Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Sport and Physical Activity 05826/ 05827/ 05828/ Unit 1: Body systems and the effects of physical activity
|
|
|
- Darlene Daniel
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIAL Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Sport and Physical Activity 05826/ 05827/ 05828/ Unit 1: Body systems and the effects of physical activity Date Morning/Afternoon Time Allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: None You may use: A calculator Do not use: None INSTRUCTIONS Use black ink. Complete the boxes above with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all the questions. Write your answer to each question in the space provided. Do not write in the bar codes. INFORMATION The total mark for this paper is 70. The marks for each question are shown in brackets [ ]. This document consists of 16 pages. OCR 2015 [ / / ] Turn over
2 2 Answer all the questions. Section A 1 What type of bone is the femur? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. Long bone Short bone Flat bone Irregular bone [1] 2 Which one of the following bones forms part of the axial skeleton? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. Scapula Humerus Sternum Patella [1] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
3 3 Which one of the events listed below would benefit from a high percentage of fast glycolytic fibres? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. 3 Marathon Shot put 800 m race 400 m hurdles race [1] 4 Below are listed four components of blood. Which component fights infections? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets Plasma [1] 5 Which component of blood helps in the clotting process?... [1] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN Turn over
4 6 Which one of the following is a short-term effect of exercise on the muscular system? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. 4 Increase in the temperature of the muscles Increase in stroke volume Increase in slow twitch muscle fibres Increase in muscle mass [1] 7 Which one of the following is an appropriate value for an average person s tidal volume at rest? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. 0.1 litres 0.5 litres 1.0 litres 5.0 litres [1] 8 What term is used for the amount of air that is inspired or expired in one minute?... [1] 9 Calculate the cardiac output of an individual with a heart rate of 100 beats per minute and a stroke volume of 100 millilitres.... [1] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
5 10 How many molecules of ATP are produced in the ATP/PC system from one molecule of PC? 5... [1] Section B 11 Fig. 1 shows a synovial joint. (a) Identify A, B and C on the diagram. Fig. 1 A... [1] B... [1] C... [1] (b) Describe the function of ligaments and synovial membrane at a synovial joint [2] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN Turn over
6 6 12 Fig. 2 shows a sprinter in action. Fig. 2 Apply your knowledge of the skeletal and muscular systems to complete the following table. Joint Joint movement Muscle acting Type of contraction Knee Flexion Iliopsoas Concentric Biceps brachii [7] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
7 13 Table 1 shows the structural characteristics of slow oxidative muscle fibres. 7 Structural characteristic Size Capillaries Mitochondria Oxidative enzymes Myoglobin content Triglyceride stores Phosphocreatine store Slow oxidative fibres Small Many Many High High High Low Table 1 Explain how the structures of slow oxidative fibres aid muscle function.... [6] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN Turn over
8 14 Select the appropriate term from the list provided to complete each of the following statements: 8 tricuspid valve pulmonary artery left ventricle aortic valve venae cavae bicuspid valve (a)... allows blood to pass from the right atrium to the right ventricle but prevents backflow of blood. [1] (b)... pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta. [1] (c)... carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs. [1] 15 Explain the vascular shunt mechanism using the following terms: vasoconstrict vasodilate precapillary sphincters arterioles... [4] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
9 9 16 Fig. 3 shows a diagram of the lungs. Fig. 3 Identify A, B, C and D on the diagram A... [1] B... [1] C... [1] D... [1] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN Turn over
10 17 The following paragraph describes the mechanics of breathing during inspiration: 10 (a) Complete the paragraph by filling in the missing words. [5] The diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles.... This causes the rib cage to move... and out. The volume of the thoracic cavity.... This means that the pressure in the lungs..., causing air to... the lungs. (b) Explain how the rectus abdominus helps in expiration during exercise [2] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
11 18 Fig. 4 shows an example of the energy continuum with three sporting activities indicated. 11 Fig. 4 (a) Show your knowledge of energy systems by placing the following athletics events accurately on the continuum above. A B C Marathon Shot put 1500 m race [3] (b) Justify your placement of each event on the continuum. Marathon Shot put m race [3] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN Turn over
12 19 The following statement describes the lactic acid energy system. 12 Glycogen is broken down into glucose which is then converted into pyruvic acid in the sarcoplasm of the muscle cell. The reaction produces ATP which enables muscular contraction to take place. (a) What type of reaction is taking place in this system aerobic or anaerobic?... [1] (b) Identify the substance that pyruvic acid is converted into in this system.... [1] (c) What effect does this substance have on muscular contractions?... [1] 20 An active, healthy lifestyle has positive effects on the skeletal system but can also be potentially damaging. Describe the benefits and drawbacks of exercise on the skeletal system.... [5] OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
