgh Pirates Shoulder & Arm Care Manual Compliments of Glossary of Medical Terms commonly used in these programs: Abduction: Movement of any extremity away from the midline of the body. (Example:
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Manua l Therapy Technique s f or t he Shoulder. LCD R Joe Strunc e PT, DSc, OCS, FAAOMPT
 Manua l Therapy Technique s f or t he Shoulder LCD R Joe Strunc e PT, DSc, OCS, FAAOMPT Shoulde r Techniques GH Physiological Mvmts Flexion (Grade 4) Abduction (Grade 4) External Rotation (Grade 4) Internal
Manua l Therapy Technique s f or t he Shoulder LCD R Joe Strunc e PT, DSc, OCS, FAAOMPT Shoulde r Techniques GH Physiological Mvmts Flexion (Grade 4) Abduction (Grade 4) External Rotation (Grade 4) Internal
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
Bringing Back the Shoulders
 Bringing Back the Shoulders Mike Kamal Peak performance in competition should always be the primary goal of training. The unfortunate and sometimes unavoidable consequences of sport are fatigue, breakdown
Bringing Back the Shoulders Mike Kamal Peak performance in competition should always be the primary goal of training. The unfortunate and sometimes unavoidable consequences of sport are fatigue, breakdown
Important rehabilitation management concepts to consider for a postoperative physical therapy rtsa program are:
 : General Information: Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH) arthritis when it is associated with irreparable rotator cuff
: General Information: Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH) arthritis when it is associated with irreparable rotator cuff
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463
 Phase I Passive Range of Motion Phase (postop week 1-2) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory response Achieve gradual restoration of gentle active range of motion Enhance/ensure adequate scapular function
Phase I Passive Range of Motion Phase (postop week 1-2) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory response Achieve gradual restoration of gentle active range of motion Enhance/ensure adequate scapular function
Upper limb injuries. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Pain in the limbs: May be classified under 4 headings: 1. Joint pain 2. Soft tissue pain 3. Neurogenic pain 4. Orthopaedic causes (fractures,
Upper limb injuries Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Pain in the limbs: May be classified under 4 headings: 1. Joint pain 2. Soft tissue pain 3. Neurogenic pain 4. Orthopaedic causes (fractures,
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis
 Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions
 Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
More Joint & Bursa Injuries
 Unraveling the Mystery of Shoulder Pain: More Joint & Bursa Injuries Presented by Dr. Ben Benjamin Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. [email protected] 1 Thank You [email protected]
Unraveling the Mystery of Shoulder Pain: More Joint & Bursa Injuries Presented by Dr. Ben Benjamin Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. [email protected] 1 Thank You [email protected]
Upper Extremity Special Tests. Cervical Tests. TMJ Dysfunction
 Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
Postoperative Protocol For Posterior Labral Repair/ Capsular Plication-- Dr. Trueblood
 Postoperative Protocol For Posterior Labral Repair/ Capsular Plication-- Dr. Trueblood Indications: Posterior shoulder instability is a relatively uncommon finding in normal adult shoulders. The most common
Postoperative Protocol For Posterior Labral Repair/ Capsular Plication-- Dr. Trueblood Indications: Posterior shoulder instability is a relatively uncommon finding in normal adult shoulders. The most common
Overhead Throwing: A Strength & Conditioning Approach to Preventative Injury
 By: Michael E. Bewley, MA, CSCS, C-SPN, USAW-I, President, Optimal Nutrition Systems Strength & Conditioning Coach for Basketball Sports Nutritionist for Basketball University of Dayton Overhead Throwing:
By: Michael E. Bewley, MA, CSCS, C-SPN, USAW-I, President, Optimal Nutrition Systems Strength & Conditioning Coach for Basketball Sports Nutritionist for Basketball University of Dayton Overhead Throwing:
SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS
 EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column
 Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
technique The Arm Lines BODYREADING THE MERIDIANS @WORK ESSENTIAL SKILLS MYOFASCIAL TECHNIQUES By Thomas Myers
 technique ODYREDING THE MERIDINS @WORK ESSENTIL SKILLS MYOFSCIL TECHNIQUES The rm Lines y Thomas Myers In our continuing series on visual assessment via the natomy Trains lines, let us now explore odyreading
technique ODYREDING THE MERIDINS @WORK ESSENTIL SKILLS MYOFSCIL TECHNIQUES The rm Lines y Thomas Myers In our continuing series on visual assessment via the natomy Trains lines, let us now explore odyreading
