The Emerging Power Crisis in Embedded Processors: What can a (poor) Compiler do?
|
|
|
- Anis Carroll
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Emerging Power Crisis in Embedded Processors: What can a (poor) Compiler do? L. N. Chakrapani College of Computing Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia, P. Korkmaz, V. J. Mooney III, K. V. Palem, K. Puttaswamy School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia, W. F. Wong Dept. of Computer Science National University of Singapore Singapore Abstract It is widely acknowledged that even as VLSI technology advances, there is a looming crisis that is an important obstacle to the widespread deployment of mobile embedded devices, namely that of power. This problem can be tackled at many levels like devices, logic, operating systems, microarchitecture and compiler. While there have been various proposals for specific compiler optimizations for power, there has not been any attempt to systematically map out the space for possible improvements. In this paper, we quantitatively characterize the limits of what a compiler can do in optimizing for power using precise modeling of a state-of-the-art embedded processor in conjunction with a robust compiler. We provide insights to how compiler optimizations interact with the internal workings of a processor from the perspective of power consumption. The goal is to point out the promising and not so promising directions of work in this area, to guide the future compiler designer. 1. Introduction The widespread deployment of embedded processors in mobile devices promises to open up new frontiers in applications. However, an important barrier that can severely limit this development is the issue of power consumption. An energy efficient device, i.e. one that consumes low amount of power over time, can potentially last longer and would require less bulky power supply units. In most devices, the computing element accounts for a high portion of the energy consumption [1]. This is a well-known issue and is being attacked from various fronts. Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. To copy otherwise, or republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. CASES 01, November 16-17, 2001, Atlanta, Georgia, USA. Copyright 2001 ACM /01/0011 $5.00. First is the design of low power VLSI devices and logic. It is well known that these make the most significant contribution to saving power. Next is the use of novel micro-architecture techniques such as voltage scaling. The third front is in the software runtime system like the operating system, which can utilize power saving microarchitectural features and schedule tasks accordingly. An obvious trick the operating system can play, for example, is to put the processor in a low power mode during idle periods. Lastly, given an application, a compiler can attempt to optimize it for power. It is this last issue, which this paper will address. There have been a number of studies on compiler optimizations for power, for example [4]. However, as far as we know, there are no systematic studies that address the following question: what phenomena in the interactions of the compiler, the application and the micro-architecture of a processor gives rise to energy savings? The main contributions of this paper are as follows: We present an integrated infrastructure consisting of a compiler and a gate-level model for a state-of-the-art embedded processor, namely an ARM-like processor [7], which we used to study precise energy consumption patterns. Actual power measurements on a StrongARM development board are also used to support our claims. We quantitatively characterize the subtle interactions that accounts for power savings achieved by compiler optimizations. We classify compiler optimizations into broad categories of how they achieve power savings and in doing so; point out the promising directions of research in this area. We point out the limitations compilers face in existing embedded processors when optimizing for power.
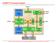
2 It is hoped that this exploration will serve as a map for compiler writers wishing to tackle this important issue. The paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we present the detailed model of our experiment infrastructure. In Section 3, we address a number of fundamental questions regarding compiler optimizations for power by means of carefully crafted experiments. These experiments were performed using our precise processor model simulator as well as actual measurements on a development board. In Section 4, we propose a taxonomy of compiler optimizations for power and examine how previous proposals can be fitted in our classification system. In Section 5, we propose a number of recommendations arising from the insights we gained from the experiments. This is followed by a conclusion. 2. The Anatomy and Physiology of a Processor The twin issues of modeling and optimization of power consumption have to be addressed at several layers for an accurate and thorough result. Previous compiler optimization research in this area has either relied on actual Trimaran power measurements of the processors [2] or has relied on architectural simulation [3], mathematical techniques and regression to model the behavior of the hardware. Actual measurement of the power consumed by a processor is difficult and error prone. Even if achieved, detailed information and insight regarding the power consumed by each of the architectural subsystems might not be available. On the other hand mathematical techniques, regression and architectural simulation might fail to provide accurate and reliable results. Our power research infrastructure consists of an optimizing compiler infrastructure called Trimaran [6]. A backend of Trimaran, called Triceps has been developed to generate code, which targets the ARM [7] architecture. The second part consists of a Verilog model of an ARM-like RISC processor developed by the University of Michigan [5]. The RTL core has been synthesized with the Synopsys Design Compiler [8] targeted towards a 0.25 micron TSMC library. The synthesized gate level netlist is placed and routed using Cadence Silicon Ensemble and Cadence Virtuoso. Verilog RTL ARM Assembly Verilog Model Synthesis Switching Activity Place and Route Technology Parameters External Bus and Memory Models On-Chip Power System Level Power Fig 1. Infrastructure for Power measurement
3 Synopsys Power Compiler is used as the power estimation and analysis tool. This tool has two interfaces, one to the simulation environment and the other to the synthesis environment. The switching activity of the various functional units of the ARM-like 1 processor for a particular benchmark assembly generated by Trimaran is obtained from the simulation environment. Then the switching activity is annotated onto the synthesis environment to provide measurements of static and dynamic power. External models for bus and main memory are fed with the switching activity on the bus to obtain a measure of power dissipated by the bus and main memory. Thus our infrastructure provides an accurate and detailed estimate of the gate level power consumption while functioning as a seamless infrastructure for detailed and accurate study of compiler optimizations, architectural innovations and their impact on power and performance. The experiments are organized into studies of the ALU subsystem, the Register file and the Instruction and Data cache. In addition to the Trimaran Verilog RTL infrastructure described above, there is a StrongARM SA 110-based development board called Skiff from the Compaq Western Research Laboratories. The processor on the board has a power supply that is distinct from that used by the other components on the board. Power consumed by the processor is measured by means of a sensitive measurement device measuring the current drawn by the processor. Experiments are run on this board and the results are crosschecked with those produced by the Trimaran Verilog RTL infrastructure. Since the latter measures actual power consumption albeit at the granularity of the entire SOC processor while the former only models the core processor, measurements taken by both methods do not agree in absolute terms. However, what is important is whether the correlation of the results are preserved as this serves as an important verification of the model s results. 3. The Key Insights The experiments were conducted on the power measurement infrastructure with an aim of answering specific questions to get an insight into power dissipation and energy consumption. I. The ALU Subsystem A) Does reduction in switching activity reduce power? It was proposed in [9] that reduction in switching activities of the ALU translates to energy savings. To explore this, segments of code which compute the same value, but one which is optimized for minimal switching of the inputs and the other for which is modified for maximum switching were run on the model and power numbers collected. The Hamming distance, which is a count of the number of bit flips between two values, was considered as a measure of switching. Alu Switching Average Power (in milliwatts) Regfile + Alu Power (Trimaran- Verilog RTL Measurement) (Skiff Board Measurements) Maximum Switching Minimum Switching 1 Since the actual details of the internal ARM micro-architecture is proprietary information, the Verilog model we used is that of a RISC approximation that executes the ARM instruction set.