13 13 Section C 21 A sports team that you are coaching is not taking warm ups seriously before training sessions. Explain the effects of a warm up on the cardiovascular and muscular systems and how they may be beneficial to the individuals you are coaching.... [10] END OF QUESTION PAPER OCR 2015 SPECIMEN Turn over
14 14 BLANK PAGE PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
15 15 BLANK PAGE PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE OCR 2015 SPECIMEN Turn over
16 16 Copyright Information: Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (OCR) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group. Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. OCR 2015 SPECIMEN
17 SPECIMEN Sample Assessment Material LEVEL 3 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL IN SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1: Body systems and the effects of physical activity MARK SCHEME Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes MAXIMUM MARK 70 This document consists of 7 pages
18 Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity Mark Scheme SPECIMEN Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 Long bone 1 2 Sternum 1 3 Shot put 1 4 White blood cells 1 5 Platelets 1 6 Increase in the temperature of the muscles litres 1 8 Minute ventilation 1 Accept minute volume 9 10 litres per minute/10,000 millilitres per minute 1 Must specify units 10 1 (ATP) 1 11 (a) A Synovial fluid B Joint capsule C Articular/hyaline cartilage 3 (b) 1. (Ligaments) attach bone to bone/stabilise the joint/prevent dislocation 2. (Synovial membrane) secretes/produces synovial fluid/increases mobility 2 OCR
19 Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity Mark Scheme SPECIMEN Question Answer Marks Guidance 12 7 Missing words are bold and Joint Joint movement Muscle acting Type of contraction italicised in table. Knee Flexion Biceps femoris/ semimembranosus/ semitendonosus Concentric Hip Flexion Iliopsoas Concentric Elbow Flexion Biceps brachii Isometric (Many capillaries) means good supply of oxygenated blood to muscles 2. (Many mitochondria) means lots of sites/places where aerobic energy is produced 3. (Oxidative enzymes high) means improved ability to work aerobically 4. (Myoglobin content high) means muscles can receive more oxygen from blood 5. (Triglyceride stores high) means greater store of aerobic energy 6. (Phosphocreatine store low) means limited ability to produce energy anaerobically 7. (Muscle fibre type) has high endurance/high aerobic capacity 8. (Muscle fibre type) has high resistance to fatigue 9. (Muscle fibre type) has limited ability to produce strength/speed/power 6 14 (a) Tricuspid valve 1 (b) Left ventricle 1 (c) Pulmonary artery 1 OCR
20 Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity Mark Scheme SPECIMEN Question Answer Marks Guidance Arterioles to the working muscles vasodilate 2. Arterioles to non-essential organs/stomach/gut vasoconstrict 3. Precapillary sphincters to working muscles are opened/dilated 4. Precapillary sphincters to non-essential organs are closed/constricted 4 NB. Underlined words must be present in answer to gain mark. Words in bold can have acceptable alternatives i.e. 16 A Trachea B Bronchiole C Bronchus D Alveolus synonyms. 4 Accept plurals for C and D. 17 (a) The diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles contract. This causes the rib cage to move up/upwards and out. The volume of the thoracic cavity increases. This means that the pressure in the lungs decreases, causing air to enter the lungs. 5 Accept synonyms for missing words. (b) 1. (During exercise) rectus abdominus contracts 2. This helps to move the ribs downwards/inwards 3. Reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity 4. Increases the pressure in the lungs 5. Forces more air out of the lungs 2 For point 5 there must be a suggestion of more air leaving lungs than at rest. 18 (a) A Marathon must be near to aerobic end of continuum B Shot put must be at the anaerobic end of continuum C 1500m must be in central third of continuum 3 Marathon does have some anaerobic elements. (b) A Marathon an endurance event/low intensity/long duration B Shot put involves (explosive) strength/power/speed/high intensity/short duration C 1500 m race has elements of speed/muscular endurance and lower intensity/lasts more than three minutes 3 For 1500 m answer must cover both aerobic and anaerobic elements. NB. Do not accept use of aerobic/anaerobic for justification, e.g. Marathon is an aerobic event. OCR
21 Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity Mark Scheme SPECIMEN Question Answer Marks Guidance 19 (a) Anaerobic 1 (b) Lactic acid/lactate 1 (c) Causes fatigue 1 20 (Describe the benefits and drawbacks of exercise on the skeletal system). (benefits)(submax 3) Increased strength of bones Increased range of movement around joints Increased bone density/increased calcium/collagen storage Prevention of osteoporosis/reduced risk of (osteo)arthritis Increased stability of joint Increased strength of ligaments/connective tissue Increased thickness of articular/hyaline cartilage Improved posture/body alignment (drawbacks)(submax 3) Overuse injuries/stress fractures/tendonitis/bursitis Shin splints/osgood Schlatters/tennis elbow/runners knee/golfers elbow Growth plate injuries Back strains/postural problems (linked to weight training or incorrect techniques) Fractures/dislocations/torn ligaments (linked to contact sports) Osteoarthritis 21 Explain the effects of a warm up on the cardiovascular and muscular systems and how they may be beneficial to the individuals you are coaching ( Cardiovascular ) 1. Light jog/cardiovascular exercise/submaximal exercise increases heart rate/stroke volume/cardiac output 2. Increases blood flow to muscles More oxygenated blood to muscles Reduced lactic acid build up in muscles Reduces DOMS/muscle soreness Level 3 (8 10 marks) A comprehensive answer: Detailed knowledge and understanding Effective analysis/evaluation and/or discussion/explanation/develop ment OCR
