Section 1: Development of the Atomic Theory Pages 82-87
|
|
|
- Loren Lamb
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Study Guide Chapter 4 Atomic Theory and The Atom Section 1: Development of the Atomic Theory Pages THE BEGINNING OF ATOMIC THEORY 1. What does the word atom mean? a. dividable b. invisible c. hard particles d. not able to be divided 2. Why weren t Democritus s ideas accepted? a. Bohr did not agree with his theory. b. Dalton proved Democritus wrong. c. Aristotle did not agree with his theory. d. Rutherford proved Democritus wrong. From Aristotle to Modern Science 3. What is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided? a. a nucleus b. a proton c. an atom d. a neutron DALTON S ATOMIC THEORY BASED ON EXPERIMENTS 4.Which of the following ideas was part of Dalton s theories? a. All substances are made of atoms. b. Atoms can be divided. c. Atoms can be destroyed. d. Most substances are made of atoms. Holt Science and Technology 9 Introduction to Atoms
2 Not Quite Correct 5. What happened in the late 1800s? a. Dalton created a new theory. b. Dalton disproved his own theory. c. Dalton s theory was proved. d. Dalton s theory changed. THOMSON S DISCOVERY OF ELECTRONS 6. What did Thomson discover about atoms? a. Atoms cannot be divided. b. There are small particles inside atoms. c. There are no small particles in atoms. d. All atoms have negative charges. Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. electrons particles positively 7. Thomson discovered that a charged plate in a cathode-ray tube attracted an invisible beam. 8. Thomson concluded that the beam was made of that have negative electric charges. 9. The negatively charged particles Thompson discovered are called Holt Science and Technology 10 Introduction to Atoms
3 Like Plums in a Pudding 10. What did Thomson believe about electrons? a. They are mixed throughout an atom. b. They are in the center of an atom. c. They are positively charged. d. They are absent from an atom. RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC SHOOTING GALLERY Surprising Results 11. What did Rutherford expect all the charged particles to do? a. to pass right through the gold foil b. to deflect to the sides of the gold foil c. to bounce straight back d. to become blobs of matter WHERE ARE THE ELECTRONS? 12. Which of the following statements is NOT true of Rutherford s results? a. Some of the particles turned to one side. b. Some of the particles did not move. c. Most of the particles passed through the gold foil. d. Some of the particles bounced straight back. 13. What did Rutherford realize about atoms? a. Atoms are mostly empty space. b. Atoms are helium. c. Atoms are gold particles. d. Atoms are large particles. Holt Science and Technology 11 Introduction to Atoms
4 Far From the Nucleus 14. What positively charged part did Rutherford believe was in the center of an atom? a. an electron b. a nucleus c. a particle d. a proton Bohr s Electron Levels 15. What did Bohr study? a. the way atoms react to light b. the size of atoms c. the diameter of the nucleus d. the division of atoms 16. How did Bohr s model propose that electrons move around the nucleus? a. a variety of ways b. haphazardly c. between the levels d. in certain paths The Modern Atomic Theory 17. What model represents current atomic theory? a. electron-cloud model b. plum-pudding model c. Rutherford s model d. Bohr s model Holt Science and Technology 12 Introduction to Atoms
5 Section 2: The Atom Pages HOW SMALL IS AN ATOM? Circle the letter of the best answer for the question. 18. Which of the following statements is true? a. A penny has about 20,000 atoms. b. A penny has more atoms than the Earth has people. c. Aluminum is made up of large-sized atoms. d. Aluminum atoms have a diameter of about 3 cm. WHAT IS INSIDE AN ATOM? The Nucleus Read the description. Then, draw a line from the dot next to each description to the matching word. 19. particle with no electrical charge 20. particle that is positively charged 21. particle that is negatively charged 22. part that contains most of the mass of an atom a. electron b. nucleus c. proton d. neutron e. atomic mass unit HOW DO ATOMS OF DIFFERENT ELEMENTS DIFFER? Starting Simply Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. helium hydrogen electron 23. The simplest atom is the atom. 24. The simplest atom has one proton and one 25. If you build an atom using two protons, two neutrons, and two electrons, you have built an atom of Holt Science and Technology 13 Introduction to Atoms
