Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers
|
|
|
- Marvin Dennis
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers
2 2 Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Since the mid-1960s, health care providers have offered newborn screening for phenylketonuria (PKU) to all infants born in Saskatchewan. Today, newborn screening has expanded to screen for at least 30 plus metabolic and endocrine disorders. Individually, these disorders are rare, but will, as a group, affect eight to 10 out of 13,000 newborns in the province each year. The Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory in Regina conducts all testing for congenital disorders. Early detection. Early treatment. Big benefits. These babies appear normal at birth and, unless they are screened, might otherwise not be identified to have one of these disorders until irreversible damage has occurred. If not treated, these conditions are associated with recurrent illnesses and/or developmental disabilities and/or death. Early diagnosis and treatment can result in significantly improved or positive outcomes. In some, preventive care can improve or maintain the quality of life of these babies. For babies who start to become ill soon after birth, newborn screening may save valuable time and resources in making a definite diagnosis. Informed parents make smart choices It s important that you, as a health care provider, emphasize to parents that newborn screening is part of their baby s routine care and could save their baby s life and/or prevent serious health problems. The vast majority of parents agree to have their baby screened. Should a parent refuse newborn screening, the decision should be documented in the baby s medical records and the parents will be required to sign a refusal form. What health care providers need to do A newborn screening specimen card should be completed between one day (24 hours) and seven days after the birth of the infant: ideally, between two days (48 hours) and three days (72 hours) after birth. If tested before 24 hours of age, the baby s health care provider should repeat the test within five days, at the first postnatal check-up. Blood spots from infants are collected using the heelprick method, which is detailed on the back of the specimen card. If you are providing care for an infant who is premature (i.e. less than 37 weeks gestation), ill, has been transfused, or has been on total parenteral nutrition (TPN) or antibiotics, please refer to the Special Considerations section on the next page. Submitting cards: time is critical It is critical that the Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory receives the newborn screening specimen card as soon as possible after the blood spots are collected. Therefore, the cards should be sent no later than 24 hours after collection and, ideally, as soon as the blood spots are dry (four to six hours after collection). Babies with some of the conditions screened will start to become ill and may suffer irreversible damage soon after birth. Rapid diagnosis and treatment can prevent this damage. Screening test results: positive and negative Once the Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory has received and analyzed the specimen card, one of the following will occur: Negative The infant under your care screens negative for all conditions. A report is issued by mail to both the referring hospital and should be filed in the baby s medical records. Repeat Sample If the initial sample is insufficient or unacceptable, or if the results are equivocal, you will be contacted and asked to obtain another sample from the newborn as soon as possible and repeat the submission procedure. Positive The infant under your care screens positive for a disorder. A screen positive does not necessarily mean that the baby has a disorder, but that it needs further investigation. The Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory will immediately notify your
3 regional treatment centre (the Metabolic Clinic in Saskatoon) about the screen positive result and the clinic will arrange with you or the infant s parent(s) for confirmatory testing. If a diagnosis of a disorder is confirmed, the clinic will provide management, counselling and follow-up. A report is also issued by mail to the referring hospital and health care provider, and should be filed in the baby s medical records. The screening test: there are limitations It s important to remember that, as with all screening tests, there will be false positive and false negative results. False positives will increase parental anxiety, while false negatives will give a misleading sense of reassurance. If a baby in your care exhibits symptoms of a particular disorder, but the newborn screen was negative, the child should be investigated and managed appropriately and the relevant consultant specialist should be contacted immediately for further advice. There is wide clinical variation in some of the disorders that the newborn screen detects. Therefore, there will be so-called affected individuals babies who are confirmed by diagnostic testing to have a particular disorder who will remain asymptomatic even without treatment or will only have very mild symptoms. Special considerations Prematurity or illness Infants who are premature (i.e. less than 37 weeks gestation) or who are sick should have their first specimen collected for newborn screening when they are five to seven days old. Premature infants will often have a high thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level and may screen positive for congenital hypothyroidism. However, on repeat specimens, results can be differentiated into false and true positives. Prematurity or illness in an infant being screened should be clearly indicated on the newborn screening specimen card. Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) and antibiotics The Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory can analyze heel-prick blood spots from infants who have had TPN (hyperalimentation) or antibiotics. However, levels of certain amino acids and organic acids can be elevated in these infants. In order to ensure the most accurate analysis, the administration of these therapies should be clearly indicated on the newborn screening specimen card. For additional information on newborn screening, visit Transfusions Infants who are affected with one of the disorders screened for by the Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory may be missed if they have had a recent blood transfusion. Normal levels of newborn screening analytes may be found in these cases because of the donor blood. Ideally, a specimen card should be completed before transfusion. Disorders Screened Organic Acid Disorders Organic Acidemias (OA) are a class of inherited metabolic disorders that occur when the body cannot metabolize certain amino acids and fats. This leads to an accumulation of organic acids in the blood and urine, which can cause serious health problems. Clinical symptoms of OA may include acute encephalopathy, 3
4 4 vomiting, metabolic acidosis, ketosis, dehydration or coma, hyperammonemia, lactic acidosis, hypoglycemia, failure to thrive, hypotonia, global developmental delay, sepsis, hematological disorders, and death. Newborns with OAs are perfectly healthy at birth, but may become quite ill within the first few days of life, even before the results of the newborn screening are known. Treatment often involves a low-protein diet and/or a diet low in specific amino acids and/or dietary supplements (such as carnitine, biotin, riboflavin), medical foods or other medications. It is very important for affected individuals to avoid fasting. Included in the OAs for which Saskatchewan screens are isovaleric acidemia (IVA), glutaric acidemia type 1 (GA1), HMG-CoA lyase deficiency (HMG), multiple carboxylase deficiency (MCD), methylmalonic acidemia, 3-Methylcrotonyl- CoA carboxylase (MCC) deficiency, propionic acidemia (PROP), B-Ketothiolase (BKT) deficiency, and dienoyl CoA reductase deficiency. Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects (FAODs) The breakdown of fatty acids in the mitochondria is an essential part of the body s ability to produce energy, especially if an infant has nothing to eat for more than a few hours, for instance, during illness. Fatty acids are transported into the cell and then into the mitochondria. Once in the mitochondria, the carbon chains or fatty acids are metabolized two at a time, using specific enzymes. If the transporter molecule(s) or any of the enzymes used to reduce the number of carbons in the chain are missing, an accumulation of fatty acids in the body occurs and causes hypoketotic hypoglycemia and tissue damage, especially liver, muscle, and heart disease. Lethargy, seizures, coma, and sudden death are also signs of FAODs. An undiagnosed FAOD can present as sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Dietary supplementation with carnitine and/or cornstarch may also be part of the treatment for FAODs. It is very important for affected individuals to avoid fasting. Included in the FAODs for which Saskatchewan screens are medium chain and short chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase (MCAD) and SCAD deficiency, very long chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase (VLCAD) deficiency, long chain 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency, trifunctional protein (TFP) deficiency, and carnitine uptake defect (CUD). Amino Acid Disorders These disorders occur when the body cannot either metabolize or produce certain amino acids, resulting in the toxic accumulation of some substances and the deficiency of other substances. Amino acids are derived from protein. Treatment often involves a low-protein diet and/or a diet low in specific amino acids. Specific medications and/or vitamins may also be prescribed, depending on the disorder. It is very important for affected individuals to avoid fasting.
5 Examples: Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a condition in which individuals cannot use phenylalanine properly so it builds up in the blood (hyperphenylalaninemia). Without treatment, phenylalanine accumulation will cause severe and irreversible developmental disabilities, eczema, and other problems. Saskatchewan has screened for PKU since Tyrosinemia (TYR) occurs when tyrosine cannot be properly metabolized, leading to an accumulation of this amino acid and its metabolites in the liver, kidneys, and the central nervous system, causing liver disease and other problems. Homocystinuria (HCY) occurs when homocystine accumulates in the urine. It is caused most commonly by a deficiency in an enzyme called cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS). Affected babies can have developmental disabilities and failure to thrive. They may also develop eye problems, skeletal problems, and a high chance of developing blood clots. Citrullinemia (CIT) and argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) are urea cycle defects. The urea cycle is the body s system for excreting waste nitrogen and ammonia, and for synthesizing arginine and urea. Hyperammonemia results when one of the enzymes in the urea cycle functions improperly. Symptoms can include lethargy, vomiting, coma, seizures, liver disease, failure to thrive, and death. Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) occurs when the amino acids, leucine, isoleucine, and valine cannot be metabolized. Symptoms include poor feeding, lethargy, convulsions, and even death. The urine of an affected child can have the odour of burnt sugar or maple syrup, giving the disorder its name. Other Disorders Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) can cause developmental disabilities and failure to thrive if not recognized and treated. It is a relatively common condition and is the result of a thyroid hormone deficiency. Saskatchewan has screened for CH by measuring thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in blood since Thyroid hormone replacement is a very effective treatment. