Zinc and zinc nanoparticles: biological role and application in biomedicine
|
|
|
- Claribel Rodgers
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
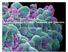
1 Ukrainica Bioorganica Acta 1 (2013) Zinc and zinc nanoparticles: biological role and application in biomedicine К.І. Bogutska 1 *, Yu.P. Sklyarov 2, Yu.І. Prylutskyy 1 1 Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv 64, Volodymyrska Str., Kyiv, 01601, Ukraine 2 O. Bogomolets National Medical University 13, T. Shevchenko Avenue, Kyiv, 01601, Ukraine Summary. Due to nanodimension of functional components of living cells, the application of nanotechnologies in biomedical purposes is an important problem for today. One of the most promising directions is to use zinc nanoparticles for molecular diagnostics, target delivery of drugs, developing new pharmaceutical preparations. The paper presents the data on biological properties of zinc and its compounds, their location in the organism and role in important biological processes, which show the ways of possible practical applications of zinc nanoparticles in biomedicine. Particular attention is paid to the role of ion s zinc in muscle functioning. Keywords: zinc, zinc nanoparticles, functional properties, biomedical applications. Introduction. The currently existing nanoparticles are classified by their chemical composition, namely: 1) metallic nanoparticles (Au, Ag, Cu, Fe, Zn (Fig. 1), etc.); 2) nanoparticles of metal and non-metal oxides (FeO, VO, AlO, ZnO (Fig. 2, Tabl. 1), etc.); 3) semiconductor nanoparticles (ZnS, CdSе, ZnSe, CdS, etc.); 4) carbon nanoparticles (fullerenes, nanotubes, graphene [1-5], diamond); 5) nanoparticles of organically modified layered silicates and alumosilicates (nanoclays of different compositions); 6) nanoparticles of organic dendrite polymers (dendrimers of different composition); 7) quantum dots [6, 7]. Zinc and zinc nanoparticles (Figs. 1 and 2) can be classified into 1-3 and 7 groups, respectively. At present the medicinal preparations based on nanoparticles of metals (silver, gold, iron and others) 5-16 nm in size are considered to be the most promising for practical applications in biomedicine. It has been found that high-disperse powders of nanometals (magnesium, copper, zinc, etc.) as well as their oxides show a pronounced biological activity [8]. They are used both independently and in complexes with organic compounds. These nanoparticles are not only capable of inhibiting aggregation of colloid solutions and increase their stability but also can deliver medical preparations to the target location of pathological process [9]. In particular, nanozinc has been used in non-organic complex- * Corresponding author. Tel.: address: biophys@univ.kiev.ua К.І. Bogutska, Yu.P. Sklyarov, Yu.І. Prylutskyy, 2013 Fig. 1. A typical electron microscopy image of Zn nanoparticles. 9
2 К.І. Bogutska, Yu.P. Sklyarov, Yu.І. Prylutskyy Fig. 2. A typical electron microscopy image of ZnO nanoparticles. es with different chemical elements such as ZnS, ZnO (Figs. 2 and 3; Table 1), etc. The applications of nanoparticles are wide and diverse: interactions of nanomaterials with living cells and tissues, researches in polymer nanocoupling, creation of biohybrid systems (artificial muscles), regenerative medicine (protometrocytes and nervous cells, bone tissue), nanomedicine (drug delivery, cell therapy) and others [9, 10]. It has been found that chemical and biological properties of nanoparticles are essentially different from the properties of the initial material from which they are made. When entering the organism, it takes metal nanoparticles certain time to dissolve, bind to bioligands and reach the target. Therefore their action may be prolongated, which is important factor in medical treatment that should be taken into account. Moreover, metal nanoparticles are less toxic in comparison with metal salts and their action on the organism has multifunctional character [6, 9]. Thus, a depot of high-disperse zinc powder created in the body will ensure slow intake of this microelement into the organism in dozes close to physiological, which may prove one of the ways to obtain durable therapeutic action, for example in case of ethanol dependence, since chronic alcohol intoxication is one of the main causes of zinc deficiency development in the organism [11]. The role of zinc in life activity of organism. Zinc is known to be one of the most essential microelements indispensable for vital functions. Zinc that comes into the organism from food and water is mainly absorbed in small intestine, and then it is transported to blood plasma, where it is bound by albumins and globulins, or to the tissues in which it is deposited in zinc and cadmium accumulating protein. Zinc is included in the structure of metalloenzymes and hormonal complexes. The property of zinc to take part in the processes of forming ligands with organic molecules explains why it is widely available in different biological systems. However, zinc distribution in tissues may change, since zinc can be displaced by other cations accumulated in proteins. The transport and metabolism of zinc in the organism is characterized by its fast assimilation. At the same time its deficiency is often caused by pathological conditions, and decreased concentration of zinc cations may, in turn, influence vital processes in cells [12, 13]. For example, zinc plays important role in such biological processes as growth and division of cells, ceratogenesis, osteogenesis, immune response, wound reparation postsurgical wounds included; it also plays role in reproduction and functioning of pancreas. As known zinc exists in biological systems in two forms: bound zinc and chemically reactive Zn 2+ (Table 2). It is a structural constituent of Dependence of mass concentration on the dimension of ZnO particles and their concentration in the unit of volume Sample density, * N, N, N, N, kg/m 3 d=20 nm d=50 nm d=100 nm d=200 nm ZnO Table 1 10 Ukrainica Bioorganica Acta 1 (2013)
