2013 Australasian College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Discussion Adelaide
|
|
|
- Merryl Dickerson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade An evaluaton of the methods used to assess the effectveness of mandatory bcycle helmet legslaton n New Zealand Wang, J.J.J. 1,2 Grzebeta, R. 1 Walter, S. 3 & Olver, J. 2 1 Transport and Road Safety, Unversty of New South Wales 2 School of Mathematcs and Statstcs, Unversty of New South Wales 3 Centre of Health Systems and Safety Research, Unversty of New South Wales Abstract Mandatory helmet legslaton (MHL) was ntroduced n New Zealand (NZ) n January Prevous studes have shown a sgnfcant reducton n cyclng head njury assocated wth MHL; however, one analyss has suggested a dmnshng return n head njury reducton wth ncreased helmet wearng rates. The am of ths study s to crtcally assess the valdty of methods and conclusons from studes evaluatng the effect of MHL on head njury n NZ. We emphasse the mportance of accurately and objectvely presentng data and the need for a proper subsequent analyss for vald nference. Ths plays a paramount role n the communcaton of research fndngs as they heavly nfluence the publc percepton of road safety and the effectveness of polcy nterventons. Keywords Mandatory helmet legslaton, New Zealand, head njures, statstcal methods, tme trends Introducton The New Zealand helmet legslaton for cyclsts came nto effect on 1 January The legslaton requres all cyclsts to wear a standard approved cycle helmet for all on-road cyclng (Cycles: Road rules and equpment (Factsheet1), 2013). Several case-control studes n the past have shown that cycle helmets do reduce the rsk of a bran njury (Bambach et al., 2013). Smlarly, recent bomechancal testng has shown clear evdence that bcycle helmets reduce substantally potental njury to the head from both lnear and angular mpact acceleratons (McIntosh et al, 2013). Moreover, a recent nvestgaton by the authors nvestgatng the long-term trends n cyclst head and arm njures, ndcate the ntal observed beneft of the mandatory helmet law n New South Wales has been mantaned over the ensung decades (Olver et al, 2013). Wth ths n mnd, the am of the legslaton s to ncrease the helmet wearng rate, n an effort to reduce head njures to cyclsts. Pror to the law, voluntary helmet use had been wdely promoted n New Zealand. Ths ncludes natonal and local publcty and awareness campagns startng n the late 1980s. As a result, voluntary helmet wearng rates ncreased steadly durng that tme. The helmet wearng rate ncreased from vrtually zero n 1986 to 84%, 62% and 39% n September 1992 for prmary school chldren (5-12 years of age), secondary school chldren (13-18 years) and adult commuters (over 18 years), respectvely (Scuffham, et al., 2000). Just after the legslaton, helmet wearng rates ncreased to above 90% for all cyclst age groups. Note that the data used n each of the referenced studes n ths paper are from hosptalsaton or coronal data. None of these data sources nclude nformaton on helmet wearng. However, there exst helmet wearng estmates for the general cyclng populaton from yearly studes n New Zealand. 1
2 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade Research has been conducted to examne the assocaton between helmet wearng rates and rates of head njury to cyclsts n New Zealand. Scuffham and Langley (1999) studed the effect of voluntary helmet wearng on serous head njury to cyclsts. Ther results revealed the ncrease n helmet wearng rates had lttle assocaton wth the percentage of head njures to njured cyclsts for all three age groups. A later study by Povey et al. (1999) assessed the effect of cycle helmet wearng on hosptalsed njures between 1990 and 1996, usng cyclst lmb fractures as a measure of exposure. They reported that the ncrease n helmet wearng assocated wth the mandatory helmet law accounted for a 20% reducton n head njures to cyclsts nvolved n motor vehcle crashes and between 24 and 32% n non-motor vehcle crashes. Scuffham et al. (2000) extended the study by Scuffham and Langley (1999) by usng a longer tme frame ( ) and a general fndng was helmet wearng sgnfcantly reduced head njures to cyclsts n all age groups. In partcular, they estmated that the helmet law averted 139 head njures over a 3-year perod. Sandar Tn Tn et al. (2010) nvestgated exposure-based rates of on-road njures to cyclsts that resulted n death or hosptal npatent treatment over the perod Ther analyss showed the rates of traumatc bran njures were lower n and as compared to whle there was an ncreasng trend n the rates of njures to other body parts. Clarke (2012) revewed publcally avalable data, ncludng the njury data n Sandar Tn Tn et al. (2010), to evaluate the effcacy of the New Zealand bcycle helmet law n terms of safety, health, law enforcement, accdent compensaton, envronmental ssues and cvl lbertes. One of the conclusons of Clarke s study was that the New Zealand helmet law reduced cyclng usage by 51% and has contrbuted to 53 premature deaths per year due to reluctance to cycle and lack of exercse. Whle conclusons from prevous research regardng the effectveness of the New Zealand helmet law are mxed, t s mportant to crtcally assess the methodologes used n those analyses snce flawed statstcal methods and arguments lead to erroneous results and hence undermne conclusons based on these results. Robnson (2001) revewed the results of Povey et al. (1999) and suggested the apparent reducton n head njury was not due to ncreased helmet wearng, but rather an artefact caused by falure to ft tme trends n ther model. Olver (2012), n a commentary regardng Clarke s study (2012), noted the author faled to meet any of the necessary crtera to establsh a causal relatonshp and hence the orgnal conclusons were not fully supported. The purpose of ths paper s to revew studes assessng the effectveness of the New Zealand bcycle helmet law and crtcally evaluate the statstcal methods used n some of the analyses. We conclude wth general recommendatons for the choce of data and the use of approprate statstcal models for future research on ths topc. Methodology Ths evaluaton revews some exstng studes on the assocaton of helmet wearng and the mandatory helmet law wth head njures to cyclsts n New Zealand. We dscuss the sutablty of the statstcal approaches employed n these studes and suggest alternatve approaches where possble. We chose studes based on Google Scholar and Pubmed searches usng the keywords New Zealand bcycle helmet. Studes that dd not analyse New Zealand data or were unrelated to bcycle helmet use and cyclng head njury were excluded. 2
3 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade Results and Dscussons Povey et al. (1999) and Robnson (2001) Povey et al. (1999) examned the effect of helmet wearng on hosptalsed head njures between 1990 and 1996, usng cyclst lmb fractures as a measure of cyclng exposure. Cyclng njures from motor vehcle and non-motor vehcle crashes were analysed separately. Addtonally, njures from non-motor crashes were further broken down nto three age groups: prmary school age (5-12 years), secondary school age (13-18) and adult (age 19 and above). For statstcal analyss, a log-lnear model was ftted to the rato of head to lmb njures and the proporton of surveyed cyclsts who were wearng a helmet was used as an explanatory varable as below ln( HEAD / LIMB ) = α + β( HELMET ) + ε (1) where the errors ε are assumed to be ndependent, dentcally dstrbuted normal random varables. The authors estmated 24%, 32% and 28% reducton n head njury due to the helmet law for prmary, secondary and adult cyclsts n non-motor vehcle crashes. For motor vehcle crashes, the estmated reducton was 20% overall. Robnson (2001) suggested the effects estmated n Povey et al. s study were an artefact caused by falure to ft tme trends n the above model. It s mportant to note here the potental weakness of Povey s analyss s the assumpton of ndependent errors for sequentally collected data. However, nether Povey et al. nor Robnson appears to have checked the valdty of ths assumpton. For the case where the errors are serally correlated, t s possble to adequately model equaton (1) wthout tme trends by assumng an autocorrelaton error structure, for example, we can replace the error by v = φ 1 + ε, (2) v and use readly avalable estmaton methods. Fttng tme trends does not drectly address ths ssue for serally correlated data. Usng the resduals from model (1), we found lttle to no seral autocorrelaton (Durbn Watson statstc s 1.8). To demonstrate the potental bas assocated wth falure to ft tme trends, Robnson created some hypothetcal data contanng no effect of helmet wearng. The data contans only a lnear trend n whch the rato of head to lmb njures falls by 0.1 every year. Robnson then fts the followng lnear model for ths data: rato = α + β( HELMET ) + ε (3) and obtaned a hghly sgnfcant estmate for β, whch Robnson clamed was spurous. However, ths result s not as spurous as Robnson clamed, snce the varable HELMET s hghly correlated wth tme (r=0.90). To nvestgate ths further, we regress HELMET on TIME, and obtaned a statstcally sgnfcant estmate for the slope (p=0.0056). Hence, even the hypothetcal data contans no effect of helmet wearng by constructon, the varable 3
4 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade HELMET s hghly sgnfcant n predctng the rato of head to lmb njures because both the varable and the outcome can be predcted usng a lnear functon of TIME. We also found the correlaton between HELMET and the hypothetcal data s the same as the one between HELMET and TIME. Ths result s not surprsng as the tme dependent component n the varable HELMET s used to account for the varablty n the data. The remanng effect of HELMET does not mprove the ft of the model as a smple lnear model fts the data (whch s nothng else but a straght lne) perfectly (R 2 =1, resdual S.E.=0). The left graph n Fgure 1 plots the hypothetcal rato of head to lmb njures n Robnson s example and the ftted values usng HELMET as the only explanatory varable. The plot on the rght n Fgure 1 llustrates much of the varablty n yearly helmet wearng percentages s explaned by a lnear model n tme. Fgure 1 (a): hypothetcal rato of head to lmb njures and ftted values (b): smple lnear regresson of helmet wearng percentage on tme Although the example by Robnson ams to demonstrate that gnored tme trends result n bases from the model, the approach adopted requres more careful consderaton. Frstly, the hypothetcal data n Robnson s example s not smulated data as stated n the paper because they are not randomly drawn from a data-generatng process or model. As a result, there s no random error assocated wth each observaton. Hence, a completely determnstc mathematcal model s suffcent for ths data, and there s no need to ft model (3). Moreover, a determnstc model assumes that the model parameters are known and the outcome s certan gven a fxed nput value, whch s never the case n real applcatons. Hence the hypothetcal data used n Robnson s example s rather napproprate n ths stuaton. The orgnal study by Povey et al. used a lnear model for the log of head to lmb njury counts. 4
