2. Equilateral Triangles
|
|
|
- Hortense Wheeler
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2. Equilateral Triangles Recall the well-known theorem of van Schooten. Theorem 1 If ABC is an equilateral triangle and M is a point on the arc BC of C(ABC) then MA = MB + MC. Proof Use Ptolemy on the cyclic quadrilateral ABM C. (Figure 1) In fact, using the Ptolemy inequality for quadrilaterals, we get the following van Schooten inequality. Figure 1: Theorem 2 Let ABC be an equilateral triangle. Then if M is any point in the plane of ABC we have 1 Pompeiu Triangle MA MB + MC. We get the following well-known theorem of D. Pompeiu as an immediate consequence of the previous inequality. Theorem Let M be any point in the plane of an equilateral triangle ABC. Then the distances MA, MB and MC can be the sidelengths of a triangle. 1
2 Proof It follows immediately since MA MB + MC The triangle is degenerate if M lies on the arc BC of the circumcircle C(ABC). A triangle with side lengths MA, MB and MC is called a Pompeiu triangle. When M is in the interior of ABC, then the pompeiu triangle can be explicitly constructed. Locate N so that the triangle BNM is equilateral. Now consider the triangles We have and AMB and BNC, AB = BC, BM = BN M BA = 60 M BC = C BN. Thus the triangles are similar, in fact CBN is got by rotating triangle ABM through 60 anti-clockwise in the diagram. Thus AM = CN, Figure 2: and so the triangle N M C has side lengths equal to M A, M B and M C. Thus N M C is the Pompeiu triangle. The measure of the angles of the Pompeiu triangle in terms of the angles subtended at M by the vertices of ABC and the area of the Pompeiu triangle are given by the following result of the distinguished Romanian born Sabin Tabirca Theorem 4 (Tabirca) If ABC is an equilateral triangle, and M is an interior point of ABC, then the angles of the Pompeiu triangle and its area are as follows: (a) the angles are the angles B MC 60, C MA 60 and A MB 60 ; 2
3 (b) the area S (Pompeiu triangle) is 1 (area of ABC) 4 MO 2, where O is circumcentre of the triangle ABC. Proof (a) In the triangle NMC, C MN = C MB N MB = C MB 60, C NM Notation: S(ABC). = C NB M NB = C NM 60 = A MB 60, and, finally, MĈN = 180 {C MN + C NM} = 180 {C MB 60 + A MB 60 } = 00 {60 A MC} = {A MC 60 }. The area of a triangle ABC is denoted by Figure : (b) In the diagram, NMC is the Pompeiu triangle which we now denote by T p. Then: S(T p ) where a = BC = CA = AB. = 1 ( CM. MN ) sin(c MN) 2 = 1 2 CM. BM sin(c MB 60 ) = 1 2 CM. BM {sin(c MB). 1 cos(c MB). 2 2 } = 1 4 CM. BM sin(c MB) CM MB cos(c MB) 4 = 1 2 S(CMB) 8 { CM 2 + BM 2 a 2 },
4 Thus S(T p ) = S(CMB) Similarly we can show that 8 { CM 2 + BM 2 a 2 }. S(T p ) = 1 2 S(CMA) 8 { CM 2 + MA 2 a 2 }, and S(T p ) = 1 2 S(BMA) 8 { BM 2 + MA 2 a 2 }. Adding, we get S(T p ) = 1 2 S(ABC) 8 {2( MA 2 + MB 2 + MC 2 ) a 2 }. Recall the Leibniz formula which states that for any triangle ABC with centroid G and point M MA 2 + MB 2 + MC 2 = MG { AB 2 + BC 2 + CA 2 } In the case of an equilateral triangle, G = 0, the centre of the circumcircle and a 2 = AB 2 = BC 2 = CA 2 so MA 2 + MB 2 + MC 2 = MO 2 +a 2. Thus S(T p ) = 1 2 S(ABC) 8 {6 MO 2 + 2a 2 a 2 } = 1 2 S(ABC) 8 6 MO a2. Since ABC is equilateral with side length a, S(ABC) = 4 a2, so S(T p ) = 1 2 S(ABC) 4 MO S(ABC) = S(ABC) 4 MO 2. Thus S(T p ) = 1 S(ABC) 4 MO 2, as required. 4
5 2 Fermat-Toricelli Point Let ABC be any triangle and on each side construct externally three equilateral triangles ABC 1, BCA 1 and CAB 1. Then we have the following theorem. Theorem 5 (a) The three circumcircles of the equilateral triangles intersect in a point T, i.e. C(ABC 1 ) C(BCA 1 ) C(CAB 1 ) = {T }. (b) The lines AA 1, BB 1 and CC 1 are concurrent at T, i.e. AA 1 BB 1 CC 1 = {T }. (c) AA 1 = BB 1 = CC 1 = T A + T B + T C. (d) For all points M in the plane of ABC, MA + MB + MC AA 1 = T A + T B + T C. Figure 4: i.e. the point T minimises the expression MA + MB + MC. The point T is called the Toricelli-Fermat point. Proof (a) Let {A, T } be the intersection points of the circles C(ABC 1 ) and C(ACB 1 ). Then since Because C 1 BT A is cyclic, A T B = 180 AĈ1B = 120. B 1 AT C is cyclic, A T C = 180 AB 1 C = 120. Thus BT C = 120 also. Thus B T C + BÂ1C = 180. Figure 5: 5
6 and so BA 1 CT is cyclic, i.e. T C(A 1 BC) (b) We claim that C 1, T, C are collinear points. A T C = 120, A T C 1 = A BC 1 = 60 giving AT C + AT C 1 = 180, i.e. C, T and C 1 are collinear. Similarly A, T, A 1 and B, T, B 1 are collinear. (c) We claim that CC 1 = T A + T B + T C. Since T C(AC 1 B) and AC 1 B is equilateral, then by van Schooten s theorem T C 1 = T A + T B. Thus CC 1 = CT + T C 1 = T C + T A + T B, as required. Similarly for AA 1 and BB 1. (d) Now let M be any point in the plane of ABC. Then, since ABC 1 is equilateral: MC 1 MA + MB Thus MA + MB + MC MC + MC 1 CC 1 = T A + T B + T C So the point of a triangle which minimises the sum of the distances to the three vertices is the Toricelli-Fermat point. One could ask the question of weighted distances to the vertices and ask which point(s) minimise weighted sums. This is the question we now investigate. 6
7 Generalised Fermat-Toricelli Theorem Let x, y and z be the side length of a triangle αβγ with x the length of the side opposite vertex α, y the length of the side opposite β and z the length of the side opposite γ. On an arbitrary triangle ABC construct externally triangles similar to αβγ with vertices positioned as indicated in Figure 6. (a) Then their circumcircles intersect at a point T 1, i.e. C(ABC 1 ) C(BCA 1 ) C(CAB 1 ) = {T 1 } (b) The lines AA 1, BB 1 and CC 1 are concurrent, i.e. AA 1 BB 1 CC 1 = {T 1 } (c) x AA 1 = y BB 1 = z CC 1 = x AT 1 = y BT 1 = z CT 1 (d) For any point M in the plane of ABC, Figure 6: x MA + y MB + z MC x AA 1 = x AT 1 + y BT 1 + z CT 1 Thus the point T 1 minimises the weighted distances of a point to the vertices. Proof The construction of the proof is similar to the proofs in the special case when x = y = z. (a) Let C(ABC 1 ) C(ACB 1 ) = {A, T 1 }. 7 Figure 7:
8 Since and AT 1 BC 1 is cyclic, A T 1 B = 180 γ, AT 1 CB 1 is cyclic, so A T 1 C = 180 β. Thus B T 1 C = 60 {A T 1 B + A T 1 C} = 60 {180 γ β = 180 { γ + β} = α. Thus T 1 BA 1 C is cyclic, i.e. T 1 C(BA 1 C), as required. (b) We claim that A T 1 C 1 + A T 1 C = 180 and from this it follows that T 1 lies on CC 1. In a similar way, we get that T 1 also belongs to the line segments BB 1 and AA 1. To show that A T 1 C 1 + A T 1 C = 180, we have, since, AT 1 CB 1 is cyclic, AT 1 C = 180 β. Also, A T 1 C 1 + A BC 1 = 180, as required. (c) Since the triangles A 1 BC and αβγ are similar, then A 1 B z = A 1C y = BC x. Thus A 1 B = BC z x, and A 1 C = BC y x. Since T 1 C(BCA 1 ), then, by Ptolemy, Figure 8: 8
