Can we avoid the traps of 3T imaging?
|
|
|
- Virginia Wilkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Can we avoid the traps of 3T imaging? Poster No.: C-1473 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Kiss, J. Martos, L. R. Kozak, B. Lombay ; Budapest/HU, Miskolc/HU Keywords: MR physics, Neuroradiology brain, Computer applications, MRDiffusion/Perfusion, MR-Functional imaging, MR-Spectroscopy, Manometry DOI: /ecr2015/C-1473 Any information contained in this pdf file is automatically generated from digital material submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service. ECR is not responsible for the content of these pages and does not make any representations regarding the content or accuracy of material in this file. As per copyright regulations, any unauthorised use of the material or parts thereof as well as commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method ist strictly prohibited. You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold ECR harmless from and against any and all claims, damages, costs, and expenses, including attorneys' fees, arising from or related to your use of these pages. Please note: Links to movies, ppt slideshows and any other multimedia files are not available in the pdf version of presentations. Page 1 of 29
2 Aims and objectives In recent years 3T MRI has become more and more common in the clinical practice and it increasingly occupies the place of 1.5T systems. Unfortunately transferring the 1.5T protocols to 3T systems were not really straightforward and sometimes not even successful [1]. There are several advantages of 3T MRI: faster sequences, new techniques and advanced hardware. Due to the growing number of 3T MRIs the clinical application spectrum have substantially broadened to almost all anatomical areas including e.g. musculoskeletal [2, 3], abdominal [4, 5], cardiac [6], angiographic [7, 8, 9], and wholebody imaging [10, 11]. Besides the many advantages, there are some disadvantages and artifacts e.g. high B0 and B1 inhomogeneity, chemical shift effects, artifacts from blood flow, magnetohydrodynamics-, susceptibility artifacts. In some cases contrast visualization is decreased [12, 13]. One of the main disadvantages of 3T scanners is the high specific absorption rate (SAR) [14], there are many articles dealing with SAR limit, and sequence optimization. To avoid the possible drawbacks many strategies have been described recently, but given the numerous drawbacks the question is still valid: is 3T clearly ready to meet all the clinical needs today? The purpose of this study to present the most relevant artifacts, present at 3T MRI, to review, compare and choose the best of the possible strategies, reducing them, if possible. We also aim to compare image artifacts and possible solutions 1.5-, and 3T MRI. Methods and materials Here we review imaging data of more than 400 patients including 40 children examined between and on a 1.5T-, (Magnetom Symphony, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) and two 3T (Magnetom Verio, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) MRI machines. Scans from different body region were systematically reviewed to show the main advantages, artifacts and their consequences, possible compensations and their effects (the latter mainly on the 3T systems, see Fig 1. / Table 1.). Problems in detail: Specific Absorption Rate reduction. Decreased contrast visualization between gray and white matter on T1weighted brain images. Page 2 of 29
3 Time-Of-Flight (TOF) MR angiography background suppression. Mitigating the susceptibility artifacts originating from metal implants. Decreased liquor signal intensity on T2-weighted lumbar spine images. In the first case we measured the Contrast to Noise Ratio (CNR) between the gray and white matter. A Region of Interest (ROI) approach was applied to measure the mean ± standard deviation. For the other cases 5 radiologist reviewed the images independently in a qualitative manner. Determining if image quality is acceptable upon applying solution based on Table 1. They also determined their subjective best solution for a given problem. In some cases we suggested other techniques/sequences to solve these imaging problems. Page 3 of 29
4 Fig. 1: Table 1. Important factors affecting image quality and possible compensations at 3T [15, 16, 17, 18, 19] Page 4 of 29
5 References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Images for this section: Page 5 of 29
6 Fig. 1: Table 1. Important factors affecting image quality and possible compensations at 3T [15, 16, 17, 18, 19] Page 6 of 29
7 Results SAR limit's problem Knowing and handling SAR limits are important in the clinical practice, especially at the abdomen, extremities and spine examinations to avoid the sudden stopping of measurement, due to exceeding the acceptable SAR. SAR can be easily reduced by reducing the slice number, voxel size or change other sequence parameter, and however these manipulations can sometimes seriously decrease image quality. To avoid this "trap" is better to change RF pulse type (from high/normal to low SAR), to reduce the turbo factor/echo train lengths or to increase the concatenations). T1 value: Contrast differentiation on T1-weighted brain Spin Echo images, on 1,5-, and 3T MRI system (Fig 2., Fig 3.). Fig. 2: T1-weighted Spin echo sequence about the brain on 1.5T (TR: 500 ms, TE: 11 ms). Page 7 of 29
8 References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Fig. 3: T1-weighted Spin echo sequence about the brain on 3T (TR: 620 ms, TE: 9 ms). References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU There is clear contrast between the white-, and gray matter on 1.5T with some visible noise (Fig 2.), while contrast is diminished on at 3T - despite the better overall image quality (Fig 3.). Suggested solution: reducing the flip angle (FA) [17]. Lower the FA, improves CNR in some slices (Fig 4/a.) while not affecting other parts of the (Fig 4/b.). Page 8 of 29
9 Fig. 4: The results of lower FA (70 degree): visible contrast differentiation (a.). Contrast difference was lost on other slices (b.). References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU We couldn't correct this problem of Spin Echo imaging, so we tried different sequences to find the best one of brain disorder analysis (Fig 5.). Page 9 of 29
10 Fig. 5: Four different types of T1-weighted sequences about the brain. The gray-, and white contrast visualization is invisible on the conventional Spin Echo (a.) and SPACE (b.) sequences. Good contrast is visible only the temporal-lobe on the 2D Flash sequence (c.). The best option is the MPRAGE sequence, with inversion time (d.). References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Time-Of-Flight MR angiography - TOF MRA At 3T the TOF sequence provides superior spatial resolution, thus improved vessel contrast, better background tissues. However there are few cases, when background Page 10 of 29
