Understanding the Ruminant Animal Digestive System
|
|
|
- Ralph Marshall
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
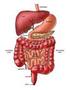
1 Understanding the Ruminant Animal Digestive System Ruminant livestock include cattle, sheep, and goats. Ruminants are hoofed mammals that have a unique digestive system that allows them to better use energy from fibrous plant material than other herbivores. Unlike monogastrics such as swine and poultry, ruminants have a digestive system designed to ferment feedstuffs and provide precursors for energy for the animal to use. By better understanding how the digestive system of the ruminant works, livestock producers can better understand how to care for and feed ruminant animals. Ruminant Digestive Anatomy and Function The ruminant digestive system uniquely qualifies ruminant animals such as cattle to efficiently use high roughage feedstuffs, including forages. Anatomy of the ruminant digestive system includes the mouth, tongue, salivary glands (producing saliva for buffering rumen ph), esophagus, fourcompartment stomach (rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum), pancreas, gall bladder, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum), and large intestine (cecum, colon, and rectum). A ruminant uses its mouth (oral cavity) and tongue to harvest forages during grazing or to consume harvested feedstuffs. Cattle harvest forages during grazing by wrapping their tongues around the plants and then pulling to tear the forage for consumption. On average, cattle take from 25,000 to more than 40,000 prehensile bites to harvest forage while grazing each day. They typically spend more than onethird of their time grazing, one-third of their time ruminating (cud chewing), and slightly less than one-third of their time idling where they are, neither grazing nor ruminating. The roof of the ruminant mouth is a hard/soft palate without incisors. The lower jaw incisors work against this hard dental pad. The incisors of grass/roughage selectors are wide with a shovel-shaped crown, while those of concentrate selectors are narrower and chiselshaped. Premolars and molars match between upper and lower jaws. These teeth crush and grind plant material during initial chewing and rumination. Saliva aids in chewing and swallowing, contains enzymes for breakdown of fat (salivary lipase) and starch (salivary amylase), and is involved in nitrogen recycling to the rumen. Saliva s most important function is to buffer ph levels in the reticulum and rumen. A mature cow produces up to 50 quarts of saliva per day, but this varies, depending on the amount of time spent chewing feed, because that stimulates saliva production. Forage and feed mixes with saliva containing sodium, potassium, phosphate, bicarbonate, and urea when consumed, to form a bolus. That bolus then moves from the mouth to the reticulum through a tube-like passage called the esophagus. Muscle contractions and pressure differences carry these substances down the esophagus to the reticulum. Ruminants eat rapidly, swallowing much of their feedstuffs without chewing it sufficiently (< 1.5 inches). The esophagus functions bidirectionally in ruminants, allowing them to regurgitate their cud for further chewing, if necessary. The process of rumination or chewing the cud is where forage and other feedstuffs are
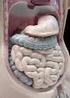
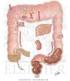
2 forced back to the mouth for further chewing and mixing with saliva. This cud is then swallowed again and passed into the reticulum. Then the solid portion slowly moves into the rumen for fermentation, while most of the liquid portion rapidly moves from the reticulorumen into the omasum and then abomasum. The solid portion left behind in the rumen typically remains for up to 48 hours and forms a dense mat in the rumen, where microbes can use the fibrous feedstuffs to make precursors for energy. True ruminants, such as cattle, sheep, goats, deer, and antelope, have one stomach with four compartments: the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasums. The ruminant stomach occupies almost 75 percent of the abdominal cavity, filling nearly all of the left side and extending significantly into the right side. The relative size of the four compartments is as follows: the rumen and reticulum comprise 84 percent of the volume of the total stomach, the omasum 12 percent, and the abomasum 4 percent. The rumen is the largest stomach compartment, holding up to 40 gallons in a mature cow. The reticulum holds approximately 5 gallons in the mature cow. Typically, the rumen and reticulum are considered one organ because they have similar functions and are separated only by a small muscular fold of tissue. They are collectively referred to as the reticulorumen. The omasum and abomasum hold up to 15 and 7 gallons, respectively, in the mature cow. The reticulorumen is home to a population of microorganisms (microbes or rumen bugs ) that include bacteria, protozoa, and fungi. These microbes ferment and break down plant cell walls into their carbohydrate fractions and produce volatile fatty