Volcanic evolution of the island of Tenerife (Canary Islands) in the light of new K-Ar data
|
|
|
- Bethany Price
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Volcanology and Geotherrnal Research, 44 (1990) Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam Volcanic evolution of the island of Tenerife (Canary Islands) in the light of new K-Ar data Eumenio Ancocheaa, José María Fustera, Elisa lbarrolab, Antonio Cendreroc, Juan coellod, Francisco ~ ernan~, Jean M. Cantagrele and Colette Jamonde udepartarnento de Petrología y Geoquírnica, Facultad de Ciencias Geológicas, Universidad Cornplutense, Ciudad Universitaria, Madrid, Spain b ~. ~ de. Petrología, ~. Instituto de Geología Económica, CSIC-Universidad Cornplutense, Facultad de Ciencias Geológicas, Ciudad Universitaria, Madrid, Spain QCITTYM (División de Ciencias de la Tierra), Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Cantabria, Av.Los Castros s/n, Santander, Spain d~epartarnento de Edafología y Geología, Universidad de La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain edeparternent ide Gkologie CNRS, L.A.10 Université Clerrnont-II, 5, rue Kessler, Clerrnont-Ferrand, France (Received June 21, 1989; revised and accepted May 3, 1990) ABSTRACT Ancochea, E., Fuster J.M., Ibarrola, E., Cendrero, A., Coello, J., Hernan, F., Cantagrel, J.M. and Jamond, C., Volcanic evolution of the island of Tenerife (Canary Island) in the light of new K-Ar data. J. Volcanol. Geotherrn. Res., 44: New age determinations from Tenerife, together with those previously published (93 in all), provide a fairly comprehensive picture of the volcanic evolution of the island. The oldest volcanic series, with ages starting in the late Miocene, are formed mainly by basalts with some trachytes and phonolites which appear in Anaga, Teno and Roque del Conde massifs. In Anaga (NE), three volcanic cycles occurred: one older than 6.5 Ma, a second one between 6.5 and 4.5 Ma, with a possible gap between 5.4 and 4.8 Ma. and a late cycle around 3.6 Ma. In Teno (NW), after some undated units. the activity took place between 6.7 and 4.5 Ma, with two main series separated by a possible pause between 6.2 and 5.6 Ma. In the zone of Roque del Conde (S), the ages are scattered between 11.6 and 3.5 Ma. Between 3.3 and 1.9 Ma, the whole island underwent a period of volcanic quiescence and erosion. The large Caaadas volcano, made up of basalts, trachytes and phonolites, was built essentiaiiy between 1.9 and 0.2 Ma. To the NE of this'central volcano, linking it with Anaga, is a chain of basaltic emission centers, with a peak of activity around 0.8 Ma. The Cañadas Caldera had several collapse phases, associated with large ignimbrite emissions. There were, at least, an older phase more than 1 Ma old, on the western part of the volcano, and a younger one, less than 0.6 Ma old, in the eastern side. The two large "valleys" of Guimar and la Orotava were formed by large landslides less than 0.8 Ma ago, and probably before 0.6 Ma ago. The present Cañadas caldera was formed by another landslide, less than 0.2 Ma ago. This caldera was later filled by the huge Teide volcano, which has been active even in historic times. During the same period a series of small volcanoes erupted at scattered locations throughout the island. The average eruptive rate in Tenerife was 0.3 km3/ka, with relatively small variations for the different eruptive periods. This island and La Gomera represent a model of growth by discontinuous pulses of volcanic activity, separated by gaps often coinciding with episodes of destruction of the edifices and sometimes extended for several million years. The neighbouring Gran Canaria, on the other hand, had an initial, rapid "shield-building phase" during which more than 90% of the island was built, and a series of smaiier pulses at a much later period. A comparison between these three central islands indicates that the previously postulated westward displacement in time of a gap in the volcanic activity is valid only as a first approximation. Several gaps are present on each island, overlapping in time and not clearly supporting either of the models proposed to explain the evolution of the Canaries.
2 232 E. ANCOCHEA ET AL. General geological features of Tenerife Tenerife is the largest (2058 km2)and highest (3718 m) island of the Canaries. It occupies a central position in the Archipelago and is one of the most complex from the volcanological point of view. The oldest visible unit on the island is the "Old Basaltic Series", forrned of basaltic lavas and pyroclastics, with some salic differentiates, typically occurring as dykes and domes emplaced at the terminal part of the basaltic emissions. This "series" forms three deeply eroded edifices, not visibly connected, in the NE (Anaga), NW (Teno) and S of the island (Fig. 1). The younger volcanic sequences formed at the centralcomposite volcano of Las Cañadas, with basaltic, trachybasaltic, trachytic and phonolitic materials, and along a SW-NE ridge linking Las Cañadas and Anaga, the Cordillera Dorsal, with predomi- Fig. l. Simplified geological map of Tenerife. 1 = Recent Series; 2 = "Caiiadas" Series; 3 = "Dorsal" Series; 4 = Old Basaltic Series; 5 = Caldera rim; 6 = Main trend of the "Dorsal" and scarps of Güimar and La Orotava; 7 = Dated dykes. Age in Ma: ovals, this work; squares, previous data. AR = Arico; AT = Arco de Taganana; BT = Barranco de Tamadaya; DH = Caiiada de Diego Hernández; F = La Fortaleza; G = Guaza; IC = Icod; LS = Lomo Simón; MA = Masca; RV = Roque Vento; SA = El Sauzal, TE = Tejina; TI = Tigaiga.