5 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade Robnson s example should be at least consstent n modellng the log of that rato, nstead of modellng the ratos themselves. Robnson argued that trends, f present, should be common to all cyclsts. Hence the mean head to lmb rato for prmary and secondary school chldren s used as an estmate of trend. It was then shown, that the mean squared error (MSE), calculated as sum[predctedactual] 2 /[number of cases] (rather than mean[predcted-actual] 2 /[number of cases] as stated n Robnson, 2001) was much better when based on predctons from trends as compared to predctons from helmet wearng rates from the model of Povey et al. (1999). However, the most ntutve approach to account for tme trend would be to nclude tme as a varable n the model. We then ft a smple lnear regresson model to the rato of adult head to lmb njures usng tme as the only varable. The ftted values are reported n Table 1. The MSE, based on predcton from only a lnear tme trend, s better than both MSEs n Povey et al. and Robnson s studes. Hence n terms of MSE as a measure of the model s ft to the observed data, the lnear tme trend model provdes a better ft than the one usng estmated trend gven by the mean head to lmb rato for prmary and secondary school chldren. Note that provded the data gven n Table 1 of Robnson (2001) were correct, we could not reproduce the results gven n Table 1 of Povey et al. (1999) usng the SAS procedure GENMOD. Hence the predcted values reported n Table 1 under Povey et al. are what we obtaned from estmatng model (3). Note also that the orgnal model n Povey et al. (1999) s for the log rato of head to lmb njures. However, n subsecton 4.1 of the paper, the authors mentoned that the above model was ftted to each of these three data seres n Fgure 4 from ther paper, whch shows the proporton of head njured (head/(head+lmb) 100%). Table 1 Rato of head to lmb njures accordng to the model of Povey et al. (1999), from fttng a trend derved from the rato of head to lmb njures n chldren (Robnson, 2001) and from fttng a lnear tme trend Year Rato of head/lmb (R=HI/L) Predcton of R Povey et al. Robnson Tme trend MSE Changes Helmet wearng (%) Based on Povey et al. s model (Model (1)), we examne the effect of addng a lnear tme trend n the log-lnear model as follows: ln( HEAD / LIMB ) = α + β( HELMET ) + γ ( TIME ) + ε, (4) 5
6 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade where TIME conssts of the numbered consecutve tme ponts n the seres (TIME=1,2,,7). We ft the above model usng the only avalable data, namely adult cyclng njures not nvolvng a motor vehcle, usng the lm functon n R (R Core Team, 2012). Results are reported n Table 2. Agan, note that the results under Povey (Model 3) are what we estmated from estmatng Model 3, nstead of the ones taken from Povey et al. (1999). We found a sgnfcant negatve estmate of the varable TIME and the varable HELMET becomes hghly nsgnfcant n the presence of a lnear tme trend. The model ncludng a tme trend provdes a much better ft to the data n terms of adjusted multple R 2, estmated resdual standard error and Akake nformaton crteron (AIC). Gven ths result, we are nterested n knowng the relatve performance of the model nvolvng only the tme trend. Hence we ft a thrd model to the data: ln( HEAD / LIMB ) = α + δ ( TIME ) + ε, (5) Results are gven n Table 2. Although the estmate of TIME does not change much from Model 4, a much smaller p-value s obtaned, ndcatng that t s a hghly sgnfcant varable n predctng the rato of head to lmb njures for adult non-motor crashes. Moreover, Model 5 provdes a superor ft as compared to Model 4, n terms of multple R 2, resdual S.E. and AIC. Hence for ths data set, addng the varable HELMET to a model whch contans a TIME varable does not mprove the ft of the model. The orgnal data, wth the ftted values under the three models are shown n Fgure 2. It can be seen from the plot that the ftted values usng Model 4 and Model 5 are almost ndstngushable and the addton of HELMET does not result n very dfferent ftted values. Table 2 Parameter estmates under three models Povey (Model 3) Model 4 Model 5 Estmate of α 0.34 (0.07, 0.61) 0.37 (0.17, 0.50) 0.34 (0.22, 0.46) p-value Estmate of β (-1.02, -0.20) (-0.54, 0.60) p-value Estmate of γ (-0.17, -0.02) p-value Estmate of δ (-0.12, -0.06) p-value Adjusted R Resdual S.E AIC The problem wth fttng a model wth both HELMET and TIME s mult- collnearty: the predctor varables HELMET and TIME are hghly correlated. We beleve ths s the case here because a multple regresson fnds an nsgnfcant estmated coeffcent of HELMET and yet a smple lnear regresson on ths varable shows the estmate s sgnfcantly dfferent from zero. One of the consequences of mult- collnearty s that 6
7 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade whle controllng for other varables (for example TIME), the estmate of a varable (such as HELMET) tends to be less precse, hence ts nfluence on the dependent varable cannot be as accurately estmated. An alternatve method such as rdge regresson can be used to cope wth the problem of mult- collnearty. However, the major problem here s the lack of data to carry out accurate statstcal nference: the degrees of freedom are 5, 4 and 5 for Models 3-5 respectvely. In other words, these are the effectve sample szes or the amount of useful nformaton we have for each model. Fgure 2 Plot of the log rato of head to lmb njures and comparson of ftted values under three models To check for resdual ndependence and normalty assumptons, we produced resdual plots as well as normal quantle plots for each of the three models as shown n Fgure 3. There seems to be some pattern n the resdual plots for models 4 and 5, hence the resdual ndependence assumpton may not be satsfed n these cases. In fact, snce many road safety data consst of sets of observatons that are sequentally ordered over tme, ssues arse n the analyss of these data snce they may not be ndependent. A general approach for dealng wth ths type of data s to employ specalsed tme seres models such as ARIMA-type and state space models. However, the use of more dedcated tme seres s dscouraged by lack of data n ths case. For a dscusson of approprate tme seres analyss technques used n road safety research, see Commandeur et al. (2012). Generally speakng, we recommend the use of monthly data rather than yearly data when monthly data are avalable. Ths s because monthly data contan more nformaton and are able to capture partcular characterstcs (such as seasonal patterns) than the yearly data where these effects are averaged out. In terms of assessng the effect of cycle helmet wearng on hosptalsed head njures, ths data set s lmted. The data conssts of adult non-motor vehcle njures; hence certan proporton of ths group may be crashes that occurred off-road ncludng recreatonal cyclng, whereas the cyclng helmet law apples to all on-road cyclsts n New Zealand. Therefore a more nformatve data set s perhaps the motor vehcle njury counts. Furthermore, t s mportant to dstngush tme trends from the effects of explanatory varables, n ths case, 7
8 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade helmet wearng. However, how to properly account for tme trends n a model remans an open queston. In fact, Robnson (2001) rased a concern regardng the analyss of Povey et al. (1999). However, the man ssue s not so much about modfyng the model structure, for example, addng an addtonal varable to model a lnear tme trend, but more about checkng for model assumpton, whch both Povey et al. and Robnson have omtted. After checkng the resdual plots and test for seral correlaton, t seems that the model assumptons for Model (4) are satsfed and hence the results and conclusons n Povey et al. s analyss are vald. Nonetheless, we showed that a model wth a lnear tme trend outperformed the one wth helmet wearng rate as the explanatory varable. We also showed that ncludng both tme trend and helmet wearng rate n the model may cause a mult-collnearty problem snce they are hghly correlated. Clarke (2012) Fgure 3 Resdual plots and quantle plots for three models Clarke compared hghly aggregated data from before and after the helmet law was ntroduced. He found that from 1989 to 1990 (four years before the helmet law) to (13 years after the law), there was a 51% drop n the average number of hours cycled per person. He clamed that ths sgnfcant drop was completely attrbutable to helmet law. Frstly, observatons on adjacent dates are more correlated than dates farther apart. That s, njures and cyclng rates near the ntroducton of the helmet law are more lkely to be nfluenced by the law. However, no data are presented around the date of the helmet law n New Zealand and the concluson that the helmet law dscouraged cyclng to a sgnfcant 8
9 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade extent s undermned by comparng data from tme perods that are not near the mandatory helmet law date. To analyse the effect of an nterventon, t s mportant to effectvely estmate the trend before and after the nterventon n order to assess whether or not any observed decrease/ncrease around the tme of the nterventon s part of a longer downward/upward trend. Hence t s mportant to account for background trend and the estmaton of trends cannot be acheved by smply comparng two ponts n tme on ether sde of the law. In fact, prevous studes have noted a declne n rdershp back to 1986 for commuters (Tn Tn, 2009) whch began long before the mandatory helmet law n 1994 and before the substantal ncrease n helmet wearng that began n 1990 (Povey et al., 1999). Ths downward trend s not n any form captured n Clarke s analyss. Compared wth the pre-law perod , Clarke showed that cyclsts had a 20% hgher accdent rate (adjusted for mllons of hours spent travellng) by Clarke then assocates ths ncrease n overall accdent rate wth the helmet use. Reasons provded nclude Safety n Numbers, rsk compensaton and balance and rdng stablty aspects. However, when we compare the pre-law data to a perod that s more relevant to the mandatory helmet law, that s, , there are substantal drops n cyclst njures overall (-17%) and serous njures wth an abbrevated njury score (AIS) greater than or equal to 3 (-53%) after adjustng for mllons of hours spent travellng. The artcle notes the rato of cyclst and pedestran fataltes s 0.24 for the fve year perod pre-law. A comparson s then made wth the four year perod (rato: 0.27). Frstly the rato should be 0.26 as the cyclsts deaths were 39 nstead of the 41 stated n the artcle. Hence ncreasng the totals to equate pre law levels of cyclng (snce the average hours cyclng reduced by 51%), would gve total of 80 and the rato s 47% nstead of the 49% calculated n the artcle. However when we choose a tme perod that s closer to the helmet law, say , the rato of cyclst to pedestran fataltes s 0.22 and after adjustng for changes to numbers of hours cycled and walked (average hours walked ncreased by 2% and cyclng reduced by 40%), the rato s 38%. Addtonally, there s a 23% declne n cyclst fataltes n the mmedate three years post-law ( ) compared wth the precedng three years pre-law ( ) whch s not dscussed n the artcle. Clarke also fals to dscuss that the change n the cyclst to pedestran fatalty rato s nfluenced by changes n general regardng pedestran and cyclst safety envronment and not the helmet law or helmet wearng alone. The author does not address possble confoundng factors and attrbutes all declnes n cyclng rates and ncreases n cyclng fataltes/njures to the helmet law. In the artcle Clarke sourced for bcycle njures, Tn Tn et al. (2010) lsts several reasons apart from the helmet law for declnes n cyclng rates and ncreases n njures. These nclude the lack of a cyclng focus n the New Zealand road safety agenda, an ncrease n chldren beng drven to school due to parental concerns of safety and pre-law declne n cyclng rates. Hence choosng arbtrary tme perods on ether sde of the law and drawng a concluson that the hgher accdent rate s assocated wth helmet use based on computng ratos rather than statstcal nference, may convey msleadng nformaton and deas on the mpact of polcy nterventons, for nstance, the mandatory helmet law n New Zealand. Furthermore, the helmet laws are enacted to ncrease helmet wearng n an attempt to mtgate bcycle related head njures and do not offer njury protecton to other body parts. However, 9
