B.Sc.Ag. (Hons) Level 2 Semester II (Introductory Entomology: Sense Organs of Insect) ENTO: 253 INTRODUCTORY ENTOMOLOGY SENSE ORGANS OF INSECT
|
|
|
- Emory Fowler
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENTO: 253 INTRODUCTORY ENTOMOLOGY SENSE ORGANS OF INSECT Course Teacher: Dr. Md. Razzab Ali, Associate Professor Department of Entomology, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University Attention: This note is just only for guideline Sense organ The sensory organs are primarily responsible for the reception of stimuli and pass them on to the neuro-muscular system, resulting in the varied behavior patterns of insects. Classification of insect sense organs According to the various stimuli perceived, they are classified into the following: 1. Mechanoreceptors 2. Chemoreceptors 3. Temperature and humidity receptor 4. Photoreceptors or visual organ 1. Mechanoreceptor Mechanoreceptors are the sense organs of insect, which respond to the sense of touch due to contact with external solid objects, current of air and water or even because of internal body pressure. The principal mechanoreceptors are: i. The tactile organs or trichoid sensilla ii. The campaniform organs iii. The chordotonal organs i. The tactile organs or trichoid sensilla The trichoid sensilla are the simple articulated sensory hairs and distributed on the entire body surface and commonly called as the sensilla. Construction of tactile organ: They are made up of cuticle and articulated within the socket with the body wall. The trichoid sensillum is formed by two cells; the hair by the trichogen cell and the socket by the tormogen cell. Both the cells are modified epidermal cells. Each sensillum is innervated by a bipolar sensory neuron. The dendrite of the neuron is enclosed at the base of the hair by a cuticular tubular sheath, called the scolopale. It is, in some case, provided with a distal cap, called the scolopale cap. Location of tactile organs: Trichoid sensilla present on the antennae, tarsi, tibia and cerci. These organs of the insects sub-serving the sense of touch. Functions of tactile organs a. There are some trichoid hair plates at the joints of various appendages and function as proprioceptors during sliding of the segments over each other. b. There are tactile hair- beds on the facial region of the head of locusts and Lepidoptera, on the neck of dragonflies, on the wing margins of Lepidoptera which are responding to the air movements during flight. c. The tactile hairs of the antennae and lower segments of legs perceive earth-bornvibrations in terrestrial insects and water surface vibrations in aquatic insects. Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 1 of 9
2 ii. The campaniform sensilla: The campaniform sensilla cannot be seen externally but recognized from the dome-shaped cuticular areas. They elevated above or depressed below the general body surface. Cell structure and arrangement is similar to that of trichoid sensilla. Location: They occur in various parts of the body, wing-base, halteres, cerci, palps and on the base of trochanter, femora, tibia and tarsal segments. Mechanism of campaniform sensilla: The cuticular stretches and the forces exerted on the cuticle by muscles and gravitational forces stimulate the campaniform sensilla. The campaniform sensilla function as the proprioceptors. They respond to the mechanical stimuli, in terrestrial insects, water pressure in aquatic insects and air pressure in flying insects. Fig.: Campaniform sensillum (left), and section through campaniform sensillum to show stiffening rod of cuticle running along cuticular plate present in some species. iii. Chordotonal organ Chordotonal organ consists of single unit or group of similar unit is called scolopidia. They are sub-cuticular and are attached to the cuticle at one or both end often no sign of their presence. Each scolopidia consists of three cells: a. Neuron b. Scolopale cell or enveloping cell c. Cap cell Location: The chordotonal organs occur in legs at femoral, distal tibial and tibio-tarsal regions, in abdomen and wing base. Mechanism of Chordotonal organ: They are stimulated by passive movement of segments, tension of muscles, internal pressure changed due to blood and tracheae. Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 2 of 9
3 Fig.: Single chordotonal sensillum (left), and Chordotonal organ Specialized chordotonal organ a. Johnstons organ b. Auditory or tympanal organ a. Johnstons organ Jonstons organ is a specialized chordotonal organ in the 2 nd antennal segment, occurs in all adult insect except Collembola and Diplura. It consists of single mass or several groups of scolopidia and is highly developed in Culicidae, where the pedicel is enlarged. Axon of sense cells run back and enter the antennal nerve. It perceives movement of antennal flagellum and flight speed indicator. b. Auditory or tympanal organ: Tympanal organs are present in the adult of many insect species. Tympanal organ consists of a thin layer of cuticular structure, called tympanic membrane, air sac and a group of chordotonal organ. Tympanic membrane and air sac form drum, sound waves that strike the drum cause it to vibrate and therefore the sensilla to be stimulated. Fig.: Jhonston s organs. (A) Hairy antenna of a male mosquito showing a swollen pedicel that houses Jhonston s organ; (B) a diagrammatic section through Jhonston s organ Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 3 of 9