9 T 1 A 1. BC = BT 1 CA 1 + CT 1 BA 1 = BT 1. BC y x + CT 1 BC z x Dividing across by BC and multiplying by x, we get x T 1 A 1 = y BT 1 + z CT 1. Thus x T 1 A 1 + y BT 1 + z CT 1 = x T 1 A + x T 1 A 1 = x AA 1. Similarly, we can show that x T 1 A +y T 1 B +z T 1 C = y BB 1 = z CC 1 (d) Now take a point M C(BCA 1 ). Then, by the Ptolemy inequality, BM CA 1 + CM. BA 1 > MA 1 BC Proceeding as in (c) above, we get x MA + y MB + z MC > x AA 1 = x T 1 A + y T 1 B + z T 1 C as required. Remarks 1. Now suppose that the positive weights x, y and z are not the sides of a triangle, i.e. suppose x y + z What then is the point which minimises the quantity x MA + y MB + z MC? where M is any point in the plane of ABC. To decide this, consider 9
10 x MA + y MB + z MC y( MA + MB ) + z( MA + MC ), since x y + z y AB + z AC = x AA + y AB + z AC Thus the point A(vertex) minimises the quantity x MA + y MB + z MC 2. Suppose we take then the weighted expression x = sin(bâc) = sin Â, y = sin(a BC) = sin B, z = sin(bĉa) = sin Ĉ, sin(â) MA + sin( B) MB + sin(ĉ) MC is minimised when M = O the centre of the circumcircle of ABC. If we take x = sin(â), y = sin( B) and z = sin(ĉ), then sin(â) MA + sin( B) MB + sin(ĉ) MC is minimised when M = H, the orhthocentre. B 4. If x = sin(â ), y = sin( ) and z = sin(ĉ ) then sin(â 2 B ) MA + (sin ) MB + sin(ĉ 2 2 ) MC is minimised when M = I, the incentre. 10
Exercise Set 3. Similar triangles. Parallel lines
 Exercise Set 3. Similar triangles Parallel lines Note: The exercises marked with are more difficult and go beyond the course/examination requirements. (1) Let ABC be a triangle with AB = AC. Let D be an
Exercise Set 3. Similar triangles Parallel lines Note: The exercises marked with are more difficult and go beyond the course/examination requirements. (1) Let ABC be a triangle with AB = AC. Let D be an
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Chapter 1. The Medial Triangle
 Chapter 1. The Medial Triangle 2 The triangle formed by joining the midpoints of the sides of a given triangle is called the medial triangle. Let A 1 B 1 C 1 be the medial triangle of the triangle ABC
Chapter 1. The Medial Triangle 2 The triangle formed by joining the midpoints of the sides of a given triangle is called the medial triangle. Let A 1 B 1 C 1 be the medial triangle of the triangle ABC
Chapter 3. Inversion and Applications to Ptolemy and Euler
 Chapter 3. Inversion and Applications to Ptolemy and Euler 2 Power of a point with respect to a circle Let A be a point and C a circle (Figure 1). If A is outside C and T is a point of contact of a tangent
Chapter 3. Inversion and Applications to Ptolemy and Euler 2 Power of a point with respect to a circle Let A be a point and C a circle (Figure 1). If A is outside C and T is a point of contact of a tangent
San Jose Math Circle April 25 - May 2, 2009 ANGLE BISECTORS
 San Jose Math Circle April 25 - May 2, 2009 ANGLE BISECTORS Recall that the bisector of an angle is the ray that divides the angle into two congruent angles. The most important results about angle bisectors
San Jose Math Circle April 25 - May 2, 2009 ANGLE BISECTORS Recall that the bisector of an angle is the ray that divides the angle into two congruent angles. The most important results about angle bisectors
Inversion. Chapter 7. 7.1 Constructing The Inverse of a Point: If P is inside the circle of inversion: (See Figure 7.1)
 Chapter 7 Inversion Goal: In this chapter we define inversion, give constructions for inverses of points both inside and outside the circle of inversion, and show how inversion could be done using Geometer
Chapter 7 Inversion Goal: In this chapter we define inversion, give constructions for inverses of points both inside and outside the circle of inversion, and show how inversion could be done using Geometer
Projective Geometry - Part 2
 Projective Geometry - Part 2 Alexander Remorov alexanderrem@gmail.com Review Four collinear points A, B, C, D form a harmonic bundle (A, C; B, D) when CA : DA CB DB = 1. A pencil P (A, B, C, D) is the
Projective Geometry - Part 2 Alexander Remorov alexanderrem@gmail.com Review Four collinear points A, B, C, D form a harmonic bundle (A, C; B, D) when CA : DA CB DB = 1. A pencil P (A, B, C, D) is the
INCIDENCE-BETWEENNESS GEOMETRY
 INCIDENCE-BETWEENNESS GEOMETRY MATH 410, CSUSM. SPRING 2008. PROFESSOR AITKEN This document covers the geometry that can be developed with just the axioms related to incidence and betweenness. The full
INCIDENCE-BETWEENNESS GEOMETRY MATH 410, CSUSM. SPRING 2008. PROFESSOR AITKEN This document covers the geometry that can be developed with just the axioms related to incidence and betweenness. The full
Incenter Circumcenter
 TRIANGLE: Centers: Incenter Incenter is the center of the inscribed circle (incircle) of the triangle, it is the point of intersection of the angle bisectors of the triangle. The radius of incircle is
TRIANGLE: Centers: Incenter Incenter is the center of the inscribed circle (incircle) of the triangle, it is the point of intersection of the angle bisectors of the triangle. The radius of incircle is
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this paper, we will
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this paper, we will
Conjectures. Chapter 2. Chapter 3
 Conjectures Chapter 2 C-1 Linear Pair Conjecture If two angles form a linear pair, then the measures of the angles add up to 180. (Lesson 2.5) C-2 Vertical Angles Conjecture If two angles are vertical
Conjectures Chapter 2 C-1 Linear Pair Conjecture If two angles form a linear pair, then the measures of the angles add up to 180. (Lesson 2.5) C-2 Vertical Angles Conjecture If two angles are vertical
3.1 Triangles, Congruence Relations, SAS Hypothesis
 Chapter 3 Foundations of Geometry 2 3.1 Triangles, Congruence Relations, SAS Hypothesis Definition 3.1 A triangle is the union of three segments ( called its side), whose end points (called its vertices)
Chapter 3 Foundations of Geometry 2 3.1 Triangles, Congruence Relations, SAS Hypothesis Definition 3.1 A triangle is the union of three segments ( called its side), whose end points (called its vertices)
Selected practice exam solutions (part 5, item 2) (MAT 360)
 Selected practice exam solutions (part 5, item ) (MAT 360) Harder 8,91,9,94(smaller should be replaced by greater )95,103,109,140,160,(178,179,180,181 this is really one problem),188,193,194,195 8. On
