Section 11.4: Equations of Lines and Planes
|
|
|
- Daniella Lawson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 11.4: Equations of Lines and Planes Definition: The line containing the point ( 0, 0, 0 ) and parallel to the vector v = A, B, C has parametric equations = 0 + At, = 0 + Bt, = 0 + Ct, where t R is a parameter. These equations can be epressed in vector form as R(t) = 0 + At, 0 + Bt, 0 + Ct. v = A, B, C 0, 0, 0 R t = 0 + At, 0 + Bt, 0 + Ct Figure 1: Graph of the line with direction vector v passing through ( 0, 0, 0 ). Note: If A, B, and C are nonero, then the smmetric equations of the line are 0 A = 0 B = 0 C. Eample: Find parametric and smmetric equations of the line passing through the points (1, 1, 2) and (2, 1, 5). The line is defined b the vector v = 2 1, 1 ( 1), 5 2 = 1, 2, 3. Thus, parametric equations of the line are = 2 + t, = 1 + 2t, = 5 + 3t.
2 The smmetric equations of the line are 2 = 1 2 = 5 3. Definition: A vector N that is orthogonal to ever vector in a plane is called a normal vector to the plane. N v Figure 2: Illustration of a normal vector, N, to a plane. Theorem: (Equation of a Plane) An equation of the plane containing the point ( 0, 0, 0 ) with normal vector N = A, B, C is A( 0 ) + B( 0 ) + C( 0 ) = 0. Note: The equation of an plane can be epressed as A + B + C = D. This is called the standard form of the equation of a plane. Eample: Find an equation of the plane passing through the points P = ( 1, 2, 1), Q = (0, 3, 2), and R = (1, 1, 4). Two vectors in the plane are P Q = 1, 5, 1, P R = 2, 1, 5.
3 A normal vector to the plane is P Q P R = Thus, an equation of the plane is = 26, 7, 9. 26( + 1) + 7( 2) + 9( 1) = = 3. Eample: Find an equation of the plane passing through the point P = (1, 6, 4) and containing the line defined b R(t) = 1 + 2t, 2 3t, 3 t. The line passes through the point Q = (1, 2, 3) and has direction vector v = 2, 3, 1. Another vector in the plane is P Q = 0, 4, 1. A normal vector to the plane is The equation of the plane is P Q v = = 1, 2, 8. ( 1) 2( 6) + 8( 4) = = 21. Eample: Find the point at which the line defined b R(t) = 4 t, 3 + t, 2t intersects the plane defined b + 3 = 5. Substituting the parametric equations into the equation of the plane gives + 3 = 5 (4 t) (3 + t) + 3(2t) = 5 4t + 1 = 5 t = 1. Thus, the point of intersection is (3, 4, 2).
4 Definition: Two planes are parallel if the have the same normal vector (i.e. their normal vectors are parallel). Note: If two planes are not parallel, then the intersect in a line. The angle between the two planes is the angle between their normal vectors. Eample: Consider the planes defined b = 2 and = 3. (a) Find the angle between the planes. The normal vectors are N 1 = 4, 2, 1 and N 2 = 2, 1, 4. If θ is the angle between the planes, then N cos θ = 1 N 2 N 1 N 2 = 2 = Therefore, ( ) 2 θ = cos (b) Find parametric equations for the line of intersection. To find the equation of the line of intersection, we need a point on the line and a direction vector. Since the line lies in both planes, it is orthogonal to both N 1 and N 2. Thus, a direction vector for the line is N 1 N 2 = = 7, 18, 8. Since the direction vector is not horiontal, the line must intersect the -plane ( = 0). Substituting = 0 into the equations for the planes gives { 4 2 = = 3. It follows that = 1 and = 1. Thus, (1, 1, 0) is a point on the line of intersection. The parametric equations are = 1 + 7t, = t, = 8t.
5 Theorem: (Distance from a Point to a Plane) The distance from ( 0, 0, 0 ) to the plane A + B + C + D = 0 is given b d = A 0 + B 0 + C 0 + D A2 + B 2 + C 2. Eample: Find the distance between the parallel planes 2 2+ = 10 and = 2. The planes are parallel since their normal vectors are parallel. Indeed, 2 N 1 = 2 2, 2, 1 = 4, 4, 2 = N 2. Find a point on one plane and then find the distance from this point to the other plane. Setting = = 0, the second plane contains (0, 0, 1). Now the distance between the planes is d = 2(0) 2(0) = 9 3 = 3. Definition: Two lines in R 3 are skew if the are not parallel and do not intersect. Parallel Intersecting Skew Figure 3: Illustration of parallel (red), intersecting (blue), and skew (green) lines. Note: Skew lines lie in parallel planes. Eample: Find the distance between the skew lines defined b L 1 : R1 (t) = 1 + t, 2 + 6t, 2t, L 2 : R2 (s) = 2 + 2s, s, 3 + 5s.
6 The lines lie in parallel planes P 1 and P 2. Thus, the distance between the lines is the distance between the planes. The common normal vector of the planes is orthogonal to the direction vectors v 1 = 1, 6, 2 and v 2 = 2, 14, 5. That is, N = = 2, 1, 2. To define the planes P 1 and P 2, we need points on the planes (on the lines L 1 and L 2 ). Setting t = 0, we find that (1, 2, 0) lies on L 1 and in P 1. Setting s = 0, we find that (2, 4, 3) lies on L 2 and in P 2. Thus, the equation of plane P 2 is 2( 2) ( 4) + 2( + 3) = = 0. The distance from the point (1, 2, 0) (in P 1 ) to the plane P 2 defined b = 0 is d = 2(1) 2 + 2(0) = 6 3 = 2.