6 Building Bigger Atoms atomic mass unit atomic number neutrons 26. An atom does not have to have equal numbers of protons and 27. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the of that atom. 28. The SI unit used to express the masses of particles in atoms is called the ISOTOPES 29. What do isotopes always have? a. the same number of protons b. the same number of neutrons c. a different atomic number d. the same mass 30. How are isotopes of the same element different? a. They have different numbers of protons. b. They have different numbers of neutrons. c. They have the same number of electrons. d. They have different numbers of ions. Properties of Isotopes 31. Which phrase best describes radioactive isotopes? a. They are stable. b. They never change. c. They are unstable. d. They don t produce energy. Holt Science and Technology 14 Introduction to Atoms
7 Telling Isotopes Apart 32. What is the mass number of an isotope that has 5 protons, 6 neutrons, and 5 electrons? a. 1 c. 10 b. 11 d. 16 Naming Isotopes 33. Carbon has an atomic number of 6. How many neutrons does carbon-12 have? a. 12 c. 6 b. 8 d. 18 Calculating the Mass of an Element Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. mass number atomic mass 34. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom is the 35. The weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element is the FORCES IN ATOMS Strong force Weak force Electromagnetic force Gravitational force 36. Protons stay together in the nucleus because of 37. Objects are pulled toward one another because of 38. An important force in radioactive atoms is 39. The electrons are held around the nucleus because of Holt Science and Technology 15 Introduction to Atoms
Development of the Atomic Theory
 Development of the Atomic Theory Atom The smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. Element A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances
Development of the Atomic Theory Atom The smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. Element A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances
History of the Atom & Atomic Theory
 Chapter 5 History of the Atom & Atomic Theory You re invited to a Thinking Inside the Box Conference Each group should nominate a: o Leader o Writer o Presenter You have 5 minutes to come up with observations
Chapter 5 History of the Atom & Atomic Theory You re invited to a Thinking Inside the Box Conference Each group should nominate a: o Leader o Writer o Presenter You have 5 minutes to come up with observations
Atomic Calculations. 2.1 Composition of the Atom. number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number
 2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
The Models of the Atom
 The Models of the Atom All life, whether in the form of trees, whales, mushrooms, bacteria or amoebas, consists of cells. Similarly, all matter, whether in the form of aspirin, gold, vitamins, air or minerals,
The Models of the Atom All life, whether in the form of trees, whales, mushrooms, bacteria or amoebas, consists of cells. Similarly, all matter, whether in the form of aspirin, gold, vitamins, air or minerals,
2 The Structure of Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
9/13/2013. However, Dalton thought that an atom was just a tiny sphere with no internal parts. This is sometimes referred to as the cannonball model.
 John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom
 NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom Chemistry is the study of matter and its properties. Those properties can be explained by examining the atoms that compose the matter. An atom is the smallest particle
NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom Chemistry is the study of matter and its properties. Those properties can be explained by examining the atoms that compose the matter. An atom is the smallest particle
SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table
 Lesson Topics Covered SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table 1 Note: History of Atomic Theory progression of understanding of composition of matter; ancient Greeks and
Lesson Topics Covered SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table 1 Note: History of Atomic Theory progression of understanding of composition of matter; ancient Greeks and
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S. The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39)
 ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
For convenience, we may consider an atom in two parts: the nucleus and the electrons.
 Atomic structure A. Introduction: In 1808, an English scientist called John Dalton proposed an atomic theory based on experimental findings. (1) Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms.
Atomic structure A. Introduction: In 1808, an English scientist called John Dalton proposed an atomic theory based on experimental findings. (1) Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms.
