by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin
|
|
|
- Peter Hardy
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to and search under anterior neck. The anterior neck is problematic for many massage therapists. You may avoid working this region for two reasons. First, many endangerment sites are located in the anterior neck, including the trachea, thyroid gland, brachial plexus of nerves, and carotid artery. Second, working in this region can be uncomfortable if you are not skilled and familiar with it. The contours of the transverse processes of the vertebrae are rather sharp and having soft tissue pressed against them can be painful. Even with these concerns, however, working the anterior neck can be very beneficial for the health of your client, especially one who has suffered a whiplash injury. Therefore, learning how to work the musculature of the anterior neck can be a valuable addition 159
2 THE MUSCLES OF THE NTEIO NECK FIGUE 1 is a superficial anterior view. The platysma is shown on the right and removed on the left. L TE L Trachea Common carotid artery Internal jugular vein Hyoid bone Thyroid cartilage Platysma Thyroid gland Sternocleidomastoid SUPEIO Mandible INFEIO Hyoid muscles Mastoid process Longus capitus Longus colli Common carotid artery Internal jugular vein Sternocleidomastoid Levator Scapulae Scalenes Upper trapezius Omohyoid L TE L FIGUE 1B is a deep anterior view. The right side illustrates the SCM, scalene group and the prevertebral group. The left side has the SCM removed for a better view of the other muscles to a massage therapist s practice. nd the first step to learning how to safely and effectively work the anterior neck is learning how to identify, locate and palpate the muscles of this region. The anterior neck is home to a number of important muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid (SCM), scalene group and the prevertebral group of muscles (Figures 1 and 1B).* Functionally, the muscles of the anterior neck are flexors of the neck at the spinal joints. Consequently, during a typical whiplash accident when a person s head and neck are forcibly thrown back into extension, the muscles of the anterior neck are excessively stretched, triggering the muscle spindle stretch reflex. This results in tightness and spasming of the muscles of the anterior neck. Beyond local pain from the tightness of these muscles, tightness of the SCM is associated with proprioceptive disturbances of the neck, often resulting in dizziness. Tightness of the scalenes can be associated with compression upon nerves that provide innervation to the upper extremity. Finally, tightness of the prevertebral muscles can cause referral pain that is interpreted as a sore throat. Given the prevalence of whiplash injuries, and the variety and extent of signs and symptoms that can result, there can be tremendous value in working the anterior neck musculature of our clients! 160 mtj/massage therapy journalspring 2006 Subclavian artery Brachial plexus Clavicle Scalenes * The hyoid group of muscles is also located in the anterior neck. This article will not address their palpation. Figure 1 courtesy The Muscular System Manual by Joseph Muscolino. Mosby, Figure 1B courtesy of Joseph Muscolino. 1st rib The Scalene and Prevertebral Muscles While most of you are knowledgeable and comfortable working the SCM, the scalenes and prevertebral muscles are less often addressed. We will begin by locating and palpating the SCM. The SCM will then be used as a landmark for the location and palpation of the scalene and prevertebral muscle groups. The SCM has two heads a sternal
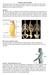
3 PLPTION OF THE SCM and a clavicular head. Inferiorly, the sternal head attaches onto the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicular head attaches onto the medial clavicle. Both heads conjoin and attach superiorly onto the mastoid process of the temporal bone and superior nuchal line of the occipital bone. The SCM can be easily palpated with the client seated or supine. With the client seated, stand to the side that will be palpated. sk the client to first rotate the head and neck at the spinal joints to the opposite side (contralateral rotation) and slightly laterally flex the head and neck to the same side (ipsilateral lateral flexion) (Figure 2). Now resist the client from further lateral flexion (Figure 2B) and the two heads of the SCM will be visible and palpable. It is important to make sure that the client maintains the contralateral rotation; this is especially so for the sternal head because this head is more active in creating the rotation component of the SCM s actions. If the clavicular head is not readily palpable, ask the client to increase the force of resistance of ipsilateral lateral flexion because the clavicular