Selected practice exam solutions (part 5, item ) (MAT 360) Harder 8,91,9,94(smaller should be replaced by greater )95,103,109,140,160,(178,179,180,181 this is really one problem),188,193,194,195 8. On
Collinearity and concurrence
 Collinearity and concurrence Po-Shen Loh 23 June 2008 1 Warm-up 1. Let I be the incenter of ABC. Let A be the midpoint of the arc BC of the circumcircle of ABC which does not contain A. Prove that the
Collinearity and concurrence Po-Shen Loh 23 June 2008 1 Warm-up 1. Let I be the incenter of ABC. Let A be the midpoint of the arc BC of the circumcircle of ABC which does not contain A. Prove that the
Chapter 6 Notes: Circles
 Chapter 6 Notes: Circles IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle. Any line segment
Chapter 6 Notes: Circles IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle. Any line segment
IMO Geomety Problems. (IMO 1999/1) Determine all finite sets S of at least three points in the plane which satisfy the following condition:
 IMO Geomety Problems (IMO 1999/1) Determine all finite sets S of at least three points in the plane which satisfy the following condition: for any two distinct points A and B in S, the perpendicular bisector
IMO Geomety Problems (IMO 1999/1) Determine all finite sets S of at least three points in the plane which satisfy the following condition: for any two distinct points A and B in S, the perpendicular bisector
Analytical Geometry (4)
 Analytical Geometry (4) Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 3: Space, shape and measurement Assessment Standard As 3(c) and AS 3(a) The gradient and inclination of a straight line
Analytical Geometry (4) Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 3: Space, shape and measurement Assessment Standard As 3(c) and AS 3(a) The gradient and inclination of a straight line
Chapters 6 and 7 Notes: Circles, Locus and Concurrence
 Chapters 6 and 7 Notes: Circles, Locus and Concurrence IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of
Chapters 6 and 7 Notes: Circles, Locus and Concurrence IMPORTANT TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are at a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of
Mathematics Notes for Class 12 chapter 10. Vector Algebra
 1 P a g e Mathematics Notes for Class 12 chapter 10. Vector Algebra A vector has direction and magnitude both but scalar has only magnitude. Magnitude of a vector a is denoted by a or a. It is non-negative
1 P a g e Mathematics Notes for Class 12 chapter 10. Vector Algebra A vector has direction and magnitude both but scalar has only magnitude. Magnitude of a vector a is denoted by a or a. It is non-negative
Solutions to Practice Problems
 Higher Geometry Final Exam Tues Dec 11, 5-7:30 pm Practice Problems (1) Know the following definitions, statements of theorems, properties from the notes: congruent, triangle, quadrilateral, isosceles
Higher Geometry Final Exam Tues Dec 11, 5-7:30 pm Practice Problems (1) Know the following definitions, statements of theorems, properties from the notes: congruent, triangle, quadrilateral, isosceles
A Nice Theorem on Mixtilinear Incircles
 A Nice Theorem on Mixtilinear Incircles Khakimboy Egamberganov Abstract There are three mixtilinear incircles and three mixtilinear excircles in an arbitrary triangle. In this paper, we will present many
A Nice Theorem on Mixtilinear Incircles Khakimboy Egamberganov Abstract There are three mixtilinear incircles and three mixtilinear excircles in an arbitrary triangle. In this paper, we will present many
Intermediate Math Circles October 10, 2012 Geometry I: Angles
 Intermediate Math Circles October 10, 2012 Geometry I: Angles Over the next four weeks, we will look at several geometry topics. Some of the topics may be familiar to you while others, for most of you,
Intermediate Math Circles October 10, 2012 Geometry I: Angles Over the next four weeks, we will look at several geometry topics. Some of the topics may be familiar to you while others, for most of you,
SIMSON S THEOREM MARY RIEGEL
 SIMSON S THEOREM MARY RIEGEL Abstract. This paper is a presentation and discussion of several proofs of Simson s Theorem. Simson s Theorem is a statement about a specific type of line as related to a given
SIMSON S THEOREM MARY RIEGEL Abstract. This paper is a presentation and discussion of several proofs of Simson s Theorem. Simson s Theorem is a statement about a specific type of line as related to a given
Trigonometric Functions and Triangles
 Trigonometric Functions and Triangles Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw STate University August 27, 2010 Abstract This handout defines the trigonometric function of angles and discusses the relationship between
Trigonometric Functions and Triangles Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw STate University August 27, 2010 Abstract This handout defines the trigonometric function of angles and discusses the relationship between
Advanced Euclidean Geometry
 dvanced Euclidean Geometry What is the center of a triangle? ut what if the triangle is not equilateral?? Circumcenter Equally far from the vertices? P P Points are on the perpendicular bisector of a line
dvanced Euclidean Geometry What is the center of a triangle? ut what if the triangle is not equilateral?? Circumcenter Equally far from the vertices? P P Points are on the perpendicular bisector of a line
The Use of Dynamic Geometry Software in the Teaching and Learning of Geometry through Transformations
 The Use of Dynamic Geometry Software in the Teaching and Learning of Geometry through Transformations Dynamic geometry technology should be used to maximize student learning in geometry. Such technology
The Use of Dynamic Geometry Software in the Teaching and Learning of Geometry through Transformations Dynamic geometry technology should be used to maximize student learning in geometry. Such technology
Definitions, Postulates and Theorems
 Definitions, s and s Name: Definitions Complementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 o Supplementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 o A statement that can be proven
Definitions, s and s Name: Definitions Complementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 o Supplementary Angles Two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 o A statement that can be proven
Section 8.8. 1. The given line has equations. x = 3 + t(13 3) = 3 + 10t, y = 2 + t(3 + 2) = 2 + 5t, z = 7 + t( 8 7) = 7 15t.
