Physics 9 Fall 2009 Homework 9 - Solutions
|
|
|
- Sharlene Gibbs
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 . Chapter 36 - Exercise 5. Physics 9 Fall 2009 Homework 9 - s What are V R and V C if the emf frequency in the figure is 0 khz? The voltage are V R = IR, and V C = IX C, where the capitative reactance is X C = E /ωc = /2πfC. The peak current is I = 0. So, the peak current is I = R2 + X 2 C = R 2 +X 2 C (2π (0 4 ) ) 2 = 0.04 A. So, we can now find V R = IR = = 6.0 V V C = IX C = π(0 4 )( ) = 8.0 V
2 2. Chapter 36 - Exercise 27. A series RLC circuit consists of a 50 Ω resistor, a 3.3 mh inductor, and a 480 nf capacitor. It is connected to an oscillator with a peak voltage of 5.0 V. Determine the impedance, the peak current, and the phase angle at frequencies (a) 3000 Hz, (b) 4000 Hz, and (c) 5000 Hz. The impedance is Z = ( R 2 + (X C X L ) 2 = R 2 + 2πfL ) 2, 2πfC while the peak current is I = /Z, and the phase angle is φ = tan [ X L X C ] [ ] R = tan 2πfL /2πfC. So, all we have to do is to plug in each of values for the different R frequencies. Doing so, we get the following table 3000 Hz 4000 Hz 5000 Hz Z 70 Ω 50 Ω 62 Ω I A 0.00 A A φ
3 3. Chapter 36 - Exercise 3. The motor of an electric drill draws a 3.5 A current at the power-line voltage of 20 V rms. What is the motor s power if the current lags the voltage by 20? The average power supplied by the motor is P source = I rms V rms cos φ, where I rms is the current drawn by the motor (3.5 A, in this case). So, we just plug everything in. P source = I rms V rms cos φ = (3.5) (20) cos 20 = 400 W. 3
4 4. Chapter 36 - Problem 37. (a) Evaluate V C in the figure at emf frequencies, 3, 0, 30, and 00 khz. (b) Graph V C versus frequency. Draw a smooth curve through your five points. (a) The voltage across the capacitor is V C = IX C, where I = =. So, ωc 2πfC, and X C = R 2 +XC 2 V C = IX C = = 2πfC R 2 + (2πfC) 2 + (2πfRC) 2. So, plugging in the values gives f (khz) V C (V) (b) The graph is seen to the right. Notice that the voltage approaches zero as the frequency increases. The circuit acts like a low-pass filter, blocking out higher frequencies. 4
5 5. Chapter 36 - Problem 38. (a) Evaluate V R in the figure at emf frequencies 00, 300, 000, 3000, and 0,000 Hz. (b) Graph V R versus frequency. Draw a smooth curve through your five points. (a) The voltage across the resistor is V R = IR, where I = 2πfC. So, V R = IR = So, plugging in the values gives R 2 + (2πfC) 2. f (Hz) V R (V) , , and X C = = R 2 +XC 2 ωc (b) The graph is seen to the right. Notice that the voltage approaches the full 0 V as the frequency increases, while for low frequencies the voltage drops. The circuit acts like a high-pass filter, blocking out lower frequencies. 5
6 6. Chapter 36 - Problem 42. (a) What is the peak current supplied by the emf in the figure? (b) What is the peak voltage across the 3.0 µf capacitor? (a) The circuit can be redrawn in terms of a single equivalent capacitor. The two parallel capacitors combine together to give an equivalent capacitance of 6 µf, which then combines with the 3 µf capacitor for a net capacitance of 2 µf. Then, the current is I = V X C = = 2πfCE /2πfC 0. Thus, the peak current is I = 2πfC = 2π (200) (2 0 9 ) (0) = 25 ma. (b) All the current passes though the 3 µf capacitor, and so the peak voltage is V C = IX C = I. Notice that since I = 2πfC 2πfC eqv, then V C = I = 2πfCeqv E 2πfC 2πfC 0 =. So, we find C eqv C V C = C eqv C = 2 0 =.67 0 = 6.7 V. 3 6
7 7. Chapter 36 - Problem 43. You have a resistor and a capacitor of unknown values. First, you charge the capacitor and discharge it through the resistor. By monitoring the capacitor voltage on an oscilloscope, you see that the voltage decays to half its initial value in 2.5 ms. You then use the resistor and capacitor to make a low-pass filter. What is the crossover frequency f c? The crossover frequency is f c = ωc =. The voltage across a capacitor falls off 2π 2πRC exponentially fast as V = V 0 e t/rc. If the voltage falls to half its initial value in a time t 0, then V (t 0 ) = V 0 2 = V 0e t 0/RC 2 = e t 0/RC. Taking natural logs of both sides and solving gives RC = t 0. Then, since f ln 2 c = we have f c = ln 2. 2πt 0 With numbers, f c = ln 2 2πt 0 = π ( ) 44 Hz. 2πRC, 7