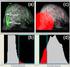
11 suppression is not advantageous, e.g. to detect neurovascular compression, affecting the trigeminal nerve. It is easy to detect on 1.5T - TOF MRA, without MTC pulse. On 3T there are 2 two possible solutions: Decreasing the resolution. Reducing the flip angle Trigeminal nerve detection (Fig 6/a. white arrows) wasn't correct because of the image quality, but 3D VIBE (Volume Interpolated Breath-hold Examination) with fat suppression (Fig 6/b.) was successful for the correct identification of nerve. Fig. 6: TOF MRA: establishing the the presence of neurovascular compression is nearly impossible because of the too noisy image noise and the reduced visibility of the trigeminal nerve is viewless (a. - white arrows). The problem can be solved with FS VIBE sequence - the nerve is detectable (b. - red arrows). References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Magnetic susceptibility This artifact mainly presents with high intensity on echo-planar diffusion weighted images (Fig 7/a). Possible solution: larger receiver bandwidth and/or a decreased echo time; even better solution: PAT (Parallel Acquisition Technique; Grappa and Sense). Using Page 11 of 29
12 PAT acquisition time was the same, the signal to noise ratio (SNR) were lower and artifacts were reduced successfully (Fig 7/b). Fig. 7: Diffusion weighted image with low TE and high receiver bandwidth, without PAT (a.) - with visible susceptibility artifacts (white arrows). Same sequences with PAT (Grappa) - the artifacts were reduced (b.). References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Orthopedic metal implants in the spine may cause more extensive susceptibility artifacts at 3T than at 1.5T (Fig 8.). Page 12 of 29
13 Fig. 8: Susceptibility artifacts from metal implant at 3T, and 1.5T (a.). The artifacts appeared markedly on 3T images (b.). References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU These could be reduce using conventional Turbo Spin Echo sequences with higher bandwidth (Fig 9/a. - WARP technique - Siemens), but flow artifacts will then be amplified (Fig 9/b). Flow artifacts can be reduced with a 3D SPACE (Sampling Perfection with Application optimized Contrasts using different flip angle Evolution) sequence (Fig 10.) with low turbo factor. Page 13 of 29
14 Fig. 9: T2-weighted axial images about the cervical spine - with metal implant. The susceptibility artifact appeared strongly on the gradient echo image (Fig 8/a). It could reduce with TSE sequence - however the flow artifacts were amplified (Fib 8/b). References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Fig. 10: T2-weighted SPACE axial and coronal images about the cervical spine - the flow artifacts were eliminated. References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Reduced Liquor Intensity Page 14 of 29
15 Signal intensity is much better on 3T than 1.5T. Of course we have to increase the TR at 3T. Interestingly there is a special artifact on the T2-weighted L-spine images - significant signal intensity reduction on the right or left side of the images (Fig 11/a.). Fig. 11: Fig 11. T2-weighted sagittalis L-spine images with significant signal decay on the left side. Fig 10/b show the same image after the correction. References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Possible solution: change concatenation (distribution of the slices to be measured over multiple measurements) values from 1 to 2, and apply a saturation band (Fig 11/b). This artifact is a typical 3T system issue, however with the use of more concatenation there is less slice cross talk and therefore less "saturation" in the slices. Images for this section: Page 15 of 29
16 Fig. 2: T1-weighted Spin echo sequence about the brain on 1.5T (TR: 500 ms, TE: 11 ms). Page 16 of 29
17 Fig. 3: T1-weighted Spin echo sequence about the brain on 3T (TR: 620 ms, TE: 9 ms). Fig. 4: The results of lower FA (70 degree): visible contrast differentiation (a.). Contrast difference was lost on other slices (b.). Page 17 of 29
18 Fig. 5: Four different types of T1-weighted sequences about the brain. The gray-, and white contrast visualization is invisible on the conventional Spin Echo (a.) and SPACE (b.) sequences. Good contrast is visible only the temporal-lobe on the 2D Flash sequence (c.). The best option is the MPRAGE sequence, with inversion time (d.). Page 18 of 29
19 Fig. 6: TOF MRA: establishing the the presence of neurovascular compression is nearly impossible because of the too noisy image noise and the reduced visibility of the trigeminal nerve is viewless (a. - white arrows). The problem can be solved with FS VIBE sequence - the nerve is detectable (b. - red arrows). Fig. 7: Diffusion weighted image with low TE and high receiver bandwidth, without PAT (a.) - with visible susceptibility artifacts (white arrows). Same sequences with PAT (Grappa) - the artifacts were reduced (b.). Page 19 of 29
20 Fig. 8: Susceptibility artifacts from metal implant at 3T, and 1.5T (a.). The artifacts appeared markedly on 3T images (b.). Fig. 9: T2-weighted axial images about the cervical spine - with metal implant. The susceptibility artifact appeared strongly on the gradient echo image (Fig 8/a). It could reduce with TSE sequence - however the flow artifacts were amplified (Fib 8/b). Page 20 of 29
21 Fig. 10: T2-weighted SPACE axial and coronal images about the cervical spine - the flow artifacts were eliminated. Fig. 11: Fig 11. T2-weighted sagittalis L-spine images with significant signal decay on the left side. Fig 10/b show the same image after the correction. Page 21 of 29
22 Conclusion Real and unavoidable problems play very important role in the sequence optimization. The SAR limit is a real "trap", because without change the sequence's parameters we will get noisy and unacceptable results. We suggest to modify the sequence's parameters instead of choosing another sequence(s). In our example the best way was to modify the RF-pulse type and to decrease the resolution. Great problem is to increase the contrast between the gray-, and white matter on the T1weighted Spin-Echo images. The lower flip angle could be a better route, but it didn't work on our systems. The only solution was using another sequence e.g. MPRAGE which apply Inversion Recovery technique to provide the contrast differentiation. We couldn't find optimal TOF's sequence values to identify the trigeminal nerve and determine the neurovascular compression. 3D VIBE sequence with fat suppression could be a solution. Using PAT sequences play an important role in reducing susceptibility artifacts on diffusion weighted sequences. In some cases however, the PAT caused significant artifacts, but it can be compensated. Susceptibility artifacts due to metal implants could be eliminated using TSE sequences while flow artifacts could be reduced with SPACE sequences, but in this case the turbo factors were limited. Finally we could compensate the T2-weighted L-spine intensity issue arising at 3T using changes in concatenation parameters. We summarize our results in two tables (Table 2. and Table 3. - see Fig 12. and Fig 13.). Page 22 of 29
