KMχ /γ = (1.3E -23 )(88.2)( E 20 ) 3.05 = T g = (302)*( / ( ) ) = 44.5 o K
|
|
|
- Josephine Reeves
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problem Set #5 Solutions Chemical ngineering 60/60 Problem 8.4 We re given T g as 0 o C and given the viscosity at 5 o C, and asked to find the viscosity at 40 o C. We can use equation 8.48 (WLF equation). Assume in this equation that log is log base 0. We solve for η g and use this value to determine η(40). Base 0 η g = η(t) exp(40.57(t-t g )/(5.6+T-T g )) = Poises, with T=5 o, T g =0 o C, η(5)=6 8 Poises η(40 o C) = η g exp(40.57(t g -T)/(-5.6-T+T g )) =.97 6 Poises, using T=40 o C, T g =0 o C, η g from above. As expected viscosity decreases with increasing temperature. Problem 8. The copolymerization of divinyl benzene (structure on page 00 in sperling) could be viewed in two manners. First, copolymerization in itself can act to elevate the glass transition temperature. Second, the divinyl benzene is difunctional and can act as a crosslinker. The relative magnitudes of the two shifts in T g can be calculated using the formulas of sections 8.8. and , respectively. Copolymerization: We use the Fox equation. This makes several assumptions, including assumed miscibility and that the product of the c pi T i = constant for both the components; according to Sperling, this latter condition is applicable for random copolymers. The mass fractions of divinyl benzene and vinyl acetate are M =(30)(0.05)/((0.05*30)+0.95*86))=0.0737, and M =-M =0.963, respectively. We are given T =(9+73 o K)=30 o K. We are not given any information on the glass transition temperature of poly(divinyl benzene). To first approximation, we can treat it as being very high molecular weight polystyrene, since we know that both molecular weight and cross-linking increase T g. But we d expect T g to be even higher since polymerization of a difunctional monomer will likely lead to a very highly crosslinked, perhaps even fully gelled polymer. From Table 8.8, a T g for polystyrene is 368 o C. From Figure 8.5, very high molecular weight PS has T g ~378 o C. Let s assume a T g of 400 o K, and see what kind of effect this has on the copolymer T g. T = (0.0737/ /30) - = o K, or a shift in T g of close to 5.6 o. Remember this is considering a fairly high T g for the divinyl benzene component. Crosslinking: quation 8.6 is the pertinent equation. K is given in Table 8.9 as roughly.3-3. M is the mer molecular weight. We use a molar average of the two components: eg M = (0.05* *86) = 88. g/mol. χ is the number of crosslinkers by gram. Assume
2 that each divinyl benzene act as a crosslinker, and consider a 00 mol sample. The total number of crosslinkers (divinyl benzene molecules) in the sample is 5 mol * molecules/mol. The total weight of this sample is 5 mol * 30 g/mol + 95 mol * 86 g/mol = 880g. Then χ =5 * / 880 = g -. γ is the number of flexible bonds per mer, backbone, and side chain. Table 8.9 gives values of and 4 for polystyrene and PMMA respectively. This variable is somewhat cryptic; a first guess would be that all single bonds are flexible bonds; styrene then has two noting that the vinyl double bond becomes a single bond on polymerization. By the same treatment, however, methyl methacrylate would have γ=5 but its real value is 4. The exact value will not change the shift in T g immensely, so taking styrene and methyl methacrylate as analogous to divinyl benzene and vinyl acetate, respectively, gives γ = 4 and γ = 3, respectively. A molar average of these values gives γ = 3.05 which is what we use. Then we have: KMχ /γ = (.3-3 )(88.)( ) 3.05 = T g = (30)*( / (-0.834) ) = 44.5 o K This is a much larger value than that obtained by the copolymerization method. Thus we see that crosslinking in this case plays a much larger role in increasing the glass transition temperature. Combining the two results, we might expect the new T g to be o C. Problem 9. We have a rectangular prism of an elastomer which is crosslinked with a tetrafunctional molecule. We are given the stress at 5 o C in this material for an elongation of α=5/0 =.5. a) The appropriate equation is 9.70, and for a tetrafunctional crosslinker the front factor is ½. We assume that there is no swelling so r i =r o. Solving for n, n = σ/kt (α - /α ) - Note: 0 dynes/cm = N/m. Substituting in values k=.38-3 J/K, T=98 o K, α=.5, and σ =.5 6 N/m yield n = 57.5 mol m -3 = mol cm -3. Multiplying by advogodro s number yields chains/cm 3. b) Using the results of part a) and changing α =.5 gives σ = dyne/cm. c) Here we just change the temperature so T=373 o C, and α =.5 again. We get σ = dyne/cm. Problem 9.3 We consider only the final state. A drawing of this state is shown below: A B 0 o C x x 50 o C
