CLASS. CBSE-i GEOGRAPHY. Unit-1 MYSTUDENTS MANUAL CITY HOME. Shiksha Kendra, 2, Community Centre, Preet Vihar, Delhi India
|
|
|
- Kevin Tate
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CBSE-i GEOGRAPHY CLASS VI Unit-1 CITY MYSTUDENTS MANUAL HOME Shiksha Kendra, 2, Community Centre, Preet Vihar, Delhi India
2
3 CLASS VI Unit-1 CBSE-i GEOGRAPHY MY CITY HOME STUDENTS MANUAL Shiksha Kendra, 2, Community Centre, Preet Vihar, Delhi India
4 The CBSE-International is grateful for permission to reproduce and/or translate copyright material used in this publication. The acknowledgements have been included wherever appropriate and sources from where the material has been taken duly mentioned. In case anything has been missed out, the Board will be pleased to rectify the error at the earliest possible opportunity. All Rights of these documents are reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, printed or transmitted in any form without the prior permission of the CBSE-i. This material is meant for the use of schools who are a part of the CBSE-International only.
5 Preface This International Curriculum initiated by Central Board of Secondary Education - (CBSE) is a progressive step in making the educational content and methodology more sensitive and responsive to the global needs. It signifies the emergence of a fresh thought process in imparting a curriculum which would restore the autonomy of the learner to pursue the learning process in harmony with the existing personal, social and cultural ethos. The Central Board of Secondary Education has been providing support to the academic needs of the learners worldwide. It has about schools affiliated to it and over 158 schools situated in more than 23 countries. The Board has always been conscious of the varying needs of the learners and has been working towards contextualizing certain elements of the learning process to the physical, geographical, social and cultural environment in which they are engaged. The International Curriculum being designed by CBSE-i, has been visualized and developed with these requirements in view. The nucleus of the entire process of constructing the curricular structure is the learner. The objective of the curriculum is to nurture learner autonomy, given the fact that every learner is unique. The learner has to understand, appreciate, protect and build on values, beliefs and traditional wisdom, make the necessary modifications, improvisations and additions wherever and whenever necessary. The recent scientific and technological advances have thrown open the gateways of knowledge at an astonishing pace. The speed and methods of assimilating knowledge have put forth many challenges to educators, forcing them to rethink their approaches for knowledge processing by their learners. In this context, it has become imperative for them to incorporate those skills which will enable young learners to become 'life long learners'. The ability to stay current, to upgrade skills with emerging technologies, to understand the nuances involved in change management and the relevant life skills have to be a part of the learning domains of the global learners. The CBSE-i curriculum has taken cognizance of these requirements. The CBSE-i aims to carry forward the basic strength of the Indian system of education while promoting critical and creative thinking skills, effective communication skills, interpersonal and collaborative skills along with information and media skills. There is an inbuilt flexibility in the curriculum, as it provides a foundation and an extension curriculum, in all subject areas to cater to the different pace of learners. The CBSE introduced classes I and X in the session as a pilot project in schools. It was further extended to classes II, VI and X in the session In the seesion , CBSE-i is going to enter in third year with classes III, VII and XI. The focus of CBSE-i is to ensure that the learner is stress-free and committed to active learning. The learner would be evaluated on a continuous and comprehensive basis consequent to the mutual interactions between the teacher and the learner. There are some non-evaluative components in the curriculum which would be commented upon by the teachers and the school. The objective of this part or the core of the curriculum is to scaffold the learning experiences and to relate tacit knowledge with formal knowledge. This would involve trans-disciplinary linkages that would form the core of the learning process. Perspectives, SEWA (Social Empowerment through Work and Action), Life Skills and Research would be the constituents of this 'Core'. The Core skills are the most significant aspects of a learner's holistic growth and learning curve. The International Curriculum has been designed keeping in view the foundations of the National Curricular Framework (NCF 2005) NCERT and the experience gathered by the Board over the last seven decades in imparting effective learning to millions of learners, many of whom are now global citizens. The Board does not interpret this development as an alternative to other curricula existing at the international level, but as an exercise in providing the much needed Indian leadership for global education at the school level. The International Curriculum would evolve building on learning experiences inside the classroom over a period of time. The Board while addressing the issues of empowerment with the help of the schools' administering this system strongly recommends that practicing teachers become skillful learners on their own and also transfer their learning experiences to their peers through the interactive platforms provided by the Board. I profusely thank Shri G. Balasubramanian, former Director (Academics), CBSE, Dr. Sadhana Parashar, Director (Training) CBSE, Dr. Srijata Das, Education Officer CBSE, CBSE along with all the Officers involved in the development and implementation of this material. The CBSE-i website enables all stakeholders to participate in this initiative through the discussion forums provided on the portal. Any further suggestions for modifying any part of this document are welcome. Vineet Joshi Chairman, CBSE
6 Advisory Conceptual Framework Shri Vineet Joshi, Chairman, CBSE Shri G. Balasubramanian, Former Director (Acad), CBSE Dr. Sadhana Parashar, Director (Training), CBSE Ms. Abha Adams, Consultant, Step by Step, School, Noida Dr. Sadhana Parashar, Director (Training), CBSE Ideators VI-VIII Ms. Aditi Mishra Ms. Preeti Hans Ms. Charu Maini Ms. Malini Sridhar Ms. Guneet Ohri Ms. Neelima Sharma Dr. Usha Sharma Ms. Leela Raghavan Ms. Sudha Ravi Ms. Gayatri Khanna Prof. Chand Kiran Saluja Dr. Rashmi Sethi Ms. Himani Asija Ms. Urmila Guliani Dr. Meena Dhani Ms. Seema Rawat Ms. Neerada Suresh Ms. Anuradha Joshi Ms. Vijay Laxmi Raman Ms. Suman Nath Bhalla Dr. Rajesh Hassija Mrs. Sonali Sinha Mrs. Avanita Bir Prof. Om Vikas Material Production Groups: Classes VI-VIII English : Ms. Neha Sharma Ms. Dipinder Kaur Ms. Sarita Ahuja Ms. Gayatri Khanna Ms. Preeti Hans Ms. Rachna Pandit Ms. Renu Anand Ms. Sheena Chhabra Ms. Veena Bhasin Ms. Trishya Mukherjee Ms. Neerada Suresh Ms. Sudha Ravi Ms. Ratna Lal Ms. Ritu Badia Vashisth Ms. Vijay Laxmi Raman Core - Research Ms. Renu Anand Ms. Gayatri Khanna Dr. N K Sehgal Ms. Anita Sharma Ms. Rashmi Kathuria Ms. Neha Sharma Ms. Neeta Rastogi Ms. Manjushtha Bose Ms. Varsha Manku Dr. K L Chopra Chemistry Ms. Poonam Kumar Mendiratta Ms. Rashmi Sharma Ms. Kavita Kapoor Ms. Divya Arora Physics : Ms. Vidhu Narayanan Ms. Meenambika Menon Ms. Patarlekha Sarkar Ms. Neelam Malik Biology: Mr. Saroj Kumar Ms. Rashmi Ramsinghaney Ms. Prerna Gosain Ms. Seema Kapoor Mr. Manish Panwar Ms. Vikram Yadav Ms. Monika Chopra Ms. Jaspreet Kaur Ms. Preeti Mittal Ms. Shipra Sarcar Ms. Leela Raghavan Mathematics : Dr. Ram Avtar Mr. Mahendra Shankar Ms. Deepa Gupta Ms. Gayatri Chowhan Ms. N Vidya Ms. Mamta Goyal Ms. Chhavi Raheja Hindi: Mr. Akshay Kumar Dixit Ms. Veena Sharma Ms. Nishi Dhanjal Ms. Kiran Soni CORE-SEWA Ms. Vandna Ms. Nishtha Bharati Ms. Seema Bhandari Ms. Seema Chopra Ms. Reema Arora Ms. Neha Sharma ICT Mr. Yogesh Kumar Chief Co-ordinator : Dr. Srijata Das, EO Coordinators: Ms. Nancy Sehgal Ms. Purvi Srivastava Ms. Babita Mahajan Ms. Ritu Arora Ms. Swati Panhani Ms. Chanchal Chandna Geography: Ms. Suparna Sharma Ms. Aditi Babbar History : Ms. Leeza Dutta Ms. Kalpana Pant Ms. Ruchi Mahajan Political Science: Ms. Kanu Chopra Ms. Shilpi Anand Economics : Ms. Leela Garewal Ms. Anita Yadav CORE-Perspectives Ms. Madhuchhanda Ms. Varsha Seth Ms. Neha Sharma Ms. Sugandh Sharma, EO Dr Rashmi Sethi, EO Ms. S. Radha Mahalakshmi, E O Ms. Madhuchhanda, RO (Inn) Mr. Navin Maini, RO (Tech) Shri Al Hilal Ahmed, AEO Shri R. P. Singh, AEO Ms. Anjali Chhabra, AEO Ms. Neelima Sharma, Consultant (English) Sh. R. P. Sharma Consultant (Science) Ms. Reema Arora Consultant (Chemistry) Mr. Sanjay Sachdeva, SO
