Lesson 8.6 Exercises, pages
|
|
|
- Allyson Hamilton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 8.6 Exercises, pages A 3. Expand using Pascal s triangle. a) (x + 1) 5 The exponent is 5, so use the terms in row 6 of Pascal s triangle as coefficients: 1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1 (x 1) 5 1(x) 5 5(x) 4 (1) 10(x) 3 (1) 2 10(x) 2 (1) 3 5(x) 1 (1) 4 1(1) 5 x 5 5x 4 10x 3 10x 2 5x 1 b) (x - 1) 6 The exponent is 6, so use the terms in row 7 of Pascal s triangle as coefficients: 1, 6, 15, 20, 15, 6, 1 (x 1) 6 1(x) 6 6(x) 5 ( 1) 15(x) 4 ( 1) 2 20(x) 3 ( 1) 3 c) (x + y) 4 The exponent is 4, so use the terms in row 5 of Pascal s triangle as coefficients: 1, 4, 6, 4, 1 (x y) 4 1(x) 4 (x) 3 (y) 6(x) 2 (y) 2 (x)(y) 3 1(y) 4 d) (x - y) 8 15(x) 2 ( 1) 4 6(x)( 1) 5 1( 1) 6 x 6 6x 5 15x 4 20x 3 15x 2 6x 1 x 4 x 3 y 6x 2 y 2 xy 3 y 4 The exponent is 8, so use the terms in row 9 of Pascal s triangle as coefficients: 1, 8, 28, 56, 70, 56, 28, 8, 1 (x y) 8 1(x) 8 8(x) 7 ( y) 28(x) 6 ( y) 2 56(x) 5 ( y) 3 70(x) 4 ( y) 4 56(x) 3 ( y) 5 28(x) 2 ( y) 6 8(x)( y) 7 1( y) 8 x 8 8x 7 y 28x 6 y 2 56x 5 y 3 70x 4 y 4 56x 3 y 5 28x 2 y 6 8xy 7 y 8 4. Determine each missing number in the expansion of (x + y) 7. x 7 +nx 6 y + 21x 5 y x n y 3 +nx 3 y x n + 7xy 6 + The exponent is 7, so the coefficients of the terms in the expansion are the terms in row 8 of Pascal s triangle: 1, 7, 21, 35, 35, 21, 7, 1 The exponents in each term must add to 7. The exponents of the powers of x start at 7 and decrease by 1 each time. The exponents of the powers of y start at 0 and increase by 1 each time. So, the missing numbers are: 7, 4, 35, 2, 5, 7 5. Determine the indicated term in each expansion. a) the last term in (x + 1) 9 The last term in the expansion of (x y) n is. So, the last term in the expansion of (x 1) 9 is 1 9, or 1. b) the 1st term in (x - 1) 12 The first term in the expansion of (x y) n is x n. So, the first term in the expansion of (x 1) 12 is x
2 B 6. a) Multiply 4 factors of (x - 5). (x 5) 4 (x 5)(x 5)(x 5)(x 5) (x 2 10x 25)(x 2 10x 25) x 4 10x 3 25x 2 10x 3 100x 2 250x 25x 2 250x 625 x 4 20x 3 150x 2 500x 625 b) Use the binomial theorem to expand (x - 5) 4. Substitute: n, y 5 (x 5) 4 (x) 4 (x) 4 1 ( 5) (x) 4 2 ( 5) 2 (x) 4 3 ( 5) 3 ( 5) 4 1(x) 4 (x) 3 ( 5) 6(x) 2 (25) (x) 1 ( 125) 1(625) x 4 20x 3 150x 2 500x 625 c) Compare the two methods. What conclusions can you make? I find it easier to use the binomial theorem; it saves time and it is less cumbersome than multiplying 4 factors. 7. Expand using the binomial theorem. a) (x + 2) 6 Substitute: n 6, y 2 (x 2) 6 6 (x) 6 6 (x) 6 1 (2) 6 (x) 6 2 (2) 2 6 (x) 6 3 (2) 3 6 (x) 6 4 (2) 4 6 (x) 6 5 (2) 5 6 C 6 (2) 6 1(x) 6 6(x) 5 (2) 15(x) 4 (4) 20(x) 3 (8) 15(x) 2 (16) 6(x) 1 (32) 1(64) x 6 12x 5 60x 4 160x 3 240x 2 192x 64 b) (x 2-3) 5 Substitute: n 5, x x 2, y 3 (x 2 3) 5 5 (x 2 ) 5 5 (x 2 ) 4 ( 3) 5 (x 2 ) 3 ( 3) 2 5 (x 2 ) 2 ( 3) 3 5 (x 2 ) 1 ( 3) 4 5 ( 3) 5 1(x 10 ) 5(x 2 ) 4 ( 3) 10(x 2 ) 3 (9) 10(x 2 ) 2 ( 27) 5(x 2 ) 1 (81) 1( 243) x 10 15x 8 90x 6 270x 4 05x DO NOT COPY. P