10 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade the fataltes and njury counts presented n Clarke s paper are for all bcycle related njures and hence trends n head njures/fataltes before and after the helmet law cannot be estmated usng ths data. The exposure data came from the Land Transport Safety Authorty collected n the perods , and and the Ongong New Zealand Household Survey was collected n As a result, njury rates relatve to the amount of cyclng are only estmable durng those years. Ths study shed no lght on the cyclng envronment n a four year wndow around the mandatory helmet law. In concluson, due to weakness n the analyss and choce of data partcularly the four year absence of data around the tme helmet laws were ntroduced, the concluson that the mandatory helmet law halved the number of cyclsts and contrbuted to 53 deaths each year s hghly questonable f not msleadng. Scuffham and Langley (1997) The authors examned the serous njury trends for three age groups of cyclsts admtted to publc hosptals between 1980 and 1992; twelve months before the ntroducton of helmet legslaton. The njury data were grouped nto correspondng sx-month ntervals centred around the month of the helmet survey, totallng a sample sze of 26. A Posson regresson model s constructed for the number of njured cyclsts wth a head njury and the total number of cyclsts admtted s used as the offset. Covarates ncluded n the lnear part of the regresson model nclude admsson polcy varable, helmet wearng varable and tme. The admsson polcy varable, defned as the number of head njured non-cyclsts dvded by the total number of njured non-cyclsts, s used to account any possble changes n hosptal admsson polces for head and non-head njures; helmet wearng s represented as a categorcal varable ndcatng the helmet wearng perod: no helmets ( ), some helmet wearng (1986-md 1989) and a lot of wearng helmets (md ). Tme was a contnuous varable representng any underlyng tme trend to capture any gradual change n rsk of head njury. The results ndcated that there was no sgnfcant dfference n the underlyng downward trend between each age group and the only sgnfcant varable n the model s tme. Also there was no sgnfcant dfference n cyclsts head njures n the perods of no helmets or some helmets compared to a lot of helmets when helmet wearng was hgh. Hence the authors concluded that the downward trend n head njures was smply because of the underlyng tme trend and was ndependent of helmet wearng. Ths result s not surprsng when lookng at the percentage of head njures n Fgure 2 n Scuffham and Langley (1997). From Fgure 2, we observe that the head njury percentages are declnng gradually over tme for all three age groups. Throughout the sample perod, we do not observe any abrupt changes to the percentage of head njures. Hence the changes n head njures n ths case, may well be explaned by just a temporal trend. Ths s n clear contrast wth the study conducted on hosptal admsson counts of cyclst head njures from New South Wales, Australa (Walter et al., 2011), where there was an abrupt and sgnfcant reducton n head njury rates compared to arm njury rates mmedately followng the ntroducton of mandatory helmet legslaton. To examne the effect of the helmet law, the authors choose to model t as a contnuous functon of helmet wearng rather as a step functon because helmet wearng proporton had been ncreasng steadly n the years leadng up to the legslaton due to the promoton of voluntary helmet use n New Zealand. On the other hand, the study by Walter et al. (2011) 10
11 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade used an ndcator varable to represent the helmet legslaton as the helmet wearng rate n New South Wales ncreased from approxmately 20% to more than 60% among chldren and over 70% for adults wthn two months of the legslaton comng nto effect. The problem wth ncludng both helmet wearng and tme n the Scuffham and Langley (1997) regresson model s agan mult-collnearty. Removng the tme trend for nstance, may result n a sgnfcant estmate of the helmet wearng varable. The result of the Scuffham and Langley (1997) study showed that ncreasng helmet wearng pre-law n New Zealand has had lttle assocaton wth serous head njures to cyclsts, whch s nconsstent wth the results of some case control studes (Thompson et al. (1989), Thomas et al. (1994)). Scuffham and Langley (1997) also compared ther results wth a Vctoran study (Cameron et al., 1994) who suggested that apart from helmet wearng rate, other factors such as major ntatves at drnk/drvng and speed reducton may also reduce the number of cyclsts nvolved n crashes. Scuffham et al. (2000) Ths study used a smlar model as the one n Scuffham and Langley (1997). However, a negatve bnomal was assumed for the dependent varable n place of the usual Posson dstrbuton. Independent varables nclude hosptal admsson varable and helmet wearng rate, whereas temporal trend was not ncluded n the model. The results ndcated the helmet wearng rate varable was negatve and sgnfcant, and that a 1% ncrease n the helmet wearng rate was assocated wth a reducton n overall head njures by 0.43% for all age groups. The authors explaned that the reason for not ncludng a lnear varable to account for observed trends s that the addton of a tme-trend varable caused the helmet wearng proporton to become nsgnfcant. That s, a tme-trend varable swamped the real effect. However, what s consdered as real effect s not so clear. If addng a lnear tme varable caused the helmet wearng varable to become nsgnfcant, then perhaps much of the varaton n the outcome seres (.e., the number of cyclsts wth head njury) can be modelled just by a lnear temporal trend snce the helmet wearng rate tself, can be modelled as a functon of tme. Hence, the separaton of helmet wearng effect from the background temporal trend s the key ssue. As mentoned by Scuffham et al. (2000), there was a substantal seasonal pattern for cyclst head and non-head njures as seen n Fgure 2. However, ths seasonal pattern was not explctly modelled and nether covarates (helmet wearng rate and hosptal admsson polcy varable) are able to take seasonalty nto account. One way to account for seasonalty s to ntroduce dummy varables to capture seasonal fluctuatons n the data seres. However, to account for monthly varaton for example, an extra 11 dummy varables needs to be added to the model and there must be suffcent data to make t reasonable n terms of degrees of freedom. Another way s to seasonally adjust the data usng for example, the X11 method, pror to fttng a model, as was done n Bernat et al. (2004) and Walter et al. (2011). Concluson In evaluatons of mandatory helmet laws, researchers need to ensure that ther conclusons are not based on statstcally flawed analyses and arguments. As an example, based on peerrevewed studes from several countres, Attewell et al. (2001) performed a formal metaanalyss and concluded that there s a statstcally sgnfcant effect of bcycle helmets n preventng serous njury and even death. Elvk (2011), however, n a re-analyss of Attewell 11
12 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade et al. (2001) reported nflated estmates of the effects of helmets due to ther falure to control for publcaton bas and tme trend bas. However, due to data and analytc errors, Elvk (n press) has publshed a full length corrgendum to ths paper. Subsequently, Churches (2013) reported dffculty n reproducng Elvk s (n press) results and estmated a substantally larger beneft of helmet wearng, usng the same data as Elvk. To non-specalsts, they may not be aware of the statstcal ssues nvolved n reachng certan conclusons. In fact, many statstcally flawed studes have been cted extensvely n publc debate over bcycle helmet laws (Olver et al., submtted). These studes may have nfluenced how the meda, publc and polcymakers perceve bcycle helmets and mandatory helmet laws. The assessment of an nterventon through the analyss of routnely collected observatonal data s non-trval and requres careful model specfcaton and statstcal analyss. As shown n ths study, falure to address mportant ssues such as checkng model assumptons, multcollnearty between explanatory varables, etc., can result n msleadng or ncorrect conclusons. References Attewell, R.G., Glase, K. & McFadden, M. (2001). Bcycle helmet effcacy: a meta-analyss. Accdent Analyss and Preventon, 33, Bambach M.R., Mtchell R.J., Grzebeta R.H., Olver J., (2013) The effectveness of helmets n bcycle collsons wth motor vehcles: A case control study, Accdent Analyss and Preventon 53 (2013) Bernat, D.H., Dunsmur, W.T.M. & Wagenaar, A.C. (2004). Effects of lowerng the legal BAC to 0.08 on sngle-vehcle-nghttme fatal traffc crashes n 19 jursdctons. Accdent Analyss and Preventon, 36(6), Cameron, M.H., Vulcan, A.P., Fnch, C.F. & Newstead, S.V. (1994). Mandatory bcycle helmet use followng a decade of helmet promoton n Vctora Australa - an evaluaton. Accdent Analyss & Preventon, 26, Churches, T. (2013). The benefts of reproducble research: a publc health example. Avalable at: (accessed ) Clark, C.F. (2012). Evaluaton of New Zealand s bcycle helmet law. The New Zealand Medcal Journal, 125(1349), Commandeur, J.J.F., Bjleveld, F.D., Bergel-Hayat, R., Antonou, C., Yanns, G. & Papadmtrou, E. (2012). On statstcal nference n tme seres analyss of the evoluton of road safety. Accdent Analyss & Preventon, Cycles: Road rules and equpment (Factsheet1) (2013). Retreved from Elvk, R. (2011). Publcaton bas and tme-trend bas n meta-analyss of bcycle helmet effcacy: a re-analyss of Attewell, Glase and McFadden, Accdent Analyss and Preventon, 43,
13 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade Elvk, R. (n press). Corrgendum to: Publcaton bas and tme-trend bas n meta-analyss of bcycle helmet effcacy: A re-analyss of Attewell, Glase and McFadden, Accdent Analyss and Preventon. McIntosh A.S., La A. and Schlter E. (2013) Bcycle Helmets: Head Impact Dynamcs n Helmeted and Unhelmeted Oblque Impact Tests, Traffc Injury Preventon, 14:5, , DOI: / Olver, J. (2012). Don t blame mandatory helmets for cyclst deaths n New Zealand. The Conversaton. Avalable at: Olver, J., Grzebeta, R., Wang, J.J.J. & Walter, S. (submtted). Statstcal Errors n Ant- Helmet Arguments. Proceedngs of the 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference. Olver, J., Walter, S. and Grzebeta, R. (2013). Long term bcycle related head njury trends for New South Wales, Australa followng mandatory helmet legslaton. Accdent Analyss & Preventon, 50, Povey, L.J., Frth, W.J. & Graham, P. G. (1999). Cycle helmet effectveness n New Zealand. Accdent Analyss & Preventon, 31, R Core Team (2012). R: A language and envronment for statstcal computng. R Foundaton for Statstcal Computng, Venna, Austra. ISBN , URL Robnson, D.L. (2001). Changes n head njury wth the New Zealand bcycle helmet law. Accdent Analyss & Preventon, 33, Scuffham, P. & Langley, J.D. (1997). Trends n cycle njury n New Zealand under voluntary helmet use. Accdent Analyss & Preventon, 29, 1-9. Scuffham, P., Alsop, J., Cryer, C. & Langley, J.D. (2000). Head njures to bcyclsts and the New Zealand bcycle helmet law. Accdent Analyss & Preventon, 32, Thomas, S., Acton, C. & Nxon, J. (1994). Effectveness of bcycle helmets n preventng head njury n chldren: case-control study. Brtsh Medcal Journal, 308, Thompson, R.S., Rvara, F.P. & Thompson, D.C. (1989). A case-control study of the effectveness of bcycle safety helmets. New England Journal of Medcne, 320, Tn Tn, S., Woodward, A., Thornley, S. & Ameratunga, S. (2009). Cyclng and walkng to walk n New Zealand, : regonal and ndvdual dfferences, and ponters to effectve nterventons. Internatonal Journal of Behavoral Nutrton and Physcal Actvty, 6(1):64. Tn Tn, S., Woodward, A. & Ameratunga, S. (2010). Injures to pedal cyclsts on New Zealand roads, BMC Publc Health, 10:
14 2013 Australasan College of Road Safety Conference A Safe System: The Road Safety Dscusson Adelade Walter, S.R., Olver, J., Churches, T. & Grzebeta, R. (2011). The mpacts of compulsory cycle helmet legslaton on cyclst head njures n New South Wales, Australa. Accdent Analyss and Preventon, 43,
Causal, Explanatory Forecasting. Analysis. Regression Analysis. Simple Linear Regression. Which is Independent? Forecasting
 Causal, Explanatory Forecastng Assumes cause-and-effect relatonshp between system nputs and ts output Forecastng wth Regresson Analyss Rchard S. Barr Inputs System Cause + Effect Relatonshp The job of
Causal, Explanatory Forecastng Assumes cause-and-effect relatonshp between system nputs and ts output Forecastng wth Regresson Analyss Rchard S. Barr Inputs System Cause + Effect Relatonshp The job of
An Alternative Way to Measure Private Equity Performance
 An Alternatve Way to Measure Prvate Equty Performance Peter Todd Parlux Investment Technology LLC Summary Internal Rate of Return (IRR) s probably the most common way to measure the performance of prvate
An Alternatve Way to Measure Prvate Equty Performance Peter Todd Parlux Investment Technology LLC Summary Internal Rate of Return (IRR) s probably the most common way to measure the performance of prvate
Can Auto Liability Insurance Purchases Signal Risk Attitude?
 Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 2011, Vol. 10, No. 2, 159-164 Can Auto Lablty Insurance Purchases Sgnal Rsk Atttude? Chu-Shu L Department of Internatonal Busness, Asa Unversty, Tawan Sheng-Chang
Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 2011, Vol. 10, No. 2, 159-164 Can Auto Lablty Insurance Purchases Sgnal Rsk Atttude? Chu-Shu L Department of Internatonal Busness, Asa Unversty, Tawan Sheng-Chang
Analysis of Premium Liabilities for Australian Lines of Business
 Summary of Analyss of Premum Labltes for Australan Lnes of Busness Emly Tao Honours Research Paper, The Unversty of Melbourne Emly Tao Acknowledgements I am grateful to the Australan Prudental Regulaton
Summary of Analyss of Premum Labltes for Australan Lnes of Busness Emly Tao Honours Research Paper, The Unversty of Melbourne Emly Tao Acknowledgements I am grateful to the Australan Prudental Regulaton
CHAPTER 14 MORE ABOUT REGRESSION
 CHAPTER 14 MORE ABOUT REGRESSION We learned n Chapter 5 that often a straght lne descrbes the pattern of a relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. For nstance, n Example 5.1 we explored the relatonshp
CHAPTER 14 MORE ABOUT REGRESSION We learned n Chapter 5 that often a straght lne descrbes the pattern of a relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. For nstance, n Example 5.1 we explored the relatonshp
How To Calculate The Accountng Perod Of Nequalty
 Inequalty and The Accountng Perod Quentn Wodon and Shlomo Ytzha World Ban and Hebrew Unversty September Abstract Income nequalty typcally declnes wth the length of tme taen nto account for measurement.
Inequalty and The Accountng Perod Quentn Wodon and Shlomo Ytzha World Ban and Hebrew Unversty September Abstract Income nequalty typcally declnes wth the length of tme taen nto account for measurement.
An Evaluation of the Extended Logistic, Simple Logistic, and Gompertz Models for Forecasting Short Lifecycle Products and Services
 An Evaluaton of the Extended Logstc, Smple Logstc, and Gompertz Models for Forecastng Short Lfecycle Products and Servces Charles V. Trappey a,1, Hsn-yng Wu b a Professor (Management Scence), Natonal Chao
An Evaluaton of the Extended Logstc, Smple Logstc, and Gompertz Models for Forecastng Short Lfecycle Products and Servces Charles V. Trappey a,1, Hsn-yng Wu b a Professor (Management Scence), Natonal Chao
Latent Class Regression. Statistics for Psychosocial Research II: Structural Models December 4 and 6, 2006
 Latent Class Regresson Statstcs for Psychosocal Research II: Structural Models December 4 and 6, 2006 Latent Class Regresson (LCR) What s t and when do we use t? Recall the standard latent class model
Latent Class Regresson Statstcs for Psychosocal Research II: Structural Models December 4 and 6, 2006 Latent Class Regresson (LCR) What s t and when do we use t? Recall the standard latent class model
benefit is 2, paid if the policyholder dies within the year, and probability of death within the year is ).
 REVIEW OF RISK MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS AND INSURANCE Loss and nsurance: When someone s subject to the rsk of ncurrng a fnancal loss, the loss s generally modeled usng a random varable or
REVIEW OF RISK MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS AND INSURANCE Loss and nsurance: When someone s subject to the rsk of ncurrng a fnancal loss, the loss s generally modeled usng a random varable or
The Development of Web Log Mining Based on Improve-K-Means Clustering Analysis
 The Development of Web Log Mnng Based on Improve-K-Means Clusterng Analyss TngZhong Wang * College of Informaton Technology, Luoyang Normal Unversty, Luoyang, 471022, Chna wangtngzhong2@sna.cn Abstract.
The Development of Web Log Mnng Based on Improve-K-Means Clusterng Analyss TngZhong Wang * College of Informaton Technology, Luoyang Normal Unversty, Luoyang, 471022, Chna wangtngzhong2@sna.cn Abstract.
Answer: A). There is a flatter IS curve in the high MPC economy. Original LM LM after increase in M. IS curve for low MPC economy
 4.02 Quz Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons (30/00 ponts) Please, crcle the correct answer for each of the followng 0 multple-choce questons. For each queston, only one of the answers s correct.
4.02 Quz Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons (30/00 ponts) Please, crcle the correct answer for each of the followng 0 multple-choce questons. For each queston, only one of the answers s correct.
DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT
 CelersSystems DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT PREPARED BY James E Aksel, PMP, PMI-SP, MVP For Addtonal Informaton about Earned Value Management Systems and reportng, please contact: CelersSystems,
CelersSystems DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT PREPARED BY James E Aksel, PMP, PMI-SP, MVP For Addtonal Informaton about Earned Value Management Systems and reportng, please contact: CelersSystems,
Exhaustive Regression. An Exploration of Regression-Based Data Mining Techniques Using Super Computation
 Exhaustve Regresson An Exploraton of Regresson-Based Data Mnng Technques Usng Super Computaton Antony Daves, Ph.D. Assocate Professor of Economcs Duquesne Unversty Pttsburgh, PA 58 Research Fellow The
Exhaustve Regresson An Exploraton of Regresson-Based Data Mnng Technques Usng Super Computaton Antony Daves, Ph.D. Assocate Professor of Economcs Duquesne Unversty Pttsburgh, PA 58 Research Fellow The
The Current Employment Statistics (CES) survey,
 Busness Brths and Deaths Impact of busness brths and deaths n the payroll survey The CES probablty-based sample redesgn accounts for most busness brth employment through the mputaton of busness deaths,
Busness Brths and Deaths Impact of busness brths and deaths n the payroll survey The CES probablty-based sample redesgn accounts for most busness brth employment through the mputaton of busness deaths,
HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA*
 HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA* Luísa Farnha** 1. INTRODUCTION The rapd growth n Portuguese households ndebtedness n the past few years ncreased the concerns that debt
HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA* Luísa Farnha** 1. INTRODUCTION The rapd growth n Portuguese households ndebtedness n the past few years ncreased the concerns that debt
Criminal Justice System on Crime *
 On the Impact of the NSW Crmnal Justce System on Crme * Dr Vasls Sarafds, Dscplne of Operatons Management and Econometrcs Unversty of Sydney * Ths presentaton s based on jont work wth Rchard Kelaher 1
On the Impact of the NSW Crmnal Justce System on Crme * Dr Vasls Sarafds, Dscplne of Operatons Management and Econometrcs Unversty of Sydney * Ths presentaton s based on jont work wth Rchard Kelaher 1
Calculation of Sampling Weights
 Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Decision Tree Model for Count Data
 Proceedngs of the World Congress on Engneerng 2012 Vol I Decson Tree Model for Count Data Yap Bee Wah, Norashkn Nasaruddn, Wong Shaw Voon and Mohamad Alas Lazm Abstract The Posson Regresson and Negatve
Proceedngs of the World Congress on Engneerng 2012 Vol I Decson Tree Model for Count Data Yap Bee Wah, Norashkn Nasaruddn, Wong Shaw Voon and Mohamad Alas Lazm Abstract The Posson Regresson and Negatve
To manage leave, meeting institutional requirements and treating individual staff members fairly and consistently.