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 Instructor: Longfei Li Math 43 Lecture Notes.5 Equations of Lines and Planes What do we need to determine a line? D: a point on the line: P 0 (x 0, y 0 ) direction (slope): k 3D: a point on the line: P
Instructor: Longfei Li Math 43 Lecture Notes.5 Equations of Lines and Planes What do we need to determine a line? D: a point on the line: P 0 (x 0, y 0 ) direction (slope): k 3D: a point on the line: P
Lines and Planes in R 3
 .3 Lines and Planes in R 3 P. Daniger Lines in R 3 We wish to represent lines in R 3. Note that a line may be described in two different ways: By specifying two points on the line. By specifying one point
.3 Lines and Planes in R 3 P. Daniger Lines in R 3 We wish to represent lines in R 3. Note that a line may be described in two different ways: By specifying two points on the line. By specifying one point
10.5. Click here for answers. Click here for solutions. EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES. 3x 4y 6z 9 4, 2, 5. x y z. z 2. x 2. y 1.
 SECTION EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES 1 EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 1 Find a vector equation and parametric equations for the line passing through
SECTION EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES 1 EQUATIONS OF LINES AND PLANES A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 1 Find a vector equation and parametric equations for the line passing through
Math 241 Lines and Planes (Solutions) x = 3 3t. z = 1 t. x = 5 + t. z = 7 + 3t
 Math 241 Lines and Planes (Solutions) The equations for planes P 1, P 2 and P are P 1 : x 2y + z = 7 P 2 : x 4y + 5z = 6 P : (x 5) 2(y 6) + (z 7) = 0 The equations for lines L 1, L 2, L, L 4 and L 5 are
Math 241 Lines and Planes (Solutions) The equations for planes P 1, P 2 and P are P 1 : x 2y + z = 7 P 2 : x 4y + 5z = 6 P : (x 5) 2(y 6) + (z 7) = 0 The equations for lines L 1, L 2, L, L 4 and L 5 are
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 25 Notes
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.5 in the text. Equations of Lines A line can be viewed, conceptually, as the set of all points in space that
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.5 in the text. Equations of Lines A line can be viewed, conceptually, as the set of all points in space that
Equations Involving Lines and Planes Standard equations for lines in space
 Equations Involving Lines and Planes In this section we will collect various important formulas regarding equations of lines and planes in three dimensional space Reminder regarding notation: any quantity
Equations Involving Lines and Planes In this section we will collect various important formulas regarding equations of lines and planes in three dimensional space Reminder regarding notation: any quantity
Math 241, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 9/24/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.1-14.3. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 9/24/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.1-14.3. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
2.1 Three Dimensional Curves and Surfaces
 . Three Dimensional Curves and Surfaces.. Parametric Equation of a Line An line in two- or three-dimensional space can be uniquel specified b a point on the line and a vector parallel to the line. The
. Three Dimensional Curves and Surfaces.. Parametric Equation of a Line An line in two- or three-dimensional space can be uniquel specified b a point on the line and a vector parallel to the line. The
Section 9.5: Equations of Lines and Planes
 Lines in 3D Space Section 9.5: Equations of Lines and Planes Practice HW from Stewart Textbook (not to hand in) p. 673 # 3-5 odd, 2-37 odd, 4, 47 Consider the line L through the point P = ( x, y, ) that
Lines in 3D Space Section 9.5: Equations of Lines and Planes Practice HW from Stewart Textbook (not to hand in) p. 673 # 3-5 odd, 2-37 odd, 4, 47 Consider the line L through the point P = ( x, y, ) that
Name Class. Date Section. Test Form A Chapter 11. Chapter 11 Test Bank 155
 Chapter Test Bank 55 Test Form A Chapter Name Class Date Section. Find a unit vector in the direction of v if v is the vector from P,, 3 to Q,, 0. (a) 3i 3j 3k (b) i j k 3 i 3 j 3 k 3 i 3 j 3 k. Calculate
Chapter Test Bank 55 Test Form A Chapter Name Class Date Section. Find a unit vector in the direction of v if v is the vector from P,, 3 to Q,, 0. (a) 3i 3j 3k (b) i j k 3 i 3 j 3 k 3 i 3 j 3 k. Calculate
Section 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 Section 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Generalizing Linear Equations One of the main aspects of single variable calculus was approximating graphs of functions by lines - specifically, tangent lines.
Section 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Generalizing Linear Equations One of the main aspects of single variable calculus was approximating graphs of functions by lines - specifically, tangent lines.
MA261-A Calculus III 2006 Fall Homework 3 Solutions Due 9/22/2006 8:00AM
 MA6-A Calculus III 6 Fall Homework Solutions Due 9//6 :AM 9. # Find the parametric euation and smmetric euation for the line of intersection of the planes + + z = and + z =. To write down a line euation,
MA6-A Calculus III 6 Fall Homework Solutions Due 9//6 :AM 9. # Find the parametric euation and smmetric euation for the line of intersection of the planes + + z = and + z =. To write down a line euation,
Determine whether the following lines intersect, are parallel, or skew. L 1 : x = 6t y = 1 + 9t z = 3t. x = 1 + 2s y = 4 3s z = s
 Homework Solutions 5/20 10.5.17 Determine whether the following lines intersect, are parallel, or skew. L 1 : L 2 : x = 6t y = 1 + 9t z = 3t x = 1 + 2s y = 4 3s z = s A vector parallel to L 1 is 6, 9,
Homework Solutions 5/20 10.5.17 Determine whether the following lines intersect, are parallel, or skew. L 1 : L 2 : x = 6t y = 1 + 9t z = 3t x = 1 + 2s y = 4 3s z = s A vector parallel to L 1 is 6, 9,
1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D
 40 CHAPTER 1. VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE Figure 1.16: Line through P 0 parallel to v 1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D Recall that given a point P = (a, b, c), one can draw a vector from
40 CHAPTER 1. VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE Figure 1.16: Line through P 0 parallel to v 1.5 Equations of Lines and Planes in 3-D Recall that given a point P = (a, b, c), one can draw a vector from
L 2 : x = s + 1, y = s, z = 4s + 4. 3. Suppose that C has coordinates (x, y, z). Then from the vector equality AC = BD, one has
 The line L through the points A and B is parallel to the vector AB = 3, 2, and has parametric equations x = 3t + 2, y = 2t +, z = t Therefore, the intersection point of the line with the plane should satisfy:
The line L through the points A and B is parallel to the vector AB = 3, 2, and has parametric equations x = 3t + 2, y = 2t +, z = t Therefore, the intersection point of the line with the plane should satisfy:
Section 8.8. 1. The given line has equations. x = 3 + t(13 3) = 3 + 10t, y = 2 + t(3 + 2) = 2 + 5t, z = 7 + t( 8 7) = 7 15t.