4 Fig.: Surface view of tibial tympanal organ of Decticus (Tettigoniidae) Fig.: Transverse section through tympanal organ of Decticus Chemoreceptor Chemoreceptor is sensitive to chemicals, stimulation by chemicals can occur in the following different ways: 1. Olfactory or smell chemoreceptor: They provide sense of smell. Mechanism of perception of chemicals in gaseous state at high concentration is known as olfaction. 2. Gustatory or contact chemoreceptor: They provide sense of taste. Mechanism of perception of chemicals in liquid state at high concentration as known as contact chemoreceptor. Construction and form of Chemoreceptor Chemoreceptor consists of one or more neurons associated with cuticular structures having small pores through which molecules enter and stimulate dendrites. Cuticular structures have wide variety of forms. a. Trichoid sensilla: Sensory cells provided with hairs. b. Sensilla basiconica: Sensory cells provided with peg-like or cone-like structure. c. Sensilla coeloconica: Sensory cells provided with pits. d. Sensilla placodea: Sensory cells provided with plates. Functions of chemoreceptor Chemoreception, essentially taste (gustation) and smell (olfaction), is an extremely significant process in the Insecta, as it initiates some of their most important behavior patterns that is section of food, oviposition site, location of host or mate, and responses to commercial attractants and repellents. Location of chemoreceptor Organs of taste are common on ii. The mouthparts, especially the palps, iii. The antennae (Hymenoptera), iv. Tarsi (many Lepidoptera, Diptera, and the honeybee), v. Ovipositor (parasitic Hymenoptera and some Diptera) and vi. General body surface. Organs of smell are located on the following sites: i. The antennae are the primary site of olfactory organs and often bear many thousands of these structures. ii. The mouthparts also carry olfactory structures in many species. Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 4 of 9
5 Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 5 of 9
6 Photoreceptors Photoreceptors may be defined as the ability to perceive light in visible or near visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Organism have to be a pigment capable of absorbing light of a given wave length and a means of producing a nervous impulse as a result of this absorption. Three types of photoreceptive structures found in insects: 1. Compound eyes 2. Dorsal ocelli 3. Lateral ocelli (stemmata) Compound eyes Most adult insects have a pair of compound eyes. The compound eyes are composed of a large number of alike structural units called ommatidium. The number of ommatidium varies from insect to insects. Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 6 of 9
7 The structural parts of an Ommatidium The ommatidium consists of the followings structural parts: i. The cornea: It is outmost part of the ommatidium. It is transparent, colorless and biconvex modified cuticular area often termed as a facet or lens. ii. The corneagen cells: They are the epidermal or hypodermal cells lying behind the cornea. A group of two corneagen cells secretes a single lens. iii. The cone or semper cells: Beneath the cornea, there are four distinct cells. Generally they secrete the crystalline and form a cone. In most cases, these cells are represented by the nuclei only, called the semper cells. iv. The retinula cells: The crystalline cone is followed by a long retina forming a basal part of an ommatidium. It is firmed from a group of alike seven retinula cells as pigmented visual cells. Each retinula cell posteriorly terminates above the basement membrane and gives out a post retinal axonal fibre running towards the optical lobe. The inner margin of the retinula cell lying around the ommatidial axis is highly differentiated from rest of the cell body, and it is called the rhabdomere. These rhabdomere of all 7 retinula cells extend the whole length of the retina and form a rhabdom. The rhabdom is nothing but an internal optic rod having a fibrillar structures, and it becomes a central axis of retina. v. The pigment or iris cells: There are two groups of iris cells, one around the crystalline cone cells and the other around the retinula, called the primary and secondary iris cells, respectively. Each group of iris cells is composed of six cells arrange in a short of circlet. The secondary iris cells separate one ommatidium from the neighbour one. Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 7 of 9