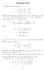 . The given line has equations Section 8.8 x + t( ) + 0t, y + t( + ) + t, z 7 + t( 8 7) 7 t. The line meets the plane y 0 in the point (x, 0, z), where 0 + t, or t /. The corresponding values for x and
. The given line has equations Section 8.8 x + t( ) + 0t, y + t( + ) + t, z 7 + t( 8 7) 7 t. The line meets the plane y 0 in the point (x, 0, z), where 0 + t, or t /. The corresponding values for x and
www.pioneermathematics.com
 Problems and Solutions: INMO-2012 1. Let ABCD be a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. Suppose AB = 2+ 2 and AB subtends 135 at the centre of the circle. Find the maximum possible area of ABCD. Solution:
Problems and Solutions: INMO-2012 1. Let ABCD be a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. Suppose AB = 2+ 2 and AB subtends 135 at the centre of the circle. Find the maximum possible area of ABCD. Solution:
1 Solution of Homework
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe February 4, 2011 Name: 1 Solution of Homework 10 Problem 1.1 (Common tangents of two circles). How many common tangents do two circles have. Informally draw all different cases,
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe February 4, 2011 Name: 1 Solution of Homework 10 Problem 1.1 (Common tangents of two circles). How many common tangents do two circles have. Informally draw all different cases,
Cevians, Symmedians, and Excircles. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16
 Cevians, Symmedians, and Excircles MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian
Cevians, Symmedians, and Excircles MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian
2009 Chicago Area All-Star Math Team Tryouts Solutions
 1. 2009 Chicago Area All-Star Math Team Tryouts Solutions If a car sells for q 1000 and the salesman earns q% = q/100, he earns 10q 2. He earns an additional 100 per car, and he sells p cars, so his total
1. 2009 Chicago Area All-Star Math Team Tryouts Solutions If a car sells for q 1000 and the salesman earns q% = q/100, he earns 10q 2. He earns an additional 100 per car, and he sells p cars, so his total
5.3 The Cross Product in R 3
 53 The Cross Product in R 3 Definition 531 Let u = [u 1, u 2, u 3 ] and v = [v 1, v 2, v 3 ] Then the vector given by [u 2 v 3 u 3 v 2, u 3 v 1 u 1 v 3, u 1 v 2 u 2 v 1 ] is called the cross product (or
53 The Cross Product in R 3 Definition 531 Let u = [u 1, u 2, u 3 ] and v = [v 1, v 2, v 3 ] Then the vector given by [u 2 v 3 u 3 v 2, u 3 v 1 u 1 v 3, u 1 v 2 u 2 v 1 ] is called the cross product (or
Mathematics 3301-001 Spring 2015 Dr. Alexandra Shlapentokh Guide #3
 Mathematics 3301-001 Spring 2015 Dr. Alexandra Shlapentokh Guide #3 The problems in bold are the problems for Test #3. As before, you are allowed to use statements above and all postulates in the proofs
Mathematics 3301-001 Spring 2015 Dr. Alexandra Shlapentokh Guide #3 The problems in bold are the problems for Test #3. As before, you are allowed to use statements above and all postulates in the proofs
Chapter 3.1 Angles. Geometry. Objectives: Define what an angle is. Define the parts of an angle.
 Chapter 3.1 Angles Define what an angle is. Define the parts of an angle. Recall our definition for a ray. A ray is a line segment with a definite starting point and extends into infinity in only one direction.
Chapter 3.1 Angles Define what an angle is. Define the parts of an angle. Recall our definition for a ray. A ray is a line segment with a definite starting point and extends into infinity in only one direction.
Most popular response to
 Class #33 Most popular response to What did the students want to prove? The angle bisectors of a square meet at a point. A square is a convex quadrilateral in which all sides are congruent and all angles
Class #33 Most popular response to What did the students want to prove? The angle bisectors of a square meet at a point. A square is a convex quadrilateral in which all sides are congruent and all angles
Angles in a Circle and Cyclic Quadrilateral
 130 Mathematics 19 Angles in a Circle and Cyclic Quadrilateral 19.1 INTRODUCTION You must have measured the angles between two straight lines, let us now study the angles made by arcs and chords in a circle
130 Mathematics 19 Angles in a Circle and Cyclic Quadrilateral 19.1 INTRODUCTION You must have measured the angles between two straight lines, let us now study the angles made by arcs and chords in a circle
Class-10 th (X) Mathematics Chapter: Tangents to Circles
 Class-10 th (X) Mathematics Chapter: Tangents to Circles 1. Q. AB is line segment of length 24 cm. C is its midpoint. On AB, AC and BC semicircles are described. Find the radius of the circle which touches
Class-10 th (X) Mathematics Chapter: Tangents to Circles 1. Q. AB is line segment of length 24 cm. C is its midpoint. On AB, AC and BC semicircles are described. Find the radius of the circle which touches
Math 531, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 531, Exam 1 Information. 9/21/11, LC 310, 9:05-9:55. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 1A - 1F. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/531fa11/531.html)
Math 531, Exam 1 Information. 9/21/11, LC 310, 9:05-9:55. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 1A - 1F. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/531fa11/531.html)
Geometric Transformations
 Geometric Transformations Definitions Def: f is a mapping (function) of a set A into a set B if for every element a of A there exists a unique element b of B that is paired with a; this pairing is denoted
Geometric Transformations Definitions Def: f is a mapping (function) of a set A into a set B if for every element a of A there exists a unique element b of B that is paired with a; this pairing is denoted
11 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament
 11 th nnual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday February 008 Individual Round: Geometry Test 1. [] How many different values can take, where,, are distinct vertices of a cube? nswer: 5. In a unit
11 th nnual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday February 008 Individual Round: Geometry Test 1. [] How many different values can take, where,, are distinct vertices of a cube? nswer: 5. In a unit
Ceva s Theorem. Ceva s Theorem. Ceva s Theorem 9/20/2011. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 11
 MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 11 The three lines containing the vertices A, B, and C of ABC and intersecting opposite sides at points L, M, and N, respectively, are concurrent if and only if 2 3 1
MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 11 The three lines containing the vertices A, B, and C of ABC and intersecting opposite sides at points L, M, and N, respectively, are concurrent if and only if 2 3 1