8 8. Chapter 36 - Problem 5. For the circuit in the figure, (a) What is the resonance frequency, in both rad/s and Hz? (b) Find V R and V C at resonance. (c) How can V C be larger than? Explain. (a) The resonance frequency is ω R = LC, and so f R = ωc 2π = 2π LC. Thus, ω c = LC = = rad/s. f c = 2π = LC 2π = Hz. (b) At resonance, X C = X L, and so Z = R, giving I = /R, or amp. This gives V R = IR = 0 = 0 V. Furthermore, V C = IX C = I/ω R C. We found the resonance frequency in part (a), and so substituting in gives V C = = V. (c) We know that, for the instantaneous values, v R + v C + v L = E, but this isn t true for the peak values. At resonance, v L and v C cancel each other out, but can each be big, if they are compensated by an equally big v R. This lets the peak values be larger than the peak current, due to the cancellation. 8
9 9. Chapter 36 - Problem 57. Show that the impedance of a series RLC circuit can be written Z = R 2 + ω 2 L 2 ( ω0/ω 2 2 ) 2. The impedance Z = R 2 + (X L X C ) 2, where X L ωl, and X C =. Now, ωc (X L X C ) 2 = ( ) ωl 2 ωc = ω 2 L ( ) 2. 2 ω 2 LC But, LC =, where ω ω0 2 0 is the natural resonant frequency. Thus, (X L X C ) 2 = ω 2 L ( 2 ω2 0 ). So, we find that ω 2 Z = ( ) R 2 + ω 2 L 2 ω2 0. ω 2 9
10 0. Chapter 36 - Problem 68. (a) Show that the average power loss in a series RLC circuit is P avg = ω 2 E 2 rmsr ω 2 R 2 + L 2 (ω 2 ω 2 0) 2. (b) Prove that the energy dissipation is a maximum at ω = ω 0. (a) The average power dissipated is P avg = I rms E rms cos φ, where I rms = E rms /Z, and cos φ = R/Z. Thus, P avg = E 2 rmsr/z 2. Now, since /LC = ω 2 0. So, Z 2 = R 2 + (X L X C ) 2 ) 2 = R 2 + ( ωl ( ωc ) = R 2 + L2 ω ω LC = R 2 + L2 (ω 2 ω ω 0) 2 2, 2 P avg = ErmsR 2 rmsrω 2 2 R 2 + L2 (ω ω 2 ω0) 2 2 = E R 2 ω 2 + L 2 (ω 2 ω0) (b) The power dissipated depends on the frequency, ω. It is a maximum when d P dω avg = 0. So, taking the derivative gives ( 2ErmsRω 2 R 2 ω 2 + L 2 (ω 2 ω0) 2 2) ErmsRω 2 2 (2ωR 2 + 2L 2 (ω 2 ω0) 2 2ω) (R 2 ω 2 + L 2 (ω 2 ω 20) 2) 2 = 0. This reduces to (ω 2 ω 2 0) 2 2ω 2 (ω 2 ω 2 0) = 0, which is solved by ω = ω 0. So, the power is maximized when ω = ω 0, i.e., when the system is at resonance! 0
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents. Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49
 Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
Physics 6C, Summer 2006 Homework 2 Solutions
 Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
Inductors in AC Circuits
 Inductors in AC Circuits Name Section Resistors, inductors, and capacitors all have the effect of modifying the size of the current in an AC circuit and the time at which the current reaches its maximum
Inductors in AC Circuits Name Section Resistors, inductors, and capacitors all have the effect of modifying the size of the current in an AC circuit and the time at which the current reaches its maximum
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Chapter 10. RC Circuits ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
Homework #11 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering
 Homework #11 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering 2. A circular coil has a 10.3 cm radius and consists of 34 closely wound turns of wire. An externally produced magnetic field of
Homework #11 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering 2. A circular coil has a 10.3 cm radius and consists of 34 closely wound turns of wire. An externally produced magnetic field of
Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
Diodes have an arrow showing the direction of the flow.