8 The mechanism of image formation: i. The apposition mechanism: It is a mechanism of image formation in the bright day light by most of the diurnal insects. The pigment cells envelop the ommatidia completely and thus the rays of light can enter from the central point of the dioptric apparatus. Different ommatidia finally produced a single complete, erect image of an object. ii. The super position mechanism: It is a mechanism of image formation in poor light generally during night, mostly the nocturnal insects. At night time the pigment cells become contracts so that the light from the wide visual field can enter to the rhabdom of retinula cells obliquely. So light can enter centrally and obliquely. Each rhabdom therefore receives the light from several cones of neighboring ommatidia. Hence there is an overlapping of points of light. The image thus formed from a group of rays refracted by neighboring cones, called the superposition image. It is erect in position and represents merely a part of an image. The compound image is formed after an amalgamation of all such images and it is the final form of a complete superposition image. Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 8 of 9
9 Dorsal and Lateral Ocelli: Created by Dr. Md. Razzab Ali Page 9 of 9
Honey Bee Biology. Dr. Debbie Delaney
 Honey Bee Biology Dr. Debbie Delaney Morphology of the Honey Bee The honey bee has three body divisions Head Thorax Abdomen Head Drawing modified from R. E. Snodgrass Exoskeleton Body Hairs Morphology
Honey Bee Biology Dr. Debbie Delaney Morphology of the Honey Bee The honey bee has three body divisions Head Thorax Abdomen Head Drawing modified from R. E. Snodgrass Exoskeleton Body Hairs Morphology
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
SPECIAL SENSES. Introduction: Activity 1: Observation of the Human Eye Model
 SPECIAL SENSES Introduction: The special senses include vision, hearing, equilibrium (balance), taste and smell. In these activities you will be performing a series of physiological tests for each of these
SPECIAL SENSES Introduction: The special senses include vision, hearing, equilibrium (balance), taste and smell. In these activities you will be performing a series of physiological tests for each of these
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
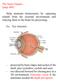 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology. Sensory Adaptation. Four Steps to Sensation. Types of Sensors Structural Design
 Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
A concise guide to Safety Glasses, the different standards and the effects of light on the eye. Contents. Links. Year of publication: 2010
 A concise guide to Safety Glasses, the different standards and the effects of light on the eye Year of publication: 2010 Produced by the leading supplier of Safety Glasses in the UK. All Rights Reserved.
A concise guide to Safety Glasses, the different standards and the effects of light on the eye Year of publication: 2010 Produced by the leading supplier of Safety Glasses in the UK. All Rights Reserved.
Class Insecta - The insects
 A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors
 Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors Diego Betancourt and Carlos del Río Antenna Group, Public University of Navarra, Campus
Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors Diego Betancourt and Carlos del Río Antenna Group, Public University of Navarra, Campus
The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Lecture Goals. The Insect Circulatory System. The Insect Circulatory System
 The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems What are some of the main roles of the human circulatory system? Lecture Goals Understand the open circulatory system in insects. Recognize the lack of integration
The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems What are some of the main roles of the human circulatory system? Lecture Goals Understand the open circulatory system in insects. Recognize the lack of integration
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system
 Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
 Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Science In Action 8 Unit C - Light and Optical Systems. 1.1 The Challenge of light
 1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Perception of Different. Sugars by Blowflies
 Fly lab report p. 1 SAMPLE LAB REPORT Perception of Different Sugars by Blowflies by Alexander Hamilton Biology 101 October 24, 2009 Lab Partners: Sharon Flynn, Andi Alexander Fly lab report p. 2 ABSTRACT
Fly lab report p. 1 SAMPLE LAB REPORT Perception of Different Sugars by Blowflies by Alexander Hamilton Biology 101 October 24, 2009 Lab Partners: Sharon Flynn, Andi Alexander Fly lab report p. 2 ABSTRACT
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
THE SENSE OF TOUCH. Roope Raisamo and Jukka Raisamo
 THE SENSE OF TOUCH Roope Raisamo and Jukka Raisamo Tampere Unit for Computer-Human Interaction School of Information Sciences University of Tampere, Finland Outline for the talk Introduction to the sense
THE SENSE OF TOUCH Roope Raisamo and Jukka Raisamo Tampere Unit for Computer-Human Interaction School of Information Sciences University of Tampere, Finland Outline for the talk Introduction to the sense
Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Review Vocabulary spectrum: a range of values or properties