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is an inherited defect in which the adrenal gland cannot make cortisol and overproduces male hormones. Without cortisol, infants may be unable to regulate salt and fluids, and can die. Some newborns with CAH can be symptomatic at birth with virilization of females. Replacement of deficient hormones is an effective means of preventing a salt-wasting crisis and preventing long-term complications. Biotinidase deficiency (BIOT) - Biotinidase is essential for the recycling of the vitamin biotin, which, in turn, is an enzyme cofactor. These enzymes, the carboxylases, are important in the production of certain fats and carbohydrates and for the breakdown of proteins. Features of this disorder include neurological symptoms, such as developmental disabilities and seizures, and cutaneous symptoms, such as hair loss and skin rash, which can be effectively treated with biotin supplementation. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease that affects the lungs and digestive system. The body produces thick mucus that may interfere with lung function and/or digestion. Approximately one in 3600 children born in Canada has CF. Galactosemia (GALT) Lactose is the main sugar in breast milk, cow s milk, and many infant formulas. This sugar is metabolized into glucose and galactose in the intestine. Individuals with galactosemia are not able to break down galactose. This can result in lifethreatening complications including feeding problems, failure to thrive, liver damage, bleeding, and sepsis in untreated infants. A diet restricted in lactose is very effective in preventing these complications. Even with early treatment, however, children with galactosemia are at increased risk for developmental disabilities, speech problems, abnormalities of motor functions and, in females, premature ovarian failure. Please note: The disorders for which the Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory screens may change over time. For the most current list, please check the Saskatchewan Disease Control website at 5
6 having a disorder until irreversible damage has occurred. In many cases, preventive care can improve or maintain the quality of life of these babies and their families. For babies who start to become ill soon after birth, newborn screening may save valuable time and resources in making a definite diagnosis. These conditions, if not treated, are associated with recurrent illnesses and/or developmental disabilities and/or death. Early diagnosis and treatment can result in a normal outcome. That s why it s so important to discuss newborn screening with your patients. Points to discuss with expectant parents Offer newborn screening Newborn screening is strongly recommended for all babies born in Saskatchewan as part of neonatal care. Results are very accurate and cover 30 plus different conditions. These are disorders of metabolism and the endocrine system. Discussion Guide This discussion guide will help you to counsel your patients and answer their questions about newborn screening. The brochure Newborn Screening: A healthy start leads to a healthier life is also available to provide to your patient. Health care providers offer newborn screening to all infants born in Saskatchewan. Although screening for phenylketonuria (PKU) and congenital hypothyroidism (CH) have been offered in Saskatchewan since 1965 and 1978, respectively, newborn screening expanded to cover 30 plus disorders. Newborn screening is a strongly recommended part of neonatal care since babies affected with these disorders usually appear normal at birth. Unless they undergo screening, they may not be identified as Discuss the benefits of testing Identifying a baby with one of the disorders is beneficial because early diagnosis and treatment can prevent consequences such as recurrent illnesses and/or developmental disabilities and/or death. Discuss how testing is done The blood sample is obtained by pricking the baby s heel. The blood is transferred to a special paper card and sent to the Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory. Testing must be timely Acceptable samples can be taken between one day (24 hours) and seven days after birth, although the best time to collect the blood sample is when the baby is between two days (48 hours) and three days (72 hours) old. If a baby is tested before one day (24 hours) of age, the test should be repeated within five days, at the first postnatal check-up. Babies with some of the disorders screened will start to become ill and may suffer irreversible damage right from birth. Rapid diagnosis and treatment can prevent this damage. 6
7 A repeat sample is sometimes required It may be that the first sample was not taken properly, the amount of blood taken was not enough to complete the testing, or there was some other problem with the sample. If requested, a repeat blood sample should be taken as soon as possible. Discuss the difference between a screening test and a diagnostic test A screening test determines if there is a high or low risk that a baby has a particular condition. Only a subsequent diagnostic test will determine with certainty if the baby is affected with a condition or not. The baby screens positive for one of the disorders. A screen positive does not necessarily mean that the baby has the condition but only that further investigation is required. The Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory will contact the Metabolic Clinic in Saskatoon, which will, in turn, immediately notify the baby s health care provider or parents about the screen positive result and arrange for confirmatory testing. If a diagnosis of a condition is confirmed, the clinic will provide management counselling and follow-up. Discuss possible results of screening The baby screens negative for all disorders. A report is issued by mail to the health care provider/referring hospital. Over 99 per cent of babies who have the newborn screen will have a negative result. 7
