Newborn screening policy and guidelines
|
|
|
- Owen Underwood
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011
2
3 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011
4 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including brochures and the e-learning tool are available at: Newborn Screening Laboratory PO Box 1100, Parkville 3052 Result and sample enquiries: phone: (03) fax: (03) Counselling enquiries: phone: (03) Department of Health, Screening and Cancer Prevention Unit phone: (03) If you would like to receive this publication in an accessible format, please phone using the National Relay Service if required, or This document is also available in PDF format on the internet at: Published by Prevention and Population Health Branch, Victorian Government Department of Health, Melbourne, Victoria Copyright, State of Victoria, Department of Health, 2011 This publication is copyright, no part may be reproduced by any process except in accordance with the provisions of the Copyright Act Authorised by the State Government of Victoria, 50 Lonsdale Street, Melbourne. Printed on sustainable paper by Impact Digital, Units 3-4, 306 Albert Street, Brunswick, Victoria, August 2011 ( )
5 Contents Contacts Policy statement 5 Rationale 6 Newborn screening in Victoria 7 Storage and access to screening cards 7 Roles and responsibilities for newborn screening 8 Newborn screening guidelines for service providers 9 Informing parents about screening 9 Written consent for screening 9 Decline of screening 9 Sample collection 10 Screening results and follow up 10 Appendix 1 11 Appendix 2 12 Relevant legislation & guidelines 12
6 Newborn screening policy and guidelines
7 Policy statement Newborn screening is an important public health program that facilitates the early identifi cation and management of babies at risk of having rare but serious medical conditions that can affect normal development. Newborn screening must be offered to parents 1 of all babies born in Victoria. To support informed decision making, parents are to be given written and verbal information prior to screening, ideally in the third trimester of pregnancy. Written consent for screening must be obtained before a blood sample is collected from the baby. Hospitals and service providers 2 are responsible for ensuring that a completed screening card is submitted to the Newborn Screening Laboratory for all births, including those babies who are not tested. Hospitals and service providers are responsible for ensuring that all births have either a screening result recorded or a completed decline form in the mother s medical record. Employers are responsible for ensuring that staff are aware of their role and responsibilities in relation to newborn screening and are competent to undertake the task. 1 Or legal guardians. 2 Including independent midwives 5
8 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Rationale A policy of written consent is being introduced to improve the quality of the screening program and to promote informed choice for parents. Newborn screening in Australia is a voluntary program. In Victoria, parents are currently required to give verbal consent for a blood sample to be collected for screening. Research 3 has shown parents do not receive adequate information prior to screening and are not aware of the choices available to them. Also, the existing process of verbal consent has been found to be ad hoc and inconsistent. In response, the Department of Health is implementing a new written consent process to support parents, to strengthen program quality and safety and ensure legal obligations are met. 3 Suriadi, C, Jovanovska, M & Quinlivan, J 2004, Factors affecting mothers knowledge of genetic screening, Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, vol. 44, pp ; Hider, K & Naksook, C 2007, Identifying Fundamental Problems with the Victorian Newborn Screening Program, Health Issues, no. 90, pp
9 Newborn screening in Victoria Newborn screening (NBS) has been available to all babies born in Victoria since the late 1960s. The program is funded by the Victorian Department of Health, which contracts the Victorian Clinical Genetics Service (VCGS) to operate the Newborn Screening Laboratory based at The Royal Children s Hospital in Melbourne. Screening is a quick, safe and effective way to identify newborns at risk of having a rare but serious medical condition. Early identifi cation allows for early intervention (usually with diet and/or medication) and can lead to a signifi cant reduction in morbidity and mortality for affected infants. Currently, conditions that can be identifi ed through newborn screening include phenylketonuria (PKU), congenital hypothyroidism, cystic fi brosis (CF) and approximately 22 other metabolic conditions that affect fat or protein metabolism (Appendix 1). Screening is conducted using a small blood sample obtained by pricking the baby s heel, hours after birth. This sample is collected onto an absorbent paper card and is processed at the Newborn Screening Laboratory. Storage and access to screening cards Storage and access to the screening cards are governed by a number of pieces of state legislation (Appendix 2). All screening cards collected in public and private institutions in Victoria are considered public records under the Public Records Act After screening, the cards are stored in the laboratory for a period of two years in line with National