Metabolic Typing and Your Digestion
|
|
|
- Gillian Byrd
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Metabolic Typing and Your Digestion Copyright Healthexcel 1987, 2000, 2005 The purpose of our metabolic typing programs is to balance body chemistry and maximize metabolic efficiency by properly addressing metabolic individuality. It is our belief that the presence of any degenerative disease (85% - 90% of diseases afflicting our population) is due to the failure to do just that. Thus, one way or the other, all degenerative disease has its origin in malnutrition. For us, the idea of malnutrition takes on an entirely different light when viewed through the perspective of metabolic typing and metabolic individuality. We know that someone can eat the best organic foods and take the finest supplements that money can buy, yet still develop or fail to reverse degenerative disease. Time and again we have seen that this can be due to the failure to meet one's genetically-based requirements for nutritional, biochemical individuality. Digestion -- Prerequisite For Utilization However, there is yet another component to the equation -- the efficient digestion (and absorption) of the nutrients we consume. Even if we eat the right kinds of foods for our metabolic types, it is still necessary to properly digest those foods in order to benefit from their nutritional value. If the proper food for your metabolic type is eaten and the proper supplements are taken, that is one thing. It is quite another for that food and those nutrients to be absorbed into your body. In other words, just because a food goes down your esophagus, it does not mean that the nutrients will make it to your cells. First, digestion must prepare the food to enable it to penetrate the wall of your intestines. But if the food does not encounter the proper acid and enzymes, it will not digest and thereby will not absorb properly, potentially causing malnourishment, as well as making your body fertile ground for the development of infectious and degenerative diseases. Normal digestion is a complex cascade of events beginning when food is placed in the mouth and ending with elimination about 24 hours later. Normal digestion requires thorough chewing, mixing of food with enzymes, efficient swallowing, followed by exposure to a large quantity of acid and enzyme in the stomach. About two hours later, the chyme (food in the process of digestion) is moved on to the small intestine where it is bathed in bile, bile salts and more enzymes. More absorption occurs, and the chyme is mixed with bacteria to aid in digestion. Hypochlorhydria -- An "Epidemic" There is a common, frequently undiagnosed and usually untreated condition known as hypochlorhydria. Hypochlorhydria is the underproduction of hydrochloric acid by the stomach. Hydrochloric acid (HCL) is responsible for three important functions: 1. It begins the breakdown of protein 2. In the presence of food, it activates an enzyme called "pepsin," which further breaks down protein 3. It is necessary for the breakdown and utilization of minerals, especially calcium. For the most part, hypochlorhydria is a condition that is left undiagnosed and untreated. Years ago the only lab tests available were so difficult to administer that it was easier to rationalize not making the diagnosis and not treating the illness. This test involved shoving a tube down the esophagus and periodically suctioning out the stomach contents after a meal, so the acidity of Metabolic Typing & Your Digestion 1 of 6
2 those contents could be measured. In the late 1960s, the Heidelberg test was developed. This elegant (but expensive) device involves swallowing a capsule about the size of a vitamin pill that can measure the stomach acid content. But this relatively simple ability to diagnose hypochlorhydria is infrequently used due to the mistaken belief by most practitioners that hypochlorhydria is not worth treating -- astonishing when sales of antacids, acid blockers and ulcer medications consistently top the list of drug sales. The situation is further complexed by the fact that the symptoms of hypochlorhydria are similar to those of hyperchlorhydria. Burping, belching, bloating, "heartburn," gas, sour stomach, undigested food in stool, a voracious appetite (due to cellular "starvation"), food sitting in stomach too long, slow digestion, inability to eat a large meal due to feeling full quickly, constipation, and diarrhea can all be due to insufficient HCL production. Thus, many of those who have too little HCL production are treated as though they have too much. When the stomach is deficient in HCL production, food eaten lies in the stomach and ferments leading