4 It can be seen that there is virtually no improvement in power dissipation and energy consumption. This is in accordance with earlier studies on other architectures [2]. Hence the applicability of this technique should be further investigated before being pursued as a viable optimization for power and energy. B) Do all type of ALU instructions consume the same amount power? To explore this different types of instructions were run in a loop and the power numbers collected. It is observed that logical and add / subtract instructions consume the same amount of power and multiply consumes higher amount of power as well as takes a longer number of cycles to complete, thereby consuming more energy. Hence strength reduction by replacing multiplies with a series of additions and shifts would be beneficial. Further, since multiply takes only about 30% more power than adds and subtracts, care should be taken so that the number of instructions replacing multiply is no more than 30% of the total number of cycles taken by multiply instruction. Otherwise, the penalty incurred due to a larger cycle count would have a negative impact on energy even though the instructions themselves have a positive impact on power. II. The Register File A) Does the number of accesses to the register files play a role in power consumption? Two experiments, one that accesses values from registers and another that uses immediate operands were run on the Skiff board as well as on the Verilog model. Register Operands Immediate Operands ALU + Reg File Power It can be observed that while the system power measured from the board shows a difference, the Verilog model does not. This is because in the model for both immediate as well as register operands the register file is accessed and in the appropriate operand is multiplexed into the ALU. In general, we can assume that number of accesses to the register file matters. Hence aggressive copy propagation and constant propagation should be done. Wherever possible immediate addressing should be used. The effectiveness of these optimizations is architecture dependent. B) Does the value accessed from the register file affect power? To explore this question, examples were constructed that access values from the register with maximum, intermediate and minimum amount of switching. Hamming distance was taken as a measure of switching. It is observed that more the switching of the value accessed from the register file more is the reported power consumption. The combined ALU and Register file power consumption is observed to increase by about 12% between minimum switching and maximum switching. This suggests a possible course of optimization through instruction scheduling and code transformation so as to minimize switching in register file access. Regfile + Alu Power Maximum Switching Intermediate Switching Minimum Switching III. The Cache subsystem A) Do the number of accesses to the cache affect power? Three sections of code were run on the Trimaran-Verilog model and on the skiff board and the power numbers were collected. The code accessed the data cache 100%, 50% and 0% of times respectively. It is observed that there is about 24% more power consumption between no access to the data cache and full access to the data cache. Data Cache Power Maximum Access Intermediate Access Minimum Access B) Does the value accessed from the cache matter? To determine if heavy switching in the value accessed from the cache plays a role in power and energy consumption, experiments were setup where in one instance values were accessed alternately such that all 32 bits of the value
5 switched. In the latter case no bits switched in the cache access. The measured power numbers are: Data Cache Power Maximum Switching Minimum Switching Whereas the Trimaran-Verilog model does not show any variation the actual system power shows about 2.5% decrease in power. From this we can conclude implementation details of the cache play a role and power savings in case of no switching is perceptible but very less. One optimization that can be performed is to optimize cache accesses so that the accessed values don t switch as much. 4. The Taxonomy Based on our study, we would like to propose taxonomy of compiler optimizations from the perspective of power. We can classify all known compiler optimizations [10] into one of three classes. Class A Optimizations These optimizations benefit energy due to an improvement in performance. For a program, the energy consumed is a product of the average power dissipation per cycle and the number of cycles taken for completion. Any reduction in the number of cycles in the completion time would automatically translate into improvements in energy consumption [4]. Most of the current optimizations for power fall under this category. Reductions in the number of loads and stores, procedure cloning, loop unrolling, procedure inlining, loop transformations, partial redundancy elimination are a few examples. Class B Optimizations These optimizations benefit energy while having no impact or a decrease in performance. Innovations in instruction scheduling, register pipelining, innovations in code selection to replace high power dissipating instructions with other instructions are a few examples. Class C Optimizations These optimizations are the ones that are bad for power dissipation and energy consumption. Typically the optimizations that have a negative impact on performance also have a negative impact on energy consumption. 5. Recommendations 5.1. To the Compiler Designer Based on the results presented above it is clear that the highest impact on energy consumption is by improving the performance of the code. Using the current day architectures the only optimizations for power that can be done is scheduling register accesses so that the register file switching is minimized and proper code selection and aggressive but careful strength reduction to replace power hogging instructions with other less power consuming instructions To the Computer Architect Based on the measurements above it is clear that with current day architectures, novel compiler optimizations that target power are few. However there are several architectural innovations that can be exposed to the compiler so that many more Class B optimizations are facilitated. Examples would be a bit width sensitive ALU that can derive hints from the compiler, compiler controlled voltage and frequency scaling among other things. 