 The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
ε: Voltage output of Signal Generator (also called the Source voltage or Applied
 Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
RLC Series Resonance
 RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
Chapter 35 Alternating Current Circuits
 hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 1500-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across?
 PHYS Practice Problems hapters 8- hapter 8. 45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 5-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across? The power and current can be used to find the peak voltage,
PHYS Practice Problems hapters 8- hapter 8. 45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 5-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across? The power and current can be used to find the peak voltage,
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering)
 Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Chapter 11. Inductors ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Chapter 12 Driven RLC Circuits
 hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators
 Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
2. A conductor of length 2m moves at 4m/s at 30 to a uniform magnetic field of 0.1T. Which one of the following gives the e.m.f. generated?
 Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
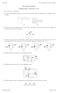 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4
 DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3. AC Circuit Analysis
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3 AC Circuit Analysis 3.1 Introduction The steady-state behavior of circuits energized by sinusoidal sources is an important area of study for several reasons. First, the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 3 AC Circuit Analysis 3.1 Introduction The steady-state behavior of circuits energized by sinusoidal sources is an important area of study for several reasons. First, the
Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum
 WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. December 2011
 AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
= V peak 2 = 0.707V peak
 BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
CHAPTER 30: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits
 HAPTE 3: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and A ircuits esponses to Questions. (a) For the maximum value of the mutual inductance, place the coils close together, face to face, on the same axis.
HAPTE 3: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and A ircuits esponses to Questions. (a) For the maximum value of the mutual inductance, place the coils close together, face to face, on the same axis.
Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007
 [ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
[ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
CHAPTER 31. E max = 15.1 V
 CHAPTER 31 Note: Unless otherwise indicated, the symbols I, V, E, and P denote the rms values of I, V, and E and the average power. 1* A 00-turn coil has an area of 4 cm and rotates in a magnetic field
CHAPTER 31 Note: Unless otherwise indicated, the symbols I, V, E, and P denote the rms values of I, V, and E and the average power. 1* A 00-turn coil has an area of 4 cm and rotates in a magnetic field
Three phase circuits
 Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-1 Mutual Inductance Mutual inductance: a changing current in one coil will induce a current in a second coil: Coil 1 produces a flux
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-1 Mutual Inductance Mutual inductance: a changing current in one coil will induce a current in a second coil: Coil 1 produces a flux
The Time Constant of an RC Circuit
 The Time Constant of an RC Circuit 1 Objectives 1. To determine the time constant of an RC Circuit, and 2. To determine the capacitance of an unknown capacitor. 2 Introduction What the heck is a capacitor?
The Time Constant of an RC Circuit 1 Objectives 1. To determine the time constant of an RC Circuit, and 2. To determine the capacitance of an unknown capacitor. 2 Introduction What the heck is a capacitor?