8 Resources For more information on Saskatchewan s newborn screening and the conditions screened for by the test, please visit or contact the Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory at (306) or (306) Saskatchewan Disease Control Laboratory Saskatchewan Ministry of Health Lloyd Place 3211 Albert Street Regina, Saskatchewan S4S 5W6 New address in the fall 2009 Other resources American Academy of Pediatrics: OrphaNet (information about rare disorders): National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD): Used and adapted with permission from the Government of Ontario. June/09
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Newborn Screening Test
 Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Your newborn baby s blood test
 Newborn Screening Free health checks for your baby Your newborn baby s blood test The Newborn Metabolic Screening Programme All babies are checked at birth to see that all is well. Some of your baby s
Newborn Screening Free health checks for your baby Your newborn baby s blood test The Newborn Metabolic Screening Programme All babies are checked at birth to see that all is well. Some of your baby s
Alabama Newborn Screening Program
 Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners
 Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
Newborn screening policy and guidelines
 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners. Newborn screening
 Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS
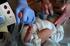 COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233
 State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233 Welcome and Introductions Review of Agenda Approval of December 2011 Minutes Commissioner
State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233 Welcome and Introductions Review of Agenda Approval of December 2011 Minutes Commissioner
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines
 Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project
 Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project Susan Tanksley, PhD MSGRCC Annual Meeting July 14, 2011 The Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measure Project (TNSPMP) is funded through a cooperative
Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project Susan Tanksley, PhD MSGRCC Annual Meeting July 14, 2011 The Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measure Project (TNSPMP) is funded through a cooperative
Practitioner s Manual
 Oregon Practitioner s Manual The Oregon Practitioner s Manual Oregon Health & Science University Cary Harding, MD Stephen L. LaFranchi, MD Gregory Thomas, MD Michael Wall, MD Oregon Health Authority Public
Oregon Practitioner s Manual The Oregon Practitioner s Manual Oregon Health & Science University Cary Harding, MD Stephen L. LaFranchi, MD Gregory Thomas, MD Michael Wall, MD Oregon Health Authority Public
MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM
 Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program
 Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism. Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology
 A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD
 FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
STATE STATUTES AND REGULATIONS ON DIETARY TREATMENT OF DISORDERS IDENTIFIED THROUGH NEWBORN SCREENING JURISDICTION AND CITATION
 Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy
 MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
Part I Failure to Thrive
 Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
Georgia Newborn Screening Manual
 Georgia Newborn Screening Manual for Metabolic Diseases & Hemoglobinopathies A Practitioner s Guide Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Family Health Branch GEORGIA NEWBORN
Georgia Newborn Screening Manual for Metabolic Diseases & Hemoglobinopathies A Practitioner s Guide Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Family Health Branch GEORGIA NEWBORN
NUTRITION OF THE BODY
 5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU)
 DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES
 HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
HOW TO CARE FOR A PATIENT WITH DIABETES INTRODUCTION Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in the United States, and diabetes is a disease that affects the way the body handles blood sugar. Approximately
Ammonia (plasma, blood)
 Ammonia (plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Ammonia 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Ammonia has the formula NH 3. At physiological
Ammonia (plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Ammonia 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Ammonia has the formula NH 3. At physiological
FAILURE TO THRIVE What Is Failure to Thrive?
 FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
ICD-9-CM/ICD-10-CM Codes for MNT
 / Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
/ Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy
 Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Making the Connections District 75 NYCDOE
 Medical Syndromes and Their Effect on Learning Making the Connections District 75 NYCDOE Cerebral Palsy The most frequent medical condition in 12:1:4 classes Associated with other disabilities including
Medical Syndromes and Their Effect on Learning Making the Connections District 75 NYCDOE Cerebral Palsy The most frequent medical condition in 12:1:4 classes Associated with other disabilities including
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
An introduction to metabolic disorders
 12 An introduction to metabolic disorders Individual inborn or congenital errors of metabolism are very rare. However, more than 1400 inherited metabolic diseases have been described. Many of these disorders
12 An introduction to metabolic disorders Individual inborn or congenital errors of metabolism are very rare. However, more than 1400 inherited metabolic diseases have been described. Many of these disorders
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR
 ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain.
 Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 35
 Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Preconception Clinical Care for Women Medical Conditions
 Preconception Clinical Care for Women All women of reproductive age are candidates for preconception care; however, preconception care must be tailored to meet the needs of the individual. Given that preconception
Preconception Clinical Care for Women All women of reproductive age are candidates for preconception care; however, preconception care must be tailored to meet the needs of the individual. Given that preconception
ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME
 ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME Policy NHP only reimburses participating DME vendors for the provision of medically necessary enteral and parenteral formulae and nutritional
ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME Policy NHP only reimburses participating DME vendors for the provision of medically necessary enteral and parenteral formulae and nutritional
Hypothyroidism. Written by Donald Yung Edited by Dianna Louie. Basic Embryology and Anatomy
 Hypothyroidism Written by Donald Yung Basic Embryology and Anatomy The thyroid gland consists of two lobes connected by an isthmus and is located anterior to the trachea at the base of the neck. During
Hypothyroidism Written by Donald Yung Basic Embryology and Anatomy The thyroid gland consists of two lobes connected by an isthmus and is located anterior to the trachea at the base of the neck. During
NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION DEFECT
 NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION DEFECT National Centre for Inherited Metabolic Disorders 2.1 NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION
NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION DEFECT National Centre for Inherited Metabolic Disorders 2.1 NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security
 Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net
 1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
Obstetric Cholestasis (itching liver disorder) Information for parents-to-be
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Obstetric Cholestasis (itching liver disorder) Information for parents-to-be page 2 You have been given this leaflet because you have been diagnosed with (or are suspected
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Obstetric Cholestasis (itching liver disorder) Information for parents-to-be page 2 You have been given this leaflet because you have been diagnosed with (or are suspected
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
Share the important information in this Medication Guide with members of your household.
 MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
Blood Transfusion. There are three types of blood cells: Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets.
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER
 Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER 80% of children and adults with FA have an endocrine abnormality Endocrine cells make a hormone (message) Carried in bloodstream
Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER 80% of children and adults with FA have an endocrine abnormality Endocrine cells make a hormone (message) Carried in bloodstream
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406
 Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Premature Infant Care
 Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Less stress for you and your pet
 Less stress for you and your pet Canine hyperadrenocorticism Category: Canine Cushing s disease, Cushing s syndrome Affected Animals: Although dogs of almost every age have been reported to have Cushing
Less stress for you and your pet Canine hyperadrenocorticism Category: Canine Cushing s disease, Cushing s syndrome Affected Animals: Although dogs of almost every age have been reported to have Cushing
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
 Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's Gestational Diabetes
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health?
 Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Is Insulin Effecting Your Weight Loss and Your Health? Teressa Alexander, M.D., FACOG Women s Healthcare Associates www.rushcopley.com/whca 630-978-6886 Obesity is Epidemic in the US 2/3rds of U.S. adults
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child
 Screening Programmes Congenital hypothyroidism and your child What is congenital hypothyroidism (CHT)? About 1 in 3000 babies born in the UK has CHT. Congenital means the baby is born with the condition.
Screening Programmes Congenital hypothyroidism and your child What is congenital hypothyroidism (CHT)? About 1 in 3000 babies born in the UK has CHT. Congenital means the baby is born with the condition.
UPLC/MSMS in the analysis of physiological steroids. May 2012. Anders Feldthus. Anders_Feldthus@Waters.com. 2012 Waters Corporation 1
 UPLC/MSMS in the analysis of physiological steroids Anders Feldthus Anders_Feldthus@Waters.com May 2012 2012 Waters Corporation 1 Clinical Chemistry Mass Spectrometry Citations (1955-2006) 70 Number of
UPLC/MSMS in the analysis of physiological steroids Anders Feldthus Anders_Feldthus@Waters.com May 2012 2012 Waters Corporation 1 Clinical Chemistry Mass Spectrometry Citations (1955-2006) 70 Number of
How to Fill Out Newborn Screening Cards
 How to Fill Out Newborn Screening Cards It is extremely important to fill out the screening card accurately and completel. Inaccurate or missing information may affect the accuracy of the screening results
How to Fill Out Newborn Screening Cards It is extremely important to fill out the screening card accurately and completel. Inaccurate or missing information may affect the accuracy of the screening results
Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrometry
 DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
Streptococcal Infections
 Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
Streptococcal Infections Introduction Streptococcal, or strep, infections cause a variety of health problems. These infections can cause a mild skin infection or sore throat. But they can also cause severe,
APPLICATION OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN TSH NEONATAL SCREENING FOR MONITORING OF IODINE DEFICIENCY AREAS IN THAILAND
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH APPLICATION OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN TSH NEONATAL SCREENING FOR MONITORING OF IODINE DEFICIENCY AREAS IN THAILAND Wiyada Charoensiriwatana 1, Pongsant
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH APPLICATION OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN TSH NEONATAL SCREENING FOR MONITORING OF IODINE DEFICIENCY AREAS IN THAILAND Wiyada Charoensiriwatana 1, Pongsant
The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function.
