Inherited Metabolic Disorders. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
|
|
|
- Moses Phelps
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inherited Metabolic Disorders Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
2 Inherited Metabolic Disorders Although originally related to defects in specific enzymes (e.g. phenylalanine hydroxylase) this category of genetic diseases now includes receptors (e.g. the insulin receptor), transporters (e.g. amino acid transport proteins) and structural proteins (e.g. dystrophin). Today about 200 disorders are known that are classified as inborn errors of metabolism (i.e. enzyme defects), at least a further 100 conditions are known where a non-enzymic protein is defective.
3 Phenotypic analysis Routine phenotypic screening of newborn infants for metabolic disorders was first introduced in the early 1960s. In many countries it is now standard for every newborn infant to be tested for phenylketonuria and hypothyroidism. More than 50 other tests can be performed on the same filter paper blood sample. The introduction of Tandem Mass Spectrometry allows considerable expansion of the range of disorders tested for. There are many social, ethical and legal implications associated with the use of these programmes.
4 Before a condition is considered suitable for mass screening it should ideally meet the following criteria: it should be frequent and severe enough to be a public health concern; it should cause a known spectrum of symptoms; the screening test should be simple and reliable and should have a low incidence of false-positive and false-negative results; the condition should be amenable to treatment; appropriate diagnostic tests must be available and arrangements for follow-up treatment should be in place; there should be a positive cost-benefit ratio to society.
5 Screening Practice Parental education and consent (educational material for parents, informed consent, informed dissent). Ensure screening of every infant (early discharge, births out of hospital, < 1% missed in UK). Timing of test (before discharge, before 72 hours of age and after at least 24 hours of normal protein and lactose feeding; rescreening?). Type of blood sample (cord blood not acceptable because most metabolites do not accumulate until after birth; infant heel blood sample). Fate of blood sample?
6 Genotypic analysis (analysis of DNA) Molecular-based techniques can be used for: the preclinical diagnosis of individuals at risk; the identification of carriers; the safe, prenatal diagnosis of numerous genetic conditions; the confirmation of biochemical screening tests; the prediction of phenotypic severity of a disorder.
7 Direct mutation analysis With this approach, the gene responsible for the condition has been characterised and the mutation identified. These mutations may consist of major structural rearrangements detectable by Southern blotting. The mutations may be base pair substitutions, small insertions or deletions that can be detected by PCR-based methods. Fundamental problems with the use of genotypic analysis as a newborn screening procedure are the occurrence of genetic heterogeneity and spontaneous mutation.
8 Indirect analysis When the gene responsible for a condition has not been identified, or when the gene is known but the mutations are too heterogeneous to be tested for directly, the presence of the mutation can be inferred by linkage analysis. When the gene responsible for the condition is known, RFLPs in and around the gene can be used to follow the segregation of the mutant allele in the family.
9 There are limitations with this approach: numerous family members must be analysed; there is the possibility of prediction error because of recombination (i.e. two markers separated by 1x10 6 base pairs recombine in 1% of meiosis); affected individuals for an autosomal dominant condition or carriers for a recessive condition must be heterozygous for at least one marker in order for the normal allele to be differentiated from the mutant allele.
10 DNA microarray technology for neonatal screening Newborn blood provides high quality DNA for use in highly multiplexed PCR. Archived blood spots stored years can yield high-quality genomic DNA. Microarrays allow numerous amplification products to be coanalysed in a single assay. New manufacturing processes have reduced the cost of microarray technology to the point where it is practical for population screening of genetic diseases. High throughput is achieved by automation at every step.
11 Screening for Inherited Metabolic Disorders Condition Incidence Symptoms Special Considerations Phenylketonuria (phenylalanine hydroxylase) Maple Syrup Urine Disease (branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase) 1/12,000 Mental retardation Variants not uncommon. 1/250,000 CNS damage, death Rapid onset of symptoms. Homocystinuria (cystathionine synthase) Tyrosinemia (fumarylaceto-acetase) 1/250,000 Late onset mental retardation Methionine may not be elevated in all forms of the disease. 1/150,000 Liver, kidney damage Transient tyrosinemia of newborn is common. Hypothyroidism 1/4,000 Mental retardation, growth delay Galactosemia (hexose 1-phosphate uridylyltransferase) 1/60,000 Liver, kidney, CNS damage, death Late onset of disorder is common. Galactose only rises after lactose ingestion. Galactokinase Deficiency 1/250,000 Cataracts - Biotinidase Deficiency 1/250,000 Acidosis, skin rashes, growth failure, death Sickle Cell Diseases 1/400 Anaemia, bone, kidney damage death Enzyme affected by heat, storage and transfusions. Specimens must be obtained before transfusions. Heterozygote detection can create problems of follow-up and counselling. Cystic Fibrosis 1/2,500 Pancreatic and respiratory dysfunction, malnutrition, death High incidence of false positive and falsenegative results. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (steroid 21-hydroxylase) 1/12,000 electrolytic imbalances, shock death Rapid onset of shock in severe cases.