7 Contents 1. Location: 1 Concept and its Meaning 2. Cardinal Direction: Definition and Tool of Spatial Geography 3. Map Reading: 4 Skill to Relate Exact Position of a Place with Help of given Reference 4. Latitude and Longitude: 9 Definition and Importance as Points of Reference.
8 UNIT-I MY HOME, MY CITY- WHERE I LIVE INTRODUCTION A map is a representation of a portion of earth s surface. The features found on the ground are represented by colours, symbols and conventional signs. A map provides information of various ground features like height of natural features, vegetation cover, settlements, rivers and routes of travel. A map can help to visualise in mind what the place looks like. Maps can lead to all sorts of discoveries. Explorers drew maps to record features of land they visited and yet due to lack of overall location perception Columbus reached America in search of route to India! The amazing world of maps helps us to understand how geography shapes the world. Empowered with the tools of scale and grid they help to find places and describe where they are. MY HOME, MY CITY-WHERE I LIVE - AN OVERVIEW Location of a place means the position of a place in relation to a locality say a suburb, town, city or country. It describes where a place is. It is important to know the location of a place in order to get ones bearings, to get a sense of belonging. 'Direction' tells more about the location e.g. which way? How to reach a particular place? Otherwise we would be lost. 1
9 DO IT YOURSELF Study the cartoon and answer the following questions: i) What is the importance of the sign board in this picture? ii) Why has the sign board brought a smile on the face of the traveller? There are four main directions also known as the cardinal directions. They can be seen marked on a compass. The sun rises in the east and sets in the west this gives us the two main directions and with their help we get to know the other directions. Cardinal directions Cardinal Directions We also have four sub directions or intermediate directions. For example, we can mark the direction between north (N) and east (E) as north-east (NE) similarly we have north-west (NW) south-east (SE) and south-west (SW) 2
10 North Star Location Intermediate Directions Source: There is another way to find directions is by seeing the position of the stars at night. In the Northern Hemisphere we can locate the north with the help of the constellation the Great Bear (also called Big Dipper). The last two stars in the cup shape of the great bear point to Polaris, the North Star, and this lies above the North Pole. If we are facing the North, South is behind us, East is to our right and West is to our left. THINK AND LIST OH GOD! I AM LOST!!! How can a person avoid getting lost? A good question and there is probably no simple answer (except never leaving home). However, there are some tried and true techniques that help. List out these techniques with the help of the content given above. 3
11 Sketches and Maps Sketch- It is a free hand rough drawing of an area giving approximate directions between two points of reference. It is not accurate but gives a fair idea of the direction to reach the point of reference. A sketch map showing the relative size of Arabia as compared to neighbouring countries Map: A map is a flat, representation of the earth or a part of the earth s surface on a flat piece of paper. It helps understand where we are in relation to other people and places. The most famous ancient maps of the world were made in the 2nd Century A.D by the Greek scholar, Claudius Ptolemy. We can read the map like a story only if we understand the language of the map. Therefore we need to know the basic elements or the basis of map making. The five basic elements of a map are the title, direction, scale, and key and grid system. Title: It introduces us to the map. All maps have a title telling the reader what the map is about. Example: Apache Peak Quadrangle, Arizona. Title of map encircled 4
12 Direction: Most Maps show directions with an arrow at the top right hand corner that point to the direction of the north, called a north line. Another symbol on the map that shows direction is the compass, sometimes called the compass rose. North line Compass Rose A compass is a devise consisting of a magnetic needle that always points north and south when it is at rest. The compass shows where north and south are, after which it is easy to find all other directions. It is a great device for navigators at all times. DO YOU KNOW? The true North Pole is right at the top of the world in the middle of the Arctic Ocean. A compass needle, a tiny magnet, doesn t point to true North but to an area in Northern Canada called Magnetic North. There is also a magnetic South Pole. The magnetic poles move slightly from year to year. Globe: A globe is a three-dimensional map of the earth represented on a sphere. 5
13 Scale: No feature of the earth's surface can fit on to a plain piece of paper. Actual size of an area cannot be shown on a map, so most maps are drawn on the basis of a relationship between sizes on land to size on map. This is known as the scale of a map. The scale of a map compares the size of the map with real size of a place. A scale is a ratio between distances on the map to a proportionate distance on the ground. Example: Scale: 1cm =250 km means that 1cm on the map represents a distance of 250km on the ground. The scale of the maps is generally shown at the bottom of the map. A map can be drawn to many different scales, depending on its purpose. Small Scale Map: They represent large areas of the earth. The purpose of such a map is to show a small amount of detail about a large area. Since they show large areas on a small piece of paper, they have to use a small scale e.g. 1cm =100km. 6
14 An atlas is an example of a small scale map as it shows large areas like countries and continents. Large Scale map: They represent a small area of the earth. Its purpose is to show large amount of detail about a small area. The scale used is large, eg 1cm =1km A road map, that shows streets and important buildings of a neighbourhood, is an example of large scale map. DO IT YOURSELF: BEING A MAP MAKER Make a Land Use Map Material required: local map, coloured paper, pen, scissors, and glue. 1. Use a map of your town to draw a simple sketch of your immediate surrounding area. 2. Find out what different buildings are being used for in the selected area. 3. Make a list of those being used for shops, homes, banks, etc. 4. Choose different colours for each type of land use. Then cut and paste coloured paper shapes to cover each building to show how it is used. 5. Finally, draw a key to explain a map. Map legend or key: explains the symbols used on a map. It is also called a map key because it unlocks the meaning of a map's symbols. 7