acids (VFAs), such as acetate (used for fat synthesis), priopionate (used for glucose synthesis), and butyrate from these carbohydrates. The animal later uses these VFAs for energy. The reticulum is called the honeycomb because of the honeycomb appearance of its lining. It sits underneath and toward the front of the rumen, lying against the diaphragm. Ingesta flow freely between the reticulum and rumen. The main function of the reticulum is to collect smaller digesta particles and move them into the omasum, while the larger particles remain in the rumen for further digestion. Honeycomb interior lining of the reticulum in an 8-week old calf Right-sided view of ruminant digestive tract Left-sided view of ruminant digestive tract The reticulum also traps and collects heavy/dense objects the animal consumes. When a ruminant consumes a nail, wire, or other sharp heavy object, it is very likely the object will be caught in the reticulum. During normal digestive tract contractions, this object can penetrate the reticulum wall and make its way to the heart, where it can lead to hardware disease. The reticulum is sometimes referred to as the hardware stomach. Hardware disease is discussed in detail in Mississippi State University Extension Service Publication 2519, Beef Cattle Nutritional Disorders. The rumen is sometimes called the paunch. It is lined with papillae for nutrient absorption and divided by muscular pillars into the dorsal, ventral, caudodorsal, and caudoventral sacs. The rumen acts as a fermentation vat by hosting microbial fermentation. About 50 to 65 percent of starch and soluble sugar consumed is digested in the rumen. Rumen microorganisms (primarily bacteria) digest cellulose from plant cell walls, digest complex starch, synthesize protein from nonprotein nitrogen, and synthesize B vitamins and vitamin
3 K. Rumen ph typically ranges from 6.5 to 6.8. The rumen environment is anaerobic (without oxygen). Gases produced in the rumen include carbon dioxide, methane, and hydrogen sulfide. The gas fraction rises to the top of the rumen above the liquid fraction. enzymes secreted from the pancreas, such as pancreatic lipase (breaks down fats). These secretions help prepare proteins for absorption in the intestines. The ph in the abomasum generally ranges from 3.5 to 4.0. The chief cells in the abomasum secrete mucous to protect the abomasal wall from acid damage. Interior lining of the rumen, revealing papillae in an 8-week old calf The omasum is spherical and connected to the reticulum by a short tunnel. It is called the many piles or the butcher s bible in reference to the many folds or leaves that resemble pages of a book. These folds increase the surface area, which increases the area that absorbs nutrients from feed and water. Water absorption occurs in the omasum. Cattle have a highly developed, large omasum. Interior lining of the omasum, revealing the many piles tissue folds in an 8-week old calf The abomasum is the true stomach of a ruminant. It is the compartment that is most similar to a stomach in a nonruminant. The abomasum produces hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes, such as pepsin (breaks down proteins), and receives digestive Interior lining of the abomasum, the true stomach, in an 8-week old calf The small and large intestines follow the abomasum as further sites of nutrient absorption. The small intestine is a tube up to 150 feet long with a 20-gallon capacity in a mature cow. Digesta entering the small intestine mix with secretions from the pancreas and liver, which elevate the ph from 2.5 to between 7 and 8. This higher ph is needed for enzymes in the small intestine to work properly. Bile from the gall bladder is secreted into the first section of the small intestine, the duodenum, to aid in digestion. Active nutrient absorption occurs throughout the small intestine, including rumen bypass protein absorption. The intestinal wall contains numerous finger-like projections called villi that increase intestinal surface area to aid in nutrient absorption. Muscular contractions aid in mixing digesta and moving it to the next section. The large intestine absorbs water from material passing through it and then excretes the remaining material as feces from the rectum. The cecum is a large blind pouch at the beginning of the large intestine, approximately 3 feet long with a 2-gallon capacity in the mature cow. The cecum serves little function in a ruminant, unlike its role in horses. The colon is the site of most of the water absorption in the large intestine. Ruminant Digestive Development Immature ruminants, such as young, growing calves from birth to about 2 to 3 months of age, are functionally nonruminants. The reticular groove (sometimes referred to as esophageal groove) in these young animals is formed by muscular folds of the reticulum. It shunts milk directly to the omasum and then aboma-