 . The given line has equations Section 8.8 x + t( ) + 0t, y + t( + ) + t, z 7 + t( 8 7) 7 t. The line meets the plane y 0 in the point (x, 0, z), where 0 + t, or t /. The corresponding values for x and
. The given line has equations Section 8.8 x + t( ) + 0t, y + t( + ) + t, z 7 + t( 8 7) 7 t. The line meets the plane y 0 in the point (x, 0, z), where 0 + t, or t /. The corresponding values for x and
Section 2.4: Equations of Lines and Planes
 Section.4: Equations of Lines and Planes An equation of three variable F (x, y, z) 0 is called an equation of a surface S if For instance, (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) S if and only if F (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) 0. x + y
Section.4: Equations of Lines and Planes An equation of three variable F (x, y, z) 0 is called an equation of a surface S if For instance, (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) S if and only if F (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) 0. x + y
MAT 1341: REVIEW II SANGHOON BAEK
 MAT 1341: REVIEW II SANGHOON BAEK 1. Projections and Cross Product 1.1. Projections. Definition 1.1. Given a vector u, the rectangular (or perpendicular or orthogonal) components are two vectors u 1 and
MAT 1341: REVIEW II SANGHOON BAEK 1. Projections and Cross Product 1.1. Projections. Definition 1.1. Given a vector u, the rectangular (or perpendicular or orthogonal) components are two vectors u 1 and
Lines and Planes 1. x(t) = at + b y(t) = ct + d
 1 Lines in the Plane Lines and Planes 1 Ever line of points L in R 2 can be epressed as the solution set for an equation of the form A + B = C. The equation is not unique for if we multipl both sides b
1 Lines in the Plane Lines and Planes 1 Ever line of points L in R 2 can be epressed as the solution set for an equation of the form A + B = C. The equation is not unique for if we multipl both sides b
Geometric description of the cross product of the vectors u and v. The cross product of two vectors is a vector! u x v is perpendicular to u and v
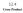 12.4 Cross Product Geometric description of the cross product of the vectors u and v The cross product of two vectors is a vector! u x v is perpendicular to u and v The length of u x v is uv u v sin The
12.4 Cross Product Geometric description of the cross product of the vectors u and v The cross product of two vectors is a vector! u x v is perpendicular to u and v The length of u x v is uv u v sin The
9 Multiplication of Vectors: The Scalar or Dot Product
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 9 Multiplication of Vectors: The Scalar or Dot Product Up to this point we have defined what vectors are and discussed basic notation
Arkansas Tech University MATH 934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 9 Multiplication of Vectors: The Scalar or Dot Product Up to this point we have defined what vectors are and discussed basic notation
Linear Equations in Linear Algebra
 1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.5 SOLUTION SETS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS HOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS A system of linear equations is said to be homogeneous if it can be written in the form A 0, where A
1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.5 SOLUTION SETS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS HOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS A system of linear equations is said to be homogeneous if it can be written in the form A 0, where A
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 8.5. VECTORS 5 (Vector equations of straight lines) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 8.5 VECTORS 5 (Vector equations of straight lines) by A.J.Hobson 8.5.1 Introduction 8.5. The straight line passing through a given point and parallel to a given vector 8.5.3
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 8.5 VECTORS 5 (Vector equations of straight lines) by A.J.Hobson 8.5.1 Introduction 8.5. The straight line passing through a given point and parallel to a given vector 8.5.3
Section 1.4. Lines, Planes, and Hyperplanes. The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables
 The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables Section 1.4 Lines, Planes, Hyperplanes In this section we will add to our basic geometric understing of R n by studying lines planes. If we do this carefully,
The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables Section 1.4 Lines, Planes, Hyperplanes In this section we will add to our basic geometric understing of R n by studying lines planes. If we do this carefully,
= y y 0. = z z 0. (a) Find a parametric vector equation for L. (b) Find parametric (scalar) equations for L.
 Math 21a Lines and lanes Spring, 2009 Lines in Space How can we express the equation(s) of a line through a point (x 0 ; y 0 ; z 0 ) and parallel to the vector u ha; b; ci? Many ways: as parametric (scalar)
Math 21a Lines and lanes Spring, 2009 Lines in Space How can we express the equation(s) of a line through a point (x 0 ; y 0 ; z 0 ) and parallel to the vector u ha; b; ci? Many ways: as parametric (scalar)
(a) We have x = 3 + 2t, y = 2 t, z = 6 so solving for t we get the symmetric equations. x 3 2. = 2 y, z = 6. t 2 2t + 1 = 0,
 Name: Solutions to Practice Final. Consider the line r(t) = 3 + t, t, 6. (a) Find symmetric equations for this line. (b) Find the point where the first line r(t) intersects the surface z = x + y. (a) We
Name: Solutions to Practice Final. Consider the line r(t) = 3 + t, t, 6. (a) Find symmetric equations for this line. (b) Find the point where the first line r(t) intersects the surface z = x + y. (a) We
LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON
 LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we derive the equations for lines and planes living in 3-space, as well as define the angle between two non-parallel planes, and determine the distance
LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we derive the equations for lines and planes living in 3-space, as well as define the angle between two non-parallel planes, and determine the distance
Lecture 14: Section 3.3
 Lecture 14: Section 3.3 Shuanglin Shao October 23, 2013 Definition. Two nonzero vectors u and v in R n are said to be orthogonal (or perpendicular) if u v = 0. We will also agree that the zero vector in
Lecture 14: Section 3.3 Shuanglin Shao October 23, 2013 Definition. Two nonzero vectors u and v in R n are said to be orthogonal (or perpendicular) if u v = 0. We will also agree that the zero vector in
Identifying second degree equations
 Chapter 7 Identifing second degree equations 7.1 The eigenvalue method In this section we appl eigenvalue methods to determine the geometrical nature of the second degree equation a 2 + 2h + b 2 + 2g +
Chapter 7 Identifing second degree equations 7.1 The eigenvalue method In this section we appl eigenvalue methods to determine the geometrical nature of the second degree equation a 2 + 2h + b 2 + 2g +
Equations of Lines and Planes
 Calculus 3 Lia Vas Equations of Lines and Planes Planes. A plane is uniquely determined by a point in it and a vector perpendicular to it. An equation of the plane passing the point (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) perpendicular
Calculus 3 Lia Vas Equations of Lines and Planes Planes. A plane is uniquely determined by a point in it and a vector perpendicular to it. An equation of the plane passing the point (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) perpendicular
Solutions to old Exam 1 problems
 Solutions to old Exam 1 problems Hi students! I am putting this old version of my review for the first midterm review, place and time to be announced. Check for updates on the web site as to which sections
Solutions to old Exam 1 problems Hi students! I am putting this old version of my review for the first midterm review, place and time to be announced. Check for updates on the web site as to which sections
CHAPTER FIVE. 5. Equations of Lines in R 3
 118 CHAPTER FIVE 5. Equations of Lines in R 3 In this chapter it is going to be very important to distinguish clearly between points and vectors. Frequently in the past the distinction has only been a
118 CHAPTER FIVE 5. Equations of Lines in R 3 In this chapter it is going to be very important to distinguish clearly between points and vectors. Frequently in the past the distinction has only been a
Lines & Planes. Packages: linalg, plots. Commands: evalm, spacecurve, plot3d, display, solve, implicitplot, dotprod, seq, implicitplot3d.