3 Zinc and zinc nanoparticles: biological role and application in biomedicine A B Fig. 3. A typical electron microscopy image of ZnO nanoparticles in colloid solution (А) and their size distribution (B). many zinc-binding proteins including the molecules of cellular signalling pathways [14, 15]. Over the recent years the researchers have studied zinc, zinc ions and compounds and their effect on organism as biomarkers and antioxidants, as well as intravital and lethal distribution in tissues, activity in certain structures (cell membranes, proteins, etc.), toxicity, and as a promising pharmaceutical target [14-17]. It has been long consiered that zinc is not toxic, but recent studies in vivo evidence about its toxic action [11, 18]. However, the mechanism of its harmful effect in the organism has not yet been revealed. Zinc plays important role in controlling apoptosis. The excess of zinc may cause cell death due to apoptosis or necrosis [19, 20]. Researchers distinguish two main antiapoptotic functions of zinc: (1) direct action on apoptosis regulators especially on enzyme belonging to caspase family, which may prevent oxidation injury, and (2) decrease the damage caused by toxins by inhibiting induction caspase activity aimed at preparation and start of apoptosis. This process is triggered, when the concentration of intracellular zinc decreases. Thus, zinc-deficiency may considerably increase the frequency of apoptosis events in tissues [21]. There are several possible biochemical mechanisms through which zinc reduces oxidative stress in cells. In particular, it has been found that zinc has negative effect on the synthesis of antiinflammatory cytokines (for example, tumour necrosis factor α and interleukin 1β) that produce active forms of oxygen and therefore this metal can function in the organism as antioxidant [22]. Current and perspective applications of nanozinc compounds in biomedicine. Due to nanodimension, zinc particles acquire unique physical and chemical properties which may be different from those they posses in the known metal compounds. This allows using them in new biomedical applications [8, 9, 23-26]. For example, the ability of ZnO nanoparticles to absorb a wide spectrum of radiation (ultraviolet, microwave, infrared and at radiofrequencies) can be used for manufacturing cosmetic creams, ointments, etc., which protect organism from ultraviolet radiation. Zinc oxide is a semiconducting material. Producing nanocomposits by immobilizing ZnO nanoparticles on the surface of graphene results in formation of efficient sensor elements [27]. It has been reported that materials based on ZnO nanoparticles can be used in infrared and electrochemical sensors [28, 29]. To produce of bio- Sample Ion radius, nm Physicochemical characteristics of Zn 2+ ion Enthalpy of hydration H, kj/mole z 2 /r, ev E, ev E- H, ev W, ev Zn 2+ 0, ,82 27,35 5,86 10,68 Table
4 К.І. Bogutska, Yu.P. Sklyarov, Yu.І. Prylutskyy sensor the platinum electrode coated with a film made from ZnO nanoparticles and polypyrrole, on which csantoxidase is immobilised. The enzyme-modified electrode is applied to detect csantin (it generates electric signal during oxidation of hydrogen peroxide formed in processing csantin by csantinoxidase). The biosensor produced in this way is stable in storage at the temperature of 4 С and endures 200 operations within 100 days [30]. ZnO nanoparticles have found analogous application in electrochemical biosensor for detecting glucose [28]. ZnO nanoparticles of nm in size display antibacterial properties [31], which is now used in textile industry for producing fabrics for cloths. When in contact with human body the fabrics serves as a substrate, on which microbes may grow and this growth of microorganisms can be prevented by using ZnO nanoparticles in the production of fabrics [32]. Nanodiagnostics is another field where nanotechnologies are applied. At present they are used in clinical diagnostics to increase sensitivity of investigations and early detection of various diseases. For this purpose the most promising are nanoparticles less than 10 nm in size (quantum dots). They are characterized by large spectral absorption activity and can be used as fluorescent markers of biomolecules [23]. Quantum dots of nanozinc are bright photoresistant fluorophores. Colloidal nanocrystalline quantum dots of CdSe/ZnS possess unique size-dependent optical properties, which makes them an alternative to fluorescent organic dyes. Besides the ability to emit light CdSe/ZnS possess such characteristics as photostability, hydrophobility and biocompatiblity. The binding quantum dot protected by polymer with multifunctional receptor makes it possible to distinguish the detailed structure of cell skeleton under electron microscope. With the help of quantum dots the problem of visualizing the motion of individual molecules in living cells has been solved, which allows real time observations, impossible by using organic dyes. Quantum dots investigations may provide deeper insight into the dynamics of receptors, biomolecule transport and enzyme functioning. Nanozinc compounds have found application in identifying antigens in malignant tumors. CdSe/ZnS nanocrystals conjugated with polyclonal antibodies are used as immune markers. P-glycoprotein, for example, is detected by the method of immune fluorescence by zinc nanocompounds, which are also used for three-dimensional analysis of one of the main mediators of tumour drug resistance [25, 33]. The immune marking p-glycoprotein by nanocrystals conjugated with antibodies is 4200 and 2600 times more stable to photobleaching than flouresceinisothiocyanate-antibodies and Р-phycoerythrinantibodies respectively. This conjugation is highly specific. ZnS nanoparticles covered by L-cysteine are used in the method of synchronous fluorescence, when the intensity of fluorescence grows synchronously for all nanoparticles in presence of protein molecules [34]. This method reveals all proteins composing blood serum of human body. This is a very sensitive, simple and stable method that has a wide linear range in comparison with other physical and chemical methods. ZnS nanoparticles have low toxicity and high stability. They are resistant to photobleaching (in contrast to organic phluorophores) and their fluorescence is bright. In contrast to traditionally used organic markers the zinc nanoparticles ensure accuracy in detecting proteins and tracing their biomolecular dynamics: protein coagulation, transduction and enzyme catalysis. Semiconducting nanoparticles are considered to be a new class of fluorescent probes for molecular and cellular fluorescence microscopy [9, 23]. Because of their size, these nanoparticles posses unique optic properties, that differ from those displayed by organic dyes or fluorescing proteins. For example, CdSe/ZnS particles of about 2 nm emit blue colour, while the same particles of 7 nm in size emit red colour. Fluorescing semiconducting nanoparticles such as ZnS, CdSе, ZnSe or combined structures of CdSe/ZnS and others have larger surface area, where a greater number of different functional groups can be located. This allows creating nanoparticles that could perform diagnostic and therapeutic tasks [9]. In future, the laboratory methods of detecting biomarkers with the help of fluorescent semiconducting nanoparticles may become a real breakthrough of nanobiotechnologies. In such case, that is very important, the toxicity of nanomaterials will not be able to produce any toxic effect on 12 Ukrainica Bioorganica Acta 1 (2013)