15 Different maps may use different symbols but there are certain symbols that are used throughout the world. These are called conventional symbols. There is an understanding among the nations of the world regarding the use of these symbols. SOME IMPORTANT CONVENTIONAL SYMBOLS CONVENTIONAL SIGNS Source: fire.ca.gov 8
16 Grid system: A grid is a network of lines. The lines are numbered to give the position of each square. The horizontal and vertical network of lines is the lines of latitude (known as parallels) and longitude (known as meridians). They divide the world into Northern, Southern and Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The lines of latitude and longitude form the grid. A Grid Eratosthenes was the first to realise that any place in the world can be pinpointed precisely with the help of a network of lines forming squares on the map. This network is called a grid. The lines are numbered to give the position of each square. Lines of Latitude: Some important parallels are Equator at 0⁰, Tropic of Cancer at 23.5⁰ N, Tropic of Capricorn at 23.5⁰ S, Arctic Circle at 66.5⁰ N and Antarctic Circle at 66.5⁰ S. "The largest circle, the one equally distant from each of the poles, is called the equator. It is called 'zero' degrees latitude. (The '0' is shown in red on the diagram.) The other lines of latitude are numbered from 0 to 90 degrees going towards each of the poles. The ones going from the equator towards the North Pole (shown in blue) are 'North' latitude, and each of the numbers is followed by the letter 'N'. The ones going the other way, from the equator towards the South Pole (in shocking pink are 'south' latitude, and each of the numbers is followed by the letter 'S'). The equator (zero latitude) is the only one without any letter following the number. The poles are 90 0 N and 90 0 S. They divide the earth into various heat zones. Lines of Longitude: Some important meridians are the Prime Meridian at 0⁰ and the 180⁰meridian completing the whole circle dividing the earth into Eastern and Western Hemispheres Going towards the East, the lines are numbered from 1 to 180 degrees; going to the West, the lines are also numbered from 1 to 180 degrees, but going the other way. All the 'East' lines 9
17 between 0 and 180 (blue numbers) have the letter 'E' attached to them; all the 'West' lines between 0 and 180 (pink numbers) have a 'W' attached to them. The '0' and '180' degree lines (red numbers) do not have a letter attached to them. The 0⁰ meridian is also known as the Greenwich meridian. The longitudes help in calculating the time of a place as one move away from the Greenwich (0⁰). The time to the east of GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) is ahead of it while the time to the west of it is behind e.g. If the time at Greenwich is 12 noon then to the east of it, it will be post noon and to the west of it, the time will be pre noon. If we put both the latitude lines and the longitude lines together on the sphere, we will get the grid. Now we can locate places by giving their latitude and longitude. Source: btc.montana.edu Types of Maps: There are three main types of maps 10
18 TYPES OF MAPS Political maps are usually small scale maps which show different countries of the world. They also show parts of nations such as states and the borders between states and countries. A political map can show borders using lines. Countries and their parts are shown in different colours. Capital cities and important towns are also shown on political maps. 11
19 Physical maps are small scale maps which show the surface of the earth or parts of it. Land forms like mountains, valleys and plains, rivers and other relief features are shown on such maps. These maps use different colours for different relief features. Thematic maps represent particular features only, such as weather, roads, distribution of population, rainfall, wheat growing areas, minerals, etc. Topographical maps can be categorized as thematic maps. These are large scale maps which give detailed information of the relief of the land. 12
20 Atlas An atlas is a collection of maps of the world, the continents and the selected countries. Besides maps, an atlas may also include information and diagrams dealing with topics like the earth in space and geographical features and population data. An atlas is a guide to the world and can be used in many ways. You can look up places, find out the relief of the land, the resources available there, 13
21 GLOSSARY Cardinal Points: The major directions, North, South, East and West of the compass. Conventional symbols: The symbols that are used to show various features on the map. Globe: A three dimensional model of the Earth. Grid: A grid is a series of evenly spaced imaginary lines that intersect with one another at right angles. One set of lines are distributed across the globe horizontally, and one set of lines are distributed vertically. Intermediate Directions: Apart from the four major directions, there are four intermediate directions that help in locating a place viz., North-East, South-East, North-West and South- West. Large Scale Map: A map that depicts a small territory is referred to as a large scale map. A large scale map only shows a small area, but it shows it in great detail. Latitude: Angular distance of a place North or South of the equator. They are also called parallels. Longitude: Angular distance of a place East or West of the Prime Meridian. They are also called meridians. Map: A representation of the curved surface of the Earth or a part of it on a flat sheet of paper according to a given scale. North Line: The vertical line with an arrow at the top, marked with the letter N, indicating the North direction. Physical Map: Maps that show natural features on the Earth s surface like rivers, mountains, plateaus etc. Plan: A detailed drawing of a very small area using a very large scale. Political Map: Map that show boundaries of countries states, cities and towns. 14
22 Scale: The relation between the map distance and the corresponding distance on the ground. Sketch: A rough drawing showing few features of an area without using a scale. Small Scale Map: A map depicting a large area called a small scale map. A small scale map shows more territory, but it is less detailed. Thematic Map: Map that is based on a particular theme or a topic like vegetation, population, rainfall etc. 15
23 WORKSHEET NO.1 Name Class Section Q1. Below is a cartoon strip. Read it and answer the questions that follow: 1. What is the character in the cartoon struggling to know? 2. Why is he getting confused? 3. What according to you is the right way to answer his question? 4. What are the main requisites for reaching/moving out of a place? 16
24 WORKSHEET NO.2 Name Class Section 1. For each direction in the compass rose, write something that is located in that direction from your home. 17
25 WORKSHEET NO.3 Name Class Section 1. Given below are the two images. Both are the maps of regions in China. Look at them closely and find out the differences between the two.(clues are present on the two images) 18
26 19
27 WORKSHEET NO.4 Name Class Section 1. Follow the directions and answer the questions below. Source: http// 1. Colour the water in light blue, colour the mountains in purple, colour the land in light green, and colour the key in yellow. 2. What is the name of the largest island above? 3. What is the name of the ocean in the map? 4. Which island is at the farthest west? 5. Which island is at the farthest south? 6. Draw a red "X" at latitude 20 o N, longitude 157 o W. 7. About how many miles is it from Hilo to Captain Cook? 8. What direction would you travel to go from Hilo to Mauna Kea? 20
