EARTHQUAKE HAZARD POTENTIAL IN OMAN
|
|
|
- Gerald Douglas
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
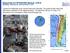
1 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD POTENTIAL IN OMAN Mohammed QAMARUDDIN 1 And Ali AL-HARTHY 2 SUMMARY The assessment of seismic hazard involves in collecting and evaluating a wide range of data pertaining to the history and occurrence of earthquakes in a region and to their origin. Considerable efforts have already been made for assessing seismic hazard in the Sultanate of Oman and various other aspects to seismic monitoring. Through these efforts, it has been established that a major fault exists in the Gulf of Oman (offshore Muscat). Also, it is known now that recent earth movements have occurred in Jabal Salak, Jabal Khubayb and Batinah Coastal Plains area. Although, there are few instrumentally recorded earthquakes in Oman, but the available geological, geophysical and historical data do suggest a low to moderate level of seismicity such that an earthquake of Modified Mercalli (MM) intensity of VII or greater could occur. Therefore, the possibility of an earthquake in the Sultanate of could never be ruled out. Prior to 1980 very few earthquakes had been reported in the Sultanate of Oman mainly because of the lack of local seismographic stations or perhaps it was difficult to receive signals from events in Oman. After 1980, new stations in Norway, Sweden and England reported nearly all earthquakes. Much development projects in different parts of Oman have been undertaken to develop its modern infrastructures. Therefore, seismic zoning map and other basic data are required for the development of standard code for seismic design of structures in Oman. In view of this, a study has been undertaken to collect and evaluate a wide range of seismic data to develop standard codes for seismic design of structures. The results of the study have been presented in this paper. It turns out from the present study that much information, which have been collected and evaluated, are not enough for the development of the code of practice for earthquake resistant design of structures INTRODUCTION Middle East is known from historic records to be seismically active. In the recent past, major earthquake shocks have not been reported in the Arabian Gulf region. Mortimer-Lloyd [1983] reported active seismic zone along the Red Sea coast resulting in earthquakes in Yemen (1982) and Egypt (1992). He also reported that parts of the Sultanate of Oman and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) fall into a seismic zone in which an earthquake of Modified Mercalli (MM) intensity of VII or greater could occur. Also parts of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE and major part of the Sultanate of Oman fall into a seismic zone in which a seismic shock of MM intensity up to V or VI could occur. Many areas in the Middle East have witnessed much increase in construction activities in recent years. Therefore, it is important that structures such as telecommunication, airports and harbors, hospitals, schools and utility and other services should remain largely undamaged in the event of an earthquake shock. There are several reports of felt earthquakes in the Sultanate (Fig. 1) during the period from years 977 to 1998 (Table 1). The historical records suggest a possibility of damage during the Qalhat earthquake of 15th century [Dickson, 1986]. Some major events, however, that occurred at a great distance away in southern Iran, Pakistan or Yemen have been reported in Oman. Several individuals reported [Dickson, 1986] effects of November 27, 1 2 Dept of Civil Eng, College of Eng, Sultan Qaboos University, P. O. Box 33, Al-Khod 123, Oman, mqamar@squ.edu.om Dept of Civil Eng, College of Eng, Sultan Qaboos University, P. O. Box 33, Al-Khod 123, Oman, mqamar@squ.edu.om
2 1945 earthquake (M = 8.2) whose epicenter was just off the southeastern Iranian Makran Coast about 470 km from Muscat (Oman). Witnesses reported damage, casualties, and a Tsunami surge. Also, April 18, 1983 earthquake (M = 6.5) that occurred in Baluchistan was felt by residents of multistory buildings in Muscat (590 km) and was also felt in Buraimi (Oman) at an even greater distance. Yemen earthquake (M = 5.7) of December 13, 1982 was also felt by resident in Salalah (Southern Oman) [Dickson, 1986]. Some faults were reported in the Batinah Coastal Plain in Oman north to the Daymaniyat islands (Fig. 2). Khaboura fault zone [Dickson, 1986] is located in south of Sohar about 80 km to the vicinity of Ras A ssawadi along coast (Fig. 2). Earthquake magnitudes recorded along the northeastern margin of Arabian Plate have ranged up to the most severe record magnitude of 8.2 (November 27, 1945). However, there are some seismic data from the National Geophysical Data Center in Denver, Colorado (U.S.A). It turns out from such seismic data that all the earthquakes that occurred in an area between E to E and N to N (Fig. 3) show that the significant seismic activity