4 sum, bypassing the reticulorumen. The rumen in these animals must be inoculated with rumen microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. This is thought to be accomplished through mature ruminants licking calves and environmental contact with these microorganisms. Immature ruminants must undergo reticulorumenomasal growth, including increases in volume and muscle. In a calf at birth, the abomasum is the largest compartment of the stomach, making up more than 50 percent of the total stomach area. The reticulorumen and omasum account for 35 percent and 14 percent of the total stomach area in the newborn calf. As ruminants develop, the reticulorumen and omasum grow rapidly and account for increasing proportions of the total stomach area. In mature cattle, the abomasum encompasses only 21 percent of the total stomach capacity, whereas the reticulorumen and omasum make up 62 and 24 percent, respectively, of the total stomach area. Rumen papillae (sites of nutrient absorption) lengthen and decrease in numbers as part of rumen development. Relative proportions of stomach compartments in cattle and sheep at various ages Because immature ruminants do not have a functional rumen, feeding recommendations differ for developing ruminants compared with adult ruminants. For instance, it is recommended immature ruminants are not allowed access to feeds containing non-protein nitrogen such as urea. Developing ruminants are also more sensitive to gossypol and dietary fat levels than mature ruminants. Design nutritional programs for ruminants considering animal age. Ruminant Feeding Types Based on the diets they prefer, ruminants can be classified into distinct feeding types: concentrate selectors, grass/roughage eaters, and intermediate types. The relative sizes of various digestive system organs differ by ruminant feeding type, creating differences in feeding adaptations. Knowledge of grazing preferences and adaptations amongst ruminant livestock species helps in planning grazing systems for each individual species and also for multiple species grazed together or on the same acreage. Concentrate selectors have a small reticulorumen in relation to body size and selectively browse trees and shrubs. Deer and giraffes are examples of concentrate selectors. Animals in this group of ruminants select plants and plant parts high in easily digestible, nutrient dense substances such as plant starch, protein, and fat. For example, deer prefer legumes over grasses. Concentrate selectors are very limited in their ability to digest the fibers and cellulose in plant cell walls. Grass/roughage eaters (bulk and roughage eaters) include cattle and sheep. These ruminants depend on diets of grasses and other fibrous plant material. They prefer diets of fresh grasses over legumes but can adequately manage rapidly fermenting feedstuffs. Grass/roughage eaters have much longer intestines relative to body length and a shorter proportion of large intestine to small intestine as compared with concentrate selectors.
5 Goats are classified as intermediate types and prefer forbs and browse such as woody, shrubby type plants. This group of ruminants has adaptations of both concentrate selectors and grass/roughage eaters. They have a fair though limited capacity to digest cellulose in plant cell walls. Carbohydrate Digestion Forages On high-forage diets ruminants often ruminate or regurgitate ingested forage. This allows them to chew their cud to reduce particle size and improve digestibility. As ruminants are transitioned to higher concentrate (grain-based) diets, they ruminate less. Once inside the reticulorumen, forage is exposed to a unique population of microbes that begin to ferment and digest the plant cell wall components and break these components down into carbohydrates and sugars. Rumen microbes use carbohydrates along with ammonia and amino acids to grow. The microbes ferment sugars to produce VFAs (acetate, propionate, butyrate), methane, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon dioxide. The VFAs are then absorbed across the rumen wall, where they go to the liver. Once at the liver, the VFAs are converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis. Because plant cell walls are slow to digest, this acid production is very slow. Coupled with routine rumination (chewing and rechewing of the cud) that increases salivary flow, this makes for a rather stable ph environment (around 6.0). High-Concentrate Feedstuffs (Grains) When ruminants are fed high-grain or concentrate rations, the digestion process is similar to forage digestion, with a few exceptions. Typically, on a high-grain diet, there is less chewing and ruminating, which leads to less salivary production and buffering agents being produced. Additionally, most grains have a high concentration of readily digestible carbohydrates, unlike the more structural carbohydrates found in plant cell walls. This readily digestible carbohydrate is rapidly digested, resulting in an increase in VFA production. The relative concentrations of the VFAs are also changed, with propionate being produced in the greatest quantity, followed by acetate and butyrate. Less methane and heat are produced as well. The increase in VFA production leads to a more acidic environment (ph 5.5). It also causes a shift in the microbial population by decreasing the forage using microbial population and potentially