23 Page 23 of 29
24 Fig. 12: Table 2. The usable and unusable solutions References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Fig. 13: Table 3. Avoidable and unavoidable problems and their solutions References: Neuroradiology, National Institute of Clinical Neuroscience, Department of Radiology; - Budapest/HU Images for this section: Page 24 of 29
25 Page 25 of 29
26 Fig. 12: Table 2. The usable and unusable solutions Fig. 13: Table 3. Avoidable and unavoidable problems and their solutions Page 26 of 29
27 Personal information References [1] Lawrence N. Tanenbaum: Clinical 3T MRI: Mastering and Challanges. Appl. Radiology 2006;35(11). [2] Filippo Del Grande, Francesco Santini, Daniel A. Herzka, Micheal R. Aro, Cooper W. Dean, Garry E. Gold, John A. Carrino: Fat-Suppression Techniques for 3T Imaging of the Musculoskeletal System. DOI: doi.org/ /rg [3] Ramnath RR. 3T MR imaging of the musculoskeletal system (Part II): clinical applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2006;14(1): [4] Kevin J. Chang, MD, and Ihab R. Kamel: Abdominal imaging at 3T: Challenges and solutions. Applied Radiology 2010;10: [5] Elmar M. Merkle and Brian M. Dale: Abdominal MRI at 3.0 T: The Basics Revisited. American Journal of Rontgenology. 2006;186: [6] John N. Oshinski, Jana G. Delfino Puneet Sharma, Ahmed M. Gharib and Roderic I. Pettigrew: Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance at 3T: Current state of the art. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2010, 12:55. [7] Kolja M. Thielfelder, Georgios Meimarakis, Konstantin Nikolau, Wieland H. Sommer, Peter Schmitt, Philipp M. Kazmierczak, Maximilian F. Reiser and Daniel Theisen: NonContrast-Enhanced MR Angiograpghy at 3T in Patients with Advanced Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease. DOI: /journal.pone [8] K. Naela, J.P. Villablancaa, R. Saleha, W. Popea, A. Naela, G. Laubb and J.P. Finna: Contrast-Enhanced MRA at 3T in the Evaluation if intracranial Aneurysms: A Comparison with Time-Of-Flight MR Angiography. AJNR November : [9] Eftychia Z. Kapsalaki, Christos D. Rountas and Kostas N. Fountas: The Role of 3T MRA in the Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms. DOI: /2012/ Page 27 of 29
28 [10] Laura M. Fayad, Jaishri Blakeley, Scott Plotkin, Brigitte Widemann and Michael A. Jacobs: Whole Body MRI at 3T with Quantitative Diffusion Weighted Imaging and Contrast-Enhanced Sequences for the Characterization of Peripheral Lesions in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2 and Schwannomatosis. DOI: /2013/ [11] Schmidt GP. Wintersperger B, Grase A, Baur-Melnyk A, Resier MF, Schoenberg SO.: High-resolution whole-body magnetic resonance imaging applications at 1,5 and 3T: a comparative study. Invest Radiology Jun;42(6): [12] Olaf Dietrich, Maximilian F. Reiser and Stefan Schoenberg: Artifacts in 3-Tesla MRI: Physical background and reduction strategies. Eur J Radiol 2008; 65(1): [13] Escher K, Shellock FG.: Evaluation of MRI artifacts at 3 Tesla for 38 commonly used cosmetics. Madn Reson Imaging 2013 Jun; 31(5): [14] Edelstein WA, Glover GH, Hardy CJ, Redington RW. The intrinsic signal-to-noise ratio in NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med 1986;3(4): [15] Fritz Schick: Whole-body MRI at high field: technical limits and clinical potential. DOI: /s [16] Vaishali V. Phalke, Sachin Gujar and Douglas J. Quint: Comparison of 3.0 versus 1.5T MR: Imaging of the spine. DOI: dx.doi.org/ /j.nic [17] Bernd L. Schmitz, Georg Grön, Florian Brausewetter, Martin H.K. Hoffmann, and Andrik J. Aschoff: Enhancing Gray-to-White Matter Contrast in 3T T1Spin-Echo Brain Scans by Optimizing Flip Angle. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26: , September [18] R. Javan, J.R. O'Rear, J. E. Machin; Fundamentals Behind the 10 most common Magnetic Resonance Imaging Artifacts with Correction Strategies and 10 High-Yield Points. DOI: /ecr2011/C [19] Charuta Dagia; Michael Ditchfield: 3T MRI in Pediatrics: Challanges and Clinical Applications. European Journal of Radiology, 68 (2008) [20] Matt A. Bernstein: Field Strength Dependence in MRI: Advantages and Artifacts at 3T. ( Page 28 of 29
29 Page 29 of 29
Utilization management for successful process optimization in radiology
 Utilization management for successful process optimization in radiology Poster No.: C-0737 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H.-P. Busch 1, W. Frewer 1, A. van Est 2 ; 1 Trier/DE, 2 Eindhoven/NL
Utilization management for successful process optimization in radiology Poster No.: C-0737 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H.-P. Busch 1, W. Frewer 1, A. van Est 2 ; 1 Trier/DE, 2 Eindhoven/NL
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging
 Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
CT findings in Differential Diagnosis between Tuberculous Pleurisy and Malignant Effusion
 CT findings in Differential Diagnosis between Tuberculous Pleurisy and Malignant Effusion Poster No.: E-0084 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. Shim, Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Keywords:
CT findings in Differential Diagnosis between Tuberculous Pleurisy and Malignant Effusion Poster No.: E-0084 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. Shim, Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Keywords:
OA related pain medication intake in subjects from the OAI incidence cohort - association with focal knee lesions and cartilage T2 measurements
 OA related pain medication intake in subjects from the OAI incidence cohort - association with focal knee lesions and cartilage T2 measurements Poster No.: C-0007 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
OA related pain medication intake in subjects from the OAI incidence cohort - association with focal knee lesions and cartilage T2 measurements Poster No.: C-0007 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Patterns of nodal spread in thoracic malignancies
 Patterns of nodal spread in thoracic malignancies Poster No.: C-0977 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: R. dos Santos, M. Duarte, J. Alpendre, J. Castaño, Z. Seabra, Â.