3 VOLCANIC EVOLUTION OF TENERIFE ISLAND. CANARY ISLANDS nantly basaltic emissions. The upper part of the Cañadas volcano was destroyed, forming a large caldera filled by the later emissions of the Teide-Pico Viejo complex. On each side of the "Dorsal" large depressions occur, the "valleys" of Güimar and La Orotava. The most recent volcanic activity is represented, on the one hand, by many, mostly basaltic, volcanoes scattered throughout the island and, on the other hand, by the central Teide-Pico Viejo edifice, with basaltic and salic emissions. The general character of the magmatic cycles which have been identified, is alkaline to highly alkaline, with an increase in alkalinity from the older to the recent series (Ibarrola, 1969, 1970; Ridley, 1970a; Brandle, 1973). More details about the geology, volcanology, petrology and geochemistry of Tenerife can be found in Jeremine (1933), Hausen (1956), Fúster et al. (1968, 1980), Ibarrola (1969, 1970), Ridley (1970 a, b, c), Arafia (1 97 l), Brandle (1 973), Hernández-Pacheco and Ibarrola (1973), Booth (1973), Coello (1973), Borley (1974), Carracedo (1975, 1979), Wolff (1985). Description and K-Ar chronology of the volcanic series This paper: is based on 48 new K-Ar determinations, which together with the 45 previously published by Abdel-Monem et al. (1 972), Carracedo (1975, 1979) and Féraud (1981), provide a new and more precise geochronological frarnework for the understanding of the volcanic evolution of the island. The analytical methods (with replicate analyses that confirm their accuracy) have been described elsewhere (Cantagrel et al., 1984). Most K-Ar analyses were performed on wholerock samples, but olivine and clinopyroxene were removed from seven samples. Five analyses were for feldspar crystal separates. The analytical results are presented in Table 1. The location and a brief description of the samples are given in the Appendix. Old Basaltic Series This unit was already mentioned by Fritsch and Reiss (1868) as well as by Hausen (1956) and Bravo (1962). According to Hausen (1956) the ''basaltic tableland series" included al1 the basaltic rocks in Anaga, Teno, Roque del Conde, Cordillera Dorsal, scarps of Güimar and La Orotava and the bottom of some deep valleys in the northern and southern parts of the island. Fúster et al. (1968) pointed out the existence of two Old Basaltic Series, 1 and 11, although they failed to show their distribution in their map. The first K-Ar data, obtained by Abdel Monem et al. (1972), established clearly the large age difference which separates the Anaga and Teno rocks from the ones in Güimar and Tigaiga. The stratigraphic succession proposed by Coello (1973) includes in the Old Basaltic Series 1 the massifs of Anaga, Teno and Roque del Conde, as well as the bottom of severa1 deep "barrancos". The rest of the "Old Basaltic Series" is considered to form a Series 11. This distinction has remained essentially unchanged; however, the new data allow to introduce greater precission in the stratigraphy and interpretation of the different edifices. Anaga This massif is formed mainly by a complex sequence of alkali basaltic lava flows, with abundant volcanoclastic layers, intruded by subvolcanic bodies (dykes, domes, laccoliths) of basalts, trachybasalts, trachytes and phonolites. The series dips roughly seawards on al1 sides, except in the north, and has a total thickness of about 1000 m. Dueto the existing structure the oldest unit (Lower Series 1) appears in the north, in a large arcuate landform called "Arco de Taganana". This unit is formed. by volcanoclastic rocks, some debris-flow deposits and small intrusive bodies (gabbros, syenites) cut by dykes. Abdel Monem et al. (1972)
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
The felsic dikes of La Gomera (Canary Islands): identi cation of cone sheet and radial dike swarms
 Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 120 (2003) 197^206 The felsic dikes of La Gomera (Canary Islands): identi cation of cone sheet and radial dike swarms E. Ancochea a;, J.L. Bra«ndle a, M.J.
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 120 (2003) 197^206 The felsic dikes of La Gomera (Canary Islands): identi cation of cone sheet and radial dike swarms E. Ancochea a;, J.L. Bra«ndle a, M.J.
VOLCANIC EDIFICES AND MORPHOLOGIES OF THE CANARY ISLANDS
 C H A P T E R14 VOLCANIC EDIFICES AND MORPHOLOGIES OF THE CANARY ISLANDS Roques de García: The Roque Chinchado. Teide s Peak in the background. The Canary Islands, located in the NE sector of the Central
C H A P T E R14 VOLCANIC EDIFICES AND MORPHOLOGIES OF THE CANARY ISLANDS Roques de García: The Roque Chinchado. Teide s Peak in the background. The Canary Islands, located in the NE sector of the Central
How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form?