ATOMS: ATOMIC STRUCTURE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 ATOMS: ATOMIC STRUCTURE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTION ONE: MODELS OF THE ATOM (2011;1) At different times scientists have proposed various descriptions or models of the atom to match experimental evidence
ATOMS: ATOMIC STRUCTURE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTION ONE: MODELS OF THE ATOM (2011;1) At different times scientists have proposed various descriptions or models of the atom to match experimental evidence
Elements, Atoms & Ions
 Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom
 Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom 1. For most elements, an atom has A. no neutrons in the nucleus. B. more protons than electrons. C. less neutrons than electrons. D. just as many electrons as protons.
Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom 1. For most elements, an atom has A. no neutrons in the nucleus. B. more protons than electrons. C. less neutrons than electrons. D. just as many electrons as protons.
5.1 Evolution of the Atomic Model
 5.1 Evolution of the Atomic Model Studying the atom has been a fascination of scientists for hundreds of years. Even Greek philosophers, over 2500 years ago, discussed the idea of there being a smallest
5.1 Evolution of the Atomic Model Studying the atom has been a fascination of scientists for hundreds of years. Even Greek philosophers, over 2500 years ago, discussed the idea of there being a smallest
6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234
 Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234 Key Concepts: 3. Elements are organized according to their atomic number and electron arrangement on the periodic table.
Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234 Key Concepts: 3. Elements are organized according to their atomic number and electron arrangement on the periodic table.
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS Problems: 1-70 then after Chapter 9, complete 71-94, 103-104, 107-108, 113-114 4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element All matter
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS Problems: 1-70 then after Chapter 9, complete 71-94, 103-104, 107-108, 113-114 4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element All matter
Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure
 Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Atomic Structure OBJECTIVES SCHEDULE PREPARATION VOCABULARY MATERIALS. For each team of four. The students. For the class.
 activity 4 Atomic Structure OBJECTIVES Students are introduced to the structure of the atom and the nature of subatomic particles. The students are introduced to the properties of protons, neutrons, and
activity 4 Atomic Structure OBJECTIVES Students are introduced to the structure of the atom and the nature of subatomic particles. The students are introduced to the properties of protons, neutrons, and
7.4. Using the Bohr Theory KNOW? Using the Bohr Theory to Describe Atoms and Ions
 7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
Objectives. PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics. Constituents of Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Basic Atomic Theory
 PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
The Structure of the Atom
 The Structure of the Atom Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Section 4. Early Ideas About Matter pages 02 05 Section 4. Assessment page 05. Contrast the methods
The Structure of the Atom Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Section 4. Early Ideas About Matter pages 02 05 Section 4. Assessment page 05. Contrast the methods
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter
 Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
Atomic Theory Part 1
 Atomic Theory Part 1 Reading: Ch 2 sections 1 6, 8 Homework: Chapter 2: 39, 47, 43, 49, 51*, 53, 55, 57, 71, 73, 77, 99, 103 (optional) * = important homework question The Atomic Theory (John Dalton, 1803)
Atomic Theory Part 1 Reading: Ch 2 sections 1 6, 8 Homework: Chapter 2: 39, 47, 43, 49, 51*, 53, 55, 57, 71, 73, 77, 99, 103 (optional) * = important homework question The Atomic Theory (John Dalton, 1803)
Atoms and Elements [6th grade]
![Atoms and Elements [6th grade] Atoms and Elements [6th grade]](/thumbs/40/21183873.jpg) Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design Summer 6-11-2015 Atoms and Elements [6th grade] Jennifer J. Wray Trinity University, [email protected]
Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design Summer 6-11-2015 Atoms and Elements [6th grade] Jennifer J. Wray Trinity University, [email protected]
Level 3 Achievement Scale
 Unit 1: Atoms Level 3 Achievement Scale Can state the key results of the experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, Chadwick, and Bohr and what this lead each to conclude. Can explain that
