EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 Memory 1. Memory Basics
|
|
|
- Polly Merritt
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 Memory 1 March 17, 2005 John Wawrzynek Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 1 Memory Basics Uses: Whenever a large collection of state elements is required. data & program storage general purpose registers buffering table lookups CL implementation Example RAM: Register file from microprocessor clk Types: RAM - random access memory ROM - read only memory EPROM, FLASH - electrically programmable read only memory regid = register identifier (address of word in memory) sizeof(regid) = log2(# of reg) WE = write enable Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 2 1
2 Definitions Memory Interfaces for Accessing Data Asynchronous (unclocked): A change in the address results in data appearing Synchronous (clocked): A change in address, followed by an edge on CLK results in data appearing or write operation occurring. A common arrangement is to have synchronous write operations and asynchronous read operations. Volatile: Looses its state when the power goes off. Nonvolatile: Retains it state when power goes off. Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 3 For read operations, functionally the regfile is equivalent to a 2-D array of flip-flops with tristate outputs on each: Register File Internals Cell with added write logic: These circuits are just functional abstractions of the actual circuits used. How do we go from "regid" to "SEL"? Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 4 2
3 Regid (address) Decoding The function of the address decoder is to generate a one-hot code word from the address. The output is use for row selection. Many different circuits exist for this function. A simple one is shown to the right. Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 5 Standard Internal Memory Organization 2-D arrary of bit cells. Each cell stores one bit of data. Special circuit tricks are used for the cell array to improve storage density. (We will look at these later) RAM/ROM naming convention: examples: 32 X 8, "32 by 8" => 32 8-bit words 1M X 1, "1 meg by 1" => 1M 1-bit words Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 6 3
4 Read Only Memory (ROM) Simply for of memory. No write operation needed. Functional Equivalence: Connections to Vdd used to store a logic 1, connections to GND for storing logic 0. address decoder bit-cell array Full tri-state buffers are not needed at each cell point. In practice, single transistors are used to implement zero cells. Logic one s are derived through precharging or bit-line pullup transistor. Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 7 Column MUX in ROMs and RAMs: Controls physical aspect ratio Important for physical layout and to control delay on wires. In DRAM, allows time-multiplexing of chip address pins Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 8 4
5 Cascading Memory Modules (or chips) Example: assemblage of 256 x 8 ROM using 256 x 4 modules: example: 1K x * ROM using 256 x 4 modules: each module has tri-state outputs: Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 9 Memory Components Types: Volatile: Random Access Memory (RAM): DRAM "dynamic" SRAM "static" Non-volatile: Read Only Memory (ROM): Mask ROM "mask programmable" EPROM "electrically programmable" EEPROM "erasable electrically programmable" FLASH memory - similar to EEPROM with programmer integrated on chip Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 10 5
6 Volatile Memory Comparison The primary difference between different memory types is the bit cell. SRAM Cell DRAM Cell word line word line bit line bit line bit line Larger cell lower density, higher cost/bit No refresh required Simple read faster access Standard IC process natural for integration with logic Smaller cell higher density, lower cost/bit Needs periodic refresh, and refresh after read Complex read longer access time Special IC process difficult to integrate with logic circuits Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 11 Multi-ported Memory Motivation: Consider CPU core register file: 1 read or write per cycle limits processor performance. Complicates pipelining. Difficult for different instructions to simultaneously read or write regfile. Common arrangement in pipelined CPUs is 2 read ports and 1 write port. sel a sel b sel c data b data a Regfile data c Motivation: I/O data buffering: disk/network data buffer CPU dual-porting allows both sides to simultaneously access memory at full bandwidth. addr a data a RW a addr b data b RW b Dual-port Memory Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 12 6
