case Statement //8-wide, 4:1 multiplexer module case1 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, d_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out);
|
|
|
- Andrea Warner
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nesting if past two levels is error prone and possibly inefficient. case excels when many tests are performed on the same expression. case works well for muxes, decoders, and next state logic. SVerilog case has implied break statement unlike C. case items are not-necessarily non-overlapping. case (case_expression) case_item1 : case_item_statement1; case_item2 : begin case_item_statement2a; case_item_statement2b; case_item_statement2c; end case_item3 : case_item_statement3; default : case_item_statement5;
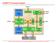
2 U42 U35 U34 //8-wide, 4:1 multiplexer module case1 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, d_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out); U23 U25 U27 U22 U24 always_comb case (sel) 2 b00 : d_out = a_in; 2 b01 : d_out = b_in; 2 b10 : d_out = c_in; 2 b11 : d_out = d_in; U41 U39 U38 U29 U31 U33 U40 U37 U26 U28 U30 U32 U36
3 Is the simulation correct? What do we do with the X? //8-wide, 4:1 multiplexer module case1 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, d_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out); always_comb case (sel) 2 b00 : d_out = a_in; 2 b01 : d_out = b_in; 2 b10 : d_out = c_in; 2 b11 : d_out = d_in; /case1/a_in 10 /case1/b_in 20 /case1/c_in 30 /case1/d_in 40 /case1/sel X /case1/d_out
4 We can use a default to propagate the X. What does this do for us? module case1 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, d_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out); always_comb case (sel) 2 b00 : d_out = a_in; 2 b01 : d_out = b_in; 2 b10 : d_out = c_in; 2 b11 : d_out = d_in; default : d_out = 8 bx; /case1/a_in 10 /case1/b_in 20 /case1/c_in 30 /case1/d_in 40 /case1/sel X /case1/d_out xx
5 - Incomplete case U17...g[6] //incomplete case, 8-wide, 3:1 mux module case2 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out); U18 U19 U20...g[5]...g[4]...g[3] always_comb case (sel) 2 b00 : d_out = a_in; 2 b01 : d_out = b_in; 2 b10 : d_out = c_in; U27 U25 U26 U24 U21 U22 U23 U15...g[2]...g[1]...g[0]...g[7] U16 Inferred memory devices in process in routine case2 line 6 in file case2.sv. =========================================================================== Register Name Type Width Bus MB AR AS SR SS ST =========================================================================== d_out_reg Latch 8 Y N N N =========================================================================== Warning: Netlist for always_comb block contains a latch. (ELAB-974) Presto compilation completed successfully.
6 a_in[6] //incomplete case statement //with default case_item module case2 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out); b_in[5] c_in[5] a_in[4] b_in[4] c_in[4] b_in[6] c_in[6] sel[1] sel[0] a_in[5] U11 U12 U13 U14 d_out[7:0] a_in[3] always_comb case (sel) 2 b00 : d_out = a_in; 2 b01 : d_out = b_in; 2 b10 : d_out = c_in; default : d_out = 8 bx; sel[1:0] c_in[7:0] sel[1:0] c_in[7:0] a_in[7:0] a_in[7:0] b_in[7:0] b_in[7:0] U18 b_in[3] c_in[3] a_in[2] b_in[2] c_in[2] a_in[1] b_in[1] c_in[1] n3 a_in[0] b_in[0] c_in[0] a_in[7] b_in[7] c_in[7] U15 U16 U17 U10 d_out[7:0] Does RTL and gate simulation differ when sel = 2 b11? What does synthesis do with the 8 bx?
7 - unique and priority to the Rescue SystemVerilog introduced two case and if statement modifiers priority unique Both give information to synthesis to aid optimization. Both are assertions (simulation error reporting mechanisms) Both imply that there is a case item for all the possible legal values that case expression might assume.
8 - unique and priority Unique Case Unique is an assertion which implies: All possible values of case expression are in the case items At simulation run time, a match must be found in case items At run time, only one match will be found in case items Unique guides synthesis It indicates that no priority logic is necessary This produces parallel decoding which may be smaller/faster Unique usage Use when each case item is unique and only one match should occur. Using a default case item removes the testing for non-existent matches, but the uniqueness test remains.