12 Summary About 200 disorders are known as inborn errors of metabolism, at least a further 100 conditions are known where a non-enzymic protein is defective. Phenotypic screening of newborns for metabolic disorders was introduced in the early 1960s. A condition should meet a number of criteria before it is considered suitable for mass screening. Genotypic analysis can be used for preclinical diagnosis of individuals at risk, identification of carriers, prenatal diagnosis, confirmation of biochemical screening tests and the prediction of phenotypic severity. Problems with genotypic analysis as a newborn screening procedure include genetic heterogeneity and spontaneous mutations. There are many social, ethical and legal implications associated with the use of these programmes.
13 References Hardin, J. et al. (2009) BMC Genetics 10, Article Number: Whole genome microarray analysis of neonatal blood. Hollegaard, M. V. et al., (2009) BMC Genomics 10, Article Number: Genome-wide scans using neonatal blood. Pollitt, R. J. (2010) Acta Paediat. 99, New technologies and blood-spot screening. Wilcken, B. (2011) J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 34, Newborn screening a review. Parini, R. & Corbetta, C. (2011) The J. Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med. 24, Metabolic screening.
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening Test
 Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Birth defects. Report by the Secretariat
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners. Newborn screening
 Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners
 Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
Part I Failure to Thrive
 Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Lecture 13: DNA Technology. DNA Sequencing. DNA Sequencing Genetic Markers - RFLPs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products of biotechnology
 Lecture 13: DNA Technology DNA Sequencing Genetic Markers - RFLPs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products of biotechnology DNA Sequencing determine order of nucleotides in a strand of DNA > bases = A,
Lecture 13: DNA Technology DNA Sequencing Genetic Markers - RFLPs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products of biotechnology DNA Sequencing determine order of nucleotides in a strand of DNA > bases = A,
Genetic testing. The difference diagnostics can make. The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association
 6 Genetic testing The difference diagnostics can make The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association Genetic INTRODUCTION testing The Department of Health published Our Inheritance, Our Future - Realising
6 Genetic testing The difference diagnostics can make The British In Vitro Diagnostics Association Genetic INTRODUCTION testing The Department of Health published Our Inheritance, Our Future - Realising
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program
 Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities
 Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Georgia Newborn Screening Manual
 Georgia Newborn Screening Manual for Metabolic Diseases & Hemoglobinopathies A Practitioner s Guide Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Family Health Branch GEORGIA NEWBORN
Georgia Newborn Screening Manual for Metabolic Diseases & Hemoglobinopathies A Practitioner s Guide Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Family Health Branch GEORGIA NEWBORN
Chapter 8: Recombinant DNA 2002 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 8: Recombinant DNA 2002 by W. H. Freeman and Company
 Genetic engineering: humans Gene replacement therapy or gene therapy Many technical and ethical issues implications for gene pool for germ-line gene therapy what traits constitute disease rather than just
Genetic engineering: humans Gene replacement therapy or gene therapy Many technical and ethical issues implications for gene pool for germ-line gene therapy what traits constitute disease rather than just
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology
 Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A future NBS candidate?