 Standards 7.3.19: Explain that human eyes respond to a narrow range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. 7.3.20: Describe that something can be seen when light waves emitted or reflected by
Standards 7.3.19: Explain that human eyes respond to a narrow range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. 7.3.20: Describe that something can be seen when light waves emitted or reflected by
All input from sensory neurons to the central nervous
 55 Sensory Systems Concept Outline 55.1 Animals employ a wide variety of sensory receptors. Categories of Sensory Receptors and Their Actions. Sensory receptors can be classified according to the type
55 Sensory Systems Concept Outline 55.1 Animals employ a wide variety of sensory receptors. Categories of Sensory Receptors and Their Actions. Sensory receptors can be classified according to the type
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services
 Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Internal anatomy and physiology D. L. A. Underwood Biology 316 - General Entomology
 Internal anatomy and physiology D. L. A. Underwood Biology 316 - General Entomology A. Digestive system 1. Foregut a. Mouth b. The pharynx may be highly modified into a pump seen in sucking insects like
Internal anatomy and physiology D. L. A. Underwood Biology 316 - General Entomology A. Digestive system 1. Foregut a. Mouth b. The pharynx may be highly modified into a pump seen in sucking insects like
Light Waves and Matter
 Name: Light Waves and Matter Read from Lesson 2 of the Light Waves and Color chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l2a.html MOP Connection: Light and Color: sublevel
Name: Light Waves and Matter Read from Lesson 2 of the Light Waves and Color chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l2a.html MOP Connection: Light and Color: sublevel
Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Nerve Cell Communication
 Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 2 forty minute class periods Teacher Provides: For each student
Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 2 forty minute class periods Teacher Provides: For each student
The Information Processing model
 The Information Processing model A model for understanding human cognition. 1 from: Wickens, Lee, Liu, & Becker (2004) An Introduction to Human Factors Engineering. p. 122 Assumptions in the IP model Each
The Information Processing model A model for understanding human cognition. 1 from: Wickens, Lee, Liu, & Becker (2004) An Introduction to Human Factors Engineering. p. 122 Assumptions in the IP model Each
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Lecture One: Brain Basics
 Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
The Eye ACCESSORY STRUCTURES
 The Eye The eye forms a visual image and projects it onto the sensory receptors (photoreceptors) of the retina. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport,
The Eye The eye forms a visual image and projects it onto the sensory receptors (photoreceptors) of the retina. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport,
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory),
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory),
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline
 Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline Five special senses Olfaction = smell Gustation = taste Vision = sight Hearing Equilibrium Special sensory receptors: 1. Distinct cells 2. Complex organ /
Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline Five special senses Olfaction = smell Gustation = taste Vision = sight Hearing Equilibrium Special sensory receptors: 1. Distinct cells 2. Complex organ /
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Anatomy of the Honey Bee
 Anatomy of the Honey Bee As a member of the insect class (Insecta), honey bees share with other insects the following characteristics. Honey bees are segmented in nearly all their body parts: three segments
Anatomy of the Honey Bee As a member of the insect class (Insecta), honey bees share with other insects the following characteristics. Honey bees are segmented in nearly all their body parts: three segments
Bony Fish Anatomy Worksheet
 Educational Material Bony Fish Anatomy Worksheet Teacher Information This activity is designed to be team-taught by the classroom and art teacher. Use this guide in conjunction with fish-related art to
Educational Material Bony Fish Anatomy Worksheet Teacher Information This activity is designed to be team-taught by the classroom and art teacher. Use this guide in conjunction with fish-related art to
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
MAKING SENSE OF ENERGY Electromagnetic Waves
 Adapted from State of Delaware TOE Unit MAKING SENSE OF ENERGY Electromagnetic Waves GOALS: In this Part of the unit you will Learn about electromagnetic waves, how they are grouped, and how each group
Adapted from State of Delaware TOE Unit MAKING SENSE OF ENERGY Electromagnetic Waves GOALS: In this Part of the unit you will Learn about electromagnetic waves, how they are grouped, and how each group
AZ State Standards. Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred.