7 Dual-ported Memory Internals Add decoder, another set of read/write logic, bits lines, word lines: dec a dec b cell array Example cell: SRAM WL 2 WL 1 b 2 b 1 b 1 b 2 address ports data ports r/w logic r/w logic Repeat everything but crosscoupled inverters. This scheme extends up to a couple more ports, then need to add additional transistors. Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 13 Memory in Desktop Computer Systems: SRAM (lower density, higher speed) used in CPU register file, on- and off-chip caches. DRAM (higher density, lower speed) used in main memory Closing the GAP: 1. Caches are growing in size. 2. Innovation targeted towards higher bandwidth for memory systems: SDRAM - synchronous DRAM RDRAM - Rambus DRAM EDORAM - extended data out SRAM Three-dimensional RAM hyper-page mode DRAM video RAM multibank DRAM Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 14 7
8 Important DRAM Examples: EDO - extended data out (similar to fast-page mode) RAS cycle fetched rows of data from cell array blocks (long access time, around 100ns) Subsequent CAS cycles quickly access data from row buffers if within an address page (page is around 256 Bytes) SDRAM - synchronous DRAM clocked interface uses dual banks internally. Start access in one bank then next, then receive data from first then second. DDR - Double data rate SDRAM Uses both rising (positive edge) and falling (negative) edge of clock for data transfer. (typical 100MHz clock with 200 MHz transfer). RDRAM - Rambus DRAM Entire data blocks are access and transferred out on a high-speed bus-like interface (500 MB/s, 1.6 GB/s) Tricky system level design. More expensive memory chips. Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 15 Non-volatile Memory Used to hold fixed code (ex. BIOS), tables of data (ex. FSM next state/output logic), slowly changing values (date/time on computer) Mask ROM Used with logic circuits for tables etc. Contents fixed at IC fab time (truly write once!) EPROM (erasable programmable) & FLASH requires special IC process (floating gate technology) writing is slower than RAM. EPROM uses special programming system to provide special voltages and timing. reading can be made fairly fast. rewriting is very slow. erasure is first required, EPROM - UV light exposure, EEPROM electrically erasable Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 16 8
9 FLASH Memory Electrically erasable In system programmability and erasability (no special system or voltages needed) On-chip circuitry (FSM) and voltage generators to control erasure and programming (writing) Erasure happens in variable sized "sectors" in a flash (16K - 64K Bytes) See: for product descriptions, etc. Compact flash cards are based on this type of memory. Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 17 Memory Specification in Verilog Memory modeled by an array of registers: reg[15:0] memword[0:1023]; // 1,024 registers of 16 bits each //Example Memory Block Specification // Uses enable to control both write and read // //Read and write operations of memory. //Memory size is 64 words of 4 bits each. module memory (Enable,ReadWrite,Address,DataIn,DataOut); input Enable,ReadWrite; input [3:0] DataIn; input [5:0] Address; output [3:0] DataOut; reg [3:0] DataOut; reg [3:0] Mem [0:63]; //64 x 4 memory (Enable or ReadWrite) if (Enable) if (ReadWrite) DataOut = Mem[Address]; //Read else Mem[Address] = DataIn; //Write else DataOut = 4'bz; //High impedance state endmodule Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 18 9
10 Memory Blocks in FPGAs LUTs can double as small RAM blocks: 4-LUT is really a 16x1 memory. Normally we think of the contents being written from the configuration bit stream, but Virtex architecture (and others) allow bits of LUT to be written and read from the general interconnect structure. achieves 16x density advantage over using CLB flipflops. Furthermore, the two LUTs within a slice can be combined to create a 16 x 2-bit or 32 x 1-bit synchronous RAM, or a 16x1-bit dual-port synchronous RAM. The Virtex-E LUT can also provide a 16-bit shift register of adjustable length. Newer FPGA families include larger on-chip RAM blocks (usually dual ported): Called block selectrams in Xilinx Virtex series 4k bits each RAM16X1S Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 19 WE D WCLK D WCLK A0 A1 A2 A3 DPRA0 DPRA1 DPRA2 DPRA3 WE A0 A1 A2 A3 RAM16X1D X4950 SPO DPO X4942 one read port, one write port O Synchronous write, asynchronous read D CE CLK A0 A1 A2 A3 SRL16E_1 X8421 Q Length controlled by A0-A3 Verilog Specification for Virtex LUT RAM module ram16x1(q, a, d, we, clk); output q; input d; input [3:0] a; input clk, we; reg mem [15:0]; clk) begin if(we) mem[a] <= d; end assign q = mem[a]; endmodule Note: synchronous write and asynchronous read. WE D WCLK A0 A1 A2 A3 RAM16X1S X4942 Deeper and/or wider RAMs can be specified and the synthesis tool will do the job of wiring together multiple LUTs. How does the synthesis tool choose to implement your RAM as a collection of LUTs or as block RAMs? O Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 20 10