 298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
Earth Materials: Intro to rocks & Igneous rocks. The three major categories of rocks Fig 3.1 Understanding Earth
 Earth Materials: 1 The three major categories of rocks Fig 3.1 Understanding Earth 2 Intro to rocks & Igneous rocks Three main categories of rocks: Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic The most common minerals
Earth Materials: 1 The three major categories of rocks Fig 3.1 Understanding Earth 2 Intro to rocks & Igneous rocks Three main categories of rocks: Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic The most common minerals
A história geológica de FERNANDO DE NORONHA. Umberto G. Cordani Instituto de Geociências - USP
 A história geológica de FERNANDO DE NORONHA Umberto G. Cordani Instituto de Geociências - USP 1960 s - CONTINENTAL DRIFT and PLATE TECTONICS 1960 - Cox & Doell Earth s magnetic reversals 1961 - Hess History
A história geológica de FERNANDO DE NORONHA Umberto G. Cordani Instituto de Geociências - USP 1960 s - CONTINENTAL DRIFT and PLATE TECTONICS 1960 - Cox & Doell Earth s magnetic reversals 1961 - Hess History
CATACLYSMIC ERUPTIONS
 CATACLYSMIC ERUPTIONS The really big ones! This figure compares the size of some recent, well-known eruptions. Note how small the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and even Vesuvius are compared to Katmai,
CATACLYSMIC ERUPTIONS The really big ones! This figure compares the size of some recent, well-known eruptions. Note how small the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and even Vesuvius are compared to Katmai,
BOWEN'S REACTION SERIES
 BOWEN'S REACTION SERIES Purpose John J. Thomas Frequently, people cannot visualize the mineral associations that form the sequences of igneous rocks that you find in the earth's crust and what happens
BOWEN'S REACTION SERIES Purpose John J. Thomas Frequently, people cannot visualize the mineral associations that form the sequences of igneous rocks that you find in the earth's crust and what happens
Dust accumulation and loess formation under the oceanic semiarid climate of Tenerife, Canary Islands
 Hungarian Geographical Bulletin 59 (2) (2010) pp. 207 230. Dust accumulation and loess formation under the oceanic semiarid climate of Tenerife, Canary Islands Abstract Éva Kis and Ferenc Schweitzer 1
Hungarian Geographical Bulletin 59 (2) (2010) pp. 207 230. Dust accumulation and loess formation under the oceanic semiarid climate of Tenerife, Canary Islands Abstract Éva Kis and Ferenc Schweitzer 1
6.E.2.2 Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Volcanic Deposits, Landscape and Geoarchaeology of Santorini, Greece 2015 Liverpool Geological Society
 Volcanic Deposits, Landscape and Geoarchaeology of Santorini, Greece 2015 Liverpool Geological Society General Information: Dates: Monday 15 th June to Saturday 20 th June 2015 Flights: from Manchester
Volcanic Deposits, Landscape and Geoarchaeology of Santorini, Greece 2015 Liverpool Geological Society General Information: Dates: Monday 15 th June to Saturday 20 th June 2015 Flights: from Manchester
89.215 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS
 NAME 89.215 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in
NAME 89.215 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in
Igneous Rocks. Geology 200 Geology for Environmental Scientists
 Igneous Rocks Geology 200 Geology for Environmental Scientists Magma Compositions Ultramafic - composition of mantle Mafic - composition of basalt, e.g. oceanic crust. 900-1200 o C, 50% SiO 2 Intermediate
Igneous Rocks Geology 200 Geology for Environmental Scientists Magma Compositions Ultramafic - composition of mantle Mafic - composition of basalt, e.g. oceanic crust. 900-1200 o C, 50% SiO 2 Intermediate
Stratigraphic Cross Sections Why study old rocks?
 rom IRIS collection: Animations of eologic Processes www.iris.edu/educate/animations Stratigraphic ross Sections Why study old rocks? The earthquake potential of an area can be determined by studying the
rom IRIS collection: Animations of eologic Processes www.iris.edu/educate/animations Stratigraphic ross Sections Why study old rocks? The earthquake potential of an area can be determined by studying the
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS
 CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
It s always summer in the Canary Islands!
 Discovering Spain - Sports & Nature beach holiday - Canary Islands - Gran Canaria - La Gomera - Parador Cruz de Tejada - Parador El Hierro - Parador La Gomera Parador La Palma - Parador Las Cañadas del
Discovering Spain - Sports & Nature beach holiday - Canary Islands - Gran Canaria - La Gomera - Parador Cruz de Tejada - Parador El Hierro - Parador La Gomera Parador La Palma - Parador Las Cañadas del
REDUCTION OF THE ECONOMIC-FINANCIAL EXPOSURE OF THE STATE AND PROTECTION OF HUMAN LIVES
 REDUCTION OF THE ECONOMIC-FINANCIAL EXPOSURE OF THE STATE AND PROTECTION OF HUMAN LIVES Models for the prevention and mitigation of damages to people and properties through an insurance coverage PRESENTATION
REDUCTION OF THE ECONOMIC-FINANCIAL EXPOSURE OF THE STATE AND PROTECTION OF HUMAN LIVES Models for the prevention and mitigation of damages to people and properties through an insurance coverage PRESENTATION
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics
 Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
Geologic History Review
 1. The climate that existed in an area during the early Paleozoic Era can best be determined by studying (1) the present climate of the area (2) recorded climate data of the area since 1700 (3) present
1. The climate that existed in an area during the early Paleozoic Era can best be determined by studying (1) the present climate of the area (2) recorded climate data of the area since 1700 (3) present
Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) Dating
 Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) Dating K-Ar Dating In 10,000 K atoms: 9326 39 K 673 41 K 1 40 K Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Argon About 1% of atmosphere is argon Three stable isotopes of argon
Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) Dating K-Ar Dating In 10,000 K atoms: 9326 39 K 673 41 K 1 40 K Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Argon About 1% of atmosphere is argon Three stable isotopes of argon
USING RELATIVE DATING AND UNCONFORMITIES TO DETERMINE SEQUENCES OF EVENTS
 EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY- EES 1005 LABORATORY THREE USING RELATIVE DATING AND UNCONFORMITIES TO DETERMINE SEQUENCES OF EVENTS Introduction In order to interpret Earth history from
EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY- EES 1005 LABORATORY THREE USING RELATIVE DATING AND UNCONFORMITIES TO DETERMINE SEQUENCES OF EVENTS Introduction In order to interpret Earth history from
PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise)
 PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise) Introduction: As discussed in our textbook, the speed at which tectonic plates move has been calculated in several
PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise) Introduction: As discussed in our textbook, the speed at which tectonic plates move has been calculated in several
MAJOR LANDFORMS IN VOLCANIC REGIONS
 MAJOR LANDFORMS IN VOLCANIC REGIONS Volcanism is not randomly distributed over the world. It is concentrated near plate boundaries where plate subduction or seafloor spreading takes place. Other occurrences
MAJOR LANDFORMS IN VOLCANIC REGIONS Volcanism is not randomly distributed over the world. It is concentrated near plate boundaries where plate subduction or seafloor spreading takes place. Other occurrences
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Continental Drift. Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on:
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on: Similarities in shorelines
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on: Similarities in shorelines
Agreement on Cooperation in Astrophysics
 Agreement on Cooperation in Astrophysics The Government of the Kingdom of Spain, the Government of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and
Agreement on Cooperation in Astrophysics The Government of the Kingdom of Spain, the Government of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and
Earth Science Landforms, Weathering, and Erosion Reading Comprehension. Landforms, Weathering, and Erosion
 Reading Comprehension Name 1 How many people have been to the Rocky Mountains or the Grand Canyon? When people go to visit these natural wonders, they may not realize that it took millions of years for
Reading Comprehension Name 1 How many people have been to the Rocky Mountains or the Grand Canyon? When people go to visit these natural wonders, they may not realize that it took millions of years for
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 1, Number 1 23 February 2000 1008, doi:10.1029/1999gc000018 ISSN: 1525-2027 The 40
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 1, Number 1 23 February 2000 1008, doi:10.1029/1999gc000018 ISSN: 1525-2027 The 40
Geologic time and dating. Geologic time refers to the ages relevant to Earth s history
 Geologic time and dating Most figures and tables contained here are from course text: Understanding Earth Fourth Edition by Frank Press, Raymond Siever, John Grotzinger, and Thomas H. Jordan Geologic time
Geologic time and dating Most figures and tables contained here are from course text: Understanding Earth Fourth Edition by Frank Press, Raymond Siever, John Grotzinger, and Thomas H. Jordan Geologic time
QUATERNARY DATING METHODS 1: RELATIVE DATING TECHNIQUES
 QUATERNARY DATING METHODS 1: RELATIVE DATING TECHNIQUES Objectives: In this lab we will examine relative dating methods used to date Quaternary glacial deposits. After this lab you should be able to: 1)
QUATERNARY DATING METHODS 1: RELATIVE DATING TECHNIQUES Objectives: In this lab we will examine relative dating methods used to date Quaternary glacial deposits. After this lab you should be able to: 1)
Transform Boundaries
 Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
INTRODUCTION. This project is about volcanoes and how they form and how they function. It will also show you the different aspects of a volcano.
 BY RYAN O MAHONY INTRODUCTION This project is about volcanoes and how they form and how they function. It will also show you the different aspects of a volcano. MAP OF VOLCANOES AROUND THE WORLD DIAGRAM
BY RYAN O MAHONY INTRODUCTION This project is about volcanoes and how they form and how they function. It will also show you the different aspects of a volcano. MAP OF VOLCANOES AROUND THE WORLD DIAGRAM
Igneous Geochemistry. What is magma? What is polymerization? Average compositions (% by weight) and liquidus temperatures of different magmas
 1 Igneous Geochemistry What is magma phases, compositions, properties Major igneous processes Making magma how and where Major-element variations Classification using a whole-rock analysis Fractional crystallization
1 Igneous Geochemistry What is magma phases, compositions, properties Major igneous processes Making magma how and where Major-element variations Classification using a whole-rock analysis Fractional crystallization
Rocks & Minerals. 10. Which rock type is most likely to be monomineralic? 1) rock salt 3) basalt 2) rhyolite 4) conglomerate
 1. Of the Earth's more than 2,000 identified minerals, only a small number are commonly found in rocks. This fact indicates that most 1) minerals weather before they can be identified 2) minerals have
1. Of the Earth's more than 2,000 identified minerals, only a small number are commonly found in rocks. This fact indicates that most 1) minerals weather before they can be identified 2) minerals have
Anomalously shallow palaeomagnetic inclinations and the question of the age of the Canarian Archipelago
 Geophys. J. nt. (199) 122, 393-0 Anomalously shallow palaeomagnetic inclinations and the question of the age of the Canarian Archipelago J. C. Carracedo and V. Soler Volcanological Station of the Canary
Geophys. J. nt. (199) 122, 393-0 Anomalously shallow palaeomagnetic inclinations and the question of the age of the Canarian Archipelago J. C. Carracedo and V. Soler Volcanological Station of the Canary
A new approach to the monitoring of deformation on Lanzarote (Canary Islands): an 8-year radar perspective
 Bull Volcanol (2003) 65:1 7 DOI 10.1007/s00445-002-0232-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Rosana Romero Daniel Carrasco Vicente Araña José Fernández A new approach to the monitoring of deformation on Lanzarote (Canary
Bull Volcanol (2003) 65:1 7 DOI 10.1007/s00445-002-0232-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Rosana Romero Daniel Carrasco Vicente Araña José Fernández A new approach to the monitoring of deformation on Lanzarote (Canary
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Le rocce erciniche nella Zona brianzonese ligure
