Internal anatomy and physiology D. L. A. Underwood Biology General Entomology
|
|
|
- Neil Bond
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Internal anatomy and physiology D. L. A. Underwood Biology General Entomology A. Digestive system 1. Foregut a. Mouth b. The pharynx may be highly modified into a pump seen in sucking insects like Lepidoptera, Hemiptera, and many Diptera. c. Posterior to the pharynx is the esophagus that is commonly modified to form a crop, or storage area. Some groups have a modified crop that is distensible (Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera, and Diptera) allowing for additional storage. d. Immediately posterior to the crop is the proventriculus, a structure that contains sclerotized teeth-like denticles. The denticles aid in grinding the food. e. Some fluid-feeding insects lack a proventriculus. f. The stomodael valve (foregut valve) regulates the flow of material from the foregut to the midgut and generally demarks the boundary between the two. g. The foregut is lined with chitinous protective layer called the intima. Many plant feeding insects consume leaves with spines and trichomes that could lacerate the lining of the gut. h. The intima prohibits absorption of nutrients. 2. Midgut a. In many insects the foregut valve has associated gastric caecae that produce digestive enzymes and increase surface area. b. The midgut is not lined by intima and most of the absorption of nutrients occurs here in the ventriculus. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 1 of 18
2 c. As in other animals, the gut is often highly modified depending upon the type of food eaten. 3. Hindgut a. The Malpighian tubules attach to the pylorus region of the hindgut. They are part of the excretory system and will be discussed below. b. Posterior to the Malpighian tubules is the anterior intestine and the highly muscularized rectum that terminates in the anus. c. The rectum functions in removing water from the fecal material. d. Water and some small molecules are removed from the gut in the hindgut so that the insect produces very dry excrement. 4. Molting a. The foregut and the hindgut are lined with a chitinous unsclerotized layer that is shed during molts. b. The gut epithelial cells are continuous with the epidermal cells. c. Before a molt, the insect takes in air or water into the digestive system to increase its internal hemolymph pressure allowing for the rupture of the cuticle. 5. Team Project - B takes notes, A speaks a. Pick two of the previous insects and predict two specific modifications of the digestive system that you would to expect to see based on the diet of the bug. 6. Modifications to the digestive system Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 2 of 18
3 Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 3 of 18
4 B. Circulatory system Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 4 of 18
5 1. Open circulatory system a. The major portion of the "blood" or hemolymph is not found within vessels. b. The hemolymph bathes the organs within the body cavity, the hemocoel. c. Insects do not rely on the circulatory system for the transport of oxygen. This instead is done by the tracheal system (see below). d. Hemolymph enters the dorsal vessel or heart via small openings called ostia. e. The hemolymph is then pumped towards the head where it then returns to the hemocoel. 2. Functions of hemolymph a. Serves as a lubricant for the movement of internal structures relative to one another. b. It is a hydraulic medium for applying pressure for molting, eversible glands are extruded via pressure changes, and some muscular contraction is opposed by hydrostatic pressure within the hemocoel. c. Hemolymph transports various substances from one tissue to another. d. Specialized cells that phagocytosize or encapsulate foreign particles are found in the hemolymph and are very important in the "immune" system of insects. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 5 of 18
6 C. Tracheal system 1. Gas exchange system that does not rely on an oxygen transport pigment. a. A few insects have hemoglobin and in some forms hemocyanin plays a role in oxygen transport. b. Consists of a system of branching tubes (tracheae) and openings to the outside called spiracles. c. Most Collembola, many Protura, and certain endoparasitic wasp larvae lack a tracheal system; gas exchange occurs via the integument. 2. Spiracles a. Simple spiracles are merely openings to the outside. b. Atriate spiracles have mechanisms that allow the insect to close the opening. i Prevents water loss ii Prevents the entry of pathogens and parasites 3. Tracheae a. Tubes that begin rather large and branch to become successively smaller and smaller as they penetrate deep within the tissues of the insect. b. They are also lined with intima that is shed during each molt. c. Chitin is lacking in the smaller tracheae. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 6 of 18
7 4. Air sacs a. Air sacs are found mainly in flying insects. b. Many potential functions, all rather speculative, including increasing the volume of air in the body for exchange, lowering the specific gravity for flight, and providing room for the growth of internal organs. 5. Tracheoles a. The smallest branches of the tracheae are the tracheoles. b. Gaseous exchange occurs here. c. Provide for a tremendous amount of surface area (there are 1.5 million tracheoles in a large silkworm larva). 6. Two types a. Open systems are found in most terrestrial insects and many aquatic forms. One or more pairs of spiracles are present. Usually the first pair is found on the mesothorax. b. Closed systems are found in many aquatic insects and the larvae of endoparasitic species. Closed systems lack spiracles and gaseous exchange between the tracheal system and the environment occurs directly through the integument. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 7 of 18