 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A future NBS candidate? Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Condition: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor deficiency, Alpha-1,
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A future NBS candidate? Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Condition: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor deficiency, Alpha-1,
STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE
 STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE LIST OF REVISIONS REVISION NO. DATE REVISED BY: PAGE/S DESCRIPTION 1 TBD GDSP 13 Initial Version II STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER
STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE HIE TOOLS USER GUIDE LIST OF REVISIONS REVISION NO. DATE REVISED BY: PAGE/S DESCRIPTION 1 TBD GDSP 13 Initial Version II STEP 2 IMPLEMENTATION: HIE TOOLS USER
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia
 Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Insurance. Chapter 7. Introduction
 65 Chapter 7 Insurance Introduction 7.1 The subject of genetic screening in relation to insurance is not new. In 1935 R A Fisher addressed the International Congress of Life Assurance Medicine on the topic,
65 Chapter 7 Insurance Introduction 7.1 The subject of genetic screening in relation to insurance is not new. In 1935 R A Fisher addressed the International Congress of Life Assurance Medicine on the topic,
Newborn Screening Issues
 Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
MEDICAL GENETICS GENERAL OBJECTIVE SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 SUBJECT MEDICAL GENETICS CREDITS Total: 4.5 Theory 2.5 Practical 2 GENERAL OBJECTIVE To provide students with terminology and knowledge from the field of human genetics that will enable them to understand
SUBJECT MEDICAL GENETICS CREDITS Total: 4.5 Theory 2.5 Practical 2 GENERAL OBJECTIVE To provide students with terminology and knowledge from the field of human genetics that will enable them to understand
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3
 Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
A Practical Guide to. Newborn Bloodspot Screening. in Ireland
 A Practical Guide to Newborn Bloodspot Screening in Ireland National Newborn Bloodspot Screening Laboratory Children s University Hospital Temple Street, Dublin 5 th Edition June 2011 National Newborn
A Practical Guide to Newborn Bloodspot Screening in Ireland National Newborn Bloodspot Screening Laboratory Children s University Hospital Temple Street, Dublin 5 th Edition June 2011 National Newborn
The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Name: 4. A typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross is a) 9:1 b) 3:4 c) 9:3:3:1 d) 1:2:1:2:1 e) 6:3:3:6
 Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484
 Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484 An act to amend Sections 124977 and 125055 of, to add Sections 1604.6 and 125002 to, and to add Article 4 (commencing with Section 123370) to Chapter 1 of Part 2 of Division
Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484 An act to amend Sections 124977 and 125055 of, to add Sections 1604.6 and 125002 to, and to add Article 4 (commencing with Section 123370) to Chapter 1 of Part 2 of Division
Alabama Newborn Screening Program
 Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Gene Mapping Techniques
 Gene Mapping Techniques OBJECTIVES By the end of this session the student should be able to: Define genetic linkage and recombinant frequency State how genetic distance may be estimated State how restriction
Gene Mapping Techniques OBJECTIVES By the end of this session the student should be able to: Define genetic linkage and recombinant frequency State how genetic distance may be estimated State how restriction
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Becker Muscular Dystrophy
 Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
The correct answer is c A. Answer a is incorrect. The white-eye gene must be recessive since heterozygous females have red eyes.
 1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE
 AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy
 Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Newborn screening policy and guidelines
 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Certain human genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia, result from single base-pair mutations in DNA. (a) Explain how a single base-pair mutation
AP BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 Certain human genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia, result from single base-pair mutations in DNA. (a) Explain how a single base-pair mutation
Suggested answers to questions
 Teacher Notes Introduction This activity encourages students to read an article which provides a good overview of the issues involved in genetic testing. It will also teach them useful reading skills,
Teacher Notes Introduction This activity encourages students to read an article which provides a good overview of the issues involved in genetic testing. It will also teach them useful reading skills,
Sickle cell anemia: Altered beta chain Single AA change (#6 Glu to Val) Consequence: Protein polymerizes Change in RBC shape ---> phenotypes
 Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING
 REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
New Estimates of the Economic Benefits of Newborn Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism in the US
 The findings and conclusions in this presentation have not been formally disseminated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and should not be construed to represent any agency determination
The findings and conclusions in this presentation have not been formally disseminated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and should not be construed to represent any agency determination
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance
 Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program
 Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009
 MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
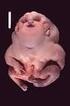 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive.