11 Each block SelectRAM (block RAM) is a fully synchronous (synchronous write and read) dual-ported (true dual port) 4096-bit RAM with independent control signals for each port. The data widths of the two ports can be configured independently, providing built-in bus-width conversion. CLKA and CLKB can be independent, providing an easy way to cross clock bounders. Around 160 of these on the 2000E. Multiples can be combined to implement, wider or deeper memories. See chapter 8 of Synplify reference manual on how to write Verilog for implied Block RAMs. Or instead, explicitly instantiate as primitive (project checkpoint will use this method). Virtex Block RAMs Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 21 Tabl WEA ENA RSTA CLKA ADDRA[#:0] DIA[#:0] WEB ENB RSTB CLKB ADDRB[#:0] DIB[#:0] DOA[#:0] DOB[#:0] 5: Block SelectRAM Port Aspect Ratios Width Depth ADDR Bus Data Bus ADDR<11:0> DATA<0> ADDR<10:0> DATA<1:0> ADDR<9:0> DATA<3:0> ADDR<8:0> DATA<7:0> ADDR<7:0> DATA<15:0> Relationship between Memory and CL Memory blocks can be (and often are) used to implement combinational logic functions: Examples: LUTs in FPGAs 1Mbit x 8 EPROM can implement 8 independent functions each of log 2 (1M)=20 inputs. The decoder part of a memory block can be considered a minterm generator. The cell array part of a memory block can be considered an OR function over a subset of rows. The combination gives us a way to implement logic functions directly in sum of products form. Several variations on this theme exist in a set of devices called Programmable logic devices (PLDs) Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 22 11
12 A ROM as AND/OR Logic Device Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 23 PLD Summary Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 24 12
13 PLA Example Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 25 PAL Example Spring 2005 EECS150 - Lec17-mem1 Page 26 13
Memory Basics. SRAM/DRAM Basics
 Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy
 1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays
 Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Storage Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Logic Data
Chapter 5 :: Memory and Logic Arrays Digital Design and Computer Architecture David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Storage Copyright 2007 Elsevier 5- ROM Logic Data
A N. O N Output/Input-output connection
 Memory Types Two basic types: ROM: Read-only memory RAM: Read-Write memory Four commonly used memories: ROM Flash, EEPROM Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM), SDRAM, RAMBUS, DDR RAM Generic pin configuration:
Memory Types Two basic types: ROM: Read-only memory RAM: Read-Write memory Four commonly used memories: ROM Flash, EEPROM Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM), SDRAM, RAMBUS, DDR RAM Generic pin configuration:
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic
 NCNU_2013_DD_7_1 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 71I 7.1 Introduction ti 7.2 Random Access Memory 7.3 Memory Decoding 7.5 Read Only Memory 7.6 Programmable Logic Array 77P 7.7 Programmable Array
NCNU_2013_DD_7_1 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 71I 7.1 Introduction ti 7.2 Random Access Memory 7.3 Memory Decoding 7.5 Read Only Memory 7.6 Programmable Logic Array 77P 7.7 Programmable Array
Memory. The memory types currently in common usage are:
 ory ory is the third key component of a microprocessor-based system (besides the CPU and I/O devices). More specifically, the primary storage directly addressed by the CPU is referred to as main memory
ory ory is the third key component of a microprocessor-based system (besides the CPU and I/O devices). More specifically, the primary storage directly addressed by the CPU is referred to as main memory
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Storing data Possible
Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu 2 Storing data Possible
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Homework # 2. Solutions. 4.1 What are the differences among sequential access, direct access, and random access?