6. Conclusion In this paper, we explored the limits of a compiler in optimizing for power for existing processor architectures. Using a precise model of a popular embedded microprocessor, supported by actual measurement on a development board, experiments carefully crafted to test specific aspects of the micro-architecture were performed. Our study reveals that to a great extent compiler optimizations for locality and performance translate to optimizations for power. This is in agreement with other similar studies. We have also identified a few opportunities for novel optimizations such as reduction in register file switching do exist. However, our experiments have shown that in order to obtain substantial gains in energy saving, innovating micro-architectural features and exposing them to the compiler is necessary. References 1. Marc A. Viredaz and Deborah A. Wallach, Power Evaluation of a Handheld Computer: A Case Study, Research Report 2001/1 Compaq Western Research Lab. 2. Vivek Tiwari, Sharad Malik and Andrew Wolfe, Compilation Techniques for Low Energy: An Overview, In 1994 Symposium on Low-Power Electronics, San Diego, CA, October David Brooks, Vivek Tiwari and Margaret Martonosi, Wattch - A Framework for architectural-level power analysis and optimizations, In Proc. Of The 27th Annual International Symposium on Computer architecture, 2000, Pages
6 4. Madhavi Valluri and Lizy John, Is Compiling for Performance == Compiling for Power? The 5th Annual Workshop on Interaction between Compilers and Computer Architectures (INTERACT-5), Monterrey, Mexico, January 20, ARM Verilog Model, tml, University of Michigan, Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. 6. Trimaran, 7. ARM Ltd., 8. Synopsys Design Compiler, _ds.html. 9. Su, C., Tsui, C., and Despain, A. Low Power Architecture Design and Compilation Techniques for High-Performance Processors. In Digest of Papers: Spring COMPCON 94, pp , February Steven S. Muchnick, Advanced Compiler Design and Implementation. Morgan-Kaufmann Publishers
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Design Cycle for Microprocessors
 Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Effective Use of Performance Monitoring Counters for Run-Time Prediction of Power
 Effective Use of Performance Monitoring Counters for Run-Time Prediction of Power W. L. Bircher, J. Law, M. Valluri, and L. K. John Laboratory for Computer Architecture Department of Electrical and Computer
Effective Use of Performance Monitoring Counters for Run-Time Prediction of Power W. L. Bircher, J. Law, M. Valluri, and L. K. John Laboratory for Computer Architecture Department of Electrical and Computer
IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR
 International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design
 Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Overview The VLSI Design program is part of two tracks in the department:
Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Overview The VLSI Design program is part of two tracks in the department:
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers
 ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
Automist - A Tool for Automated Instruction Set Characterization of Embedded Processors
 Automist - A Tool for Automated Instruction Set Characterization of Embedded Processors Manuel Wendt 1, Matthias Grumer 1, Christian Steger 1, Reinhold Weiß 1, Ulrich Neffe 2 and Andreas Mühlberger 2 1
Automist - A Tool for Automated Instruction Set Characterization of Embedded Processors Manuel Wendt 1, Matthias Grumer 1, Christian Steger 1, Reinhold Weiß 1, Ulrich Neffe 2 and Andreas Mühlberger 2 1
A Lab Course on Computer Architecture
 A Lab Course on Computer Architecture Pedro López José Duato Depto. de Informática de Sistemas y Computadores Facultad de Informática Universidad Politécnica de Valencia Camino de Vera s/n, 46071 - Valencia,
A Lab Course on Computer Architecture Pedro López José Duato Depto. de Informática de Sistemas y Computadores Facultad de Informática Universidad Politécnica de Valencia Camino de Vera s/n, 46071 - Valencia,
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications
 Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000. ILP Execution
 EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000 Lecture #11: Wednesday, 3 May 2000 Lecturer: Ben Serebrin Scribe: Dean Liu ILP Execution
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000 Lecture #11: Wednesday, 3 May 2000 Lecturer: Ben Serebrin Scribe: Dean Liu ILP Execution
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501. Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2
 Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design
 Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler
 ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
CISC, RISC, and DSP Microprocessors
 CISC, RISC, and DSP Microprocessors Douglas L. Jones ECE 497 Spring 2000 4/6/00 CISC, RISC, and DSP D.L. Jones 1 Outline Microprocessors circa 1984 RISC vs. CISC Microprocessors circa 1999 Perspective:
CISC, RISC, and DSP Microprocessors Douglas L. Jones ECE 497 Spring 2000 4/6/00 CISC, RISC, and DSP D.L. Jones 1 Outline Microprocessors circa 1984 RISC vs. CISC Microprocessors circa 1999 Perspective:
A 2-Slot Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) Interconnect Network for Gigascale Integration (GSI)
 A 2-Slot Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) Interconnect Network for Gigascale Integration (GSI) Ajay Joshi Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Atlanta, GA 3332-25
A 2-Slot Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) Interconnect Network for Gigascale Integration (GSI) Ajay Joshi Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Atlanta, GA 3332-25
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background The command over cloud computing infrastructure is increasing with the growing demands of IT infrastructure during the changed business scenario of the 21 st Century.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background The command over cloud computing infrastructure is increasing with the growing demands of IT infrastructure during the changed business scenario of the 21 st Century.