Properties of electrical signals
 DC Voltage Component (Average voltage) Properties of electrical signals v(t) = V DC + v ac (t) V DC is the voltage value displayed on a DC voltmeter Triangular waveform DC component Half-wave rectifier
DC Voltage Component (Average voltage) Properties of electrical signals v(t) = V DC + v ac (t) V DC is the voltage value displayed on a DC voltmeter Triangular waveform DC component Half-wave rectifier
LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER. Bridge Rectifier
 LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER Full-wave Rectification: Bridge Rectifier For many electronic circuits, DC supply voltages are required but only AC voltages are available.
LABORATORY 10 TIME AVERAGES, RMS VALUES AND THE BRIDGE RECTIFIER Full-wave Rectification: Bridge Rectifier For many electronic circuits, DC supply voltages are required but only AC voltages are available.
= (0.400 A) (4.80 V) = 1.92 W = (0.400 A) (7.20 V) = 2.88 W
 Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Step response of an RLC series circuit
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 5 Step response of an RLC series circuit 1 Introduction Objectives
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 5 Step response of an RLC series circuit 1 Introduction Objectives
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies
 Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
Homework Assignment 03
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 03 1. A 9-V dc power supply generates 10 W in a resistor. What peak-to-peak amplitude should an ac source have to generate the same
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 03 1. A 9-V dc power supply generates 10 W in a resistor. What peak-to-peak amplitude should an ac source have to generate the same
First Order Circuits. EENG223 Circuit Theory I
 First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
First Order Circuits EENG223 Circuit Theory I First Order Circuits A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor). The circuit will also contain resistance.
I + Understanding Impedances. Why do we need to know this?
 Understanding Impedances HSSP Audio and Speaker-building Teacher: Michael Price Why do we need to know this? We re going to build speakers using two or more different drivers (for example, a woofer and
Understanding Impedances HSSP Audio and Speaker-building Teacher: Michael Price Why do we need to know this? We re going to build speakers using two or more different drivers (for example, a woofer and
Aircraft Electrical System
 Chapter 9 Aircraft Electrical System Introduction The satisfactory performance of any modern aircraft depends to a very great degree on the continuing reliability of electrical systems and subsystems.
Chapter 9 Aircraft Electrical System Introduction The satisfactory performance of any modern aircraft depends to a very great degree on the continuing reliability of electrical systems and subsystems.
TDA2040. 20W Hi-Fi AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 20W Hi-Fi AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER DESCRIPTION The TDA2040 is a monolithic integrated circuit in Pentawatt package, intended for use as an audio class AB amplifier. Typically it provides 22W output power
20W Hi-Fi AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER DESCRIPTION The TDA2040 is a monolithic integrated circuit in Pentawatt package, intended for use as an audio class AB amplifier. Typically it provides 22W output power
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY. Fig. 8.1a Fig 8.1b
 DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits
 Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide
 Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide 1 05/2014 Study Guide for Pacific Gas & Electric Company Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Qualifying Test (CTT) About the Test The
Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide 1 05/2014 Study Guide for Pacific Gas & Electric Company Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Qualifying Test (CTT) About the Test The
12.4 UNDRIVEN, PARALLEL RLC CIRCUIT*
 + v C C R L - v i L FIGURE 12.24 The parallel second-order RLC circuit shown in Figure 2.14a. 12.4 UNDRIVEN, PARALLEL RLC CIRCUIT* We will now analyze the undriven parallel RLC circuit shown in Figure
+ v C C R L - v i L FIGURE 12.24 The parallel second-order RLC circuit shown in Figure 2.14a. 12.4 UNDRIVEN, PARALLEL RLC CIRCUIT* We will now analyze the undriven parallel RLC circuit shown in Figure
Application Note. So You Need to Measure Some Inductors?
