1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
|
|
|
- Marshall Hudson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid 1. Which of the structures listed above can be observed during a gross anatomical examination of the eye? a. 1, 2, 3, 4 & 5 b. 1, 3, 4 & 5 c. 1, 2, 3, 5 & 9 d. 1, 3, 5 & 10 e. 1, 2, 3, 5 & Which of the structures listed above cannot be observed by examining the crosssection of the eye? a. 4, 6 & 8 b. 3, 4, 6 & 8 c. 3, 6, 8 & 9 d. 4, 6, 8 & 9 e. 4, 6, 7 & 8 3. Of the following processes, which would be used to see a stationary object at a distance of 15 feet? a. Refraction b. Accommodation c. Pupillary light reflect d. A & B e. A, B & C 4. Which of the following retinal cell types are found between the outer and inner nuclear layers? a. Horizontal cells b. Ganglion cells c. Amacrine cells d. Photoreceptors
2 e. Bipolar cells 5. Which of the following sequences of retinal layers is organized closest to the vitreous humor to farthest from the vitreous humor? a. Outer nuclear, inner nuclear, ganglion b. Inner nuclear, outer nuclear, ganglion c. Outer nuclear, ganglion, inner nuclear d. Ganglion, inner nuclear, outer nuclear e. Inner nuclear, ganglion, outer nuclear 6. The cerebral hemispheric lobe that is most anterior has which of the following functions? A. Movement B. Audition C. Vision D. Olfaction E. Somatic sensation 7. Which of the following describes processing of visual information appearing in the right temporal hemi-field? a. Image is formed on left nasal retina; axons do not decussate; processed by left LGN layers 2, 4 & 6 b. Image is formed on right temporal retina; axons decussate; processed by left LGN layers 2, 3 & 5 c. Image is formed on right nasal retina; axons decussate; processed by left LGN 2, 3 & 5 d. Image is formed on right nasal retina; axons decussate; processed by left LGN layers 1, 4 & 6 e. Image is formed on left nasal retina; axons decussate; processed by right LGN layers 1, 4 & 6 8. In regards to LGN processing of an image appearing only in the left hemifield and activating only M-type ganglion cells, which of the following is True? a. Temporal image is processed by layer 1 of the right LGN b. Temporal image is processed by layers 4 & 6 of the right LGN c. Nasal image processed by layer 2 of the right LGN d. Nasal image is processed by layers 3 & 5 of the right LGN e. A & C 9. In regards to the basilar membrane, which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The base is wider than the apex.
3 b The base is stiffer than the apex. c. Low frequency sound displaces the basilar membrane near its apex. d. Sound waves with the lowest energy displace the basilar membrane near its base. e. A & D 10. Which of the following is the target of the right optic radiation? a. Right lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus b. Left lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus c. Optic chiasm d. Right primary visual cortex e. Left primary visual cortex 11. Which of the following membranes is continuous with the auditory canal? a. Basilar membrane b. Tectorial membrane c. Oval window d. Tympanic membrane e. Round window 12. In the cochlea, where are the auditory receptors located? a. Scala vestibuli b. Scala tympani. c. Organ of corti d. Basilar membrane e. Helicotrema
4 13. In regards to middle ear function, which of the following is TRUE? a. Airborne sound has higher impedance than the fluid of the inner ear. b. Sound wave pressure is mechanically amplified by the auditory canal. c. The pressure at the oval window is equal to that at the round window. d. The basilar membrane provides mechanical advantage by acting as lever. e. The inner ear is continuous with the outside world via the eustachian tube 14. All of the following are mechanical events in the auditory system EXCEPT: a. Movement of K+ through channels in the stereocilia b. Movement of hair cell stereocilia against the tectorial membrane. c. Movement of the ossicles in the middle ear d. Displacement of the basilar membrane e. Movement of the fluid within the choclea 15. Injuries to all of the following would affect nociception EXCEPT: A. Dorsal root ganglion B. Cranial nerves C. Spinal nerves D. Spinal pathway E. Dorsal column 16. All of the following are characteristics of somatosensory pathways EXCEPT: A. Information detected by pacinian corpuscles does not cross until it reaches the brainstem B. The ST pathway crosses in the spinal cord and ascends to make its first synapse in the diencephalon C. Sensory information generated by activating muscle spindle fiber ascends in the dorsal column D. The primary somatic cortex is the final target of both the DCML and ST pathways E. C & D
5 Use the following table to answer Question 17. I II III IV V Spinal nerve Dorsal root ganglion Spinal pathway Dorsal column Ventral root 17. Which of the spinal cord structures listed above includes both somatic and motor elements? A. I only B. I, II C. I, III D. I, II, IV E. I, II, V
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology. Sensory Adaptation. Four Steps to Sensation. Types of Sensors Structural Design
 Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing.