 Le rocce erciniche nella Zona brianzonese ligure Matteo Maino Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra e dell Ambiente, Università degli Studi di Pavia Pre-alpine basements of the Ligurian Alps Working group:
Le rocce erciniche nella Zona brianzonese ligure Matteo Maino Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra e dell Ambiente, Università degli Studi di Pavia Pre-alpine basements of the Ligurian Alps Working group:
Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Objectives: explain various ways the earth can be changed by natural forces define the term Geology define the terms Crust, Mantle, Outer Core and Inner Core classify
Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Objectives: explain various ways the earth can be changed by natural forces define the term Geology define the terms Crust, Mantle, Outer Core and Inner Core classify
CONFIRMATION AND CALIBRATION OF COMPUTER MODELING OF TSUNAMIS PRODUCED BY AUGUSTINE VOLCANO, ALASKA
 CONFIRMATION AND CALIBRATION OF COMPUTER MODELING OF TSUNAMIS PRODUCED BY AUGUSTINE VOLCANO, ALASKA James E. Beget Geophysical Institute and Alaska Volcano Observatory University of Alaska, Fairbanks,
CONFIRMATION AND CALIBRATION OF COMPUTER MODELING OF TSUNAMIS PRODUCED BY AUGUSTINE VOLCANO, ALASKA James E. Beget Geophysical Institute and Alaska Volcano Observatory University of Alaska, Fairbanks,
FUERTEVENTURA S URBAN TOURIST DEVELOPMENT: THE SEARCH OF THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT VERSUS TO THE CONSTRUCTIVE MASSIVE GROWTH
 ARTICLES Boletín Fuerteventura s de la Asociación urban tourist de Geógrafos development: Españoles the search N.º 59 of - 2012, the sustainable págs. 391-393 development versus to the constructive I.S.S.N.:
ARTICLES Boletín Fuerteventura s de la Asociación urban tourist de Geógrafos development: Españoles the search N.º 59 of - 2012, the sustainable págs. 391-393 development versus to the constructive I.S.S.N.:
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II
 Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
Plate Tectonics. Hi, I am Zed and I am going to take you on a trip learning about Plate Tectonics. And I am Buddy Zed s mascot
 Plate Tectonics Hi, I am Zed and I am going to take you on a trip learning about Plate Tectonics And I am Buddy Zed s mascot Continental Drift Alfred Wegener proposed that continents were not always where
Plate Tectonics Hi, I am Zed and I am going to take you on a trip learning about Plate Tectonics And I am Buddy Zed s mascot Continental Drift Alfred Wegener proposed that continents were not always where
principles of stratigraphy: deposition, succession, continuity and correlation
 Relative Age Dating Comparative Records of Time Nature of the rock record principles of stratigraphy: deposition, succession, continuity and correlation Stratigraphic tools biological succession of life:
Relative Age Dating Comparative Records of Time Nature of the rock record principles of stratigraphy: deposition, succession, continuity and correlation Stratigraphic tools biological succession of life:
Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
GEOLOGIC MAPS. PURPOSE: To be able to understand, visualize, and analyze geologic maps
 GEOLOGIC MAPS PURPOSE: To be able to understand, visualize, and analyze geologic maps Geologic maps show the distribution of the various igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks at Earth s surface in
GEOLOGIC MAPS PURPOSE: To be able to understand, visualize, and analyze geologic maps Geologic maps show the distribution of the various igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks at Earth s surface in
Magmas and Igneous Rocks
 Page 1 of 14 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Magmas and Igneous Rocks This page last updated on 03-Sep-2015 Magma and Igneous Rocks Igneous Rocks are formed by crystallization
Page 1 of 14 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Magmas and Igneous Rocks This page last updated on 03-Sep-2015 Magma and Igneous Rocks Igneous Rocks are formed by crystallization
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67)
 4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
Hydrogeological characteristics of Deccan trap formations of India
 Hard Rock Hydrosysteins (Proceedings of Rabat Symposium S2, May 1997). IAHS Publ. no. 241, 1997 75 Hydrogeological characteristics of Deccan trap formations of India B. B. S. SINGHAL Department of Earth
Hard Rock Hydrosysteins (Proceedings of Rabat Symposium S2, May 1997). IAHS Publ. no. 241, 1997 75 Hydrogeological characteristics of Deccan trap formations of India B. B. S. SINGHAL Department of Earth
Plate Tectonics. Introduction. Boundaries between crustal plates
 Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide?
 Tectonics Investigation 6: Teacher Guide Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide? In this activity, students will use the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes in a Web GIS to learn about
Tectonics Investigation 6: Teacher Guide Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide? In this activity, students will use the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes in a Web GIS to learn about
What is a rock? How are rocks classified? What does the texture of a rock reveal about how it was formed?
 CHAPTER 4 1 The Rock Cycle SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a rock? How are rocks classified? What does
CHAPTER 4 1 The Rock Cycle SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a rock? How are rocks classified? What does
For personal use only
 ANNOUNCEMENT TO THE AUSTRALIAN SECURITIES EXCHANGE: 18 March 2013 Update on Bunawan and Bahayan Permit Approvals. The Directors of Sierra Mining Limited ( Sierra ) are pleased to update shareholders on
ANNOUNCEMENT TO THE AUSTRALIAN SECURITIES EXCHANGE: 18 March 2013 Update on Bunawan and Bahayan Permit Approvals. The Directors of Sierra Mining Limited ( Sierra ) are pleased to update shareholders on
Global Geoparks in Norway
 Global Geoparks in Norway Global Geoparks are listed in order of acceptance into the Global Geoparks Network Gea Norvegica. 2 Magma.. 4 Disclaimer The Secretariat of UNESCO does not represent or endorse
Global Geoparks in Norway Global Geoparks are listed in order of acceptance into the Global Geoparks Network Gea Norvegica. 2 Magma.. 4 Disclaimer The Secretariat of UNESCO does not represent or endorse
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics. The unifying concept of the Earth sciences.
 Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Does not include complete lecture notes. Continental drift: An idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed his continental drift hypothesis in 1915 Published The Origin
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Does not include complete lecture notes. Continental drift: An idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed his continental drift hypothesis in 1915 Published The Origin
2012. Proceedings of the 11 European Geoparks Conference. AGA Associação Geoparque Arouca, Arouca, 5-6.
 References to this volume It is suggested that either the following alternatives should be used for future bibliographic references to the whole or part this volume: th Sá, A.A., Rocha, D., Paz, A. & Correia,
References to this volume It is suggested that either the following alternatives should be used for future bibliographic references to the whole or part this volume: th Sá, A.A., Rocha, D., Paz, A. & Correia,
Laboratory 6: Topographic Maps
 Name: Laboratory 6: Topographic Maps Part 1: Construct a topographic map of the Egyptian Pyramid of Khafre A topographic map is a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional space. Topographic
Name: Laboratory 6: Topographic Maps Part 1: Construct a topographic map of the Egyptian Pyramid of Khafre A topographic map is a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional space. Topographic
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Giant Quaternary landslides in the evolution of La Palma and El Hierro, Canary Islands
 Ž. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 94 1999 169 190 www.elsevier.comrlocaterjvolgeores Giant Quaternary landslides in the evolution of La Palma and El Hierro, Canary Islands Juan Carlos Carracedo
Ž. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 94 1999 169 190 www.elsevier.comrlocaterjvolgeores Giant Quaternary landslides in the evolution of La Palma and El Hierro, Canary Islands Juan Carlos Carracedo
LABORATORY TWO GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES
 EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY- EES 1005 LABORATORY TWO GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES Introduction Structural geology is the study of the ways in which rocks or sediments are arranged and deformed
EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY- EES 1005 LABORATORY TWO GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES Introduction Structural geology is the study of the ways in which rocks or sediments are arranged and deformed
Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007
 Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007 1. Please fill in the missing labels. 2. Please fill in the missing labels. 3. How many large plates form the outer shell of the earth?
Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007 1. Please fill in the missing labels. 2. Please fill in the missing labels. 3. How many large plates form the outer shell of the earth?
Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. The outer portion of the Earth is made up of about 20 distinct plates (~ 100 km thick), which move relative to each other This motion is what
Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. The outer portion of the Earth is made up of about 20 distinct plates (~ 100 km thick), which move relative to each other This motion is what
Age/sex/race in New York State
 Age/sex/race in New York State Based on Census 2010 Summary File 1 Jan K. Vink Program on Applied Demographics Cornell University July 14, 2011 Program on Applied Demographics Web: http://pad.human.cornell.edu
Age/sex/race in New York State Based on Census 2010 Summary File 1 Jan K. Vink Program on Applied Demographics Cornell University July 14, 2011 Program on Applied Demographics Web: http://pad.human.cornell.edu
Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics. Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930.
 Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930. Science is self correcting. The Scientific Method The history
Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930. Science is self correcting. The Scientific Method The history
The dynamics of magma chamber refilling at
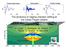 Vertical deformation Seismogram Gravity change The dynamics of magma chamber refilling at the Campi Flegrei caldera A. Longo 1, C. Montagna 1, M. Vassalli 2, P. Papale 1, D. Giudice 1, G. Saccorotti 1
Vertical deformation Seismogram Gravity change The dynamics of magma chamber refilling at the Campi Flegrei caldera A. Longo 1, C. Montagna 1, M. Vassalli 2, P. Papale 1, D. Giudice 1, G. Saccorotti 1
Geology 200 Getting Started...
 Geology 200 Getting Started... Name This handout should be completed and become a part of your Notebook for this course. This handout is intended to be a review of some important ideas from your introductory
Geology 200 Getting Started... Name This handout should be completed and become a part of your Notebook for this course. This handout is intended to be a review of some important ideas from your introductory
II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013)
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
Plate Tectonics. Earth, 9 th edition Chapter 2
 1 Plate Tectonics Earth, 9 th edition Chapter 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Continental Drift
1 Plate Tectonics Earth, 9 th edition Chapter 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Continental Drift
Exploring the Volcanic, Alteration, and Fluvio-Lacustrine History of Early Mars at the Jezero Crater Paleolake
 Exploring the Volcanic, Alteration, and Fluvio-Lacustrine History of Early Mars at the Jezero Crater Paleolake Tim Goudge 1, Bethany Ehlmann 2, Caleb Fassett 3, Jim Head 1, Jack Mustard 1, Nicolas Mangold
Exploring the Volcanic, Alteration, and Fluvio-Lacustrine History of Early Mars at the Jezero Crater Paleolake Tim Goudge 1, Bethany Ehlmann 2, Caleb Fassett 3, Jim Head 1, Jack Mustard 1, Nicolas Mangold
Landslide hazard and risk in geologically active areas. The case of the caldera of the Santorini (Thera) volcano island complex (Greece)
 Landslide hazard and risk in geologically active areas. The case of the caldera of the Santorini (Thera) volcano island complex (Greece) Prof. Efthymis Lekkas Faculty of Geology & Geoenvironment, National
Landslide hazard and risk in geologically active areas. The case of the caldera of the Santorini (Thera) volcano island complex (Greece) Prof. Efthymis Lekkas Faculty of Geology & Geoenvironment, National
Volcanic Hazards & Prediction of Volcanic Eruptions
 Page 1 of 11 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Volcanic Hazards & Prediction of Volcanic Eruptions This page last updated on 03-Jul-2012 Volcanic Hazards This lecture
Page 1 of 11 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Volcanic Hazards & Prediction of Volcanic Eruptions This page last updated on 03-Jul-2012 Volcanic Hazards This lecture
Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment
 Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment After reading the introduction to the Plate Tectonics exercises in the lab manual, complete the questions on a hard copy of this Lab Assignment. When finished, transfer your
Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment After reading the introduction to the Plate Tectonics exercises in the lab manual, complete the questions on a hard copy of this Lab Assignment. When finished, transfer your
Rocks and Plate Tectonics
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Rocks and Plate Tectonics Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is a naturally occurring, solid mass of mineral or
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Rocks and Plate Tectonics Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is a naturally occurring, solid mass of mineral or
GENERAL SCIENCE LABORATORY 1110L Lab Experiment 9B: Tracking the Hawaiian Islands: How Fast Does the Pacific Plate Move?