 Lines & Planes Introduction and Goals: This lab is simply to give you some practice with plotting straight lines and planes and how to do some basic problem solving with them. So the exercises will be
Lines & Planes Introduction and Goals: This lab is simply to give you some practice with plotting straight lines and planes and how to do some basic problem solving with them. So the exercises will be
Exam 1 Sample Question SOLUTIONS. y = 2x
 Exam Sample Question SOLUTIONS. Eliminate the parameter to find a Cartesian equation for the curve: x e t, y e t. SOLUTION: You might look at the coordinates and notice that If you don t see it, we can
Exam Sample Question SOLUTIONS. Eliminate the parameter to find a Cartesian equation for the curve: x e t, y e t. SOLUTION: You might look at the coordinates and notice that If you don t see it, we can
A vector is a directed line segment used to represent a vector quantity.
 Chapters and 6 Introduction to Vectors A vector quantity has direction and magnitude. There are many examples of vector quantities in the natural world, such as force, velocity, and acceleration. A vector
Chapters and 6 Introduction to Vectors A vector quantity has direction and magnitude. There are many examples of vector quantities in the natural world, such as force, velocity, and acceleration. A vector
Review Sheet for Test 1
 Review Sheet for Test 1 Math 261-00 2 6 2004 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And
Review Sheet for Test 1 Math 261-00 2 6 2004 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And
i=(1,0), j=(0,1) in R 2 i=(1,0,0), j=(0,1,0), k=(0,0,1) in R 3 e 1 =(1,0,..,0), e 2 =(0,1,,0),,e n =(0,0,,1) in R n.
 Length, norm, magnitude of a vector v=(v 1,,v n ) is v = (v 12 +v 22 + +v n2 ) 1/2. Examples v=(1,1,,1) v =n 1/2. Unit vectors u=v/ v corresponds to directions. Standard unit vectors i=(1,0), j=(0,1) in
Length, norm, magnitude of a vector v=(v 1,,v n ) is v = (v 12 +v 22 + +v n2 ) 1/2. Examples v=(1,1,,1) v =n 1/2. Unit vectors u=v/ v corresponds to directions. Standard unit vectors i=(1,0), j=(0,1) in
FURTHER VECTORS (MEI)
 Mathematics Revision Guides Further Vectors (MEI) (column notation) Page of MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: AS / A Level - MEI OCR MEI: C FURTHER VECTORS (MEI) Version : Date: -9-7 Mathematics
Mathematics Revision Guides Further Vectors (MEI) (column notation) Page of MK HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: AS / A Level - MEI OCR MEI: C FURTHER VECTORS (MEI) Version : Date: -9-7 Mathematics
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 Chapter 8 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 8.1 Introduction In this chapter we present a vector algebra approach to three dimensional geometry. The aim is to present standard properties of lines and planes,
Chapter 8 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 8.1 Introduction In this chapter we present a vector algebra approach to three dimensional geometry. The aim is to present standard properties of lines and planes,
Section 12.6: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Section 26: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Recall that if f is a differentiable function of x and y and z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x (x, y) and f y (x, y) give the rate
Section 26: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Recall that if f is a differentiable function of x and y and z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x (x, y) and f y (x, y) give the rate
Plotting Lines in Mathematica
 Lines.nb 1 Plotting Lines in Mathematica Copright 199, 1997, 1 b James F. Hurle, Universit of Connecticut, Department of Mathematics, 196 Auditorium Road Unit 39, Storrs CT 669-39. All rights reserved.
Lines.nb 1 Plotting Lines in Mathematica Copright 199, 1997, 1 b James F. Hurle, Universit of Connecticut, Department of Mathematics, 196 Auditorium Road Unit 39, Storrs CT 669-39. All rights reserved.
Teacher Page. 1. Reflect a figure with vertices across the x-axis. Find the coordinates of the new image.
 Teacher Page Geometr / Da # 10 oordinate Geometr (5 min.) 9-.G.3.1 9-.G.3.2 9-.G.3.3 9-.G.3. Use rigid motions (compositions of reflections, translations and rotations) to determine whether two geometric
Teacher Page Geometr / Da # 10 oordinate Geometr (5 min.) 9-.G.3.1 9-.G.3.2 9-.G.3.3 9-.G.3. Use rigid motions (compositions of reflections, translations and rotations) to determine whether two geometric
SECTION 9.1 THREE-DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS 651. 1 x 2 y 2 z 2 4. 1 sx 2 y 2 z 2 2. xy-plane. It is sketched in Figure 11.