Unit 1: Atoms Level 3 Achievement Scale Can state the key results of the experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, Chadwick, and Bohr and what this lead each to conclude. Can explain that
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
18.2 Comparing Atoms. Atomic number. Chapter 18
 As you know, some substances are made up of only one kind of atom and these substances are called elements. You already know something about a number of elements you ve heard of hydrogen, helium, silver,
As you know, some substances are made up of only one kind of atom and these substances are called elements. You already know something about a number of elements you ve heard of hydrogen, helium, silver,
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE
 ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 3 Vocabulary Words (27 words) Nucleus Atomic number Proton Mass number Neutron Isotopes Electron Atomic mass unit (amu) Energy level Average
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 3 Vocabulary Words (27 words) Nucleus Atomic number Proton Mass number Neutron Isotopes Electron Atomic mass unit (amu) Energy level Average
ANSWER KEY : BUILD AN ATOM PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom )
 ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
Unit 1 Practice Test. Matching
 Unit 1 Practice Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. proton d. electron b. nucleus e. neutron c. atom 1. the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of
Unit 1 Practice Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. proton d. electron b. nucleus e. neutron c. atom 1. the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of
Answers to Review Questions for Atomic Theory Quiz #1
 Answers to Review Questions for Atomic Theory Quiz #1 Multiple Choice Questions: 1. c 7. a 13. c 19. a 25. b 31. b 37. a 43. d 2. d 8. c 14. c 20. c 26. d 32. c 38. d 44. b 3. b 9. a 15. b 21. c 27. b
Answers to Review Questions for Atomic Theory Quiz #1 Multiple Choice Questions: 1. c 7. a 13. c 19. a 25. b 31. b 37. a 43. d 2. d 8. c 14. c 20. c 26. d 32. c 38. d 44. b 3. b 9. a 15. b 21. c 27. b
4.1 Studying Atom. Early evidence used to develop models of atoms.
 4.1 Studying Atom Early evidence used to develop models of atoms. Democritus said that all matter consisted of extremely small particles that could NOT be divided called these particles atoms from the
4.1 Studying Atom Early evidence used to develop models of atoms. Democritus said that all matter consisted of extremely small particles that could NOT be divided called these particles atoms from the
2. John Dalton did his research work in which of the following countries? a. France b. Greece c. Russia d. England
 CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
2014 Spring CHEM101 Ch1-2 Review Worksheet Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai,
 Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter
 Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
3 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS, ATOMS AND IONS
 3 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS, ATOMS AND IONS All matter is built up from chemical combinations of elements. As of 2003, there are 114 known elements, of which 88 are naturally occurring; the remaining
3 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS, ATOMS AND IONS All matter is built up from chemical combinations of elements. As of 2003, there are 114 known elements, of which 88 are naturally occurring; the remaining
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration. Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:)
 Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
( + and - ) ( - and - ) ( + and + ) Atoms are mostly empty space. = the # of protons in the nucleus. = the # of protons in the nucleus
 Atoms are mostly empty space Atomic Structure Two regions of every atom: Nucleus - is made of protons and neutrons - is small and dense Electron cloud -is a region where you might find an electron -is
Atoms are mostly empty space Atomic Structure Two regions of every atom: Nucleus - is made of protons and neutrons - is small and dense Electron cloud -is a region where you might find an electron -is
Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems
 Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems Bohr Model Class Work 1. Describe the nuclear model of the atom. 2. Explain the problems with the nuclear model of the atom. 3. According to Niels Bohr, what does n stand
Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems Bohr Model Class Work 1. Describe the nuclear model of the atom. 2. Explain the problems with the nuclear model of the atom. 3. According to Niels Bohr, what does n stand
Untitled Document. 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? 4. Which statement best describes the density of an atom s nucleus?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