 So You Need to Measure Some nductors? Take a look at the 1910 nductance Analyzer. Although specifically designed for production testing of inductors and coils, in addition to measuring inductance (L),
So You Need to Measure Some nductors? Take a look at the 1910 nductance Analyzer. Although specifically designed for production testing of inductors and coils, in addition to measuring inductance (L),
PHY114 S11 Term Exam 3
 PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam
 The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam This document contains every question from the Extra Class (Element 4) Question Pool* that requires one or more mathematical
The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam This document contains every question from the Extra Class (Element 4) Question Pool* that requires one or more mathematical
Module Title: Electrotechnology for Mech L7
 CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Autumn Examinations 2012 Module Title: Electrotechnology for Mech L7 Module Code: ELEC7007 School: School of Mechanical, Electrical and Process
CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Autumn Examinations 2012 Module Title: Electrotechnology for Mech L7 Module Code: ELEC7007 School: School of Mechanical, Electrical and Process
Frequency Response of Filters
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
 Arecibo, a large radio telescope in Puerto Rico, gathers electromagnetic radiation in the form of radio waves. These long wavelengths pass through obscuring dust clouds, allowing astronomers to create
Arecibo, a large radio telescope in Puerto Rico, gathers electromagnetic radiation in the form of radio waves. These long wavelengths pass through obscuring dust clouds, allowing astronomers to create
Application Note AN- 1095
 Application Note AN- 1095 Design of the Inverter Output Filter for Motor Drives with IRAMS Power Modules Cesare Bocchiola Table of Contents Page Section 1: Introduction...2 Section 2 : Output Filter Design
Application Note AN- 1095 Design of the Inverter Output Filter for Motor Drives with IRAMS Power Modules Cesare Bocchiola Table of Contents Page Section 1: Introduction...2 Section 2 : Output Filter Design
CHAPTER 28 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
Diode Applications. As we have already seen the diode can act as a switch Forward biased or reverse biased - On or Off.
 Diode Applications Diode Switching As we have already seen the diode can act as a switch Forward biased or reverse biased - On or Off. Voltage Rectifier A voltage rectifier is a circuit that converts an
Diode Applications Diode Switching As we have already seen the diode can act as a switch Forward biased or reverse biased - On or Off. Voltage Rectifier A voltage rectifier is a circuit that converts an
Frequency response: Resonance, Bandwidth, Q factor
 Frequency response: esonance, Bandwidth, Q factor esonance. Let s continue the exploration of the frequency response of circuits by investigating the series circuit shown on Figure. C + V - Figure The
Frequency response: esonance, Bandwidth, Q factor esonance. Let s continue the exploration of the frequency response of circuits by investigating the series circuit shown on Figure. C + V - Figure The
Since any real component also has loss due to the resistive component, the average power dissipated is 2 2R
 Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
PHYSICS 360 - LAB #2 Passive Low-pass and High-pass Filter Circuits and Integrator and Differentiator Circuits
 PHYSICS 360 - LAB #2 Passie Low-pass and High-pass Filter Circuits and Integrator and Differentiator Circuits Objectie: Study the behaior of low-pass and high-pass filters. Study the differentiator and
PHYSICS 360 - LAB #2 Passie Low-pass and High-pass Filter Circuits and Integrator and Differentiator Circuits Objectie: Study the behaior of low-pass and high-pass filters. Study the differentiator and
Power Supplies. 1.0 Power Supply Basics. www.learnabout-electronics.org. Module
 Module 1 www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Supplies 1.0 Power Supply Basics What you ll learn in Module 1 Section 1.0 Power Supply Basics. Basic functions of a power supply. Safety aspects of working
Module 1 www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Supplies 1.0 Power Supply Basics What you ll learn in Module 1 Section 1.0 Power Supply Basics. Basic functions of a power supply. Safety aspects of working
Application Guide. Power Factor Correction (PFC) Basics
 Power Factor Correction (PFC) Basics Introduction Power Factor, in simple terms, is a number between zero and one that represents the ratio of the real power to apparent power. Real power (P), measured
Power Factor Correction (PFC) Basics Introduction Power Factor, in simple terms, is a number between zero and one that represents the ratio of the real power to apparent power. Real power (P), measured
Understanding Power Impedance Supply for Optimum Decoupling