leading to a decrease in digestibility of forages. Lactic acid, a strong acid, is a byproduct of starch fermentation. Lactic acid production, coupled with the increased VFA production, can overwhelm the ruminant s ability to buffer and absorb these acids and lead to metabolic acidosis. The acidic environment leads to tissue damage within the rumen and can lead to ulcerations of the rumen wall. Take care to provide adequate forage and avoid situations that might lead to acidosis when feeding ruminants high-concentrate diets. Acidosis is discussed in detail in Mississippi State University Extension Service Publication 2519, Beef Cattle Nutritional Disorders. In addition, energy as a nutrient in ruminant diets is discussed in detail in Mississippi State University Extension Service Publication 2504, Energy in Beef Cattle Diets. Protein Digestion Two sources of protein are available for the ruminant to use: protein from feed and microbial protein from the microbes that inhabit its rumen. A ruminant is unique in that it has a symbiotic relationship with these microbes. Like other living creatures, these microbes have requirements for protein and energy to facilitate growth and reproduction. During digestive contractions, some of these microorganisms are washed out of the rumen into the abomasum where they are digested like other proteins, thereby creating a source of protein for the animal. All crude protein (CP) the animal ingests is divided into two fractions, degradable intake protein (DIP) and undegradable intake protein (UIP, also called rumen bypass protein ). Each feedstuff (such as cottonseed meal, soybean hulls, and annual ryegrass forage) has different proportions of each protein type. Rumen microbes break down the DIP into ammonia (NH 3 ) amino acids, and peptides, which are used by the microbes along with energy from carbohydrate digestion for growth and reproduction. Protein digestion in the ruminant Excess ammonia is absorbed via the rumen wall and
6 converted into urea in the liver, where it returns in the blood to the saliva or is excreted by the body. Urea toxicity comes from overfeeding urea to ruminants. Ingested urea is immediately degraded to ammonia in the rumen. When more ammonia than energy is available for building protein from the nitrogen supplied by urea, the excess ammonia is absorbed through the rumen wall. Toxicity occurs when the excess ammonia overwhelms the liver s ability to detoxify it into urea. This can kill the animal. However, with sufficient energy, microbes use ammonia and amino acids to grow and reproduce. The rumen does not degrade the UIP component of feedstuffs. The UIP bypasses the rumen and makes its way from the omasum to the abomasum. In the abomasum, the ruminant uses UIP along with microorganisms washed out of the rumen as a protein source. Protein as a nutrient in ruminant diets is discussed in detail in Mississippi State University Extension Service Publication 2499, Protein in Beef Cattle Diets. Importance of Ruminant Livestock The digestive system of ruminants optimizes use of rumen microbe fermentation products. This adaptation lets ruminants use resources (such as high-fiber forage) that cannot be used by or are not available to other animals. Ruminants are in a unique position of being able to use such resources that are not in demand by humans but in turn provide man with a vital food source. Ruminants are also useful in converting vast renewable resources from pasture into other products for human use such as hides, fertilizer, and other inedible products (such as horns and bone). One of the best ways to improve agricultural sustainability is by developing and using effective ruminant livestock grazing systems. More than 60 percent of the land area in the world is too poor or erodible for cultivation but can become productive when used for ruminant grazing. Ruminant livestock can use land for grazing that would otherwise not be suitable for crop production. Ruminant livestock production also complements crop production, because ruminants can use the byproducts of these crop systems that are not in demand for human use or consumption. Developing a good understanding of ruminant digestive anatomy and function can help livestock producers better plan appropriate nutritional programs and properly manage ruminant animals in various production systems. References
7 Church, D. C. ed The Ruminant Animal Digestive Physiology and Nutrition. Waveland Press, Inc. Prospect Heights, IL. Oltjen, J. W., and J. L. Beckett Role of ruminant livestock in sustainable agricultural systems. J. Anim. Sci. 74: Parish, J. A., M. A. McCann, R. H. Watson, N. N. Paiva, C. S. Hoveland, A. H. Parks, B. L. Upchurch, N. S. Hill, and J. H. Bouton Use of non-ergot alkaloid-producing endophytes for alleviating tall fescue toxicosis in stocker cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 81: Van Soest, P. J Nutritional Ecology of the Ruminant. Cornell University Press. Ithaca, NY. Photographs of the ruminant digestive system are courtesy of Dr. Stephanie R. Hill, assistant research professor, Animal and Dairy Sciences, Mississippi State University.