3 c) (3x - 2) 4 Substitute: n, x 3x, y 2 (3x 2) 4 (3x) 4 (3x) 3 ( 2) (3x) 2 ( 2) 2 (3x)( 2) 3 ( 2) 4 1(81x 4 ) (27x 3 )( 2) 6(9x 2 )(4) (3x)( 8) 1(16) 81x 4 216x 3 216x 2 96x 16 d) (-2 + 2x) 4 Substitute: n, x 2, y 2x ( 2 2x) 4 ( 2) 4 ( 2) 3 (2x) ( 2) 2 (2x) 2 ( 2)(2x) 3 (2x) 4 1(16) ( 8)(2x) 6(4)(4x 2 ) ( 2)(8x 3 ) 1(16x 4 ) 16 64x 96x 2 64x 3 16x 4 e) (-4 + 3x 4 ) 5 Substitute: n 5, x 4, y 3x 4 ( 4 3x 4 ) 5 5 ( 4) 5 5 ( 4) 4 (3x 4 ) 5 ( 4) 3 (3x 4 ) 2 5 ( 4) 2 (3x 4 ) 3 5 ( 4)(3x 4 ) 4 5 (3x 4 ) 5 1( 1024) 5(256)(3x 4 ) 10( 64)(9x 8 ) 10(16)(27x 12 ) 5( 4)(81x 16 ) 1(243x 20 ) x x 8 320x x x a) Write the terms in row 7 of Pascal s triangle. 1, 6, 15, 20, 15, 6, 1 b) Use your answer to part a to write the first 3 terms in each expansion. i) (x - 3) 6 The exponent is 6, so the terms in row 7 of Pascal s triangle are the coefficients of the terms in the expansion of the binomial. So, (x y) 6 1x 6 6x 5 y 15x 4 y 2... Substitute: y 3 (x 3) 6 1x 6 6x 5 ( 3) 15x 4 ( 3) 2... x 6 18x 5 135x 4... So, the first 3 terms in the expansion are: x 6 18x 5 135x 4 27
4 ii) (a + 4b) 6 (x y) 6 1x 6 6x 5 y 15x 4 y 2... Substitute: x a, y b (a b) 6 1a 6 6a 5 (4b) 15a 4 (4b) 2... a 6 24a 5 b 240a 4 b 2... So, the first 3 terms in the expansion are: a 6 24a 5 b 240a 4 b 2 iii) (-2a + 1) 6 (x y) 6 1x 6 6x 5 y 15x 4 y 2... Substitute: x 2a, y 1 ( 2a 1) 6 1( 2a) 6 6( 2a) 5 (1) 15( 2a) 4 (1) a 6 192a 5 240a 4... So, the first 3 terms in the expansion are: 64a 6 192a 5 240a 4 iv) (2x + 5y 2 ) 6 (x y) 6 1x 6 6x 5 y 15x 4 y 2... Substitute: x 2x, y 5y 2 (2x 5y 2 ) 6 1(2x) 6 6(2x) 5 (5y 2 ) 15(2x) 4 (5y 2 ) x 6 960x 5 y x 4 y 4... So, the first 3 terms in the expansion are: 64x 6 960x 5 y x 4 y 4 9. Determine the coefficient of each term. a) x 5 in (x + 1) 8 b) x 9 in (x + y) 9 x 5 is the 4th term in (x 1) 8. x 9 is the first term in the expansion The coefficient of the 4th term is: of (x y) 9. C or C So, the coefficient of x 9 is So, the coefficient of x 5 is 56. c) x 2 y in (x + y) 3 d) x 2 y 3 in (x + y) 5 The coefficients of the terms The coefficients of the terms will be the terms in row 4 of will be the terms in row 6 of Pascal s triangle: 1, 3, 3, 1 Pascal s triangle: 1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1 x 2 y is the 2nd term in the x 2 y 3 is the 4th term in the expansion of (x y) 3. expansion of (x y) 5. So, the coefficient of x 2 y is 3. So, the coefficient of x 2 y 3 is DO NOT COPY. P
5 10. Explain why the coefficients of the 3rd term and the 3rd-last term in the expansion of (x + y) n, n 2, are the same. Since each of x and y has coefficient 1, the coefficients of the terms in the expansion of (x y) n correspond to the terms in row (n 1) of Pascal s triangle. In any row of Pascal s triangle, the 3rd term and 3rd-last term are the same. 11. Determine the indicated term in each expansion. a) the last term in (3x + 2) 5 b) the 1st term in (-2x + 5) 7 The last term in the expansion of (x y) n is. Substitute: y 2, n So, the last term is 32. The first term in the expansion of (x y) n is x n. Substitute: x 2x, n 7 ( 2x) 7 128x 7 So, the 1st term is 128x 7. c) the 2nd term in (3x - 3) 4 d) the 6th term in (4x + 1) 8 The second term in the expansion of (x y) n is nx n 1 y. Substitute: x 3x, y 3, n 4(3x) 3 ( 3) 324x 3 So, the 2nd term is 324x 3. The kth term is: nc k 1 x n (k 1) y k 1 Substitute: n 8, k 6, x x, y 1 C 8 5 (4x)3 (1) 5 56(64x 3 )(1) 3584x 3 So, the 6th term is 3584x When will the coefficients of the terms in the expansion of (ax + b) n be the same as the terms in row (n + 1) of Pascal s triangle? The coefficients of the terms in the expansion of (x