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
MONITORING power consumption of a microprocessor
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUIT AND SYSTEMS-II, VOL. X, NO. Y, JANUARY XXXX 1 A Study on the use of Performance Counters to Estimate Power in Microprocessors Rance Rodrigues, Member, IEEE, Arunachalam Annamalai,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUIT AND SYSTEMS-II, VOL. X, NO. Y, JANUARY XXXX 1 A Study on the use of Performance Counters to Estimate Power in Microprocessors Rance Rodrigues, Member, IEEE, Arunachalam Annamalai,
VLIW Processors. VLIW Processors
 1 VLIW Processors VLIW ( very long instruction word ) processors instructions are scheduled by the compiler a fixed number of operations are formatted as one big instruction (called a bundle) usually LIW
1 VLIW Processors VLIW ( very long instruction word ) processors instructions are scheduled by the compiler a fixed number of operations are formatted as one big instruction (called a bundle) usually LIW
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) * Instruction set architecture of a machine fills the semantic gap between the user and the machine. * ISA serves as the starting point for the design of a new machine
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) * Instruction set architecture of a machine fills the semantic gap between the user and the machine. * ISA serves as the starting point for the design of a new machine
A Survey on ARM Cortex A Processors. Wei Wang Tanima Dey
 A Survey on ARM Cortex A Processors Wei Wang Tanima Dey 1 Overview of ARM Processors Focusing on Cortex A9 & Cortex A15 ARM ships no processors but only IP cores For SoC integration Targeting markets:
A Survey on ARM Cortex A Processors Wei Wang Tanima Dey 1 Overview of ARM Processors Focusing on Cortex A9 & Cortex A15 ARM ships no processors but only IP cores For SoC integration Targeting markets:
Chung-Ho Chen Department of Electrical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan
 A Hybrid Software-Based Self-Testing methodology for Embedded Processor Tai-Hua Lu Department of Electrical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan aaron@casmail.ee.ncku.edu.tw Chung-Ho
A Hybrid Software-Based Self-Testing methodology for Embedded Processor Tai-Hua Lu Department of Electrical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan aaron@casmail.ee.ncku.edu.tw Chung-Ho
IoT Security Platform
 IoT Security Platform 2 Introduction Wars begin when the costs of attack are low, the benefits for a victor are high, and there is an inability to enforce law. The same is true in cyberwars. Today there
IoT Security Platform 2 Introduction Wars begin when the costs of attack are low, the benefits for a victor are high, and there is an inability to enforce law. The same is true in cyberwars. Today there
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units
 Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
Computer Engineering: Incoming MS Student Orientation Requirements & Course Overview
 Computer Engineering: Incoming MS Student Orientation Requirements & Course Overview Prof. Charles Zukowski (caz@columbia.edu) Interim Chair, September 3, 2015 MS Requirements: Overview (see bulletin for
Computer Engineering: Incoming MS Student Orientation Requirements & Course Overview Prof. Charles Zukowski (caz@columbia.edu) Interim Chair, September 3, 2015 MS Requirements: Overview (see bulletin for
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
Mobile Processors: Future Trends
 Mobile Processors: Future Trends Mário André Pinto Ferreira de Araújo Departamento de Informática, Universidade do Minho 4710-057 Braga, Portugal maaraujo@mail.pt Abstract. Mobile devices, such as handhelds,
Mobile Processors: Future Trends Mário André Pinto Ferreira de Araújo Departamento de Informática, Universidade do Minho 4710-057 Braga, Portugal maaraujo@mail.pt Abstract. Mobile devices, such as handhelds,
Design Compiler Graphical Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation
 Datasheet Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation Overview Continuing the trend of delivering innovative synthesis technology, Design Compiler Graphical delivers superior quality
Datasheet Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation Overview Continuing the trend of delivering innovative synthesis technology, Design Compiler Graphical delivers superior quality
Embedded computing applications demand both
 C o v e r f e a t u r e Efficient Embedded Computing William J. Dally, James Balfour, David Black-Shaffer, James Chen, R. Curtis Harting, Vishal Parikh, Jongsoo Park, and David Sheffield, Stanford University
C o v e r f e a t u r e Efficient Embedded Computing William J. Dally, James Balfour, David Black-Shaffer, James Chen, R. Curtis Harting, Vishal Parikh, Jongsoo Park, and David Sheffield, Stanford University
PROBLEMS #20,R0,R1 #$3A,R2,R4
 506 CHAPTER 8 PIPELINING (Corrisponde al cap. 11 - Introduzione al pipelining) PROBLEMS 8.1 Consider the following sequence of instructions Mul And #20,R0,R1 #3,R2,R3 #$3A,R2,R4 R0,R2,R5 In all instructions,
506 CHAPTER 8 PIPELINING (Corrisponde al cap. 11 - Introduzione al pipelining) PROBLEMS 8.1 Consider the following sequence of instructions Mul And #20,R0,R1 #3,R2,R3 #$3A,R2,R4 R0,R2,R5 In all instructions,
Instruction Folding in a Hardware-Translation Based Java Virtual Machine
 Instruction Folding in a Hardware-Translation Based Java Virtual Machine Hitoshi Oi Department of Computer Science The University of Aizu Aizu-Wakamatsu, JAPAN hitoshi at u-aizu.ac.jp ABSTRACT Bytecode
Instruction Folding in a Hardware-Translation Based Java Virtual Machine Hitoshi Oi Department of Computer Science The University of Aizu Aizu-Wakamatsu, JAPAN hitoshi at u-aizu.ac.jp ABSTRACT Bytecode
A Programming Language for Processor Based Embedded Systems
 A Programming Language for Processor Based Embedded Systems Akihiko Inoue Hiroyuki Tomiyama Eko Fajar Nurprasetyo Hiroto Yasuura Department of Computer Science and Communication Engineering, Kyushu University
A Programming Language for Processor Based Embedded Systems Akihiko Inoue Hiroyuki Tomiyama Eko Fajar Nurprasetyo Hiroto Yasuura Department of Computer Science and Communication Engineering, Kyushu University
Computer Architectures
 Computer Architectures 2. Instruction Set Architectures 2015. február 12. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Instruction set architectures
Computer Architectures 2. Instruction Set Architectures 2015. február 12. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Instruction set architectures
İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY
 İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGİNEERİNG SOFTWARE ENGINEERING THE PROJECT OF THE INSTRUCTION SET COMPUTER ORGANIZATION GÖZDE ARAS B1205.090015 Instructor: Prof. Dr. HASAN HÜSEYİN BALIK DECEMBER
İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGİNEERİNG SOFTWARE ENGINEERING THE PROJECT OF THE INSTRUCTION SET COMPUTER ORGANIZATION GÖZDE ARAS B1205.090015 Instructor: Prof. Dr. HASAN HÜSEYİN BALIK DECEMBER
Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses.