Patterns of nodal spread in thoracic malignancies Poster No.: C-0977 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: R. dos Santos, M. Duarte, J. Alpendre, J. Castaño, Z. Seabra, Â.
Determination of bone age using MRI of hand/wrist: a pilot study
 Determination of bone age using MRI of hand/wrist: a pilot study Poster No.: C-0963 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Tomei, M. Marini, A. Stagnitti, A. sartori, L. bertana, N. Al
Determination of bone age using MRI of hand/wrist: a pilot study Poster No.: C-0963 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Tomei, M. Marini, A. Stagnitti, A. sartori, L. bertana, N. Al
MRI scanning of the claustrophobic patients
 MRI scanning of the claustrophobic patients Poster No.: C-0549 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. minov, A. Doreski, M. Popovska, G. Markoski, S. 1 2 3 2 2 1 2 2 3 Jovanoska, I. miladinovski
MRI scanning of the claustrophobic patients Poster No.: C-0549 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. minov, A. Doreski, M. Popovska, G. Markoski, S. 1 2 3 2 2 1 2 2 3 Jovanoska, I. miladinovski
Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program
 Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program Poster No.: C-0591 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program Poster No.: C-0591 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Preoperative evaluation of future remnant liver function by the contrast enhance ratio in hepatocellular image.
 Preoperative evaluation of future remnant liver function by the contrast enhance ratio in hepatocellular image. Poster No.: C-0564 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Matsushima, Y.
Preoperative evaluation of future remnant liver function by the contrast enhance ratio in hepatocellular image. Poster No.: C-0564 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Matsushima, Y.
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer
 Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Table 11: Pros and Cons of 1.5 T MRI vs. 3.0 T MRI; Safety and Technical Issues, and Clinical Applications
 Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Safety Issue 3.0 T MRI Pro 3.0 T MRI Con Immediate fringe field surrounding magnet A ferromagnetic object inadvertently brought into the scan room will experience a sharp increase in attraction toward
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging
 Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
An Image Based Semiautomatic Online Cancer Staging Program for Common Female Pelvic Malignancies
 An Image Based Semiautomatic Online Cancer Staging Program for Common Female Pelvic Malignancies Poster No.: C-1050 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Talanow; Lexington, KY/US Keywords:
An Image Based Semiautomatic Online Cancer Staging Program for Common Female Pelvic Malignancies Poster No.: C-1050 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Talanow; Lexington, KY/US Keywords:
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management
 Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
GE 3.0T NPW,TRF,FAST,F R NPW,TRF,FAST,F R
 GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
GE 3.0T 3.0T WRIST Invivo 8CH Wrist Coil Sequence Ax T2 Cor PD Cor PDFS Cor T1 Cor PD (Small FOV) FOV (mm) 80 80 80 80 40 Matrix 384x224 384x256 320x256 384x320 320x192 Phase Direction RL RL RL RL RL #
Needle crystal detector technology in mammography further dose reduction and clinical image quality with
 Needle crystal detector technology in mammography further dose reduction and clinical image quality with different beam qualities (W/Rh vs. Mo/Rh) Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific
Needle crystal detector technology in mammography further dose reduction and clinical image quality with different beam qualities (W/Rh vs. Mo/Rh) Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific
Eye lens dose measurements in Interventional Cardiology
 Eye lens dose measurements in Interventional Cardiology Poster No.: 479 Congress: ESCR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: N. Kollaros 1, E. Carinou 2, C. Plemmenos 1, I. Stathopoulos 1, V. Keywords:
Eye lens dose measurements in Interventional Cardiology Poster No.: 479 Congress: ESCR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: N. Kollaros 1, E. Carinou 2, C. Plemmenos 1, I. Stathopoulos 1, V. Keywords:
MRI SEQUENCES. 1 Gradient Echo Sequence
 5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
5 An MRI sequence is an ordered combination of RF and gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form the image. In this chapter I will describe the basic gradient echo, spin echo and inversion recovery
Development and implementation of a help desk system in a radiology department in a high complexity hospital: a South American experience
 Development and implementation of a help desk system in a radiology department in a high complexity hospital: a South American experience Poster No.: C-2409 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords:
Development and implementation of a help desk system in a radiology department in a high complexity hospital: a South American experience Poster No.: C-2409 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords:
Metastatic malignant melanoma revisited
 Metastatic malignant melanoma revisited Poster No.: C-2446 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Paulino, B. Gonçalves, P. Marques, M. Gonçalo, F. CaseiroAlves;
Metastatic malignant melanoma revisited Poster No.: C-2446 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Paulino, B. Gonçalves, P. Marques, M. Gonçalo, F. CaseiroAlves;
Normal vascular variants of the upper extremity
 Normal vascular variants of the upper extremity Poster No.: C-1039 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Paixao, A. P. Gomes, M. S. C. Sousa, I. Santiago, A. S. C. C. Germano; Amadora/PT
Normal vascular variants of the upper extremity Poster No.: C-1039 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Paixao, A. P. Gomes, M. S. C. Sousa, I. Santiago, A. S. C. C. Germano; Amadora/PT
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine
 Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations
 Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Musculoskeletal MRI Technical Considerations Garry E. Gold, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Bioengineering and Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University Outline Joint Structure Image Contrast Protocols: 3.0T
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T
 32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T Thomas Benner Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
32-Channel Head Coil Imaging at 3T Thomas Benner Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio
 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio 29 5 Factors Affecting the Signal-to-Noise Ratio In the preceding chapters we have learned how an MR signal is generated and how the collected signal is processed
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time
 Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
DICOM metadata-mining in PACS for computed radiography X-Ray exposure analysis: a mammography multisite study
 DICOM metadata-mining in PACS for computed radiography X-Ray exposure analysis: a mammography multisite study Poster No.: B-0276 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper M. R.