Test Bank - Chapter 4 Multiple Choice
 Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE
 CHAPTER 5 EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Elements are composed of indivisable particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same properties; atoms of different
CHAPTER 5 EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Elements are composed of indivisable particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same properties; atoms of different
Radioactivity & Particles
 Radioactivity & Particles Introduction... 2 Atomic structure... 2 How are these particles arranged?... 2 Atomic notation... 4 Isotopes... 4 What is radioactivity?... 5 Types of Radiation: alpha, beta and
Radioactivity & Particles Introduction... 2 Atomic structure... 2 How are these particles arranged?... 2 Atomic notation... 4 Isotopes... 4 What is radioactivity?... 5 Types of Radiation: alpha, beta and
Atomic Structure Chapter 5 Assignment & Problem Set
 Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Atomic structure. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 Atomic structure This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Atomic structure This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
 APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner Grade Level/Subject Chemistry Stage 1: Desired Results Enduring Understanding Topic 1: Elements and the Periodic Table: The placement of elements on the periodic table
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner Grade Level/Subject Chemistry Stage 1: Desired Results Enduring Understanding Topic 1: Elements and the Periodic Table: The placement of elements on the periodic table
CHM 1311: General Chemistry 1, Fall 2004 Exam #1, September 8, 2004. Name (print) SSN
 CHM 1311: General Chemistry 1, Fall 2004 Exam #1, September 8, 2004 Name (print) SSN Pledge: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam: Signature For ALL problems: SHOW ALL WORK TO GET FULL CREDIT
CHM 1311: General Chemistry 1, Fall 2004 Exam #1, September 8, 2004 Name (print) SSN Pledge: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam: Signature For ALL problems: SHOW ALL WORK TO GET FULL CREDIT
Introduction to Nuclear Physics
 Introduction to Nuclear Physics 1. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table According to the Bohr-Rutherford model of the atom, also called the solar system model, the atom consists of a central nucleus
Introduction to Nuclear Physics 1. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table According to the Bohr-Rutherford model of the atom, also called the solar system model, the atom consists of a central nucleus
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Introduction to Chemistry Exam 2 Practice Problems 1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.Atoms consist principally of what three
Introduction to Chemistry Exam 2 Practice Problems 1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.Atoms consist principally of what three
Atomic Theory: History of the Atom
 Atomic Theory: History of the Atom Atomic Theory: experimental observations that led scientists to postulate the existence of the atom (smallest bit of an element). 1. Law of Conservation of Mass -During
Atomic Theory: History of the Atom Atomic Theory: experimental observations that led scientists to postulate the existence of the atom (smallest bit of an element). 1. Law of Conservation of Mass -During
Objectives 404 CHAPTER 9 RADIATION
 Objectives Explain the difference between isotopes of the same element. Describe the force that holds nucleons together. Explain the relationship between mass and energy according to Einstein s theory
Objectives Explain the difference between isotopes of the same element. Describe the force that holds nucleons together. Explain the relationship between mass and energy according to Einstein s theory
Practice TEST 2. Explain your reasoning
 Practice TEST 2 1. Imagine taking an elevator ride from the1 st floor to the 10 th floor of a building. While moving between the 1 st and 2 nd floors the elevator speeds up, but then moves at a constant
Practice TEST 2 1. Imagine taking an elevator ride from the1 st floor to the 10 th floor of a building. While moving between the 1 st and 2 nd floors the elevator speeds up, but then moves at a constant
******* KEY ******* Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide
 Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide VOCABULARY: Write a brief definition of each term in the space provided. 1. Atoms: smallest unit of an element that has all of the properties of that
Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide VOCABULARY: Write a brief definition of each term in the space provided. 1. Atoms: smallest unit of an element that has all of the properties of that
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Chapter 13 & 14 Assignment & Problem Set
 Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
Review for Atomic Theory Quiz #1
 Review for Atomic Theory Quiz #1 Practice Multiple Choice Questions: 1. Which of the following is/are quantitative physical property(s) of matter? a) mass c) density b) volume d) all of the above 2. Which
Review for Atomic Theory Quiz #1 Practice Multiple Choice Questions: 1. Which of the following is/are quantitative physical property(s) of matter? a) mass c) density b) volume d) all of the above 2. Which
Unit 2 Atomic Structure
 Unit 2 Atomic Structure Big Idea: Atomic structure explains patterns in the behavior of elements and allows us to predict the chemical and physical behavior of a given element. The organization of elements
Unit 2 Atomic Structure Big Idea: Atomic structure explains patterns in the behavior of elements and allows us to predict the chemical and physical behavior of a given element. The organization of elements
CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers
 1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
PROTONS AND ELECTRONS
 reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Nuclear Structure. particle relative charge relative mass proton +1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass
 Protons, neutrons and electrons Nuclear Structure particle relative charge relative mass proton 1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass Protons and neutrons make up
Protons, neutrons and electrons Nuclear Structure particle relative charge relative mass proton 1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass Protons and neutrons make up
Section 1: Arranging the Elements Pages 106-112
 Study Guide Chapter 5 Periodic Table Section 1: Arranging the Elements Pages 106-112 DISCOVERING A PATTERN 1. How did Mendeleev arrange the elements? a. by increasing density b. by increasing melting point
Study Guide Chapter 5 Periodic Table Section 1: Arranging the Elements Pages 106-112 DISCOVERING A PATTERN 1. How did Mendeleev arrange the elements? a. by increasing density b. by increasing melting point
Light as a Wave. The Nature of Light. EM Radiation Spectrum. EM Radiation Spectrum. Electromagnetic Radiation
 The Nature of Light Light and other forms of radiation carry information to us from distance astronomical objects Visible light is a subset of a huge spectrum of electromagnetic radiation Maxwell pioneered
The Nature of Light Light and other forms of radiation carry information to us from distance astronomical objects Visible light is a subset of a huge spectrum of electromagnetic radiation Maxwell pioneered
Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table
 Name: Class: Date: Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Name: Class: Date: Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Radiation and the Universe Higher Exam revision questions and answers
 Radiation and the Universe Higher Exam revision questions and answers Madeley High School Q.The names of three different processes are given in List A. Where these processes happen is given in List B.
Radiation and the Universe Higher Exam revision questions and answers Madeley High School Q.The names of three different processes are given in List A. Where these processes happen is given in List B.
Tro's "Introductory Chemistry", Chapter 4
 1 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Atoms and Elements Opening figure showing a shore scene with molecules of O 2, N 2, triethyl amine (CH 3 CH 2 ) 3 N, and rocks made of silicates containing
1 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Atoms and Elements Opening figure showing a shore scene with molecules of O 2, N 2, triethyl amine (CH 3 CH 2 ) 3 N, and rocks made of silicates containing
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
3 Atomic Structure 15
 3 Atomic Structure 15 3.1 Atoms You need to be familiar with the terms in italics The diameter of the nucleus is approximately 10-15 m and an atom 10-10 m. All matter consists of atoms. An atom can be
3 Atomic Structure 15 3.1 Atoms You need to be familiar with the terms in italics The diameter of the nucleus is approximately 10-15 m and an atom 10-10 m. All matter consists of atoms. An atom can be
Structure and Properties of Atoms
 PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
NYC K-8 Science Scope and Sequence: PS Standard 4 - Properties of Matter: 3.1a, 3.3a-d MST Standard 1 Inquiry Skills MST Standard 4 Process Skills
 Modeling Rutherford s Experiment A Teacher s Guide Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based Sciences and Education Author: Lora K. Hine Lesson: http://www.lepp.cornell.edu/education/teacherresources.html
Modeling Rutherford s Experiment A Teacher s Guide Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based Sciences and Education Author: Lora K. Hine Lesson: http://www.lepp.cornell.edu/education/teacherresources.html
Chapter NP-1. Nuclear Physics. Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES
 Chapter NP-1 Nuclear Physics Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES 1.1 CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 2.0 COMPOSITION OF ATOMS 2.1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Chapter NP-1 Nuclear Physics Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES 1.1 CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 2.0 COMPOSITION OF ATOMS 2.1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Atoms and Elements. Outline Atoms Orbitals and Energy Levels Periodic Properties Homework
 Atoms and the Periodic Table The very hot early universe was a plasma with cationic nuclei separated from negatively charged electrons. Plasmas exist today where the energy of the particles is very high,
Atoms and the Periodic Table The very hot early universe was a plasma with cationic nuclei separated from negatively charged electrons. Plasmas exist today where the energy of the particles is very high,
Bohr s Model of the Atom
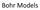 Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
Ernest Rutherford Atomic Model 1911. Plum Pudding Model J.J. Thomson 1897
 1 The arrangement of electrons in an atom determine most of the chemical properties of that atom. Electrons are what actually do the reacting. Plum Pudding Model J.J. Thomson 1897 Ernest Rutherford Atomic
1 The arrangement of electrons in an atom determine most of the chemical properties of that atom. Electrons are what actually do the reacting. Plum Pudding Model J.J. Thomson 1897 Ernest Rutherford Atomic
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements
 EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
Word Equations and Balancing Equations. Video Notes
 Word Equations and Balancing Equations Video Notes In this lesson, you will: Use the law of conservation of mass and provide standard rules for writing and balancing equations. Write and balance equations
Word Equations and Balancing Equations Video Notes In this lesson, you will: Use the law of conservation of mass and provide standard rules for writing and balancing equations. Write and balance equations
2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE
 2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE In this chapter the principles and systematics of atomic and nuclear physics are summarised briefly, in order to introduce the existence and characteristics of
2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE In this chapter the principles and systematics of atomic and nuclear physics are summarised briefly, in order to introduce the existence and characteristics of
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Methane and ethane are both made up of carbon and hydrogen. In methane, there are 12.0 g of carbon for every 4.00 g of hydrogen, a ration of 3:1 by mass. In ethane,
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Methane and ethane are both made up of carbon and hydrogen. In methane, there are 12.0 g of carbon for every 4.00 g of hydrogen, a ration of 3:1 by mass. In ethane,
Basic Nuclear Concepts
 Section 7: In this section, we present a basic description of atomic nuclei, the stored energy contained within them, their occurrence and stability Basic Nuclear Concepts EARLY DISCOVERIES [see also Section
Section 7: In this section, we present a basic description of atomic nuclei, the stored energy contained within them, their occurrence and stability Basic Nuclear Concepts EARLY DISCOVERIES [see also Section
Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table
 Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes
 Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary
 Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson
 Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
Name Date Class ELECTRONS IN ATOMS. Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics
 13 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Conceptual Curriculum Concrete concepts More abstract concepts or math/problem-solving Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics Honors Curriculum Core honors content Options
13 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Conceptual Curriculum Concrete concepts More abstract concepts or math/problem-solving Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics Honors Curriculum Core honors content Options
19.1 Bonding and Molecules
 Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table
 Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table Key Concepts The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of
Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table Key Concepts The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of
Chemistry 2 Chapter 13: Electrons in Atoms Please do not write on the test Use an answer sheet! 1 point/problem 45 points total