 Introduction Noise in power supplies is not only caused by the power supply itself, but also the load s interaction with the power supply (i.e. dynamic loads, switching, etc.). To lower load induced noise,
Introduction Noise in power supplies is not only caused by the power supply itself, but also the load s interaction with the power supply (i.e. dynamic loads, switching, etc.). To lower load induced noise,
LR Phono Preamps. Pete Millett ETF.13. [email protected]
 LR Phono Preamps Pete Millett ETF.13 [email protected] Agenda A bit about me Part 1: What is, and why use, RIAA? Grooves on records The RIAA standard Implementations of RIAA EQ networks and preamps
LR Phono Preamps Pete Millett ETF.13 [email protected] Agenda A bit about me Part 1: What is, and why use, RIAA? Grooves on records The RIAA standard Implementations of RIAA EQ networks and preamps
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA
 PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
PHASOR DIAGRAMS HANDS-ON RELAY SCHOOL WSU PULLMAN, WA. RON ALEXANDER - BPA What are phasors??? In normal practice, the phasor represents the rms maximum value of the positive half cycle of the sinusoid
The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure
 The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
Physics 102: Lecture 13 RLC circuits & Resonance
 Physics 102: Lecture 13 L circuits & esonance L Physics 102: Lecture 13, Slide 1 I = I max sin(2pft) V = I max sin(2pft) V in phase with I eview: A ircuit L V = I max X sin(2pft p/2) V lags I IE I V t
Physics 102: Lecture 13 L circuits & esonance L Physics 102: Lecture 13, Slide 1 I = I max sin(2pft) V = I max sin(2pft) V in phase with I eview: A ircuit L V = I max X sin(2pft p/2) V lags I IE I V t
LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE
 LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE Karl M. Hink, Executive Vice President Originally presented at the Power Quality 99 Conference ABSTRACT Motor protection
LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE Karl M. Hink, Executive Vice President Originally presented at the Power Quality 99 Conference ABSTRACT Motor protection
SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
 SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 25 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and ORCAD Capture CIS to better
SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 25 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and ORCAD Capture CIS to better
EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits
 EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits 1. Introduction and Goal: Exploring transient behavior due to inductors and capacitors in DC circuits; gaining experience with lab instruments.
EE 1202 Experiment #4 Capacitors, Inductors, and Transient Circuits 1. Introduction and Goal: Exploring transient behavior due to inductors and capacitors in DC circuits; gaining experience with lab instruments.
Improvements of Reliability of Micro Hydro Power Plants in Sri Lanka
 Improvements of Reliability of Micro Hydro Power Plants in Sri Lanka S S B Udugampala, V Vijayarajah, N T L W Vithanawasam, W M S C Weerasinghe, Supervised by: Eng J Karunanayake, Dr. K T M U Hemapala
Improvements of Reliability of Micro Hydro Power Plants in Sri Lanka S S B Udugampala, V Vijayarajah, N T L W Vithanawasam, W M S C Weerasinghe, Supervised by: Eng J Karunanayake, Dr. K T M U Hemapala
Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits
 AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual James M. Fiore 2 Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits by James M. Fiore Version 1.3.1, 01 March 2016 Laboratory
AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual James M. Fiore 2 Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits Laboratory Manual for AC Electrical Circuits by James M. Fiore Version 1.3.1, 01 March 2016 Laboratory
Chapter 25 Alternating Currents
 Physics Including Human Applications 554 Chapter 25 Alternating Currents GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each
Physics Including Human Applications 554 Chapter 25 Alternating Currents GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each
Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 24 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic output voltages, such as sinusoids. They accomplish this feat
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 24 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic output voltages, such as sinusoids. They accomplish this feat
REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO)
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO) Copyright 2008 Caribbean
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO) Copyright 2008 Caribbean
L and C connected together. To be able: To analyse some basic circuits.
 circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
Two year Claritycap research programme finally answers an audio capacitors influence on sound quality.