 Proceedings of the E2LP Workshop Warsaw, 2014, pp. 25 29 DOI: 10.15439/2014F672 ACSIS, Vol. 4 Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses. Jan Piwiński Email: jpiwinski@piap.pl
Proceedings of the E2LP Workshop Warsaw, 2014, pp. 25 29 DOI: 10.15439/2014F672 ACSIS, Vol. 4 Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses. Jan Piwiński Email: jpiwinski@piap.pl
Implementation Details
 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
Optimizing compilers. CS6013 - Modern Compilers: Theory and Practise. Optimization. Compiler structure. Overview of different optimizations
 Optimizing compilers CS6013 - Modern Compilers: Theory and Practise Overview of different optimizations V. Krishna Nandivada IIT Madras Copyright c 2015 by Antony L. Hosking. Permission to make digital
Optimizing compilers CS6013 - Modern Compilers: Theory and Practise Overview of different optimizations V. Krishna Nandivada IIT Madras Copyright c 2015 by Antony L. Hosking. Permission to make digital
An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing
 2009 International Symposium on Computing, Communication, and Control (ISCCC 2009) Proc.of CSIT vol.1 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing Joby Joseph1and A.
2009 International Symposium on Computing, Communication, and Control (ISCCC 2009) Proc.of CSIT vol.1 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing Joby Joseph1and A.
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain firstname.lastname@tut.fi Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain firstname.lastname@tut.fi Department of Computer
ESP-CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation
 Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
PyMTL and Pydgin Tutorial. Python Frameworks for Highly Productive Computer Architecture Research
 PyMTL and Pydgin Tutorial Python Frameworks for Highly Productive Computer Architecture Research Derek Lockhart, Berkin Ilbeyi, Christopher Batten Computer Systems Laboratory School of Electrical and Computer
PyMTL and Pydgin Tutorial Python Frameworks for Highly Productive Computer Architecture Research Derek Lockhart, Berkin Ilbeyi, Christopher Batten Computer Systems Laboratory School of Electrical and Computer
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
數 位 積 體 電 路 Digital Integrated Circuits
 IEE5049 - Spring 2012 數 位 積 體 電 路 Digital Integrated Circuits Course Overview Professor Wei Hwang 黃 威 教 授 Department of Electronics Engineering National Chiao Tung University hwang@mail.nctu.edu.tw Wei
IEE5049 - Spring 2012 數 位 積 體 電 路 Digital Integrated Circuits Course Overview Professor Wei Hwang 黃 威 教 授 Department of Electronics Engineering National Chiao Tung University hwang@mail.nctu.edu.tw Wei
RUNAHEAD EXECUTION: AN EFFECTIVE ALTERNATIVE TO LARGE INSTRUCTION WINDOWS
 RUNAHEAD EXECUTION: AN EFFECTIVE ALTERNATIVE TO LARGE INSTRUCTION WINDOWS AN INSTRUCTION WINDOW THAT CAN TOLERATE LATENCIES TO DRAM MEMORY IS PROHIBITIVELY COMPLEX AND POWER HUNGRY. TO AVOID HAVING TO
RUNAHEAD EXECUTION: AN EFFECTIVE ALTERNATIVE TO LARGE INSTRUCTION WINDOWS AN INSTRUCTION WINDOW THAT CAN TOLERATE LATENCIES TO DRAM MEMORY IS PROHIBITIVELY COMPLEX AND POWER HUNGRY. TO AVOID HAVING TO
MPSoC Designs: Driving Memory and Storage Management IP to Critical Importance
 MPSoC Designs: Driving Storage Management IP to Critical Importance Design IP has become an essential part of SoC realization it is a powerful resource multiplier that allows SoC design teams to focus
MPSoC Designs: Driving Storage Management IP to Critical Importance Design IP has become an essential part of SoC realization it is a powerful resource multiplier that allows SoC design teams to focus
GameTime: A Toolkit for Timing Analysis of Software
 GameTime: A Toolkit for Timing Analysis of Software Sanjit A. Seshia and Jonathan Kotker EECS Department, UC Berkeley {sseshia,jamhoot}@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract. Timing analysis is a key step in the
GameTime: A Toolkit for Timing Analysis of Software Sanjit A. Seshia and Jonathan Kotker EECS Department, UC Berkeley {sseshia,jamhoot}@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract. Timing analysis is a key step in the
McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures
 McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures Sheng Li, Junh Ho Ahn, Richard Strong, Jay B. Brockman, Dean M Tullsen, Norman Jouppi MICRO 2009
McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures Sheng Li, Junh Ho Ahn, Richard Strong, Jay B. Brockman, Dean M Tullsen, Norman Jouppi MICRO 2009
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN
 TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
AC 2007-2027: A PROCESSOR DESIGN PROJECT FOR A FIRST COURSE IN COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
 AC 2007-2027: A PROCESSOR DESIGN PROJECT FOR A FIRST COURSE IN COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Michael Black, American University Manoj Franklin, University of Maryland-College Park American Society for Engineering
AC 2007-2027: A PROCESSOR DESIGN PROJECT FOR A FIRST COURSE IN COMPUTER ORGANIZATION Michael Black, American University Manoj Franklin, University of Maryland-College Park American Society for Engineering
VtRES 2013. Towards Hardware Embedded Virtualization Technology: Architectural Enhancements to an ARM SoC. ESRG Embedded Systems Research Group
 Towards Hardware Embedded Virtualization Technology: Architectural Enhancements to an ARM SoC VtRES 2013 P. Garcia, T. Gomes, F. Salgado, J. Monteiro, A. Tavares Summary 1. Current landscape in 2. Embedded
Towards Hardware Embedded Virtualization Technology: Architectural Enhancements to an ARM SoC VtRES 2013 P. Garcia, T. Gomes, F. Salgado, J. Monteiro, A. Tavares Summary 1. Current landscape in 2. Embedded