9 - unique and priority Priority Case Priority is an assertion which implies: All possible values for case expression are in case items Priority guides synthesis It indicates that all other testable conditions are don t cares and may be used to simplify logic This produces logic which is possibly smaller/faster Priority usage Use to explicitly say that priority is important even though the Verilog case statement is a priority statement. Using a default case item will cause priority requirement to be dropped since all cases are available to be matched. Use of a default also indicates that more than one match in case item is OK. Priority is a bad name. Case is already a priority structure.
10 a_in[6] b_in[6] c_in[6] U11 sel[1] //incomplete case statement //with systemverilog priority modifier module case2 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out); b_in[5] c_in[5] a_in[4] b_in[4] c_in[4] a_in[3] sel[0] a_in[5] U12 U13 U14 d_out[7:0] b_in[3] always_comb priority case (sel) 2 b00 : d_out = a_in; 2 b01 : d_out = b_in; 2 b10 : d_out = c_in; sel[1:0] c_in[7:0] sel[1:0] c_in[7:0] a_in[7:0] a_in[7:0] b_in[7:0] b_in[7:0] U18 c_in[3] a_in[2] b_in[2] c_in[2] a_in[1] b_in[1] c_in[1] n3 a_in[0] b_in[0] c_in[0] a_in[7] b_in[7] c_in[7] U15 U16 U17 U10 d_out[7:0] Synthesis reminds us of the implicit claims made by priority: Warning: case2.sv:7: Case statement marked priority does not cover all possible conditions. (VER-504)
11 System Verilog priority Modifier OK, so now what happens now when sel is 2 b11? RTL Simulator issues a run-time warning. Go back, fix the RTL error that caused the disallowed case to occur. After fixing, the RTL and gate simulation will match.
12 //incomplete case priority modifier module case2 ( input [7:0] a_in, b_in, c_in, input [1:0] sel, output logic [7:0] d_out); always_comb priority case (sel) 2 b00 : d_out = a_in; 2 b01 : d_out = b_in; 2 b10 : d_out = c_in; Simulator issues warning at sel==2 11, and with sel==2 1x ** Warning: (vsim-8315) case2.sv(7): No condition is true in the unique/priority if/case statement. ** Warning: (vsim-8315) case2.sv(7): No condition is true in the unique/priority if/case statement.
13 casez Statement casez is a special version of the case expression Allows don t care s in case expression or case item casez uses? or Z as don t care instead of as a logic value Recommendation: use? as don t care, not Z. For example: case item 2b1? can match the case expressions: 2b10, 2b11, 2b1x, or 2b1z casez has overlapping case items. If more than one case item matches a case expression, the first matching case item has priority. Use caution when using this statement
14 casez Statement This is a interrupt priority encoder. Simultaneous interrupt requests may be asserted, but returns only the highest priority request. module priority_encoder_casez ( input [7:0] irq, //interrupt requests output logic [3:0] highest_pri); //encoded highest pritority interrupt always_comb begin priority casez (irq) 8 b1??????? : highest_pri = 4 h8; //interrupt 8 8 b?1?????? : highest_pri = 4 h7; //interrupt 7 8 b??1????? : highest_pri = 4 h6; //interrupt 6 8 b???1???? : highest_pri = 4 h5; //interrupt 5 8 b????1??? : highest_pri = 4 h4; //interrupt 4 8 b?????1?? : highest_pri = 4 h3; //interrupt 3 8 b??????1? : highest_pri = 4 h2; //interrupt 2 8 b???????1 : highest_pri = 4 h1; //interrupt 1 default : highest_pri = 4 h0; //no interrupts end
15 casex Statement One more case expression exists: casex. Can be useful for testbenches. Current recommendations are to not use it in synthesizible code.
SystemVerilog's priority & unique - A Solution to. "full_case" & "parallel_case" Evil Twins!