is concentrated along the Zagrous fault zone in Iran. Also, it can be seen from Fig. 2 that there are numerous epicenters along the Batinah Coastal Plain and offshore. Prior to 1980 very few earthquakes had been recorded in Oman mainly because of the lack of the local seismographic stations or perhaps it was difficult to receive signals from events in the Oman area because of placement of seismic stations [Dickson, 1986]. It is important to note that new stations in Norway, Sweden and England reported nearly all of the earthquakes after The magnitude of these earthquakes ranges from 3.9 to 4.9 on modified Ritcher scale. Considerable efforts have already been made for assessing seismic hazard in the Sultanate of Oman and various other aspects of seismic monitoring in the Sultanate of Oman. In view of this, the available seismicity and neotectonic data are briefly described in the following sections. TECTONICS AND NEOTECTONICS OF OMAN Oman is a part of the Arabian plate, which comprises the continent of Arabia as well as oceanic areas consisting of parts of the Red Sea, Arabian Sea, Gulf of Aden and Gulf of Oman (Fig. 4). Along the northeastern margin, the Arabian plate is in continental collision, which has given rise to the folded Zagros Mountains. The oceanic part of the Arabian plate is subducting along the Makran Trench. The destructive plate-margin of the Arabian plate along the Zagros and Makran is marked by intense earthquake activity. As the Arabian plate moves northeastwards, parts of the plates are differentially deformed and periodic release of such stress accumulations causes earthquakes within the plate. The 1971 Al-Kamil earthquake in Oman and the 1982 Dhammar earthquake in Yemen are examples of such intraplate earthquakes. Neotectonic structures are considered good indicators of present-day active zones. The basic idea is that the forces responsible for such structures could still be active. The Directorate General of Minerals (DGM), Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals, Sultanate of Oman has recently completed basic geological mapping of entire Oman at scales of 1: 1 00,000 and 1: An important aspect of this project was to map the Neogene (during the past 25 million years) and Quaternary (during the last 2 million years) periods. Along the coastal area of Oman (Fig. 2), several wave-cut platforms of presumably Pliocene-Quaternary age are located in excess of 500 m above the sea level suggesting enormous uplift of the region [Dickson, 1986]. Marine Pliocene-Quaternary terraces along the coast are found at elevations of m, which is considerably higher than the highest sea level suggesting uplift of several tens of metres. Normal faults on the continental shelf of the Gulf of Oman suggest very recent activity. These faults show a seafloor offset of about 200 m on seismic sections. SEISMICITY OF OMAN There are practically no instrurnentally-recorded earthquakes in Oman. The global database, however, lists an earthquake of magnitude 5.1 (Richter Scale) in AI-Kamil area in There are numerous reports of felt earthquakes in Oman (Table 1). Most of these reports represent ground shaking due to strong earthquakes occurring in the region at teleseismic distances. Figure 1 shows the felt earthquake locations. Along with felt earthquakes, this plot also shows earthquakes reported in old manuscripts including the late 15th Century Qalhat earthquake and earthquakes felt in Musandam region in the years 977, 1184 and 1483 AD. These data have been compiled in two ways. Senior citizens were asked to report on older events they had experienced in Oman. These kinds of data are not very reliable because of their dependence on human memory. In 1985, the Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals adopted a written survey form for felt earthquakes. Thus, the later reports of felt earthquakes are more reliable. It is clear from Figure 1 that Oman does experience earthquake tremors from time to time. The historical records suggest a possibility of damage during the Qalhat earthquake. The felt earthquakes are distributed mainly along the Batinah Coast Plains area and Oman Mountains region. 2
3 SEISMIC MONITORING IN OMAN Considerable effort has been made during the last fifteen years for the assessment of seismic risk in Oman. The outcome of such effort is presented in the form of the technical reports. The conclusion from first report [Dickson, 1986] is that the historical and instrumental seismicity record is limited in Oman. It has also been reported that recent earth movements are recorded in the Sultanate. The committee recommended establishment of a permanent seismological observatory in Oman. The second report [Lewis, 1992] submitted by another committee agreed with the conclusion of the first report. But, they also recommended microseismic monitoring in Oman using portable seismograph. In the last report [Carbon et al., 1994], the committee has reported discovery of a major fault in the Gulf of Oman, offshore Muscat. Also earth movements in Jabal Salak, Jabal