head is more active in creating the lateral flexion component of the SCM s actions. fter palpating the entire length of both heads of the SCM* with the muscle contracted, palpate the SCM again while it is relaxed so that its resting baseline tone can be assessed. When palpating the SCM, be careful not to place excessive pressure upon the carotid artery because this will stimulate a neurologic reflex that can lower blood pressure; you can tell if you are pressing upon the carotid artery by feeling for a pulse under your fingertips. Supine palpation of the SCM is also straightforward. The client is supine while you are seated at the head of the table. First ask the client to contralater- FIGUE 2 shows the beginning position for seated palpation. Stand behind the client and to the side that will be palpated; the client rotates the head and neck toward the opposite side and slightly laterally flexes the head and neck toward the same side. FIGUE 2B illustrates the therapist offering resistance to further lateral flexion of the head and neck toward the same side; this requires the SCM to contract, making it more palpable. FIGUE 2C demonstrates supine palpation. The client first rotates the head and neck to the opposite side and then lifts the head and neck off the table, creating a contraction of the SCM. * The clavicular head of the SCM is often not as visible as the sternal head and should be carefully palpated. Further, there is a great deal of variability regarding the relationship between the sternal and clavicular heads; often there is a gap between them, at times there is not
4 SETED PLPTION OF THE SCLENE GOUP OF MUSCLES 162 mtj/massage therapy journalspring 2006 ally rotate the head and neck fully to one side; then ask the client to lift the head and neck up off the table. The SCM will be visible and palpable (Figure 2C). Now that the SCM has been located, its lateral border can be used as a landmark for palpation of the scalene group. The scalene group of muscles is composed of three muscles the anterior, middle and posterior scalenes. (Their names reflect their positions relative to each other.) s a group, the scalenes attach inferiorly to the first and second ribs; superiorly they attach to the transverse processes of the second through seventh cervical vertebrae. To palpate the scalenes with the client seated, stand behind the client and locate the lateral border of the SCM (be sure that you have the lateral border of the clavicular head) (Figure 3). From there, move your palpating fingers slightly laterally off the SCM you will be over the scalenes. Now ask the client to take in a short quick breath through the nose and feel for the contraction of the scalenes (Figure 3B). Taking in a breath requires elevation of the ribs, which is an action of the scalene group. Once located, palpate the scalenes while they are contracted, and then while they are relaxed so that you can assess their baseline tone. Be sure to explore the entire breadth of the scalenes within the anterior aspect of the posterior triangle of the neck (Figures 4, 4B). The posterior triangle of the neck is the region of the neck bounded anteriorly by the SCM, posteriorly by the upper trapezius and inferiorly by the clavicle. Superficial within the posterior triangle are the scalenes, levator scapulae, splenius capitis and the inferior belly of the omohyoid. (These muscles are all deep to the platysma, which is very thin and does not impede palpa- tion of the muscles that are deep to it.) When palpating the scalenes, be careful not to exert excessive pressure upon the brachial plexus of nerves and/or the subclavian artery. These structures travel between the anterior and middle scalenes.* If you feel a pulse under your fingertips or the client reports tingling down the upper extremity, move your palpating fingers. FIGUE 3. Stand behind the client and locate the lateral border of the clavicular head of the SCM. FIGUE 3B. Move your palpating fingers just lateral to that and you will be over the scalene muscles. By asking the client to take in a short quick breath through the nose, the scalenes can be felt to contract. The prevertebral group of muscles consists of the longus colli, longus capitis, rectus capitis anterior and rectus capitis lateralis. Of these, the longus colli and longus capitis can be easily palpated; these two muscles lie along the anterolateral vertebral column from the vertebral level of T3 to the skull. To locate the longus muscles, we will again use the SCM as our landmark. This * When the anterior and middle scalenes are excessively tight, they can impinge upon the brachial plexus of nerves and/or the subclavian artery causing symptoms anywhere within the upper extremity. This condition is called anterior scalene syndrome and is one of the three types of thoracic outlet syndrome.