y) n correspond to the terms in row (n 1) of Pascal s triangle. So, both a and b must equal Expand and simplify (x + 1) 8 + (x - 1) 8. What strategy did you use? The coefficients of the terms in the expansion of (x 1) 8 are the terms in row 9 of Pascal s triangle: 1, 8, 28, 56, 70, 56, 28, 8, 1 The coefficients of the terms in the expansion of (x 1) 8 depend on whether the term number is odd or even. When the term numbers are odd, the coefficients are the terms in row 9 of Pascal s triangle. When the term numbers are even, the coefficients are the opposites of the terms in row 9. So, the coefficients of the terms in the expansion of (x 1) 8 are: 1, 8, 28, 56, 70, 56, 28, 8, 1 When the terms in the two expansions are added, every second term is eliminated as the sum of the terms is 0. (x 1) 8 (x 1) 8 2x 8 56x 6 140x 4 56x
6 14. a) Show that the expansion of (-2x + 1) 6 is the same as the expansion of (2x - 1) 6. Use row 7 of Pascal s triangle: 1, 6, 15, 20, 15, 6, 1 ( 2x 1) 6 1( 2x) 6 6( 2x) 5 (1) 15( 2x) 4 (1) 2 20( 2x) 3 (1) 3 15( 2x) 2 (1) 4 6( 2x) 1 (1) 5 (1) 6 64x 6 6( 32x 5 ) 15(16x 4 ) 20( 8x 3 ) 15(4x 2 ) 6( 2x) 1 64x 6 192x 5 240x 4 160x 3 60x 2 12x 1 (2x 1) 6 1(2x) 6 6(2x) 5 ( 1) 15(2x) 4 ( 1) 2 20(2x) 3 ( 1) 3 15(2x) 2 ( 1) 4 6(2x) 1 ( 1) 5 ( 1) 6 64x 6 6(32x 5 )( 1) 15(16x 4 ) 20(8x 3 )( 1) 15(4x 2 ) 6(2x)( 1) 1 64x 6 192x 5 240x 4 160x 3 60x 2 12x 1 b) Will (-ax + b) n always have the same expansion as (ax - b) n? Explain. No, when n is odd, the expansions will not be the same. For example, look at the first terms in the expansions of ( 2x 1) 3 and (2x 1) 3. For ( 2x 1) 3 : the 1st term in the expansion is: 1( 2x) 3 8x 3 For (2x 1) 3 : the 1st term in the expansion is: 1(2x) 3 8x 3 Since the 1st terms are different, the expansions are not the same. 15. Which binomial power when expanded results in 16x 4-32x x 2-8x + 1? What strategy did you use to find out? The first term is 16x 4. The exponent of x is 4, so the binomial has the form (ax b) 4. The coefficient a must be 4 16: a 2, or a 2 The last term is 1, so b is either 1 or 1 because ( 1) 4 1 4, or 1. The terms alternate in sign, so the coefficients a and b must have different signs. The binomial power is either ( 2x 1) 4 or (2x 1) Expand using the binomial theorem. a) (0.2x - 1.2y) 5 Substitute: n 5, x 0.2x, y 1.2y (0.2x 1.2y) 5 5 (0.2x) 5 5 (0.2x) 4 ( 1.2y) 5 (0.2x) 3 ( 1.2y) 2 5 (0.2x) 2 ( 1.2y) 3 5 (0.2x)( 1.2y) 4 5 ( 1.2y) 5 1( x 5 ) 5(0.0016x 4 )( 1.2y) 10(0.008x 3 )(1.44y 2 ) 10(0.04x 2 )( 1.728y 3 ) 5(0.2x)(2.0736y 4 ) 1( y 5 ) x x 4 y x 3 y x 2 y xy y 5 30 DO NOT COPY. P
7 b) a 3 8 a bb 4 Substitute: n, x 3, y 1 8 a 6 b a 3 8 a bb a ab a 3 8 ab 3 a 1 6 bb a 3 8 ab 2 a 1 6 bb 2 a aba1 6 bb a bb 1a a4 b a a3 ba 1 6 bb 6a 9 64 a2 ba 1 36 b2 b a 3 8 aba b3 b 1a b4 b a a3 b a2 b ab b a a3 b a2 b ab b4 C 17. Determine the 3rd term in the expansion of (x 2 + 2x + 1) 6. (x 2 2x 1) (x 1) 2 So, (x 2 2x 1) 6 ((x 1) 2 ) 6 (x 1) 12 The coefficients in the expansion of (x 1) 12 are the terms in row 13 of Pascal s triangle. The 3rd term in row 13 is 66. So, the 3rd term in the expansion of (x 2 2x 1) 6 is: 66(x) 10 (1) 2, or 66x a) Show that C + C + C C + C = n 0 n 1 n 2 n n - 1 n n 2n Express 2 n as the binomial (1 1) n and expand: (1 1) n (1) n (1) n 1 (1) (1) n 2 (1) (1)(1) n 1 (1) n So, 2 n... 1 b) What does the relationship in part a indicate about the sum of the terms in any row of Pascal s triangle? C, C, C,... C, 0 n 1 n 2 n n 1 n n are the terms in row (n 1) of the triangle. From part a, the sum of these terms is 2 n. So, the sum of the terms in any row of Pascal s triangle is a power of 2. 31