28 2. Dot to Dot Mystery Map Connect the dots to draw the borders to find the map of the country. Then use a globe or atlas to figure out which country you have drawn. 21
29 WORKSHEET NO.5 Name Class Section 1. Label the Latitude and Longitude: Using the terms given below, label latitudes and longitudes on the world map. 90º N 45º N 0º Latitude 45º S 90º S 180º W 135º W 90º W 45º W 0º Longitude 45º E 90º E 135º E 180º E 22
30 WORKSHEET NO.6 Name Class Section Answer the following questions and mark the locations. i. Draw a red line along the equator (0 degrees latitude). ii. iii. iv. Draw a purple line along the Prime Meridian (0 degrees longitude). In which ocean is the location 10 degrees S latitude, 75 degrees E longitude located? Mark it on the map with a blue "X" and write the name of the ocean. In which ocean is the location 30 degrees N latitude, 60 degrees W longitude located? Mark it on the map with a blue "Y" and write the name of the ocean. v. Mark the following cities on the map in red: a) LA. Los Angeles: 34 N, 118 W b) LO. London: 51 N, 0 W c) MO. Moscow: 55 N, 37 E d) MU. Mumbai: 19 N, 72 E e) NY. New York: 40 N, 74 W 23
31 RESOURCES Social Science Text Book for Class 6 NCERT A Text Book of Geography 6 Rita Rajen Knowledge Navigator Physical Geography Class 9 academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/geology/leveson/core/linksa/latlong - menu.html http// 24
32 CENTRAL BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Shiksha Kendra, 2, Community Centre, Preet Vihar, Delhi India
The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT MIDDLE SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes NAME: CLASS VI SEC: ROLL NO: DATE:.04.2015 I NAME THE FOLLOWING: 1. A small spherical model of the Earth:
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT MIDDLE SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE The Globe Latitudes and Longitudes NAME: CLASS VI SEC: ROLL NO: DATE:.04.2015 I NAME THE FOLLOWING: 1. A small spherical model of the Earth:
Lines on Maps and Globes. Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4
 Lines on Maps and Globes Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4 Fourth Grade Social Studies Standard Map: Chart/Globe The learner will be able to use maps, charts, graphs, and globes
Lines on Maps and Globes Cross Curricular Writing Activity Social Studies Grade 4 Fourth Grade Social Studies Standard Map: Chart/Globe The learner will be able to use maps, charts, graphs, and globes
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+
 World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+ Activity Goal To use the global grid system of latitude and longitude to find specific locations on a world map. Materials Needed: A pencil, a ruler,
World Map Lesson 4 - The Global Grid System - Grade 6+ Activity Goal To use the global grid system of latitude and longitude to find specific locations on a world map. Materials Needed: A pencil, a ruler,
Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars
 Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars Vocabulary List Adult Education at Scienceworks Pre-visit Activity 1: What is longitude and latitude? Activity 2: Using the Southern Cross to find
Pre and post-visit activities - Navigating by the stars Vocabulary List Adult Education at Scienceworks Pre-visit Activity 1: What is longitude and latitude? Activity 2: Using the Southern Cross to find
Solar Angles and Latitude
 Solar Angles and Latitude Objectives The student will understand that the sun is not directly overhead at noon in most latitudes. The student will research and discover the latitude ir classroom and calculate
Solar Angles and Latitude Objectives The student will understand that the sun is not directly overhead at noon in most latitudes. The student will research and discover the latitude ir classroom and calculate
Week 1. Week 2. Week 3
 Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Grades 3-5. Benchmark A: Use map elements or coordinates to locate physical and human features of North America.
 Grades 3-5 Students use knowledge of geographic locations, patterns and processes to show the interrelationship between the physical environment and human activity, and to explain the interactions that
Grades 3-5 Students use knowledge of geographic locations, patterns and processes to show the interrelationship between the physical environment and human activity, and to explain the interactions that
Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond
 Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
Stellarium 1 Stellarium a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the classroom and beyond Stephen Hughes Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Gardens
Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007
 Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007 1. In the illustration shown below what navigational features are represented by A, B, and C? Note that A is a critical city in defining
Topographic Maps Practice Questions and Answers Revised October 2007 1. In the illustration shown below what navigational features are represented by A, B, and C? Note that A is a critical city in defining
Stage 4. Geography. Blackline Masters. By Karen Devine
 1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide
 Name: Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide There are three main sections to this module: terrestrial coordinates, celestial equatorial coordinates, and understanding how the ecliptic is related to
Name: Basic Coordinates & Seasons Student Guide There are three main sections to this module: terrestrial coordinates, celestial equatorial coordinates, and understanding how the ecliptic is related to
Lines of Latitude and Longitude
 ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
Celestial Observations
 Celestial Observations Earth experiences two basic motions: Rotation West-to-East spinning of Earth on its axis (v rot = 1770 km/hr) (v rot Revolution orbit of Earth around the Sun (v orb = 108,000 km/hr)
Celestial Observations Earth experiences two basic motions: Rotation West-to-East spinning of Earth on its axis (v rot = 1770 km/hr) (v rot Revolution orbit of Earth around the Sun (v orb = 108,000 km/hr)
Introduction to Geography
 High School Unit: 1 Lesson: 1 Suggested Duration: 3 days Introduction to Lesson Synopsis: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to geography and geography terminology, to teach students about
High School Unit: 1 Lesson: 1 Suggested Duration: 3 days Introduction to Lesson Synopsis: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to geography and geography terminology, to teach students about
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Send all inquiries to: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 8787 Orion Place Columbus, Ohio 43240-4027 ISBN 0-07-824996-1. Printed in the United States of America
 Copyright by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to reproduce the material contained herein on the condition that such material be reproduced only for classroom use;
Copyright by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to reproduce the material contained herein on the condition that such material be reproduced only for classroom use;
The Basics of Navigation
 The Basics of Navigation Knowledge of map reading and the use of the compass is an indispensable skill of bushcraft. Without this skill, a walker is a passenger and mere follower on a trip. To become a
The Basics of Navigation Knowledge of map reading and the use of the compass is an indispensable skill of bushcraft. Without this skill, a walker is a passenger and mere follower on a trip. To become a
MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE?
 MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE? Grade Level: Kindergarten Presented by: Karen Davis and Tamara Young, Tate Elementary, Van Buren, AR Length of unit:5 lessons I. ABSTRACT A. This unit focuses
MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE? Grade Level: Kindergarten Presented by: Karen Davis and Tamara Young, Tate Elementary, Van Buren, AR Length of unit:5 lessons I. ABSTRACT A. This unit focuses
Coordinate Systems. Orbits and Rotation
 Coordinate Systems Orbits and Rotation Earth orbit. The earth s orbit around the sun is nearly circular but not quite. It s actually an ellipse whose average distance from the sun is one AU (150 million
Coordinate Systems Orbits and Rotation Earth orbit. The earth s orbit around the sun is nearly circular but not quite. It s actually an ellipse whose average distance from the sun is one AU (150 million
Map reading made easy
 Map reading made easy What is a map? A map is simply a plan of the ground on paper. The plan is usually drawn as the land would be seen from directly above. A map will normally have the following features:
Map reading made easy What is a map? A map is simply a plan of the ground on paper. The plan is usually drawn as the land would be seen from directly above. A map will normally have the following features:
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES
 6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
Allows teachers to print reports for individual students or an entire class.
 Map and Globe Skills Developed by teachers and geography specialists, Map and Globe Skills provides the strategies, skills and practice your students need to develop a strong understanding of basic mapping
Map and Globe Skills Developed by teachers and geography specialists, Map and Globe Skills provides the strategies, skills and practice your students need to develop a strong understanding of basic mapping
WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense
 WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Wendy S. Hyndman, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Doreen W. Jennings, Lincoln
WE VE GOT THE WHOLE WORLD IN OUR HANDS: Geography Spatial Sense Grade Level: Written by: Length of Unit: Third Grade Wendy S. Hyndman, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Doreen W. Jennings, Lincoln
Motion & The Global Positioning System (GPS)
 Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
Grade Level: K - 8 Subject: Motion Prep Time: < 10 minutes Duration: 30 minutes Objective: To learn how to analyze GPS data in order to track an object and derive its velocity from positions and times.
WHAT MAPS SHOW US Maps do 4 things:
 WHAT MAPS SHOW US Maps show us a range of features, for example: Landforms: Settlement: Communication: Land Use: Geology: Other Info: - hills - valleys - mountains - isolated dwellings - farms - villages
WHAT MAPS SHOW US Maps show us a range of features, for example: Landforms: Settlement: Communication: Land Use: Geology: Other Info: - hills - valleys - mountains - isolated dwellings - farms - villages
How do you find a place on a globe? How do you look up a place based on latitude and longitude?
 Why are globes tilted? Most Replogle globes are made to tilt at an angle of 23.5º to match the actual tilt of the earth in relationship to our sun. Incidentally, it is this tilting of the earth relative
Why are globes tilted? Most Replogle globes are made to tilt at an angle of 23.5º to match the actual tilt of the earth in relationship to our sun. Incidentally, it is this tilting of the earth relative
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* GEOGRAPHY 0460/02 Paper 2 Geographical skills For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* GEOGRAPHY 0460/02 Paper 2 Geographical skills For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER
Searching Land Records thru the BLM General Land Office Records.
 Searching Land Records thru the BLM General Land Office Records. Land Records can be an exciting addition to your family history search. The United States Government transferred ownership of land to millions
Searching Land Records thru the BLM General Land Office Records. Land Records can be an exciting addition to your family history search. The United States Government transferred ownership of land to millions
The Celestial Sphere. Questions for Today. The Celestial Sphere 1/18/10
 Lecture 3: Constellations and the Distances to the Stars Astro 2010 Prof. Tom Megeath Questions for Today How do the stars move in the sky? What causes the phases of the moon? What causes the seasons?
Lecture 3: Constellations and the Distances to the Stars Astro 2010 Prof. Tom Megeath Questions for Today How do the stars move in the sky? What causes the phases of the moon? What causes the seasons?
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
UNIT I INTRODUCTION. This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
UNIT I INTRODUCTION This unit deals with Location space relations and India s place in the world CHAPTER INDIA LOCATION You have already seen the map of India in the previous classes. Now you closely examine
Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems
 Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems How do we model the earth? Datums Datums mathematically describe the surface of the Earth. Accounts for mean sea level, topography, and gravity models. Projections
Earth Coordinates & Grid Coordinate Systems How do we model the earth? Datums Datums mathematically describe the surface of the Earth. Accounts for mean sea level, topography, and gravity models. Projections
Noon Sun Angle = 90 Zenith Angle
 Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
Noon Sun Angle Worksheet Name Name Date Subsolar Point (Latitude where the sun is overhead at noon) Equinox March 22 nd 0 o Equinox September 22 nd 0 o Solstice June 22 nd 23.5 N Solstice December 22 nd
3D Drawing. Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces
 3D Drawing Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces The following document helps describe the basic process for generating a 3D representation of a simple 2D plan. For this exercise we will be
3D Drawing Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces The following document helps describe the basic process for generating a 3D representation of a simple 2D plan. For this exercise we will be
The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual
 The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual 'What's the good of Mercator's North Poles and Equators, Tropics, Zones
The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual The Map Grid of Australia 1994 A Simplified Computational Manual 'What's the good of Mercator's North Poles and Equators, Tropics, Zones
Tectonic plates have different boundaries.
 KEY CONCEPT Plates move apart. BEFORE, you learned The continents join and break apart The sea floor provides evidence that tectonic plates move The theory of plate tectonics helps explain how the plates
KEY CONCEPT Plates move apart. BEFORE, you learned The continents join and break apart The sea floor provides evidence that tectonic plates move The theory of plate tectonics helps explain how the plates
Geography I Pre Test #1
 Geography I Pre Test #1 1. The sun is a star in the galaxy. a) Orion b) Milky Way c) Proxima Centauri d) Alpha Centauri e) Betelgeuse 2. The response to earth's rotation is a) an equatorial bulge b) polar
Geography I Pre Test #1 1. The sun is a star in the galaxy. a) Orion b) Milky Way c) Proxima Centauri d) Alpha Centauri e) Betelgeuse 2. The response to earth's rotation is a) an equatorial bulge b) polar
USING MAPS AND GLOBES
 USING MAPS AND GLOBES Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, Colorado Springs Charter Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately one week (five
USING MAPS AND GLOBES Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, Colorado Springs Charter Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately one week (five
Earth-Sun Relationships. The Reasons for the Seasons
 Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Earth-Sun Relationships The Reasons for the Seasons Solar Radiation The earth intercepts less than one two-billionth of the energy given off by the sun. However, the radiation is sufficient to provide
Which month has larger and smaller day time?
 ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
PRACTICAL BLOCK COMPASS BASICS. Compass Basics. Introduction. The Silva Compass
 Compass Basics Introduction The first compass was, no doubt, a magnetised ore-bearing rock or stone, that when suspended, would always point the same way. No one knows who first discovered the compass;
Compass Basics Introduction The first compass was, no doubt, a magnetised ore-bearing rock or stone, that when suspended, would always point the same way. No one knows who first discovered the compass;
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
compass Encyclopedic Entry
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry compass For
Navigation: Latitude and Longitude
 Sextants and Chronometers Help Sailors Find Their Position at Sea Latitude lines run horizontally across the globe and are used to measure distances north and south of the equator. Sailors used a sextant
Sextants and Chronometers Help Sailors Find Their Position at Sea Latitude lines run horizontally across the globe and are used to measure distances north and south of the equator. Sailors used a sextant
CLASS X UNIT-6. CBSE-i GEOGRAPHY. Teachers Manual. Tertiary Activities. Shiksha Kendra, 2, Community Centre, Preet Vihar,Delhi-110 092 India
 CBSE-i GEOGRAPHY Teachers Manual CLASS X UNIT-6 Tertiary Activities Shiksha Kendra, 2, Community Centre, Preet Vihar,Delhi-110 092 India CBSE-i Teachers Manual Tertiary Activities CLASS X UNIT-6 Shiksha
CBSE-i GEOGRAPHY Teachers Manual CLASS X UNIT-6 Tertiary Activities Shiksha Kendra, 2, Community Centre, Preet Vihar,Delhi-110 092 India CBSE-i Teachers Manual Tertiary Activities CLASS X UNIT-6 Shiksha
3D Drawing. Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces
 3D Drawing Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces The following document helps describe the basic process for generating a 3D representation of a simple 2D plan. For this exercise we will be
3D Drawing Single Point Perspective with Diminishing Spaces The following document helps describe the basic process for generating a 3D representation of a simple 2D plan. For this exercise we will be
Maps A Primer for Content & Production of Topographic Base Maps For Design Presented by SurvBase, LLC
 Maps A Primer for Content & Production of Topographic Base Maps For Design Presented by Definition and Purpose of, Map: a representation of the whole or a part of an area. Maps serve a wide range of purposes.
Maps A Primer for Content & Production of Topographic Base Maps For Design Presented by Definition and Purpose of, Map: a representation of the whole or a part of an area. Maps serve a wide range of purposes.
Maps and Cartography
 Maps and Cartography GIS Research & Map Collection Maps Tutorial: The Elements of a Map Ball State University Libraries A destination for research, learning, and friends The Map: A Geographer s Most Important
Maps and Cartography GIS Research & Map Collection Maps Tutorial: The Elements of a Map Ball State University Libraries A destination for research, learning, and friends The Map: A Geographer s Most Important
Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons
 Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you
Lab Activity on the Causes of the Seasons 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you
Sun Earth Relationships
 1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere tilts away from sun) 23.5 2 Solar radiation
1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere tilts away from sun) 23.5 2 Solar radiation
Cycles in the Sky. Teacher Guide: Cycles in the Sky Page 1 of 8 2008 Discovery Communications, LLC
 Cycles in the Sky What is a Fun damental? Each Fun damental is designed to introduce your younger students to some of the basic ideas about one particular area of science. The activities in the Fun damental
Cycles in the Sky What is a Fun damental? Each Fun damental is designed to introduce your younger students to some of the basic ideas about one particular area of science. The activities in the Fun damental
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones
 Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
Display Policy for Learning Environments
 Display Policy for Learning Environments 1 Contents Section 1 1. Aims p.3 2. Policy Background p.3 3. Linking policy to curriculum priorities p.3 4. Purpose of display p.3-4 Section 2 5. The learning environment
Display Policy for Learning Environments 1 Contents Section 1 1. Aims p.3 2. Policy Background p.3 3. Linking policy to curriculum priorities p.3 4. Purpose of display p.3-4 Section 2 5. The learning environment
NCSS Theme #1 Lesson Plan: Culture
 NCSS Theme #1 Lesson Plan: Culture Lesson Title: World Religions Lesson Author: Kathryn Yarbrough Key Curriculum Words: Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, religion, monotheism, polytheism
NCSS Theme #1 Lesson Plan: Culture Lesson Title: World Religions Lesson Author: Kathryn Yarbrough Key Curriculum Words: Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, religion, monotheism, polytheism
A Few Facts about Antarctica
 A Few Facts about Antarctica Antarctica is the continent that surrounds the South Pole, the southernmost point at the bottom of the earth. Antarctica is a continent because it is land that is covered by
A Few Facts about Antarctica Antarctica is the continent that surrounds the South Pole, the southernmost point at the bottom of the earth. Antarctica is a continent because it is land that is covered by
LILLIAN PITAWANAKWAT LESSON PLAN 2006 All Rights Reserved 4D Interactive Inc. 416-530-2752 1
 Elder Lillian Pitawanakwat Nation Ojibwe/Potawotami Lesson Plan Grade Level Junior (Grades 1-6) Time Required 3 4 hours Subject Strand Links Geography Natural Science Astronomy Traditional Teachings The
Elder Lillian Pitawanakwat Nation Ojibwe/Potawotami Lesson Plan Grade Level Junior (Grades 1-6) Time Required 3 4 hours Subject Strand Links Geography Natural Science Astronomy Traditional Teachings The
Educator s Guide to Learning about Mexico Using Google Earth
 Educator s Guide to Learning about Mexico Using Google Earth Overview: Students will research the physical features of Mexico using Google Earth to learn about Mexico s oceans, gulfs, bays, lagoons, rivers,
Educator s Guide to Learning about Mexico Using Google Earth Overview: Students will research the physical features of Mexico using Google Earth to learn about Mexico s oceans, gulfs, bays, lagoons, rivers,
Phases of the Moon. Preliminaries:
 Phases of the Moon Sometimes when we look at the Moon in the sky we see a small crescent. At other times it appears as a full circle. Sometimes it appears in the daylight against a bright blue background.
Phases of the Moon Sometimes when we look at the Moon in the sky we see a small crescent. At other times it appears as a full circle. Sometimes it appears in the daylight against a bright blue background.
SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS
 SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: Geographic information systems and Map projections. Content that needs to be covered for examination
SESSION 8: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND MAP PROJECTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: Geographic information systems and Map projections. Content that needs to be covered for examination
Unit 6 Direction and angle
 Unit 6 Direction and angle Three daily lessons Year 4 Spring term Unit Objectives Year 4 Recognise positions and directions: e.g. describe and find the Page 108 position of a point on a grid of squares
Unit 6 Direction and angle Three daily lessons Year 4 Spring term Unit Objectives Year 4 Recognise positions and directions: e.g. describe and find the Page 108 position of a point on a grid of squares
Solar energy and the Earth s seasons
 Solar energy and the Earth s seasons Name: Tilt of the Earth s axis and the seasons We now understand that the tilt of Earth s axis makes it possible for different parts of the Earth to experience different
Solar energy and the Earth s seasons Name: Tilt of the Earth s axis and the seasons We now understand that the tilt of Earth s axis makes it possible for different parts of the Earth to experience different
CONTENTS. Page 3 What is orienteering? Page 4 Activity: orienteering map bingo. Page 5 Activity: know your colours. Page 6 Choosing your compass
 THE RIGHT DIRECTION SCOUT ORIENTEER ACTIVITY BADGE CONTENTS Page What is orienteering? Page 4 Activity: orienteering map bingo Page 5 Activity: know your colours Page 6 Choosing your compass Page 7 Activity:
THE RIGHT DIRECTION SCOUT ORIENTEER ACTIVITY BADGE CONTENTS Page What is orienteering? Page 4 Activity: orienteering map bingo Page 5 Activity: know your colours Page 6 Choosing your compass Page 7 Activity:
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage
 Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
6. The greatest atmospheric pressure occurs in the 1) troposphere 3) mesosphere 2) stratosphere 4) thermosphere
 1. The best evidence of the Earth's nearly spherical shape is obtained through telescopic observations of other planets photographs of the Earth from an orbiting satellite observations of the Sun's altitude
1. The best evidence of the Earth's nearly spherical shape is obtained through telescopic observations of other planets photographs of the Earth from an orbiting satellite observations of the Sun's altitude
OBJECTIVES. Identify the means by which latitude and longitude were created and the science upon which they are based.
 Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: isolines, gradient, topographic map, contour interval, hachured lines, profile, latitude, longitude, hydrosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, elevation, model EARTH
Name: Key OBJECTIVES Correctly define: isolines, gradient, topographic map, contour interval, hachured lines, profile, latitude, longitude, hydrosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, elevation, model EARTH
SOUTH AMERICA CONTENTS. What s in This Book... 2. Section 1: South America in the World... 3. Section 2: Political Divisions of South America...
 SOUTH CONTENTS What s in This Book 2 Section 1: 3 Section 2: Political Divisions of 1 Section 3: Physical Features of 41 Section 4: Valuable Resources of 67 Section : n Culture 89 Section 6: Assessment
SOUTH CONTENTS What s in This Book 2 Section 1: 3 Section 2: Political Divisions of 1 Section 3: Physical Features of 41 Section 4: Valuable Resources of 67 Section : n Culture 89 Section 6: Assessment
Experiment 5: Magnetic Fields of a Bar Magnet and of the Earth
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 Experiment 5: Magnetic Fields of a Bar Magnet and of the Earth OBJECTIVES 1. To examine the magnetic field associated with a
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 Experiment 5: Magnetic Fields of a Bar Magnet and of the Earth OBJECTIVES 1. To examine the magnetic field associated with a
EARTH SCIENCES - TYPES OF MAPS TEACHER GUIDE
 EARTH SCIENCES - TYPES OF MAPS TEACHER GUIDE MATERIALS: Electronic Reader - Maps 5 different types of maps (see lab) inflatable globes local topographical map Objective: To understand the uses and importance
EARTH SCIENCES - TYPES OF MAPS TEACHER GUIDE MATERIALS: Electronic Reader - Maps 5 different types of maps (see lab) inflatable globes local topographical map Objective: To understand the uses and importance
Numeracy and mathematics Experiences and outcomes
 Numeracy and mathematics Experiences and outcomes My learning in mathematics enables me to: develop a secure understanding of the concepts, principles and processes of mathematics and apply these in different
Numeracy and mathematics Experiences and outcomes My learning in mathematics enables me to: develop a secure understanding of the concepts, principles and processes of mathematics and apply these in different
HOW TO TAKE A COMPASS READING
 FENG SHUI Chinese Astrology Akashic Records Healing the Planet, One Living Space at a Time TM HOW TO TAKE A COMPASS READING There are five easy steps required to take an accurate compass reading of the
FENG SHUI Chinese Astrology Akashic Records Healing the Planet, One Living Space at a Time TM HOW TO TAKE A COMPASS READING There are five easy steps required to take an accurate compass reading of the
NCSS Standards 1. d. compare ways in which people from different cultures think about and deal with their physical environment and social conditions;
 NCSS Standards 1 National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS) Curriculum Standards for Social Studies Standard I. Culture study of culture and cultural diversity, so that the learner can a. explore and
NCSS Standards 1 National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS) Curriculum Standards for Social Studies Standard I. Culture study of culture and cultural diversity, so that the learner can a. explore and
Lesson #13 Congruence, Symmetry and Transformations: Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Math Buddies -Grade 4 13-1 Lesson #13 Congruence, Symmetry and Transformations: Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Goal: Identify congruent and noncongruent figures Recognize the congruence of plane
Math Buddies -Grade 4 13-1 Lesson #13 Congruence, Symmetry and Transformations: Translations, Reflections, and Rotations Goal: Identify congruent and noncongruent figures Recognize the congruence of plane
Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon
 Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon Background: You can measure your latitude in earth's northern hemisphere by finding out the altitude of the celestial equator from the southern
Measuring Your Latitude from the Angle of the Sun at Noon Background: You can measure your latitude in earth's northern hemisphere by finding out the altitude of the celestial equator from the southern
4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation
 4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation 4.1 Details on Great Circles In fig. GN 4.1 two Great Circle/Rhumb Line cases are shown, one in each hemisphere. In each case the shorter distance between
4 The Rhumb Line and the Great Circle in Navigation 4.1 Details on Great Circles In fig. GN 4.1 two Great Circle/Rhumb Line cases are shown, one in each hemisphere. In each case the shorter distance between
IAntarcticaI. IArctic Ocean I. Where in the World? Arctic Ocean. Pacific Ocean. Pacific Ocean. Atlantic Ocean. North America.