8 7. Two types of ventilation - passive and active ventilation a. In passive ventilation the insect employs no pumping or other movements to aid the passage of gases into and out of the tracheae. i The insect may control the flow by opening and closing the spiracles. ii Generally effective for smaller insects and those with well-ventilated air sacs. b. In active ventilation, the insect increases air movement by pumping movements of the abdomen, thorax, and even protraction and retraction of the head. i In many larger bodied and/or active insects requiring large volumes of gas for exchange, the movements of the body are coordinated with opening and closing of the spiracles to produce a unidirectional flow of gases through the body. Air moves into the animal via the thoracic spiracles and out of the body via the abdominal spiracles. 8. Ventilation in aquatic insects a. Immature aquatic insects with closed tracheal systems rely entirely on passive diffusion of gases through the integument into and out of the tracheae. i In smaller bodied immatures, passive diffusion is adequate with the use of the tracheal system. ii Many larger bodied aquatic insects posses tracheal gills, integumental evaginations covered by a very thin cuticle and well supplied with tracheae and tracheoles. iii Other larger bodied insects may have spiracular gills or cuticular gills. b. Aquatic insects with open tracheal systems obtain oxygen in a variety of ways. i Some surface periodically. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 8 of 18
9 ii All require a hydrofuge structure that functions in breaking the surface film of the water thereby exposing the spiracles to the atmospherere. iii Hydrofuge structures are usually made of "hairs" that are resistant to wetting causing the water near the surface to be repelled from the hydrofuge areas. iv Many aquatic Hemiptera and Coleoptera carry air stores in the form of bubbles. These bubbles are held in place by hydrofuge hairs and/or the shape of the body forms a storage area. v Many insects carry stores of air and are able to replenish the oxygen without surfacing. vi Stores of oxygen act as a "physical gill" where the partial pressure differential of the oxygen between the gill and the water results in oxygen diffusing into the gill from its dissolved state. Nitrogen in the air store does not readily diffuse into the water and thus prevents the air store from collapsing. vii A plastron is a very thin layer of gas held firmly in place by tiny hydrofuge hairs. The spiracles open directly into this thin layer. viii Other insects tap directly into aquatic plants to obtain oxygen. 9. Team Project - C takes notes, B speaks a. Which state of the tracheal system, open or closed, is ancestral to the Hexapoda? Why? Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 9 of 18
10 D. Excretory system 1. The function of the excretory system is to maintain chemical homeostasis. a. The hemolymph is cleansed of metabolic wastes, usually nitrogenous, and toxins, and the concentration of salt and water are regulated. b. The Malpighian tubules and the hindgut comprise the excretory system. 2. Malpighian tubules a. Attached to the gut, they float freely within the hemocoel and are bathed in hemolymph. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 10 of 18
11 b. They vary in number from two to 250 or more. c. They also vary with respect to the distal ends and the location and direction of the flow of substances into and out of the tubule lumen. d. The Malpighian tubules function in removing toxins, nitrogenous wastes, and ions to maintain ionic concentrations within the hemolymph. 3. Rectum of the hindgut a. Water and other small ions are removed from the gut by the rectum. 4. Diet and environment a. The ionic composition of an insect's diet is very often very different from that in the hemolymph requiring the active transport of some ions either into the gut for excretion or from the gut into the hemolymph. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 11 of 18
12 Assassin bug Bot fly Cockroach Walking stick Swallowtail b-fly Potato beetle b. Similarly, the abiotic conditions of the environment influence whether an insect must conserve or excrete water or salt. i Freshwater insects must constantly excrete water that enters the body passively through the integument. ii Many terrestrial insects tend to lose water via evaporation while exchanging gases, while some plant sap feeders ingest so much water that they are challenged with excreting excess water and concentrating nutrients. iii Saltwater insects tend to lose water via passive diffusion through the integument. 5. Nitrogenous excretion a. Most aquatic insects excrete ammonia. i Ammonia is highly toxic but soluble in water. ii Only insects that have access to lots of water can excrete ammonia. b. Terrestrial forms or those species that are water-limited excrete uric acid. i Uric acid is insoluble in water and relatively non-toxic. ii The ability to form uric acid is often cited as one of the reasons members of the Arthropoda have been so successful on land relative to other invertebrates. iii Cockroaches store their uric acid. It is thought that during the Carboniferous period (about 345 million years ago) when cockroaches first evolved, there was an extreme shortage of nitrogen. Cockroaches that could store and reuse their nitrogenous wastes had greater fitness than those that could not. Cockroaches also have a symbiotic relationship with bacteria that produce uricase, the enzyme necessary to convert uric acid into a useable form. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 12 of 18