to gas, burning and bloating. For those people, reaching for their Tums or Maalox is the worst thing that they can do since it only alleviates the burning symptoms but actually over the long haul just contributes to the real problem! The Need For HCL Stomach acid serves many important functions, not only in digestion, but also in keeping the body free from disease. Many bacteria enter the body with food. Some of them are not friendly to human life. In a normal stomach, these bacteria are doused with acid and die. In a person with hypochlorhydria, these bacteria are escorted into the small intestine along with a generous food supply. It has been shown that people with hypochlorhydria have more than their share of infections. The ever present yeast organism makes its entrance via the mouth. Many people with the so-called "yeast syndrome" are unable to get rid of their yeast because the organism continues to reinfect the body through the mouth. Another important function of hydrochloric acid is the stimulation of pancreatic enzyme and bile release into the small intestine. Without enough pancreatic enzymes and bile, the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and vitamins A and E, is severely compromised, inadvertently causing undernutrition even with an excellent diet. The following conditions have been linked to hypochlorhydria: Acne rosacea Adrenal insufficiency Allergies Anemia Arthritis Asthma Autoimmune Diseases Celiac Disease Chronic fatigue Chronic hepatitis Diabetes mellitus Dry skin Gallbladder disease GERD - misdiagnosed acid reflux, but really hypochlorhydria Hypoglycemia Infections increased - parasitic, yeast, bacterial Lupus erythematosis Nail weaknesses Osteoporosis Poor night vision Psoriasis Rheumatic arthritis Stomach cancer risk increased Thyroid disorders Vitiligo Metabolic Typing & Your Digestion 2 of 6
3 Along with a deficiency of HCL, the same cells (the parietal cells) which make HCL also make pepsinogen, which is converted to pepsin in an acid environment. Therefore, pepsin usually is also deficient and therefore also must be replaced along with HCL for best results. HCL Supplementation It has been our experience over the last 25 years that most people who come to us for help are deficient in HCL (as well as enzymes). This is why all of our programs recommend HCL and digestive enzymes as a matter of course. What we can't determine, however, is how much should be taken. This is where you as a Metabolic Typing Advisor come in. Here's what you should do: 1. Educate your client as to the importance of HCL in their digestion and overall health 2. Inform them of the specific symptoms that may suggest HCL deficiency 3. Encourage them to find their own optimum tolerance level for HCL supplementation. Here's how: In general, we recommend that someone start out with 1 HCL with each meal. [Take HCL before or right at the start of the meal.) After 3 days, if this produces no burning or worsening of existing burning symptoms in the stomach, increase to 2 HCL with each meal. Again wait 3 days and if no burning is present, increase to 3 with each meal, continuing in this fashion until 5 with each meal is reached, if necessary. If at any time a burning sensation in the stomach ensues, drop back down to the previous intake. In other words, if 4 with each meal produces no burning, but 5 with each meal does, drop down to 4 with each meal. Then, stay at that level until at some point burning commences at which time you should drop down one more. For example, were you to work up to 5 HCL and 5 produces burning, you would drop back to and hold at 4. Then when 4 produces burning, drop down to 3. When 3 produces burning, drop down to 2. Continue in this manner until no HCL is required. When even 1 HCL produces burning, this likely will mean that the body is now producing sufficient levels of its own HCL and substitution is no longer needed. Some "experts" believe that supplementing with HCL will weaken even further the body's ability to produce its own HCL. Although this may be true for someone not following a proper metabolic typing program, our experience has been just the opposite. By eating the right foods for your metabolic type AND by assuring efficient digestion and absorption of those nutrients, the stomach's inherent ability to produce sufficient HCL can be restored (along with all other metabolic functions). Degenerative processes can be reversed into regenerative processes. Here's how the negative spiral of degeneration works: If you don't eat the right foods for your metabolic type, the body loses its efficiencies (e.g., digestive efficiency) over time, little by little As digestion worsens, fewer and fewer nutrients are absorbed As less nutrients are absorbed, digestive efficiency weakens further Etc. (The cycle keeps feeding on itself, going ever deeper into degeneration) Health-building processes of regeneration work exactly in reverse. Ingesting, digesting, absorbing, and utilizing foods right for your metabolic type will balance body chemistry, rebuild organs and glands, and maximize metabolic efficiency over time. Metabolic Typing & Your Digestion 3 of 6