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring
 1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping
 386 CHAPTER 6 Factoring and Applications 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
386 CHAPTER 6 Factoring and Applications 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
Factoring (pp. 1 of 4)
 Factoring (pp. 1 of 4) Algebra Review Try these items from middle school math. A) What numbers are the factors of 4? B) Write down the prime factorization of 7. C) 6 Simplify 48 using the greatest common
Factoring (pp. 1 of 4) Algebra Review Try these items from middle school math. A) What numbers are the factors of 4? B) Write down the prime factorization of 7. C) 6 Simplify 48 using the greatest common
( ) FACTORING. x In this polynomial the only variable in common to all is x.
 FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
Factoring and Applications
 Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
4. Binomial Expansions
 4. Binomial Expansions 4.. Pascal's Triangle The expansion of (a + x) 2 is (a + x) 2 = a 2 + 2ax + x 2 Hence, (a + x) 3 = (a + x)(a + x) 2 = (a + x)(a 2 + 2ax + x 2 ) = a 3 + ( + 2)a 2 x + (2 + )ax 2 +
4. Binomial Expansions 4.. Pascal's Triangle The expansion of (a + x) 2 is (a + x) 2 = a 2 + 2ax + x 2 Hence, (a + x) 3 = (a + x)(a + x) 2 = (a + x)(a 2 + 2ax + x 2 ) = a 3 + ( + 2)a 2 x + (2 + )ax 2 +
Radicals - Rationalize Denominators
 8. Radicals - Rationalize Denominators Objective: Rationalize the denominators of radical expressions. It is considered bad practice to have a radical in the denominator of a fraction. When this happens
8. Radicals - Rationalize Denominators Objective: Rationalize the denominators of radical expressions. It is considered bad practice to have a radical in the denominator of a fraction. When this happens
Algebra Cheat Sheets
 Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
15.1 Factoring Polynomials
 LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
Algebraic expressions are a combination of numbers and variables. Here are examples of some basic algebraic expressions.
 Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials
 Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Name Intro to Algebra 2. Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring
 Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
AIP Factoring Practice/Help
 The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
Question 2: How do you solve a matrix equation using the matrix inverse?
 Question : How do you solve a matrix equation using the matrix inverse? In the previous question, we wrote systems of equations as a matrix equation AX B. In this format, the matrix A contains the coefficients
Question : How do you solve a matrix equation using the matrix inverse? In the previous question, we wrote systems of equations as a matrix equation AX B. In this format, the matrix A contains the coefficients
Factoring Flow Chart
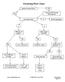 Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property and take out the GCF.
 Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
How To Factor By Gcf In Algebra 1.5
 7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
NSM100 Introduction to Algebra Chapter 5 Notes Factoring
 Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials 4-1-2014 The opposite of multiplying polynomials is factoring. Why would you want to factor a polynomial? Let p(x) be a polynomial. p(c) = 0 is equivalent to x c dividing p(x). Recall
Factoring Polynomials 4-1-2014 The opposite of multiplying polynomials is factoring. Why would you want to factor a polynomial? Let p(x) be a polynomial. p(c) = 0 is equivalent to x c dividing p(x). Recall
Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals
 8. Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals Objective: Multiply and divide radicals using the product and quotient rules of radicals. Multiplying radicals is very simple if the index on all the radicals
8. Radicals - Multiply and Divide Radicals Objective: Multiply and divide radicals using the product and quotient rules of radicals. Multiplying radicals is very simple if the index on all the radicals
2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction:
 2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction: As is usually the case when learning a new concept in mathematics, the new concept is the reverse of the previous one. Remember how you first learned
2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction: As is usually the case when learning a new concept in mathematics, the new concept is the reverse of the previous one. Remember how you first learned
Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section
 Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section What is algebra? Operations with algebraic terms Mathematical properties of real numbers Order of operations What is Algebra? Algebra is
Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section What is algebra? Operations with algebraic terms Mathematical properties of real numbers Order of operations What is Algebra? Algebra is
Multiplying and Dividing Radicals
 9.4 Multiplying and Dividing Radicals 9.4 OBJECTIVES 1. Multiply and divide expressions involving numeric radicals 2. Multiply and divide expressions involving algebraic radicals In Section 9.2 we stated
9.4 Multiplying and Dividing Radicals 9.4 OBJECTIVES 1. Multiply and divide expressions involving numeric radicals 2. Multiply and divide expressions involving algebraic radicals In Section 9.2 we stated
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation
 CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation Prof. David Marshall School of Computer Science & Informatics Factorisation Factorisation is a way of
CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation Prof. David Marshall School of Computer Science & Informatics Factorisation Factorisation is a way of
Combinatorial Proofs
 Combinatorial Proofs Two Counting Principles Some proofs concerning finite sets involve counting the number of elements of the sets, so we will look at the basics of counting. Addition Principle: If A
Combinatorial Proofs Two Counting Principles Some proofs concerning finite sets involve counting the number of elements of the sets, so we will look at the basics of counting. Addition Principle: If A
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS
 MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations
 Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder).
 Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS. + + x 2. x n. a 11 a 12 a 1n b 1 a 21 a 22 a 2n b 2 a 31 a 32 a 3n b 3. a m1 a m2 a mn b m
 MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 1. SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND MATRICES 1.1. Representation of a linear system. The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 +
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 1. SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND MATRICES 1.1. Representation of a linear system. The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 +
Factors and Products
 CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
In algebra, factor by rewriting a polynomial as a product of lower-degree polynomials
 Algebra 2 Notes SOL AII.1 Factoring Polynomials Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Factoring Review Factor: rewrite a number or expression as a product of primes; e.g. 6 = 2 3 In algebra, factor by rewriting
Algebra 2 Notes SOL AII.1 Factoring Polynomials Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Factoring Review Factor: rewrite a number or expression as a product of primes; e.g. 6 = 2 3 In algebra, factor by rewriting
UNIT 5 VOCABULARY: POLYNOMIALS
 2º ESO Bilingüe Page 1 UNIT 5 VOCABULARY: POLYNOMIALS 1.1. Algebraic Language Algebra is a part of mathematics in which symbols, usually letters of the alphabet, represent numbers. Letters are used to
2º ESO Bilingüe Page 1 UNIT 5 VOCABULARY: POLYNOMIALS 1.1. Algebraic Language Algebra is a part of mathematics in which symbols, usually letters of the alphabet, represent numbers. Letters are used to
Using the ac Method to Factor
 4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
7-6. Choosing a Factoring Model. Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable IN T RO DUC E T EACH. Standards for Mathematical Content
 7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
Lesson 9: Radicals and Conjugates
 Student Outcomes Students understand that the sum of two square roots (or two cube roots) is not equal to the square root (or cube root) of their sum. Students convert expressions to simplest radical form.
Student Outcomes Students understand that the sum of two square roots (or two cube roots) is not equal to the square root (or cube root) of their sum. Students convert expressions to simplest radical form.