DICOM metadata-mining in PACS for computed radiography X-Ray exposure analysis: a mammography multisite study Poster No.: B-0276 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper M. R.
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs
 Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Angio-CT preoperative planning of inferior limb free flaps in plastic surgery
 Angio-CT preoperative planning of inferior limb free flaps in plastic surgery Poster No.: C-3046 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular Authors: L. Saba, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, G.
Angio-CT preoperative planning of inferior limb free flaps in plastic surgery Poster No.: C-3046 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular Authors: L. Saba, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, G.
THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI. Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider
 THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider Departments of *Radiology, *Electrical Engineering, and Psychology University
THEORY, SIMULATION, AND COMPENSATION OF PHYSIOLOGICAL MOTION ARTIFACTS IN FUNCTIONAL MRI Douglas C. Noll* and Walter Schneider Departments of *Radiology, *Electrical Engineering, and Psychology University
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery.
 Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
3/30/2013. Disclosure. Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization. MRI, 35 year ago. MRI Today. Outlines
 http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
ParaVision 6. Innovation with Integrity. The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research.
 ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
Comparison between photoacoustic mammography images of breasts cancers and histological staining patterns of CD31 and carbonic anhydrase IX
 Comparison between photoacoustic mammography images of breasts cancers and histological staining patterns of CD31 and carbonic anhydrase IX Poster No.: C-1893 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Comparison between photoacoustic mammography images of breasts cancers and histological staining patterns of CD31 and carbonic anhydrase IX Poster No.: C-1893 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Abdominal CT Perfusion: Effects of Breath Control Technique
 Abdominal CT Perfusion: Effects of Breath Control Technique Poster No.: C-0068 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa, T. Kanda, Y. Ohno, Y. Fujisawa, N. Negi, M. 1 1 2 1 1 1
Abdominal CT Perfusion: Effects of Breath Control Technique Poster No.: C-0068 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa, T. Kanda, Y. Ohno, Y. Fujisawa, N. Negi, M. 1 1 2 1 1 1
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 12: Spin Echo
 Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
Module : Spin Echo Spin Echo Objectives Review the SE PSD. Review the concepts of T, T, and T*. Spin Echo PSD RF Gz Gy 90 80 Gx Spin Echo - SE Spin echo is a standard pulse sequence on Signa MRi/LX and
Overview. Optimizing MRI Protocols. Image Contrast. Morphology & Physiology. User Selectable Parameters. Tissue Parameters
 Overview Optimizing MRI Protocols Clinical Practice & Compromises Geoffrey D. Clarke, Radiology Department University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Pulse timing parameters for adjusting
Overview Optimizing MRI Protocols Clinical Practice & Compromises Geoffrey D. Clarke, Radiology Department University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Pulse timing parameters for adjusting
University Children s Hospital Basel
 Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
Cooperation Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI www.siemens.com/skyra University Children s Hospital Basel Siemens International Reference Center Pediatric MRI Answers for life. Partnering
Flip-angle-optimized fast dynamic T 1 mapping with a 3D gradient-echo sequence
 Flip-angle-optimized fast dynamic T 1 mapping with a 3D gradient-echo sequence Olaf Dietrich 1, Maximilian Freiermuth 1, Linus Willerding 2, Maximilian F. Reiser 1, Michael Peller 1 1 Josef Lissner Laboratory
Flip-angle-optimized fast dynamic T 1 mapping with a 3D gradient-echo sequence Olaf Dietrich 1, Maximilian Freiermuth 1, Linus Willerding 2, Maximilian F. Reiser 1, Michael Peller 1 1 Josef Lissner Laboratory
MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols
 MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols Structural scans SIEMENS MAGNETOM ConnectomA syngo MR D11 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Default\AAHScout_64 TA:0:14 PAT:3 Voxel size:1.6 1.6 1.6 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :fl
MGH Adult Diffusion Data Scanning Protocols Structural scans SIEMENS MAGNETOM ConnectomA syngo MR D11 \\USER\INVESTIGATORS\Default\AAHScout_64 TA:0:14 PAT:3 Voxel size:1.6 1.6 1.6 mm Rel. SNR:1.00 :fl
Second look ultrasound examination for breast lesions: MRI and pathologic correlation
 Second look ultrasound examination for breast lesions: MRI and pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-0559 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Serrano Tamayo, E. López Soriano, M. Muñoz
Second look ultrasound examination for breast lesions: MRI and pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-0559 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Serrano Tamayo, E. López Soriano, M. Muñoz
MRI Physics for Radiologists
 Alfred L. Horowitz MRI Physics for Radiologists A Visual Approach Second Edition With 94 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Alfred
Alfred L. Horowitz MRI Physics for Radiologists A Visual Approach Second Edition With 94 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Alfred
Respiratory dynamic MRI for determining aortic invasion of thoracic neoplasms
 Respiratory dynamic MRI for determining aortic invasion of thoracic neoplasms Poster No.: C-0760 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. J. Hong, J. Hur, H.-J. Lee, Y. J. Kim, B. W. Choi;
Respiratory dynamic MRI for determining aortic invasion of thoracic neoplasms Poster No.: C-0760 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. J. Hong, J. Hur, H.-J. Lee, Y. J. Kim, B. W. Choi;
Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica. E. Pagani, M. Filippi
 Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica E. Pagani, M. Filippi DW-MRI DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED MRI Principles Diffusion results from a microspic random motion known as Brownian motion THE RANDOM WALK How
Diffusione e perfusione in risonanza magnetica E. Pagani, M. Filippi DW-MRI DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED MRI Principles Diffusion results from a microspic random motion known as Brownian motion THE RANDOM WALK How
What s new in Trendsetting Applications?