Khubayb, and Batinah Coastal Plains area have been reported. The DGM, Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals has documented recent earth movements during the course of geological mapping of Oman. Assessment and mitigation of earthquake risk has been recognized as a major global problem [UNESCO, 1976]. Program of Assessment and Mitigation of Earthquake Risk in the Arab Region [PAMERAR, 1983] has been evolved under the UNESCO framework. As a starting point towards this goal many countries in the region, like Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Jordan, Egypt and Pakistan, have already established seismological observatories and networks. But, seismic monitoring in the Arabian Peninsula region is at now a very early stage. In view of this, the need for seismic monitoring in Oman has been well recognized. A national level committee known as Higher Committee on Seismic Monitoring, has been established in The Higher Committee then set up a Technical Committee on Seismic Monitoring (TCEQM) to design a plan for seismic monitoring in the Sultanate of Oman. The technical committee was formed involving experts from the Ministry of Communication, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals and the Sultan Qaboos University (SQU). The objectives of the technical committee are as follows Compilation of information for historical and instrumental seismicity in Oman. Compilation of neotectonic in Oman. Study of earthquake monitoring programs in the Gulf and neighbouring countries. Designing a work plan for earthquake monitoring in Oman. PORTABLE SEISMOGRAPHS Sultan Qaboos University acquired three portable seismographs in December, 1997 to carry out a survey of natural ground vibrations aimed at selecting site for permanent stations. These instruments are temporarily deployed at different places from time to time. Besides the ground vibrations, they also record earthquakes in the region. Firstly, two portable seismographs were installed temporarily, one located at the SQU and the other at Qairoon Hariti, north of Salalah. The portable seismograph installed at the SQU recorded the Afghanistan earthquake and Pakistani nuclear explosions in May 1998 [TCEQM, 1998]. Records of the seismograph installed on the SQU campus were examined which confirmed the report that an earthquake was felt in the capital area (Muscat) on June 10, This earthquake was located in southern Iran and had a magnitude of 4.6 on the Richter scale. Secondly, the portable seismographs were installed at Khutum and Bisya towns. A series of three earthquakes occurred in the Rustaq area on December 9, These earthquakes were felt by many people in the area and were recorded by the two seismographs, which were installed at Khutum and Bisya. The magnitude of these recorded earthquakes were between 1.8 to 2.8 [TCEQM, 1998]. Again, an earthquake of magnitude 2.7 occurred in the Rustaq area on April 27, 1999 and continued during the following four days recording 30 seismic shocks [TCEQM, 1999]. These seismic shocks were recorded on both Khutum and Bisya temporary stations with magnitudes in the range of 1.5 to 3.2. In view of the continued seismic disturbances around the Rustaq area, the three portable seismographs have been moved close to the affected area in order to record earthquakes and to calculate their parameters as precisely as possible. The seismic activities (highest magnitude recorded as 2.2) in the area were continuously monitored from May 14 to 31, Since, many seismic activities have been instrumentally recorded in a span of about eighteen months only after the installation of the portable seismographs in the Sultanate. Therefore, the establishment of a permanent network is expected to provide much more and precise information on the earthquake activities in the Sultanate of Oman. Site selection to locate these permanent stations has already been completed. Now, the government has already approved [TCEQM, 1999] the revised project proposal submitted by the technical committee and 3
4 therefore, the follow up process has started. This project may also seek to collaborate with other neighbouring countries to better address the earthquake monitoring in the Arabian Peninsula region. CONCLUSIONS Based on the present study, the following conclusions are derived: The available geological and historical data suggest a low to moderate level of seismicity such that an earthquake of MM intensity of VII or greater could occur. This result may be corroborated by the fact that after the installation of the portable seismographs in the Sultanate, much seismic activities have been instrumentally recorded in a very short period of about eighteen months only. Finally, it is concluded from the present study that much information, which have been collected and evaluated, are not enough for the development of the code of practice for earthquake resistant design of structures. REFERENCES 1. Carbon, D. R., P. Philip. H. and LeMetour, J Recent Tectonics in the Northern Oman Mountains: Coexistence of