 Verilog's "full_case" & "parallel_case" Evil Twins! Clifford E. Cummings Sunburst Design, Inc. ABSTRACT At Boston SNUG 1999, I introduced the evil twins of Verilog synthesis, "full_case" and "parallel_case.[2]"
Verilog's "full_case" & "parallel_case" Evil Twins! Clifford E. Cummings Sunburst Design, Inc. ABSTRACT At Boston SNUG 1999, I introduced the evil twins of Verilog synthesis, "full_case" and "parallel_case.[2]"
Multiplexers Two Types + Verilog
 Multiplexers Two Types + Verilog ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and ystems Laboratory Lab 7 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To become familiar with continuous ments and procedural
Multiplexers Two Types + Verilog ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and ystems Laboratory Lab 7 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To become familiar with continuous ments and procedural
Chapter 2 Ensuring RTL Intent
 Chapter 2 Ensuring RTL Intent A user starts the design of his block, by describing the functionality of the block in the form of RTL. The RTL code is then synthesized to realize the gate level connectivity
Chapter 2 Ensuring RTL Intent A user starts the design of his block, by describing the functionality of the block in the form of RTL. The RTL code is then synthesized to realize the gate level connectivity
ECE 451 Verilog Exercises. Sept 14, 2007. James Barnes ([email protected])
 ECE 451 Verilog Exercises Sept 14, 2007 James Barnes ([email protected]) Organization These slides give a series of self-paced exercises. Read the specification of each exercise and write your
ECE 451 Verilog Exercises Sept 14, 2007 James Barnes ([email protected]) Organization These slides give a series of self-paced exercises. Read the specification of each exercise and write your
More Verilog. 8-bit Register with Synchronous Reset. Shift Register Example. N-bit Register with Asynchronous Reset.
 More Verilog 8-bit Register with Synchronous Reset module reg8 (reset, CLK, D, Q); input reset; input [7:0] D; output [7:0] Q; reg [7:0] Q; if (reset) Q = 0; else Q = D; module // reg8 Verilog - 1 Verilog
More Verilog 8-bit Register with Synchronous Reset module reg8 (reset, CLK, D, Q); input reset; input [7:0] D; output [7:0] Q; reg [7:0] Q; if (reset) Q = 0; else Q = D; module // reg8 Verilog - 1 Verilog
Synthesizable Finite State Machine Design Techniques Using the New SystemVerilog 3.0 Enhancements
 Clifford E. Cummings SNUG-2003 San Jose, CA Voted Best Paper 2 nd Place Sunburst Design, Inc. ABSTRACT This paper details RTL coding and synthesis techniques of Finite State Machine (FSM) design using
Clifford E. Cummings SNUG-2003 San Jose, CA Voted Best Paper 2 nd Place Sunburst Design, Inc. ABSTRACT This paper details RTL coding and synthesis techniques of Finite State Machine (FSM) design using
Memory Elements. Combinational logic cannot remember
 Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
SVA4T: SystemVerilog Assertions - Techniques, Tips, Tricks, and Traps
 SVA4T: SystemVerilog Assertions - Wolfgang Ecker, Volkan Esen, Thomas Kruse, Thomas Steininger Infineon Technologies Peter Jensen Syosil Consulting Abstract ABV (Assertion Based Verification) is a very
SVA4T: SystemVerilog Assertions - Wolfgang Ecker, Volkan Esen, Thomas Kruse, Thomas Steininger Infineon Technologies Peter Jensen Syosil Consulting Abstract ABV (Assertion Based Verification) is a very
Digital Design Verification
 Digital Design Verification Course Instructor: Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Dept of Computer Sc. and Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Even Semester Course No: CS 676 1 Verification??? What is meant
Digital Design Verification Course Instructor: Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Dept of Computer Sc. and Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Even Semester Course No: CS 676 1 Verification??? What is meant
AES1. Ultra-Compact Advanced Encryption Standard Core. General Description. Base Core Features. Symbol. Applications
 General Description The AES core implements Rijndael encoding and decoding in compliance with the NIST Advanced Encryption Standard. Basic core is very small (start at 800 Actel tiles). Enhanced versions
General Description The AES core implements Rijndael encoding and decoding in compliance with the NIST Advanced Encryption Standard. Basic core is very small (start at 800 Actel tiles). Enhanced versions
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS
 VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745. Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation
 Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla ([email protected]) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla ([email protected]) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z <= A; else Z <= B; end if; end process;
 if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z
if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z
Life Cycle of a Memory Request. Ring Example: 2 requests for lock 17
 Life Cycle of a Memory Request (1) Use AQR or AQW to place address in AQ (2) If A[31]==0, check for hit in DCache Ring (3) Read Hit: place cache word in RQ; Write Hit: replace cache word with WQ RDDest/RDreturn