5 Zinc and zinc nanoparticles: biological role and application in biomedicine the organism, since biopsy material for diagnostics will be examined in the laboratory in vitro. Nanozinc compounds with insulin and highmolecular substances foster prolongation of hypoglycemic drug action in contrast with duration of insulin effect. Moreover, this kind of nanostructure with amphotericin-в, antifungal drug of systemic action, decreases nephrotoxic effect of this pharmaceutic [35]. Another example demonstrating how available nanozinc changes the properties of complex chemical compounds or gives them new properties is the system of designed peptide with Eudragit s-100 (anionic polymer based on methacrylate; in this structure the surfactant is used as peptide) [36]. Nanozinc increases the elasticity of polymerpeptide compound, which decreases their absorbability [25]. The investigation of toxic effect of ZnO nanoparticles ( nm) in mice has shown that parenteral administration causes damage in liver, heart, spleen, pancreas and bones [37]. When ZnO nanoparticles delivered through thrachea, they cause, depending on doze, the pneumonia, proliferation and thickening of alveolar membranes, loss of weight and anemia in mice [38]. In vitro experiments have shown that ZnO and Zn 2+ nanoparticles activate complex cytotoxic paths in bronchi epithelial cells and macrophages, which include intercellular flows of calcium, mitochondrial depolarization and leak of plasmolemma [39]. There are also reports about the study of 65 Zn activity on bioprobes by using gamma spectrometry equipment, which was performed with the aim to reveal bioavailability of zinc from zinc oxide nanoparticles [40]. The main problem that prevents a fast development of cancer therapy methods is the inability of anticancer drugs to distinguish between healthy and cancerous cells. This is a cause of complications and side effect of chemotherapy. It has been found that oxide zinc nanoparticles can selectively kill cancerous cells [41, 42]. Moreover, the process of interaction between ZnO nanoparticles and cancerous cells can be monitored. For example, the selectivity of nanoparticles may be enhanced if interdependence is found between the proteins attacking cancerous cells (monoclonal antibodies and peptides) and small protein molecules bound to cancerous cells, or if they are used to deliver drugs to the target. The action of ZnO nanoparticles (cytotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoflakes (ZnO NFs)) has been studies in a model of human muscle carcinoma [43]. In general, the zinc-containing medicinal preparations, vitamin and mineral complexes including, have ummunomodulatory, antibacterial and antifungal effect [23-25]. ZnO nanoparticles have shown pronounced anti-inflammatory and reparation action in treating experimental septic wounds. They are included in the composition of cosmetics, which protect skin from burns and cancerogenic action of ultraviolet radiation [23]. Zinc is also used in radioisotope diagnostics, in particular as a marker for zinccontaining enzymes. Zinc sulfide is applied in testing blood coagulation. In recent years zinc compounds (gluconate, asparaginate, picolinate, etc.) have become widely used in dermatology, endocrinology and in therapy of immune deficiency states. Zinc and muscles. Human body contains about 1,3-2,3 g of zinc, almost 90 % of total amount of which is in the muscles and bones [12]. High level of zinc content is known to be not only in endocrine glands but also cells of muscles (1,4-7,1 mg per 100 g of tissue). In other reports the content of zinc in the muscles comprises 240 mg/kg [24]. In the heart the mechanism of controlling intercellular distribution of Zn 2+ and its change during the cycle of functioning has not been revealed so far [44-46]. The research in changes of Zn 2+ homeostasis have been performed by using specific fluorescent dye FluoZin-3 and mass-spectroscopy, which allows «mapping» the metal in the biological tissue [47]. For example, zinc has been found to be distributed inhomogeneously with the average concentration of 26 mg per gram of tissue [12]. The results show that zinc is accumulated mainly in the muscle fibres of endocardium. Zinc is distributed evenly in sarcoplasma reticulume, while in myocardium fibres it is concentrated mainly in anisotropic disks of myofibrils, that is, in the regions, which consist of myosin. The investigations of microelement content in different regions of the left ventricle in patients with ischemic coronary disease, dilated cardiomyopathy and critical heart failure 13
6 К.І. Bogutska, Yu.P. Sklyarov, Yu.І. Prylutskyy by X-ray fluorescence analysis with synchronous emission, have revealed disbalance in microelement contents, in particular an increase the content of zinc [47, 48]. In the result of research in cardioprotecting properties of zinccontaining compounds an assumption has been made about the ability of zinc ions to decreased ischemic and postischemic damages of tissues due to antagonism with copper reactivity [49]. The researchers report that Zn 2+ influences ATPase activity of myosin and superprecipitation of cardiac muscle actomyosin, probably, being able to replace calcium and magnesium ions (although this displacement is less efficient for superprecipitation reaction and ATP-hydrolysis process) and modulate actin-myosin interaction by changing functional characteristics of actomyosin macromolecules of cardiac muscles [50]. Conclusions. Current nanotechnologies make it possible to design nanoparticles with desired physicochemical and biological properties. Zinc and its compounds can open wide possibilities of biomedical applications due to nanosize, optical, chemical, biological and pharmaceutical properties. The researches in this field also have practical importance due to possibility to regulate functional activity of muscles using zinc ions both in normal and pathological states. Надійшла до редакції р. Цинк та наночастинки цинку: біологічна роль і використання в біомедицині К.І. Богуцька 1, Ю.П. Скляров 2, Ю.І. Прилуцький 1 1 Київський національний університет імені Тараса Шевченка вул. Володимирська, 64, Київ, 01601, Україна 2 Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця бульв. Т. Шевченка, 13, Київ, 01601, Україна Резюме. Враховуючи нанорозмірність функціональних компонентів живих клітин, застосування нанотехнологій у біомедичних цілях наразі є актуальним завданням. Один з таких напрямів використання наночастинок, зокрема цинку, для молекулярної діагностики, адресної доставки лікарських засобів, розробки нових фармакологічних препаратів. Представлені дані біологічних властивостей цинку та його сполук, знаходження в організмі та участі у біологічно важливих процесах, що уможливлює практичне використання цих наночастинок у біомедицині. Окремо розглянуто роль іонів цинку у функціонуванні м язів. Ключові слова: цинк, наночастинки цинку, функціональні властивості, біомедичне застосування. 1. Prylutska S.V., Remenyak O.V., Goncharenko Yu.V., Prylutskyy Yu.I. Carbon nanotubes as a new class of materials for bionanotehnology // Biotechnology Vol. 2, No. 2. P (in Ukrainian). 2. Sagalianov I.Yu., Prylutskyy Yu.I., Radchenko T.M., Tatarenko V.А. Graphene systems: methods of preparations and processing, structure and functional properties // Usp. Metal Physics Vol. 11, No. 1. P (in Ukrainian). 3. Rotko D.M., Prylutska S.V., Bogutska K.I., Prylutskyy Yu.I. Carbon nanotubes as a new material for neuroengineering // Biotechnology Vol. 4, No. 5. P (in Ukrainian). 