 SECTION 9.1 THREE-DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS 651 SOLUTION The inequalities 1 2 2 2 4 can be rewritten as 2 FIGURE 11 1 0 1 s 2 2 2 2 so the represent the points,, whose distance from the origin is
SECTION 9.1 THREE-DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS 651 SOLUTION The inequalities 1 2 2 2 4 can be rewritten as 2 FIGURE 11 1 0 1 s 2 2 2 2 so the represent the points,, whose distance from the origin is
Notes from February 11
 Notes from February 11 Math 130 Course web site: www.courses.fas.harvard.edu/5811 Two lemmas Before proving the theorem which was stated at the end of class on February 8, we begin with two lemmas. The
Notes from February 11 Math 130 Course web site: www.courses.fas.harvard.edu/5811 Two lemmas Before proving the theorem which was stated at the end of class on February 8, we begin with two lemmas. The
Graphing Equations. with Color Activity
 Graphing Equations with Color Activity Students must re-write equations into slope intercept form and then graph them on a coordinate plane. 2011 Lindsay Perro Name Date Between The Lines Re-write each
Graphing Equations with Color Activity Students must re-write equations into slope intercept form and then graph them on a coordinate plane. 2011 Lindsay Perro Name Date Between The Lines Re-write each
Some Comments on the Derivative of a Vector with applications to angular momentum and curvature. E. L. Lady (October 18, 2000)
 Some Comments on the Derivative of a Vector with applications to angular momentum and curvature E. L. Lady (October 18, 2000) Finding the formula in polar coordinates for the angular momentum of a moving
Some Comments on the Derivative of a Vector with applications to angular momentum and curvature E. L. Lady (October 18, 2000) Finding the formula in polar coordinates for the angular momentum of a moving
w = COI EYE view direction vector u = w ( 010,, ) cross product with y-axis v = w u up vector
 . w COI EYE view direction vector u w ( 00,, ) cross product with -ais v w u up vector (EQ ) Computer Animation: Algorithms and Techniques 29 up vector view vector observer center of interest 30 Computer
. w COI EYE view direction vector u w ( 00,, ) cross product with -ais v w u up vector (EQ ) Computer Animation: Algorithms and Techniques 29 up vector view vector observer center of interest 30 Computer
SECTION 2.2. Distance and Midpoint Formulas; Circles
 SECTION. Objectives. Find the distance between two points.. Find the midpoint of a line segment.. Write the standard form of a circle s equation.. Give the center and radius of a circle whose equation
SECTION. Objectives. Find the distance between two points.. Find the midpoint of a line segment.. Write the standard form of a circle s equation.. Give the center and radius of a circle whose equation
Chapter 4.1 Parallel Lines and Planes
 Chapter 4.1 Parallel Lines and Planes Expand on our definition of parallel lines Introduce the idea of parallel planes. What do we recall about parallel lines? In geometry, we have to be concerned about
Chapter 4.1 Parallel Lines and Planes Expand on our definition of parallel lines Introduce the idea of parallel planes. What do we recall about parallel lines? In geometry, we have to be concerned about
Math 115 HW #8 Solutions
 Math 115 HW #8 Solutions 1 The function with the given graph is a solution of one of the following differential equations Decide which is the correct equation and justify your answer a) y = 1 + xy b) y
Math 115 HW #8 Solutions 1 The function with the given graph is a solution of one of the following differential equations Decide which is the correct equation and justify your answer a) y = 1 + xy b) y
( 1)2 + 2 2 + 2 2 = 9 = 3 We would like to make the length 6. The only vectors in the same direction as v are those
 1.(6pts) Which of the following vectors has the same direction as v 1,, but has length 6? (a), 4, 4 (b),, (c) 4,, 4 (d), 4, 4 (e) 0, 6, 0 The length of v is given by ( 1) + + 9 3 We would like to make
1.(6pts) Which of the following vectors has the same direction as v 1,, but has length 6? (a), 4, 4 (b),, (c) 4,, 4 (d), 4, 4 (e) 0, 6, 0 The length of v is given by ( 1) + + 9 3 We would like to make
1. Equations for lines on the plane and planes in the space.
 1. Equations for lines on the plane and planes in the space. 1.1. General implicit vector equation. (1) a r=α This equation defines a line in the plane and a plane in the 3-space. Here r is the radius-vector
1. Equations for lines on the plane and planes in the space. 1.1. General implicit vector equation. (1) a r=α This equation defines a line in the plane and a plane in the 3-space. Here r is the radius-vector
Surface Normals and Tangent Planes
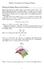 Surface Normals and Tangent Planes Normal and Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Because the equation of a plane requires a point and a normal vector to the plane, nding the equation of a tangent plane to
Surface Normals and Tangent Planes Normal and Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Because the equation of a plane requires a point and a normal vector to the plane, nding the equation of a tangent plane to
Numerical Analysis Lecture Notes
 Numerical Analysis Lecture Notes Peter J. Olver 5. Inner Products and Norms The norm of a vector is a measure of its size. Besides the familiar Euclidean norm based on the dot product, there are a number
Numerical Analysis Lecture Notes Peter J. Olver 5. Inner Products and Norms The norm of a vector is a measure of its size. Besides the familiar Euclidean norm based on the dot product, there are a number
Section 7.2 Linear Programming: The Graphical Method
 Section 7.2 Linear Programming: The Graphical Method Man problems in business, science, and economics involve finding the optimal value of a function (for instance, the maimum value of the profit function
Section 7.2 Linear Programming: The Graphical Method Man problems in business, science, and economics involve finding the optimal value of a function (for instance, the maimum value of the profit function
In this this review we turn our attention to the square root function, the function defined by the equation. f(x) = x. (5.1)
 Section 5.2 The Square Root 1 5.2 The Square Root In this this review we turn our attention to the square root function, the function defined b the equation f() =. (5.1) We can determine the domain and
Section 5.2 The Square Root 1 5.2 The Square Root In this this review we turn our attention to the square root function, the function defined b the equation f() =. (5.1) We can determine the domain and
Parametric Curves. (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia. Oct 8, 2015
 Parametric Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 8, 2015 1 Introduction A curve in R 2 (or R 3 ) is a differentiable function α : [a,b] R 2 (or R 3 ). The initial point is α[a] and the final point
Parametric Curves (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Oct 8, 2015 1 Introduction A curve in R 2 (or R 3 ) is a differentiable function α : [a,b] R 2 (or R 3 ). The initial point is α[a] and the final point
α = u v. In other words, Orthogonal Projection
 Orthogonal Projection Given any nonzero vector v, it is possible to decompose an arbitrary vector u into a component that points in the direction of v and one that points in a direction orthogonal to v
Orthogonal Projection Given any nonzero vector v, it is possible to decompose an arbitrary vector u into a component that points in the direction of v and one that points in a direction orthogonal to v
1.3. DOT PRODUCT 19. 6. If θ is the angle (between 0 and π) between two non-zero vectors u and v,
 1.3. DOT PRODUCT 19 1.3 Dot Product 1.3.1 Definitions and Properties The dot product is the first way to multiply two vectors. The definition we will give below may appear arbitrary. But it is not. It
1.3. DOT PRODUCT 19 1.3 Dot Product 1.3.1 Definitions and Properties The dot product is the first way to multiply two vectors. The definition we will give below may appear arbitrary. But it is not. It
1 Determine whether an. 2 Solve systems of linear. 3 Solve systems of linear. 4 Solve systems of linear. 5 Select the most efficient
 Section 3.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 163 SECTION 3.1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES Objectives 1 Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of a system of linear
Section 3.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 163 SECTION 3.1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES Objectives 1 Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of a system of linear
Connecting Transformational Geometry and Transformations of Functions
 Connecting Transformational Geometr and Transformations of Functions Introductor Statements and Assumptions Isometries are rigid transformations that preserve distance and angles and therefore shapes.