Pathology Accreditation Advisory Council (NPAAC) guidelines. This allows further clinical testing if needed and is also a requirement for laboratory quality control. Currently, after the two-year period of laboratory storage all cards are stored indefi nitely in a secure, off-site facility. Parents and individuals 18 years or older have the right to request transfer of the card to them after it has been stored for a minimum of two years. In line with state legislation, stored cards may be accessed by Victoria Police with a court order and by the coroner. Cards may also be used for ethics approved, de-identifi ed research. Identifi ed cards may be accessed for research use only with the consent of the parents. At the time of sample collection, parents have the right to specify that the sample is not available for de-identifi ed research use. 7
10 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Roles and responsibilities for newborn screening Department of Health program funding program monitoring program policy development Hospital/maternity service provider development of hospital policies to support newborn screening program quality and safety provision of information to parents ensure all parents are offered screening appropriate record keeping screening result or decline for all births support continuing education for midwives about newborn screening assign responsibility for newborn screening to an individual who will: be the fi rst point of contact for the laboratory ensure timely delivery of screening cards to the laboratory ensure every birth has a screening result or a decline form on fi le Midwife provision of information and discussion of screening with parents offer of screening obtain written consent appropriate sample collection record refusal sign hospital decline form and generate a card for the laboratory Newborn Screening Laboratory, The Royal Children s Hospital timely screening of all samples received timely reporting of results to all hospitals/providers timely requests for repeat samples made to hospital/provider timely contact with hospital/clinical specialist to arrange diagnostic testing if required provision of regular feedback to hospitals/providers in terms of consent compliance and sample quality 8
11 Newborn screening guidelines for service providers Informing parents about screening Before sample collection, staff must ensure parents are properly informed about screening and its importance. The information brochure Newborn screening: for the health of your baby should be provided to parents during the last trimester. The information must be discussed with parents and is available in a number of community languages at: Hospitals/providers must ensure parents 4 of all newborns are offered screening. Written consent for screening Implied consent for screening is inadequate. Staff must obtain written consent from a parent prior to sample collection. Written consent is provided by reading and signing a section of the screening card. After reading the brochure and discussing the test with their midwife, one parent is to complete the consent section on the card. This section also allows parents to indicate their preference with regard to the secondary use of the screening card in de-identifi ed health research. Making screening cards available for research use is a personal choice and should not deter parents from having their baby screened. Parents have the right to request that the card is not available for research use. In addition, parents should be informed of their ability to request transfer of the screening card after a period of two years. Decline of screening While newborn screening is strongly recommended for all babies, it is a voluntary program in Australia. If parents wish to decline screening, it is important to discuss their reasons and ensure they are aware of the risks (with referral to a paediatrician or newborn screening counsellor if necessary). If parents choose to decline, a signed screening card indicating that the test was declined must be provided to the laboratory. A hospital record of decline must also be signed by the parent and fi led in the medical record. A screening card must be sent to the laboratory this is a record that parents were offered, and declined screening. The laboratory is not aware of a birth until they receive a screening card. This is an important record for the laboratory. A decline of screening form must be signed and kept in the mother s record this is the equivalent hospital record that screening was declined. 4 Or legal guardians. 9
12 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Sample collection Newborn screening is carried out using a blood sample obtained by pricking the baby s heel, hours after birth. Inaccurate results can occur when the sample is collected outside these times. Screening cards must be sent daily to the screening laboratory, after air-drying. Guidelines for sample collection are available here: More information and a video of collection are available in the newborn screening e-learning tool at: Screening results and follow up The screening laboratory will issue a report of results on a weekly basis (electronic or paper) to all hospitals/providers. 