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions
 6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
Factoring Polynomials
 UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
Factoring Guidelines. Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms. 2008 Shirley Radai
 Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
Factoring Guidelines Greatest Common Factor Two Terms Three Terms Four Terms 008 Shirley Radai Greatest Common Factor 008 Shirley Radai Factoring by Finding the Greatest Common Factor Always check for
1.3 Algebraic Expressions
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
SOL Warm-Up Graphing Calculator Active
 A.2a (a) Using laws of exponents to simplify monomial expressions and ratios of monomial expressions 1. Which expression is equivalent to (5x 2 )(4x 5 )? A 9x 7 B 9x 10 C 20x 7 D 20x 10 2. Which expression
A.2a (a) Using laws of exponents to simplify monomial expressions and ratios of monomial expressions 1. Which expression is equivalent to (5x 2 )(4x 5 )? A 9x 7 B 9x 10 C 20x 7 D 20x 10 2. Which expression
Vieta s Formulas and the Identity Theorem
 Vieta s Formulas and the Identity Theorem This worksheet will work through the material from our class on 3/21/2013 with some examples that should help you with the homework The topic of our discussion
Vieta s Formulas and the Identity Theorem This worksheet will work through the material from our class on 3/21/2013 with some examples that should help you with the homework The topic of our discussion
FACTORING POLYNOMIALS
 296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
How To Solve The Social Studies Test
 Math 00 Homework #0 Solutions. Section.: ab. For each map below, determine the number of southerly paths from point to point. Solution: We just have to use the same process as we did in building Pascal
Math 00 Homework #0 Solutions. Section.: ab. For each map below, determine the number of southerly paths from point to point. Solution: We just have to use the same process as we did in building Pascal
6.4 Special Factoring Rules
 6.4 Special Factoring Rules OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor a sum of cubes. By reversing the rules for multiplication
6.4 Special Factoring Rules OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor a sum of cubes. By reversing the rules for multiplication
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Systems of Equations and Matrices Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Systems of Equations and Matrices Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
SPECIAL PRODUCTS AND FACTORS
 CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS
 278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
278 (6 2) Chapter 6 Factoring 6.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS In this section Prime Factorization of Integers Greatest Common Factor Finding the Greatest Common Factor for Monomials Factoring Out the
Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any.
 Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
Algebra 2 - Chapter Prerequisites Vocabulary Copy in your notebook: Add an example of each term with the symbols used in algebra 2 if there are any. P1 p. 1 1. counting(natural) numbers - {1,2,3,4,...}
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials
 Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
FACTORING ax 2 bx c. Factoring Trinomials with Leading Coefficient 1
 5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
A Concrete Introduction. to the Abstract Concepts. of Integers and Algebra using Algebra Tiles
 A Concrete Introduction to the Abstract Concepts of Integers and Algebra using Algebra Tiles Table of Contents Introduction... 1 page Integers 1: Introduction to Integers... 3 2: Working with Algebra Tiles...
A Concrete Introduction to the Abstract Concepts of Integers and Algebra using Algebra Tiles Table of Contents Introduction... 1 page Integers 1: Introduction to Integers... 3 2: Working with Algebra Tiles...
Lesson 9: Radicals and Conjugates
 Student Outcomes Students understand that the sum of two square roots (or two cube roots) is not equal to the square root (or cube root) of their sum. Students convert expressions to simplest radical form.
Student Outcomes Students understand that the sum of two square roots (or two cube roots) is not equal to the square root (or cube root) of their sum. Students convert expressions to simplest radical form.
In the above, the number 19 is an example of a number because its only positive factors are one and itself.
 Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
Introduction Assignment
 PRE-CALCULUS 11 Introduction Assignment Welcome to PREC 11! This assignment will help you review some topics from a previous math course and introduce you to some of the topics that you ll be studying
PRE-CALCULUS 11 Introduction Assignment Welcome to PREC 11! This assignment will help you review some topics from a previous math course and introduce you to some of the topics that you ll be studying
5.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS
 C H A P T E R 5 Factoring he sport of skydiving was born in the 1930s soon after the military began using parachutes as a means of deploying troops. T Today, skydiving is a popular sport around the world.
C H A P T E R 5 Factoring he sport of skydiving was born in the 1930s soon after the military began using parachutes as a means of deploying troops. T Today, skydiving is a popular sport around the world.
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
 Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Polynomials. Key Terms. quadratic equation parabola conjugates trinomial. polynomial coefficient degree monomial binomial GCF
 Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method
 6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
Factoring Polynomials Factoring Factoring is the process of writing a polynomial as the product of two or more polynomials. The factors of 6x 2 x 2 are 2x + 1 and 3x 2. In this section, we will be factoring
expression is written horizontally. The Last terms ((2)( 4)) because they are the last terms of the two polynomials. This is called the FOIL method.
 A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
How To Solve Factoring Problems
 05-W4801-AM1.qxd 8/19/08 8:45 PM Page 241 Factoring, Solving Equations, and Problem Solving 5 5.1 Factoring by Using the Distributive Property 5.2 Factoring the Difference of Two Squares 5.3 Factoring
05-W4801-AM1.qxd 8/19/08 8:45 PM Page 241 Factoring, Solving Equations, and Problem Solving 5 5.1 Factoring by Using the Distributive Property 5.2 Factoring the Difference of Two Squares 5.3 Factoring
Chapter 7 - Roots, Radicals, and Complex Numbers
 Math 233 - Spring 2009 Chapter 7 - Roots, Radicals, and Complex Numbers 7.1 Roots and Radicals 7.1.1 Notation and Terminology In the expression x the is called the radical sign. The expression under the
Math 233 - Spring 2009 Chapter 7 - Roots, Radicals, and Complex Numbers 7.1 Roots and Radicals 7.1.1 Notation and Terminology In the expression x the is called the radical sign. The expression under the
By reversing the rules for multiplication of binomials from Section 4.6, we get rules for factoring polynomials in certain forms.
 SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:.
 MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping
 296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
Factoring Special Polynomials
 6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS EXPECTED BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE
 MODULE - 1 Quadratic Equations 6 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS In this lesson, you will study aout quadratic equations. You will learn to identify quadratic equations from a collection of given equations and write
MODULE - 1 Quadratic Equations 6 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS In this lesson, you will study aout quadratic equations. You will learn to identify quadratic equations from a collection of given equations and write
2) Based on the information in the table which choice BEST shows the answer to 1 906? 906 899 904 909
 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ) Multiplying a number by results in what type of. even. 0. even.,0. odd..,0. even ) Based on the information in the table which choice BEST shows the answer to 0? 0 0 0 )
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ) Multiplying a number by results in what type of. even. 0. even.,0. odd..,0. even ) Based on the information in the table which choice BEST shows the answer to 0? 0 0 0 )
SOLVING EQUATIONS WITH RADICALS AND EXPONENTS 9.5. section ( 3 5 3 2 )( 3 25 3 10 3 4 ). The Odd-Root Property
 498 (9 3) Chapter 9 Radicals and Rational Exponents Replace the question mark by an expression that makes the equation correct. Equations involving variables are to be identities. 75. 6 76. 3?? 1 77. 1
498 (9 3) Chapter 9 Radicals and Rational Exponents Replace the question mark by an expression that makes the equation correct. Equations involving variables are to be identities. 75. 6 76. 3?? 1 77. 1
SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
 (Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
(Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons. Stanley Ocken. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013
 Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons Prof. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013 An important feature of the following Beamer slide presentations is that you, the reader, move
Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons Prof. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013 An important feature of the following Beamer slide presentations is that you, the reader, move
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III
 Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
Year 9 set 1 Mathematics notes, to accompany the 9H book.
 Part 1: Year 9 set 1 Mathematics notes, to accompany the 9H book. equations 1. (p.1), 1.6 (p. 44), 4.6 (p.196) sequences 3. (p.115) Pupils use the Elmwood Press Essential Maths book by David Raymer (9H
Part 1: Year 9 set 1 Mathematics notes, to accompany the 9H book. equations 1. (p.1), 1.6 (p. 44), 4.6 (p.196) sequences 3. (p.115) Pupils use the Elmwood Press Essential Maths book by David Raymer (9H
BEGINNING ALGEBRA ACKNOWLEDMENTS
 BEGINNING ALGEBRA The Nursing Department of Labouré College requested the Department of Academic Planning and Support Services to help with mathematics preparatory materials for its Bachelor of Science
BEGINNING ALGEBRA The Nursing Department of Labouré College requested the Department of Academic Planning and Support Services to help with mathematics preparatory materials for its Bachelor of Science
Pre-Calculus II Factoring and Operations on Polynomials
 Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors
 Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors Brenda Meery Kaitlyn Spong Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) www.ck12.org Chapter 6. Factoring CHAPTER
Veterans Upward Bound Algebra I Concepts - Honors Brenda Meery Kaitlyn Spong Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) www.ck12.org Chapter 6. Factoring CHAPTER
CAHSEE on Target UC Davis, School and University Partnerships
 UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c
 Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
Euler s Formula Math 220
 Euler s Formula Math 0 last change: Sept 3, 05 Complex numbers A complex number is an expression of the form x+iy where x and y are real numbers and i is the imaginary square root of. For example, + 3i
Euler s Formula Math 0 last change: Sept 3, 05 Complex numbers A complex number is an expression of the form x+iy where x and y are real numbers and i is the imaginary square root of. For example, + 3i
COWLEY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE REVIEW GUIDE Compass Algebra Level 2
 COWLEY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE REVIEW GUIDE Compass Algebra Level This study guide is for students trying to test into College Algebra. There are three levels of math study guides. 1. If x and y 1, what
COWLEY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE REVIEW GUIDE Compass Algebra Level This study guide is for students trying to test into College Algebra. There are three levels of math study guides. 1. If x and y 1, what
Polynomial. Functions. 6A Operations with Polynomials. 6B Applying Polynomial. Functions. You can use polynomials to predict the shape of containers.