4. Prylutska S.V., Kichmarenko Yu.M., Bogutska K.I., Prylutskyy Yu.I. Fullerene C60 and its derivatives as anticancer agents: problems and prospects // Biotechnology Vol. 5, No. 3. P (in Ukrainian). 5. Prylutska S.V., Rotko D.M., Prylutskyy Yu.I., Rybalchenko V.K. Toxicity of carbon nanostructures in vitro and in vivo systems // Modern Problems Toxicol No P (in Ukrainian). 6. Chekman I.S. Nanoparticles: Properties and application prospects // Ukr. Biokhim. Zh Vol. 81, No. 1. P (in Ukrainian). 7. Chekman I.S., Gorchakova N.A., Ozeychuk O.Y. References Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: classification // Sci. Bulletin of O. Bogomolets National Medical University No. 2. P (in Ukrainian). 8. Andrusishina I.N. Metal nanoparticles: Ways of receiving, physical and chemical properties, methods of research and toxicity assessment // Modern Problems Toxicol No. 3. P (in Russian). 9. Meshalkin Yu.P., Bgatova N.P. Prospects and problems of the use of inorganics nanoparticles in oncology // J. Siberian Federal Univ. Biology No. 1. P (in Russian). 10. Mikityuk M.V. Nanoparticles and prospects for their application in biology and medicine // Problems Ecology Med Vol. 15, No P (in Ukrainian). 11. Glushchenko N.N., Skalny A.V. Zinc nanoparticles toxicity and biological properties // Actual Problems Transport Med No. 3(21). P (in Russian). 12. Avtzin А.P., Zchavoronkov А.А., Rish М.А., Strochkova L.S. Microelementoses in humans: Etiology, classification, organ pathology. М.: Меdicine, p. (in Russian). 13. Skalniy A.V., Rudakov I.A. Bioelements in Medicine. M.: Onix 21 Century, p. (in Russian). 14 Ukrainica Bioorganica Acta 1 (2013)
7 Zinc and zinc nanoparticles: biological role and application in biomedicine 14. Maret W. Metals on the move: zinc ions in cellular regulation and in the coordination dynamics of zinc proteins // Biometals Vol. 24, No. 3. Р Hirano T., Murakami M., Fukada T., Nishida K., Yamasaki S., Suzuki T. Roles of zinc and zinc signaling in immunity: zinc as an intracellular signaling molecule // Adv. Immunol Vol. 97. Р Maret W. Molecular aspects of human cellular zinc homeostasis: redox control of zinc potentials and zinc signals // Biometals No. 1. Р Anzellotti A., Farrell N. Zinc metalloproteins as medicinal targets // Chem. Soc. Rev Vol. 37, No. 8. Р Bozym R., Chimienti F., Giblin L., Gross G., Korichneva I., Li Y., Libert S., Maret W., Parviz M., Frederickson C., Thompson R. Free zinc ions outside a narrow concentration range are toxic to a variety of cells in vitro // Exp. Biol. Med Vol. 235, No. 6. Р Prasad A.S. Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells // Mol. Med Vol. 14, No Р Akhtar M.J., Ahamed M., Kumar S., Khan M.M., Ahmad J., Alrokayan S.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species // Int. J. Nanomed Vol. 7. P John E., Laskow T.C., Buchser W.J., Pitt B.R., Basse P.H., Butterfield L.H., Kalinski P., Lotze M.T. Zinc in innate and adaptive tumor immunity // J. Trans. Med Vol. 8. Р Valko M., Morris H., Cronin M.T. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress // Curr. Med. Chem Vol. 12, No. 10. Р Use of nanozinc and nanoaluminium compounds in medicine // nanotechnology/ Chekman I.S., Ulberg Z.R., Rudenko A.D., Marushko Yu.V., Grusina T.G., Reznichenko L.S., Dybkova S.M., Grebelnik A.I. Zinc and nanozinc: Properties, application in clinical practice // P. 1-6 (in Ukrainian). 25. Chekman I.S., Lamazian G.R. Nanozinc: Property, application in medical practice // Ukr. Sci. Med. Youth J No. 1. P (in Ukrainian). 26. ZnO nanostructures: Growth and applications // J. Nanoengin. Nanomanufact Special issue Shalyapina A.Ya., Solovyova A.Yu., Zaporozhets M.A., Khokhlov E.M., Plotnichenko V.G., Buslaeva E.Yu., Rustamova E.G., Gubin S.P. Composite materials based on graphene and zinc oxide nanoparticles // Bulle-tin of MITXT Vol. 7, No. 5. P (in Russian). 28. Lei Y., Yan X., Zhao J., Liu X., Song Y., Luo N., Zhang Y. Improved glucose electrochemical biosensor by appropriate immobilization of nano-zno // Colloids Surf. Biointerfaces Vol. 82, No. 1. Р Shiryaev M.A., Baranov A.N. Synthesis and modification of zinc oxide nanostructures for conductometric immunosensor development // Nanosystems: Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics Vol. 4, No. 1. P (in Russian). 30. Devi R., Thakur M., Pundir C.S. Construction and application of an amperometric xanthine biosensor basedon zinc oxide nanoparticles-polypyrrole composite film // Biosens. Bioelectron Vol. 26, No. 8. Р Wahab R., Mishra A., Yun S. I., Kim Y.S., Shin H.S. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles prepared via non-hydrolytic solution route // Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol Vol. 87, No. 5. Р Dastjerdi R., Montazer M. A review on the application of inorganic nanostructured materials in the modification of textiles: focus on antimicrobial properties // Colloids Surf. Biointerfaces Vol. 79, No. 1. Р Sukhanova A., Devy J., Venteo L., Kaplan H., Artemyev M., Oleinikov V., Klinov D., Pluot M., Cohen J.H., Nabiev I. Biocompatible fluorescent nanocrystals for immunolabeling of membrane proteins and cells // Anal. Biochem Vol. 324, No. 1. P Zhu C.Q., Zhao D.H., Chen J.L., Li Y.X., Wang le Y., Wang L., Zhou Y.Y., Zhuo S.J., Wu Y.Q. Application of L-cysteine-capped nano-zns as a fluorescence probe for the determination of proteins // Anal. Bioanal. Chem Vol. 378, No. 3. P Tiyaboonchai W., Limpeanchob N. Formulation and characterization of amphotericin B-chitosan-dextran sulfate nanoparticles // Int. J. Pharmaceutics Vol P Dexter A.F., Malcolm A.S., Zeng B., Kennedy D., Middelberg A.P. Mixed system of Eudragit s-100 with a designed amphipathic peptide: control of interfacial elasticity by solution composition // Langmuir Vol. 24, No. 7. P Wang B., Feng W.Y, Wang T.C., Jia G., Wang M., Shi J.W., Zhang F., Zhao Y.L., Chai Z.F. Acute toxicological impact of nano- and submicro-scaled zinc oxide powder on healthy adult mice // J. Nanoparticle Res Vol. 10, No. 2. P Liu Z. Acute toxicity of nano-sized zinc oxide in ICR mice via intratracheal instillation // J. Environ. Occup. Med Vol. 25, No. 4. Р George S., Pokhrel S., Xia T., Gilbert B., Ji Z., Schowalter M., Rosenauer A., Damoiseaux R., Bradley K.A., Madler L., Nel A.E. Use of a rapid cytotoxicity screening approach to engineer a safer zinc oxide nanoparticle through iron doping // ACS Nano Vol. 4, No. 1. Р Raspopov R.V., Buzulukov Yu.P., Marchenkov N.S., Solovyev V.Yu., Demin V.F., Kalistratova V.S., Gmoshinsky I.V., Khotimchenko S.A. The bioavailability zinc oxide nanoparticles. Study methods of radionuclide indicator // Food Questions Vol. 9, No. 6. P (in Russian). 41. Thurber A., Wingett D.G., Rasmussen J.W., Layne J., Johnson L., Tenne D.A., Zhang J., Hanna C.B., Punnoose A. Improving the selective cancer killing ability of ZnO nanoparticles using Fe doping // Nanotoxicol Vol. 6, No. 4. P Taccola L., Raffa V., Riggio C., Vittorio O., Iorio M.C., Vanacore R., Pietrabissa A., Cuschieri A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles as selective killers of proliferating cells // Int. J. Nanomed Vol. 6. P Syed M. Usman Ali, Fakhar-e-Alam M., Wazir Z., Kashif M., Atif M., Willander M., Syed W.A. Cytotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoflakes (ZnO NFs) in human muscle carcinoma // In. J. Med. Med. Sci Vol. 2, No. 1. Р