61. Pascal s Hexagon Theorem.
 . Pascal s Hexagon Theorem. Prove that the three points of intersection of the opposite sides of a hexagon inscribed in a conic section lie on a straight line. Hexagon has opposite sides,;, and,. Pascal
. Pascal s Hexagon Theorem. Prove that the three points of intersection of the opposite sides of a hexagon inscribed in a conic section lie on a straight line. Hexagon has opposite sides,;, and,. Pascal
www.sakshieducation.com
 LENGTH OF THE PERPENDICULAR FROM A POINT TO A STRAIGHT LINE AND DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO PAPALLEL LINES THEOREM The perpendicular distance from a point P(x 1, y 1 ) to the line ax + by + c 0 is ax1+ by1+ c
LENGTH OF THE PERPENDICULAR FROM A POINT TO A STRAIGHT LINE AND DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO PAPALLEL LINES THEOREM The perpendicular distance from a point P(x 1, y 1 ) to the line ax + by + c 0 is ax1+ by1+ c
CHAPTER 1 CEVA S THEOREM AND MENELAUS S THEOREM
 HTR 1 V S THOR N NLUS S THOR The purpose of this chapter is to develop a few results that may be used in later chapters. We will begin with a simple but useful theorem concerning the area ratio of two
HTR 1 V S THOR N NLUS S THOR The purpose of this chapter is to develop a few results that may be used in later chapters. We will begin with a simple but useful theorem concerning the area ratio of two
IMO Training 2008 Circles Yufei Zhao. Circles. Yufei Zhao.
 ircles Yufei Zhao yufeiz@mit.edu 1 Warm up problems 1. Let and be two segments, and let lines and meet at X. Let the circumcircles of X and X meet again at O. Prove that triangles O and O are similar.
ircles Yufei Zhao yufeiz@mit.edu 1 Warm up problems 1. Let and be two segments, and let lines and meet at X. Let the circumcircles of X and X meet again at O. Prove that triangles O and O are similar.
ON THE SIMSON WALLACE THEOREM
 South Bohemia Mathematical Letters Volume 21, (2013), No. 1, 59 66. ON THE SIMSON WALLACE THEOREM PAVEL PECH 1, EMIL SKŘÍŠOVSKÝ2 Abstract. The paper deals with the well-known Simson Wallace theorem and
South Bohemia Mathematical Letters Volume 21, (2013), No. 1, 59 66. ON THE SIMSON WALLACE THEOREM PAVEL PECH 1, EMIL SKŘÍŠOVSKÝ2 Abstract. The paper deals with the well-known Simson Wallace theorem and
5.1 Midsegment Theorem and Coordinate Proof
 5.1 Midsegment Theorem and Coordinate Proof Obj.: Use properties of midsegments and write coordinate proofs. Key Vocabulary Midsegment of a triangle - A midsegment of a triangle is a segment that connects
5.1 Midsegment Theorem and Coordinate Proof Obj.: Use properties of midsegments and write coordinate proofs. Key Vocabulary Midsegment of a triangle - A midsegment of a triangle is a segment that connects
25 The Law of Cosines and Its Applications
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 103: Trigonometry Dr Marcel B Finan 5 The Law of Cosines and Its Applications The Law of Sines is applicable when either two angles and a side are given or two sides and an
Arkansas Tech University MATH 103: Trigonometry Dr Marcel B Finan 5 The Law of Cosines and Its Applications The Law of Sines is applicable when either two angles and a side are given or two sides and an
Geometry Regents Review
 Name: Class: Date: Geometry Regents Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest
Name: Class: Date: Geometry Regents Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest
Vector Notation: AB represents the vector from point A to point B on a graph. The vector can be computed by B A.
 1 Linear Transformations Prepared by: Robin Michelle King A transformation of an object is a change in position or dimension (or both) of the object. The resulting object after the transformation is called
1 Linear Transformations Prepared by: Robin Michelle King A transformation of an object is a change in position or dimension (or both) of the object. The resulting object after the transformation is called
Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant:
 12.1: Tangent Lines Congruent Circles: circles that have the same radius length Diagram of Examples Center of Circle: Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant: Tangent to A Circle: a line in the plane
12.1: Tangent Lines Congruent Circles: circles that have the same radius length Diagram of Examples Center of Circle: Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant: Tangent to A Circle: a line in the plane
Conjectures for Geometry for Math 70 By I. L. Tse
 Conjectures for Geometry for Math 70 By I. L. Tse Chapter Conjectures 1. Linear Pair Conjecture: If two angles form a linear pair, then the measure of the angles add up to 180. Vertical Angle Conjecture:
Conjectures for Geometry for Math 70 By I. L. Tse Chapter Conjectures 1. Linear Pair Conjecture: If two angles form a linear pair, then the measure of the angles add up to 180. Vertical Angle Conjecture:
Lecture 24: Saccheri Quadrilaterals
 Lecture 24: Saccheri Quadrilaterals 24.1 Saccheri Quadrilaterals Definition In a protractor geometry, we call a quadrilateral ABCD a Saccheri quadrilateral, denoted S ABCD, if A and D are right angles
Lecture 24: Saccheri Quadrilaterals 24.1 Saccheri Quadrilaterals Definition In a protractor geometry, we call a quadrilateral ABCD a Saccheri quadrilateral, denoted S ABCD, if A and D are right angles
Name Date Class. Lines and Segments That Intersect Circles. AB and CD are chords. Tangent Circles. Theorem Hypothesis Conclusion
 Section. Lines That Intersect Circles Lines and Segments That Intersect Circles A chord is a segment whose endpoints lie on a circle. A secant is a line that intersects a circle at two points. A tangent
Section. Lines That Intersect Circles Lines and Segments That Intersect Circles A chord is a segment whose endpoints lie on a circle. A secant is a line that intersects a circle at two points. A tangent
Objective: To distinguish between degree and radian measure, and to solve problems using both.
 CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1 Teacher s Guide Radian Measure AW 3.2 MP 4.1 Objective: To distinguish between degree and radian measure, and to solve problems using both. Prerequisites Define the following concepts.
CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1 Teacher s Guide Radian Measure AW 3.2 MP 4.1 Objective: To distinguish between degree and radian measure, and to solve problems using both. Prerequisites Define the following concepts.
Warm-up Theorems about triangles. Geometry. Theorems about triangles. Misha Lavrov. ARML Practice 12/15/2013
 ARML Practice 12/15/2013 Problem Solution Warm-up problem Lunes of Hippocrates In the diagram below, the blue triangle is a right triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. What is the total area of the green
ARML Practice 12/15/2013 Problem Solution Warm-up problem Lunes of Hippocrates In the diagram below, the blue triangle is a right triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. What is the total area of the green
4. How many integers between 2004 and 4002 are perfect squares?
 5 is 0% of what number? What is the value of + 3 4 + 99 00? (alternating signs) 3 A frog is at the bottom of a well 0 feet deep It climbs up 3 feet every day, but slides back feet each night If it started
5 is 0% of what number? What is the value of + 3 4 + 99 00? (alternating signs) 3 A frog is at the bottom of a well 0 feet deep It climbs up 3 feet every day, but slides back feet each night If it started
Classical theorems on hyperbolic triangles from a projective point of view
 tmcs-szilasi 2012/3/1 0:14 page 175 #1 10/1 (2012), 175 181 Classical theorems on hyperbolic triangles from a projective point of view Zoltán Szilasi Abstract. Using the Cayley-Klein model of hyperbolic
tmcs-szilasi 2012/3/1 0:14 page 175 #1 10/1 (2012), 175 181 Classical theorems on hyperbolic triangles from a projective point of view Zoltán Szilasi Abstract. Using the Cayley-Klein model of hyperbolic
Section 9-1. Basic Terms: Tangents, Arcs and Chords Homework Pages 330-331: 1-18
 Chapter 9 Circles Objectives A. Recognize and apply terms relating to circles. B. Properly use and interpret the symbols for the terms and concepts in this chapter. C. Appropriately apply the postulates,
Chapter 9 Circles Objectives A. Recognize and apply terms relating to circles. B. Properly use and interpret the symbols for the terms and concepts in this chapter. C. Appropriately apply the postulates,
Chapter 5.1 and 5.2 Triangles
 Chapter 5.1 and 5.2 Triangles Students will classify triangles. Students will define and use the Angle Sum Theorem. A triangle is formed when three non-collinear points are connected by segments. Each
Chapter 5.1 and 5.2 Triangles Students will classify triangles. Students will define and use the Angle Sum Theorem. A triangle is formed when three non-collinear points are connected by segments. Each
Baltic Way 1995. Västerås (Sweden), November 12, 1995. Problems and solutions
 Baltic Way 995 Västerås (Sweden), November, 995 Problems and solutions. Find all triples (x, y, z) of positive integers satisfying the system of equations { x = (y + z) x 6 = y 6 + z 6 + 3(y + z ). Solution.
Baltic Way 995 Västerås (Sweden), November, 995 Problems and solutions. Find all triples (x, y, z) of positive integers satisfying the system of equations { x = (y + z) x 6 = y 6 + z 6 + 3(y + z ). Solution.
MAGIC SQUARES. What you see here is a magic square, much like the addition and subtraction squares you may have used as a child.
 MAGIC SQUARES What you see here is a magic square, much like the addition and subtraction squares you may have used as a child. These magic squares are even more talented, as they all follow the rules
MAGIC SQUARES What you see here is a magic square, much like the addition and subtraction squares you may have used as a child. These magic squares are even more talented, as they all follow the rules
6.1 Basic Right Triangle Trigonometry
 6.1 Basic Right Triangle Trigonometry MEASURING ANGLES IN RADIANS First, let s introduce the units you will be using to measure angles, radians. A radian is a unit of measurement defined as the angle at
6.1 Basic Right Triangle Trigonometry MEASURING ANGLES IN RADIANS First, let s introduce the units you will be using to measure angles, radians. A radian is a unit of measurement defined as the angle at
On Triangles with Vertices on the Angle Bisectors
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 247 253. FORUM GEOM SSN 1534-1178 On Triangles with Vertices on the ngle isectors Eric Danneels bstract. We study interesting properties of triangles whose vertices
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 247 253. FORUM GEOM SSN 1534-1178 On Triangles with Vertices on the ngle isectors Eric Danneels bstract. We study interesting properties of triangles whose vertices
CIRCLE COORDINATE GEOMETRY
 CIRCLE COORDINATE GEOMETRY (EXAM QUESTIONS) Question 1 (**) A circle has equation x + y = 2x + 8 Determine the radius and the coordinates of the centre of the circle. r = 3, ( 1,0 ) Question 2 (**) A circle
CIRCLE COORDINATE GEOMETRY (EXAM QUESTIONS) Question 1 (**) A circle has equation x + y = 2x + 8 Determine the radius and the coordinates of the centre of the circle. r = 3, ( 1,0 ) Question 2 (**) A circle