Life Cycle of a Memory Request (1) Use AQR or AQW to place address in AQ (2) If A[31]==0, check for hit in DCache Ring (3) Read Hit: place cache word in RQ; Write Hit: replace cache word with WQ RDDest/RDreturn
Getting off the ground when creating an RVM test-bench
 Getting off the ground when creating an RVM test-bench Rich Musacchio, Ning Guo Paradigm Works [email protected],[email protected] ABSTRACT RVM compliant environments provide
Getting off the ground when creating an RVM test-bench Rich Musacchio, Ning Guo Paradigm Works [email protected],[email protected] ABSTRACT RVM compliant environments provide
E158 Intro to CMOS VLSI Design. Alarm Clock
 E158 Intro to CMOS VLSI Design Alarm Clock Sarah Yi & Samuel (Tae) Lee 4/19/2010 Introduction The Alarm Clock chip includes the basic functions of an alarm clock such as a running clock time and alarm
E158 Intro to CMOS VLSI Design Alarm Clock Sarah Yi & Samuel (Tae) Lee 4/19/2010 Introduction The Alarm Clock chip includes the basic functions of an alarm clock such as a running clock time and alarm
Verilog: always @ Blocks
 Verilog: always @ Blocks hris Fletcher U Berkeley Version 0.2008.9.4 September 5, 2008 Introduction Sections. to.6 discuss always@ blocks in Verilog, and when to use the two major flavors of always@ block,
Verilog: always @ Blocks hris Fletcher U Berkeley Version 0.2008.9.4 September 5, 2008 Introduction Sections. to.6 discuss always@ blocks in Verilog, and when to use the two major flavors of always@ block,
ModelSim-Altera Software Simulation User Guide
 ModelSim-Altera Software Simulation User Guide ModelSim-Altera Software Simulation User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01102-2.0 Document last updated for Altera Complete
ModelSim-Altera Software Simulation User Guide ModelSim-Altera Software Simulation User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-01102-2.0 Document last updated for Altera Complete
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers
 ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic
 Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs
 Application Note: CoolRunner CPLDs R XAPP339 (v.3) October, 22 Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs Summary This application note provides a functional description of VHDL and Verilog source code
Application Note: CoolRunner CPLDs R XAPP339 (v.3) October, 22 Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs Summary This application note provides a functional description of VHDL and Verilog source code
Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL
 Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 2012 Combinational Logic in a Dataflow Style Hierarchy: Instantiating Components (entities) Combinational Logic
Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 2012 Combinational Logic in a Dataflow Style Hierarchy: Instantiating Components (entities) Combinational Logic
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Assertion Synthesis Enabling Assertion-Based Verification For Simulation, Formal and Emulation Flows
 Assertion Synthesis Enabling Assertion-Based Verification For Simulation, Formal and Emulation Flows Manual Assertion Creation is ABV Bottleneck Assertion-Based Verification adopted by leading design companies
Assertion Synthesis Enabling Assertion-Based Verification For Simulation, Formal and Emulation Flows Manual Assertion Creation is ABV Bottleneck Assertion-Based Verification adopted by leading design companies
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design. Part 3: Verilog Tutorial. http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
Quartus Prime Standard Edition Handbook Volume 3: Verification
 Quartus Prime Standard Edition Handbook Volume 3: Verification Subscribe QPS5V3 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Simulating Altera Designs 1 QPS5V3 Subscribe This document describes
Quartus Prime Standard Edition Handbook Volume 3: Verification Subscribe QPS5V3 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Simulating Altera Designs 1 QPS5V3 Subscribe This document describes
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition
 RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected]. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
ESP-CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation
 Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Introduction to Functional Verification. Niels Burkhardt
 Introduction to Functional Verification Overview Verification issues Verification technologies Verification approaches Universal Verification Methodology Conclusion Functional Verification issues Hardware
Introduction to Functional Verification Overview Verification issues Verification technologies Verification approaches Universal Verification Methodology Conclusion Functional Verification issues Hardware
The Advanced JTAG Bridge. Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09
 The Advanced JTAG Bridge Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09 Copyright (C) 2008-2009 Nathan Yawn Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the
The Advanced JTAG Bridge Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09 Copyright (C) 2008-2009 Nathan Yawn Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the