 The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
The Sense Organs... (page 409) Help maintain homeostasis by capturing stimuli from the external environment and relaying them to the brain for processing. Ex. Eye structure - protected by bony ridges and
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology
 Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
Hearing and Deafness 1. Anatomy & physiology Chris Darwin Web site for lectures, lecture notes and filtering lab: http://www.lifesci.susx.ac.uk/home/chris_darwin/ safari 1 Outer, middle & inner ear Capture;
SPECIAL SENSES. Introduction: Activity 1: Observation of the Human Eye Model
 SPECIAL SENSES Introduction: The special senses include vision, hearing, equilibrium (balance), taste and smell. In these activities you will be performing a series of physiological tests for each of these
SPECIAL SENSES Introduction: The special senses include vision, hearing, equilibrium (balance), taste and smell. In these activities you will be performing a series of physiological tests for each of these
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
The Visual Cortex 0 http://www.tutis.ca/neuromd/index.htm 20 February 2013
 T he Visual Cortex 0 Chapter contents Contents Chapter 2... 0 T he Visual Cortex... 0 Chapter Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Optic Chiasm... 2 Where do the eye's ganglion cells project to?... 3 To where
T he Visual Cortex 0 Chapter contents Contents Chapter 2... 0 T he Visual Cortex... 0 Chapter Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Optic Chiasm... 2 Where do the eye's ganglion cells project to?... 3 To where
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Nervous System: Special Senses (Chapter 17) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE SENSORY SYSTEM SUBCOURSE MD0582 EDITION 100
 U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE SENSORY SYSTEM SUBCOURSE MD0582 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE SENSORY SYSTEM SUBCOURSE MD0582 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION. Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology
 PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06)
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing (added 09/06) 1. Briefly review the anatomy of the cochlea. What is the cochlear blood supply? SW 2. Discuss the effects of the pinna, head and ear canal on the transmission
Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline
 Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline Five special senses Olfaction = smell Gustation = taste Vision = sight Hearing Equilibrium Special sensory receptors: 1. Distinct cells 2. Complex organ /
Chapter 17 The Special Senses Lecture Outline Five special senses Olfaction = smell Gustation = taste Vision = sight Hearing Equilibrium Special sensory receptors: 1. Distinct cells 2. Complex organ /
An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye
 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye Changes in the eyelid fissure A, Graves disease stare. B, Myathenia gravis. C, Congenital ptosis of right eye. D, Levator disinsertion. E, Horner syndrome
An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye Changes in the eyelid fissure A, Graves disease stare. B, Myathenia gravis. C, Congenital ptosis of right eye. D, Levator disinsertion. E, Horner syndrome
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
The Eye ACCESSORY STRUCTURES
 The Eye The eye forms a visual image and projects it onto the sensory receptors (photoreceptors) of the retina. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport,
The Eye The eye forms a visual image and projects it onto the sensory receptors (photoreceptors) of the retina. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport,
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus
 Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
MODERN CLINICAL OPTOMETRY BILLING & CODING THE MEDICAL EYE EXAMINATION. Definitions of Eye Examinations. Federal Government Definition
 MODERN CLINICAL OPTOMETRY BILLING & CODING THE MEDICAL EYE EXAMINATION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Definitions of Eye Examinations Optometry
MODERN CLINICAL OPTOMETRY BILLING & CODING THE MEDICAL EYE EXAMINATION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Definitions of Eye Examinations Optometry
Common visual symptoms and findings in MS: Clues and Identification
 Common visual symptoms and findings in MS: Clues and Identification Teresa C Frohman, PA-C, MSCS Neuro-ophthalmology Research Manager, UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas Professor Biomedical Engineering,
Common visual symptoms and findings in MS: Clues and Identification Teresa C Frohman, PA-C, MSCS Neuro-ophthalmology Research Manager, UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas Professor Biomedical Engineering,
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
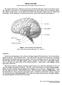 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain
 Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Lecture One: Brain Basics
 Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
 CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
iocutouchtm for ipad Contents of Videos and Still Images Anatomy 906. Normal Eye and Orbit - no labels 907. Normal Eye and Orbit - with labels
 iocutouchtm for ipad Contents of Videos and Still Images Anatomy 906. Normal Eye and Orbit - no labels 907. Normal Eye and Orbit - with labels Normal Eye 474. Normal Eye overview 476. Cornea - overview