5 Parents will not be contacted when screening results are normal. Positive screens will be followed up immediately with parents and the associated hospital/paediatrician by clinical staff from VCGS. A repeat collection will be requested by the laboratory for inadequate/contaminated samples or samples giving borderline abnormal results. The request will be mailed to the relevant hospital/ provider, along with an attached screening card. While concerning for some parents, reassurance should be given that repeat samples usually return a normal result. Each hospital must identify a newborn screening liaison person 6. This individual will be the fi rst point of contact for the laboratory. In particular, this person will be responsible for handling requests for repeat samples and will be required to check that the weekly report of screening results from the laboratory matches the hospital birth record. It is the responsibility of all hospitals to make certain every birth is accounted for. There may be legal implications for hospitals if appropriate records are not maintained. 5 including independent midwives 6 Independent midwives will work directly with laboratory staff 10
13 Appendix 1 # Disorder Other names 1 Hypothyroidism 2 Cystic fi brosis Disorders detected by tandem mass spectrometry: 3 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA lyase HMG CoA lyase 4 3-methylglutaryl CoA hydratase 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type 1 5 Argininosuccinic aciduria Argininosuccinate lyase 6 Citrullinaemia type 1 Argininosuccinate synthetase 7 Beta ketothiolase T2 defi ciency, 3-oxothiolase 8 Maple syrup urine disease MSUD, branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase (mild/ intermittent forms may not be detected) 9 Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 CPT1 10 Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 CPT2 11 Carnitine uptake defect CUD, systemic carnitine defi ciency, carnitine transporter defect, OCTN2 defect 12 Carnitine-acyl carnitine translocase CACT 13 Cobalamin disorders cblc, cbld, cblf disease 14 Homocystinuria Cystathionine betasynthase, CBS (vitamin responsive forms may not be detected) 15 Glutaric aciduria type 1 Glutaryl CoA dehydrogenase, GA1 16 Holocarboxylase synthase HCS, multiple carboxylase defi ciency, MCD 17 Isovaleryl CoA dehydrogenase Isovaleric acidaemia, IVA 18 Medium-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase MCAD 19 Methylmalonic acidaemia Methylmalonyl CoA mutase, MMA, cbla, cblb disease 20 Mitochodrial trifunctional protein Long-chain hydroxy acyl carnitine dehydrogenase, LCHAD, MTP 21 Multiple acyl CoA dehydrogenase MADD, glutaric aciduria type 2, GA2, ETF defi ciency 22 Phenylketonuria PKU, phenylalanine hydroxylase, including tetrahydrobiopterin defects 23 Propionic acidaemia Propionyl CoA carboxylase, PA, ketotic hyperglycinaemia 24 Tyrosinaemia 2 Tyrosine aminotransferase 25 Very long chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase VLCAD NB: other disorders are occasionally detected as part of the newborn screening testing, including disorders affecting the mother 11
14 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Appendix 2 Relevant legislation and guidelines In various ways, the following pieces of legislation apply to the newborn screening cards and the blood samples and data derived from them. This legislation governs storage of the cards, access during storage and also their appropriate disposal. Health Records Act 2001 (Vic) screening cards are health information for the purposes of the health records act. Information Privacy Act 2000 (Vic) Privacy Act 1988 (Cth) Public Records Act 1973 (Vic) all screening cards collected in public and private institutions are classifi ed as public records. Human Tissue Act 1982 (Vic) National Pathology Accreditation Advisory Council (NPAAC) Requirements for the Retention of Laboratory Records and Diagnostic Material (Fifth Edition 2009) Human Genetics Society of Australia (HGSA) Newborn Bloodspot Screening Policy
15
16
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners. Newborn screening
 Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Alabama Newborn Screening Program
 Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines
 Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Newborn screening sample collection guidelines Detailed information about the newborn screening program, including correct sample collection techniques, can be found in the e-learning tool available at:
Newborn Screening Test
 Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS
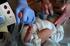 COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM
 Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy
 MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
STATE STATUTES AND REGULATIONS ON DIETARY TREATMENT OF DISORDERS IDENTIFIED THROUGH NEWBORN SCREENING JURISDICTION AND CITATION
 Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
Newborn Screening Issues
 Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
Information for parents considering adoption of their child
 Information for parents considering adoption of their child Published by the Victorian Government Department of Human Services Melbourne, Victoria Copyright State of Victoria 2008 This publication is copyright,
Information for parents considering adoption of their child Published by the Victorian Government Department of Human Services Melbourne, Victoria Copyright State of Victoria 2008 This publication is copyright,
Cord Blood - Public and Private Cord Blood Banking