 11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions
 Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE
 SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Genetic Technology. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Genetic Technology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An application of using DNA technology to help environmental scientists
Name: Class: Date: Genetic Technology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An application of using DNA technology to help environmental scientists
BioBoot Camp Genetics
 BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
Chapter 3. Chapter Outline. Chapter Outline 9/11/10. Heredity and Evolu4on
 Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Chapter 3 Heredity and Evolu4on Chapter Outline The Cell DNA Structure and Function Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis The Genetic Principles Discovered by Mendel Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Misconceptions
Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis affects various systems in children and young adults, including the following:
 Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
The Case of Baby Joe by Kristen L.W. Walton Page 1
 The Case of Baby Joe: Chronic Infections in an Infant by Kristen L.W. Walton SPIRE Postdoctoral Fellowship Program University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Part I Background At birth, Baby Joe appeared
The Case of Baby Joe: Chronic Infections in an Infant by Kristen L.W. Walton SPIRE Postdoctoral Fellowship Program University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Part I Background At birth, Baby Joe appeared
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines
 Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Bio 102 Practice Problems Genetic Code and Mutation
 Bio 102 Practice Problems Genetic Code and Mutation Multiple choice: Unless otherwise directed, circle the one best answer: 1. Beadle and Tatum mutagenized Neurospora to find strains that required arginine
Bio 102 Practice Problems Genetic Code and Mutation Multiple choice: Unless otherwise directed, circle the one best answer: 1. Beadle and Tatum mutagenized Neurospora to find strains that required arginine
Newborn Screening in New York State. A Guide for Health Professionals
 New York State Department of Health Newborn Screening in New York State A Guide for Health Professionals Newborn Screening Program Wadsworth Center New York State Department of Health Empire State Plaza
New York State Department of Health Newborn Screening in New York State A Guide for Health Professionals Newborn Screening Program Wadsworth Center New York State Department of Health Empire State Plaza
Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism
 Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism California Department of Health Services Genetic Disease Branch www.dhs.ca.gov/gdb To Parents: California State Law requires that all babies have the
Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism California Department of Health Services Genetic Disease Branch www.dhs.ca.gov/gdb To Parents: California State Law requires that all babies have the
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Genetics Test Biology I
 Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
Genetic Testing: Scientific Background for Policymakers
 Genetic Testing: Scientific Background for Policymakers Amanda K. Sarata Specialist in Health Policy December 19, 2011 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress Congressional
Genetic Testing: Scientific Background for Policymakers Amanda K. Sarata Specialist in Health Policy December 19, 2011 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress Congressional
2. True or False? The sequence of nucleotides in the human genome is 90.9% identical from one person to the next. False (it s 99.
 1. True or False? A typical chromosome can contain several hundred to several thousand genes, arranged in linear order along the DNA molecule present in the chromosome. True 2. True or False? The sequence
1. True or False? A typical chromosome can contain several hundred to several thousand genes, arranged in linear order along the DNA molecule present in the chromosome. True 2. True or False? The sequence
D. Vitamin D. 1. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3
 D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES. Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD
 LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis. Evaluation for single gene disorders
 Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis Evaluation for single gene disorders What is Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis? Preimplantation genetic diagnosis or PGD is a technology that allows genetic testing of
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis Evaluation for single gene disorders What is Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis? Preimplantation genetic diagnosis or PGD is a technology that allows genetic testing of
CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Marrying a relative. Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other?
 Marrying a relative Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other? The simple answer to this question is Yes, there is an increased chance.
Marrying a relative Is there an increased chance that a child will have genetic problems if its parents are related to each other? The simple answer to this question is Yes, there is an increased chance.
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine
 Micronova 20.11.2012 Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine Kristiina Assoc. professor, Director of Genetic Department HUSLAB, Helsinki University Central Hospital The Human Genome Packed
Micronova 20.11.2012 Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine Kristiina Assoc. professor, Director of Genetic Department HUSLAB, Helsinki University Central Hospital The Human Genome Packed
Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling. Chapter 20
 Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling Chapter 20 What is Gene Therapy? Treating a disease by replacing, manipulating or supplementing a gene The act of changing an individual s DNA sequence to fix a non-functional
Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling Chapter 20 What is Gene Therapy? Treating a disease by replacing, manipulating or supplementing a gene The act of changing an individual s DNA sequence to fix a non-functional
Prior Authorization Form
 Prior Authorization Form Growth Hormone This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date. Fax signed forms to CVS/Caremark at
Prior Authorization Form Growth Hormone This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date. Fax signed forms to CVS/Caremark at
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Biochemistry
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Biochemistry The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences /Clinical Biochemistry, is awarded by the Faculty of Graduate Studies
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Biochemistry The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences /Clinical Biochemistry, is awarded by the Faculty of Graduate Studies