5 THE POSTEIO TINGLE OF THE NECK SUPEIO FIGUE 4 shows a lateral view of the muscles located superficially within the posterior triangle. P O ST E Splenius Capitis Hyoid bone N TE I O Levator scapulae Scalenes Sternocleidomastoid I O Upper trapezius Omohyoid Clavicle INFEIO FIGUE 4B shows an anterior view of the posterior triangle with the borders drawn. Even though it is named the posterior triangle, its location in the neck is primarily anterolateral. Outline of posterior triangle Figure 4 courtesy The Muscular System Manual by Joseph Muscolino. Mosby, Figure 4B courtesy of Joseph Muscolino
6 SETED PLPTION OF THE LONGUS COLLI ND LONGUS CPITIS MUSCLES OF THE PEVETEBL GOUP >> To read tips on how to prevent neck pain, go to condheat/pain/necktips.htm. FIGUE 5. Begin by locating the medial border of the sternal head of the SCM 164 mtj/massage therapy journalspring 2006 time, locate the medial border of the sternal head of the SCM. Next, palpate just medial to that. Because the longus muscles are located deep against the spine, to access them you must gently, but firmly, sink into the tissue in the posterior direction aiming toward the spinal column. It is important that this be done slowly or it will be very uncomfortable for the client. To bring out a contraction of these muscles so that they are more palpable, resist the client from flexing the head and neck against your hand. When palpating the longus muscles, be careful not to exert too much pressure against the trachea. Otherwise, it will be irritated, and the client may involuntarily cough. (See right, Figures 5-5C for this series.) While many therapists are hesitant to approach the muscles of the anterior neck, it usually only takes a little practice to locate and palpate them, and only a little more practice to become smooth and comfortable at it. Of course, the more proficient you become, the more comfortable these palpations are for you and the client. Once you are proficient at palpating these muscles, working them in a therapeutic manner easily follows! Joseph E. Muscolino, DC, is an instructor at the Connecticut Center for Massage Therapy and the owner of Learn- Muscles in edding, Connecticut. He is also the author of The Muscular System Manual & Kinesiology textbook (Elsevier, 2006). FIGUE 5B. Then move just medial to that. Because these muscles are deep, you must sink into the tissue toward the spine, slowly, in a gentle but firm manner. FIGUE 5C. Then ask the client to try to flex the head and neck against your resistance. This will cause the muscles to contract, making them more easily palpable.
Stretching the Low Back THERAPIST ASSISTED AND CLIENT SELF-CARE STRETCHES FOR THE LUMBOSACRAL SPINE
 EXPERT CONTENT by Joseph E. Muscolino photos by Yanik Chauvin body mechanics THE ESSENCE OF MOST MANUAL THERAPIES, and certainly clinical orthopedic massage therapy, is to loosen taut soft tissues, thereby
EXPERT CONTENT by Joseph E. Muscolino photos by Yanik Chauvin body mechanics THE ESSENCE OF MOST MANUAL THERAPIES, and certainly clinical orthopedic massage therapy, is to loosen taut soft tissues, thereby
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column
 Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
Effective Treatments for the Neck
 Effective Treatments for the Neck A manual therapy course to improve your treatment of radicular pain and foraminal impingement syndromes www.advancedmassageeducation.com 1 Effective Treatments for the
Effective Treatments for the Neck A manual therapy course to improve your treatment of radicular pain and foraminal impingement syndromes www.advancedmassageeducation.com 1 Effective Treatments for the
SPINE. Postural Malalignments 4/9/2015. Cervical Spine Evaluation. Thoracic Spine Evaluation. Observations. Assess position of head and neck
 SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Level IA: Submental Group
 IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
TRIGGER POINTS. Trigger Point Therapy Can Be Used To Help You With These Common Conditions: MIGRAINES TENSION HEADACHE NECK AND JAW PAIN
 TRIGGER POINTS Muscles account for more than 60% of the human body mass, making up the largest part of our bodies. They are responsible for all movement of the human body. With such an enormous responsibility,
TRIGGER POINTS Muscles account for more than 60% of the human body mass, making up the largest part of our bodies. They are responsible for all movement of the human body. With such an enormous responsibility,
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Reading, Writing & Posture
 Expert Content body mechanics by Joseph E. Muscolino Healthy posture of the upper body when reading and writing is dependent upon the location and angulation of the surface that we are reading and/or writing
Expert Content body mechanics by Joseph E. Muscolino Healthy posture of the upper body when reading and writing is dependent upon the location and angulation of the surface that we are reading and/or writing
Muscles of the Spinal Column. Chapter 12
 Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
Ron Schenk PT, PhD 1
 Ron Schenk PT, PhD 1 Objectives Describe the anatomy of the neck (cervical spine) and low back (lumbar spine) Describe the risk factors associated with neck and low back injury Describe physical therapy
Ron Schenk PT, PhD 1 Objectives Describe the anatomy of the neck (cervical spine) and low back (lumbar spine) Describe the risk factors associated with neck and low back injury Describe physical therapy