 ECE337 / CS341, Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: Victor Manuel Murray Herrera Date assigned: 09/19/05, 05:00 PM Due back: 09/30/05, 8:00 AM Homework # 2 Solutions
ECE337 / CS341, Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: Victor Manuel Murray Herrera Date assigned: 09/19/05, 05:00 PM Due back: 09/30/05, 8:00 AM Homework # 2 Solutions
Memory unit. 2 k words. n bits per word
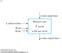 9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
Exploiting Stateful Inspection of Network Security in Reconfigurable Hardware
 Exploiting Stateful Inspection of Network Security in Reconfigurable Hardware Shaomeng Li, Jim Tørresen, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics University of Oslo N-0316 Oslo, Norway {shaomenl, jimtoer,
Exploiting Stateful Inspection of Network Security in Reconfigurable Hardware Shaomeng Li, Jim Tørresen, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics University of Oslo N-0316 Oslo, Norway {shaomenl, jimtoer,
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization
 Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Features. DDR SODIMM Product Datasheet. Rev. 1.0 Oct. 2011
 Features 200pin, unbuffered small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-2100, PC-2700, PC3-3200 Single or Dual rank 256MB(32Megx64), 512MB (64Meg x 64), 1GB(128 Meg x
Features 200pin, unbuffered small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-2100, PC-2700, PC3-3200 Single or Dual rank 256MB(32Megx64), 512MB (64Meg x 64), 1GB(128 Meg x
With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as:
 Memory Classification With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as: - random access memories (RAM), - sequentially accessible memory (SAM), - direct access memory (DAM), - contents
Memory Classification With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as: - random access memories (RAM), - sequentially accessible memory (SAM), - direct access memory (DAM), - contents
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8
 GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 2 Outline Introduction
Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 2 Outline Introduction
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS
 SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic devices Implementing logic with PLDs Static hazards
 Points ddressed in this Lecture Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic
Points ddressed in this Lecture Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic
Computers. Hardware. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer
 Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Random Access Memory (RAM) Types of RAM. RAM Random Access Memory Jamie Tees SDRAM. Micro-DIMM SO-DIMM
 Random Access Memory (RAM) Sends/Receives data quickly between CPU This is way quicker than using just the HDD RAM holds temporary data used by any open application or active / running process Multiple
Random Access Memory (RAM) Sends/Receives data quickly between CPU This is way quicker than using just the HDD RAM holds temporary data used by any open application or active / running process Multiple
Memory ICS 233. Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Prof. Muhamed Mudawar
 Memory ICS 233 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Random
Memory ICS 233 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Prof. Muhamed Mudawar College of Computer Sciences and Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Random
Semiconductor Memories
 Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor memories array capable of storing large quantities of digital information are essential to all digital systems Maximum realizable data storage capacity of a single
Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor memories array capable of storing large quantities of digital information are essential to all digital systems Maximum realizable data storage capacity of a single
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory
 CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives. Units of Memory Capacity. CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 2007-08) Memory and I/O address Decoders. By Dr.
 CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 27-8) Memory and I/O address ecoders By r. Mehmet Bodur You will be able to: Objectives efine the capacity, organization and types of the semiconductor memory devices Calculate
CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 27-8) Memory and I/O address ecoders By r. Mehmet Bodur You will be able to: Objectives efine the capacity, organization and types of the semiconductor memory devices Calculate
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 11 Memory Management Computer Architecture Part 11 page 1 of 44 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte, M.Sc. Benjamin
Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 11 Memory Management Computer Architecture Part 11 page 1 of 44 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte, M.Sc. Benjamin
Technical Note. Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA. Overview. TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview
 Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Handout 17. by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal. Memory Unit and Read Only Memories
 Handout 17 by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal Memory Unit and Read Only Memories Objective: - To discuss different types of memories used in 80x86 systems for storing digital information. - To learn the electronic
Handout 17 by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal Memory Unit and Read Only Memories Objective: - To discuss different types of memories used in 80x86 systems for storing digital information. - To learn the electronic
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Random-Access Memory (RAM) The Memory Hierarchy. SRAM vs DRAM Summary. Conventional DRAM Organization. Page 1