 Chemistry 2 Chapter 13: Electrons in Atoms Please do not write on the test Use an answer sheet! 1 point/problem 45 points total 1. Calculate the energy in joules of a photon of red light that has a frequency
Chemistry 2 Chapter 13: Electrons in Atoms Please do not write on the test Use an answer sheet! 1 point/problem 45 points total 1. Calculate the energy in joules of a photon of red light that has a frequency
Homework #10 (749508)
 Homework #10 (749508) Current Score: 0 out of 100 Description Homework on quantum physics and radioactivity Instructions Answer all the questions as best you can. 1. Hewitt10 32.E.001. [481697] 0/5 points
Homework #10 (749508) Current Score: 0 out of 100 Description Homework on quantum physics and radioactivity Instructions Answer all the questions as best you can. 1. Hewitt10 32.E.001. [481697] 0/5 points
Cathode Rays Figure 1: Figure 2:
 Cathode Rays The first ideas about electrons came from experiments with cathode-ray tubes. A forerunner of neon signs, fluorescent lights, and TV picture tubes, a typical cathode-ray tube is a partially
Cathode Rays The first ideas about electrons came from experiments with cathode-ray tubes. A forerunner of neon signs, fluorescent lights, and TV picture tubes, a typical cathode-ray tube is a partially
Matter. Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole
 Matter Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole Atomic Mass Unit Chemists of the nineteenth century realized that, in order to measure the mass of an atomic particle, it was useless to use the standard
Matter Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole Atomic Mass Unit Chemists of the nineteenth century realized that, in order to measure the mass of an atomic particle, it was useless to use the standard
Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name
 Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name HPS # date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based
Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name HPS # date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based
Elements in the periodic table are indicated by SYMBOLS. To the left of the symbol we find the atomic mass (A) at the upper corner, and the atomic num
 . ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
An Atom Apart by Leslie Cargile
 Have you ever walked through a cloud of gnats on a hot summer, only to have them follow you? No matter how you swat at them, or even if you run, they won t leave you alone. If so, then you have something
Have you ever walked through a cloud of gnats on a hot summer, only to have them follow you? No matter how you swat at them, or even if you run, they won t leave you alone. If so, then you have something
GCSE Additional Science Physics Contents Guide
 GCSE Additional Science Contents Guide Copyright Boardworks Ltd 2007 Boardworks Ltd The Gallery 54 Marston Street Oxford OX4 1LF 08703 50 55 60 [email protected] www.boardworks.co.uk 04-07 contains
GCSE Additional Science Contents Guide Copyright Boardworks Ltd 2007 Boardworks Ltd The Gallery 54 Marston Street Oxford OX4 1LF 08703 50 55 60 [email protected] www.boardworks.co.uk 04-07 contains
Chemistry. The student will be able to identify and apply basic safety procedures and identify basic equipment.
 Chemistry UNIT I: Introduction to Chemistry The student will be able to describe what chemistry is and its scope. a. Define chemistry. b. Explain that chemistry overlaps many other areas of science. The
Chemistry UNIT I: Introduction to Chemistry The student will be able to describe what chemistry is and its scope. a. Define chemistry. b. Explain that chemistry overlaps many other areas of science. The
The Atom and the Periodic Table. Electron Cloud Structure Energy Levels Rows on the Periodic Table Bohr Models Electron Dot Diagrams
 The Atom and the Periodic Table Electron Cloud Structure Energy Levels Rows on the Periodic Table Bohr Models Electron Dot Diagrams Review The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups.
The Atom and the Periodic Table Electron Cloud Structure Energy Levels Rows on the Periodic Table Bohr Models Electron Dot Diagrams Review The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups.
Main properties of atoms and nucleus
 Main properties of atoms and nucleus. Atom Structure.... Structure of Nuclei... 3. Definition of Isotopes... 4. Energy Characteristics of Nuclei... 5. Laws of Radioactive Nuclei Transformation... 3. Atom
Main properties of atoms and nucleus. Atom Structure.... Structure of Nuclei... 3. Definition of Isotopes... 4. Energy Characteristics of Nuclei... 5. Laws of Radioactive Nuclei Transformation... 3. Atom
Atoms and Molecules. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4
 Atoms and Molecules Preparation Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Describe how atoms are the building blocks of matter
Atoms and Molecules Preparation Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Describe how atoms are the building blocks of matter