Carpal Tunnel Pain. STRETCH YOUR: 1) Wrist Flexors 2) Wrist Extensors 3) Wrist Decompression 4) Neck (see other chapters for more examples)
 Carpal Tunnel Pain STRETCH YOUR: 1) Wrist Flexors 2) Wrist Extensors 3) Wrist Decompression 4) Neck (see other chapters for more examples) wrist flexors wrist extensors carpal tunnel Athletic Edge - www.athleticedge.biz
Carpal Tunnel Pain STRETCH YOUR: 1) Wrist Flexors 2) Wrist Extensors 3) Wrist Decompression 4) Neck (see other chapters for more examples) wrist flexors wrist extensors carpal tunnel Athletic Edge - www.athleticedge.biz
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions
 Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain
 Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Shoulder and Related Upper Extremity Radiating Pain ICD-9-CM codes: 723.3 Cervical brachial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain codes: d4301 Carrying in the hands (Taking or transporting
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy
 Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
The Neck: Whiplash & Central Ligament Sprains. Presented by Dr. Ben Benjamin
 Debilitating Orthopedic Injury Sampler #1 The Neck: Whiplash & Central Ligament Sprains Presented by Dr. Ben Benjamin Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. [email protected]
Debilitating Orthopedic Injury Sampler #1 The Neck: Whiplash & Central Ligament Sprains Presented by Dr. Ben Benjamin Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. [email protected]
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
MD 2016. Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy. A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
Who are these patients? Neck Pain in Voice Disorders. Etiologies of Cervicalgia. Role of Physical Therapy in Treatment of Voice Disorders
 Role of Physical Therapy in Treatment of Voice Disorders DAVID O. FRANCIS, MD MS VANDERBILT VOICE CENTER NOVEMBER 5, 2011 Singers Who are these patients? Performers Athletes Exercise with weights Heavy
Role of Physical Therapy in Treatment of Voice Disorders DAVID O. FRANCIS, MD MS VANDERBILT VOICE CENTER NOVEMBER 5, 2011 Singers Who are these patients? Performers Athletes Exercise with weights Heavy
Massage Therapy Practice.com Client Self Care Manual
 Massage Therapy Practice.com Client Self Care Manual Massage Therapy Basics The Muscular Imprint of Tension Muscle Pain and Massage Stages of Recovery From Injury Stretching Basics Hydrotherapy Epsom Salts
Massage Therapy Practice.com Client Self Care Manual Massage Therapy Basics The Muscular Imprint of Tension Muscle Pain and Massage Stages of Recovery From Injury Stretching Basics Hydrotherapy Epsom Salts
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys
 Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
Anatomy for Workers Compensation Attorneys Donato J. Borrillo MD JD Plant Medical Advisor Chrysler/Jeep Assembly Toledo Zoll, Kranz, and Borgess May 16, 2015 Imaging studies neck 1 Bulge and herniation
by joe muscolino body mechanics
 by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Spine Evaluation. Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Spine Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling? Mechanism:
Spine Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling? Mechanism:
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24
 Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
Basic techniques of pulmonary physical therapy (I) 100/04/24 Evaluation of breathing function Chart review History Chest X ray Blood test Observation/palpation Chest mobility Shape of chest wall Accessory
X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary
 X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary Introduction Exercising your neck can make it stronger, more flexible and reduce neck pain that is caused by stress and fatigue. This reference summary describes
X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary Introduction Exercising your neck can make it stronger, more flexible and reduce neck pain that is caused by stress and fatigue. This reference summary describes
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
STRESS. Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING AND YOUR BODY. www.neorthopt.
 Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause
Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause
Cervicothoracic Mobility Exercises
 Cervicothoracic Mobility Exercises Upper Cervical Mobility Exercises... 2 Lower Cervical Mobility Exercises... 3 Cervicothoracic Junction Mobility Exercises... 4 1 st Rib Mobility Exercises... 5 Cervical
Cervicothoracic Mobility Exercises Upper Cervical Mobility Exercises... 2 Lower Cervical Mobility Exercises... 3 Cervicothoracic Junction Mobility Exercises... 4 1 st Rib Mobility Exercises... 5 Cervical
UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY
 UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause health problems. Most people equate stress with high blood pressure, a heart attack
UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause health problems. Most people equate stress with high blood pressure, a heart attack
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
ENT Emergencies. Injuries of the Neck. Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital
 ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California.
 Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California. In this issue, we focus on a 23-year-old female patient referred by her
Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California. In this issue, we focus on a 23-year-old female patient referred by her
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI
 CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
Sheet 1A. Treating short/tight muscles using MET. Pectorals. Upper trapezius. Levator scapula
 Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
CHAPTER 32 QUIZ. Handout 32-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
 F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
F10001-Ch02.qxd 4/7/06 9:04 AM Page 11 Spine 2 THE CERVICAL SPINE AND NECK The cervical spine has three functions: supporting the head, allowing for the head s ROM and housing the spinal cord (Fig. 2.1).
PRACTICE GUIDELINE TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
What is Pilates? Pilates for Horses?
 What is Pilates? Pilates is a conditioning system that increases core stability, strength and body awareness; redresses imbalances, and re aligns the body from the inside out. It can improve posture, achieve
What is Pilates? Pilates is a conditioning system that increases core stability, strength and body awareness; redresses imbalances, and re aligns the body from the inside out. It can improve posture, achieve
Psoas Syndrome. The pain is worse from continued standing and from twisting at the waist without moving the feet.
 Psoas Syndrome The iliopsoas muscle is a major body mover but seldom considered as a source of pain. Chronic lower back pain involving the hips, legs, or thoracic regions can often be traced to an iliopsoas
Psoas Syndrome The iliopsoas muscle is a major body mover but seldom considered as a source of pain. Chronic lower back pain involving the hips, legs, or thoracic regions can often be traced to an iliopsoas
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Senior pets are not unlike senior citizens.
 P ro c e d u re s P ro G E R I A T R I C S / R E H A B I L I T A T I O N Peer Reviewed Christine Jurek, DVM, CCRT, & Laurie McCauley, DVM, CCRT TOPS Veterinary Rehab, Grayslake, Illinois Physical Rehabilitation
P ro c e d u re s P ro G E R I A T R I C S / R E H A B I L I T A T I O N Peer Reviewed Christine Jurek, DVM, CCRT, & Laurie McCauley, DVM, CCRT TOPS Veterinary Rehab, Grayslake, Illinois Physical Rehabilitation
Headaches!!! What can Physical Therapy do??? Paul Wortley PT Rocky Mountain Therapy Services
 Headaches!!! What can Physical Therapy do??? Paul Wortley PT Rocky Mountain Therapy Services Take 2 Aspirin and Call Me in the Morning FACTS During the past year, nearly 90-95% men and women have had a
Headaches!!! What can Physical Therapy do??? Paul Wortley PT Rocky Mountain Therapy Services Take 2 Aspirin and Call Me in the Morning FACTS During the past year, nearly 90-95% men and women have had a
It is a syndrome characterized by chronic pain caused by multiple trigger points and
 1 WHAT IS MYOFASCIAL PAIN SYNDROME? It is a syndrome characterized by chronic pain caused by multiple trigger points and myofascial tightening. The term fascial pertains to the muscle, and it is a lining
1 WHAT IS MYOFASCIAL PAIN SYNDROME? It is a syndrome characterized by chronic pain caused by multiple trigger points and myofascial tightening. The term fascial pertains to the muscle, and it is a lining
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
SpineFAQs. Whiplash. What causes this condition?
 SpineFAQs Whiplash Whiplash is defined as a sudden extension of the cervical spine (backward movement of the neck) and flexion (forward movement of the neck). This type of trauma is also referred to as
SpineFAQs Whiplash Whiplash is defined as a sudden extension of the cervical spine (backward movement of the neck) and flexion (forward movement of the neck). This type of trauma is also referred to as
The Thorax - Anterior and Lateral Chest Wall
 The Thorax - Anterior and Lateral Chest Wall by Marc Heller,DC When we think of the thorax, most of us think of the thoracic vertebrae and the posterior ribs. When examining for thoracic restrictions,
The Thorax - Anterior and Lateral Chest Wall by Marc Heller,DC When we think of the thorax, most of us think of the thoracic vertebrae and the posterior ribs. When examining for thoracic restrictions,
Cervical Spine Applied Anatomy. Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education
 Cervical Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Objectives Discuss concepts relevant to pathophysiology and differential diagnosis for headache
Cervical Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Objectives Discuss concepts relevant to pathophysiology and differential diagnosis for headache
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED
 MOON SHOULDER GROUP ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED PROGRAM Introduction The Shoulder MOON group is a Multi-center Orthopaedic Outcomes Network, a consortium of institutions working together
MOON SHOULDER GROUP ROTATOR CUFF REHABILITATION THERAPIST DIRECTED PROGRAM Introduction The Shoulder MOON group is a Multi-center Orthopaedic Outcomes Network, a consortium of institutions working together
WHIPLASH! Therapeutic Massage by Lucy Lucy Dean, LMT, NMT, MMT. Helpful and effective treatment with Neuromuscular Therapy. What does Whiplash mean?