 12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
Blood Testing Protocols. Disclaimer
 Blood Testing Protocols / Page 2 Blood Testing Protocols Here are the specific test protocols recommend by Dr. J.E. Williams. You may request these from your doctor or visit www.readyourbloodtest.com to
Blood Testing Protocols / Page 2 Blood Testing Protocols Here are the specific test protocols recommend by Dr. J.E. Williams. You may request these from your doctor or visit www.readyourbloodtest.com to
Infant and young child feeding practices.
 Infant and young child feeding practices. Few things engender more anxiety than symptoms associated with feeding. Early difficulties can influence a mothers relationship with her baby for months or even
Infant and young child feeding practices. Few things engender more anxiety than symptoms associated with feeding. Early difficulties can influence a mothers relationship with her baby for months or even
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse
 Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Pregnancy and Substance Abuse Introduction When you are pregnant, you are not just "eating for two." You also breathe and drink for two, so it is important to carefully consider what you put into your
Male New Patient Package
 Male New Patient Package The contents of this package are your first step to restore your vitality. Please take time to read this carefully and answer all the questions as completely as possible. Thank
Male New Patient Package The contents of this package are your first step to restore your vitality. Please take time to read this carefully and answer all the questions as completely as possible. Thank
Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism
 Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism California Department of Health Services Genetic Disease Branch www.dhs.ca.gov/gdb To Parents: California State Law requires that all babies have the
Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism California Department of Health Services Genetic Disease Branch www.dhs.ca.gov/gdb To Parents: California State Law requires that all babies have the
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory
 NEWBORN SCREENING August 2001 Be Kind To Tiny Feet A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory HEMOGLOBINOPATHIES Second Edition Follow-up procedures for hemoglobinopathy
NEWBORN SCREENING August 2001 Be Kind To Tiny Feet A newsletter of the Newborn Screening Program and the Newborn Screening Laboratory HEMOGLOBINOPATHIES Second Edition Follow-up procedures for hemoglobinopathy
Kidney or renal disease
 Kidney or renal disease VETERINARY GUIDE 6 The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products out of the blood to form urine. Disease of the kidneys is one of the most common problems affecting middle-aged
Kidney or renal disease VETERINARY GUIDE 6 The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products out of the blood to form urine. Disease of the kidneys is one of the most common problems affecting middle-aged
Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis affects various systems in children and young adults, including the following:
 Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY. 12a. FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Dr. Lana Zinger, QCC CUNY 12a FOCUS ON Your Risk for Diabetes Your Risk for Diabetes! Since 1980,Diabetes has increased by 50 %. Diabetes has increased by 70 percent
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient
 Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Mucolipidoses. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 Mucolipidoses U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Mucolipidoses What are the mucolipidoses? The mucolipidoses (ML) are a group of inherited metabolic diseases that
Mucolipidoses U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Mucolipidoses What are the mucolipidoses? The mucolipidoses (ML) are a group of inherited metabolic diseases that
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels*
 Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
GSCE CHILD DEVELOPMENT: REVISION TIPS!