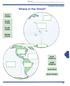 Name ------------------------------ Where in the World? Continents and s Arctic Pacific Pacific Atlantic.1.... 0" o ". North America South America Antarctica Arctic 261 Name Where in the World Continents
Name ------------------------------ Where in the World? Continents and s Arctic Pacific Pacific Atlantic.1.... 0" o ". North America South America Antarctica Arctic 261 Name Where in the World Continents
Activity 10 - Universal Time
 Activity 10 - Universal Time Teacher s Guide Scientists use the Universal Time reference to talk about data that is taken around the globe. Universal Time is the time kept in the time zone centered on
Activity 10 - Universal Time Teacher s Guide Scientists use the Universal Time reference to talk about data that is taken around the globe. Universal Time is the time kept in the time zone centered on
Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions
 Chapter 2 Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions 2.1 Purpose The main goal of this lab is for you to gain an understanding of how the sky changes during the night and over the course of a year. We will
Chapter 2 Orientation to the Sky: Apparent Motions 2.1 Purpose The main goal of this lab is for you to gain an understanding of how the sky changes during the night and over the course of a year. We will
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum
 Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
Answer Keys to Unit Tests
 Reading Geography Series Answer Keys to Unit Tests Unit 1 The Five Themes of Geography Unit 2 Patterns in Physical Geography Unit 3 Natural Resources 7 Portage & Main Press Unit Test for The Five Themes
Reading Geography Series Answer Keys to Unit Tests Unit 1 The Five Themes of Geography Unit 2 Patterns in Physical Geography Unit 3 Natural Resources 7 Portage & Main Press Unit Test for The Five Themes
Lesson 26: Reflection & Mirror Diagrams
 Lesson 26: Reflection & Mirror Diagrams The Law of Reflection There is nothing really mysterious about reflection, but some people try to make it more difficult than it really is. All EMR will reflect
Lesson 26: Reflection & Mirror Diagrams The Law of Reflection There is nothing really mysterious about reflection, but some people try to make it more difficult than it really is. All EMR will reflect
A Correlation of. Pearson myworld Social Studies Grade 2 Florida Edition. To the Monroe County Curriculum Guide
 A Correlation of Pearson myworld Social Studies Grade 2 Florida Edition To the Monroe County Curriculum Guide Table of Contents HISTORICAL THINKING SKILLS... 3 Unit 1- Rules and Laws... 4 Unit 2: Citizenship:
A Correlation of Pearson myworld Social Studies Grade 2 Florida Edition To the Monroe County Curriculum Guide Table of Contents HISTORICAL THINKING SKILLS... 3 Unit 1- Rules and Laws... 4 Unit 2: Citizenship:
Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives
 Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives Standard 1: Citizenship characterize and good citizenship by building social networks of reciprocity and trustworthiness (Civic Dispositions).
Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives Standard 1: Citizenship characterize and good citizenship by building social networks of reciprocity and trustworthiness (Civic Dispositions).
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems. Long History of Mapping. The Earth is Flat. Long History of Mapping
 The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems Intro to Mapping & GIS The Earth is Flat Day to day, we live life in a flat world sun rises in east, sets in west sky is above, ground is below
The Earth Really is Flat! The Globe and Coordinate Systems Intro to Mapping & GIS The Earth is Flat Day to day, we live life in a flat world sun rises in east, sets in west sky is above, ground is below
STANDARD 3.1 Greece & Rome. STANDARD 3.2 - Mali
 2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS
 INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
INTRODUCTION CELESTIAL CLOCK - THE SUN, THE MOON, AND THE STARS This is a scientific presentation to provide you with knowledge you can use to understand the sky above in relation to the earth. Before
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector. Destination #3
 Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
Changes in Our Sky Grade Two
 Ohio Standards Connection: Earth and Space Sciences Benchmark A Observe constant and changing patterns of objects in the day and night sky. Indicator 2 Observe and describe how the sun, moon and stars
Ohio Standards Connection: Earth and Space Sciences Benchmark A Observe constant and changing patterns of objects in the day and night sky. Indicator 2 Observe and describe how the sun, moon and stars
UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System
 Practical Cartographer s Reference #01 UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System 180 174w 168w 162w 156w 150w 144w 138w 132w 126w 120w 114w 108w 102w 96w 90w 84w 78w 72w 66w 60w 54w 48w 42w
Practical Cartographer s Reference #01 UTM: Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System 180 174w 168w 162w 156w 150w 144w 138w 132w 126w 120w 114w 108w 102w 96w 90w 84w 78w 72w 66w 60w 54w 48w 42w
Unit One Study Guide
 Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
Unit One Study Guide Terms BCE: Before the Common Era. Referring to the time before Christ s birth. CE: Common Era. Referring to the time after Christ s birth. BC: Before Christ. Referring to the time
Magnetic Storm PROGRAM OVERVIEW
 Magnetic Storm PROGRAM OVERVIEW NOVA explores what creates Earth s magnetic field and why it might be headed for a reversal. Solar Wind Earth The program: explains how scientists think Earth s magnetic
Magnetic Storm PROGRAM OVERVIEW NOVA explores what creates Earth s magnetic field and why it might be headed for a reversal. Solar Wind Earth The program: explains how scientists think Earth s magnetic
ACQUIRING MINERAL RIGHTS IN THE NORTHWEST TERRITORIES
 ACQUIRING MINERAL RIGHTS IN THE NORTHWEST TERRITORIES Introduction Establishing and maintaining strong working relationships between the mineral industry and Northwest Territories (NWT) residents and community
ACQUIRING MINERAL RIGHTS IN THE NORTHWEST TERRITORIES Introduction Establishing and maintaining strong working relationships between the mineral industry and Northwest Territories (NWT) residents and community
Future Landscapes. Research report CONTENTS. June 2005
 Future Landscapes Research report June 2005 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Original ideas for the project 3. The Future Landscapes prototype 4. Early usability trials 5. Reflections on first phases of development
Future Landscapes Research report June 2005 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Original ideas for the project 3. The Future Landscapes prototype 4. Early usability trials 5. Reflections on first phases of development
Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston
 Chapter 6: SOLAR GEOMETRY Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston SOLAR GEOMETRY AS A DETERMINING FACTOR OF HEAT GAIN, SHADING AND THE POTENTIAL OF DAYLIGHT PENETRATION...
Chapter 6: SOLAR GEOMETRY Full credit for this chapter to Prof. Leonard Bachman of the University of Houston SOLAR GEOMETRY AS A DETERMINING FACTOR OF HEAT GAIN, SHADING AND THE POTENTIAL OF DAYLIGHT PENETRATION...
II. III. IV. RESOURCES A. Best Buy Bargain Books, Social Studies K-1 by Frank Schaffer ISBN 0867344512
 What on Earth is...a Map?...a Globe? Grade Level: Kindergarten Written by: Lisa Fagan Cross County Elementary, Teressa Davis Vanndale Elementary, Amy Searcy, and Cheryl Green Hickory Ridge Elementary,
What on Earth is...a Map?...a Globe? Grade Level: Kindergarten Written by: Lisa Fagan Cross County Elementary, Teressa Davis Vanndale Elementary, Amy Searcy, and Cheryl Green Hickory Ridge Elementary,
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
Give students a lesson in navigation from the points of the compass to GPS mapping.
 Lesson 5: Teaching Directions, Maps, and Coordinates Give students a lesson in navigation from the points of the compass to GPS mapping. by Jenny Parma; curriculum by Diane Petersen and Karen Dvornich
Lesson 5: Teaching Directions, Maps, and Coordinates Give students a lesson in navigation from the points of the compass to GPS mapping. by Jenny Parma; curriculum by Diane Petersen and Karen Dvornich
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones
 Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