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Case 2. 30 year old involved in a MVA complaining of chest pain. Bruising over the right upper chest. Your Diagnosis
 Case 2 30 year old involved in a MVA complaining of chest pain. Bruising over the right upper chest. Your Diagnosis Diagnosis: Posterior Sterno-clavicular dislocation [PSCD] A posterior sterno-clavicular
Case 2 30 year old involved in a MVA complaining of chest pain. Bruising over the right upper chest. Your Diagnosis Diagnosis: Posterior Sterno-clavicular dislocation [PSCD] A posterior sterno-clavicular
A BIOMECHANICAL COMPARISON OF THE FRONT AND REAR LAT PULL- DOWN EXERCISE
 A BIOMECHANICAL COMPARISON OF THE FRONT AND REAR LAT PULL- DOWN EXERCISE By GARY MICHAEL (GM) PUGH A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
A BIOMECHANICAL COMPARISON OF THE FRONT AND REAR LAT PULL- DOWN EXERCISE By GARY MICHAEL (GM) PUGH A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
Rotator Cuff Tears in Football
 Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Rehabilitation Guidelines For SLAP Lesion Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines For SLAP Lesion Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular surface of
Rehabilitation Guidelines For SLAP Lesion Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular surface of
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
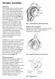 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED
 MOON SHOULDER GROUP ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED PROGRAM Introduction The Shoulder MOON group is a Multi-center Orthopaedic Outcomes Network, a consortium of institutions working together
MOON SHOULDER GROUP ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED PROGRAM Introduction The Shoulder MOON group is a Multi-center Orthopaedic Outcomes Network, a consortium of institutions working together
Biceps Tenodesis Protocol
 Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that has undergone
Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that has undergone
Spinal and shoulder complex posture. II: thoracic alignment and shoulder complex position in normal
 27- Spinal and shoulder complex posture. II: thoracic alignment and shoulder complex position in normal and osteoporotic women Elsie Culham and Malcolm Peat School of Rehabilitation Therapy, Queen s University,
27- Spinal and shoulder complex posture. II: thoracic alignment and shoulder complex position in normal and osteoporotic women Elsie Culham and Malcolm Peat School of Rehabilitation Therapy, Queen s University,
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on
Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Pilates for Breast Cancer Patients with Frozen Shoulder
 Pilates for Breast Cancer Patients with Frozen Shoulder Casey Canino February 1, 2015 New York Comprehensive Global Format September 19, 2014- January 18, 2015 ABSTRACT PILATES FOR BREAST CANCER PATIENTS
Pilates for Breast Cancer Patients with Frozen Shoulder Casey Canino February 1, 2015 New York Comprehensive Global Format September 19, 2014- January 18, 2015 ABSTRACT PILATES FOR BREAST CANCER PATIENTS
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Anterior Capsular Repair Rehabilitation Program Methodist Sports Medicine Center, Indianapolis, IN Department of Physical Therapy
 Anterior Capsular Repair Rehabilitation Program Methodist Sports Medicine Center, Indianapolis, IN Department of Physical Therapy Anterior Capsule reconstruction is a surgical procedure utilized for anterior
Anterior Capsular Repair Rehabilitation Program Methodist Sports Medicine Center, Indianapolis, IN Department of Physical Therapy Anterior Capsule reconstruction is a surgical procedure utilized for anterior
REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY
 William J. Robertson, MD UT Southwestern Orthopedics 1801 Inwood Rd. Dallas, TX 75390-8882 Office: (214) 645-3300 Fax: (214) 3301 billrobertsonmd.com REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY The shoulder is a ball
William J. Robertson, MD UT Southwestern Orthopedics 1801 Inwood Rd. Dallas, TX 75390-8882 Office: (214) 645-3300 Fax: (214) 3301 billrobertsonmd.com REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY The shoulder is a ball
Knee Injuries What are the ligaments of the knee?
 As sporting participants or observers, we often hear a variety of terms used to describe sport-related injuries. Terms such as sprains, strains and tears are used to describe our aches and pains following
As sporting participants or observers, we often hear a variety of terms used to describe sport-related injuries. Terms such as sprains, strains and tears are used to describe our aches and pains following
28% have partial tear of the rotator cuff.