 WHIPLASH! Helpful and effective treatment with Neuromuscular Therapy Therapeutic Massage by Lucy Lucy Dean, LMT, NMT, MMT What does Whiplash mean? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain
WHIPLASH! Helpful and effective treatment with Neuromuscular Therapy Therapeutic Massage by Lucy Lucy Dean, LMT, NMT, MMT What does Whiplash mean? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury. Canadian Family Physician
 Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Cervical Whiplash: Considerations in the Rehabilitation of Cervical Myofascial Injury 1 Canadian Family Physician Volume 32, September 1986 Arthur Ameis, MD Dr. Ames practices physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Cervical Exercise: How important is it? What can be done? The Backbone of Spine Treatment. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Cervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine Treatment How important is it? What can be done? North American Spine Society Public Education Series Important: If you have had an accident that started your neck
Cervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine Treatment How important is it? What can be done? North American Spine Society Public Education Series Important: If you have had an accident that started your neck
Whiplash Injuries - A Modern Epidemic
 Ch 1 'Whiplash' 10/5/04 11:03 am Page 5 1 Whiplash Injuries - A Modern Epidemic INTRODUCTION The existence of whiplash injury following a road traffic accident has been the subject of much controversy.
Ch 1 'Whiplash' 10/5/04 11:03 am Page 5 1 Whiplash Injuries - A Modern Epidemic INTRODUCTION The existence of whiplash injury following a road traffic accident has been the subject of much controversy.
Standard of Care: Cervical Radiculopathy
 Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Diagnosis: Cervical radiculopathy, injury to one or more nerve roots, has multiple presentations. Symptoms may include pain in the cervical spine
Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Diagnosis: Cervical radiculopathy, injury to one or more nerve roots, has multiple presentations. Symptoms may include pain in the cervical spine
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Any rapid head movement can cause a Whiplash. ALTERNATIVE CARE CHIROPRACTIC Reston, Virginia
 ALTERNATIVE CARE CHIROPRACTIC Reston, Virginia P ROV E N R E L I E F F RO M W H I P L A S H Any rapid head movement can cause a Whiplash injury. Although whiplash is commonly associated with car accidents
ALTERNATIVE CARE CHIROPRACTIC Reston, Virginia P ROV E N R E L I E F F RO M W H I P L A S H Any rapid head movement can cause a Whiplash injury. Although whiplash is commonly associated with car accidents
Completing the Loop: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury. Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC
 : Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
: Management of the Adolescent Sports Injury Adam Thomas, PT, DPT, ATC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbufpo 8s3As On field assessment can be the most efficient when the health care provider has observed
Whiplash Associated Disorder
 Whiplash Associated Disorder The pathology Whiplash is a mechanism of injury, consisting of acceleration-deceleration forces to the neck. Mechanism: Hyperflexion/extension injury Stationary vehicle hit
Whiplash Associated Disorder The pathology Whiplash is a mechanism of injury, consisting of acceleration-deceleration forces to the neck. Mechanism: Hyperflexion/extension injury Stationary vehicle hit
CHAPTER 3: BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES. Standing Quad Stretch Athletic Edge - www.athleticedge.biz - (650) 815-6552
 CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
Thoracic and Chest Pain Anatomy Risk Factors and Prevention Posture: Increased thoracic curve
 Thoracic and Chest Pain The thoracic spine is the region of the spine least likely to be injured in sport when compared to the cervical and lumbar region. However, this region can contribute to lumbar
Thoracic and Chest Pain The thoracic spine is the region of the spine least likely to be injured in sport when compared to the cervical and lumbar region. However, this region can contribute to lumbar
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders
 Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Thoracic Spine. Anatomy, Kinesiology and Pathology of the Thoracic Spine. Thoracic Spine. Function of the Thoracic Spine.