13 E. "Fat" bodies 1. Synthesis and secretion a. Larval-specific storage proteins (e.g. calliphorin) b. Vitellogenin (female-specific hemolymph protein) c. Lipoprotein and lipophorin (transport molecules) d. Juvenile hormone carrier proteins e. Juvenile hormone esterases f. Hemoglobin in Chironomus larvae (molecule is considered a storage protein) g. Diapause proteins h. Production of mixed-function oxidases (MFOs) 2. Mobilization and storage of reserves to be used as precursors for metabolism in other tissues a. Lipids b. Glycogen c. Proteins F. Nervous system 1. The neuron a. The basic functional unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. b. The neuron consists of a cell body, one or more axons, and dendrites. c. Three general types of neurons i Unipolar neurons have a single stalk from the cell body that connects with the axon. ii In bipolar neurons, the cell body bears an axon and a single, branched or unbranched dendrite. iii Multipolar neurons have an axon and several branched dendrites. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 13 of 18
14 2. Team Project - A takes notes, B speaks a. Give one potential type of stimulus where a bipolar neuron would be ideal. b. Give one potential type of stimulus where a multipolar neuron would be ideal. c. Neurons 'communicate' with one another and with other cells either electrically or chemically via neurotransmitters through small spaces called synapses. d. Actions may be either excitatory or inhibitory. e. Areas where neurons are concentrated are called ganglia. f. Nerves are bundles of axons. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 14 of 18
15 3. Central nervous system a. The central nervous system is composed of a double chain of ganglia joined by longitudinal connectives. b. The anterior ganglion is the brain. The brain connects to the ventral chain of ganglia via two connectives that travel around the pharynx. The brain connects to the eyes, ocelli, and antennae. c. The subesophageal ganglion is highly complex and innervates the sense organs and muscles associated the mouthparts, the salivary glands, and the neck region. In many insects the subesophageal ganglion is also the primary excitatory or inhibitory influence on motor activity of the whole insect. d. The frontal ganglion connects the brain to the stomatogastric subsystem. e. The hypocerebral ganglion is associated with two endocrine glands one of which is the corpus allatum that produces JH (juvenile hormone). f. The thoracic ganglia contain the sensory and motor centers for their respective segments. In some insects these three ganglia are fused into one. g. In the ancestral state, each abdominal segment possesses a ganglion with the final ganglion associated with the genitalia. More derived taxa show a reduction in the number of abdominal ganglia. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 15 of 18
16 Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 16 of 18
17 4. Visceral nervous system a. Nerves associated with the brain, salivary glands, and the foregut are the stomatogastric subsystem. These include the frontal ganglion and the hypocerebral ganglion. b. The nerves associated with the ventral nerve cord are the ventral viscera subsystem. c. The caudal visceral subsystem is associated with the posterior segments of the abdomen (the caudal region) including the reproductive system. 5. Peripheral nervous system a. All of the nerves with synapses to the central and the visceral nervous systems comprise the peripheral nervous system. b. These nerves are associated with sensory structures. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 17 of 18
18 6. An overall view of the interrelationships of the insect nervous system. Internal anatomy and physiology - Page 18 of 18
The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Lecture Goals. The Insect Circulatory System. The Insect Circulatory System
 The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems What are some of the main roles of the human circulatory system? Lecture Goals Understand the open circulatory system in insects. Recognize the lack of integration
The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems What are some of the main roles of the human circulatory system? Lecture Goals Understand the open circulatory system in insects. Recognize the lack of integration
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Class Insecta - The insects
 A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. The alimentary canal of insects is a long, muscular, and tubular structure extending from mouth to
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The alimentary canal of insects is a long, muscular, and tubular structure extending from mouth to anus. It is differentiated into three regions viz., Foregut,
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The alimentary canal of insects is a long, muscular, and tubular structure extending from mouth to anus. It is differentiated into three regions viz., Foregut,
How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion. How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion. How Organisms Exchange Gases: Respiratory Organs
 How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion Gas is exchanged between respiratory medium and body fluids through diffusion across a respiratory surface To effectively exchange gases, the surface must
How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion Gas is exchanged between respiratory medium and body fluids through diffusion across a respiratory surface To effectively exchange gases, the surface must