8 К.І. Bogutska, Yu.P. Sklyarov, Yu.І. Prylutskyy 44. Korichneva I. Zinc dynamics in the myocardial redox signaling network // Antioxid. Redox Signal Vol. 8, No Р Antonov A.R., Vaskina E.A., Chernyakin Yu.D. Exchange of biometal in myocardial infarction: a clinical and experimental study // Pathol. Physiol. Experim. Therapy P (in Russian). 46. Tuncay E., Bilginoglu A., Sozmen N., Zeydanli E., Ugur M., Vassort G., Turan B. Intracellular free zinc during cardiac excitation-contraction cycle: calcium and redox dependencies // Cardiovasc. Res Vol. 89, No. 3. Р Okuneva G.N., Cherniavskii А.M., Levicheva Е.N., Loginova І.Yu., Volkov А.M., Trunova V.A., Zvereva V.V. Content of microelements in left ventricular myocardium of patients with ischemic heart disease. Data of roentgenofluorescent analysis with the use of synchrotron irradiation // Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 10. P (in Russian). 48. Okuneva G.N., Karas kov A.M., Cherniavskii A.M., Volkov A.M., Trunova V.A., Zvereva V.V. Role of chemical elements in development of chronic heart failure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy // Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Surg Vol. 4, No. 5. P (in Russian). 49. Atahan E., Ergun Y., Kurutas E., Alici T. Protective effect of zinc aspartate on long-term ischemiareperfusion injury in rat skeletal muscle // Biol. Trace Elem. Res Vol. 137, No. 2. Р Bogutska K.I., Prylutskyy Yu.I. Influence of zinc ions on myosin ATPase activity and superprecipitation reaction of actomyosin of cardiac muscle // Biopolymers and Cell Vol. 27, No. 6. P (in Ukrainian). 16 Ukrainica Bioorganica Acta 1 (2013)
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Research Background Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the body cannot produce sufficient insulin in their pancreas to adequately control the level of glucose in their blood
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Research Background Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the body cannot produce sufficient insulin in their pancreas to adequately control the level of glucose in their blood
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
Safe Nano Design Molecule Manufacturing Market
 August 14 16, 212 College of Nanoscale Science & Engineering (CNSE) of the University at Albany National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Prevention through Design Program Safe Nano
August 14 16, 212 College of Nanoscale Science & Engineering (CNSE) of the University at Albany National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Prevention through Design Program Safe Nano
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Nanotechnology in Cancer Treatment and Detection. Richard Acosta
 Nanotechnology in Cancer Treatment and Detection Richard Acosta Motivation Ineffectiveness of many Cancer treatments Numerous side effects Difficulties in early Cancer detection No immunization Scale and
Nanotechnology in Cancer Treatment and Detection Richard Acosta Motivation Ineffectiveness of many Cancer treatments Numerous side effects Difficulties in early Cancer detection No immunization Scale and
In Situ DNA-Templated Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Ultrasensitive and Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of MicroRNA
 Supporting Information for In Situ DNA-Templated Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Ultrasensitive and Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of MicroRNA Cuiyun Yang, Kai Shi, Baoting Dou, Yun Xiang,*
Supporting Information for In Situ DNA-Templated Synthesis of Silver Nanoclusters for Ultrasensitive and Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of MicroRNA Cuiyun Yang, Kai Shi, Baoting Dou, Yun Xiang,*
TOTAL PROTEIN FIBRINOGEN
 UNIT: Proteins 16tproteins.wpd Task Determination of Total Protein, Albumin and Globulins Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Explain the ratio of albumin and globulin
UNIT: Proteins 16tproteins.wpd Task Determination of Total Protein, Albumin and Globulins Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Explain the ratio of albumin and globulin
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
CHEMICAL SENSORS 1. DEFINITION
 CHEMICAL SENSORS 1. DEFINITION A chemical sensor is a device that transforms chemical information (composition, presence of a particular element or ion, concentration, chemical activity, partial pressure
CHEMICAL SENSORS 1. DEFINITION A chemical sensor is a device that transforms chemical information (composition, presence of a particular element or ion, concentration, chemical activity, partial pressure
AREA STUDIES -RUSSIA (Regional Sustainable Development Review) Vol. II High Technology and Health Care in Russia - E.V. Yurtov and N.M.
 HIGH TECHNOLOGY AND HEALTH CARE IN RUSSIA Department of Industrial Ecology, Mendeleyev University of Chemical Technology, Russia Keywords: medicine, technology, lasers, sorption, artificial organs, membranes,
HIGH TECHNOLOGY AND HEALTH CARE IN RUSSIA Department of Industrial Ecology, Mendeleyev University of Chemical Technology, Russia Keywords: medicine, technology, lasers, sorption, artificial organs, membranes,
The Physiology of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species. I. Introduction Definition, Source, function and Purpose
 The Physiology of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species I. Introduction Definition, Source, function and Purpose A. Definition of free radicals and reactive oxygen species
The Physiology of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species I. Introduction Definition, Source, function and Purpose A. Definition of free radicals and reactive oxygen species
Molecular Spectroscopy
 Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
Exploratory Brief on Nanomedicine or the Application of Nanotechnology in Human Healthcare
 Exploratory Brief on Nanomedicine or the Application of Nanotechnology in Human Healthcare Paula Corabian, Dagmara Chojecki March 6, 2012 Objectives Provincial Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Program
Exploratory Brief on Nanomedicine or the Application of Nanotechnology in Human Healthcare Paula Corabian, Dagmara Chojecki March 6, 2012 Objectives Provincial Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Program
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Week 30. Water Balance and Minerals
 Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Name Period Overview 1. What is a hormone? 2. Why does a hormone elicit a response only with target cells? 3. The body has two long-distance regulating systems. Which involves chemical signals by hormones?
Name Period Overview 1. What is a hormone? 2. Why does a hormone elicit a response only with target cells? 3. The body has two long-distance regulating systems. Which involves chemical signals by hormones?