 What s new in Trendsetting Applications? Leading. With MAGNETOM. Answers for life. What s new in trendsetting applications? Growth with Body MRI FREEZEit 2 Quiet Suite Advanced WARP 1,3 DotGO 1 MyoMaps
What s new in Trendsetting Applications? Leading. With MAGNETOM. Answers for life. What s new in trendsetting applications? Growth with Body MRI FREEZEit 2 Quiet Suite Advanced WARP 1,3 DotGO 1 MyoMaps
MRI DATA PROCESSING. Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira. Introduction
 MRI DATA PROCESSING Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a clinical exam that is safe to the patient. Nevertheless, it s very important to attend
MRI DATA PROCESSING Compiled by: Nicolas F. Lori and Carlos Ferreira Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a clinical exam that is safe to the patient. Nevertheless, it s very important to attend
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging of the Liver at 3.0 Tesla Using Tracking Only Navigator Echo (TRON): a Feasibility Study
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:1027 1033 (2009) Original Research Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging of the Liver at 3.0 Tesla Using Tracking Only Navigator Echo (TRON): a Feasibility Study Marko
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:1027 1033 (2009) Original Research Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging of the Liver at 3.0 Tesla Using Tracking Only Navigator Echo (TRON): a Feasibility Study Marko
ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 63. 41 ~ 49, 2000 ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS ERIKO SHIBAHARA 1, HIROSHI FUKATSU
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 63. 41 ~ 49, 2000 ORIGINAL PAPER WATER FAT SEPARATION USING THE SINGLE ACQUISITION SANDWICH TYPE 3-POINT DIXON METHOD TO OPTIMIZE KNEE JOINT SCANS ERIKO SHIBAHARA 1, HIROSHI FUKATSU
Spectral Adiabatic Inversion Recovery (SPAIR) MR imaging of the Abdomen
 Spectral Adiabatic Inversion Recovery (SPAIR) MR imaging of the Abdomen Thomas C. Lauenstein Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology, University Hospital Essen, Germany
Spectral Adiabatic Inversion Recovery (SPAIR) MR imaging of the Abdomen Thomas C. Lauenstein Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology, University Hospital Essen, Germany
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698
 SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
SITE IMAGING MANUAL ACRIN 6698 Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Biomarkers for Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: A sub-study of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL Version: 1.0 Date: May 28, 2012
GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT
 GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT Formal requirements and procedures OVERVIEW This document is intended to help a principle investigator set up a research project using magnetic resonance imaging
GUIDE TO SETTING UP AN MRI RESEARCH PROJECT Formal requirements and procedures OVERVIEW This document is intended to help a principle investigator set up a research project using magnetic resonance imaging
Technical Note. Frank J. Rybicki, Robert V. Mulkern, Richard L. Robertson, Caroline D. Robson, Taylor Chung, and Jingfei Ma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :798 80, October 00 Technical Note Fast Three-Point Dixon MR Imaging of the Retrobulbar Space with Low-Resolution Images for Phase Correction: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo Inversion
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :798 80, October 00 Technical Note Fast Three-Point Dixon MR Imaging of the Retrobulbar Space with Low-Resolution Images for Phase Correction: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo Inversion
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA
 MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Human Cervical Spinal Cord at 3 Tesla
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:21 27 (2002) Original Research In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Human Cervical Spinal Cord at 3 Tesla Jeffrey R. Korzan, BSc, 1 Monica Gorassini, PhD,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:21 27 (2002) Original Research In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Human Cervical Spinal Cord at 3 Tesla Jeffrey R. Korzan, BSc, 1 Monica Gorassini, PhD,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 PRIMARY CERTIFICATION DIDACTIC AND CLINICAL COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS EFFECTIVE JANUARY 2014 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet
PRIMARY CERTIFICATION DIDACTIC AND CLINICAL COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS EFFECTIVE JANUARY 2014 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet
THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY
 THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY The Widest Wide Bore in the Industry 74cm Oval Bore Provides a comfortable and spacious environment around the patient WIT Monitor Allows technologist to review and
THE WIDEST WIDE-BORE IN THE INDUSTRY The Widest Wide Bore in the Industry 74cm Oval Bore Provides a comfortable and spacious environment around the patient WIT Monitor Allows technologist to review and
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
Artifacts caused by transcranial magnetic stimulation coils and EEG electrodes in T 2 *-weighted echo-planar imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 18 (2000) 479 484 Technical Note Artifacts caused by transcranial magnetic stimulation coils and EEG electrodes in T 2 *-weighted echo-planar imaging J. Baudewig a,b, W. Paulus
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 18 (2000) 479 484 Technical Note Artifacts caused by transcranial magnetic stimulation coils and EEG electrodes in T 2 *-weighted echo-planar imaging J. Baudewig a,b, W. Paulus
3T MRI in evaluation of asbestos-related thoracic diseases preliminary results
 92 research article 3T MRI in evaluation of asbestos-related thoracic diseases preliminary results Janez Podobnik 1, Igor Kocijancic 1, Viljem Kovac 2, Igor Sersa 3 1 Institute of Radiology, University
92 research article 3T MRI in evaluation of asbestos-related thoracic diseases preliminary results Janez Podobnik 1, Igor Kocijancic 1, Viljem Kovac 2, Igor Sersa 3 1 Institute of Radiology, University
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 31 (2013) 1439 1444 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Magnetic Resonance Imaging journal homepage: www.mrijournal.com Technical notes Evaluation of MRI issues for an
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 31 (2013) 1439 1444 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Magnetic Resonance Imaging journal homepage: www.mrijournal.com Technical notes Evaluation of MRI issues for an
Technique and Safety of. by Pierluigi Castellone, Electronics Engineer Brain Products General Manager
 Technique and Safety of performing EEG/fMRI measurements by Pierluigi Castellone, Electronics Engineer Brain Products General Manager Contents of the presentation Why recording simultaneous EEG and fmri?
Technique and Safety of performing EEG/fMRI measurements by Pierluigi Castellone, Electronics Engineer Brain Products General Manager Contents of the presentation Why recording simultaneous EEG and fmri?