8 Copyright 2009 by Mississippi State University. All rights reserved. This publication may be copied and distributed without alteration for nonprofit educational purposes provided that credit is given to the Mississippi State University Extension Service. By Dr. Jane A. Parish, Associate Extension/Research Professor; Dr. J. Daniel Rivera, Assistant Extension Professor; and Dr. Holly T. Boland, Assistant Research/Extension Professor Discrimination based upon race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or veteran s status is a violation of federal and state law and MSU policy and will not be tolerated. Discrimination based upon sexual orientation or group affiliation is a violation of MSU policy and will not be tolerated. Publication 2503 Extension Service of Mississippi State University, cooperating with U.S. Department of Agriculture. Published in furtherance of Acts of Congress, May 8 and June 30, MELISSA J. MIXON, Interim Director POD 08-09
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Ruminant Digestive System
 Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
The Goat s Digestive System. Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County
 The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf
 3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION
 EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Mammalian digestive tracts
 Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology
 Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources. Introduction
 Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Teaching Basic Equine Nutrition Part II: Equine Digestive Anatomy and Physiology
 Teaching Basic Equine Nutrition Part II: Equine Digestive Anatomy and Physiology Introduction A sound nutritional program is important to ensure that horses are happy, healthy, and perform to their best.
Teaching Basic Equine Nutrition Part II: Equine Digestive Anatomy and Physiology Introduction A sound nutritional program is important to ensure that horses are happy, healthy, and perform to their best.
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
World of Dairy Cattle Nutrition
 World of Dairy Cattle Nutrition INTRODUCTION Most kids are taught to eat their fruits and vegetables. Why? Because they are good for you, and provide several essential vitamins and minerals for a healthy,
World of Dairy Cattle Nutrition INTRODUCTION Most kids are taught to eat their fruits and vegetables. Why? Because they are good for you, and provide several essential vitamins and minerals for a healthy,
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management
 Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA3038 Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management Steven M. Jones Associate Professor Animal Science Animals have different types of digestive systems based
Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA3038 Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management Steven M. Jones Associate Professor Animal Science Animals have different types of digestive systems based
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets
 Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock
 Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock High moisture conditions often lead to crop damage and losses. Some losses are from grain sprouting in the head before harvest. These sprouted grains
Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock High moisture conditions often lead to crop damage and losses. Some losses are from grain sprouting in the head before harvest. These sprouted grains
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
Classifications of animals: ruminant vs non-ruminant carnivore: meat-eating herbivore: plant-eating omnivore: both meat and plant-eating
 Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
Digestion and Metabolism Digestive tract one long, continuous tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus Functions Ingestion Grinding Digestion/absorption of food Elimination of solid wastes Classifications
1. About dairy cows. Breed of dairy cows
 1. About dairy cows Breed of dairy cows Holstein Holstein is a typical dairy cow, and 99% of dairy cows in Japan are Holsteins. They are originally from the Netherlands and Holstein region of Germany.
1. About dairy cows Breed of dairy cows Holstein Holstein is a typical dairy cow, and 99% of dairy cows in Japan are Holsteins. They are originally from the Netherlands and Holstein region of Germany.