Compressive and Extensional Structures, Report Submitted to the Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals, Sultanate of Oman, 14p. 2. Dickson, P Preliminary Assessment of the Earthquake Hazard in the Sultanate of Oman. UNDP Consultancy Report, 30p. 3. Lewis, M. J Requirement of Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals for Seismic Stations, UN Consultancy Report Submitted to the Ministry of Petroleum and Minerals, Sultanate of Oman, 116p. 4. Mortimer-Lloyd, J. D Earthquakes and Seismic Zones in the Middle East, Building Research Establishment, Department of Environment, London, pp PAMERAR Assessment and Mitigation of Earthquake Risk in the Arab Region, UNESCO Report Prepared for the Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development, Islamic Development Bank, (Paris- UNESCO), 251p. 6. TCEQM Reports on Earthquakes Recorded by Portable Seismographs, Technical Committee on Earthquake Monitoring, Sultanate of Oman (Unpublished). 7. TCEQM Reports on Earthquakes Recorded by Portable Seismographs, Technical Committee on Earthquake Monitoring, Sultanate of Oman (Unpublished). 8. UNESCO Intergovernmental Conference on the Assessment and Mitigation of Earthquake Risk, Paris February Final Report (Paris-UNESCO), 50p. Table 1: Felt Earthquakes in Oman Site Place/City Year(s) of Felt Earthquake(s) 1 Shinas 1935,1945,1955, Liwa Saham 1944, Buraimi 1965, Al Qabil 1934, 1968, Nakhal 1965 (2)* 7 Seeb Muscat 1958, 1965 (4), 1967, 1969, 1983 (2)* 9 Quriyat 1965 (3)* 10 Musara Sumayyah Ghugrat Al-Tam 1965 (2)* 13 Sinaw Qalhat Late 15th Century 15 Al Kamil Al Wafi Bilad Bani Bu Hasan Masirah Salalah 1982, Musandam 977, 1184, Al Hallaniyat 1995 * Number of earthquake occurrence 4
5 5
6 6
7 7
8 8
Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India.
 Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India. A major earth quake occurred in Gujarat, India on January 26,2000. (Origin time 03:16 GMT, Location 23.399N
Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India. A major earth quake occurred in Gujarat, India on January 26,2000. (Origin time 03:16 GMT, Location 23.399N
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form?
 298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones
 Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK
 SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy
 February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008
 Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
Plate Tectonics. Introduction. Boundaries between crustal plates
 Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics. The unifying concept of the Earth sciences.
 Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
Chapter 2. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics: Learning Goals
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
The seismic activity in the area of Greece between 1966 and 1969
 The seismic activity in the area of Greece between 1966 and 1969 P. A. GIANNAKOPOULOS * Received on March 28'", 1972 SUMMARY. The earthquake activity in the area of Greece for the years 1966, 1967, 1968
The seismic activity in the area of Greece between 1966 and 1969 P. A. GIANNAKOPOULOS * Received on March 28'", 1972 SUMMARY. The earthquake activity in the area of Greece for the years 1966, 1967, 1968
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II
 Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION
 Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics
 Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 laurel@princeton.edu Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 laurel@princeton.edu Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Possible Inundation Map of Coastal Areas of Gujarat with a Tsunamigenic Earthquake
 Indian Minerals, Vol.61(3-4) & 62 (1-4), (July, 2007 - December, 2008); pp. 59-64 Possible Inundation Map of Coastal Areas of Gujarat with a Tsunamigenic Earthquake A. P. Singh 1*, U. Bhonde 1, B. K. Rastogi
Indian Minerals, Vol.61(3-4) & 62 (1-4), (July, 2007 - December, 2008); pp. 59-64 Possible Inundation Map of Coastal Areas of Gujarat with a Tsunamigenic Earthquake A. P. Singh 1*, U. Bhonde 1, B. K. Rastogi
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk
 Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey
 The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67)
 4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet
 Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. The outer portion of the Earth is made up of about 20 distinct plates (~ 100 km thick), which move relative to each other This motion is what
Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. The outer portion of the Earth is made up of about 20 distinct plates (~ 100 km thick), which move relative to each other This motion is what
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude
 Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
A RACE WITH TIME IN THE EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN REGION