4 Enzyme Supplementation In general, the same principles that apply to working with HCL apply to working with the digestive enzymes. The digestive enzymes (Enzigest) used in our programs are plant-based. As such, they have a much wider ph range of utilization than animal-based products. As a result, they are highly effective for a wider range of individuals. In order to be active, enzymes will only function within a certain ph range. For example, animalbased enzymes like pancreatin are only active in a ph range of about But our plantbased formulas are active between This means they are extremely effective digestive aids, even for those individuals who have very altered ph in their digestive tracts. Once you have determined the proper amount of HCL supplementation, then add in the Enzigest to the program. Minimum intake is 1 with each meal. One could take up to 6 with a meal but that is rarely necessary. Use anywhere from 1-6 with each meal as needed to assure maximum digestion. Use the same traits listed above for digestive insufficiency as your guide and also include intestinal gas in your list. Enzymes Info The de-naturalization effects from modern food-processing techniques often result in the depletion of the nutrient value and vitality of our food. One important factor which may be destroyed in processing as well as in improper food preparation is enzymes. Enzymes are substances which make life possible and which are found in natural, live foods and also in your body. Enzymes are the work force of the body. Without them, chemical reactions cannot take place, and hormones, minerals, and vitamins cannot carry out their functions. There are believed to be hundreds of thousands of enzymes in the body; different enzymes perform different functions. Without them, life cannot exist. Although the voluminous extent of their activity is beyond the scope of this guide, some activities of enzymes are: Digest food to a size capable of being absorbed into the blood Rebuild food into tissue of muscle, bone, organs, glands, etc. Work to store food in the liver and muscles for fuel later on Coagulate blood Attach iron to red blood cells Eliminate carbon dioxide from the lungs Promote oxidation Attack waste material in the blood and prepare it for elimination Change protein into sugar or fat Change carbohydrate into fat Change fat into carbohydrate You can have all the raw materials necessary for good health vitamins, minerals, intrinsic factors, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, amino acids, etc. but enzymes are necessary in order for your body to utilize all the raw materials in its life-supporting activities of metabolism. At birth, we acquire a limited supply of enzymes. Throughout our lifetime, as enzymes perform their function, they are destroyed and eliminated from the body. It is vital to your health and longevity that your enzymes be replenished in the body from your diet and that your diet provide a sufficient source of enzymes. [Note: Read Food Enzymes, by Edward Howell.] The critical role of enzymes in the maintenance of health and well-being was dramatically demonstrated in an experiment now known as The Pottenger Cat Studies, which was performed by Francis Pottenger, M.D., in Metabolic Typing & Your Digestion 4 of 6
5 For ten years, Dr. Pottenger studied two groups of cats who lived in outdoor pens which were placed side by side. At the beginning of the experiment, the two groups were as identical in health and characteristics as possible. During the course of the entire experiment, one group was fed exclusively cooked food; the other group was fed only raw food. Although the foods given the two groups were identical in kind and amount, the cooked food was devoid of enzymes (enzymes are totally destroyed at 220 degrees). Throughout the entire experiment, the group fed the raw food remained healthy and normal in all respects. The group fed the enzyme-deficient cooked food was a different story altogether. They developed all manner of degenerative conditions which affected their physiologies as well as their behavior. Their coats lost their luster; their bone structures developed deformities; their behavior became hyperactive, aggressive and wild. And by the 7th