iocutouchtm for ipad Contents of Videos and Still Images Anatomy 906. Normal Eye and Orbit - no labels 907. Normal Eye and Orbit - with labels Normal Eye 474. Normal Eye overview 476. Cornea - overview
So, how do we hear? outer middle ear inner ear
 The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
The ability to hear is critical to understanding the world around us. The human ear is a fully developed part of our bodies at birth and responds to sounds that are very faint as well as sounds that are
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
IMAGE ASSISTANT: OPHTHALMOLOGY
 IMAGE ASSISTANT: OPHTHALMOLOGY Summary: The Image Assistant has been developed to provide medical doctors with a software tool to search, display, edit and use medical illustrations of their own specialty,
IMAGE ASSISTANT: OPHTHALMOLOGY Summary: The Image Assistant has been developed to provide medical doctors with a software tool to search, display, edit and use medical illustrations of their own specialty,
All input from sensory neurons to the central nervous
 55 Sensory Systems Concept Outline 55.1 Animals employ a wide variety of sensory receptors. Categories of Sensory Receptors and Their Actions. Sensory receptors can be classified according to the type
55 Sensory Systems Concept Outline 55.1 Animals employ a wide variety of sensory receptors. Categories of Sensory Receptors and Their Actions. Sensory receptors can be classified according to the type
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses
 Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Skin - heaviest organ in the body Cutaneous System Epidermis is the outer layer of the skin, which is made up of dead skin cells Dermis is below the epidermis and contains
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Skin - heaviest organ in the body Cutaneous System Epidermis is the outer layer of the skin, which is made up of dead skin cells Dermis is below the epidermis and contains
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Processing the Image or Can you Believe what you see? Light and Color for Nonscientists PHYS 1230
 Processing the Image or Can you Believe what you see? Light and Color for Nonscientists PHYS 1230 Optical Illusions http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/mot_mib/index.html Vision We construct images unconsciously
Processing the Image or Can you Believe what you see? Light and Color for Nonscientists PHYS 1230 Optical Illusions http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/mot_mib/index.html Vision We construct images unconsciously
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
The Eye: Anatomy, Histology & Histopathology. Gillian Shaw, DVM, MS September 9, 2011 gilliancshaw@gmail.com
 The Eye: Anatomy, Histology & Histopathology Gillian Shaw, DVM, MS September 9, 2011 gilliancshaw@gmail.com Overview Macroscopic Anatomy Some clinical presentations of eye disease Microscopic Anatomy Normal
The Eye: Anatomy, Histology & Histopathology Gillian Shaw, DVM, MS September 9, 2011 gilliancshaw@gmail.com Overview Macroscopic Anatomy Some clinical presentations of eye disease Microscopic Anatomy Normal
The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software
 Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Getting Ready for ICD-10. Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute
 Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute Chart Documentation: Will your documentation stand up to ICD-10? Do you always mark which eye, severity or status of the disease (chronic or acute), site, etiology
Dianna Hoskins, OCS Cincinnati Eye Institute Chart Documentation: Will your documentation stand up to ICD-10? Do you always mark which eye, severity or status of the disease (chronic or acute), site, etiology
Human Physiology Study Questions-2
 Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Light and Sound. Pupil Booklet
 Duncanrig Secondary School East Kilbride S2 Physics Elective Light and Sound Name: Pupil Booklet Class: SCN 3-11a - By exploring the refraction of light when passed through different materials, lenses
Duncanrig Secondary School East Kilbride S2 Physics Elective Light and Sound Name: Pupil Booklet Class: SCN 3-11a - By exploring the refraction of light when passed through different materials, lenses
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
4/17/2012. General Senses
 General Senses The general senses are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. Receptors for those sensations are distributed throughout the body. A sensory receptor is a specialized
General Senses The general senses are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception. Receptors for those sensations are distributed throughout the body. A sensory receptor is a specialized
Preparing for ICD-10 Advance Preparation for Implementation Charles Brownlow, OD drbrownlow@pmi-eyes.com
 Preparing for ICD-10 Advance Preparation for Implementation Charles Brownlow, OD drbrownlow@pmi-eyes.com International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9, ICD-10) Both include codes for all medical conditions,
Preparing for ICD-10 Advance Preparation for Implementation Charles Brownlow, OD drbrownlow@pmi-eyes.com International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9, ICD-10) Both include codes for all medical conditions,
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Optical Illusion Eye Tricks. This one will make you dizzy. Try focusing on just the center circle while moving your head.