 Two year Claritycap research programme finally answers an audio capacitors influence on sound quality. ClarityCap have been supplying high-quality audio capacitors to some of the world s top HiFi and loudspeaker
Two year Claritycap research programme finally answers an audio capacitors influence on sound quality. ClarityCap have been supplying high-quality audio capacitors to some of the world s top HiFi and loudspeaker
Lecturer: James Grimbleby URL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email: j.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk
 AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
Analog signals are those which are naturally occurring. Any analog signal can be converted to a digital signal.
 3.3 Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) Analog signals are those which are naturally occurring. Any analog signal can be converted to a digital signal. 1 3.3 Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) WCB/McGraw-Hill
3.3 Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) Analog signals are those which are naturally occurring. Any analog signal can be converted to a digital signal. 1 3.3 Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) WCB/McGraw-Hill
TDA2040. 20W Hi-Fi AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 20W Hi-Fi AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER DESCRIPTION The TDA2040 is a monolithic integrated circuit in Pentawatt package, intended for use as an audio class AB amplifier. Typically it provides 22W output power
20W Hi-Fi AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER DESCRIPTION The TDA2040 is a monolithic integrated circuit in Pentawatt package, intended for use as an audio class AB amplifier. Typically it provides 22W output power
Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters
 Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters Physics335 Student October 3, 27 Physics 335-Section Professor J. Hobbs Partner: Physics335 Student2 Abstract Basic RC-filters were constructed and properties such as
Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters Physics335 Student October 3, 27 Physics 335-Section Professor J. Hobbs Partner: Physics335 Student2 Abstract Basic RC-filters were constructed and properties such as
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups
 Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited [email protected] www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited [email protected] www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Experiment 8: Undriven & Driven RLC Circuits
 Experiment 8: Undriven & Driven RLC Circuits Answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper and turn them in before the lab 1. RLC Circuits Consider the circuit at left, consisting of an AC function
Experiment 8: Undriven & Driven RLC Circuits Answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper and turn them in before the lab 1. RLC Circuits Consider the circuit at left, consisting of an AC function
Slide 1 / 26. Inductance. 2011 by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESISTANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESI STANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE P R E A M B L E This problem is adapted from an on-line knowledge enhancement module for a PGCE programme. It is used to cover
CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESI STANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE P R E A M B L E This problem is adapted from an on-line knowledge enhancement module for a PGCE programme. It is used to cover
Oscillations and Regenerative Amplification using Negative Resistance Devices
 Oscillations and Regenerative Amplification using Negative Resistance Devices Ramon Vargas Patron [email protected] INICTEL The usual procedure for the production of sustained oscillations in tuned
Oscillations and Regenerative Amplification using Negative Resistance Devices Ramon Vargas Patron [email protected] INICTEL The usual procedure for the production of sustained oscillations in tuned
Electrical Resonance
 Electrical Resonance (R-L-C series circuit) APPARATUS 1. R-L-C Circuit board 2. Signal generator 3. Oscilloscope Tektronix TDS1002 with two sets of leads (see Introduction to the Oscilloscope ) INTRODUCTION
Electrical Resonance (R-L-C series circuit) APPARATUS 1. R-L-C Circuit board 2. Signal generator 3. Oscilloscope Tektronix TDS1002 with two sets of leads (see Introduction to the Oscilloscope ) INTRODUCTION
AC Generators. Basic Generator
 AC Generators Basic Generator A basic generator consists of a magnetic field, an armature, slip rings, brushes and a resistive load. The magnetic field is usually an electromagnet. An armature is any number
AC Generators Basic Generator A basic generator consists of a magnetic field, an armature, slip rings, brushes and a resistive load. The magnetic field is usually an electromagnet. An armature is any number
Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2010, 2011 and 2012