12. Parallels. Then there exists a line through P parallel to l.
 12. Parallels Given one rail of a railroad track, is there always a second rail whose (perpendicular) distance from the first rail is exactly the width across the tires of a train, so that the two rails
12. Parallels Given one rail of a railroad track, is there always a second rail whose (perpendicular) distance from the first rail is exactly the width across the tires of a train, so that the two rails
Unit 8: Congruent and Similar Triangles Lesson 8.1 Apply Congruence and Triangles Lesson 4.2 from textbook
 Unit 8: Congruent and Similar Triangles Lesson 8.1 Apply Congruence and Triangles Lesson 4.2 from textbook Objectives Identify congruent figures and corresponding parts of closed plane figures. Prove that
Unit 8: Congruent and Similar Triangles Lesson 8.1 Apply Congruence and Triangles Lesson 4.2 from textbook Objectives Identify congruent figures and corresponding parts of closed plane figures. Prove that
CHAPTER 8 QUADRILATERALS. 8.1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 8 QUADRILATERALS 8.1 Introduction You have studied many properties of a triangle in Chapters 6 and 7 and you know that on joining three non-collinear points in pairs, the figure so obtained is
CHAPTER 8 QUADRILATERALS 8.1 Introduction You have studied many properties of a triangle in Chapters 6 and 7 and you know that on joining three non-collinear points in pairs, the figure so obtained is
Unit 3: Circles and Volume
 Unit 3: Circles and Volume This unit investigates the properties of circles and addresses finding the volume of solids. Properties of circles are used to solve problems involving arcs, angles, sectors,
Unit 3: Circles and Volume This unit investigates the properties of circles and addresses finding the volume of solids. Properties of circles are used to solve problems involving arcs, angles, sectors,
Triangle Centers MOP 2007, Black Group
 Triangle Centers MOP 2007, Black Group Zachary Abel June 21, 2007 1 A Few Useful Centers 1.1 Symmedian / Lemmoine Point The Symmedian point K is defined as the isogonal conjugate of the centroid G. Problem
Triangle Centers MOP 2007, Black Group Zachary Abel June 21, 2007 1 A Few Useful Centers 1.1 Symmedian / Lemmoine Point The Symmedian point K is defined as the isogonal conjugate of the centroid G. Problem
Linear Algebra Notes for Marsden and Tromba Vector Calculus
 Linear Algebra Notes for Marsden and Tromba Vector Calculus n-dimensional Euclidean Space and Matrices Definition of n space As was learned in Math b, a point in Euclidean three space can be thought of
Linear Algebra Notes for Marsden and Tromba Vector Calculus n-dimensional Euclidean Space and Matrices Definition of n space As was learned in Math b, a point in Euclidean three space can be thought of
Conic Construction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its Angle Bisectors
 onic onstruction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its ngle isectors Paul Yiu bstract. We study an extension of the problem of construction of a triangle from the feet of its internal angle bisectors. Given
onic onstruction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its ngle isectors Paul Yiu bstract. We study an extension of the problem of construction of a triangle from the feet of its internal angle bisectors. Given
6 Commutators and the derived series. [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1.
![6 Commutators and the derived series. [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1. 6 Commutators and the derived series. [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1.](/thumbs/19/254057.jpg) 6 Commutators and the derived series Definition. Let G be a group, and let x,y G. The commutator of x and y is [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1. Note that [x,y] = e if and only if xy = yx (since x 1 y 1 = (yx) 1 ). Proposition
6 Commutators and the derived series Definition. Let G be a group, and let x,y G. The commutator of x and y is [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1. Note that [x,y] = e if and only if xy = yx (since x 1 y 1 = (yx) 1 ). Proposition
/27 Intro to Geometry Review
 /27 Intro to Geometry Review 1. An acute has a measure of. 2. A right has a measure of. 3. An obtuse has a measure of. 13. Two supplementary angles are in ratio 11:7. Find the measure of each. 14. In the
/27 Intro to Geometry Review 1. An acute has a measure of. 2. A right has a measure of. 3. An obtuse has a measure of. 13. Two supplementary angles are in ratio 11:7. Find the measure of each. 14. In the
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 Chapter 8 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 8.1 Introduction In this chapter we present a vector algebra approach to three dimensional geometry. The aim is to present standard properties of lines and planes,
Chapter 8 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 8.1 Introduction In this chapter we present a vector algebra approach to three dimensional geometry. The aim is to present standard properties of lines and planes,
Unit 2 - Triangles. Equilateral Triangles
 Equilateral Triangles Unit 2 - Triangles Equilateral Triangles Overview: Objective: In this activity participants discover properties of equilateral triangles using properties of symmetry. TExES Mathematics
Equilateral Triangles Unit 2 - Triangles Equilateral Triangles Overview: Objective: In this activity participants discover properties of equilateral triangles using properties of symmetry. TExES Mathematics
1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Which type of construction is best represented by the steps given above?
 1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Step 1: Place the compass on one endpoint of the line segment. Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width
1. A student followed the given steps below to complete a construction. Step 1: Place the compass on one endpoint of the line segment. Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width
GEOMETRY. Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12
 GEOMETRY Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12 OBJECTIVE Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic
GEOMETRY Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.12 OBJECTIVE Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Thursday, August 16, 2012 8:30 to 11:30 a.m.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 16, 2012 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 16, 2012 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of your
Three Lemmas in Geometry
 Winter amp 2010 Three Lemmas in Geometry Yufei Zhao Three Lemmas in Geometry Yufei Zhao Massachusetts Institute of Technology yufei.zhao@gmail.com 1 iameter of incircle T Lemma 1. Let the incircle of triangle
Winter amp 2010 Three Lemmas in Geometry Yufei Zhao Three Lemmas in Geometry Yufei Zhao Massachusetts Institute of Technology yufei.zhao@gmail.com 1 iameter of incircle T Lemma 1. Let the incircle of triangle
MATHEMATICS Grade 12 EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY: CIRCLES 02 JULY 2014
 EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY: CIRCLES 02 JULY 2014 Checklist Make sure you learn proofs of the following theorems: The line drawn from the centre of a circle perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord The angle
EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY: CIRCLES 02 JULY 2014 Checklist Make sure you learn proofs of the following theorems: The line drawn from the centre of a circle perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord The angle
The common ratio in (ii) is called the scaled-factor. An example of two similar triangles is shown in Figure 47.1. Figure 47.1
 47 Similar Triangles An overhead projector forms an image on the screen which has the same shape as the image on the transparency but with the size altered. Two figures that have the same shape but not
47 Similar Triangles An overhead projector forms an image on the screen which has the same shape as the image on the transparency but with the size altered. Two figures that have the same shape but not
Law of Cosines. If the included angle is a right angle then the Law of Cosines is the same as the Pythagorean Theorem.