 ROTATOR CUFF TENDON RUPTURE Anatomy: 1. Rotator cuff consists of: Subscapularis anteriorly, Supraspinatus superiorly and Infraspinatus and Teres minor posteriorly. 2 Biceps tendon is present in the rotator
ROTATOR CUFF TENDON RUPTURE Anatomy: 1. Rotator cuff consists of: Subscapularis anteriorly, Supraspinatus superiorly and Infraspinatus and Teres minor posteriorly. 2 Biceps tendon is present in the rotator
POSTERIOR CAPSULAR SHIFT REHABILITATION PROTOCOL
 POSTERIOR CAPSULAR SHIFT REHABILITATION PROTOCOL The goal of this rehabilitation program is to return the patient/athlete to their activity/sport as quickly and safely as possible while maintaining a stable
POSTERIOR CAPSULAR SHIFT REHABILITATION PROTOCOL The goal of this rehabilitation program is to return the patient/athlete to their activity/sport as quickly and safely as possible while maintaining a stable
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Rotator Cuff Repair
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body
 SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body Perform each exercise: 30 secs each x 2 rounds or 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps Monday & Wednesday or Tuesday & Thursday Standing Squat Muscles: glutes (butt), quadriceps (thigh) Stand
SAMPLE WORKOUT Full Body Perform each exercise: 30 secs each x 2 rounds or 2-3 sets of 8-12 reps Monday & Wednesday or Tuesday & Thursday Standing Squat Muscles: glutes (butt), quadriceps (thigh) Stand
PN 001-6979 Rev. A (08/21/06) The Bowflex Xtreme SE Home Gym Owner s Manual and Fitness Guide
 PN 001-6979 Rev. A (08/21/06) The Bowflex Xtreme SE Home Gym Owner s Manual and Fitness Guide CONGRATULATIONS on your commitment to improving your health and fitness! With the Bowflex Xtreme SE home gym,
PN 001-6979 Rev. A (08/21/06) The Bowflex Xtreme SE Home Gym Owner s Manual and Fitness Guide CONGRATULATIONS on your commitment to improving your health and fitness! With the Bowflex Xtreme SE home gym,
Terminology of Human Walking From North American Society for Gait and Human Movement 1993 and AAOP Gait Society 1994
 Gait Cycle: The period of time from one event (usually initial contact) of one foot to the following occurrence of the same event with the same foot. Abbreviated GC. Gait Stride: The distance from initial
Gait Cycle: The period of time from one event (usually initial contact) of one foot to the following occurrence of the same event with the same foot. Abbreviated GC. Gait Stride: The distance from initial
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics
 Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Direct 3-dimensional measurement of scapular kinematics during dynamic movements in vivo
 Direct 3-dimensional measurement of scapular kinematics during dynamic movements in vivo Philip W. McClure, PhD, PT, a Lori A. Michener, MEd, PT, ATC, b Brian J. Sennett, MD, c and Andrew R. Karduna, PhD,
Direct 3-dimensional measurement of scapular kinematics during dynamic movements in vivo Philip W. McClure, PhD, PT, a Lori A. Michener, MEd, PT, ATC, b Brian J. Sennett, MD, c and Andrew R. Karduna, PhD,
ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED PROGRAM
 ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information
ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED PROGRAM Contact us! Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200 1215 21st Avenue South Nashville, TN 37232-8828 For more information
Understanding Planes and Axes of Movement
 Understanding Planes and Axes of Movement Terminology When describing the relative positions of the body parts or relationship between those parts it is advisable to use the same standard terminology.
Understanding Planes and Axes of Movement Terminology When describing the relative positions of the body parts or relationship between those parts it is advisable to use the same standard terminology.
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Arthroscopic Capsular Shift
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Arthroscopic Capsular Shift The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Arthroscopic Capsular Shift The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared to a golf ball on a tee. This is because the articular
Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella
 Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella Purpose: To increase knee extension. Precautions: Do not compress the patella against the femoral condyles. Do not force the knee into hyperextension
Patellofemoral Joint: Superior Glide of the Patella Purpose: To increase knee extension. Precautions: Do not compress the patella against the femoral condyles. Do not force the knee into hyperextension
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Long head of bicep Acromion Figure 1 Shoulder anatomy Supraspinatus Image Copyright 2010 UW Health Sports Medicine Center. Short head of bicep
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Long head of bicep Acromion Figure 1 Shoulder anatomy Supraspinatus Image Copyright 2010 UW Health Sports Medicine Center. Short head of bicep
Posture. Let s look at. in the head is jutting. the norm. you know if your belt. If you belt. lower body. 2 sections, upper. pulls?
 Fixing the Computer Guy Posture Lower back/h hip stability Let s look at ideal posture for a minute. Look at your profile in the mirror. Chances are you re gonna find that your head is jutting forward,
Fixing the Computer Guy Posture Lower back/h hip stability Let s look at ideal posture for a minute. Look at your profile in the mirror. Chances are you re gonna find that your head is jutting forward,