STUDENT BACKGROUND READING FOR EXPERIMENT C: COLORIMETRIC GOLD NANOSENSOR
 STUDENT BACKGROUND READING FOR EXPERIMENT C: In this experiment you will synthesize and test a plasmonic colorimetric nanosensor made of nanoparticles of gold. Here we provide you with some background
STUDENT BACKGROUND READING FOR EXPERIMENT C: In this experiment you will synthesize and test a plasmonic colorimetric nanosensor made of nanoparticles of gold. Here we provide you with some background
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Effect of ph on the Size of Gold Nanoparticles
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 159-164 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Effect of ph on the
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 159-164 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Effect of ph on the
AAGPs TM Anti-Aging Glyco Peptides. Enhancing Cell, Tissue and Organ Integrity Molecular and biological attributes of lead AAGP molecule
 AAGPs TM Anti-Aging Glyco Peptides Enhancing Cell, Tissue and Organ Integrity Molecular and biological attributes of lead AAGP molecule 1 Acknowledgements This presentation was prepared by Dr. Samer Hussein
AAGPs TM Anti-Aging Glyco Peptides Enhancing Cell, Tissue and Organ Integrity Molecular and biological attributes of lead AAGP molecule 1 Acknowledgements This presentation was prepared by Dr. Samer Hussein
What is nanotoxicology?
 What is nanotoxicology? How to estimate the potential hazard related to nanoparticles? Dissemination report October 2008 DR-225 200810-5 Project ID NMP2-CT-2005-515843 An European Integrated Project Supported
What is nanotoxicology? How to estimate the potential hazard related to nanoparticles? Dissemination report October 2008 DR-225 200810-5 Project ID NMP2-CT-2005-515843 An European Integrated Project Supported
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri
 http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
serum protein and A/ G ratio
 serum protein and A/ G ratio Blood plasma contains at least 125 individual proteins. Serum ( as contrasted with plasma) is deficient in those coagulation protein which are consumed during the process of
serum protein and A/ G ratio Blood plasma contains at least 125 individual proteins. Serum ( as contrasted with plasma) is deficient in those coagulation protein which are consumed during the process of
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient
 Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Chapter 8. Summary and Perspectives
 Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes
 Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes Enzymes: as a catalyst, an enzyme increases the rate of a reaction by changing the way a reaction takes place, but is itself not changed at the end of the reaction. An
Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes Enzymes: as a catalyst, an enzyme increases the rate of a reaction by changing the way a reaction takes place, but is itself not changed at the end of the reaction. An
Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life
 Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life Vitality for Life supplements with patented Oligo Oligo U.S. Patent No. 8,273,393 Reinventing the Multivitamin Our modern diets have the majority of us gorging
Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life Vitality for Life supplements with patented Oligo Oligo U.S. Patent No. 8,273,393 Reinventing the Multivitamin Our modern diets have the majority of us gorging
Name Date Class CHAPTER 1 REVIEW. Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 1 REVIEW Matter and Change SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. a Technological development of a chemical product often (a) lags behind basic research
CHAPTER 1 REVIEW Matter and Change SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. a Technological development of a chemical product often (a) lags behind basic research
Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials
 Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials PhD theses Gabriella Kecskeméti Department of Optics and Quantum Electronics University of Szeged Supervisor: Dr. Béla Hopp senior research fellow Department
Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials PhD theses Gabriella Kecskeméti Department of Optics and Quantum Electronics University of Szeged Supervisor: Dr. Béla Hopp senior research fellow Department
5.111 Principles of Chemical Science
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.111 Principles
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.111 Principles
Version 1 2015. Module guide. Preliminary document. International Master Program Cardiovascular Science University of Göttingen
 Version 1 2015 Module guide International Master Program Cardiovascular Science University of Göttingen Part 1 Theoretical modules Synopsis The Master program Cardiovascular Science contains four theoretical
Version 1 2015 Module guide International Master Program Cardiovascular Science University of Göttingen Part 1 Theoretical modules Synopsis The Master program Cardiovascular Science contains four theoretical
Key Results of 2008 Leem Nanomedecine Study
 Key Results of 2008 Leem Nanomedecine Study Nanobio Dialogue Session Annick Schwebig,, M.D., General Manager, Actelion Pharmaceuticals France Vice-President of Leem Biotech Committee EuroBio,, Paris, October
Key Results of 2008 Leem Nanomedecine Study Nanobio Dialogue Session Annick Schwebig,, M.D., General Manager, Actelion Pharmaceuticals France Vice-President of Leem Biotech Committee EuroBio,, Paris, October
Nanotechnology for Food Processing and Packaging
 Nanotechnology for Food Processing and Packaging John D. Floros Professor & Head Department of Food Science Pennsylvania State University www.foodscience.psu.edu Information Sources Pennsylvania State
Nanotechnology for Food Processing and Packaging John D. Floros Professor & Head Department of Food Science Pennsylvania State University www.foodscience.psu.edu Information Sources Pennsylvania State
Scanning Electron Microscopy Services for Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
 Scanning Electron Microscopy Services for Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Author: Gary Brake, Marketing Manager Date: August 1, 2013 Analytical Testing Laboratory www.atl.semtechsolutions.com Scanning Electron
Scanning Electron Microscopy Services for Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Author: Gary Brake, Marketing Manager Date: August 1, 2013 Analytical Testing Laboratory www.atl.semtechsolutions.com Scanning Electron
2. John Dalton did his research work in which of the following countries? a. France b. Greece c. Russia d. England
 CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
MAB Solut. MABSolys Génopole Campus 1 5 rue Henri Desbruères 91030 Evry Cedex. www.mabsolut.com. is involved at each stage of your project
 Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
BNG 331 Cell-Tissue Material Interactions. Biomaterial Surfaces
 BNG 331 Cell-Tissue Material Interactions Biomaterial Surfaces Course update Updated syllabus Homework 4 due today LBL 5 Friday Schedule for today: Chapter 8 Biomaterial surface characterization Surface
BNG 331 Cell-Tissue Material Interactions Biomaterial Surfaces Course update Updated syllabus Homework 4 due today LBL 5 Friday Schedule for today: Chapter 8 Biomaterial surface characterization Surface
WHEY PROTEIN IMPORTANCE. Dan Phillips
 WHEY PROTEIN IMPORTANCE Dan Phillips Studies on whey demonstrate it's an even better protein supplement than previously thought. Although whey protein's health benefits have only recently been elucidated,
WHEY PROTEIN IMPORTANCE Dan Phillips Studies on whey demonstrate it's an even better protein supplement than previously thought. Although whey protein's health benefits have only recently been elucidated,
Your Life Your Health Cariodmetabolic Risk Syndrome Part VII Inflammation chronic, low-grade By James L. Holly, MD The Examiner January 25, 2007
 Your Life Your Health Cariodmetabolic Risk Syndrome Part VII Inflammation chronic, low-grade By James L. Holly, MD The Examiner January 25, 2007 The cardiometabolic risk syndrome is increasingly recognized
Your Life Your Health Cariodmetabolic Risk Syndrome Part VII Inflammation chronic, low-grade By James L. Holly, MD The Examiner January 25, 2007 The cardiometabolic risk syndrome is increasingly recognized
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body. Vitamin A
 What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
B) atomic number C) both the solid and the liquid phase D) Au C) Sn, Si, C A) metal C) O, S, Se C) In D) tin D) methane D) bismuth B) Group 2 metal
 1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) molar mass D) oxidation number 2. Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) molar mass D) oxidation number 2. Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and
NO More Heart Disease
 NO More Heart Disease Nitric Oxide Information NO is one of the simplest molecules in biology, comprised of just two atoms one atom of nitrogen (N) and one of oxygen (O). Through NO s structure is simple,
NO More Heart Disease Nitric Oxide Information NO is one of the simplest molecules in biology, comprised of just two atoms one atom of nitrogen (N) and one of oxygen (O). Through NO s structure is simple,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING
 CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements
 EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
 Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Matter, Materials, Crystal Structure and Bonding. Chris J. Pickard
 Matter, Materials, Crystal Structure and Bonding Chris J. Pickard Why should a theorist care? Where the atoms are determines what they do Where the atoms can be determines what we can do Overview of Structure
Matter, Materials, Crystal Structure and Bonding Chris J. Pickard Why should a theorist care? Where the atoms are determines what they do Where the atoms can be determines what we can do Overview of Structure
Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I
 Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I By: James L. Holly, MD Oxidative Stress refers to effects from endogenous (produced in the body) toxins (free radicals) produced in the body by normal metabolism
Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I By: James L. Holly, MD Oxidative Stress refers to effects from endogenous (produced in the body) toxins (free radicals) produced in the body by normal metabolism
Why is a Comprehensive Metabolic Blood Chemistry panel included in the FNHP?