 A RACE WITH TIME IN THE EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN REGION Walter W HAYS 1 SUMMARY The August 17, 1999 Izmit, Turkey earthquake disaster demonstrated the need for accelerating regional programs such as, Reduction
A RACE WITH TIME IN THE EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN REGION Walter W HAYS 1 SUMMARY The August 17, 1999 Izmit, Turkey earthquake disaster demonstrated the need for accelerating regional programs such as, Reduction
Locating the Epicenter and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake
 Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Seismic Waves Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk. Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey
 Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum
 Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013)
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
TRAINING SYSTEM AND INFORMATION NETWORK FOR EARTHQUAKE DISASTER MITIGATION
 TRAINING SYSTEM AND INFORMATION NETWORK FOR EARTHQUAKE DISASTER MITIGATION T. Saito 1, N. Hurukawa 2, T.Yokoi 2, T. Hara 2, B. Shibazaki 2, Y. Fujii 2, S. Koyama 2, T. Kashima 2 and T. Mukai 2 1 International
TRAINING SYSTEM AND INFORMATION NETWORK FOR EARTHQUAKE DISASTER MITIGATION T. Saito 1, N. Hurukawa 2, T.Yokoi 2, T. Hara 2, B. Shibazaki 2, Y. Fujii 2, S. Koyama 2, T. Kashima 2 and T. Mukai 2 1 International
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
1. You are about to begin a unit on geology. Can anyone tell me what geology is? The study of the physical earth I.
 PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
A Region by Any Other Name...
 A Region by Any Other Name.... Janet Hall Bethany Public Schools, Bethany, Oklahoma jhall@bps.k12.ok.us OVERVIEW: It is often true that a place may be categorized as belonging to more than one region,
A Region by Any Other Name.... Janet Hall Bethany Public Schools, Bethany, Oklahoma jhall@bps.k12.ok.us OVERVIEW: It is often true that a place may be categorized as belonging to more than one region,
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel
 PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise)
 PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise) Introduction: As discussed in our textbook, the speed at which tectonic plates move has been calculated in several
PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise) Introduction: As discussed in our textbook, the speed at which tectonic plates move has been calculated in several
The Aegean: plate tectonic evolution in Mediterranean
 The Aegean: plate tectonic evolution in Mediterranean Written by: Martin Reith Field course Naxos in September 2014, Group B Abstract The Mediterranean Sea, as known today, resulted from various geological
The Aegean: plate tectonic evolution in Mediterranean Written by: Martin Reith Field course Naxos in September 2014, Group B Abstract The Mediterranean Sea, as known today, resulted from various geological
Assessment of Impact of the December 26, 2004 Tsunami In Aceh Province Indonesia
 Assessment of Impact of the December 26, 2004 Tsunami In Aceh Province Indonesia Jay H. Samek, David L. Skole, and Walter Chomentowski December 30, 2004 Center for Global Change and Earth Observations
Assessment of Impact of the December 26, 2004 Tsunami In Aceh Province Indonesia Jay H. Samek, David L. Skole, and Walter Chomentowski December 30, 2004 Center for Global Change and Earth Observations
Step 2: Learn where the nearest divergent boundaries are located.
 What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE
 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
ABSG Consulting, Tokyo, Japan Email: tkubo@absconsulting.co.jp 2. Professor, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan 3
 Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Earthquakes Natural and Induced. Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University
 Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Continental Drift. Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on:
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on: Similarities in shorelines
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on: Similarities in shorelines
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake
 Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Overview. NRC Regulations for Seismic. Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. NRC History. How we Regulate
 Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
( 1 ) Overview of Safety Measures ( 2 ) Overview of Measures for Attaining Greater Safety and Reliability
 Contents 1 Effort for New Regulatory Requirements ( 1 ) Overview of a Gist of New Regulatory Requirements in Nuclear Regulation Authority ( 2 ) Major Requirements of a Gist of New Regulatory Requirements
Contents 1 Effort for New Regulatory Requirements ( 1 ) Overview of a Gist of New Regulatory Requirements in Nuclear Regulation Authority ( 2 ) Major Requirements of a Gist of New Regulatory Requirements
Name Date Class. By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter.
 CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
Tectonic plates push together at convergent boundaries.
 KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
Horizon Survey and Geotechnical Companies
 Oil & Gas Directory Middle East - 2013 147 Horizon Survey and Geotechnical Companies Corporate P r ofile OUR PEDIGREE Horizon provides comprehensive survey and geotechnical services to the offshore industry
Oil & Gas Directory Middle East - 2013 147 Horizon Survey and Geotechnical Companies Corporate P r ofile OUR PEDIGREE Horizon provides comprehensive survey and geotechnical services to the offshore industry
Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics. Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930.
 Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930. Science is self correcting. The Scientific Method The history
Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930. Science is self correcting. The Scientific Method The history
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers.
 1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers. Which statement about the deposition of the sediments best explains why these layers have the curved shape shown? 1) Sediments were
1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers. Which statement about the deposition of the sediments best explains why these layers have the curved shape shown? 1) Sediments were
Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates.
 Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q.
 Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes?
 Curry School of Education, University of Virginia www.teacherlink.org/content/science/ Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes? In this activity, students go to the United States Geological Survey (USGS)
Curry School of Education, University of Virginia www.teacherlink.org/content/science/ Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes? In this activity, students go to the United States Geological Survey (USGS)
Part III - Administrative, Procedural, and Miscellaneous. Tax Relief for Those Involved in Operation Iraqi Freedom. Notice 2003-21
 Part III - Administrative, Procedural, and Miscellaneous Tax Relief for Those Involved in Operation Iraqi Freedom Notice 2003-21 PURPOSE This notice provides guidance in a question and answer format on
Part III - Administrative, Procedural, and Miscellaneous Tax Relief for Those Involved in Operation Iraqi Freedom Notice 2003-21 PURPOSE This notice provides guidance in a question and answer format on
Tax Relief for Those Involved in Operation Iraqi Freedom Notice 2003 21
 Tax Relief for Those Involved in Operation Iraqi Freedom Notice 2003 21 PURPOSE This notice provides guidance in a question and answer format on the tax relief provided under Executive Order No. 12744,
Tax Relief for Those Involved in Operation Iraqi Freedom Notice 2003 21 PURPOSE This notice provides guidance in a question and answer format on the tax relief provided under Executive Order No. 12744,
Evolving a new Geodetic Positioning Framework: An Australian Perspective
 Evolving a new Geodetic Positioning Framework: An Australian Perspective G. Johnston, J. Dawson Outline Introduction Precise Positioning National Geospatial Reference Systems Asia Pacific Reference Frame
Evolving a new Geodetic Positioning Framework: An Australian Perspective G. Johnston, J. Dawson Outline Introduction Precise Positioning National Geospatial Reference Systems Asia Pacific Reference Frame
Plotting Earthquakes LESSON
 13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
DEEP AZIMUTHAL SEISMIC ANISOTROPY IN THE WESTERNANATOLIA AND AEGEAN SUBDUCTION ZONE
 DEEP AZIMUTHAL SEISMIC ANISOTROPY IN THE WESTERNANATOLIA AND AEGEAN SUBDUCTION ZONE G. Polat -1 and M.N. Ozel -1 Adress: 1- Boğaziçi University, Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institution,
DEEP AZIMUTHAL SEISMIC ANISOTROPY IN THE WESTERNANATOLIA AND AEGEAN SUBDUCTION ZONE G. Polat -1 and M.N. Ozel -1 Adress: 1- Boğaziçi University, Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institution,
College of Science and Health ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & GEOGRAPHY Course Outline
 College of Science and Health ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & GEOGRAPHY Course Outline 1. TITLE OF COURSE AND COURSE NUMBER: General Geology ENV 115, 4 credits 2. DESCRIPTION OF THE COURSE: Includes the study
College of Science and Health ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & GEOGRAPHY Course Outline 1. TITLE OF COURSE AND COURSE NUMBER: General Geology ENV 115, 4 credits 2. DESCRIPTION OF THE COURSE: Includes the study
Exploring plate motion and deformation in California with GPS