 Corporate Polces & Procedures Human Resources - Document CPP216 Leave Management Frst Produced: Current Verson: Past Revsons: Revew Cycle: Apples From: 09/09/09 26/10/12 09/09/09 3 years Immedately Authorsaton:
Corporate Polces & Procedures Human Resources - Document CPP216 Leave Management Frst Produced: Current Verson: Past Revsons: Revew Cycle: Apples From: 09/09/09 26/10/12 09/09/09 3 years Immedately Authorsaton:
Statistical Methods to Develop Rating Models
 Statstcal Methods to Develop Ratng Models [Evelyn Hayden and Danel Porath, Österrechsche Natonalbank and Unversty of Appled Scences at Manz] Source: The Basel II Rsk Parameters Estmaton, Valdaton, and
Statstcal Methods to Develop Ratng Models [Evelyn Hayden and Danel Porath, Österrechsche Natonalbank and Unversty of Appled Scences at Manz] Source: The Basel II Rsk Parameters Estmaton, Valdaton, and
IDENTIFICATION AND CORRECTION OF A COMMON ERROR IN GENERAL ANNUITY CALCULATIONS
 IDENTIFICATION AND CORRECTION OF A COMMON ERROR IN GENERAL ANNUITY CALCULATIONS Chrs Deeley* Last revsed: September 22, 200 * Chrs Deeley s a Senor Lecturer n the School of Accountng, Charles Sturt Unversty,
IDENTIFICATION AND CORRECTION OF A COMMON ERROR IN GENERAL ANNUITY CALCULATIONS Chrs Deeley* Last revsed: September 22, 200 * Chrs Deeley s a Senor Lecturer n the School of Accountng, Charles Sturt Unversty,
What is Candidate Sampling
 What s Canddate Samplng Say we have a multclass or mult label problem where each tranng example ( x, T ) conssts of a context x a small (mult)set of target classes T out of a large unverse L of possble
What s Canddate Samplng Say we have a multclass or mult label problem where each tranng example ( x, T ) conssts of a context x a small (mult)set of target classes T out of a large unverse L of possble
Staff Paper. Farm Savings Accounts: Examining Income Variability, Eligibility, and Benefits. Brent Gloy, Eddy LaDue, and Charles Cuykendall
 SP 2005-02 August 2005 Staff Paper Department of Appled Economcs and Management Cornell Unversty, Ithaca, New York 14853-7801 USA Farm Savngs Accounts: Examnng Income Varablty, Elgblty, and Benefts Brent
SP 2005-02 August 2005 Staff Paper Department of Appled Economcs and Management Cornell Unversty, Ithaca, New York 14853-7801 USA Farm Savngs Accounts: Examnng Income Varablty, Elgblty, and Benefts Brent
PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIGIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION
 PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION Danny Cohen-Zada Department of Economcs, Ben-uron Unversty, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel Wllam Sander Department of Economcs, DePaul
PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION Danny Cohen-Zada Department of Economcs, Ben-uron Unversty, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel Wllam Sander Department of Economcs, DePaul
1. Measuring association using correlation and regression
 How to measure assocaton I: Correlaton. 1. Measurng assocaton usng correlaton and regresson We often would lke to know how one varable, such as a mother's weght, s related to another varable, such as a
How to measure assocaton I: Correlaton. 1. Measurng assocaton usng correlaton and regresson We often would lke to know how one varable, such as a mother's weght, s related to another varable, such as a
Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Statistical Association, August 5-9, 2001
 Proceedngs of the Annual Meetng of the Amercan Statstcal Assocaton, August 5-9, 2001 LIST-ASSISTED SAMPLING: THE EFFECT OF TELEPHONE SYSTEM CHANGES ON DESIGN 1 Clyde Tucker, Bureau of Labor Statstcs James
Proceedngs of the Annual Meetng of the Amercan Statstcal Assocaton, August 5-9, 2001 LIST-ASSISTED SAMPLING: THE EFFECT OF TELEPHONE SYSTEM CHANGES ON DESIGN 1 Clyde Tucker, Bureau of Labor Statstcs James
Module 2 LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Lesson 3 Lossless Compresson: Huffman Codng Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:. Defne and measure source entropy..
Module LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Lesson 3 Lossless Compresson: Huffman Codng Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:. Defne and measure source entropy..
SIMPLE LINEAR CORRELATION
 SIMPLE LINEAR CORRELATION Smple lnear correlaton s a measure of the degree to whch two varables vary together, or a measure of the ntensty of the assocaton between two varables. Correlaton often s abused.
SIMPLE LINEAR CORRELATION Smple lnear correlaton s a measure of the degree to whch two varables vary together, or a measure of the ntensty of the assocaton between two varables. Correlaton often s abused.
Hot and easy in Florida: The case of economics professors
 Research n Hgher Educaton Journal Abstract Hot and easy n Florda: The case of economcs professors Olver Schnusenberg The Unversty of North Florda Cheryl Froehlch The Unversty of North Florda We nvestgate
Research n Hgher Educaton Journal Abstract Hot and easy n Florda: The case of economcs professors Olver Schnusenberg The Unversty of North Florda Cheryl Froehlch The Unversty of North Florda We nvestgate
The Application of Fractional Brownian Motion in Option Pricing
 Vol. 0, No. (05), pp. 73-8 http://dx.do.org/0.457/jmue.05.0..6 The Applcaton of Fractonal Brownan Moton n Opton Prcng Qng-xn Zhou School of Basc Scence,arbn Unversty of Commerce,arbn zhouqngxn98@6.com
Vol. 0, No. (05), pp. 73-8 http://dx.do.org/0.457/jmue.05.0..6 The Applcaton of Fractonal Brownan Moton n Opton Prcng Qng-xn Zhou School of Basc Scence,arbn Unversty of Commerce,arbn zhouqngxn98@6.com
HARVARD John M. Olin Center for Law, Economics, and Business
 HARVARD John M. Oln Center for Law, Economcs, and Busness ISSN 1045-6333 ASYMMETRIC INFORMATION AND LEARNING IN THE AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE MARKET Alma Cohen Dscusson Paper No. 371 6/2002 Harvard Law School
HARVARD John M. Oln Center for Law, Economcs, and Busness ISSN 1045-6333 ASYMMETRIC INFORMATION AND LEARNING IN THE AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE MARKET Alma Cohen Dscusson Paper No. 371 6/2002 Harvard Law School
The OC Curve of Attribute Acceptance Plans
 The OC Curve of Attrbute Acceptance Plans The Operatng Characterstc (OC) curve descrbes the probablty of acceptng a lot as a functon of the lot s qualty. Fgure 1 shows a typcal OC Curve. 10 8 6 4 1 3 4
The OC Curve of Attrbute Acceptance Plans The Operatng Characterstc (OC) curve descrbes the probablty of acceptng a lot as a functon of the lot s qualty. Fgure 1 shows a typcal OC Curve. 10 8 6 4 1 3 4
CHAPTER 5 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITATIVE VARIABLES
 CHAPTER 5 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITATIVE VARIABLES In ths chapter, we wll learn how to descrbe the relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. Remember (from Chapter 2) that the terms quanttatve varable
CHAPTER 5 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITATIVE VARIABLES In ths chapter, we wll learn how to descrbe the relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. Remember (from Chapter 2) that the terms quanttatve varable
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK. Sample Stability Protocol
 CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
Estimating Total Claim Size in the Auto Insurance Industry: a Comparison between Tweedie and Zero-Adjusted Inverse Gaussian Distribution
 Estmatng otal Clam Sze n the Auto Insurance Industry: a Comparson between weede and Zero-Adjusted Inverse Gaussan Dstrbuton Autora: Adrana Bruscato Bortoluzzo, Italo De Paula Franca, Marco Antono Leonel
Estmatng otal Clam Sze n the Auto Insurance Industry: a Comparson between weede and Zero-Adjusted Inverse Gaussan Dstrbuton Autora: Adrana Bruscato Bortoluzzo, Italo De Paula Franca, Marco Antono Leonel
Evaluating the Effects of FUNDEF on Wages and Test Scores in Brazil *
 Evaluatng the Effects of FUNDEF on Wages and Test Scores n Brazl * Naérco Menezes-Flho Elane Pazello Unversty of São Paulo Abstract In ths paper we nvestgate the effects of the 1998 reform n the fundng
Evaluatng the Effects of FUNDEF on Wages and Test Scores n Brazl * Naérco Menezes-Flho Elane Pazello Unversty of São Paulo Abstract In ths paper we nvestgate the effects of the 1998 reform n the fundng
SPEE Recommended Evaluation Practice #6 Definition of Decline Curve Parameters Background:
 SPEE Recommended Evaluaton Practce #6 efnton of eclne Curve Parameters Background: The producton hstores of ol and gas wells can be analyzed to estmate reserves and future ol and gas producton rates and
SPEE Recommended Evaluaton Practce #6 efnton of eclne Curve Parameters Background: The producton hstores of ol and gas wells can be analyzed to estmate reserves and future ol and gas producton rates and
Traffic-light a stress test for life insurance provisions
 MEMORANDUM Date 006-09-7 Authors Bengt von Bahr, Göran Ronge Traffc-lght a stress test for lfe nsurance provsons Fnansnspetonen P.O. Box 6750 SE-113 85 Stocholm [Sveavägen 167] Tel +46 8 787 80 00 Fax
MEMORANDUM Date 006-09-7 Authors Bengt von Bahr, Göran Ronge Traffc-lght a stress test for lfe nsurance provsons Fnansnspetonen P.O. Box 6750 SE-113 85 Stocholm [Sveavägen 167] Tel +46 8 787 80 00 Fax
Forecasting the Direction and Strength of Stock Market Movement
 Forecastng the Drecton and Strength of Stock Market Movement Jngwe Chen Mng Chen Nan Ye cjngwe@stanford.edu mchen5@stanford.edu nanye@stanford.edu Abstract - Stock market s one of the most complcated systems
Forecastng the Drecton and Strength of Stock Market Movement Jngwe Chen Mng Chen Nan Ye cjngwe@stanford.edu mchen5@stanford.edu nanye@stanford.edu Abstract - Stock market s one of the most complcated systems
ANALYZING THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUALITY, TIME, AND COST IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
 ANALYZING THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUALITY, TIME, AND COST IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING Matthew J. Lberatore, Department of Management and Operatons, Vllanova Unversty, Vllanova, PA 19085, 610-519-4390,
ANALYZING THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUALITY, TIME, AND COST IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING Matthew J. Lberatore, Department of Management and Operatons, Vllanova Unversty, Vllanova, PA 19085, 610-519-4390,
PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) Lecture 12
 14 The Ch-squared dstrbuton PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) Lecture 1 If a normal varable X, havng mean µ and varance σ, s standardsed, the new varable Z has a mean 0 and varance 1. When ths standardsed
14 The Ch-squared dstrbuton PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) Lecture 1 If a normal varable X, havng mean µ and varance σ, s standardsed, the new varable Z has a mean 0 and varance 1. When ths standardsed
A Novel Methodology of Working Capital Management for Large. Public Constructions by Using Fuzzy S-curve Regression
 Novel Methodology of Workng Captal Management for Large Publc Constructons by Usng Fuzzy S-curve Regresson Cheng-Wu Chen, Morrs H. L. Wang and Tng-Ya Hseh Department of Cvl Engneerng, Natonal Central Unversty,
Novel Methodology of Workng Captal Management for Large Publc Constructons by Usng Fuzzy S-curve Regresson Cheng-Wu Chen, Morrs H. L. Wang and Tng-Ya Hseh Department of Cvl Engneerng, Natonal Central Unversty,
Forecasting the Demand of Emergency Supplies: Based on the CBR Theory and BP Neural Network
 700 Proceedngs of the 8th Internatonal Conference on Innovaton & Management Forecastng the Demand of Emergency Supples: Based on the CBR Theory and BP Neural Network Fu Deqang, Lu Yun, L Changbng School
700 Proceedngs of the 8th Internatonal Conference on Innovaton & Management Forecastng the Demand of Emergency Supples: Based on the CBR Theory and BP Neural Network Fu Deqang, Lu Yun, L Changbng School
STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL
 Mcroarray Center STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL Lecture 6 Some Advanced Topcs Dr. Petr Nazarov 14-01-013 petr.nazarov@crp-sante.lu Statstcal data analyss n Ecel. 6. Some advanced topcs Correcton for
Mcroarray Center STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL Lecture 6 Some Advanced Topcs Dr. Petr Nazarov 14-01-013 petr.nazarov@crp-sante.lu Statstcal data analyss n Ecel. 6. Some advanced topcs Correcton for