Connecting Transformational Geometr and Transformations of Functions Introductor Statements and Assumptions Isometries are rigid transformations that preserve distance and angles and therefore shapes.
1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Which type of construction is best represented by the steps given above?
 1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Step 1: Place the compass on one endpoint of the line segment. Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width
1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Step 1: Place the compass on one endpoint of the line segment. Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width
Geometry 1. Unit 3: Perpendicular and Parallel Lines
 Geometry 1 Unit 3: Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Geometry 1 Unit 3 3.1 Lines and Angles Lines and Angles Parallel Lines Parallel lines are lines that are coplanar and do not intersect. Some examples
Geometry 1 Unit 3: Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Geometry 1 Unit 3 3.1 Lines and Angles Lines and Angles Parallel Lines Parallel lines are lines that are coplanar and do not intersect. Some examples
Bicycle Math. presented to the Olivetti Club. Timothy E. Goldberg. March 30, 2010. Cornell University Ithaca, New York
 Bicycle Math presented to the Olivetti Club Timothy E. Goldberg Cornell University Ithaca, New York March 30, 2010 Abstract Some pretty interesting mathematics, especially geometry, arises naturally from
Bicycle Math presented to the Olivetti Club Timothy E. Goldberg Cornell University Ithaca, New York March 30, 2010 Abstract Some pretty interesting mathematics, especially geometry, arises naturally from
Chapter 8. Lines and Planes. By the end of this chapter, you will
 Chapter 8 Lines and Planes In this chapter, ou will revisit our knowledge of intersecting lines in two dimensions and etend those ideas into three dimensions. You will investigate the nature of planes
Chapter 8 Lines and Planes In this chapter, ou will revisit our knowledge of intersecting lines in two dimensions and etend those ideas into three dimensions. You will investigate the nature of planes
Math 2443, Section 16.3
 Math 44, Section 6. Review These notes will supplement not replace) the lectures based on Section 6. Section 6. i) ouble integrals over general regions: We defined double integrals over rectangles in the
Math 44, Section 6. Review These notes will supplement not replace) the lectures based on Section 6. Section 6. i) ouble integrals over general regions: We defined double integrals over rectangles in the
5 VECTOR GEOMETRY. 5.0 Introduction. Objectives. Activity 1
 5 VECTOR GEOMETRY Chapter 5 Vector Geometry Objectives After studying this chapter you should be able to find and use the vector equation of a straight line; be able to find the equation of a plane in
5 VECTOR GEOMETRY Chapter 5 Vector Geometry Objectives After studying this chapter you should be able to find and use the vector equation of a straight line; be able to find the equation of a plane in
1 Functions, Graphs and Limits
 1 Functions, Graphs and Limits 1.1 The Cartesian Plane In this course we will be dealing a lot with the Cartesian plane (also called the xy-plane), so this section should serve as a review of it and its
1 Functions, Graphs and Limits 1.1 The Cartesian Plane In this course we will be dealing a lot with the Cartesian plane (also called the xy-plane), so this section should serve as a review of it and its
Solving Systems of Equations
 Solving Sstems of Equations When we have or more equations and or more unknowns, we use a sstem of equations to find the solution. Definition: A solution of a sstem of equations is an ordered pair that
Solving Sstems of Equations When we have or more equations and or more unknowns, we use a sstem of equations to find the solution. Definition: A solution of a sstem of equations is an ordered pair that
Orthogonal Projections and Orthonormal Bases
 CS 3, HANDOUT -A, 3 November 04 (adjusted on 7 November 04) Orthogonal Projections and Orthonormal Bases (continuation of Handout 07 of 6 September 04) Definition (Orthogonality, length, unit vectors).
CS 3, HANDOUT -A, 3 November 04 (adjusted on 7 November 04) Orthogonal Projections and Orthonormal Bases (continuation of Handout 07 of 6 September 04) Definition (Orthogonality, length, unit vectors).
1.(6pts) Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (2, 5, 1) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9.