generation, they had lost the capacity to reproduce. As an interesting sidelight, the vegetation which grew in the pen of the raw food-fed cats was healthy and profuse. The vegetation in the pen of the cooked food-fed cats was sparse and unhealthy in appearance. This was due to the lack of enzymes in their feces which failed to fertilize the soil, unlike that of the enzyme-rich feces of the other group who existed on the enzyme-rich raw food diet. Be Enzyme Rich Unfortunately, all too many people eat a diet which is not only high in unnatural, chemicalized, processed and nutrient depleted food, but they also eat a large percentage of cooked food which has totally destroyed the enzyme content. As a result, the body is forced to use its own enzymes to help digest the food that might otherwise be used in rebuilding bodily tissue or in other important metabolic activities. This enzyme shortage may contribute significantly to metabolic imbalance, inefficiency and degeneration. Many researchers also believe this to be a contributing factor in premature aging and obesity. Raw food contains enzymes which may help replenish your body's enzyme pools as well as to actually help in the digestion of your food. Because it is very difficult to make up enzyme depletions exclusively from food sources, enzyme supplementation is a vital part of your Healthexcel Program. As an integral part of your health-building program then, it is important to: Select whole, natural food whenever possible, and Prepare food properly in order to: 1. Eliminate any toxic substances 2. Acquire the maximum nutrient value Metabolic Types and Digestion Typically, differences do exist in "normal" digestive capacity between metabolic types. The digestive functions are dependent on and influenced by autonomic, endocrine and nutrient balances. In general, the parasympathetic system "turns on" digestive organs and secretions and the sympathetic system shuts them off. Potassium is needed for HCL production. Thus, parasympathetics and fast oxidizers (both high in potassium) tend to have higher HCL and enzyme production, while sympathetics and slow oxidizers tend toward less production of digestive secretions. Blood Type O's also have higher HCL production and Blood Type A's tend to have lower production. Although these facts are true in principle, in practice each case must be individually considered. Remember that within any metabolic type, there can exist good or poor efficiency. For example, even though one's overall style of functioning may be accurately classified as Parasympathetic Dominant, it is still possible that inefficiency can exist in a localized function, even in HCL production. Therefore, in clinical practice it is best to assume nothing. The infinite variability expressed through human metabolic individuality will fool you more often than not. It is better to just follow the practical steps given above to determine each person's tolerance level and work from there. Metabolic Typing & Your Digestion 5 of 6
6 Conclusion Bottom line?... Maximize digestive capacity to maximize rate of progress and benefits of any metabolic typing program. If necessary, HCL can also be taken after a particularly heavy meal. And additional Enzigest can be taken anytime, even between meals, away from food. Taking a few Enzigest before bed is a great way to assure complete digestion of the day's food intake. As the saying goes, "It all starts with digestion." So, optimize the use of Healthexcel's incomparable metabolic type digestive aid formulations in your practice and see the difference both in yourself and your clients. Copyright Healthexcel 1987, 2000, 2005 Metabolic Typing & Your Digestion 6 of 6
Long Term Use of Antacid Medications Can Cause an Increased Risk for Osteoporosis and Much More
 Long Term Use of Antacid Medications Can Cause an Increased Risk for Osteoporosis and Much More By: Jeremie Pederson D.C., C.S.C.S. Many people are concerned about the FDA news release dated May 25, 2010
Long Term Use of Antacid Medications Can Cause an Increased Risk for Osteoporosis and Much More By: Jeremie Pederson D.C., C.S.C.S. Many people are concerned about the FDA news release dated May 25, 2010
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Stomach Acid - an Overlooked Digestive Aid
 Stomach Acid - an Overlooked Digestive Aid Almost everyone has experienced an upset stomach due to improper eating at one time or another. Yet, chronic indigestion affects millions of people every day.
Stomach Acid - an Overlooked Digestive Aid Almost everyone has experienced an upset stomach due to improper eating at one time or another. Yet, chronic indigestion affects millions of people every day.
Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox
 What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Without intrinsic factor, which is a unique protein made in the stomach, vitamin B12 cannot gain access to the rest of the body where it is needed.
 What is vitamin B12? Vitamin B12 is one of the most controversial members of the vitamin family collectively referred to as the "B-complex" vitamins. Although the full chemical structure of B12 was not
What is vitamin B12? Vitamin B12 is one of the most controversial members of the vitamin family collectively referred to as the "B-complex" vitamins. Although the full chemical structure of B12 was not
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
ph balance The Importance of ph Balance in Maintaining Health
 Testing ph Balance. Body ph and Blood ph as Indicators of Health Below is what you will hopefully find useful in finding out more about your body's ph and how to test it. There are different opinions about
Testing ph Balance. Body ph and Blood ph as Indicators of Health Below is what you will hopefully find useful in finding out more about your body's ph and how to test it. There are different opinions about
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes?
 Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Name Date Period. Keystone Review Enzymes
 Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Enzymes. A. a lipid B. a protein C. a carbohydrate D. a mineral
 Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life
 Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life Vitality for Life supplements with patented Oligo Oligo U.S. Patent No. 8,273,393 Reinventing the Multivitamin Our modern diets have the majority of us gorging
Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life Vitality for Life supplements with patented Oligo Oligo U.S. Patent No. 8,273,393 Reinventing the Multivitamin Our modern diets have the majority of us gorging
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Presentation Notes Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
 Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
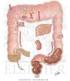 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version
 The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Surgical Weight Loss. Mission Bariatrics
 Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
7 Reasons You Can t Eat the Foods You Love!
 Dr. Susan Plank s Report: 7 Reasons You Can t Eat the Foods You Love! Betsy Coltrain sat feeling miserable on the couch. She had just finished eating dinner and began to feel the uncomfortable fullness,
Dr. Susan Plank s Report: 7 Reasons You Can t Eat the Foods You Love! Betsy Coltrain sat feeling miserable on the couch. She had just finished eating dinner and began to feel the uncomfortable fullness,
Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488
 Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488 SUMMARY Type 1 diabetes Onset common in Children Insulin requiring Immune origins with attack on the
Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488 SUMMARY Type 1 diabetes Onset common in Children Insulin requiring Immune origins with attack on the
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Seriously, talk. tell. test. Celiac Disease.
 Seriously, Celiac Disease. talk. If you have celiac disease, your family members might have it too. Talk to them about your experience and how celiac disease runs in families. Tell them the facts. Urge
Seriously, Celiac Disease. talk. If you have celiac disease, your family members might have it too. Talk to them about your experience and how celiac disease runs in families. Tell them the facts. Urge
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN. by DAVID SALINGER. www.hair-loss-centre.com.au
 HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN by DAVID SALINGER HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN Loss of hair does worry people and when you realise that so many factors can be responsible for hair loss, you can appreciate that it is important
HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN by DAVID SALINGER HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN Loss of hair does worry people and when you realise that so many factors can be responsible for hair loss, you can appreciate that it is important
The Digestive System
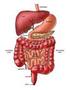 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
YOUR LAST DIET IDEAL PROTEIN
 YOUR LAST DIET IDEAL PROTEIN OBJECTIVES Explain the science and history that supports the Ideal Protein Diet method. Describe the risks and benefits of diet participation. Give you the details of what
YOUR LAST DIET IDEAL PROTEIN OBJECTIVES Explain the science and history that supports the Ideal Protein Diet method. Describe the risks and benefits of diet participation. Give you the details of what
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body. Vitamin A
 What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
Regulation of Metabolism. By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I
 Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I By: James L. Holly, MD Oxidative Stress refers to effects from endogenous (produced in the body) toxins (free radicals) produced in the body by normal metabolism
Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I By: James L. Holly, MD Oxidative Stress refers to effects from endogenous (produced in the body) toxins (free radicals) produced in the body by normal metabolism
Week 6: Digestive Health
 WEIGHT LOSS BEGINS WITH DIGESTIVE HEALTH Your digestive system is one of the most essential components of your entire body. According to a recent survey, people have a keen interest in digestive health
WEIGHT LOSS BEGINS WITH DIGESTIVE HEALTH Your digestive system is one of the most essential components of your entire body. According to a recent survey, people have a keen interest in digestive health
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
Vitamin D. Sources of vitamin D
 1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
1 has been in the news frequently this past year, including an article in The New York Times on November 16, 2009. So what is this vitamin? Why is it important? Most people have heard that vitamin D is
How To Get Healthy
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Calories. 23 calories from fat + 48 calories from carbohydrates + 32 calories from protein = 103 Calories in 1 cup of 1% milk
 Calories What's the magical formula to achieve your weight goals? Calorie needs are based on individual needs. In order for your weight to stay the same, the energy (or Calories) you consume must equal
Calories What's the magical formula to achieve your weight goals? Calorie needs are based on individual needs. In order for your weight to stay the same, the energy (or Calories) you consume must equal
How do Patients Take THE GIFT from Mother Earth, BEST FULVIC and Humic and Fulvic Based Supplements?