 1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
Physics 2102 Lecture 19. Physics 2102
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Physics 2102 Lecture 19 Ch 30: Inductors and RL Circuits Nikolai Tesla What are we going to learn? A road map Electric charge Electric force on other electric charges Electric
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Physics 2102 Lecture 19 Ch 30: Inductors and RL Circuits Nikolai Tesla What are we going to learn? A road map Electric charge Electric force on other electric charges Electric
Using the Impedance Method
 Using the Impedance Method The impedance method allows us to completely eliminate the differential equation approach for the determination of the response of circuits. In fact the impedance method even
Using the Impedance Method The impedance method allows us to completely eliminate the differential equation approach for the determination of the response of circuits. In fact the impedance method even
RC NETWORKS SALES GUIDE
 SALES GUIDE INTRODUCTION TO Recent developments in electronic equipment have shown the following trends: Increasing demands for numerical control machines, robotics and technically advanced appliances
SALES GUIDE INTRODUCTION TO Recent developments in electronic equipment have shown the following trends: Increasing demands for numerical control machines, robotics and technically advanced appliances
Measuring Insulation Resistance of Capacitors
 Application Note Measuring Insulation Resistance of Capacitors A common use of high resistance measuring instruments (often called megohmmeters or insulation resistance testers) is measuring the insulation
Application Note Measuring Insulation Resistance of Capacitors A common use of high resistance measuring instruments (often called megohmmeters or insulation resistance testers) is measuring the insulation
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02
 104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
What you will do. Build a 3-band equalizer. Connect to a music source (mp3 player) Low pass filter High pass filter Band pass filter
 Audio Filters What you will do Build a 3-band equalizer Low pass filter High pass filter Band pass filter Connect to a music source (mp3 player) Adjust the strength of low, high, and middle frequencies
Audio Filters What you will do Build a 3-band equalizer Low pass filter High pass filter Band pass filter Connect to a music source (mp3 player) Adjust the strength of low, high, and middle frequencies
RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope Physics Lab X
 Objective RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope Physics Lab X In this series of experiments, the time constant of an RC circuit will be measured experimentally and compared with the theoretical expression for
Objective RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope Physics Lab X In this series of experiments, the time constant of an RC circuit will be measured experimentally and compared with the theoretical expression for
Inrush Current. Although the concepts stated are universal, this application note was written specifically for Interpoint products.
 INTERPOINT Although the concepts stated are universal, this application note was written specifically for Interpoint products. In today s applications, high surge currents coming from the dc bus are a
INTERPOINT Although the concepts stated are universal, this application note was written specifically for Interpoint products. In today s applications, high surge currents coming from the dc bus are a
5B5BBasic RC Oscillator Circuit
 5B5BBasic RC Oscillator Circuit The RC Oscillator which is also called a Phase Shift Oscillator, produces a sine wave output signal using regenerative feedback from the resistor-capacitor combination.
5B5BBasic RC Oscillator Circuit The RC Oscillator which is also called a Phase Shift Oscillator, produces a sine wave output signal using regenerative feedback from the resistor-capacitor combination.
Introduction to the Smith Chart for the MSA Sam Wetterlin 10/12/09 Z +
 Introduction to the Smith Chart for the MSA Sam Wetterlin 10/12/09 Quick Review of Reflection Coefficient The Smith chart is a method of graphing reflection coefficients and impedance, and is often useful
Introduction to the Smith Chart for the MSA Sam Wetterlin 10/12/09 Quick Review of Reflection Coefficient The Smith chart is a method of graphing reflection coefficients and impedance, and is often useful
Reading assignment: All students should read the Appendix about using oscilloscopes.
 10. A ircuits* Objective: To learn how to analyze current and voltage relationships in alternating current (a.c.) circuits. You will use the method of phasors, or the vector addition of rotating vectors
10. A ircuits* Objective: To learn how to analyze current and voltage relationships in alternating current (a.c.) circuits. You will use the method of phasors, or the vector addition of rotating vectors