 Anatomy, Kinesiology and Pathology of the Thoracic Spine Beth K. Deschenes, PT, MS, OCS Thoracic Spine Consists of thorax, rib cage and sternum 12 vertebrae and 12 ribs Function of the Thoracic Spine Support
Anatomy, Kinesiology and Pathology of the Thoracic Spine Beth K. Deschenes, PT, MS, OCS Thoracic Spine Consists of thorax, rib cage and sternum 12 vertebrae and 12 ribs Function of the Thoracic Spine Support
Neck and Headache Pain
 Neck and Headache Pain ICD-9-CM code: 723.2 cervicocranial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain code: d4158 Maintaining a body position, other specified - specified as: maintaining the
Neck and Headache Pain ICD-9-CM code: 723.2 cervicocranial syndrome ICF codes: Activities and Participation Domain code: d4158 Maintaining a body position, other specified - specified as: maintaining the
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE HIP The Hip Joint ANATOMY OF THE HIP The hip bones are divided into 5 areas, which are: Image: www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/ hwkb17_042.jpg The hip joint is
Specific massage movements.
 Specific massage movements. Exclusive Body Digi-Esth Esthétique movements Awakening Prelude 5 min + Specific movements Relaxing 30 min Aromatic bags 30 min Plantar 20 min Hands 10 min = Position of the
Specific massage movements. Exclusive Body Digi-Esth Esthétique movements Awakening Prelude 5 min + Specific movements Relaxing 30 min Aromatic bags 30 min Plantar 20 min Hands 10 min = Position of the
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Headache. Neuromuscular changes in cervicogenic headache and implications for practice. Cervicogenic Headache. Cervicogenic Headache
 Headache Neuromuscular changes in cervicogenic and implications for practice Deborah Falla Headache is a common complaint which only 1% of the population escape in their lifetimes The most common are the
Headache Neuromuscular changes in cervicogenic and implications for practice Deborah Falla Headache is a common complaint which only 1% of the population escape in their lifetimes The most common are the
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
How to Get and Keep a Healthy Back. Amy Eisenson, B.S. Exercise Physiologist
 How to Get and Keep a Healthy Back Amy Eisenson, B.S. Exercise Physiologist Lesson Objectives Statistics of Back Pain Anatomy of the Spine Causes of Back Pain Four Work Factors Core Muscles Connection
How to Get and Keep a Healthy Back Amy Eisenson, B.S. Exercise Physiologist Lesson Objectives Statistics of Back Pain Anatomy of the Spine Causes of Back Pain Four Work Factors Core Muscles Connection
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
*A discrete, hypersensitive nodule within tight band of muscle or fascia that present with classic pattern of pain referral that does not follow
 A patient presents with c/o cervical spine pain and chronic headaches that radiates across the top of his head. He also experiences frequent bouts of nausea, dizziness and indigestion. The patient also
A patient presents with c/o cervical spine pain and chronic headaches that radiates across the top of his head. He also experiences frequent bouts of nausea, dizziness and indigestion. The patient also
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report
 Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Pathoanatomical Changes of the Brachial Plexus and of C5-C6 Following Whiplash-Type Injury: A Case Report 1 Journal Of Whiplash & Related Disorders Vol. 1, No, 1, 2002 Gunilla Bring, Halldor Jonsson Jr.,
Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Case Studies Updated 10.24.11
 S O L U T I O N S Case Studies Updated 10.24.11 Hill DT Solutions Cervical Decompression Case Study An 18-year-old male involved in a motor vehicle accident in which his SUV was totaled suffering from
S O L U T I O N S Case Studies Updated 10.24.11 Hill DT Solutions Cervical Decompression Case Study An 18-year-old male involved in a motor vehicle accident in which his SUV was totaled suffering from
Spinal Compression Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
SPASMODIC TORTICOLLIS OR CERVICAL DYSTONIA
 By Jean Pierre BLETON Physical Therapist of the of the Neurology Department of Pr : J L MAS Head of the Department of Functional Retraining Of the Centre Raymond Garcin ( Hôpital Sainte Anne PARIS) Supervised
By Jean Pierre BLETON Physical Therapist of the of the Neurology Department of Pr : J L MAS Head of the Department of Functional Retraining Of the Centre Raymond Garcin ( Hôpital Sainte Anne PARIS) Supervised