 How do Patients Take THE GIFT from Mother Earth, BEST FULVIC and Humic and Fulvic Based Supplements? Patients typically start taking THE GIFT from Mother Earth. THE GIFT from Mother Earth is a highly-concentrated
How do Patients Take THE GIFT from Mother Earth, BEST FULVIC and Humic and Fulvic Based Supplements? Patients typically start taking THE GIFT from Mother Earth. THE GIFT from Mother Earth is a highly-concentrated
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease
 High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406
 Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
FDRM By Nichlas Brandon Last Updated: 09/18/2013
 Page 1 of 9 The following information contained herein is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Table of Contents SUGAR AND CANCER...
Page 1 of 9 The following information contained herein is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Table of Contents SUGAR AND CANCER...
Importance of water for weight loss
 Importance of water for weight loss Most people do not drink enough water; one reason for this is because they have gotten out of the habit. If you are trying to lose weight, drinking plenty of water is
Importance of water for weight loss Most people do not drink enough water; one reason for this is because they have gotten out of the habit. If you are trying to lose weight, drinking plenty of water is
Growth & Feeding Puppies Karen Hedberg BVSc 2007. Growth
 Growth & Feeding Puppies Karen Hedberg BVSc 2007 Size and End Weight : Growth Dogs come in all sizes and shapes and have enormous variation in their final body weights. Dogs generally can be fed a very
Growth & Feeding Puppies Karen Hedberg BVSc 2007 Size and End Weight : Growth Dogs come in all sizes and shapes and have enormous variation in their final body weights. Dogs generally can be fed a very
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health?
 Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
What Causes Cancer-related Fatigue?
 What Causes Cancer-related Fatigue? The causes of cancer-related fatigue are not fully understood. It may be the cancer and/or the cancer treatment. Cancer and cancer treatment can change normal protein
What Causes Cancer-related Fatigue? The causes of cancer-related fatigue are not fully understood. It may be the cancer and/or the cancer treatment. Cancer and cancer treatment can change normal protein
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR
 ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
Overview. Nutritional Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. How does the liver affect nutritional status?
 Overview Nutritional Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Tracy Burch, RD, CNSD Kovler Organ Transplant Center Northwestern Memorial Hospital Importance of nutrition therapy in PBC Incidence and pertinence
Overview Nutritional Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Tracy Burch, RD, CNSD Kovler Organ Transplant Center Northwestern Memorial Hospital Importance of nutrition therapy in PBC Incidence and pertinence
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Blood Transfusion. There are three types of blood cells: Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets.
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf
 3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
FAILURE TO THRIVE What Is Failure to Thrive?
 FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age
 Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Calcium and Vitamin D: Important at Every Age National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Peptic Ulcer. Anatomy The stomach is a hollow organ. It is located in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
 Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Peptic Ulcer Introduction A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. Peptic ulcers may also develop in the esophagus. Nearly
Copyright 2010 by Advanced Bionutritionals, LLC
 Copyright 2010 by Advanced Bionutritionals, LLC All rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction of this report or its contents by xerography, facsimile, or any other means is illegal, except for brief quotations
Copyright 2010 by Advanced Bionutritionals, LLC All rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction of this report or its contents by xerography, facsimile, or any other means is illegal, except for brief quotations
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
The role of negative -ION in the improvement of our health
 What are IONS and where do they come from? IONS are particles with a positive or a negative electrical charge The percentage and number of +IONS and -IONS change depending on the time and place. IONS can
What are IONS and where do they come from? IONS are particles with a positive or a negative electrical charge The percentage and number of +IONS and -IONS change depending on the time and place. IONS can
First Name. Profession. Weight lbs. Weight 1 year ago lbs. Min. Adult Weight lbs. at age Maximum Weight lbs. at age
 Date Time Dietary consultation involves a health profile whose purpose is not to establish a diagnosis, but rather to determine a client's health status in order to guide his or her weight loss plan. A
Date Time Dietary consultation involves a health profile whose purpose is not to establish a diagnosis, but rather to determine a client's health status in order to guide his or her weight loss plan. A
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol. Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Healing Depression Naturally
 Healing Depression Naturally By Peter Bongiorno ND, LAc and Pina LoGiudice ND, LAc Directors of Inner Source Health (www.innersourcehealth.com) While everyone experiences the blues from time to time, depression
Healing Depression Naturally By Peter Bongiorno ND, LAc and Pina LoGiudice ND, LAc Directors of Inner Source Health (www.innersourcehealth.com) While everyone experiences the blues from time to time, depression
Managing Anemia When You Are on Dialysis. Stage 5
 Managing Anemia When You Are on Dialysis Stage 5 What is anemia? Anemia happens when your red blood cells are in short supply. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body, giving
Managing Anemia When You Are on Dialysis Stage 5 What is anemia? Anemia happens when your red blood cells are in short supply. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body, giving
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. For People With CKD Stages 1 4
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario)
 Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY. 12a. FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
NAME: DATE: Home Economics: The parts of the digestive system and their functions. Home Economics
 Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Blood Sugar & Glycaemic Index
 Nutrition Blood Sugar & Glycaemic Index Lesley Loizou The human body is designed to run on carbohydrates (CHO). While we can use protein and fat for energy, the easiest and most smoke-free fuel is carbohydrate.
Nutrition Blood Sugar & Glycaemic Index Lesley Loizou The human body is designed to run on carbohydrates (CHO). While we can use protein and fat for energy, the easiest and most smoke-free fuel is carbohydrate.
ENZAR FORTE TABLETS. (derived from Pancreatin USP) Sodium tauroglycocholate BPC 65mg (with sugar coating containing essential carminative oils)
 ENZAR FORTE TABLETS COMPOSITION Each enteric-coated tablet contains: Amylase activity -15,000 USP units Lipase activity -4,000 USP units Protease activity -15,000 USP units of (derived from Pancreatin
ENZAR FORTE TABLETS COMPOSITION Each enteric-coated tablet contains: Amylase activity -15,000 USP units Lipase activity -4,000 USP units Protease activity -15,000 USP units of (derived from Pancreatin
The Digestive System
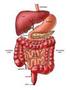 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
16 Very Important THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW About Cancer Cells
 16 Very Important THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW About Cancer Cells By Ingo Logé and Fitness Forever 1. Every person has cancer cells in the body. These cancer cells do not show up in the standard tests until
16 Very Important THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW About Cancer Cells By Ingo Logé and Fitness Forever 1. Every person has cancer cells in the body. These cancer cells do not show up in the standard tests until
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand
 Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism. Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology
 A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security
 Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