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION
 Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
BEC Feed Solutions. Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions
 BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
Caecotrophy in Rabbits
 Caecotrophy In Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. January 2008 Caecotrophy in Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
Caecotrophy In Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. January 2008 Caecotrophy in Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
PRACTICAL ECONOMICS OF "ACCELERATED" CALF FEEDING PROGRAMS
 PRACTICAL ECONOMICS OF "ACCELERATED" CALF FEEDING PROGRAMS Howard Tyler Department of Animal Science Iowa State University Labor costs per animal and costs per unit of gain are higher in the preweaned
PRACTICAL ECONOMICS OF "ACCELERATED" CALF FEEDING PROGRAMS Howard Tyler Department of Animal Science Iowa State University Labor costs per animal and costs per unit of gain are higher in the preweaned
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
Digestive System. Student Learning Objectives: Structures to be studied: Introduction
 Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Pre-requisites: Successful completion of 4th grade science and the 4th grade science assessment.
 Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
High-Fiber Low-Starch Diets: The New Nutritional Wisdom Kathleen Crandell, Ph.D.
 High-Fiber Low-Starch Diets: The New Nutritional Wisdom Kathleen Crandell, Ph.D. Just about everybody has heard the hype about low-starch or high-fiber diets for horses, but what is the rationale behind
High-Fiber Low-Starch Diets: The New Nutritional Wisdom Kathleen Crandell, Ph.D. Just about everybody has heard the hype about low-starch or high-fiber diets for horses, but what is the rationale behind
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System. The large intestine, or colon, holds waste products until elimination can occur. Its main function is to absorb.
 The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows
 Feed Management A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College
Feed Management A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
Presentation Notes Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
 Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands
 Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands Cooperative Extension Service Circular 564 College of Agriculture and Home Economics CONTENTS General ruminant nutrition...
Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands Cooperative Extension Service Circular 564 College of Agriculture and Home Economics CONTENTS General ruminant nutrition...
Feeding Corn to Beef Cows
 ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version
 The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System
 General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Why Do Animals Eat the Bark and Wood of Trees and Shrubs?
 Purdue University Forestry and Natural Resources FNR-203 Forestry & Natural Resources PURDUE UNIVERSITY Why Do Animals Eat the Bark and Wood of Trees and Shrubs? William R. Chaney, Professor of Tree Physiology
Purdue University Forestry and Natural Resources FNR-203 Forestry & Natural Resources PURDUE UNIVERSITY Why Do Animals Eat the Bark and Wood of Trees and Shrubs? William R. Chaney, Professor of Tree Physiology
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario)
 Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs
 61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
What a re r Lipids? What a re r Fatty y Ac A ids?
 2010 - Beef Cattle In-Service Training Inclusion of Lipids into Beef Cattle Diets Reinaldo F. Cooke, Ph. D. Oregon State University EOARC, Burns What are Lipids? Organic compounds Plant and animal compounds
2010 - Beef Cattle In-Service Training Inclusion of Lipids into Beef Cattle Diets Reinaldo F. Cooke, Ph. D. Oregon State University EOARC, Burns What are Lipids? Organic compounds Plant and animal compounds
Energy in the New Dairy NRC. Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University
 Energy in the New Dairy NRC Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University Introduction Energy is vital to the function of all cells, and thus physiologically, it is vital
Energy in the New Dairy NRC Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University Introduction Energy is vital to the function of all cells, and thus physiologically, it is vital
Summary. Keywords: methanol, glycerin, intake, beef cattle. Introduction
 Effect of Methanol Infusion on Intake and Digestion of a Grain-based Diet by Beef Cattle K.N. Winsco, N.M. Kenney, R.O. Dittmar, III, J.A. Coverdale, J.E. Sawyer, and T.A. Wickersham Texas A & M University,
Effect of Methanol Infusion on Intake and Digestion of a Grain-based Diet by Beef Cattle K.N. Winsco, N.M. Kenney, R.O. Dittmar, III, J.A. Coverdale, J.E. Sawyer, and T.A. Wickersham Texas A & M University,
Introduction. Digestive System. Physiology. Anatomy. Physiology. Alimentary Canal. Chapter 21
 Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