 Policy Directive Ministry of Health, NSW 73 Miller Street North Sydney NSW 2060 Locked Mail Bag 961 North Sydney NSW 2059 Telephone (02) 9391 9000 Fax (02) 9391 9101 http://www.health.nsw.gov.au/policies/
Policy Directive Ministry of Health, NSW 73 Miller Street North Sydney NSW 2060 Locked Mail Bag 961 North Sydney NSW 2059 Telephone (02) 9391 9000 Fax (02) 9391 9101 http://www.health.nsw.gov.au/policies/
The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights in Victoria
 The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights in Victoria The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights in Victoria The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights describes
The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights in Victoria The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights in Victoria The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights The Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights describes
Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrometry
 DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
A fine inheritance, but it s not all in the bag
 A fine inheritance, but it s not all in the bag Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. The Willink Unit, Manchester - a fine
A fine inheritance, but it s not all in the bag Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. The Willink Unit, Manchester - a fine
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
 Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
An introduction to metabolic disorders
 12 An introduction to metabolic disorders Individual inborn or congenital errors of metabolism are very rare. However, more than 1400 inherited metabolic diseases have been described. Many of these disorders
12 An introduction to metabolic disorders Individual inborn or congenital errors of metabolism are very rare. However, more than 1400 inherited metabolic diseases have been described. Many of these disorders
Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project
 Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project Susan Tanksley, PhD MSGRCC Annual Meeting July 14, 2011 The Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measure Project (TNSPMP) is funded through a cooperative
Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measures Project Susan Tanksley, PhD MSGRCC Annual Meeting July 14, 2011 The Texas Newborn Screening Performance Measure Project (TNSPMP) is funded through a cooperative
Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484
 Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484 An act to amend Sections 124977 and 125055 of, to add Sections 1604.6 and 125002 to, and to add Article 4 (commencing with Section 123370) to Chapter 1 of Part 2 of Division
Senate Bill No. 1555 CHAPTER 484 An act to amend Sections 124977 and 125055 of, to add Sections 1604.6 and 125002 to, and to add Article 4 (commencing with Section 123370) to Chapter 1 of Part 2 of Division
A Practical Guide to. Newborn Bloodspot Screening. in Ireland
 A Practical Guide to Newborn Bloodspot Screening in Ireland National Newborn Bloodspot Screening Laboratory Children s University Hospital Temple Street, Dublin 5 th Edition June 2011 National Newborn
A Practical Guide to Newborn Bloodspot Screening in Ireland National Newborn Bloodspot Screening Laboratory Children s University Hospital Temple Street, Dublin 5 th Edition June 2011 National Newborn
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Chapter 3: Healthy Start Risk Screening
 Introduction Healthy Start legislation requires that all pregnant women and infants be offered screening for risk factors that may affect their pregnancy, health, or development. The prenatal and infant
Introduction Healthy Start legislation requires that all pregnant women and infants be offered screening for risk factors that may affect their pregnancy, health, or development. The prenatal and infant
If you are signing for a minor child, you refers to your child throughout the consent document.
 CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Adult Patient or Parent, for Minor Patient INSTITUTE: National Cancer Institute PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Raffit Hassan, M.D. STUDY TITLE: Tissue Procurement
CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Adult Patient or Parent, for Minor Patient INSTITUTE: National Cancer Institute PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Raffit Hassan, M.D. STUDY TITLE: Tissue Procurement
PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP
 PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP PUBLIC HEALTH ACTIVITIES & SERVICES INVENTORY TECHNICAL NOTES HEALTHY FAMILY DEVELOPMENT Nurse-Family Partnership Nurse-Family Partnership is a voluntary program of
PUBLIC HEALTH IMPROVEMENT PARTNERSHIP PUBLIC HEALTH ACTIVITIES & SERVICES INVENTORY TECHNICAL NOTES HEALTHY FAMILY DEVELOPMENT Nurse-Family Partnership Nurse-Family Partnership is a voluntary program of
In recent years the number of DNA genetic tests that you can
 Inside How accurate are the tests? 2 How useful are the tests? 2 What can Direct-to-Consumer DNA genetic tests tell me? 2 What happens to my personal information? 3 What protections are there in Australia?
Inside How accurate are the tests? 2 How useful are the tests? 2 What can Direct-to-Consumer DNA genetic tests tell me? 2 What happens to my personal information? 3 What protections are there in Australia?