3 We make the assertion that any cross section is subject to the same amount of force*. If it were not, then rearrangement would occur (ie the line between the two pieces or rubber band would shift). Hence we can write two equations, one each for the force in each of the rubber bands, and equate the two. This approach allows for a change in the cross sectional area in each rubber band but assumes an infinitely fast jump in dimensions at the interface. We also assume ideal elastomers, in which poisson s ratio is ½, and volume is conserved during deformation. Hence if the original cross sectional area of the bands was A, then the area at any deformation is given by A/α. Define: α A = (40-x)/0 α B = (x)/0 In Rubber Band A: F = A/α A RTn(α A /α A ) In B: F = A/α B RTn(α B /α B ) Now we simply equate the two forces and solve for x with eg maple. (Maple did a poor job solving analytically, so I just plotted the two functions to solve for x). We come up with an answer of x = 4. cm. * Why force and not stress? My thought is the following. The condition for equilibrium from eg Newton s laws is really summation forces = 0. If we consider a particle or mass and draw a free body diagram for it, we consider all the forces on it, not the stresses. In this case the stresses will not be the same because the cross sectional areas of each rubber band are different. During the derivations in class however, we assumed uniform cross sectional areas, so the forces and stresses were both equal across elements in series.
4 > amm:=/aa*ta*(aa - /aa^); > bmm:=/ab*tb*(ab - /ab^); amm := bmm := TA aa aa TB ab ab aa ab > aa:=(40-x)/0; > ab:=x/0; > TA:=0+73; > TB:=50+73; aa := 4 0 x ab := 0 x TA := 93 TB := 43 > plot({amm,bmm}, x= ); >
5 Problem 0-3 The total strain in the system can be determined as the sum of the strains in the upper dashpot and in the lower spring/dashpot system, that is: ε = ε + ε Region ε Region ε The stress which is applied is a function of t as shown below: σ t o a) Derive the strain (length) for 0<t<t o We can consider regions and separately, each having a stress σ applied to it. This assertion can be proven just by taking a free body diagram at the node between and. For the strain ε, we can write d ε dt = σ, η so integrating with initial condition ε (t=0) = 0 yields: ε = σ t, η so this portion of the model extends linearly with time. For the strain ε, we must consider that the strain in both arms must be the same, and that the total stress supported by both arms is equal to the sum of the stresses in each arm. If the stress across the spring is σ s and the stress across the dashpot is σ d then we know that t σ = σ d + σ s σ d ε dt = d η σ ε s =
6 Solving for the stresses in the last two equations and plugging them back into the first equation gives dε σ = η + ε quation * dt Solving this equation by use of an integrating factor or other means yields = σ t ε exp( η So this region begins with zero strain (the dashpot prevents instantaneous deformation) and increases exponentially to the limiting value dictated by the spring. Therefore the total strain in of the system in the region 0<t<t o is = + = σ + σ ε ε ε t exp( η t η A plot of this strain is shown below schematically. ε ε σ/η ε σ/ b) For this portion we want the strain for t>t o. The stress is removed and the system allowed to relax. Again the strain is that for the two regions added. The dashpot at the top of the system cannot relax without a restoring force to cause it to contract. Since there is no such storing force (the applied stress is zero, not compressive), it remains strained to a value ε = σ for all t>t o. The second region can relax however. The spring portion asserts t η o a restoring force because it is stretched. This causes a decrease in the strain toward zero, but again the rate is limited by the dashpot. Qualitatively we expect an exponential decrease in strain from the value at t o to zero with infinite time. This can be shown by considering equation * (which still applies) and setting σ=0.