1.1 The University may award Higher Doctorate degrees as specified from time-to-time in UPR AS11 1.
 HIGHER DOCTORATE DEGREES SUMMARY OF PRINCIPAL CHANGES General changes None Secton 3.2 Refer to text (Amendments to verson 03.0, UPR AS02 are shown n talcs.) 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 The Unversty may award Hgher
HIGHER DOCTORATE DEGREES SUMMARY OF PRINCIPAL CHANGES General changes None Secton 3.2 Refer to text (Amendments to verson 03.0, UPR AS02 are shown n talcs.) 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 The Unversty may award Hgher
Understanding the Impact of Marketing Actions in Traditional Channels on the Internet: Evidence from a Large Scale Field Experiment
 A research and educaton ntatve at the MT Sloan School of Management Understandng the mpact of Marketng Actons n Tradtonal Channels on the nternet: Evdence from a Large Scale Feld Experment Paper 216 Erc
A research and educaton ntatve at the MT Sloan School of Management Understandng the mpact of Marketng Actons n Tradtonal Channels on the nternet: Evdence from a Large Scale Feld Experment Paper 216 Erc
Joe Pimbley, unpublished, 2005. Yield Curve Calculations
 Joe Pmbley, unpublshed, 005. Yeld Curve Calculatons Background: Everythng s dscount factors Yeld curve calculatons nclude valuaton of forward rate agreements (FRAs), swaps, nterest rate optons, and forward
Joe Pmbley, unpublshed, 005. Yeld Curve Calculatons Background: Everythng s dscount factors Yeld curve calculatons nclude valuaton of forward rate agreements (FRAs), swaps, nterest rate optons, and forward
Abstract. 260 Business Intelligence Journal July IDENTIFICATION OF DEMAND THROUGH STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION MODELING FOR IMPROVED DEMAND FORECASTING
 260 Busness Intellgence Journal July IDENTIFICATION OF DEMAND THROUGH STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION MODELING FOR IMPROVED DEMAND FORECASTING Murphy Choy Mchelle L.F. Cheong School of Informaton Systems, Sngapore
260 Busness Intellgence Journal July IDENTIFICATION OF DEMAND THROUGH STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION MODELING FOR IMPROVED DEMAND FORECASTING Murphy Choy Mchelle L.F. Cheong School of Informaton Systems, Sngapore
Multiple-Period Attribution: Residuals and Compounding
 Multple-Perod Attrbuton: Resduals and Compoundng Our revewer gave these authors full marks for dealng wth an ssue that performance measurers and vendors often regard as propretary nformaton. In 1994, Dens
Multple-Perod Attrbuton: Resduals and Compoundng Our revewer gave these authors full marks for dealng wth an ssue that performance measurers and vendors often regard as propretary nformaton. In 1994, Dens
Is There A Tradeoff between Employer-Provided Health Insurance and Wages?
 Is There A Tradeoff between Employer-Provded Health Insurance and Wages? Lye Zhu, Southern Methodst Unversty October 2005 Abstract Though most of the lterature n health nsurance and the labor market assumes
Is There A Tradeoff between Employer-Provded Health Insurance and Wages? Lye Zhu, Southern Methodst Unversty October 2005 Abstract Though most of the lterature n health nsurance and the labor market assumes
On the Optimal Control of a Cascade of Hydro-Electric Power Stations
 On the Optmal Control of a Cascade of Hydro-Electrc Power Statons M.C.M. Guedes a, A.F. Rbero a, G.V. Smrnov b and S. Vlela c a Department of Mathematcs, School of Scences, Unversty of Porto, Portugal;
On the Optmal Control of a Cascade of Hydro-Electrc Power Statons M.C.M. Guedes a, A.F. Rbero a, G.V. Smrnov b and S. Vlela c a Department of Mathematcs, School of Scences, Unversty of Porto, Portugal;
Capacity-building and training
 92 Toolkt to Combat Traffckng n Persons Tool 2.14 Capacty-buldng and tranng Overvew Ths tool provdes references to tranng programmes and materals. For more tranng materals, refer also to Tool 9.18. Capacty-buldng
92 Toolkt to Combat Traffckng n Persons Tool 2.14 Capacty-buldng and tranng Overvew Ths tool provdes references to tranng programmes and materals. For more tranng materals, refer also to Tool 9.18. Capacty-buldng
Covariate-based pricing of automobile insurance
 Insurance Markets and Companes: Analyses and Actuaral Computatons, Volume 1, Issue 2, 2010 José Antono Ordaz (Span), María del Carmen Melgar (Span) Covarate-based prcng of automoble nsurance Abstract Ths
Insurance Markets and Companes: Analyses and Actuaral Computatons, Volume 1, Issue 2, 2010 José Antono Ordaz (Span), María del Carmen Melgar (Span) Covarate-based prcng of automoble nsurance Abstract Ths
High Correlation between Net Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Willingness to Pay (Empirical Evidence from European Mobile Markets)
 Hgh Correlaton between et Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Wllngness to Pay (Emprcal Evdence from European Moble Marets Ths paper shows that the correlaton between the et Promoter Score
Hgh Correlaton between et Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Wllngness to Pay (Emprcal Evdence from European Moble Marets Ths paper shows that the correlaton between the et Promoter Score
Analysis of Demand for Broadcastingng servces
 Analyss of Subscrpton Demand for Pay-TV Manabu Shshkura * Norhro Kasuga ** Ako Tor *** Abstract In ths paper, we wll conduct an analyss from an emprcal perspectve concernng broadcastng demand behavor and
Analyss of Subscrpton Demand for Pay-TV Manabu Shshkura * Norhro Kasuga ** Ako Tor *** Abstract In ths paper, we wll conduct an analyss from an emprcal perspectve concernng broadcastng demand behavor and
Evaluating credit risk models: A critique and a new proposal
 Evaluatng credt rsk models: A crtque and a new proposal Hergen Frerchs* Gunter Löffler Unversty of Frankfurt (Man) February 14, 2001 Abstract Evaluatng the qualty of credt portfolo rsk models s an mportant
Evaluatng credt rsk models: A crtque and a new proposal Hergen Frerchs* Gunter Löffler Unversty of Frankfurt (Man) February 14, 2001 Abstract Evaluatng the qualty of credt portfolo rsk models s an mportant
14.74 Lecture 5: Health (2)
 14.74 Lecture 5: Health (2) Esther Duflo February 17, 2004 1 Possble Interventons Last tme we dscussed possble nterventons. Let s take one: provdng ron supplements to people, for example. From the data,
14.74 Lecture 5: Health (2) Esther Duflo February 17, 2004 1 Possble Interventons Last tme we dscussed possble nterventons. Let s take one: provdng ron supplements to people, for example. From the data,
Risk-based Fatigue Estimate of Deep Water Risers -- Course Project for EM388F: Fracture Mechanics, Spring 2008
 Rsk-based Fatgue Estmate of Deep Water Rsers -- Course Project for EM388F: Fracture Mechancs, Sprng 2008 Chen Sh Department of Cvl, Archtectural, and Envronmental Engneerng The Unversty of Texas at Austn
Rsk-based Fatgue Estmate of Deep Water Rsers -- Course Project for EM388F: Fracture Mechancs, Sprng 2008 Chen Sh Department of Cvl, Archtectural, and Envronmental Engneerng The Unversty of Texas at Austn
Study on Model of Risks Assessment of Standard Operation in Rural Power Network
 Study on Model of Rsks Assessment of Standard Operaton n Rural Power Network Qngj L 1, Tao Yang 2 1 Qngj L, College of Informaton and Electrcal Engneerng, Shenyang Agrculture Unversty, Shenyang 110866,
Study on Model of Rsks Assessment of Standard Operaton n Rural Power Network Qngj L 1, Tao Yang 2 1 Qngj L, College of Informaton and Electrcal Engneerng, Shenyang Agrculture Unversty, Shenyang 110866,
Assessing the Fairness of a Firm s Allocation of Shares in Initial Public Offerings: Adapting a Measure from Biostatistics
 Assessng the Farness of a Frm s Allocaton of Shares n Intal Publc Offerngs: Adaptng a Measure from Bostatstcs by Efstatha Bura and Joseph L. Gastwrth Department of Statstcs The George Washngton Unversty
Assessng the Farness of a Frm s Allocaton of Shares n Intal Publc Offerngs: Adaptng a Measure from Bostatstcs by Efstatha Bura and Joseph L. Gastwrth Department of Statstcs The George Washngton Unversty
Traditional versus Online Courses, Efforts, and Learning Performance
 Tradtonal versus Onlne Courses, Efforts, and Learnng Performance Kuang-Cheng Tseng, Department of Internatonal Trade, Chung-Yuan Chrstan Unversty, Tawan Shan-Yng Chu, Department of Internatonal Trade,
Tradtonal versus Onlne Courses, Efforts, and Learnng Performance Kuang-Cheng Tseng, Department of Internatonal Trade, Chung-Yuan Chrstan Unversty, Tawan Shan-Yng Chu, Department of Internatonal Trade,
Online Appendix Supplemental Material for Market Microstructure Invariance: Empirical Hypotheses
 Onlne Appendx Supplemental Materal for Market Mcrostructure Invarance: Emprcal Hypotheses Albert S. Kyle Unversty of Maryland akyle@rhsmth.umd.edu Anna A. Obzhaeva New Economc School aobzhaeva@nes.ru Table
Onlne Appendx Supplemental Materal for Market Mcrostructure Invarance: Emprcal Hypotheses Albert S. Kyle Unversty of Maryland akyle@rhsmth.umd.edu Anna A. Obzhaeva New Economc School aobzhaeva@nes.ru Table
The Use of Analytics for Claim Fraud Detection Roosevelt C. Mosley, Jr., FCAS, MAAA Nick Kucera Pinnacle Actuarial Resources Inc.