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners
 Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM
 AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
Women s Health Victoria
 Women s Health Victoria Termination of Pregnancy Post 20 Weeks Background Paper March 2007 Prepared by Kerrilie Rice Policy and Research Officer Published by Level 1, 123 Lonsdale Street Melbourne Victoria
Women s Health Victoria Termination of Pregnancy Post 20 Weeks Background Paper March 2007 Prepared by Kerrilie Rice Policy and Research Officer Published by Level 1, 123 Lonsdale Street Melbourne Victoria
Rh D Immunoglobulin (Anti-D)
 Document Number PD2006_074 Rh D Immunoglobulin (Anti-D) Publication date 29-Aug-2006 Functional Sub group Clinical/ Patient Services - Maternity Clinical/ Patient Services - Medical Treatment Population
Document Number PD2006_074 Rh D Immunoglobulin (Anti-D) Publication date 29-Aug-2006 Functional Sub group Clinical/ Patient Services - Maternity Clinical/ Patient Services - Medical Treatment Population
The California Prenatal Screening Program
 The California Prenatal Screening Program Quad Marker Screening One blood specimen drawn at 15 weeks - 20 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester) Serum Integrated Screening Prenatal Patient Booklet - English
The California Prenatal Screening Program Quad Marker Screening One blood specimen drawn at 15 weeks - 20 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester) Serum Integrated Screening Prenatal Patient Booklet - English
Australian Bone Marrow Donor Registry PROTECTING YOUR PRIVACY OUR PRIVACY POLICY
 Australian Bone Marrow Donor Registry PROTECTING YOUR PRIVACY OUR PRIVACY POLICY WHO ARE WE? The Australian Bone Marrow Donor Registry (ABMDR) is a non-profit organisation that manages the processes of
Australian Bone Marrow Donor Registry PROTECTING YOUR PRIVACY OUR PRIVACY POLICY WHO ARE WE? The Australian Bone Marrow Donor Registry (ABMDR) is a non-profit organisation that manages the processes of
Exceptional People. Exceptional Care. Antenatal Appointment Schedule for Normal Healthy Women with Singleton Pregnancies
 Exceptional People. Exceptional Care. Antenatal Appointment Schedule for Normal Healthy Women with Singleton Pregnancies First Antenatal Contact with the GP Obtain medical and obstetric history. Measure
Exceptional People. Exceptional Care. Antenatal Appointment Schedule for Normal Healthy Women with Singleton Pregnancies First Antenatal Contact with the GP Obtain medical and obstetric history. Measure
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
Pregnancy and hypothyroidism
 Pregnancy and hypothyroidism Departments of Endocrinology & Obstetrics Patient Information What What is hypothyroidism? is hypothyroidism? Hypothyroidism means an underactive thyroid gland, which does
Pregnancy and hypothyroidism Departments of Endocrinology & Obstetrics Patient Information What What is hypothyroidism? is hypothyroidism? Hypothyroidism means an underactive thyroid gland, which does
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand
 Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand Questions and Answers 1. What are Nutrient Reference Values? The Nutrient Reference Values outline the levels of intake of essential nutrients considered,
National Survey of Pre- and Post- Analytical Performance Measures Used in Newborn Screening Programs
 National Survey of Pre- and Post- Analytical Performance Measures Used in Newborn Screening Programs Simran Tiwana, MBA* Susan Tanksley, PhD* Brad Therrell, PhD Donna Williams, BS* Mirsa Douglass, MBA*
National Survey of Pre- and Post- Analytical Performance Measures Used in Newborn Screening Programs Simran Tiwana, MBA* Susan Tanksley, PhD* Brad Therrell, PhD Donna Williams, BS* Mirsa Douglass, MBA*
Review of the Department of Health and Human Services management of a critical issue at Djerriwarrh Health Services
 Review of the Department of Health and Human Services management of a critical issue at Djerriwarrh Health Services November 2015 Review Panel Adjunct Professor Debora Picone AM Mr Kieran Pehm Contents
Review of the Department of Health and Human Services management of a critical issue at Djerriwarrh Health Services November 2015 Review Panel Adjunct Professor Debora Picone AM Mr Kieran Pehm Contents
Unsaturated and Odd-Chain Fatty Acid Catabolism
 Unsaturated and dd-hain Fatty Acid atabolism March 24, 2003 Bryant Miles The complete oxidation of saturated fatty acids containing an even number of carbon atoms is accomplished by the β-oxidation pathway.
Unsaturated and dd-hain Fatty Acid atabolism March 24, 2003 Bryant Miles The complete oxidation of saturated fatty acids containing an even number of carbon atoms is accomplished by the β-oxidation pathway.