Computer organization
 Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
HDL Simulation Framework
 PPC-System.mhs CoreGen Dateien.xco HDL-Design.vhd /.v SimGen HDL Wrapper Sim-Modelle.vhd /.v Platgen Coregen XST HDL Simulation Framework RAM Map Netzliste Netzliste Netzliste UNISIM NetGen vcom / vlog.bmm.ngc.ngc.ngc
PPC-System.mhs CoreGen Dateien.xco HDL-Design.vhd /.v SimGen HDL Wrapper Sim-Modelle.vhd /.v Platgen Coregen XST HDL Simulation Framework RAM Map Netzliste Netzliste Netzliste UNISIM NetGen vcom / vlog.bmm.ngc.ngc.ngc
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 [email protected] http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 [email protected] http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Low Cost System on Chip Design for Audio Processing
 Low Cost System on Chip Design for udio Processing 1 yas Kanta Swain, 2 Kamala Kanta Mahapatra bstract System-on-Chip (SoC) design is an integration of multi million transistors in a single chip for alleviating
Low Cost System on Chip Design for udio Processing 1 yas Kanta Swain, 2 Kamala Kanta Mahapatra bstract System-on-Chip (SoC) design is an integration of multi million transistors in a single chip for alleviating
Quartus II Handbook Volume 3: Verification
 Quartus II Handbook Volume 3: Verification Subscribe QII5V3 2015.05.04 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Simulating Altera Designs 1 2015.05.04 QII5V3 Subscribe This document describes
Quartus II Handbook Volume 3: Verification Subscribe QII5V3 2015.05.04 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Simulating Altera Designs 1 2015.05.04 QII5V3 Subscribe This document describes
Using SystemVerilog Assertions for Creating Property-Based Checkers
 Using SystemVerilog Assertions for Creating Property-Based Checkers Eduard Cerny Synopsys, Inc. Marlborough, USA [email protected] Dmitry Korchemny Intel Corp. Haifa, Israel [email protected]
Using SystemVerilog Assertions for Creating Property-Based Checkers Eduard Cerny Synopsys, Inc. Marlborough, USA [email protected] Dmitry Korchemny Intel Corp. Haifa, Israel [email protected]
Getting the Most Out of Synthesis
 Outline Getting the Most Out of Synthesis Dr. Paul D. Franzon 1. Timing Optimization Approaches 2. Area Optimization Approaches 3. Design Partitioning References 1. Smith and Franzon, Chapter 11 2. D.Smith,
Outline Getting the Most Out of Synthesis Dr. Paul D. Franzon 1. Timing Optimization Approaches 2. Area Optimization Approaches 3. Design Partitioning References 1. Smith and Franzon, Chapter 11 2. D.Smith,
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
System Verilog Testbench Tutorial Using Synopsys EDA Tools
 System Verilog Testbench Tutorial Using Synopsys EDA Tools Developed By Abhishek Shetty Guided By Dr. Hamid Mahmoodi Nano-Electronics & Computing Research Center School of Engineering San Francisco State
System Verilog Testbench Tutorial Using Synopsys EDA Tools Developed By Abhishek Shetty Guided By Dr. Hamid Mahmoodi Nano-Electronics & Computing Research Center School of Engineering San Francisco State
EE360: Digital Design I Course Syllabus
 : Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Fall 2008 Course Description This course introduces students to the basic concepts of digital systems, including analysis and design. Both combinational and sequential
: Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Fall 2008 Course Description This course introduces students to the basic concepts of digital systems, including analysis and design. Both combinational and sequential
Implementation Details
 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
3. VERILOG HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE
 3. VERILOG HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE The previous chapter describes how a designer may manually use ASM charts (to describe behavior) and block diagrams (to describe structure) in top-down hardware
3. VERILOG HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE The previous chapter describes how a designer may manually use ASM charts (to describe behavior) and block diagrams (to describe structure) in top-down hardware
Verification & Design Techniques Used in a Graduate Level VHDL Course
 Verification & Design Techniques Used in a Graduate Level VHDL Course Prof. Swati Agrawal, BE, MS (SUNY, Buffalo, NY USA) 1 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Bhilai Institute
Verification & Design Techniques Used in a Graduate Level VHDL Course Prof. Swati Agrawal, BE, MS (SUNY, Buffalo, NY USA) 1 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Bhilai Institute
Design Verification & Testing Design for Testability and Scan
 Overview esign for testability (FT) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit Reduce the cost and time associated with test development Reduce the execution time of performing
Overview esign for testability (FT) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit Reduce the cost and time associated with test development Reduce the execution time of performing
Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
earlier in the semester: The Full adder above adds two bits and the output is at the end. So if we do this eight times, we would have an 8-bit adder.