 Random-ccess Memor (RM) The Memor Hierarch Topics Storage technologies and trends Localit of reference Caching in the hierarch Ke features RM is packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is a cell (one bit
Random-ccess Memor (RM) The Memor Hierarch Topics Storage technologies and trends Localit of reference Caching in the hierarch Ke features RM is packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is a cell (one bit
Table 1: Address Table
 DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
Chapter 6. Inside the System Unit. What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future. What You Will Learn... Describing Hardware Performance
 What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design
 Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Memory Systems. Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Cell
 Memory Systems This chapter begins the discussion of memory systems from the implementation of a single bit. The architecture of memory chips is then constructed using arrays of bit implementations coupled
Memory Systems This chapter begins the discussion of memory systems from the implementation of a single bit. The architecture of memory chips is then constructed using arrays of bit implementations coupled
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet
 Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
DDR SDRAM SODIMM. MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com
 SODIMM MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
SODIMM MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
Slide Set 8. for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
DDR4 Memory Technology on HP Z Workstations
 Technical white paper DDR4 Memory Technology on HP Z Workstations DDR4 is the latest memory technology available for main memory on mobile, desktops, workstations, and server computers. DDR stands for
Technical white paper DDR4 Memory Technology on HP Z Workstations DDR4 is the latest memory technology available for main memory on mobile, desktops, workstations, and server computers. DDR stands for
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Memory Testing. Memory testing.1
 Memory Testing Introduction Memory Architecture & Fault Models Test Algorithms DC / AC / Dynamic Tests Built-in Self Testing Schemes Built-in Self Repair Schemes Memory testing.1 Memory Market Share in
Memory Testing Introduction Memory Architecture & Fault Models Test Algorithms DC / AC / Dynamic Tests Built-in Self Testing Schemes Built-in Self Repair Schemes Memory testing.1 Memory Market Share in
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization
 Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Understanding Memory TYPES OF MEMORY
 Understanding Memory TYPES OF MEMORY In this study unit, you ll learn about physical and logical memory. Physical memory comes in two types, random access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM). Typically,
Understanding Memory TYPES OF MEMORY In this study unit, you ll learn about physical and logical memory. Physical memory comes in two types, random access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM). Typically,
Semiconductor Device Technology for Implementing System Solutions: Memory Modules
 Hitachi Review Vol. 47 (1998), No. 4 141 Semiconductor Device Technology for Implementing System Solutions: Memory Modules Toshio Sugano Atsushi Hiraishi Shin ichi Ikenaga ABSTRACT: New technology is producing
Hitachi Review Vol. 47 (1998), No. 4 141 Semiconductor Device Technology for Implementing System Solutions: Memory Modules Toshio Sugano Atsushi Hiraishi Shin ichi Ikenaga ABSTRACT: New technology is producing
Lecture 9: Memory and Storage Technologies
 CS61: Systems Programming and Machine Organization Harvard University, Fall 2009 Lecture 9: Memory and Storage Technologies October 1, 2009 Announcements Lab 3 has been released! You are welcome to switch
CS61: Systems Programming and Machine Organization Harvard University, Fall 2009 Lecture 9: Memory and Storage Technologies October 1, 2009 Announcements Lab 3 has been released! You are welcome to switch
USB - FPGA MODULE (PRELIMINARY)
 DLP-HS-FPGA LEAD-FREE USB - FPGA MODULE (PRELIMINARY) APPLICATIONS: - Rapid Prototyping - Educational Tool - Industrial / Process Control - Data Acquisition / Processing - Embedded Processor FEATURES:
DLP-HS-FPGA LEAD-FREE USB - FPGA MODULE (PRELIMINARY) APPLICATIONS: - Rapid Prototyping - Educational Tool - Industrial / Process Control - Data Acquisition / Processing - Embedded Processor FEATURES:
NAND Flash FAQ. Eureka Technology. apn5_87. NAND Flash FAQ
 What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
DDR SDRAM SODIMM. MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.
 Features DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory
Features DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory
Lecture-3 MEMORY: Development of Memory:
 Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
SDRAM and DRAM Memory Systems Overview
 CHAPTER SDRAM and DRAM Memory Systems Overview Product Numbers: MEM-NPE-32MB=, MEM-NPE-64MB=, MEM-NPE-128MB=, MEM-SD-NPE-32MB=, MEM-SD-NPE-64MB=, MEM-SD-NPE-128MB=, MEM-SD-NSE-256MB=, MEM-NPE-400-128MB=,
CHAPTER SDRAM and DRAM Memory Systems Overview Product Numbers: MEM-NPE-32MB=, MEM-NPE-64MB=, MEM-NPE-128MB=, MEM-SD-NPE-32MB=, MEM-SD-NPE-64MB=, MEM-SD-NPE-128MB=, MEM-SD-NSE-256MB=, MEM-NPE-400-128MB=,
Optimising the resource utilisation in high-speed network intrusion detection systems.
 Optimising the resource utilisation in high-speed network intrusion detection systems. Gerald Tripp www.kent.ac.uk Network intrusion detection Network intrusion detection systems are provided to detect
Optimising the resource utilisation in high-speed network intrusion detection systems. Gerald Tripp www.kent.ac.uk Network intrusion detection Network intrusion detection systems are provided to detect
Prototyping ARM Cortex -A Processors using FPGA platforms
 Prototyping ARM Cortex -A Processors using FPGA platforms Brian Sibilsky and Fredrik Brosser April 2016 Page 1 of 17 Contents Introduction... 3 Gating... 4 RAM Implementation... 7 esign Partitioning...