The MRI Study Guide for Technologists
 The MRI Study Guide for Technologists Kenneth S. Meacham The MRI Study Guide for Technologists With 51 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest
The MRI Study Guide for Technologists Kenneth S. Meacham The MRI Study Guide for Technologists With 51 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest
MRI Department Goals. Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam. Lecture Topics
 Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam lowens2@clarian.org Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
Effective Ways to Improve Patient Cooperation and Safety in MRI Exam lowens2@clarian.org Lecture Topics MRI patient preparation Department MRI Safety Policies and Procedures MRI patient safety screening
runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging SECOND EDITION Scott A. HuetteS Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Allen W. Song Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Gregory McCarthy
runl I IUI%I/\L Magnetic Resonance Imaging SECOND EDITION Scott A. HuetteS Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Allen W. Song Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University Gregory McCarthy
NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
How To Grow With An Mri
 Growth with Body MRI Body MRI H.-Hartziekenhuis Lier 40 oz/d tussen 8 en 21 uur 3-5 body mri/d Aparte protocols voor leverletsels / pancreas, mrcp rectum, ovarium, cervix / uterus, pelvimetrie anus / fistula
Growth with Body MRI Body MRI H.-Hartziekenhuis Lier 40 oz/d tussen 8 en 21 uur 3-5 body mri/d Aparte protocols voor leverletsels / pancreas, mrcp rectum, ovarium, cervix / uterus, pelvimetrie anus / fistula
CMS Manual System Pub. 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations
 CMS Manual System Pub. 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 21 Date: September 10, 2004
CMS Manual System Pub. 100-03 Medicare National Coverage Determinations Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Transmittal 21 Date: September 10, 2004
PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience
 20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
Configuration and Use of the MR Knee Dot Engine
 Configuration and Use of the MR Knee Dot Engine Kai Reiter (RT); Sebastian Auer (RT) Radiology Herne, Herne, Germany 1 42 MAGNETOM Flash 3/2011 www.siemens.com/magnetom-world We are a radiological joint
Configuration and Use of the MR Knee Dot Engine Kai Reiter (RT); Sebastian Auer (RT) Radiology Herne, Herne, Germany 1 42 MAGNETOM Flash 3/2011 www.siemens.com/magnetom-world We are a radiological joint
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
Wireless Radio Frequency Coil for Magnetic Resonance Image of Knee Joint
 Wireless Radio Frequency Coil for Magnetic Resonance Image of Knee Joint Tomohiro Sahara, Hiroshi Tsutsui, Shigehiro Hashimoto, Shuichi Mochizuki, Kenichi Yamasaki, Hideo Kondo, Teruo Miyazaki Department
Wireless Radio Frequency Coil for Magnetic Resonance Image of Knee Joint Tomohiro Sahara, Hiroshi Tsutsui, Shigehiro Hashimoto, Shuichi Mochizuki, Kenichi Yamasaki, Hideo Kondo, Teruo Miyazaki Department
Contents I MEDICAL RADIOLOGY. Diagnostic Imaging. Editors: A. L. Baert, Leuven M. Knauth, Göttingen K. Sartor, Heidelberg
 Contents I MEDICAL RADIOLOGY Diagnostic Imaging Editors: A. L. Baert, Leuven M. Knauth, Göttingen K. Sartor, Heidelberg Contents III S. O. Schoenberg O. Dietrich M. F. Reiser (Eds.) Parallel Imaging in
Contents I MEDICAL RADIOLOGY Diagnostic Imaging Editors: A. L. Baert, Leuven M. Knauth, Göttingen K. Sartor, Heidelberg Contents III S. O. Schoenberg O. Dietrich M. F. Reiser (Eds.) Parallel Imaging in
Principles of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 Principles of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Martin A. Lindquist Department of Biostatistics; Johns Hopkins University Tor D. Wager Department of Psychology & Neuroscience; University of Colorado
1 Principles of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Martin A. Lindquist Department of Biostatistics; Johns Hopkins University Tor D. Wager Department of Psychology & Neuroscience; University of Colorado
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Difficulties of T1 brain MRI segmentation techniques M S. Atkins *a, K. Siu a, B. Law a, J. Orchard a, W. Rosenbaum a a School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University ABSTRACT This paper looks at
Difficulties of T1 brain MRI segmentation techniques M S. Atkins *a, K. Siu a, B. Law a, J. Orchard a, W. Rosenbaum a a School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University ABSTRACT This paper looks at
Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance
 Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Contents: Jorge Jovicich jovicich@mit.edu I) Historical Background II) An MR experiment - Overview - Can we scan the subject? - The subject goes into the magnet -
Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Contents: Jorge Jovicich jovicich@mit.edu I) Historical Background II) An MR experiment - Overview - Can we scan the subject? - The subject goes into the magnet -
7/16/2010. Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI. Objectives. ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010
 Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
Pulse Sequences and Acquisition Techniques for Breast MRI ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program Launched May 2010 Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN 37232 Information available:
REVEAL LINQ LNQ11. Insertable Cardiac Monitor MRI procedural information. MRI Technical Manual
 REVEAL LINQ LNQ11 Insertable Cardiac Monitor MRI procedural information MRI Technical Manual Caution: Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. The following list
REVEAL LINQ LNQ11 Insertable Cardiac Monitor MRI procedural information MRI Technical Manual Caution: Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. The following list
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Level 1
 MIAP1 Revised July 2015 MEDICAL IMAGING ADVISORY PANEL 1 Course Syllabus Magnetic Resonance Imaging Level 1 Page 1 of 13 MIAP1 MRI Course Syllabus Guide Under Revision 07 July 2015 Please refer to Medical
MIAP1 Revised July 2015 MEDICAL IMAGING ADVISORY PANEL 1 Course Syllabus Magnetic Resonance Imaging Level 1 Page 1 of 13 MIAP1 MRI Course Syllabus Guide Under Revision 07 July 2015 Please refer to Medical
Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications)
 Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications) Excelart Vantage Magnet Configuration: Ultra-short-bore Strength (or W x H): 1.5 T Homogeneity, ppm V-RMS: Dimensions of maximum