Exchange and transport
 Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
7. A selectively permeable membrane only allows certain molecules to pass through.
 CHAPTER 2 GETTING IN & OUT OF CELLS PASSIVE TRANSPORT Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells. Some substances can cross the cell membrane
CHAPTER 2 GETTING IN & OUT OF CELLS PASSIVE TRANSPORT Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells. Some substances can cross the cell membrane
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
ANSWER KEY. 6. Spiracles are small holes on the sides of an insect s abdomen. These holes enable the insect
 ANSWER KEY 1. Growth and development occur in all living organisms. When this organ in a human gets worn away it is replaced A. liver B. lung C. skin D. kidney 2. Energy is the ability to do make things
ANSWER KEY 1. Growth and development occur in all living organisms. When this organ in a human gets worn away it is replaced A. liver B. lung C. skin D. kidney 2. Energy is the ability to do make things
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Homeostasis and Transport Module A Anchor 4
 Homeostasis and Transport Module A Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - Buffers play an important role in maintaining homeostasis in organisms. - To maintain homeostasis, unicellular organisms grow, respond to the
Homeostasis and Transport Module A Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - Buffers play an important role in maintaining homeostasis in organisms. - To maintain homeostasis, unicellular organisms grow, respond to the
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Date: Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George. Score: 1) A cell with 1% solute concentration is placed in a beaker with a 5% solute concentration.
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
2. Predators have bilateral symmetry, good musculature sense organs and a well developed nervous system.
 A. A.INTRODUCTION 1. Animals are heterotrophic; they must take in food. 2. Predators have bilateral symmetry, good musculature sense organs and a well developed nervous system. 3. Bilareral symmetry (cut
A. A.INTRODUCTION 1. Animals are heterotrophic; they must take in food. 2. Predators have bilateral symmetry, good musculature sense organs and a well developed nervous system. 3. Bilareral symmetry (cut
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Pre-requisites: Successful completion of 4th grade science and the 4th grade science assessment.
 Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Insect Respiration. Spider Respiratory Systems
 Respiration In Spiders Robert Gale Breene III College of the Southwest, Carlsbad, New Mexico USA Respiration, loosely the gaseous exchange of O 2 and CO 2 in spiders, is often misunderstood, even by arachnologists.
Respiration In Spiders Robert Gale Breene III College of the Southwest, Carlsbad, New Mexico USA Respiration, loosely the gaseous exchange of O 2 and CO 2 in spiders, is often misunderstood, even by arachnologists.
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Anatomy of the Honey Bee
 Anatomy of the Honey Bee As a member of the insect class (Insecta), honey bees share with other insects the following characteristics. Honey bees are segmented in nearly all their body parts: three segments
Anatomy of the Honey Bee As a member of the insect class (Insecta), honey bees share with other insects the following characteristics. Honey bees are segmented in nearly all their body parts: three segments
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Honey Bee Biology. Dr. Debbie Delaney
 Honey Bee Biology Dr. Debbie Delaney Morphology of the Honey Bee The honey bee has three body divisions Head Thorax Abdomen Head Drawing modified from R. E. Snodgrass Exoskeleton Body Hairs Morphology
Honey Bee Biology Dr. Debbie Delaney Morphology of the Honey Bee The honey bee has three body divisions Head Thorax Abdomen Head Drawing modified from R. E. Snodgrass Exoskeleton Body Hairs Morphology
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Visit www.ncerthelp.com For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-7
 Chapter-7 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS POINTS TO REMEMBER Tissue : A group of similar cells along with intercellular substances which perform a specific function. Simple epithelium : is composed
Chapter-7 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS POINTS TO REMEMBER Tissue : A group of similar cells along with intercellular substances which perform a specific function. Simple epithelium : is composed
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue
 12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
 Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions
 Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource
 CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed
 1 Transport systems chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed Simple organisms Diffusion the free movement of particles in a liquid or a gas down a concentration
1 Transport systems chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed Simple organisms Diffusion the free movement of particles in a liquid or a gas down a concentration
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function.
 12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Nerve Cell Communication
 Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 2 forty minute class periods Teacher Provides: For each student
Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 2 forty minute class periods Teacher Provides: For each student
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment
 Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment 1a. All living things are made up of. a. cells b. tissues c. organisms d. systems 1b. All living things are made up of. 1c. Explain what cells are
Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment 1a. All living things are made up of. a. cells b. tissues c. organisms d. systems 1b. All living things are made up of. 1c. Explain what cells are
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Which of the following can be determined based on this model? The atmosphere is the only reservoir on Earth that can store carbon in any form. A.
 Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane. AP Biology
 Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane More than just a barrier Expanding our view of cell membrane beyond just a phospholipid bilayer barrier phospholipids plus Fluid Mosaic Model In 1972, S.J.
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane More than just a barrier Expanding our view of cell membrane beyond just a phospholipid bilayer barrier phospholipids plus Fluid Mosaic Model In 1972, S.J.
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
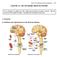 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Biology 12 June 2003 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 June 2003 rovincial Examination ANWER KEY / CORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell rocesses and Applications 3. Human Biology ub-organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I, J, K,
Biology 12 June 2003 rovincial Examination ANWER KEY / CORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell rocesses and Applications 3. Human Biology ub-organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I, J, K,