Echtzeittesten mit MathWorks leicht gemacht Simulink Real-Time Tobias Kuschmider Applikationsingenieur
 Echtzeittesten mit MathWorks leicht gemacht Simulink Real-Time Tobias Kuschmider Applikationsingenieur 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Model-Based Design Continuous Verification and Validation Requirements
Echtzeittesten mit MathWorks leicht gemacht Simulink Real-Time Tobias Kuschmider Applikationsingenieur 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Model-Based Design Continuous Verification and Validation Requirements
MSME TOOL ROOM, HYDERABAD CENTRAL INSTITUTE OF TOOL DESIGN
 MSME TOOL ROOM, HYDERABAD CENTRAL INSTITUTE OF TOOL DESIGN (An ISO 9001:2008, ISO 29990; 2010, ISO 14001:2004 & ISO 50001:2011 Certified Institution) VES COURSES 2015-20162016 10 Months Full Time Courses
MSME TOOL ROOM, HYDERABAD CENTRAL INSTITUTE OF TOOL DESIGN (An ISO 9001:2008, ISO 29990; 2010, ISO 14001:2004 & ISO 50001:2011 Certified Institution) VES COURSES 2015-20162016 10 Months Full Time Courses
From Bus and Crossbar to Network-On-Chip. Arteris S.A.
 From Bus and Crossbar to Network-On-Chip Arteris S.A. Copyright 2009 Arteris S.A. All rights reserved. Contact information Corporate Headquarters Arteris, Inc. 1741 Technology Drive, Suite 250 San Jose,
From Bus and Crossbar to Network-On-Chip Arteris S.A. Copyright 2009 Arteris S.A. All rights reserved. Contact information Corporate Headquarters Arteris, Inc. 1741 Technology Drive, Suite 250 San Jose,
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems
 ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
System-Level Display Power Reduction Technologies for Portable Computing and Communications Devices
 System-Level Display Power Reduction Technologies for Portable Computing and Communications Devices Achintya K. Bhowmik and Robert J. Brennan Intel Corporation 2200 Mission College Blvd. Santa Clara, CA
System-Level Display Power Reduction Technologies for Portable Computing and Communications Devices Achintya K. Bhowmik and Robert J. Brennan Intel Corporation 2200 Mission College Blvd. Santa Clara, CA
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors
 Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor
 Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor Product Features Brief Datasheet The Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor (SA-110), the first member of the StrongARM family of high-performance, low-power microprocessors,
Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor Product Features Brief Datasheet The Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor (SA-110), the first member of the StrongARM family of high-performance, low-power microprocessors,
EE361: Digital Computer Organization Course Syllabus
 EE361: Digital Computer Organization Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Spring 2014 Course Objectives Simply, a computer is a set of components (Processor, Memory and Storage, Input/Output Devices)
EE361: Digital Computer Organization Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Spring 2014 Course Objectives Simply, a computer is a set of components (Processor, Memory and Storage, Input/Output Devices)
ESE566 REPORT3. Design Methodologies for Core-based System-on-Chip HUA TANG OVIDIU CARNU
 ESE566 REPORT3 Design Methodologies for Core-based System-on-Chip HUA TANG OVIDIU CARNU Nov 19th, 2002 ABSTRACT: In this report, we discuss several recent published papers on design methodologies of core-based
ESE566 REPORT3 Design Methodologies for Core-based System-on-Chip HUA TANG OVIDIU CARNU Nov 19th, 2002 ABSTRACT: In this report, we discuss several recent published papers on design methodologies of core-based
On Demand Loading of Code in MMUless Embedded System
 On Demand Loading of Code in MMUless Embedded System Sunil R Gandhi *. Chetan D Pachange, Jr.** Mandar R Vaidya***, Swapnilkumar S Khorate**** *Pune Institute of Computer Technology, Pune INDIA (Mob- 8600867094;
On Demand Loading of Code in MMUless Embedded System Sunil R Gandhi *. Chetan D Pachange, Jr.** Mandar R Vaidya***, Swapnilkumar S Khorate**** *Pune Institute of Computer Technology, Pune INDIA (Mob- 8600867094;
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines
 Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada ken@unb.ca Micaela Serra
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada ken@unb.ca Micaela Serra
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING
 DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING IS PROCESS TECHNOLOGY MEETING THE GOALS PREDICTED BY SCALING THEORY? AN ANALYSIS OF MICROPROCESSOR PERFORMANCE, TRANSISTOR DENSITY, AND POWER TRENDS THROUGH SUCCESSIVE
DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING IS PROCESS TECHNOLOGY MEETING THE GOALS PREDICTED BY SCALING THEORY? AN ANALYSIS OF MICROPROCESSOR PERFORMANCE, TRANSISTOR DENSITY, AND POWER TRENDS THROUGH SUCCESSIVE
Instruction Set Design
 Instruction Set Design Instruction Set Architecture: to what purpose? ISA provides the level of abstraction between the software and the hardware One of the most important abstraction in CS It s narrow,
Instruction Set Design Instruction Set Architecture: to what purpose? ISA provides the level of abstraction between the software and the hardware One of the most important abstraction in CS It s narrow,
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic
 Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Performance Oriented Management System for Reconfigurable Network Appliances
 Performance Oriented Management System for Reconfigurable Network Appliances Hiroki Matsutani, Ryuji Wakikawa, Koshiro Mitsuya and Jun Murai Faculty of Environmental Information, Keio University Graduate