Prototyping ARM Cortex -A Processors using FPGA platforms Brian Sibilsky and Fredrik Brosser April 2016 Page 1 of 17 Contents Introduction... 3 Gating... 4 RAM Implementation... 7 esign Partitioning...
Experiment # 9. Clock generator circuits & Counters. Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa
 Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology
 Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
CS250 VLSI Systems Design Lecture 8: Memory
 CS250 VLSI Systems esign Lecture 8: Memory John Wawrzynek, Krste Asanovic, with John Lazzaro and Yunsup Lee (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2010 CMOS Bistable 1 0 Flip State 0 1 Cross-coupled inverters used to hold
CS250 VLSI Systems esign Lecture 8: Memory John Wawrzynek, Krste Asanovic, with John Lazzaro and Yunsup Lee (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2010 CMOS Bistable 1 0 Flip State 0 1 Cross-coupled inverters used to hold
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
Configuring Memory on the HP Business Desktop dx5150
 Configuring Memory on the HP Business Desktop dx5150 Abstract... 2 Glossary of Terms... 2 Introduction... 2 Main Memory Configuration... 3 Single-channel vs. Dual-channel... 3 Memory Type and Speed...
Configuring Memory on the HP Business Desktop dx5150 Abstract... 2 Glossary of Terms... 2 Introduction... 2 Main Memory Configuration... 3 Single-channel vs. Dual-channel... 3 Memory Type and Speed...
User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM
 User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM Document No. E0234E30 (Ver.3.0) Date Published April 2002 (K) Japan URL: http://www.elpida.com Elpida Memory, Inc. 2002 INTRODUCTION This manual is intended for users
User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM Document No. E0234E30 (Ver.3.0) Date Published April 2002 (K) Japan URL: http://www.elpida.com Elpida Memory, Inc. 2002 INTRODUCTION This manual is intended for users
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors
 Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Table 1 SDR to DDR Quick Reference
 TECHNICAL NOTE TN-6-05 GENERAL DDR SDRAM FUNCTIONALITY INTRODUCTION The migration from single rate synchronous DRAM (SDR) to double rate synchronous DRAM (DDR) memory is upon us. Although there are many
TECHNICAL NOTE TN-6-05 GENERAL DDR SDRAM FUNCTIONALITY INTRODUCTION The migration from single rate synchronous DRAM (SDR) to double rate synchronous DRAM (DDR) memory is upon us. Although there are many
EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops. Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
Chapter 4 System Unit Components. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Introduction. Jim Duckworth ECE Department, WPI. VHDL Short Course - Module 1
 VHDL Short Course Module 1 Introduction Jim Duckworth ECE Department, WPI Jim Duckworth, WPI 1 Topics Background to VHDL Introduction to language Programmable Logic Devices CPLDs and FPGAs FPGA architecture
VHDL Short Course Module 1 Introduction Jim Duckworth ECE Department, WPI Jim Duckworth, WPI 1 Topics Background to VHDL Introduction to language Programmable Logic Devices CPLDs and FPGAs FPGA architecture
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB
 Features DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM)
Features DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM)
Features. DDR3 SODIMM Product Specification. Rev. 1.7 Feb. 2016
 Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 204pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: DDR3-1066(PC3-8500) DDR3-1333(PC3-10600)
Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 204pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: DDR3-1066(PC3-8500) DDR3-1333(PC3-10600)
7 Series FPGA Overview
 7 Series FPGA Overview 7 Series FPGA Families Maximum Capability Lowest Power and Cost Industry s Best Price/Performance Industry s Highest System Performance Logic Cells Block RAM DSP Slices Peak DSP
7 Series FPGA Overview 7 Series FPGA Families Maximum Capability Lowest Power and Cost Industry s Best Price/Performance Industry s Highest System Performance Logic Cells Block RAM DSP Slices Peak DSP
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain firstname.lastname@tut.fi Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain firstname.lastname@tut.fi Department of Computer
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Contents. Overview... 5-1 Memory Compilers Selection Guide... 5-2
 Memory Compilers 5 Contents Overview... 5-1 Memory Compilers Selection Guide... 5-2 CROM Gen... 5-3 DROM Gen... 5-9 SPSRM Gen... 5-15 SPSRM Gen... 5-22 SPRM Gen... 5-31 DPSRM Gen... 5-38 DPSRM Gen... 5-47
Memory Compilers 5 Contents Overview... 5-1 Memory Compilers Selection Guide... 5-2 CROM Gen... 5-3 DROM Gen... 5-9 SPSRM Gen... 5-15 SPSRM Gen... 5-22 SPRM Gen... 5-31 DPSRM Gen... 5-38 DPSRM Gen... 5-47
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.
 DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR): 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR): 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
OpenSPARC T1 Processor
 OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
Byte Ordering of Multibyte Data Items
 Byte Ordering of Multibyte Data Items Most Significant Byte (MSB) Least Significant Byte (LSB) Big Endian Byte Addresses +0 +1 +2 +3 +4 +5 +6 +7 VALUE (8-byte) Least Significant Byte (LSB) Most Significant
Byte Ordering of Multibyte Data Items Most Significant Byte (MSB) Least Significant Byte (LSB) Big Endian Byte Addresses +0 +1 +2 +3 +4 +5 +6 +7 VALUE (8-byte) Least Significant Byte (LSB) Most Significant
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter
 NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
White Paper Utilizing Leveling Techniques in DDR3 SDRAM Memory Interfaces
 White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Christian Schindelhauer
 Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Solid State Disks Motivation 2 10 5 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 PRODUCTION
Algorithms and Methods for Distributed Storage Networks 3. Solid State Disks Institut für Informatik Wintersemester 2007/08 Solid State Disks Motivation 2 10 5 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 PRODUCTION
Layout of Multiple Cells
 Layout of Multiple Cells Beyond the primitive tier primitives add instances of primitives add additional transistors if necessary add substrate/well contacts (plugs) add additional polygons where needed
Layout of Multiple Cells Beyond the primitive tier primitives add instances of primitives add additional transistors if necessary add substrate/well contacts (plugs) add additional polygons where needed
Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit Design
 Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit esign Outline Sequencing Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay Clock Skew Time Borrowing Two-Phase Clocking 2 Sequencing Combinational logic output depends on current
Lecture 11: Sequential Circuit esign Outline Sequencing Sequencing Element esign Max and Min-elay Clock Skew Time Borrowing Two-Phase Clocking 2 Sequencing Combinational logic output depends on current
Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts)
 Dr. Greg Tumbush, gtumbush@uccs.edu Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
Dr. Greg Tumbush, gtumbush@uccs.edu Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
ADQYF1A08. DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits)
 General Description ADQYF1A08 DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits) The ADATA s ADQYF1A08 is a 128Mx64 bits 1GB DDR2-1066(CL6) SDRAM over clocking memory module, The SPD is programmed
General Description ADQYF1A08 DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits) The ADATA s ADQYF1A08 is a 128Mx64 bits 1GB DDR2-1066(CL6) SDRAM over clocking memory module, The SPD is programmed
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Qsys and IP Core Integration
 Qsys and IP Core Integration Prof. David Lariviere Columbia University Spring 2014 Overview What are IP Cores? Altera Design Tools for using and integrating IP Cores Overview of various IP Core Interconnect
Qsys and IP Core Integration Prof. David Lariviere Columbia University Spring 2014 Overview What are IP Cores? Altera Design Tools for using and integrating IP Cores Overview of various IP Core Interconnect
Microprocessor or Microcontroller?
 Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB
 SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
FPGA-based MapReduce Framework for Machine Learning
 FPGA-based MapReduce Framework for Machine Learning Bo WANG 1, Yi SHAN 1, Jing YAN 2, Yu WANG 1, Ningyi XU 2, Huangzhong YANG 1 1 Department of Electronic Engineering Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
FPGA-based MapReduce Framework for Machine Learning Bo WANG 1, Yi SHAN 1, Jing YAN 2, Yu WANG 1, Ningyi XU 2, Huangzhong YANG 1 1 Department of Electronic Engineering Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
DS1225Y 64k Nonvolatile SRAM
 DS1225Y 64k Nonvolatile SRAM www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Directly replaces 2k x 8 volatile
DS1225Y 64k Nonvolatile SRAM www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Directly replaces 2k x 8 volatile
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