 Forms of Energy AZ State Standards Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred. PO 1. Describe the following ways in which
Forms of Energy AZ State Standards Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred. PO 1. Describe the following ways in which
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
Exchange and transport
 Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
Brain & Mind. Bicester Community College Science Department
 B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Problem-Based Group Activities for a Sensation & Perception Course. David S. Kreiner. University of Central Missouri
 -Based Group Activities for a Course David S. Kreiner University of Central Missouri Author contact information: David Kreiner Professor of Psychology University of Central Missouri Lovinger 1111 Warrensburg
-Based Group Activities for a Course David S. Kreiner University of Central Missouri Author contact information: David Kreiner Professor of Psychology University of Central Missouri Lovinger 1111 Warrensburg
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus
 Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Processing the Image or Can you Believe what you see? Light and Color for Nonscientists PHYS 1230
 Processing the Image or Can you Believe what you see? Light and Color for Nonscientists PHYS 1230 Optical Illusions http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/mot_mib/index.html Vision We construct images unconsciously
Processing the Image or Can you Believe what you see? Light and Color for Nonscientists PHYS 1230 Optical Illusions http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/mot_mib/index.html Vision We construct images unconsciously
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
Standards Alignment Minnesota Science Standards Alignment Matrix www.brainu.org/resources/mnstds
 Lesson Summary: Neurons transfer information by releasing neurotransmitters across the synapse or space between neurons. Students model the chemical communication between pre-synaptic and post-synaptic
Lesson Summary: Neurons transfer information by releasing neurotransmitters across the synapse or space between neurons. Students model the chemical communication between pre-synaptic and post-synaptic
Preview of Period 2: Forms of Energy
 Preview of Period 2: Forms of Energy 2.1 Forms of Energy How are forms of energy defined? 2.2 Energy Conversions What happens when energy is converted from one form into another form? 2.3 Efficiency of
Preview of Period 2: Forms of Energy 2.1 Forms of Energy How are forms of energy defined? 2.2 Energy Conversions What happens when energy is converted from one form into another form? 2.3 Efficiency of
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
BIOLÓGIA ANGOL NYELVEN BIOLOGY
 Biológia angol nyelven középszint 0612 ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA 2007. május 17. BIOLÓGIA ANGOL NYELVEN BIOLOGY KÖZÉPSZINTŰ ÍRÁSBELI ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA INTERMEDIATE LEVEL WRITTEN EXAM JAVÍTÁSI-ÉRTÉKELÉSI ÚTMUTATÓ
Biológia angol nyelven középszint 0612 ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA 2007. május 17. BIOLÓGIA ANGOL NYELVEN BIOLOGY KÖZÉPSZINTŰ ÍRÁSBELI ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA INTERMEDIATE LEVEL WRITTEN EXAM JAVÍTÁSI-ÉRTÉKELÉSI ÚTMUTATÓ
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Color and Light. DELTA SCIENCE READER Overview... 125 Before Reading... 126 Guide the Reading... 127 After Reading... 133
 Color and Light T ABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment and
Color and Light T ABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment and
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Chapter 2: Forms of Energy
 Chapter 2: Forms of Energy Goals of Period 2 Section 2.1: To describe the forms of energy Section 2.2: To illustrate conversions from one form of energy to another Section 2.3 To describe energy storage
Chapter 2: Forms of Energy Goals of Period 2 Section 2.1: To describe the forms of energy Section 2.2: To illustrate conversions from one form of energy to another Section 2.3 To describe energy storage
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
9.00 EXAM 1 NOTES KOSSLYN CHAPTER 3 Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind
 The processes of sensation and perception lie at the root of our experience of feeling alive, serving as the foundation for most of what we know and do. Sensation the result of neural responses that occur
The processes of sensation and perception lie at the root of our experience of feeling alive, serving as the foundation for most of what we know and do. Sensation the result of neural responses that occur
Light and its effects
 Light and its effects Light and the speed of light Shadows Shadow films Pinhole camera (1) Pinhole camera (2) Reflection of light Image in a plane mirror An image in a plane mirror is: (i) the same size
Light and its effects Light and the speed of light Shadows Shadow films Pinhole camera (1) Pinhole camera (2) Reflection of light Image in a plane mirror An image in a plane mirror is: (i) the same size
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
THE NATURE OF LIGHT AND COLOR
 THE NATURE OF LIGHT AND COLOR THE PHYSICS OF LIGHT Electromagnetic radiation travels through space as electric energy and magnetic energy. At times the energy acts like a wave and at other times it acts
THE NATURE OF LIGHT AND COLOR THE PHYSICS OF LIGHT Electromagnetic radiation travels through space as electric energy and magnetic energy. At times the energy acts like a wave and at other times it acts
Current Staff Course Unit/ Length. Basic Outline/ Structure. Unit Objectives/ Big Ideas. Properties of Waves A simple wave has a PH: Sound and Light
 Current Staff Course Unit/ Length August August September September October Unit Objectives/ Big Ideas Basic Outline/ Structure PS4- Types of Waves Because light can travel through space, it cannot be
Current Staff Course Unit/ Length August August September September October Unit Objectives/ Big Ideas Basic Outline/ Structure PS4- Types of Waves Because light can travel through space, it cannot be
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES
 SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc).
 Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Forms of Energy Explain
 Forms of Energy Explain DIRECTIONS 1. For the Explain portion of the section, work through each slide 2. For each form there are three slides: 1. Introduce the form of energy 2. Give examples of the form
Forms of Energy Explain DIRECTIONS 1. For the Explain portion of the section, work through each slide 2. For each form there are three slides: 1. Introduce the form of energy 2. Give examples of the form
4/17/2012. General Senses
 General Senses The general senses are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. Receptors for those sensations are distributed throughout the body. A sensory receptor is a specialized
General Senses The general senses are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. Receptors for those sensations are distributed throughout the body. A sensory receptor is a specialized
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 2 The Neural Impulse Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The cell body is enclosed by the. A) cell membrane
Chapter 2 The Neural Impulse Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The cell body is enclosed by the. A) cell membrane
The Neuron and the Synapse. The Neuron. Parts of the Neuron. Functions of the neuron:
 The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation
 Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation 1. When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it is A. absorbed. B. bent away from the normal. C. bent towards from the normal. D. continues in the
Chapter 17: Light and Image Formation 1. When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction it is A. absorbed. B. bent away from the normal. C. bent towards from the normal. D. continues in the
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses
 Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Skin - heaviest organ in the body Cutaneous System Epidermis is the outer layer of the skin, which is made up of dead skin cells Dermis is below the epidermis and contains
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Skin - heaviest organ in the body Cutaneous System Epidermis is the outer layer of the skin, which is made up of dead skin cells Dermis is below the epidermis and contains
GRADE 6 SCIENCE. Demonstrate a respect for all forms of life and a growing appreciation for the beauty and diversity of God s world.
 GRADE 6 SCIENCE STRAND A Value and Attitudes Catholic Schools exist so that curriculum may be taught in the light of Gospel teachings. Teachers must reinforce Gospel truths and values so that students
GRADE 6 SCIENCE STRAND A Value and Attitudes Catholic Schools exist so that curriculum may be taught in the light of Gospel teachings. Teachers must reinforce Gospel truths and values so that students
Light and Sound. Pupil Booklet
 Duncanrig Secondary School East Kilbride S2 Physics Elective Light and Sound Name: Pupil Booklet Class: SCN 3-11a - By exploring the refraction of light when passed through different materials, lenses
Duncanrig Secondary School East Kilbride S2 Physics Elective Light and Sound Name: Pupil Booklet Class: SCN 3-11a - By exploring the refraction of light when passed through different materials, lenses
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
After a wave passes through a medium, how does the position of that medium compare to its original position?
 Light Waves Test Question Bank Standard/Advanced Name: Question 1 (1 point) The electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies are called A. radio waves. B. gamma rays. C. X-rays. D. visible light.
Light Waves Test Question Bank Standard/Advanced Name: Question 1 (1 point) The electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies are called A. radio waves. B. gamma rays. C. X-rays. D. visible light.
Eye Injuries. The Eyes The eyes are sophisticated organs. They collect light and focus it on the back of the eye, allowing us to see.
 Eye Injuries Introduction The design of your face helps protect your eyes from injury. But injuries can still damage your eyes. Sometimes injuries are severe enough that you could lose your vision. Most
Eye Injuries Introduction The design of your face helps protect your eyes from injury. But injuries can still damage your eyes. Sometimes injuries are severe enough that you could lose your vision. Most
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