Toshiba Excelart Vantage 1.5T MRI Tech Specs (Technical Specifications) Excelart Vantage Magnet Configuration: Ultra-short-bore Strength (or W x H): 1.5 T Homogeneity, ppm V-RMS: Dimensions of maximum
Subcutaneous desmoid tumors: characteristic "sun-burst" appearance on MRI and ultrasound
 Subcutaneous desmoid tumors: characteristic "sun-burst" appearance on MRI and ultrasound Poster No.: C-2241 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Milos, T. Moritz, M. Bernathova,
Subcutaneous desmoid tumors: characteristic "sun-burst" appearance on MRI and ultrasound Poster No.: C-2241 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Milos, T. Moritz, M. Bernathova,
Neuroimaging module I: Modern neuroimaging methods of investigation of the human brain in health and disease
 1 Neuroimaging module I: Modern neuroimaging methods of investigation of the human brain in health and disease The following contains a summary of the content of the neuroimaging module I on the postgraduate
1 Neuroimaging module I: Modern neuroimaging methods of investigation of the human brain in health and disease The following contains a summary of the content of the neuroimaging module I on the postgraduate
Kap 8 Image quality, signal, contrast and noise
 4/5/ FYS-KJM 474 contrast SNR MR-teori og medisinsk diagnostikk Kap 8 Image qualit, signal, contrast and noise resolution vailable MRparameters speed Main source of noise in MRI: Noise generated within
4/5/ FYS-KJM 474 contrast SNR MR-teori og medisinsk diagnostikk Kap 8 Image qualit, signal, contrast and noise resolution vailable MRparameters speed Main source of noise in MRI: Noise generated within
MEDIMAGE A Multimedia Database Management System for Alzheimer s Disease Patients
 MEDIMAGE A Multimedia Database Management System for Alzheimer s Disease Patients Peter L. Stanchev 1, Farshad Fotouhi 2 1 Kettering University, Flint, Michigan, 48504 USA pstanche@kettering.edu http://www.kettering.edu/~pstanche
MEDIMAGE A Multimedia Database Management System for Alzheimer s Disease Patients Peter L. Stanchev 1, Farshad Fotouhi 2 1 Kettering University, Flint, Michigan, 48504 USA pstanche@kettering.edu http://www.kettering.edu/~pstanche
RE: Invitation for Bid (IFB) No. Q14-32 Type of Service: Magnetic Resonance Imaging System, Maintenance Agreement and Mobile MRI Unit. Addendum No.
 VIA EMAIL DATE: June 16, 2014 TO: FROM: Prospective Proposers Maureen Crystal Director of Contracts RE: Invitation for Bid (IFB) No. Q14-32 Type of Service: Magnetic Resonance Imaging System, Maintenance
VIA EMAIL DATE: June 16, 2014 TO: FROM: Prospective Proposers Maureen Crystal Director of Contracts RE: Invitation for Bid (IFB) No. Q14-32 Type of Service: Magnetic Resonance Imaging System, Maintenance
High Field MRI: Technology, Applications, Safety, and Limitations. Brief overview of high-field MRI. The promise of high-field MRI
 High Field MRI: Technology, Applications, Safety, and Limitations R. Jason Stafford, Ph.D. Department of Imaging Physics The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Brief overview
High Field MRI: Technology, Applications, Safety, and Limitations R. Jason Stafford, Ph.D. Department of Imaging Physics The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Brief overview
510(k) Summary. This summary of 510(k) safety and effectiveness is being submitted in accordance with the requirements of 21 CFR 807.
 MAR, 2009 / \MLECH MRI-TECH Sp. z o.o., ul. Zielihska 3, 31-227 Krak6w, Poland MRI-TECH Canada, Inc. 206-3820 Cambie Street Vancouver BC V5Z 2X7 510(k) Summary This summary of 510(k) safety and effectiveness
MAR, 2009 / \MLECH MRI-TECH Sp. z o.o., ul. Zielihska 3, 31-227 Krak6w, Poland MRI-TECH Canada, Inc. 206-3820 Cambie Street Vancouver BC V5Z 2X7 510(k) Summary This summary of 510(k) safety and effectiveness
Embedded Systems in Healthcare. Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008
 Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Embedded Systems in Healthcare Pierre America Healthcare Systems Architecture Philips Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands November 12, 2008 About the Speaker Working for Philips Research since 1982 Projects
Shorter Scanning Times Through Efficient Software. Annette Tuffs. Article from the customer magazine Medical Solutions, December 2010
 Shorter Scanning Times Through Efficient Software Annette Tuffs Article from the customer magazine Medical Solutions, December 2010 www.siemens.com/healthcare-magazine Highlight Topic Efficiency: MRI A
Shorter Scanning Times Through Efficient Software Annette Tuffs Article from the customer magazine Medical Solutions, December 2010 www.siemens.com/healthcare-magazine Highlight Topic Efficiency: MRI A
FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety
 FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety Loren A. Zaremba, Ph.D. Center for Devices and Radiological Health Food and Drug Administration Outline I. Introduction II. Static Magnetic Field
FDA Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Equipment Safety Loren A. Zaremba, Ph.D. Center for Devices and Radiological Health Food and Drug Administration Outline I. Introduction II. Static Magnetic Field
Measure #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
Measure #195 (NQF 0507): Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
RF Coils... They ve Come a Long, Long Way
 GE Healthcare MR Field Notes The sensitivity area relates to the diameter of the coil. By Increasing coil size, the area of sensitivity also increases. But as with most MR princicloser a coil s position
GE Healthcare MR Field Notes The sensitivity area relates to the diameter of the coil. By Increasing coil size, the area of sensitivity also increases. But as with most MR princicloser a coil s position
Prepublication Requirements
 Issued Prepublication Requirements The Joint Commission has approved the following revisions for prepublication. While revised requirements are published in the semiannual updates to the print manuals
Issued Prepublication Requirements The Joint Commission has approved the following revisions for prepublication. While revised requirements are published in the semiannual updates to the print manuals
www.siemens.com/skyra Image Gallery MAGNETOM Skyra Answers for life.
 www.siemens.com/skyra Image Gallery MAGNETOM Skyra Answers for life. Clinical excellence, consistently. With Tim+Dot. Tim 4G (Total imaging matrix) Technology Dot (Day optimizing throughput) Engine Tim
www.siemens.com/skyra Image Gallery MAGNETOM Skyra Answers for life. Clinical excellence, consistently. With Tim+Dot. Tim 4G (Total imaging matrix) Technology Dot (Day optimizing throughput) Engine Tim
R/F. Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening. 3. Utility of Chest Tomosynthesis. 1.
 R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