 The circuit created is an 8-bit adder. The 8-bit adder adds two 8-bit binary inputs and the result is produced in the output. In order to create a Full 8-bit adder, I could use eight Full -bit adders and
The circuit created is an 8-bit adder. The 8-bit adder adds two 8-bit binary inputs and the result is produced in the output. In order to create a Full 8-bit adder, I could use eight Full -bit adders and
Altera Error Message Register Unloader IP Core User Guide
 2015.06.12 Altera Error Message Register Unloader IP Core User Guide UG-01162 Subscribe The Error Message Register (EMR) Unloader IP core (altera unloader) reads and stores data from the hardened error
2015.06.12 Altera Error Message Register Unloader IP Core User Guide UG-01162 Subscribe The Error Message Register (EMR) Unloader IP core (altera unloader) reads and stores data from the hardened error
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano
 Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes ([email protected]) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes ([email protected]) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
Download the Design Files
 Design Example Using the altlvds Megafunction & the External PLL Option in Stratix II Devices March 2006, ver. 1.0 Application Note 409 Introduction The altlvds megafunction allows you to instantiate an
Design Example Using the altlvds Megafunction & the External PLL Option in Stratix II Devices March 2006, ver. 1.0 Application Note 409 Introduction The altlvds megafunction allows you to instantiate an
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
Chapter 2 Clocks and Resets
 Chapter 2 Clocks and Resets 2.1 Introduction The cost of designing ASICs is increasing every year. In addition to the non-recurring engineering (NRE) and mask costs, development costs are increasing due
Chapter 2 Clocks and Resets 2.1 Introduction The cost of designing ASICs is increasing every year. In addition to the non-recurring engineering (NRE) and mask costs, development costs are increasing due
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays
 Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Storage Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Logic Data
Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Storage Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Logic Data
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II
 CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II 6 - Microprocessor Interfacing - Memory and Peripheral Dr. Tim Ferguson, Monash University. AUSTRALIA. Tel: +61-3-99053227 FAX: +61-3-99053574
CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II 6 - Microprocessor Interfacing - Memory and Peripheral Dr. Tim Ferguson, Monash University. AUSTRALIA. Tel: +61-3-99053227 FAX: +61-3-99053574
EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops. Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
SPI Flash Programming and Hardware Interfacing Using ispvm System
 March 2005 Introduction Technical Note TN1081 SRAM-based FPGA devices are volatile and require reconfiguration after power cycles. This requires external configuration data to be held in a non-volatile
March 2005 Introduction Technical Note TN1081 SRAM-based FPGA devices are volatile and require reconfiguration after power cycles. This requires external configuration data to be held in a non-volatile
Chapter 2 Verilog HDL for Design and Test
 Chapter 2 Verilog HDL for Design and Test In Chapter 1, we discussed the basics of test and presented ways in which hardware description languages (HDLs) could be used to improve various aspects of digital
Chapter 2 Verilog HDL for Design and Test In Chapter 1, we discussed the basics of test and presented ways in which hardware description languages (HDLs) could be used to improve various aspects of digital
Chapter 13: Verification
 Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!!
 ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
 DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
Embed-It! Integrator Online Release E-2011.03 March 2011
 USER MANUAL Embed-It! Integrator Online Release E-2011.03 March 2011 (c) 1998-2011 Virage Logic Corporation, All Rights Reserved (copyright notice reflects distribution which may not necessarily be a publication).