 Paper 1837-2014 The Use of Analytcs for Clam Fraud Detecton Roosevelt C. Mosley, Jr., FCAS, MAAA Nck Kucera Pnnacle Actuaral Resources Inc., Bloomngton, IL ABSTRACT As t has been wdely reported n the nsurance
Paper 1837-2014 The Use of Analytcs for Clam Fraud Detecton Roosevelt C. Mosley, Jr., FCAS, MAAA Nck Kucera Pnnacle Actuaral Resources Inc., Bloomngton, IL ABSTRACT As t has been wdely reported n the nsurance
ESTIMATING THE MARKET VALUE OF FRANKING CREDITS: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM AUSTRALIA
 ESTIMATING THE MARKET VALUE OF FRANKING CREDITS: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM AUSTRALIA Duc Vo Beauden Gellard Stefan Mero Economc Regulaton Authorty 469 Wellngton Street, Perth, WA 6000, Australa Phone: (08)
ESTIMATING THE MARKET VALUE OF FRANKING CREDITS: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM AUSTRALIA Duc Vo Beauden Gellard Stefan Mero Economc Regulaton Authorty 469 Wellngton Street, Perth, WA 6000, Australa Phone: (08)
STAMP DUTY ON SHARES AND ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES
 STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond Mke Hawkns Alexander Klemm THE INSTITUTE FOR FISCAL STUIES WP04/11 STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond (IFS and Unversty
STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond Mke Hawkns Alexander Klemm THE INSTITUTE FOR FISCAL STUIES WP04/11 STAMP UTY ON SHARES AN ITS EFFECT ON SHARE PRICES Steve Bond (IFS and Unversty
Overall Injury Risk to Different Drivers: Combining Exposure, Frequency, and Severity Models
 Overall Injury Rsk to Dfferent Drvers: Combnng Exposure, Frequency, and Severty Models Young-Jun Kweon Graduate Student Reseacher The Unversty of Texas at Austn fre264@mal.utexas.edu and Kara M. Kockelman
Overall Injury Rsk to Dfferent Drvers: Combnng Exposure, Frequency, and Severty Models Young-Jun Kweon Graduate Student Reseacher The Unversty of Texas at Austn fre264@mal.utexas.edu and Kara M. Kockelman
Start me up: The Effectiveness of a Self-Employment Programme for Needy Unemployed People in Germany*
 Start me up: The Effectveness of a Self-Employment Programme for Needy Unemployed People n Germany* Joachm Wolff Anton Nvorozhkn Date: 22/10/2008 Abstract In recent years actvaton of means-tested unemployment
Start me up: The Effectveness of a Self-Employment Programme for Needy Unemployed People n Germany* Joachm Wolff Anton Nvorozhkn Date: 22/10/2008 Abstract In recent years actvaton of means-tested unemployment
ECONOMICS OF PLANT ENERGY SAVINGS PROJECTS IN A CHANGING MARKET Douglas C White Emerson Process Management
 ECONOMICS OF PLANT ENERGY SAVINGS PROJECTS IN A CHANGING MARKET Douglas C Whte Emerson Process Management Abstract Energy prces have exhbted sgnfcant volatlty n recent years. For example, natural gas prces
ECONOMICS OF PLANT ENERGY SAVINGS PROJECTS IN A CHANGING MARKET Douglas C Whte Emerson Process Management Abstract Energy prces have exhbted sgnfcant volatlty n recent years. For example, natural gas prces
Estimating Total Claim Size in the Auto Insurance Industry: a Comparison between Tweedie and Zero-Adjusted Inverse Gaussian Distribution
 Avalable onlne at http:// BAR, Curtba, v. 8, n. 1, art. 3, pp. 37-47, Jan./Mar. 2011 Estmatng Total Clam Sze n the Auto Insurance Industry: a Comparson between Tweede and Zero-Adjusted Inverse Gaussan
Avalable onlne at http:// BAR, Curtba, v. 8, n. 1, art. 3, pp. 37-47, Jan./Mar. 2011 Estmatng Total Clam Sze n the Auto Insurance Industry: a Comparson between Tweede and Zero-Adjusted Inverse Gaussan
FREQUENCY OF OCCURRENCE OF CERTAIN CHEMICAL CLASSES OF GSR FROM VARIOUS AMMUNITION TYPES
 FREQUENCY OF OCCURRENCE OF CERTAIN CHEMICAL CLASSES OF GSR FROM VARIOUS AMMUNITION TYPES Zuzanna BRO EK-MUCHA, Grzegorz ZADORA, 2 Insttute of Forensc Research, Cracow, Poland 2 Faculty of Chemstry, Jagellonan
FREQUENCY OF OCCURRENCE OF CERTAIN CHEMICAL CLASSES OF GSR FROM VARIOUS AMMUNITION TYPES Zuzanna BRO EK-MUCHA, Grzegorz ZADORA, 2 Insttute of Forensc Research, Cracow, Poland 2 Faculty of Chemstry, Jagellonan
Student Performance in Online Quizzes as a Function of Time in Undergraduate Financial Management Courses
 Student Performance n Onlne Quzzes as a Functon of Tme n Undergraduate Fnancal Management Courses Olver Schnusenberg The Unversty of North Florda ABSTRACT An nterestng research queston n lght of recent
Student Performance n Onlne Quzzes as a Functon of Tme n Undergraduate Fnancal Management Courses Olver Schnusenberg The Unversty of North Florda ABSTRACT An nterestng research queston n lght of recent
THE DISTRIBUTION OF LOAN PORTFOLIO VALUE * Oldrich Alfons Vasicek
 HE DISRIBUION OF LOAN PORFOLIO VALUE * Oldrch Alfons Vascek he amount of captal necessary to support a portfolo of debt securtes depends on the probablty dstrbuton of the portfolo loss. Consder a portfolo
HE DISRIBUION OF LOAN PORFOLIO VALUE * Oldrch Alfons Vascek he amount of captal necessary to support a portfolo of debt securtes depends on the probablty dstrbuton of the portfolo loss. Consder a portfolo
Institute of Informatics, Faculty of Business and Management, Brno University of Technology,Czech Republic
 Lagrange Multplers as Quanttatve Indcators n Economcs Ivan Mezník Insttute of Informatcs, Faculty of Busness and Management, Brno Unversty of TechnologCzech Republc Abstract The quanttatve role of Lagrange
Lagrange Multplers as Quanttatve Indcators n Economcs Ivan Mezník Insttute of Informatcs, Faculty of Busness and Management, Brno Unversty of TechnologCzech Republc Abstract The quanttatve role of Lagrange
) of the Cell class is created containing information about events associated with the cell. Events are added to the Cell instance
 Calbraton Method Instances of the Cell class (one nstance for each FMS cell) contan ADC raw data and methods assocated wth each partcular FMS cell. The calbraton method ncludes event selecton (Class Cell
Calbraton Method Instances of the Cell class (one nstance for each FMS cell) contan ADC raw data and methods assocated wth each partcular FMS cell. The calbraton method ncludes event selecton (Class Cell
Bank liability structure, FDIC loss, and time to failure: A quantile regression approach
 Bank lablty structure, FDIC loss, and tme to falure: A quantle regresson approach Klaus Schaeck* October 2006 * Correspondng address: Unversty of Southampton, Hghfeld, Southampton SO17 1BJ, Unted Kngdom;
Bank lablty structure, FDIC loss, and tme to falure: A quantle regresson approach Klaus Schaeck* October 2006 * Correspondng address: Unversty of Southampton, Hghfeld, Southampton SO17 1BJ, Unted Kngdom;
Transition Matrix Models of Consumer Credit Ratings
 Transton Matrx Models of Consumer Credt Ratngs Abstract Although the corporate credt rsk lterature has many studes modellng the change n the credt rsk of corporate bonds over tme, there s far less analyss
Transton Matrx Models of Consumer Credt Ratngs Abstract Although the corporate credt rsk lterature has many studes modellng the change n the credt rsk of corporate bonds over tme, there s far less analyss
THE METHOD OF LEAST SQUARES THE METHOD OF LEAST SQUARES
 The goal: to measure (determne) an unknown quantty x (the value of a RV X) Realsaton: n results: y 1, y 2,..., y j,..., y n, (the measured values of Y 1, Y 2,..., Y j,..., Y n ) every result s encumbered
The goal: to measure (determne) an unknown quantty x (the value of a RV X) Realsaton: n results: y 1, y 2,..., y j,..., y n, (the measured values of Y 1, Y 2,..., Y j,..., Y n ) every result s encumbered
Heterogeneous Paths Through College: Detailed Patterns and Relationships with Graduation and Earnings
 Heterogeneous Paths Through College: Detaled Patterns and Relatonshps wth Graduaton and Earnngs Rodney J. Andrews The Unversty of Texas at Dallas and the Texas Schools Project Jng L The Unversty of Tulsa
Heterogeneous Paths Through College: Detaled Patterns and Relatonshps wth Graduaton and Earnngs Rodney J. Andrews The Unversty of Texas at Dallas and the Texas Schools Project Jng L The Unversty of Tulsa
APPLICATION OF PROBE DATA COLLECTED VIA INFRARED BEACONS TO TRAFFIC MANEGEMENT
 APPLICATION OF PROBE DATA COLLECTED VIA INFRARED BEACONS TO TRAFFIC MANEGEMENT Toshhko Oda (1), Kochro Iwaoka (2) (1), (2) Infrastructure Systems Busness Unt, Panasonc System Networks Co., Ltd. Saedo-cho
APPLICATION OF PROBE DATA COLLECTED VIA INFRARED BEACONS TO TRAFFIC MANEGEMENT Toshhko Oda (1), Kochro Iwaoka (2) (1), (2) Infrastructure Systems Busness Unt, Panasonc System Networks Co., Ltd. Saedo-cho
1 De nitions and Censoring
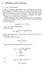 De ntons and Censorng. Survval Analyss We begn by consderng smple analyses but we wll lead up to and take a look at regresson on explanatory factors., as n lnear regresson part A. The mportant d erence
De ntons and Censorng. Survval Analyss We begn by consderng smple analyses but we wll lead up to and take a look at regresson on explanatory factors., as n lnear regresson part A. The mportant d erence
ADVERSE SELECTION IN INSURANCE MARKETS: POLICYHOLDER EVIDENCE FROM THE U.K. ANNUITY MARKET *
 ADVERSE SELECTION IN INSURANCE MARKETS: POLICYHOLDER EVIDENCE FROM THE U.K. ANNUITY MARKET * Amy Fnkelsten Harvard Unversty and NBER James Poterba MIT and NBER * We are grateful to Jeffrey Brown, Perre-Andre