 Law of Cosines In the previous section, we learned how the Law of Sines could be used to solve oblique triangles in three different situations () where a side and two angles (SAA) were known, () where
Law of Cosines In the previous section, we learned how the Law of Sines could be used to solve oblique triangles in three different situations () where a side and two angles (SAA) were known, () where
Angle bisectors of a triangle in I 2
 Mathematical Communications 3(008), 97-05 97 Angle bisectors of a triangle in I Zdenka Kolar Begović,Ružica Kolar Šuper and Vladimir Volenec Abstract. The concept of an angle bisector of the triangle will
Mathematical Communications 3(008), 97-05 97 Angle bisectors of a triangle in I Zdenka Kolar Begović,Ružica Kolar Šuper and Vladimir Volenec Abstract. The concept of an angle bisector of the triangle will
Two Applications of Desargues Theorem
 Two pplications of Desargues Theorem Prof. Florentin Smarandache, University of New Mexico, U.S.. Prof. Ion Pătraşcu, The National College Fraţii Buzeşti, Craiova, Romania In this article we will use the
Two pplications of Desargues Theorem Prof. Florentin Smarandache, University of New Mexico, U.S.. Prof. Ion Pătraşcu, The National College Fraţii Buzeşti, Craiova, Romania In this article we will use the
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 Instructor: Longfei Li Math 43 Lecture Notes.5 Equations of Lines and Planes What do we need to determine a line? D: a point on the line: P 0 (x 0, y 0 ) direction (slope): k 3D: a point on the line: P
Instructor: Longfei Li Math 43 Lecture Notes.5 Equations of Lines and Planes What do we need to determine a line? D: a point on the line: P 0 (x 0, y 0 ) direction (slope): k 3D: a point on the line: P
Semester Exam Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Are O, N, and P collinear? If so, name the line on which they lie. O N M P a. No,
Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Are O, N, and P collinear? If so, name the line on which they lie. O N M P a. No,
1.3. DOT PRODUCT 19. 6. If θ is the angle (between 0 and π) between two non-zero vectors u and v,
 1.3. DOT PRODUCT 19 1.3 Dot Product 1.3.1 Definitions and Properties The dot product is the first way to multiply two vectors. The definition we will give below may appear arbitrary. But it is not. It
1.3. DOT PRODUCT 19 1.3 Dot Product 1.3.1 Definitions and Properties The dot product is the first way to multiply two vectors. The definition we will give below may appear arbitrary. But it is not. It
Mathematics Geometry Unit 1 (SAMPLE)
 Review the Geometry sample year-long scope and sequence associated with this unit plan. Mathematics Possible time frame: Unit 1: Introduction to Geometric Concepts, Construction, and Proof 14 days This
Review the Geometry sample year-long scope and sequence associated with this unit plan. Mathematics Possible time frame: Unit 1: Introduction to Geometric Concepts, Construction, and Proof 14 days This
Test on Circle Geometry (Chapter 15)
 Test on Circle Geometry (Chapter 15) Chord Properties of Circles A chord of a circle is any interval that joins two points on the curve. The largest chord of a circle is its diameter. 1. Chords of equal
Test on Circle Geometry (Chapter 15) Chord Properties of Circles A chord of a circle is any interval that joins two points on the curve. The largest chord of a circle is its diameter. 1. Chords of equal
39 Symmetry of Plane Figures
 39 Symmetry of Plane Figures In this section, we are interested in the symmetric properties of plane figures. By a symmetry of a plane figure we mean a motion of the plane that moves the figure so that
39 Symmetry of Plane Figures In this section, we are interested in the symmetric properties of plane figures. By a symmetry of a plane figure we mean a motion of the plane that moves the figure so that
LS.6 Solution Matrices
 LS.6 Solution Matrices In the literature, solutions to linear systems often are expressed using square matrices rather than vectors. You need to get used to the terminology. As before, we state the definitions
LS.6 Solution Matrices In the literature, solutions to linear systems often are expressed using square matrices rather than vectors. You need to get used to the terminology. As before, we state the definitions
x R 2 x = (x 1, x 2 ) or p = (x, y) R 3
 Euclidean space 1 Chapter 1 Euclidean space A. The basic vector space We shall denote by R the field of real numbers. Then we shall use the Cartesian product R n = R R... R of ordered n-tuples of real
Euclidean space 1 Chapter 1 Euclidean space A. The basic vector space We shall denote by R the field of real numbers. Then we shall use the Cartesian product R n = R R... R of ordered n-tuples of real
CSU Fresno Problem Solving Session. Geometry, 17 March 2012
 CSU Fresno Problem Solving Session Problem Solving Sessions website: http://zimmer.csufresno.edu/ mnogin/mfd-prep.html Math Field Day date: Saturday, April 21, 2012 Math Field Day website: http://www.csufresno.edu/math/news
CSU Fresno Problem Solving Session Problem Solving Sessions website: http://zimmer.csufresno.edu/ mnogin/mfd-prep.html Math Field Day date: Saturday, April 21, 2012 Math Field Day website: http://www.csufresno.edu/math/news
MA 323 Geometric Modelling Course Notes: Day 02 Model Construction Problem
 MA 323 Geometric Modelling Course Notes: Day 02 Model Construction Problem David L. Finn November 30th, 2004 In the next few days, we will introduce some of the basic problems in geometric modelling, and
MA 323 Geometric Modelling Course Notes: Day 02 Model Construction Problem David L. Finn November 30th, 2004 In the next few days, we will introduce some of the basic problems in geometric modelling, and
http://www.castlelearning.com/review/teacher/assignmentprinting.aspx 5. 2 6. 2 1. 10 3. 70 2. 55 4. 180 7. 2 8. 4
 of 9 1/28/2013 8:32 PM Teacher: Mr. Sime Name: 2 What is the slope of the graph of the equation y = 2x? 5. 2 If the ratio of the measures of corresponding sides of two similar triangles is 4:9, then the
of 9 1/28/2013 8:32 PM Teacher: Mr. Sime Name: 2 What is the slope of the graph of the equation y = 2x? 5. 2 If the ratio of the measures of corresponding sides of two similar triangles is 4:9, then the
1. Find the length of BC in the following triangles. It will help to first find the length of the segment marked X.
 1 Find the length of BC in the following triangles It will help to first find the length of the segment marked X a: b: Given: the diagonals of parallelogram ABCD meet at point O The altitude OE divides
1 Find the length of BC in the following triangles It will help to first find the length of the segment marked X a: b: Given: the diagonals of parallelogram ABCD meet at point O The altitude OE divides
Lesson 18: Looking More Carefully at Parallel Lines
 Student Outcomes Students learn to construct a line parallel to a given line through a point not on that line using a rotation by 180. They learn how to prove the alternate interior angles theorem using
Student Outcomes Students learn to construct a line parallel to a given line through a point not on that line using a rotation by 180. They learn how to prove the alternate interior angles theorem using
TIgeometry.com. Geometry. Angle Bisectors in a Triangle
 Angle Bisectors in a Triangle ID: 8892 Time required 40 minutes Topic: Triangles and Their Centers Use inductive reasoning to postulate a relationship between an angle bisector and the arms of the angle.
Angle Bisectors in a Triangle ID: 8892 Time required 40 minutes Topic: Triangles and Their Centers Use inductive reasoning to postulate a relationship between an angle bisector and the arms of the angle.