22 Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity Mark Scheme SPECIMEN Question Answer Marks Guidance 3. Activates vascular shunt mechanism Vasomotor (control) centre/vcc Redistributes blood from nonessential organs to the working muscles Vasodilation/vasoconstriction of arterioles Opening/closing of precapillary sphincters 4. Increases blood temperature Reduces blood viscosity Increases diffusion of oxygen from haemoglobin to muscles Steeper diffusion gradient 5. Increases venous return (skeletal) Muscle pump squeezes veins forcing blood back towards the heart (pocket) Valves in veins ensure one-way blood flow Starling s law of the heart/increased venous return increases stroke volume (muscular ) 6. Reduces risk of injury (type of injury) muscle strains/pulls/tears increased elasticity of muscle tissue 7. Increased flexibility/extensibility of muscle/connective tissue longer term/plastic effect 8. Increases temperature of muscle decreases muscle viscosity increases speed/strength of contraction 9. Increases enzyme/metabolic activity Increases ATP production Increases activation of neural pathways Clear and consistent practical application of knowledge Accurate use of technical and specialist vocabulary High standard of written communication. At Level 3 responses are likely to include: Detailed knowledge and understanding of the effects of a warm up on both the cardiovascular and muscular systems Most points are developed Cardiac, vascular and muscular factors are both covered. Level 2 (5 7 marks) A competent answer: Satisfactory knowledge and understanding Analysis/evaluation and/or discussion/explanation/develop ment attempted with some success Some success in practical application of knowledge Technical and specialist vocabulary used with some accuracy Written communication generally fluent with few errors. At Level 2 responses are likely to include: Satisfactory knowledge and understanding of the effects of OCR
23 Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity Mark Scheme SPECIMEN Question Answer Marks Guidance a warm up on cardiovascular and muscular systems Points made but generally not developed There may be a lack of balance between the two parts of the question. Level 1 (1 4 marks) A limited answer: Basic knowledge and understanding Little or no attempt to analyse/evaluate and/or discuss/explain/develop Little or no attempt at practical application of knowledge Technical and specialist vocabulary used with limited success Written communication lacks fluency and there will be errors, some of which may be intrusive. At Level 1 responses are likely to include: Basic knowledge of the effects of a warm up on the cardiovascular and/or the muscular systems. [0 marks] No response or no response worthy of credit. OCR
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
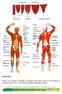 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Anatomy for Sport and Exercise
 Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
The Physiology of Fitness
 Unit 2: The Physiology of Fitness Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 5 Guided learning hours: 30 Aim and purpose R/502/5486 BTEC National This unit provides an opportunity for learners to explore the
Unit 2: The Physiology of Fitness Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 5 Guided learning hours: 30 Aim and purpose R/502/5486 BTEC National This unit provides an opportunity for learners to explore the
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
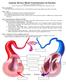 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
 Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8
 Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Accreditation Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE. Content Title: Methods of training. Practical Application/Explanation. Fartlek training. Continuous training
 Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed
 1 Transport systems chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed Simple organisms Diffusion the free movement of particles in a liquid or a gas down a concentration
1 Transport systems chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed Simple organisms Diffusion the free movement of particles in a liquid or a gas down a concentration
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance
 Learning aim B Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance Assessment criteria 2B.P5 2B.M5 2B.D2 Describe the function of the three energy systems in the production and release
Learning aim B Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance Assessment criteria 2B.P5 2B.M5 2B.D2 Describe the function of the three energy systems in the production and release
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul
 rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul Contents Acknowledgements Introduction ix xi Mandatory units 1 Anatomy for
rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul Contents Acknowledgements Introduction ix xi Mandatory units 1 Anatomy for
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
Work and Energy in Muscles
 Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
tissues are made of cells that work together, organs are )
 Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Body systems and energy for physical activity
 Body systems and energy for physical activity Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Body systems and energy for physical activity Introduction The body consists of complex structures that are made up of many parts, and
Body systems and energy for physical activity Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Body systems and energy for physical activity Introduction The body consists of complex structures that are made up of many parts, and
To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes.
 Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM"
 CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
AS Biology Revision Notes Unit 3 Physiology And Transport
 AS Biology Revision Notes Unit 3 Physiology And Transport The Heart And Circulation 1. Multicellular organisms cannot rely on their surface area to get oxygen and nutrients to all the cells. Instead they
AS Biology Revision Notes Unit 3 Physiology And Transport The Heart And Circulation 1. Multicellular organisms cannot rely on their surface area to get oxygen and nutrients to all the cells. Instead they
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Chapter 6. Components of Elasticity. Musculotendinous Unit. Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit. Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Interval Training. Interval Training
 Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Paper 1 Answer all questions. Each question is followed by four options, A, B, C and D. For each question, choose one answer only
 hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
GCE. Biology. Mark Scheme for June 2012. Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
GRADE 11F: Biology 3. UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours. Human gas exchange system and health. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011
 GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education FIRST LANGUAGE ENGLISH 0500/03 Paper 3 Directed Writing and Composition For Examination from 2015
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education FIRST LANGUAGE ENGLISH 0500/03 Paper 3 Directed Writing and Composition For Examination from 2015
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Standard Grade. Swimming. Name. Teacher. Class. P.E. Department Crieff High School. Miss Steele Jan 10 1
 Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
A1 Reasons for taking part in activity. A2 Health, fitness, exercise and performance
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Milwaukee School of Engineering Gerrits@msoe.edu. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
the Cardiovascular System
 5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education FIRST LANGUAGE ENGLISH 0500/02 Paper 2 Reading Passages (Extended) For Examination from 2015 SPECIMEN
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education FIRST LANGUAGE ENGLISH 0500/02 Paper 2 Reading Passages (Extended) For Examination from 2015 SPECIMEN
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Paper 1 May/June 2014 1 hour 15 minutes
 *99598998* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level APPLIED INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY 973/ Paper May/June 04 hour 5 minutes Candidates
*99598998* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level APPLIED INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY 973/ Paper May/June 04 hour 5 minutes Candidates
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
PHYSICAL EDUCATION IM 36
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION IM 36 IM SYLLABUS (2014) SYLLABUS 1 Physical Education IM 36 (Available in September) Syllabus 1 Paper (2hrs 30mins) & Practical (30mins) Introduction This syllabus provides candidates
PHYSICAL EDUCATION IM 36 IM SYLLABUS (2014) SYLLABUS 1 Physical Education IM 36 (Available in September) Syllabus 1 Paper (2hrs 30mins) & Practical (30mins) Introduction This syllabus provides candidates
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Text, Diagrams, Assessments, and Link to Standards Focus Questions 1) What is cellular respiration? 2) How is cellular respiration connected to breathing? 3) If
Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Text, Diagrams, Assessments, and Link to Standards Focus Questions 1) What is cellular respiration? 2) How is cellular respiration connected to breathing? 3) If
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
2. Describe the structure of a muscle fibre and explain the structural and physiological differences between fast and slow twitch muscle fibres.
 Unit 5 Biology Notes Topic 7: Run for Your Life 2. Describe the structure of a muscle fibre and explain the structural and physiological differences between fast and slow twitch muscle fibres. Muscle is
Unit 5 Biology Notes Topic 7: Run for Your Life 2. Describe the structure of a muscle fibre and explain the structural and physiological differences between fast and slow twitch muscle fibres. Muscle is
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
GCE. Physical Education. Mark Scheme for January 2012. Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit G451: An Introduction to Physical Education
 GCE Physical Education Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit G451: An Introduction to Physical Education Mark Scheme for January 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
GCE Physical Education Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit G451: An Introduction to Physical Education Mark Scheme for January 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Wednesday 19 June 2013 Afternoon
 Wednesday 19 June 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION G453/01 Principles and Concepts Across Different Areas of Physical Education *G430780613* Candidates answer on the Answer Booklet. OCR supplied
Wednesday 19 June 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION G453/01 Principles and Concepts Across Different Areas of Physical Education *G430780613* Candidates answer on the Answer Booklet. OCR supplied
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *9282687787* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2012 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
*9282687787* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2012 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