 Why is a Comprehensive Metabolic Blood Chemistry panel included in the FNHP? (A cornerstone of my approach is test, don t guess. Identifying the underlying patterns contributing to poor health is the key
Why is a Comprehensive Metabolic Blood Chemistry panel included in the FNHP? (A cornerstone of my approach is test, don t guess. Identifying the underlying patterns contributing to poor health is the key
ATOMS. Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 3 ATOMS AND MOLECULES Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following correctly represents 360 g of water? (i) 2 moles of H 2 0 (ii) 20 moles of water (iii) 6.022 10 23 molecules of water (iv)
Chapter 3 ATOMS AND MOLECULES Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following correctly represents 360 g of water? (i) 2 moles of H 2 0 (ii) 20 moles of water (iii) 6.022 10 23 molecules of water (iv)
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012. Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation. System
 Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
Chapter 11. Electrochemistry Oxidation and Reduction Reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chapter 11 Electrochemistry Oxidation and Reduction Reactions An oxidation and reduction reaction occurs in both aqueous solutions and in reactions where substances are burned
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chapter 11 Electrochemistry Oxidation and Reduction Reactions An oxidation and reduction reaction occurs in both aqueous solutions and in reactions where substances are burned
How To Understand The Human Body
 Introduction to Biology and Chemistry Outline I. Introduction to biology A. Definition of biology - Biology is the study of life. B. Characteristics of Life 1. Form and size are characteristic. e.g. A
Introduction to Biology and Chemistry Outline I. Introduction to biology A. Definition of biology - Biology is the study of life. B. Characteristics of Life 1. Form and size are characteristic. e.g. A
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research
 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death HST.035 Spring 2003 Overview of Cell Injury Cells
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death HST.035 Spring 2003 Overview of Cell Injury Cells
14/11/2014. Copper supply affects growth performance and health in growing pigs. Outline. Copper as essential trace elements
 Copper supply affects growth performance and health in growing pigs Themamiddag 4 november 2014 Outline Introduction Copper as essential trace element Paul Bikker, Jurgen van Baal, Roselinde Goselink Presence:
Copper supply affects growth performance and health in growing pigs Themamiddag 4 november 2014 Outline Introduction Copper as essential trace element Paul Bikker, Jurgen van Baal, Roselinde Goselink Presence:
Exercise 3.5 - Naming Binary Covalent Compounds:
 Chapter Exercise Key 1 Chapter Exercise Key Exercise.1 Classifying Compounds: Classify each of the following substances as either a molecular compound or an ionic compound. a. formaldehyde, CH 2 O (used
Chapter Exercise Key 1 Chapter Exercise Key Exercise.1 Classifying Compounds: Classify each of the following substances as either a molecular compound or an ionic compound. a. formaldehyde, CH 2 O (used
Preventive Telemedicine Challenges in Russia
 Preventive Telemedicine Challenges in Russia Sergey Koldybaev Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences E mail: phyto@list.ru Features of Russian Healthcare Most of qualified physicians concentrate
Preventive Telemedicine Challenges in Russia Sergey Koldybaev Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences E mail: phyto@list.ru Features of Russian Healthcare Most of qualified physicians concentrate
A FDA Perspective on Nanomedicine Current Initiatives in the US
 A FDA Perspective on Nanomedicine Current Initiatives in the US Carlos Peña, PhD Office of the Commissioner FDA September 3, 2010 Outline Context Nanotechnology Task Force report summary Identification
A FDA Perspective on Nanomedicine Current Initiatives in the US Carlos Peña, PhD Office of the Commissioner FDA September 3, 2010 Outline Context Nanotechnology Task Force report summary Identification
Custom Antibody Services
 prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM. Section B: Enzymes
 CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
 Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions
 7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions Multiple choice questions 1 B 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 A 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 B Structured questions 11 a i Maintenance of a constant internal environment within set limits i Concentration
7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions Multiple choice questions 1 B 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 A 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 B Structured questions 11 a i Maintenance of a constant internal environment within set limits i Concentration
The application of nanotechnology in the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. By Aniketa Khushu PASS WITH MERIT
 The application of nanotechnology in the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis By Aniketa Khushu PASS WITH MERIT Research Paper based on Pathology Lectures at Medlink 2010 1 Abstract: Introduction:
The application of nanotechnology in the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis By Aniketa Khushu PASS WITH MERIT Research Paper based on Pathology Lectures at Medlink 2010 1 Abstract: Introduction:
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Chapter 5 Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev: Russian Chemist credited with the discovery of the periodic table.
 Chapter 5 Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev: Russian Chemist credited with the discovery of the periodic table. How did he organize the elements? According to similarities in their chemical and physical
Chapter 5 Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev: Russian Chemist credited with the discovery of the periodic table. How did he organize the elements? According to similarities in their chemical and physical
Bottlenecks in Clinical Source Material Acquisition. Aby J. Mathew, PhD May 5, 2009 ISCT Annual Meeting San Diego, CA amathew@biolifesolutions.