7 η dε η dε =, or rearranging = dt. Integrating from times t dt o to t with the ε ε initial condition that = 0 ( ) σ t ε t o exp( yields η ( ) exp( t0 ε t = σ exp( ( t η η o t )) As predicted, this starts at ε (t o ) at t=t o and decays to zero with time. Again combining the strains yields total strain as a function of time t>t o. ( ) exp( t0 ε exp( t = σ to + σ ( t t)) o η η η A schematic plot is shown below. ε (t o ) σ/η t o t = t o Problem 0-4 Given Data: T g = 5 o C T = 30 o C n = -4 mol/cm 3 η g = 3 poises σ = 7 dynes/cm We are told that obeys rubber elasticity theory and viscosity obeys the WLF equation. We are working with a polymer following the Kelvin model (spring and dashpot in parallel). a) The governing equation for a creep experiment within the Kelvin model was already derived in the previous homework problem as ε = σ exp( t. Note that this η
8 derivation assumes that is independent of strain. In actuality this is only true for small strains, as discussed in Sperling. For small strains, ~3nRT; for larger strains = σ/ε = nrt(α-/α ) (α-)**, since ε = (l-l o )/ l o = l/ l o - = α-. We will assume only small strains apply to simplify the problem. =3nRT = 3 ( -4 mol/cm 3 )(0 6 cm 3 /m 3 )(73+30 o K)(8.34 J/molK) = N/m or dynes/cm. Viscosity obeys the WLF equation. We use the universal form of this equation log(η/η g )=-7.44(T-T g )/(5.66+T-T g ). With T-T g =5 o K and η g as given in the problem, η = Poises. One poise is a g/cms = 0 - Ns/m. So since σ/ = 7 / =.33, and /η = / s - = s -, then ε =.33 ( exp( t)) with t being in seconds, ε is unitless. The required plot is shown below. Strain Two points are worth making. First, the limiting value dictated by the spring portion of the model is reached within a few seconds. Second, the strains predicted by our treatment are reality small, so the treatment with = 3nRT is self consistent. FYI: To solve the problem exactly for larger strains one can use the exact form of the young s modulus to arrive at a non-linear first order OD for strain as a function of time. We use the same approach taken in the previous problem, arriving at equation *, d ε σ = η + ε dt. Rather than having as a constant, we assume it is a function of strain. From Sperling eqn 9.36 =nrt(α +/α).** Since α=ε+, this becomes = nrt ( ε + ) + ε +.
9 Dividing both sides by nrt gives the OD as σ η ε = + ε ( ε + ) + nrt nrt t ε +. σ η valuating the constants gives: = and = nrt nrt. Using maple s Dplot numerical plotting method gives strain as a function of time shown below: This approach does make a difference in both the rate of creep (faster) and the limiting strain (lower) compared to the case where is independent of strain. b) The rate of creep is the slope of the strain versus time plot. Obviously it might be of interest to slow this down to retain part dimensions, etc. Taking dε/dt we find that this rate is given by dε σ = exp( t / η) dt η Note that this equation gives the largest values (fastest rates of creep) at low times. This is obvious from the graph above. So we have three variables to change to slow down this rate. A decrease in the applied stress with decrease the rate of creep for all times. Sometimes though this is not an option as the part is required to be used in certain dictated working conditions. An increase in young s modulus will also decrease the creep rate for all times greater than t=0. A change in viscosity is a bit more complicated, as viscosity appears twice in the equation with competing trends. Plotting several values of viscosity shows that for low times, the rate decreases with increasing viscosity, while above a certain value of time, the creep rate increases with increasing viscosity. However the total creep experienced (proportional to the area under the curves from t=0 to infinity) is the same in all cases, provided the other variables are held constant. Since in service we would mostly be
10 concerned with the initial creep rate, then an increase in viscosity would be advantageous. Note that increasing the crosslinking density can increase both young s modulus (# active chain segments increases) and viscosity (leads to increase in T g ) making this advantageous for creep control. Creep Rate Increasing η ** Note: if you just use = σ / ε vs. Sperling 9.36 you get a different equation for. I m not sure why this discrepancy comes about. The results are similar.