 .(6pts Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9. (a x = y + 5 3 = z (b x (c (x = ( 5(y 3 = z + (d x (e (x + 3(y 3 (z = 9 = y 3
.(6pts Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9. (a x = y + 5 3 = z (b x (c (x = ( 5(y 3 = z + (d x (e (x + 3(y 3 (z = 9 = y 3
Linear algebra and the geometry of quadratic equations. Similarity transformations and orthogonal matrices
 MATH 30 Differential Equations Spring 006 Linear algebra and the geometry of quadratic equations Similarity transformations and orthogonal matrices First, some things to recall from linear algebra Two
MATH 30 Differential Equations Spring 006 Linear algebra and the geometry of quadratic equations Similarity transformations and orthogonal matrices First, some things to recall from linear algebra Two
Section 11.1: Vectors in the Plane. Suggested Problems: 1, 5, 9, 17, 23, 25-37, 40, 42, 44, 45, 47, 50
 Section 11.1: Vectors in the Plane Page 779 Suggested Problems: 1, 5, 9, 17, 3, 5-37, 40, 4, 44, 45, 47, 50 Determine whether the following vectors a and b are perpendicular. 5) a = 6, 0, b = 0, 7 Recall
Section 11.1: Vectors in the Plane Page 779 Suggested Problems: 1, 5, 9, 17, 3, 5-37, 40, 4, 44, 45, 47, 50 Determine whether the following vectors a and b are perpendicular. 5) a = 6, 0, b = 0, 7 Recall
MATH2210 Notebook 1 Fall Semester 2016/2017. 1 MATH2210 Notebook 1 3. 1.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations... 3
 MATH0 Notebook Fall Semester 06/07 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo c Copyright 009 07 by Jenny A. Baglivo. All Rights Reserved. Contents MATH0 Notebook 3. Solving Systems of Linear Equations........................
MATH0 Notebook Fall Semester 06/07 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo c Copyright 009 07 by Jenny A. Baglivo. All Rights Reserved. Contents MATH0 Notebook 3. Solving Systems of Linear Equations........................
Supporting Australian Mathematics Project. A guide for teachers Years 11 and 12. Algebra and coordinate geometry: Module 2. Coordinate geometry
 1 Supporting Australian Mathematics Project 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 1 A guide for teachers Years 11 and 1 Algebra and coordinate geometr: Module Coordinate geometr Coordinate geometr A guide for teachers (Years
1 Supporting Australian Mathematics Project 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 1 A guide for teachers Years 11 and 1 Algebra and coordinate geometr: Module Coordinate geometr Coordinate geometr A guide for teachers (Years
PROPERTIES OF ELLIPTIC CURVES AND THEIR USE IN FACTORING LARGE NUMBERS
 PROPERTIES OF ELLIPTIC CURVES AND THEIR USE IN FACTORING LARGE NUMBERS A ver important set of curves which has received considerabl attention in recent ears in connection with the factoring of large numbers
PROPERTIES OF ELLIPTIC CURVES AND THEIR USE IN FACTORING LARGE NUMBERS A ver important set of curves which has received considerabl attention in recent ears in connection with the factoring of large numbers
Graphing Quadratic Equations
 .4 Graphing Quadratic Equations.4 OBJECTIVE. Graph a quadratic equation b plotting points In Section 6.3 ou learned to graph first-degree equations. Similar methods will allow ou to graph quadratic equations
.4 Graphing Quadratic Equations.4 OBJECTIVE. Graph a quadratic equation b plotting points In Section 6.3 ou learned to graph first-degree equations. Similar methods will allow ou to graph quadratic equations
15.1. Exact Differential Equations. Exact First-Order Equations. Exact Differential Equations Integrating Factors
 SECTION 5. Eact First-Order Equations 09 SECTION 5. Eact First-Order Equations Eact Differential Equations Integrating Factors Eact Differential Equations In Section 5.6, ou studied applications of differential
SECTION 5. Eact First-Order Equations 09 SECTION 5. Eact First-Order Equations Eact Differential Equations Integrating Factors Eact Differential Equations In Section 5.6, ou studied applications of differential
1.5 SOLUTION SETS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS
 1-2 CHAPTER 1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.5 SOLUTION SETS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS Many of the concepts and computations in linear algebra involve sets of vectors which are visualized geometrically as
1-2 CHAPTER 1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.5 SOLUTION SETS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS Many of the concepts and computations in linear algebra involve sets of vectors which are visualized geometrically as
Mechanics lecture 7 Moment of a force, torque, equilibrium of a body
 G.1 EE1.el3 (EEE1023): Electronics III Mechanics lecture 7 Moment of a force, torque, equilibrium of a body Dr Philip Jackson http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/teaching/courses/ee1.el3/ G.2 Moments, torque and
G.1 EE1.el3 (EEE1023): Electronics III Mechanics lecture 7 Moment of a force, torque, equilibrium of a body Dr Philip Jackson http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/teaching/courses/ee1.el3/ G.2 Moments, torque and
SAT Math Hard Practice Quiz. 5. How many integers between 10 and 500 begin and end in 3?
 SAT Math Hard Practice Quiz Numbers and Operations 5. How many integers between 10 and 500 begin and end in 3? 1. A bag contains tomatoes that are either green or red. The ratio of green tomatoes to red
SAT Math Hard Practice Quiz Numbers and Operations 5. How many integers between 10 and 500 begin and end in 3? 1. A bag contains tomatoes that are either green or red. The ratio of green tomatoes to red
COMPONENTS OF VECTORS
 COMPONENTS OF VECTORS To describe motion in two dimensions we need a coordinate sstem with two perpendicular aes, and. In such a coordinate sstem, an vector A can be uniquel decomposed into a sum of two
COMPONENTS OF VECTORS To describe motion in two dimensions we need a coordinate sstem with two perpendicular aes, and. In such a coordinate sstem, an vector A can be uniquel decomposed into a sum of two
Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant:
 12.1: Tangent Lines Congruent Circles: circles that have the same radius length Diagram of Examples Center of Circle: Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant: Tangent to A Circle: a line in the plane
12.1: Tangent Lines Congruent Circles: circles that have the same radius length Diagram of Examples Center of Circle: Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant: Tangent to A Circle: a line in the plane
3. Solve the equation containing only one variable for that variable.
 Question : How do you solve a system of linear equations? There are two basic strategies for solving a system of two linear equations and two variables. In each strategy, one of the variables is eliminated
Question : How do you solve a system of linear equations? There are two basic strategies for solving a system of two linear equations and two variables. In each strategy, one of the variables is eliminated
Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary TERM DEFINITION GEOMETRIC FIGURE. Cannot be defined by using other figures.
 Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary 1.1 Undefined terms Cannot be defined by using other figures. Point A specific location. It has no dimension and is represented by a dot. Line Plane A connected straight path.
Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary 1.1 Undefined terms Cannot be defined by using other figures. Point A specific location. It has no dimension and is represented by a dot. Line Plane A connected straight path.
DISTANCE, CIRCLES, AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 a p p e n d i g DISTANCE, CIRCLES, AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS IN THE PLANE Suppose that we are interested in finding the distance d between two points P (, ) and P (, ) in the
a p p e n d i g DISTANCE, CIRCLES, AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS IN THE PLANE Suppose that we are interested in finding the distance d between two points P (, ) and P (, ) in the
Graphing Linear Equations
 6.3 Graphing Linear Equations 6.3 OBJECTIVES 1. Graph a linear equation b plotting points 2. Graph a linear equation b the intercept method 3. Graph a linear equation b solving the equation for We are
6.3 Graphing Linear Equations 6.3 OBJECTIVES 1. Graph a linear equation b plotting points 2. Graph a linear equation b the intercept method 3. Graph a linear equation b solving the equation for We are
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS Sstems of linear equations refer to a set of two or more linear equations used to find the value of the unknown variables. If the set of linear equations consist of two equations
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS Sstems of linear equations refer to a set of two or more linear equations used to find the value of the unknown variables. If the set of linear equations consist of two equations
11.1. Objectives. Component Form of a Vector. Component Form of a Vector. Component Form of a Vector. Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 11 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 11.1 Vectors in the Plane Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives! Write the component form of
11 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 11.1 Vectors in the Plane Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives! Write the component form of
Geometry Notes RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY
 Right Triangle Trigonometry Page 1 of 15 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right
Right Triangle Trigonometry Page 1 of 15 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right
LINEAR INEQUALITIES. less than, < 2x + 5 x 3 less than or equal to, greater than, > 3x 2 x 6 greater than or equal to,
 LINEAR INEQUALITIES When we use the equal sign in an equation we are stating that both sides of the equation are equal to each other. In an inequality, we are stating that both sides of the equation are
LINEAR INEQUALITIES When we use the equal sign in an equation we are stating that both sides of the equation are equal to each other. In an inequality, we are stating that both sides of the equation are
Module1. x 1000. y 800.
 Module1 1 Welcome to the first module of the course. It is indeed an exciting event to share with you the subject that has lot to offer both from theoretical side and practical aspects. To begin with,
Module1 1 Welcome to the first module of the course. It is indeed an exciting event to share with you the subject that has lot to offer both from theoretical side and practical aspects. To begin with,
THE PARABOLA 13.2. section
 698 (3 0) Chapter 3 Nonlinear Sstems and the Conic Sections 49. Fencing a rectangle. If 34 ft of fencing are used to enclose a rectangular area of 72 ft 2, then what are the dimensions of the area? 50.
698 (3 0) Chapter 3 Nonlinear Sstems and the Conic Sections 49. Fencing a rectangle. If 34 ft of fencing are used to enclose a rectangular area of 72 ft 2, then what are the dimensions of the area? 50.
The Dot Product. Properties of the Dot Product If u and v are vectors and a is a real number, then the following are true:
 00 000 00 0 000 000 0 The Dot Prodct Tesday, 2// Section 8.5, Page 67 Definition of the Dot Prodct The dot prodct is often sed in calcls and physics. Gien two ectors = and = , then their
00 000 00 0 000 000 0 The Dot Prodct Tesday, 2// Section 8.5, Page 67 Definition of the Dot Prodct The dot prodct is often sed in calcls and physics. Gien two ectors = and = , then their
Definition: A vector is a directed line segment that has and. Each vector has an initial point and a terminal point.
 6.1 Vectors in the Plane PreCalculus 6.1 VECTORS IN THE PLANE Learning Targets: 1. Find the component form and the magnitude of a vector.. Perform addition and scalar multiplication of two vectors. 3.
6.1 Vectors in the Plane PreCalculus 6.1 VECTORS IN THE PLANE Learning Targets: 1. Find the component form and the magnitude of a vector.. Perform addition and scalar multiplication of two vectors. 3.
A QUICK GUIDE TO THE FORMULAS OF MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS
 A QUIK GUIDE TO THE FOMULAS OF MULTIVAIABLE ALULUS ontents 1. Analytic Geometry 2 1.1. Definition of a Vector 2 1.2. Scalar Product 2 1.3. Properties of the Scalar Product 2 1.4. Length and Unit Vectors
A QUIK GUIDE TO THE FOMULAS OF MULTIVAIABLE ALULUS ontents 1. Analytic Geometry 2 1.1. Definition of a Vector 2 1.2. Scalar Product 2 1.3. Properties of the Scalar Product 2 1.4. Length and Unit Vectors
Solutions for Review Problems
 olutions for Review Problems 1. Let be the triangle with vertices A (,, ), B (4,, 1) and C (,, 1). (a) Find the cosine of the angle BAC at vertex A. (b) Find the area of the triangle ABC. (c) Find a vector
olutions for Review Problems 1. Let be the triangle with vertices A (,, ), B (4,, 1) and C (,, 1). (a) Find the cosine of the angle BAC at vertex A. (b) Find the area of the triangle ABC. (c) Find a vector
x y The matrix form, the vector form, and the augmented matrix form, respectively, for the system of equations are
 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations in Matri Form with rref Learning Goals Determine the solution of a sstem of equations from the augmented matri Determine the reduced row echelon form of the augmented
Solving Sstems of Linear Equations in Matri Form with rref Learning Goals Determine the solution of a sstem of equations from the augmented matri Determine the reduced row echelon form of the augmented
Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities
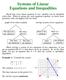 Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities Recall that every linear equation in two variables can be identified with a line. When we group two such equations together, we know from geometry what can
Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities Recall that every linear equation in two variables can be identified with a line. When we group two such equations together, we know from geometry what can