 Polynomial Functions 6A Operations with Polynomials 6-1 Polynomials 6- Multiplying Polynomials 6-3 Dividing Polynomials Lab Explore the Sum and Difference of Two Cubes 6-4 Factoring Polynomials 6B Applying
Polynomial Functions 6A Operations with Polynomials 6-1 Polynomials 6- Multiplying Polynomials 6-3 Dividing Polynomials Lab Explore the Sum and Difference of Two Cubes 6-4 Factoring Polynomials 6B Applying
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS - COMPARE THE FACTORING ac METHOD AND THE NEW DIAGONAL SUM METHOD By Nghi H. Nguyen
 SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS - COMPARE THE FACTORING ac METHOD AND THE NEW DIAGONAL SUM METHOD By Nghi H. Nguyen A. GENERALITIES. When a given quadratic equation can be factored, there are 2 best methods
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS - COMPARE THE FACTORING ac METHOD AND THE NEW DIAGONAL SUM METHOD By Nghi H. Nguyen A. GENERALITIES. When a given quadratic equation can be factored, there are 2 best methods
Simplification of Radical Expressions
 8. Simplification of Radical Expressions 8. OBJECTIVES 1. Simplify a radical expression by using the product property. Simplify a radical expression by using the quotient property NOTE A precise set of
8. Simplification of Radical Expressions 8. OBJECTIVES 1. Simplify a radical expression by using the product property. Simplify a radical expression by using the quotient property NOTE A precise set of
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
 3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
3.1 Solving Systems Using Tables and Graphs
 Algebra 2 Chapter 3 3.1 Solve Systems Using Tables & Graphs 3.1 Solving Systems Using Tables and Graphs A solution to a system of linear equations is an that makes all of the equations. To solve a system
Algebra 2 Chapter 3 3.1 Solve Systems Using Tables & Graphs 3.1 Solving Systems Using Tables and Graphs A solution to a system of linear equations is an that makes all of the equations. To solve a system
Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c
 4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
Lesson Plans for (9 th Grade Main Lesson) Possibility & Probability (including Permutations and Combinations)
 Lesson Plans for (9 th Grade Main Lesson) Possibility & Probability (including Permutations and Combinations) Note: At my school, there is only room for one math main lesson block in ninth grade. Therefore,
Lesson Plans for (9 th Grade Main Lesson) Possibility & Probability (including Permutations and Combinations) Note: At my school, there is only room for one math main lesson block in ninth grade. Therefore,
Solving Linear Systems, Continued and The Inverse of a Matrix
 , Continued and The of a Matrix Calculus III Summer 2013, Session II Monday, July 15, 2013 Agenda 1. The rank of a matrix 2. The inverse of a square matrix Gaussian Gaussian solves a linear system by reducing
, Continued and The of a Matrix Calculus III Summer 2013, Session II Monday, July 15, 2013 Agenda 1. The rank of a matrix 2. The inverse of a square matrix Gaussian Gaussian solves a linear system by reducing
Chapter 3 Section 6 Lesson Polynomials
 Chapter Section 6 Lesson Polynomials Introduction This lesson introduces polynomials and like terms. As we learned earlier, a monomial is a constant, a variable, or the product of constants and variables.
Chapter Section 6 Lesson Polynomials Introduction This lesson introduces polynomials and like terms. As we learned earlier, a monomial is a constant, a variable, or the product of constants and variables.
Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
Algebra Unpacked Content For the new Common Core standards that will be effective in all North Carolina schools in the 2012-13 school year.
 This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the Common Core (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Algebra
This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the Common Core (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Algebra
PRE-CALCULUS GRADE 12
 PRE-CALCULUS GRADE 12 [C] Communication Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. A1. Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians.
PRE-CALCULUS GRADE 12 [C] Communication Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop trigonometric reasoning. A1. Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians.
A Systematic Approach to Factoring
 A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
Taylor and Maclaurin Series
 Taylor and Maclaurin Series In the preceding section we were able to find power series representations for a certain restricted class of functions. Here we investigate more general problems: Which functions
Taylor and Maclaurin Series In the preceding section we were able to find power series representations for a certain restricted class of functions. Here we investigate more general problems: Which functions
Exponents and Radicals
 Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
Discrete Mathematics: Homework 7 solution. Due: 2011.6.03
 EE 2060 Discrete Mathematics spring 2011 Discrete Mathematics: Homework 7 solution Due: 2011.6.03 1. Let a n = 2 n + 5 3 n for n = 0, 1, 2,... (a) (2%) Find a 0, a 1, a 2, a 3 and a 4. (b) (2%) Show that
EE 2060 Discrete Mathematics spring 2011 Discrete Mathematics: Homework 7 solution Due: 2011.6.03 1. Let a n = 2 n + 5 3 n for n = 0, 1, 2,... (a) (2%) Find a 0, a 1, a 2, a 3 and a 4. (b) (2%) Show that
How To Understand And Solve A Linear Programming Problem
 At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Chapter 2: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices: 2.1: Solutions of Linear Systems by the Echelon Method Define linear systems, unique solution, inconsistent,
At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Chapter 2: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices: 2.1: Solutions of Linear Systems by the Echelon Method Define linear systems, unique solution, inconsistent,