 GENERAL SCIENCE LABORATORY 1110L Lab Experiment 9B: Tracking the Hawaiian Islands: How Fast Does the Pacific Plate Move? Background You know that the Earth s crustal plates are always moving, but how fast?
GENERAL SCIENCE LABORATORY 1110L Lab Experiment 9B: Tracking the Hawaiian Islands: How Fast Does the Pacific Plate Move? Background You know that the Earth s crustal plates are always moving, but how fast?
Recent ostracods from the Azores archipelago
 Joannea Geol. Paläont. 11: 132-136 (2011) Recent ostracods from the Azores archipelago Ricardo P. MEIRELES, Antonio FRIAS MARTINS & Sérgio ÁVILA The Azores is an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean between
Joannea Geol. Paläont. 11: 132-136 (2011) Recent ostracods from the Azores archipelago Ricardo P. MEIRELES, Antonio FRIAS MARTINS & Sérgio ÁVILA The Azores is an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean between
Engineering Geological Asset Management for Large Dams. Yasuhito SASAKI (1)
 Engineering Geological Asset Management for Large Dams Yasuhito SASAKI (1) (1) Geology Research Team, Public Works Research Institute, Japan E-mail:ya-sasa@pwri.go.jp Abstract Comprehensive inspection
Engineering Geological Asset Management for Large Dams Yasuhito SASAKI (1) (1) Geology Research Team, Public Works Research Institute, Japan E-mail:ya-sasa@pwri.go.jp Abstract Comprehensive inspection
Glacier Maps of the Sierra Nevada de Mérida, Venezuela
 Glacier Maps of the Sierra Nevada de Mérida, Venezuela Source Description Map 1 Jahn (1925) Map showing glacier cover, glacier names, summit names, and summit elevations in the Sierra Nevada de Mérida
Glacier Maps of the Sierra Nevada de Mérida, Venezuela Source Description Map 1 Jahn (1925) Map showing glacier cover, glacier names, summit names, and summit elevations in the Sierra Nevada de Mérida
The Ice Age By: Sue Peterson
 www.k5learning.com Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific
www.k5learning.com Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific
Geologic Time. This page last updated on 08-Oct-2015
 Page 1 of 16 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Geologic Time This page last updated on 08-Oct-2015 From the beginning of this course, we have stated that the Earth is
Page 1 of 16 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Geologic Time This page last updated on 08-Oct-2015 From the beginning of this course, we have stated that the Earth is
What do you imagine about the nature
 CHAPTER INTERIOR OF THE EARTH What do you imagine about the nature of the earth? Do you imagine it to be a solid ball like cricket ball or a hollow ball with a thick cover of rocks i.e. lithosphere? Have
CHAPTER INTERIOR OF THE EARTH What do you imagine about the nature of the earth? Do you imagine it to be a solid ball like cricket ball or a hollow ball with a thick cover of rocks i.e. lithosphere? Have
PATHWAYS FOR ESCAPE OF MAGMATIC CARBON DIOXIDE TO SOIL AIR AT UNZEN VOLCANO, SW JAPAN
 RADIOCARBON, Vol 46, Nr 1, 2004, p 491 496 2004 by the Arizona Board of Regents on behalf of the University of Arizona PATHWAYS FOR ESCAPE OF MAGMATIC CARBON DIOXIDE TO SOIL AIR AT UNZEN VOLCANO, SW JAPAN
RADIOCARBON, Vol 46, Nr 1, 2004, p 491 496 2004 by the Arizona Board of Regents on behalf of the University of Arizona PATHWAYS FOR ESCAPE OF MAGMATIC CARBON DIOXIDE TO SOIL AIR AT UNZEN VOLCANO, SW JAPAN
Tectonic plates push together at convergent boundaries.
 KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine
 Geologic Site of the Month February, 2002 The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine 43 14 23.88 N, 70 35 18.36 W Text by Arthur M. Hussey II, Bowdoin College and Robert G. Marvinney,, Department
Geologic Site of the Month February, 2002 The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine 43 14 23.88 N, 70 35 18.36 W Text by Arthur M. Hussey II, Bowdoin College and Robert G. Marvinney,, Department
The Geologic History of the Long Valley Caldera and the Landforms Created Within
 The Geologic History of the Long Valley Caldera and the Landforms Created Within Abstract The Long Valley caldera eruption was a major explosion which resulted in the destruction of a wide area, along
The Geologic History of the Long Valley Caldera and the Landforms Created Within Abstract The Long Valley caldera eruption was a major explosion which resulted in the destruction of a wide area, along
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
College of Science and Health ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & GEOGRAPHY Course Outline
 College of Science and Health ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & GEOGRAPHY Course Outline 1. TITLE OF COURSE AND COURSE NUMBER: General Geology ENV 115, 4 credits 2. DESCRIPTION OF THE COURSE: Includes the study
College of Science and Health ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & GEOGRAPHY Course Outline 1. TITLE OF COURSE AND COURSE NUMBER: General Geology ENV 115, 4 credits 2. DESCRIPTION OF THE COURSE: Includes the study
Mammal fauna remains in the Middle Pleistocene volcanic deposits from Northeastern Sabatini Volcanic District area (Latium, Italy)
 Mammal fauna remains in the Middle Pleistocene volcanic deposits from Northeastern Sabatini Volcanic District area (Latium, Italy) G. Sottili, P. Celletti Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università
Mammal fauna remains in the Middle Pleistocene volcanic deposits from Northeastern Sabatini Volcanic District area (Latium, Italy) G. Sottili, P. Celletti Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università
Geol 101: Physical Geology Summer 2007 EXAM 1
 Geol 101: Physical Geology Summer 2007 EXAM 1 Write your name out in full on the scantron form and fill in the corresponding ovals to spell out your name. Also fill in your student ID number in the space
Geol 101: Physical Geology Summer 2007 EXAM 1 Write your name out in full on the scantron form and fill in the corresponding ovals to spell out your name. Also fill in your student ID number in the space
MATHEMATICS KNOWLEDGE FOR TEACHING WITHIN A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE OF PRESERVICE TEACHER TRAINING
 MATHEMATICS KNOWLEDGE FOR TEACHING WITHIN A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE OF PRESERVICE TEACHER TRAINING Pedro Gómez Universidad de Granada C/. Alisios 17, Albolote 18820, Spain Phone/Fax: (34)958537304 pgomez@valnet.es
MATHEMATICS KNOWLEDGE FOR TEACHING WITHIN A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE OF PRESERVICE TEACHER TRAINING Pedro Gómez Universidad de Granada C/. Alisios 17, Albolote 18820, Spain Phone/Fax: (34)958537304 pgomez@valnet.es
P1: Rock identification (I)
 P1: Rock identification (I) Examine the rocks specimens provided with the aid of these notes. All the rocks come from Ireland, as detailed on the attached map. Answer the short question on each specimen
P1: Rock identification (I) Examine the rocks specimens provided with the aid of these notes. All the rocks come from Ireland, as detailed on the attached map. Answer the short question on each specimen
The Geology of Calavera Hills, North San Diego County, California
 The Geology of Calavera Hills, North San Diego County, California John H. Turbeville Professor of Geology and Oceanography MiraCosta College, Oceanside, California miracosta.edu/home/jturbeville Introduction
The Geology of Calavera Hills, North San Diego County, California John H. Turbeville Professor of Geology and Oceanography MiraCosta College, Oceanside, California miracosta.edu/home/jturbeville Introduction
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Igneous Rocks of the Ocean Basins. The Ocean Basins
 Page 1 of 18 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 03-Feb-2011 The The ocean basins cover the largest area of the Earth's surface. Because of plate
Page 1 of 18 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 03-Feb-2011 The The ocean basins cover the largest area of the Earth's surface. Because of plate
On the monitoring of surface displacement in connection with volcano reactivation in Tenerife, Canary Islands, using space techniques
 ISSN: 0214-4557 On the monitoring of surface displacement in connection with volcano reactivation in Tenerife, Canary Islands, using space techniques G. Rodríguez-Velasco (1), R. Romero (1), T.-T. Yu (2),
ISSN: 0214-4557 On the monitoring of surface displacement in connection with volcano reactivation in Tenerife, Canary Islands, using space techniques G. Rodríguez-Velasco (1), R. Romero (1), T.-T. Yu (2),
Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface
 PART ONE Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface Science standards To prepare students to understand the Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALRs) introduced at middle school, this series
PART ONE Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface Science standards To prepare students to understand the Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALRs) introduced at middle school, this series
Rocks and Minerals What is right under your feet?
 Rocks and Minerals What is right under your feet? Name: 1 Before you start What do you already know? What is the difference between a rock and a mineral? What are the three categories of rocks? 1. 2. 3.
Rocks and Minerals What is right under your feet? Name: 1 Before you start What do you already know? What is the difference between a rock and a mineral? What are the three categories of rocks? 1. 2. 3.
SITE. Name: Killerton. Parish: Silverton. Local Authority: East Devon. National Grid Ref: SS 973 007. OS Sheets: 1:50K, 192, 1:10K, SS90 SE
 SITE Name: Killerton Parish: Silverton Local Authority: East Devon National Grid Ref: SS 973 007 OS Sheets: 1:50K, 192, 1:10K, SS90 SE Locality Description: This site lies to the north of Exeter, just
SITE Name: Killerton Parish: Silverton Local Authority: East Devon National Grid Ref: SS 973 007 OS Sheets: 1:50K, 192, 1:10K, SS90 SE Locality Description: This site lies to the north of Exeter, just
2 Wind Erosion and Deposition
 CHAPTER 3 2 Wind Erosion and Deposition SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can wind erosion shape the
CHAPTER 3 2 Wind Erosion and Deposition SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can wind erosion shape the