Credentialling and defining the scope of clinical practice for medical practitioners
 Credentialling and defining the scope of clinical practice for medical practitioners 4 Clinical review of area mental health services 1997-2004 Credentialling and defining the scope of clinical practice
Credentialling and defining the scope of clinical practice for medical practitioners 4 Clinical review of area mental health services 1997-2004 Credentialling and defining the scope of clinical practice
HEEL PRICK PROCEDURE FOR NEWBORN BLOOD SPOT SCREENING
 HEEL PRICK PROCEDURE FOR NEWBORN BLOOD SPOT SCREENING First Issued April 2007 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change To promote a safe and effective blood spot screening procedure Planned
HEEL PRICK PROCEDURE FOR NEWBORN BLOOD SPOT SCREENING First Issued April 2007 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change To promote a safe and effective blood spot screening procedure Planned
Professional Indemnity Insurance for Eligible Midwives
 Professional Indemnity Insurance for Eligible Midwives Information Booklet Practise with confidence From 1 July 2010 IMPORTANT This document has been prepared to provide eligible midwives with key information
Professional Indemnity Insurance for Eligible Midwives Information Booklet Practise with confidence From 1 July 2010 IMPORTANT This document has been prepared to provide eligible midwives with key information
Birth defects. Report by the Secretariat
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
CONSENT FORM. Cord Blood Banking for Transplantation
 Cord Blood Program Northwest Tissue Center/Puget Sound Blood Center 921 Terry Avenue Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 292-1896 Swedish Medical Center 747 Broadway Seattle, WA 98122 (206) 386-6000 CONSENT FORM Cord
Cord Blood Program Northwest Tissue Center/Puget Sound Blood Center 921 Terry Avenue Seattle, WA 98104 (206) 292-1896 Swedish Medical Center 747 Broadway Seattle, WA 98122 (206) 386-6000 CONSENT FORM Cord
ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME
 ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME Policy NHP only reimburses participating DME vendors for the provision of medically necessary enteral and parenteral formulae and nutritional
ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME Policy NHP only reimburses participating DME vendors for the provision of medically necessary enteral and parenteral formulae and nutritional
BE IT ENACTED BY THE LEGISLATURE OF THE STATE OF ALASKA:
 LAWS OF ALASKA 01 Source SB 1 Chapter No. AN ACT Relating to direct-entry midwives. BE IT ENACTED BY THE LEGISLATURE OF THE STATE OF ALASKA: THE ACT FOLLOWS ON PAGE 1 Enrolled SB 1 AN ACT 1 Relating to
LAWS OF ALASKA 01 Source SB 1 Chapter No. AN ACT Relating to direct-entry midwives. BE IT ENACTED BY THE LEGISLATURE OF THE STATE OF ALASKA: THE ACT FOLLOWS ON PAGE 1 Enrolled SB 1 AN ACT 1 Relating to
Cover for pregnancy and childbirth
 Cover for pregnancy and childbirth 2016 How we cover pregnancy and childbirth in 2016 The Maternity Benefit covers day-to-day and in-hospital medical expenses for expectant mothers and newborns. Overview
Cover for pregnancy and childbirth 2016 How we cover pregnancy and childbirth in 2016 The Maternity Benefit covers day-to-day and in-hospital medical expenses for expectant mothers and newborns. Overview
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
 Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP [email protected] [email protected] Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP [email protected] [email protected] Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
RICHARD BYRON COLLINS CONSULTANT FORENSIC PATHOLOGIST
 CURRICULUM VITAE RICHARD BYRON COLLINS CONSULTANT FORENSIC PATHOLOGIST 2 PERSONAL DETAILS NAME: RICHARD BYRON COLLINS ADDRESS: PO BOX 3072, GEELONG WEST, VIC. 3218. DATE OF BIRTH: OCTOBER 31, 1944 PLACE
CURRICULUM VITAE RICHARD BYRON COLLINS CONSULTANT FORENSIC PATHOLOGIST 2 PERSONAL DETAILS NAME: RICHARD BYRON COLLINS ADDRESS: PO BOX 3072, GEELONG WEST, VIC. 3218. DATE OF BIRTH: OCTOBER 31, 1944 PLACE
POLICY STATEMENT 5.17
 POLICY STATEMENT 5.17 DENTAL RECORDS 1 (Including ADA Guidelines for Dental Records) 1. Introduction 1.1 Dentists have a professional and a legal obligation to maintain clinically relevant, accurate and
POLICY STATEMENT 5.17 DENTAL RECORDS 1 (Including ADA Guidelines for Dental Records) 1. Introduction 1.1 Dentists have a professional and a legal obligation to maintain clinically relevant, accurate and
What are medical records? What is the purpose of the medical record?