Performance Oriented Management System for Reconfigurable Network Appliances Hiroki Matsutani, Ryuji Wakikawa, Koshiro Mitsuya and Jun Murai Faculty of Environmental Information, Keio University Graduate
Design and Implementation of an On-Chip timing based Permutation Network for Multiprocessor system on Chip
 Design and Implementation of an On-Chip timing based Permutation Network for Multiprocessor system on Chip Ms Lavanya Thunuguntla 1, Saritha Sapa 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of ECE, HITAM, Telangana
Design and Implementation of an On-Chip timing based Permutation Network for Multiprocessor system on Chip Ms Lavanya Thunuguntla 1, Saritha Sapa 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of ECE, HITAM, Telangana
ARM Webinar series. ARM Based SoC. Abey Thomas
 ARM Webinar series ARM Based SoC Verification Abey Thomas Agenda About ARM and ARM IP ARM based SoC Verification challenges Verification planning and strategy IP Connectivity verification Performance verification
ARM Webinar series ARM Based SoC Verification Abey Thomas Agenda About ARM and ARM IP ARM based SoC Verification challenges Verification planning and strategy IP Connectivity verification Performance verification
SAN Conceptual and Design Basics
 TECHNICAL NOTE VMware Infrastructure 3 SAN Conceptual and Design Basics VMware ESX Server can be used in conjunction with a SAN (storage area network), a specialized high speed network that connects computer
TECHNICAL NOTE VMware Infrastructure 3 SAN Conceptual and Design Basics VMware ESX Server can be used in conjunction with a SAN (storage area network), a specialized high speed network that connects computer
Survey on Models to Investigate Data Center Performance and QoS in Cloud Computing Infrastructure
 Survey on Models to Investigate Data Center Performance and QoS in Cloud Computing Infrastructure Chandrakala Department of Computer Science and Engineering Srinivas School of Engineering, Mukka Mangalore,
Survey on Models to Investigate Data Center Performance and QoS in Cloud Computing Infrastructure Chandrakala Department of Computer Science and Engineering Srinivas School of Engineering, Mukka Mangalore,
CPU Organization and Assembly Language
 COS 140 Foundations of Computer Science School of Computing and Information Science University of Maine October 2, 2015 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Homework and announcements Reading: Chapter 12 Homework:
COS 140 Foundations of Computer Science School of Computing and Information Science University of Maine October 2, 2015 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Homework and announcements Reading: Chapter 12 Homework:
Assessment of RLG Trusted Digital Repository Requirements
 Assessment of RLG Trusted Digital Repository Requirements Reagan W. Moore San Diego Supercomputer Center 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla, CA 92093-0505 01 858 534 5073 moore@sdsc.edu ABSTRACT The RLG/NARA trusted
Assessment of RLG Trusted Digital Repository Requirements Reagan W. Moore San Diego Supercomputer Center 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla, CA 92093-0505 01 858 534 5073 moore@sdsc.edu ABSTRACT The RLG/NARA trusted
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
System on Chip Design. Michael Nydegger
 Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Pentium vs. Power PC Computer Architecture and PCI Bus Interface
 Pentium vs. Power PC Computer Architecture and PCI Bus Interface CSE 3322 1 Pentium vs. Power PC Computer Architecture and PCI Bus Interface Nowadays, there are two major types of microprocessors in the
Pentium vs. Power PC Computer Architecture and PCI Bus Interface CSE 3322 1 Pentium vs. Power PC Computer Architecture and PCI Bus Interface Nowadays, there are two major types of microprocessors in the
PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes
 nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
How To Design A Chip Layout
 Spezielle Anwendungen des VLSI Entwurfs Applied VLSI design (IEF170) Course and contest Intermediate meeting 3 Prof. Dirk Timmermann, Claas Cornelius, Hagen Sämrow, Andreas Tockhorn, Philipp Gorski, Martin
Spezielle Anwendungen des VLSI Entwurfs Applied VLSI design (IEF170) Course and contest Intermediate meeting 3 Prof. Dirk Timmermann, Claas Cornelius, Hagen Sämrow, Andreas Tockhorn, Philipp Gorski, Martin
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course. Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
IA-64 Application Developer s Architecture Guide
 IA-64 Application Developer s Architecture Guide The IA-64 architecture was designed to overcome the performance limitations of today s architectures and provide maximum headroom for the future. To achieve
IA-64 Application Developer s Architecture Guide The IA-64 architecture was designed to overcome the performance limitations of today s architectures and provide maximum headroom for the future. To achieve
Delay Time Analysis of Reconfigurable Firewall Unit
 Delay Time Analysis of Reconfigurable Unit Tomoaki SATO C&C Systems Center, Hirosaki University Hirosaki 036-8561 Japan Phichet MOUNGNOUL Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut's Institute of Technology
Delay Time Analysis of Reconfigurable Unit Tomoaki SATO C&C Systems Center, Hirosaki University Hirosaki 036-8561 Japan Phichet MOUNGNOUL Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut's Institute of Technology
Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design
 White Paper Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design A major benefit of programmable logic is that it accommodates changes to the system specification late in the design cycle.