 Bottlenecks in Clinical Source Material Acquisition Aby J. Mathew, PhD May 5, 2009 ISCT Annual Meeting San Diego, CA amathew@biolifesolutions.com Biopreservation What s the issue? Biopreservation considerations
Bottlenecks in Clinical Source Material Acquisition Aby J. Mathew, PhD May 5, 2009 ISCT Annual Meeting San Diego, CA amathew@biolifesolutions.com Biopreservation What s the issue? Biopreservation considerations
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies. Biochemistry Journal. August 1, 2007 405, pp.
 Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Managing Joint Venture Arrangements Between Two Biotech Companies: A Case Report. Dr. Jan Mous Midatech / PharMida May 21 st 2014
 Managing Joint Venture Arrangements Between Two Biotech Companies: A Case Report Dr. Jan Mous Midatech / PharMida May 21 st 2014 1 Midatech Ltd. Corporate verview Founded 2000 in xford, England Drug development
Managing Joint Venture Arrangements Between Two Biotech Companies: A Case Report Dr. Jan Mous Midatech / PharMida May 21 st 2014 1 Midatech Ltd. Corporate verview Founded 2000 in xford, England Drug development
100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals.
 2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1
 Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
3. What would you predict for the intensity and binding energy for the 3p orbital for that of sulfur?
 PSI AP Chemistry Periodic Trends MC Review Name Periodic Law and the Quantum Model Use the PES spectrum of Phosphorus below to answer questions 1-3. 1. Which peak corresponds to the 1s orbital? (A) 1.06
PSI AP Chemistry Periodic Trends MC Review Name Periodic Law and the Quantum Model Use the PES spectrum of Phosphorus below to answer questions 1-3. 1. Which peak corresponds to the 1s orbital? (A) 1.06
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM AS A THERAPEUTIC TARGET FOR LIVER DISEASES. Key Points
 December 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 3, pages 36-40) THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM AS A THERAPEUTIC TARGET FOR LIVER DISEASES By Sophie Lotersztajn, PhD, Ariane Mallat, MD, PhD Inserm U841, Hôpital Henri Mondor,
December 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 3, pages 36-40) THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM AS A THERAPEUTIC TARGET FOR LIVER DISEASES By Sophie Lotersztajn, PhD, Ariane Mallat, MD, PhD Inserm U841, Hôpital Henri Mondor,
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Industrial tracers - Finding leaks and blockages
 Cancer Treatment Alpha radiation is used to treat various forms of cancer. This process, called unsealed source radiotherapy, involves inserting tiny amounts of radium-226 into cancerous organs. The alpha
Cancer Treatment Alpha radiation is used to treat various forms of cancer. This process, called unsealed source radiotherapy, involves inserting tiny amounts of radium-226 into cancerous organs. The alpha
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy
 What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
Laser-induced modification of metal nanoparticles formed by laser ablation technique in liquids
 Applied Surface Science 247 (2005) 418 422 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Laser-induced modification of metal nanoparticles formed by laser ablation technique in liquids N.V. Tarasenko *, A.V. Butsen,
Applied Surface Science 247 (2005) 418 422 www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Laser-induced modification of metal nanoparticles formed by laser ablation technique in liquids N.V. Tarasenko *, A.V. Butsen,
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
OPTIMIZING OF THERMAL EVAPORATION PROCESS COMPARED TO MAGNETRON SPUTTERING FOR FABRICATION OF TITANIA QUANTUM DOTS
 OPTIMIZING OF THERMAL EVAPORATION PROCESS COMPARED TO MAGNETRON SPUTTERING FOR FABRICATION OF TITANIA QUANTUM DOTS Vojtěch SVATOŠ 1, Jana DRBOHLAVOVÁ 1, Marian MÁRIK 1, Jan PEKÁREK 1, Jana CHOMOCKÁ 1,
OPTIMIZING OF THERMAL EVAPORATION PROCESS COMPARED TO MAGNETRON SPUTTERING FOR FABRICATION OF TITANIA QUANTUM DOTS Vojtěch SVATOŠ 1, Jana DRBOHLAVOVÁ 1, Marian MÁRIK 1, Jan PEKÁREK 1, Jana CHOMOCKÁ 1,
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy
 Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
NUTRITION OF THE BODY
 5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
Non-clinical development of biologics
 Aurigon Life Science GmbH Non-clinical development of biologics Requirements, challenges and case studies Committed to Life. Sigrid Messemer vet. med. M4 Seminar March 10 th 2014 Aurigon - your full service
Aurigon Life Science GmbH Non-clinical development of biologics Requirements, challenges and case studies Committed to Life. Sigrid Messemer vet. med. M4 Seminar March 10 th 2014 Aurigon - your full service
M. Ugolini 1,2, G. Babini 1,2, G. Baiocco 1,2, D. Cappelletti 1,2, L. Mariotti 1,2, J. Morini 1,2,3 and A. Ottolenghi 1,2
 M. Ugolini 1,2, G. Babini 1,2, G. Baiocco 1,2, D. Cappelletti 1,2, L. Mariotti 1,2, J. Morini 1,2,3 and A. Ottolenghi 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale
M. Ugolini 1,2, G. Babini 1,2, G. Baiocco 1,2, D. Cappelletti 1,2, L. Mariotti 1,2, J. Morini 1,2,3 and A. Ottolenghi 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy 2 Istituto Nazionale
Chemical Engineering - CHEN
 Auburn University 1 Chemical Engineering - CHEN Courses CHEN 2100 PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (4) LEC. 3. LAB. 3. Pr. (CHEM 1110 or CHEM 1117 or CHEM 1030) and (MATH 1610 or MATH 1613 or MATH 1617
Auburn University 1 Chemical Engineering - CHEN Courses CHEN 2100 PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (4) LEC. 3. LAB. 3. Pr. (CHEM 1110 or CHEM 1117 or CHEM 1030) and (MATH 1610 or MATH 1613 or MATH 1617
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Chemical Engineering. Ohio Academic Content Standards Grade. Lesson Summary:
 Chemical Engineering Lesson Summary: Chemical engineering involves the design, construction, and operation of plants and machinery to make products such as acids, dyes, drugs, plastics, and synthetic materials.
Chemical Engineering Lesson Summary: Chemical engineering involves the design, construction, and operation of plants and machinery to make products such as acids, dyes, drugs, plastics, and synthetic materials.
Delentigo The age spot solution
 The age spot solution The age spot solution Erasing Age Spots and Equalizing the Skin Tone Delentigo targets and lightens age spots by combining two active substances incorporated into separate liposomes:
The age spot solution The age spot solution Erasing Age Spots and Equalizing the Skin Tone Delentigo targets and lightens age spots by combining two active substances incorporated into separate liposomes:
neutrons are present?
 AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