 Medical Records Contents What are medical records? 3 What is the purpose of the medical record? 3 What should my medical records contain? 4 Why are medical records important medico-legally? 6 How long
Medical Records Contents What are medical records? 3 What is the purpose of the medical record? 3 What should my medical records contain? 4 Why are medical records important medico-legally? 6 How long
How To Get A Health Insurance Policy From Mybupa
 Information Handling Policy February 2015 Page 1 1. Introduction 1.1 About Bupa In this document, we, us, our and Bupa refers to Bupa Australia Pty Ltd (ABN 81 000 057 590) and its related entities and
Information Handling Policy February 2015 Page 1 1. Introduction 1.1 About Bupa In this document, we, us, our and Bupa refers to Bupa Australia Pty Ltd (ABN 81 000 057 590) and its related entities and
INTRODUCTION TO THE UK CURRICULUM IN CLINICAL GENETICS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE UK CURRICULUM IN CLINICAL GENETICS Clinical Geneticists work in multidisciplinary regional genetic centres in the UK, in close collaboration with laboratory scientists, clinical co-workers
INTRODUCTION TO THE UK CURRICULUM IN CLINICAL GENETICS Clinical Geneticists work in multidisciplinary regional genetic centres in the UK, in close collaboration with laboratory scientists, clinical co-workers
Code of Ethics for Nurses in Australia
 Code of Ethics for Nurses in Australia Developed under the auspices of Australian Nursing Council Inc, Royal College of Nursing Australia, Australian Nursing Federation Code of Ethics for Nurses in Australia
Code of Ethics for Nurses in Australia Developed under the auspices of Australian Nursing Council Inc, Royal College of Nursing Australia, Australian Nursing Federation Code of Ethics for Nurses in Australia
Providing support to vulnerable children and families. An information sharing guide for registered school teachers and principals in Victoria
 Providing support to vulnerable children and families An information sharing guide for registered school teachers and principals in Victoria Service Coordination Tool Templates 2006 reference guide Providing
Providing support to vulnerable children and families An information sharing guide for registered school teachers and principals in Victoria Service Coordination Tool Templates 2006 reference guide Providing
ARMENIA. Albert Matevosyan MD,PhD
 Albert Matevosyan MD,PhD Neurohereditary Diseases Charity Association Head of Republic Center of Medical Genetic and Department of Medical Genetic Yerevan State Medical University Rome EUROPLAN (Italy)
Albert Matevosyan MD,PhD Neurohereditary Diseases Charity Association Head of Republic Center of Medical Genetic and Department of Medical Genetic Yerevan State Medical University Rome EUROPLAN (Italy)
Part I Failure to Thrive
 Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Know your rights and responsibilities as a private patient in hospital. Private Patients Hospital Charter
 Know your rights and responsibilities as a private patient in hospital Private Patients Hospital Charter Commonwealth of Australia 2004 ISBN 0 642 82235 2 This work is copyright. Apart from any use as
Know your rights and responsibilities as a private patient in hospital Private Patients Hospital Charter Commonwealth of Australia 2004 ISBN 0 642 82235 2 This work is copyright. Apart from any use as
Professional Indemnity Insurance Application Form for Eligible Midwives
 Professional Indemnity Insurance Application Form for Eligible Midwives This Form will be used by MIGA to consider your application for Professional Indemnity Insurance with MIGA and for your automatic
Professional Indemnity Insurance Application Form for Eligible Midwives This Form will be used by MIGA to consider your application for Professional Indemnity Insurance with MIGA and for your automatic
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD
 FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program
 Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
Tennessee Newborn Screening Program Guide for Practitioners State of Tennessee Department of Health Family Health and Wellness 710 James Robertson Parkway Nashville, TN 37243 Phone 615-532-8462 1-855-202-1357
PLEASE NOTE. For more information concerning the history of these regulations, please see the Table of Regulations.
 PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this regulation, current to February 12, 2011. It is intended for information and reference purposes
PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this regulation, current to February 12, 2011. It is intended for information and reference purposes
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Records Management Checklist. preservation. accountability. information. security. peoplep. A tool to improve records management
 Records Management Checklist preservation accountability information security busine ess peoplep A tool to improve records management preservation people security business Foreword accountability information
Records Management Checklist preservation accountability information security busine ess peoplep A tool to improve records management preservation people security business Foreword accountability information
Clinical Governance for Nurse Practitioners in Queensland
 Office of the Chief Nursing Officer Clinical Governance for Nurse Practitioners in Queensland A guide Clinical Governance for Nurse Practitioners in Queensland: A guide Queensland Health Office of the
Office of the Chief Nursing Officer Clinical Governance for Nurse Practitioners in Queensland A guide Clinical Governance for Nurse Practitioners in Queensland: A guide Queensland Health Office of the
APPENDIX B SAMPLE INFORMED CONSENT FORM
 APPENDIX B SAMPLE INFORMED CONSENT FORM B.1 INFORMED CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A RESEARCH STUDY Umbilical Cord Blood Banking for Transplantation You are being asked to take part in a research study that
APPENDIX B SAMPLE INFORMED CONSENT FORM B.1 INFORMED CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A RESEARCH STUDY Umbilical Cord Blood Banking for Transplantation You are being asked to take part in a research study that
Preconception Clinical Care for Women Medical Conditions
 Preconception Clinical Care for Women All women of reproductive age are candidates for preconception care; however, preconception care must be tailored to meet the needs of the individual. Given that preconception
Preconception Clinical Care for Women All women of reproductive age are candidates for preconception care; however, preconception care must be tailored to meet the needs of the individual. Given that preconception
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Productivity Commission Education and Training Workforce: Early Childhood Development
 Productivity Commission Education and Training Workforce: Early Childhood Development Victorian Association of Maternal and Child Health Nurses Submission The Victorian Association of Maternal and Child
Productivity Commission Education and Training Workforce: Early Childhood Development Victorian Association of Maternal and Child Health Nurses Submission The Victorian Association of Maternal and Child
JOB DESCRIPTION REPORTING TO:
 JOB DESCRIPTION SECTION ONE DESIGNATION: REPORTING TO: SENIOR MEDICAL OFFICER: HAWERA HOSPITAL HEAD OF DEPARTMENT EMERGENCY SERVICES - FOR ALL CLINICAL MATTERS, AND AS REQUIRED THE HEADS OF DEPARTMENT
JOB DESCRIPTION SECTION ONE DESIGNATION: REPORTING TO: SENIOR MEDICAL OFFICER: HAWERA HOSPITAL HEAD OF DEPARTMENT EMERGENCY SERVICES - FOR ALL CLINICAL MATTERS, AND AS REQUIRED THE HEADS OF DEPARTMENT
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder in New Zealand: Activating the. Awareness and Intervention Continuum
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder in New Zealand: Activating the Awareness and Intervention Continuum Executive Summary April 2007 This Alcohol Healthwatch briefing paper contains information on: Fetal Alcohol
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder in New Zealand: Activating the Awareness and Intervention Continuum Executive Summary April 2007 This Alcohol Healthwatch briefing paper contains information on: Fetal Alcohol
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU)
 DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
Protection of Genetic Information: An International Comparison
 Report to the Human Genetics Commission Protection of Genetic Information: An International Comparison Deborah Crosbie LL.B September 2000 Crown Copyright Financed by: Research & Development section of
Report to the Human Genetics Commission Protection of Genetic Information: An International Comparison Deborah Crosbie LL.B September 2000 Crown Copyright Financed by: Research & Development section of
A test your patients can trust.
 A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
ROYAL AUSTRALASIAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS
 1. SCOPE This policy details the College s privacy policy and related information handling practices and gives guidelines for access to any personal information retained by the College. This includes personal
1. SCOPE This policy details the College s privacy policy and related information handling practices and gives guidelines for access to any personal information retained by the College. This includes personal
On behalf of the Association of Maternal and Child Health Programs (AMCHP), I am
 Christopher Kus, M.D., M.P.H. Association of Maternal and Child Health Programs, Public Witness Testimony House Labor, Health and Human Services and Education Appropriations Subcommittee March 13, 2013
Christopher Kus, M.D., M.P.H. Association of Maternal and Child Health Programs, Public Witness Testimony House Labor, Health and Human Services and Education Appropriations Subcommittee March 13, 2013