USER MANUAL Embed-It! Integrator Online Release E-2011.03 March 2011 (c) 1998-2011 Virage Logic Corporation, All Rights Reserved (copyright notice reflects distribution which may not necessarily be a publication).
University of Texas at Dallas. Department of Electrical Engineering. EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design
 University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
ASYNCHRONOUS COUNTERS
 LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic devices Implementing logic with PLDs Static hazards
 Points ddressed in this Lecture Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic
Points ddressed in this Lecture Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Central Processing Unit
 Chapter 4 Central Processing Unit 1. CPU organization and operation flowchart 1.1. General concepts The primary function of the Central Processing Unit is to execute sequences of instructions representing
Chapter 4 Central Processing Unit 1. CPU organization and operation flowchart 1.1. General concepts The primary function of the Central Processing Unit is to execute sequences of instructions representing
Introduction. Jim Duckworth ECE Department, WPI. VHDL Short Course - Module 1
 VHDL Short Course Module 1 Introduction Jim Duckworth ECE Department, WPI Jim Duckworth, WPI 1 Topics Background to VHDL Introduction to language Programmable Logic Devices CPLDs and FPGAs FPGA architecture
VHDL Short Course Module 1 Introduction Jim Duckworth ECE Department, WPI Jim Duckworth, WPI 1 Topics Background to VHDL Introduction to language Programmable Logic Devices CPLDs and FPGAs FPGA architecture
RTL Low Power Techniques for System-On-Chip Designs
 RTL Low Power Techniques for System-On-Chip Designs Mike Gladden Motorola, Inc. Austin, TX [email protected] Indraneel Das Synopsys, Inc. Austin, TX [email protected] ABSTRACT Low power design
RTL Low Power Techniques for System-On-Chip Designs Mike Gladden Motorola, Inc. Austin, TX [email protected] Indraneel Das Synopsys, Inc. Austin, TX [email protected] ABSTRACT Low power design
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
SystemVerilog Is Getting Even Better!
 by, SystemVerilog Is Getting Even Better! An Update on the Proposed 2009 SystemVerilog Standard Part 2 presented by Clifford E. Cummings Sunburst Design, Inc. [email protected] www.sunburst-design.com
by, SystemVerilog Is Getting Even Better! An Update on the Proposed 2009 SystemVerilog Standard Part 2 presented by Clifford E. Cummings Sunburst Design, Inc. [email protected] www.sunburst-design.com
Digital Logic Design. Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits. Pu-Jen Cheng
 Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations. Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language
 Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
A low-cost, connection aware, load-balancing solution for distributing Gigabit Ethernet traffic between two intrusion detection systems
 Iowa State University Digital Repository @ Iowa State University Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2010 A low-cost, connection aware, load-balancing solution for distributing Gigabit Ethernet
Iowa State University Digital Repository @ Iowa State University Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2010 A low-cost, connection aware, load-balancing solution for distributing Gigabit Ethernet
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION
 Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Module 4 : Propagation Delays in MOS Lecture 22 : Logical Effort Calculation of few Basic Logic Circuits
 Module 4 : Propagation Delays in MOS Lecture 22 : Logical Effort Calculation of few Basic Logic Circuits Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Logical Effort of an Inverter
Module 4 : Propagation Delays in MOS Lecture 22 : Logical Effort Calculation of few Basic Logic Circuits Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Logical Effort of an Inverter
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques
 Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
SDLC Controller. Documentation. Design File Formats. Verification
 January 15, 2004 Product Specification 11 Stonewall Court Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677 USA Phone: +1-201-391-8300 Fax: +1-201-391-8694 E-mail: [email protected] URL: www.cast-inc.com Features AllianceCORE
January 15, 2004 Product Specification 11 Stonewall Court Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677 USA Phone: +1-201-391-8300 Fax: +1-201-391-8694 E-mail: [email protected] URL: www.cast-inc.com Features AllianceCORE
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users
 Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Digital Circuit Design Using Xilinx ISE Tools
 Digital Circuit Design Using Xilinx ISE Tools Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Programmable Logic Device: FPGA... 2 3. Creating a New Project... 2 4. Synthesis and Implementation of the Design... 11 5.