 Exploring plate motion and deformation in California with GPS Student worksheet Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO master teacher; Andy Newman, Georgia Institute of Technology; Shelley Olds, UNAVCO; and revised by
Exploring plate motion and deformation in California with GPS Student worksheet Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO master teacher; Andy Newman, Georgia Institute of Technology; Shelley Olds, UNAVCO; and revised by
Transform Boundaries
 Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/history_of_saudi_arabia (History of Saudi Arabia) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ibn_saud
 Abdullah Khalid Country Project Saudi Arabia History: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/history_of_saudi_arabia (History of Saudi Arabia) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ibn_saud As a state, Saudi Arabia has only
Abdullah Khalid Country Project Saudi Arabia History: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/history_of_saudi_arabia (History of Saudi Arabia) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ibn_saud As a state, Saudi Arabia has only
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system
 Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics
 Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
OCEANOGRAPHY Vol.II Morphology of Ocean Floor and Plate Tectonics - Chengsung Wang MORPHOLOGY OF OCEAN FLOOR AND PLATE TECTONICS
 MORPHOLOGY OF OCEAN FLOOR AND PLATE TECTONICS Chengsung Wang National Taiwan Ocean University, Keelung 202, Taiwan, China Keywords: Morphology of sea floor, continental margins, mid-ocean ridges, deep-sea
MORPHOLOGY OF OCEAN FLOOR AND PLATE TECTONICS Chengsung Wang National Taiwan Ocean University, Keelung 202, Taiwan, China Keywords: Morphology of sea floor, continental margins, mid-ocean ridges, deep-sea
Plate Tectonics PuzzleMap User Guide
 About this Product: Plate tectonics is a key standards-based topic taught in earth science classrooms throughout the United States. The purpose of this map is to help educators (teachers, museum tour guides,
About this Product: Plate tectonics is a key standards-based topic taught in earth science classrooms throughout the United States. The purpose of this map is to help educators (teachers, museum tour guides,
6.E.2.2 Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Japanese Saudi Business Opportunities Forum ~ Education & Human Resource Development ~ Employment System and Study Abroad Mindset of Japanese Youth
 Japanese Saudi Business Opportunities Forum ~ Education & Human Resource Development ~ Employment System and Study Abroad Mindset of Japanese Youth Mitsuhide SHIRAKI, Ph.D. Prof. Faculty of Political Science
Japanese Saudi Business Opportunities Forum ~ Education & Human Resource Development ~ Employment System and Study Abroad Mindset of Japanese Youth Mitsuhide SHIRAKI, Ph.D. Prof. Faculty of Political Science
Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1
 Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02
 Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02 This unit plan is intended to cover about seven weeks and would be appropriate for a middle school general science class or an introductory
Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02 This unit plan is intended to cover about seven weeks and would be appropriate for a middle school general science class or an introductory
UNIT I INTRODUCTION. This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
27 TH SEPTEMBER 2016 THE CONRAD HOTEL DUBAI, UAE
 27th September 2016 The Conrad Hotel, Dubai, UAE 27 TH SEPTEMBER 2016 THE CONRAD HOTEL DUBAI, UAE TELECOMS WORLD AWARDS 2016 CATEGORIES BEST OPERATOR BEST BRAND BEST CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE BEST ENTERPRISE
27th September 2016 The Conrad Hotel, Dubai, UAE 27 TH SEPTEMBER 2016 THE CONRAD HOTEL DUBAI, UAE TELECOMS WORLD AWARDS 2016 CATEGORIES BEST OPERATOR BEST BRAND BEST CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE BEST ENTERPRISE
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Correlation to. EarthComm, Second Edition. Project-Based Space and Earth System Science
 The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Achieve, Inc. on behalf of the twenty-six states and partners that collaborated on the NGSS Copyright 2013 Achieve, Inc. All rights reserved. Correlation to,
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Achieve, Inc. on behalf of the twenty-six states and partners that collaborated on the NGSS Copyright 2013 Achieve, Inc. All rights reserved. Correlation to,
Earth Science Chapter 14 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