 Optical Illusion Eye Tricks This one will make you dizzy. Try focusing on just the center circle while moving your head. Photocopy from original for best quality. H A N D O U T The Visual System The properly,
Optical Illusion Eye Tricks This one will make you dizzy. Try focusing on just the center circle while moving your head. Photocopy from original for best quality. H A N D O U T The Visual System The properly,
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system
 組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :littlebu@kmu.edu.tw
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :littlebu@kmu.edu.tw
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Human Perception and Computer Graphics
 Postgraduate Study Report DC-PSR-2004-06 Human Perception and Computer Graphics Martin Čadík Supervisor: Pavel Slavík January 2004 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering
Postgraduate Study Report DC-PSR-2004-06 Human Perception and Computer Graphics Martin Čadík Supervisor: Pavel Slavík January 2004 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering
Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice
 AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 8: What are the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound? Audition Audition, or hearing, is highly adaptive. We hear a wide range of sounds, but we hear best
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES
 SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
It s All in the Brain!
 It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
BSCI 201 - HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Spring Semester, 2012 LECTURE SYLLABUS The prerequisite for BSCI 201 is BSCI 105 or its equivalent.
 BSCI 201 - HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Spring Semester, 2012 LECTURE SYLLABUS The prerequisite for BSCI 201 is BSCI 105 or its equivalent. Attendance: Lecture - Attendance is strongly recommended, since
BSCI 201 - HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Spring Semester, 2012 LECTURE SYLLABUS The prerequisite for BSCI 201 is BSCI 105 or its equivalent. Attendance: Lecture - Attendance is strongly recommended, since
General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises
 1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates in the labyrinth.... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates in the labyrinth.... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
9.00 EXAM 1 NOTES KOSSLYN CHAPTER 3 Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind
 The processes of sensation and perception lie at the root of our experience of feeling alive, serving as the foundation for most of what we know and do. Sensation the result of neural responses that occur
The processes of sensation and perception lie at the root of our experience of feeling alive, serving as the foundation for most of what we know and do. Sensation the result of neural responses that occur
COW S EYE dissection. Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions. Safety first!
 COW S EYE dissection Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions One way to figure out how something works is to look inside it. To learn about how your eyes work, you can dissect, or take apart,
COW S EYE dissection Dissecting a Cow s Eye Step-by-Step Instructions One way to figure out how something works is to look inside it. To learn about how your eyes work, you can dissect, or take apart,
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system
 Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
COMMERCIALIZATION OF SOFTWARE FOR THE PREDICTION OF STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL CONSEQUENCES RESULTING FROM CORNEAL CORRECTIVE TREATMENTS JOSHUA LLOYD
 COMMERCIALIZATION OF SOFTWARE FOR THE PREDICTION OF STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL CONSEQUENCES RESULTING FROM CORNEAL CORRECTIVE TREATMENTS by JOSHUA LLOYD Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
COMMERCIALIZATION OF SOFTWARE FOR THE PREDICTION OF STRUCTURAL AND OPTICAL CONSEQUENCES RESULTING FROM CORNEAL CORRECTIVE TREATMENTS by JOSHUA LLOYD Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Auditory neuroanatomy: the Spanish heritage. Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1852 1934
 Auditory neuroanatomy: the Spanish heritage Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1852 1934 Rafael Lorente de Nó, 1902 1990 3 The nervous system is made up of cells. Estimates of the number of cells vary from
Auditory neuroanatomy: the Spanish heritage Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1852 1934 Rafael Lorente de Nó, 1902 1990 3 The nervous system is made up of cells. Estimates of the number of cells vary from
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Ventral Surface. The Cranial Nerves 4/5/2010. Review: Spinal Nerves
 The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors
 Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors Diego Betancourt and Carlos del Río Antenna Group, Public University of Navarra, Campus
Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors Diego Betancourt and Carlos del Río Antenna Group, Public University of Navarra, Campus
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