Digital Circuit Design Using Xilinx ISE Tools Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Programmable Logic Device: FPGA... 2 3. Creating a New Project... 2 4. Synthesis and Implementation of the Design... 11 5.
Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design
 White Paper Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design A major benefit of programmable logic is that it accommodates changes to the system specification late in the design cycle.
White Paper Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design A major benefit of programmable logic is that it accommodates changes to the system specification late in the design cycle.
Post-Configuration Access to SPI Flash Memory with Virtex-5 FPGAs Author: Daniel Cherry
 Application Note: Virtex-5 Family XAPP1020 (v1.0) June 01, 2009 Post-Configuration Access to SPI Flash Memory with Virtex-5 FPGAs Author: Daniel Cherry Summary Virtex -5 FPGAs support direct configuration
Application Note: Virtex-5 Family XAPP1020 (v1.0) June 01, 2009 Post-Configuration Access to SPI Flash Memory with Virtex-5 FPGAs Author: Daniel Cherry Summary Virtex -5 FPGAs support direct configuration
Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts)
 Dr. Greg Tumbush, [email protected] Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
Dr. Greg Tumbush, [email protected] Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
2013 MBA Jump Start Program. Statistics Module Part 3
 2013 MBA Jump Start Program Module 1: Statistics Thomas Gilbert Part 3 Statistics Module Part 3 Hypothesis Testing (Inference) Regressions 2 1 Making an Investment Decision A researcher in your firm just
2013 MBA Jump Start Program Module 1: Statistics Thomas Gilbert Part 3 Statistics Module Part 3 Hypothesis Testing (Inference) Regressions 2 1 Making an Investment Decision A researcher in your firm just
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
ECE 3401 Lecture 7. Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process)
 ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
The Deployment Production Line
 The Deployment Production Line Jez Humble, Chris Read, Dan North ThoughtWorks Limited [email protected], [email protected], [email protected] Abstract Testing and deployment
The Deployment Production Line Jez Humble, Chris Read, Dan North ThoughtWorks Limited [email protected], [email protected], [email protected] Abstract Testing and deployment
5 Combinatorial Components. 5.0 Full adder. Full subtractor
 5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
AES (Rijndael) IP-Cores
 AES (Rijndael) IP-Cores Encryption/Decryption and Key Expansion Page 1 Revision History Date Version Description 24 February 2006 1.0 Initial draft. 15 March 2006 1.1 Block diagrams added. 26 March 2006
AES (Rijndael) IP-Cores Encryption/Decryption and Key Expansion Page 1 Revision History Date Version Description 24 February 2006 1.0 Initial draft. 15 March 2006 1.1 Block diagrams added. 26 March 2006
Chapter 6 Window Operations
 Chapter 6 Window Operations...2 6.1 Window Types...2 6.1.1 Base Window...2 6.1.2 Fast Selection Window...3 6.1.3 Common Window...4 6.1.4 System Message Window...5 6.2 Create, Set, and Delete a Window...7
Chapter 6 Window Operations...2 6.1 Window Types...2 6.1.1 Base Window...2 6.1.2 Fast Selection Window...3 6.1.3 Common Window...4 6.1.4 System Message Window...5 6.2 Create, Set, and Delete a Window...7
MIMO detector algorithms and their implementations for LTE/LTE-A
 GIGA seminar 11.01.2010 MIMO detector algorithms and their implementations for LTE/LTE-A Markus Myllylä and Johanna Ketonen 11.01.2010 2 Outline Introduction System model Detection in a MIMO-OFDM system
GIGA seminar 11.01.2010 MIMO detector algorithms and their implementations for LTE/LTE-A Markus Myllylä and Johanna Ketonen 11.01.2010 2 Outline Introduction System model Detection in a MIMO-OFDM system
1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1.
 File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter
 NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376
 Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376 General Peripheral Programming Model Each peripheral has a range of addresses in the memory map peripheral has base address (i.e. 0x00A0) each register used in the peripheral
Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376 General Peripheral Programming Model Each peripheral has a range of addresses in the memory map peripheral has base address (i.e. 0x00A0) each register used in the peripheral