 GSCE CHILD DEVELOPMENT: REVISION TIPS! Assessment. There is a choice between two levels of entry: Foundation and Higher. At Foundation level (paper 1) the grades available are G to C and the Higher level
GSCE CHILD DEVELOPMENT: REVISION TIPS! Assessment. There is a choice between two levels of entry: Foundation and Higher. At Foundation level (paper 1) the grades available are G to C and the Higher level
Grow Taller 4 Idiots 2
 1 Grow Taller 4 Idiots 2 Warning and Disclaimer Every effort has been made to make this digital book as complete and as accurate as possible, but no warranty or fitness is implied. The information provided
1 Grow Taller 4 Idiots 2 Warning and Disclaimer Every effort has been made to make this digital book as complete and as accurate as possible, but no warranty or fitness is implied. The information provided
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES
 NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
what is diabetes? What actually goes wrong? Talking diabetes No.42
 Talking diabetes No.42 what is diabetes? Diabetes is the name given to a group of different conditions in which there is too much glucose in the blood. The pancreas either cannot make insulin or the insulin
Talking diabetes No.42 what is diabetes? Diabetes is the name given to a group of different conditions in which there is too much glucose in the blood. The pancreas either cannot make insulin or the insulin
Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox
 What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
What is Ai-Detox? Frequently Asked Questions: Ai-Detox Ai-Detox is a Chinese herbal medicinal formula, produced using state of the art biotechnology, which ensures the utmost standards in quality and safety.
ETIOLOGIC CLASSIFICATION. Type I diabetes Type II diabetes
 DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
Down s Syndrome Association Medical Series. Notes for parents & carers
 An updated version of one of a series of leaflets available from the Down s Syndrome Association Down s Syndrome Association Medical Series 1. THYROID DISORDER AMONG PEOPLE WITH DOWN S SYNDROME Notes for
An updated version of one of a series of leaflets available from the Down s Syndrome Association Down s Syndrome Association Medical Series 1. THYROID DISORDER AMONG PEOPLE WITH DOWN S SYNDROME Notes for
Diabetes and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives Diabetes: The #1 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor told you that you have
Newborn Screening in New York State. A Guide for Health Professionals
 New York State Department of Health Newborn Screening in New York State A Guide for Health Professionals Newborn Screening Program Wadsworth Center New York State Department of Health Empire State Plaza
New York State Department of Health Newborn Screening in New York State A Guide for Health Professionals Newborn Screening Program Wadsworth Center New York State Department of Health Empire State Plaza
MEDGUIDE SECTION. What is the most important information I should know about SEROQUEL? SEROQUEL may cause serious side effects, including:
 MEDGUIDE SECTION Medication Guide SEROQUEL (SER-oh-kwell) (quetiapine fumarate) Tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking SEROQUEL and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
MEDGUIDE SECTION Medication Guide SEROQUEL (SER-oh-kwell) (quetiapine fumarate) Tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking SEROQUEL and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Nutrition. Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT
 1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
INTELLIGENCE. Key: Alfred Binet. Key: William stern.
 1 INTELLIGENCE Total hours 14 hours Total marks 20 24 marks Approx no of questions on this chapt. (1 mark-1 or 2, 2 marks- 1 or 2, 5 marks-2, 10 marks-01) 1 Mark Questions : 1. Who gave the concept of
1 INTELLIGENCE Total hours 14 hours Total marks 20 24 marks Approx no of questions on this chapt. (1 mark-1 or 2, 2 marks- 1 or 2, 5 marks-2, 10 marks-01) 1 Mark Questions : 1. Who gave the concept of
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? TESTS TO DETECT OR DIAGNOSE KIDNEY DISEASE TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR KIDNEY DISEASE
 Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorder Case Study by Muhammad Ali Pervaiz, MD Clinical Biochemical Genetics Fellow.
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorder Case Study by Muhammad Ali Pervaiz, MD Clinical Biochemical Genetics Fellow. FOD/OAA Family Support Groups National Metabolic Conference Atlanta, Georgia July 30 & 31, 2010
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorder Case Study by Muhammad Ali Pervaiz, MD Clinical Biochemical Genetics Fellow. FOD/OAA Family Support Groups National Metabolic Conference Atlanta, Georgia July 30 & 31, 2010
Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people
 Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people www.e-imd.org What is a Urea cycle disorder/organic aciduria? The food we eat gets broken down by the body with the help of thousands of chemical
Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people www.e-imd.org What is a Urea cycle disorder/organic aciduria? The food we eat gets broken down by the body with the help of thousands of chemical
CMV: Your questions answered
 The basics about the virus CMV: Your questions answered What is CMV? CMV, or Cytomegalovirus, is a common virus that can infect people of all ages. Once CMV is in a person s body, it stays there for life.
The basics about the virus CMV: Your questions answered What is CMV? CMV, or Cytomegalovirus, is a common virus that can infect people of all ages. Once CMV is in a person s body, it stays there for life.
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP. Primary Care Provider:
 Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model
 The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