White Paper Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design A major benefit of programmable logic is that it accommodates changes to the system specification late in the design cycle.
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!!
 ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
CS101 Lecture 26: Low Level Programming. John Magee 30 July 2013 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett. Overview/Questions
 CS101 Lecture 26: Low Level Programming John Magee 30 July 2013 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett 1 Overview/Questions What did we do last time? How can we control the computer s circuits? How
CS101 Lecture 26: Low Level Programming John Magee 30 July 2013 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett 1 Overview/Questions What did we do last time? How can we control the computer s circuits? How
Low-Level Verification of Embedded Software: Addressing the Challenge
 Low-Level Verification of Embedded Software: Addressing the Challenge Sanjit A. Seshia Assistant Professor EECS, UC Berkeley FMCAD 2010 Panel October 2010 Abstraction Layers in Computing Algorithms, Protocols,
Low-Level Verification of Embedded Software: Addressing the Challenge Sanjit A. Seshia Assistant Professor EECS, UC Berkeley FMCAD 2010 Panel October 2010 Abstraction Layers in Computing Algorithms, Protocols,
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF. Compaq RAID on a Chip Technology EXECUTIVE SUMMARY CONTENTS
 TECHNOLOGY BRIEF August 1999 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISSD Technology Communications CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Introduction 3 Subsystem Technology 3 Processor 3 SCSI Chip4 PCI Bridge
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF August 1999 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISSD Technology Communications CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Introduction 3 Subsystem Technology 3 Processor 3 SCSI Chip4 PCI Bridge
Driving force. What future software needs. Potential research topics
 Improving Software Robustness and Efficiency Driving force Processor core clock speed reach practical limit ~4GHz (power issue) Percentage of sustainable # of active transistors decrease; Increase in #
Improving Software Robustness and Efficiency Driving force Processor core clock speed reach practical limit ~4GHz (power issue) Percentage of sustainable # of active transistors decrease; Increase in #
Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX
 White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
An Extension to DNA Based Fredkin Gate Circuits: Design of Reversible Sequential Circuits using Fredkin Gates
 An Extension to DNA Based Fredkin Gate Circuits: Design of Reversible Sequential Circuits using Fredkin Gates Himanshu Thapliyal and M.B Srinivas (thapliyalhimanshu@yahoo.com, srinivas@iiit.net) Center
An Extension to DNA Based Fredkin Gate Circuits: Design of Reversible Sequential Circuits using Fredkin Gates Himanshu Thapliyal and M.B Srinivas (thapliyalhimanshu@yahoo.com, srinivas@iiit.net) Center
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor
 Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
Systems on Chip Design
 Systems on Chip Design College: Engineering Department: Electrical First: Course Definition, a Summary: 1 Course Code: EE 19 Units: 3 credit hrs 3 Level: 3 rd 4 Prerequisite: Basic knowledge of microprocessor/microcontroller
Systems on Chip Design College: Engineering Department: Electrical First: Course Definition, a Summary: 1 Course Code: EE 19 Units: 3 credit hrs 3 Level: 3 rd 4 Prerequisite: Basic knowledge of microprocessor/microcontroller
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router
 Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Solution: start more than one instruction in the same clock cycle CPI < 1 (or IPC > 1, Instructions per Cycle) Two approaches:
 Multiple-Issue Processors Pipelining can achieve CPI close to 1 Mechanisms for handling hazards Static or dynamic scheduling Static or dynamic branch handling Increase in transistor counts (Moore s Law):
Multiple-Issue Processors Pipelining can achieve CPI close to 1 Mechanisms for handling hazards Static or dynamic scheduling Static or dynamic branch handling Increase in transistor counts (Moore s Law):
Implementation of Buffer Cache Simulator for Hybrid Main Memory and Flash Memory Storages
 Implementation of Buffer Cache Simulator for Hybrid Main Memory and Flash Memory Storages Soohyun Yang and Yeonseung Ryu Department of Computer Engineering, Myongji University Yongin, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
Implementation of Buffer Cache Simulator for Hybrid Main Memory and Flash Memory Storages Soohyun Yang and Yeonseung Ryu Department of Computer Engineering, Myongji University Yongin, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