ADVERSE SELECTION IN INSURANCE MARKETS: POLICYHOLDER EVIDENCE FROM THE U.K. ANNUITY MARKET * Amy Fnkelsten Harvard Unversty and NBER James Poterba MIT and NBER * We are grateful to Jeffrey Brown, Perre-Andre
Prediction of Disability Frequencies in Life Insurance
 Predcton of Dsablty Frequences n Lfe Insurance Bernhard Köng Fran Weber Maro V. Wüthrch October 28, 2011 Abstract For the predcton of dsablty frequences, not only the observed, but also the ncurred but
Predcton of Dsablty Frequences n Lfe Insurance Bernhard Köng Fran Weber Maro V. Wüthrch October 28, 2011 Abstract For the predcton of dsablty frequences, not only the observed, but also the ncurred but
7 ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA)
 7 ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA) Chapter 7 Analyss of Varance (Anova) Objectves After studyng ths chapter you should apprecate the need for analysng data from more than two samples; understand the underlyng
7 ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA) Chapter 7 Analyss of Varance (Anova) Objectves After studyng ths chapter you should apprecate the need for analysng data from more than two samples; understand the underlyng
A DYNAMIC CRASHING METHOD FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT USING SIMULATION-BASED OPTIMIZATION. Michael E. Kuhl Radhamés A. Tolentino-Peña
 Proceedngs of the 2008 Wnter Smulaton Conference S. J. Mason, R. R. Hll, L. Mönch, O. Rose, T. Jefferson, J. W. Fowler eds. A DYNAMIC CRASHING METHOD FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT USING SIMULATION-BASED OPTIMIZATION
Proceedngs of the 2008 Wnter Smulaton Conference S. J. Mason, R. R. Hll, L. Mönch, O. Rose, T. Jefferson, J. W. Fowler eds. A DYNAMIC CRASHING METHOD FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT USING SIMULATION-BASED OPTIMIZATION
Survival analysis methods in Insurance Applications in car insurance contracts
 Survval analyss methods n Insurance Applcatons n car nsurance contracts Abder OULIDI 1 Jean-Mare MARION 2 Hervé GANACHAUD 3 Abstract In ths wor, we are nterested n survval models and ther applcatons on
Survval analyss methods n Insurance Applcatons n car nsurance contracts Abder OULIDI 1 Jean-Mare MARION 2 Hervé GANACHAUD 3 Abstract In ths wor, we are nterested n survval models and ther applcatons on
Statistical algorithms in Review Manager 5
 Statstcal algorthms n Reve Manager 5 Jonathan J Deeks and Julan PT Hggns on behalf of the Statstcal Methods Group of The Cochrane Collaboraton August 00 Data structure Consder a meta-analyss of k studes
Statstcal algorthms n Reve Manager 5 Jonathan J Deeks and Julan PT Hggns on behalf of the Statstcal Methods Group of The Cochrane Collaboraton August 00 Data structure Consder a meta-analyss of k studes
Recurrence. 1 Definitions and main statements
 Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
A statistical approach to determine Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC) Rates of underground gas pipelines.
 A statstcal approach to determne Mcrobologcally Influenced Corroson (MIC) Rates of underground gas ppelnes. by Lech A. Grzelak A thess submtted to the Delft Unversty of Technology n conformty wth the requrements
A statstcal approach to determne Mcrobologcally Influenced Corroson (MIC) Rates of underground gas ppelnes. by Lech A. Grzelak A thess submtted to the Delft Unversty of Technology n conformty wth the requrements
PRACTICE 1: MUTUAL FUNDS EVALUATION USING MATLAB.
 PRACTICE 1: MUTUAL FUNDS EVALUATION USING MATLAB. INDEX 1. Load data usng the Edtor wndow and m-fle 2. Learnng to save results from the Edtor wndow. 3. Computng the Sharpe Rato 4. Obtanng the Treynor Rato
PRACTICE 1: MUTUAL FUNDS EVALUATION USING MATLAB. INDEX 1. Load data usng the Edtor wndow and m-fle 2. Learnng to save results from the Edtor wndow. 3. Computng the Sharpe Rato 4. Obtanng the Treynor Rato
Modeling Motorcycle Insurance Rate Reduction due to Mandatory Safety Courses
 Modelng Motorcycle Insurance Rate Reducton due to Mandatory Safety Courses Shujuan Huang 1 Vadveloo Jeyaraj 1 Valdez mlano 1 Garry D. Lapdus 2 1 Mathematc Department Unversty of Connectcut Storrs CT 06269
Modelng Motorcycle Insurance Rate Reducton due to Mandatory Safety Courses Shujuan Huang 1 Vadveloo Jeyaraj 1 Valdez mlano 1 Garry D. Lapdus 2 1 Mathematc Department Unversty of Connectcut Storrs CT 06269
Using Series to Analyze Financial Situations: Present Value
 2.8 Usng Seres to Analyze Fnancal Stuatons: Present Value In the prevous secton, you learned how to calculate the amount, or future value, of an ordnary smple annuty. The amount s the sum of the accumulated
2.8 Usng Seres to Analyze Fnancal Stuatons: Present Value In the prevous secton, you learned how to calculate the amount, or future value, of an ordnary smple annuty. The amount s the sum of the accumulated
Calculating the high frequency transmission line parameters of power cables
 < ' Calculatng the hgh frequency transmsson lne parameters of power cables Authors: Dr. John Dcknson, Laboratory Servces Manager, N 0 RW E B Communcatons Mr. Peter J. Ncholson, Project Assgnment Manager,
< ' Calculatng the hgh frequency transmsson lne parameters of power cables Authors: Dr. John Dcknson, Laboratory Servces Manager, N 0 RW E B Communcatons Mr. Peter J. Ncholson, Project Assgnment Manager,
How To Find The Dsablty Frequency Of A Clam
 1 Predcton of Dsablty Frequences n Lfe Insurance Bernhard Köng 1, Fran Weber 1, Maro V. Wüthrch 2 Abstract: For the predcton of dsablty frequences, not only the observed, but also the ncurred but not yet
1 Predcton of Dsablty Frequences n Lfe Insurance Bernhard Köng 1, Fran Weber 1, Maro V. Wüthrch 2 Abstract: For the predcton of dsablty frequences, not only the observed, but also the ncurred but not yet
How To Understand The Results Of The German Meris Cloud And Water Vapour Product
 Ttel: Project: Doc. No.: MERIS level 3 cloud and water vapour products MAPP MAPP-ATBD-ClWVL3 Issue: 1 Revson: 0 Date: 9.12.1998 Functon Name Organsaton Sgnature Date Author: Bennartz FUB Preusker FUB Schüller
Ttel: Project: Doc. No.: MERIS level 3 cloud and water vapour products MAPP MAPP-ATBD-ClWVL3 Issue: 1 Revson: 0 Date: 9.12.1998 Functon Name Organsaton Sgnature Date Author: Bennartz FUB Preusker FUB Schüller
Credit Limit Optimization (CLO) for Credit Cards
 Credt Lmt Optmzaton (CLO) for Credt Cards Vay S. Desa CSCC IX, Ednburgh September 8, 2005 Copyrght 2003, SAS Insttute Inc. All rghts reserved. SAS Propretary Agenda Background Tradtonal approaches to credt
Credt Lmt Optmzaton (CLO) for Credt Cards Vay S. Desa CSCC IX, Ednburgh September 8, 2005 Copyrght 2003, SAS Insttute Inc. All rghts reserved. SAS Propretary Agenda Background Tradtonal approaches to credt
The demand for private health care in the UK
 Journal of Health Economcs 19 2000 855 876 www.elsever.nlrlocatereconbase The demand for prvate health care n the UK Carol Propper ) Department of Economcs, CASE and CEPR, UnÕersty of Brstol, Brstol BS8
Journal of Health Economcs 19 2000 855 876 www.elsever.nlrlocatereconbase The demand for prvate health care n the UK Carol Propper ) Department of Economcs, CASE and CEPR, UnÕersty of Brstol, Brstol BS8
A Revised Economic Analysis of Restrictions on the Use of Cell Phones While Driving
 Rsk Analyss, Vol. 23, No. 1, 2003 A Revsed Economc Analyss of Restrctons on the Use of Cell Phones Whle Drvng Joshua T. Cohen 1 and John D. Graham 1 Evdence that cell phone use whle drvng ncreases the
Rsk Analyss, Vol. 23, No. 1, 2003 A Revsed Economc Analyss of Restrctons on the Use of Cell Phones Whle Drvng Joshua T. Cohen 1 and John D. Graham 1 Evdence that cell phone use whle drvng ncreases the
Survive Then Thrive: Determinants of Success in the Economics Ph.D. Program. Wayne A. Grove Le Moyne College, Economics Department
 Survve Then Thrve: Determnants of Success n the Economcs Ph.D. Program Wayne A. Grove Le Moyne College, Economcs Department Donald H. Dutkowsky Syracuse Unversty, Economcs Department Andrew Grodner East
Survve Then Thrve: Determnants of Success n the Economcs Ph.D. Program Wayne A. Grove Le Moyne College, Economcs Department Donald H. Dutkowsky Syracuse Unversty, Economcs Department Andrew Grodner East
Single and multiple stage classifiers implementing logistic discrimination
 Sngle and multple stage classfers mplementng logstc dscrmnaton Hélo Radke Bttencourt 1 Dens Alter de Olvera Moraes 2 Vctor Haertel 2 1 Pontfíca Unversdade Católca do Ro Grande do Sul - PUCRS Av. Ipranga,
Sngle and multple stage classfers mplementng logstc dscrmnaton Hélo Radke Bttencourt 1 Dens Alter de Olvera Moraes 2 Vctor Haertel 2 1 Pontfíca Unversdade Católca do Ro Grande do Sul - PUCRS Av. Ipranga,
Feature selection for intrusion detection. Slobodan Petrović NISlab, Gjøvik University College
 Feature selecton for ntruson detecton Slobodan Petrovć NISlab, Gjøvk Unversty College Contents The feature selecton problem Intruson detecton Traffc features relevant for IDS The CFS measure The mrmr measure
Feature selecton for ntruson detecton Slobodan Petrovć NISlab, Gjøvk Unversty College Contents The feature selecton problem Intruson detecton Traffc features relevant for IDS The CFS measure The mrmr measure