HW 10. = 3.3 GPa (483,000 psi)
 HW 10 Problem 15.1 Elastic modulus and tensile strength of poly(methyl methacrylate) at room temperature [20 C (68 F)]. Compare these with the corresponding values in Table 15.1. Figure 15.3 is accurate;
HW 10 Problem 15.1 Elastic modulus and tensile strength of poly(methyl methacrylate) at room temperature [20 C (68 F)]. Compare these with the corresponding values in Table 15.1. Figure 15.3 is accurate;
Long term performance of polymers
 1.0 Introduction Long term performance of polymers Polymer materials exhibit time dependent behavior. The stress and strain induced when a load is applied are a function of time. In the most general form
1.0 Introduction Long term performance of polymers Polymer materials exhibit time dependent behavior. The stress and strain induced when a load is applied are a function of time. In the most general form
M n = (DP)m = (25,000)(104.14 g/mol) = 2.60! 10 6 g/mol
 14.4 (a) Compute the repeat unit molecular weight of polystyrene. (b) Compute the number-average molecular weight for a polystyrene for which the degree of polymerization is 25,000. (a) The repeat unit
14.4 (a) Compute the repeat unit molecular weight of polystyrene. (b) Compute the number-average molecular weight for a polystyrene for which the degree of polymerization is 25,000. (a) The repeat unit
Physics 3 Summer 1989 Lab 7 - Elasticity
 Physics 3 Summer 1989 Lab 7 - Elasticity Theory All materials deform to some extent when subjected to a stress (a force per unit area). Elastic materials have internal forces which restore the size and
Physics 3 Summer 1989 Lab 7 - Elasticity Theory All materials deform to some extent when subjected to a stress (a force per unit area). Elastic materials have internal forces which restore the size and
Chemical Kinetics. 2. Using the kinetics of a given reaction a possible reaction mechanism
 1. Kinetics is the study of the rates of reaction. Chemical Kinetics 2. Using the kinetics of a given reaction a possible reaction mechanism 3. What is a reaction mechanism? Why is it important? A reaction
1. Kinetics is the study of the rates of reaction. Chemical Kinetics 2. Using the kinetics of a given reaction a possible reaction mechanism 3. What is a reaction mechanism? Why is it important? A reaction
Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied
 Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied Stress and strain fracture or engineering point of view: allows to predict the
Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied Stress and strain fracture or engineering point of view: allows to predict the
Polymer Melt Rheology. Introduction to Viscoelastic Behavior. Time-Temperature Equivalence
 Topics to be Covered Polymer Melt Rheology Introduction to Viscoelastic Behavior Time-Temperature Equivalence Chapter 11 in CD (Polymer Science and Engineering) Polymer Melt Rheology δ τ xy Newton s Law
Topics to be Covered Polymer Melt Rheology Introduction to Viscoelastic Behavior Time-Temperature Equivalence Chapter 11 in CD (Polymer Science and Engineering) Polymer Melt Rheology δ τ xy Newton s Law
Notes on Polymer Rheology Outline
 1 Why is rheology important? Examples of its importance Summary of important variables Description of the flow equations Flow regimes - laminar vs. turbulent - Reynolds number - definition of viscosity
1 Why is rheology important? Examples of its importance Summary of important variables Description of the flow equations Flow regimes - laminar vs. turbulent - Reynolds number - definition of viscosity
SHORE A DUROMETER AND ENGINEERING PROPERTIES
 SHORE A DUROMETER AND ENGINEERING PROPERTIES Written by D.L. Hertz, Jr. and A.C. Farinella Presented at the Fall Technical Meeting of The New York Rubber Group Thursday, September 4, 1998 by D.L. Hertz,
SHORE A DUROMETER AND ENGINEERING PROPERTIES Written by D.L. Hertz, Jr. and A.C. Farinella Presented at the Fall Technical Meeting of The New York Rubber Group Thursday, September 4, 1998 by D.L. Hertz,
HEAT UNIT 1.1 KINETIC THEORY OF GASES. 1.1.1 Introduction. 1.1.2 Postulates of Kinetic Theory of Gases
 UNIT HEAT. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES.. Introduction Molecules have a diameter of the order of Å and the distance between them in a gas is 0 Å while the interaction distance in solids is very small. R. Clausius
UNIT HEAT. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES.. Introduction Molecules have a diameter of the order of Å and the distance between them in a gas is 0 Å while the interaction distance in solids is very small. R. Clausius
Objectives. Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity and ductility of given materials.
 Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
Chapter Outline. Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads?
 Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads? Stress and Strain Tension Compression Shear Torsion Elastic deformation Plastic Deformation Yield Strength Tensile Strength Ductility
Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads? Stress and Strain Tension Compression Shear Torsion Elastic deformation Plastic Deformation Yield Strength Tensile Strength Ductility
AN EXPLANATION OF JOINT DIAGRAMS
 AN EXPLANATION OF JOINT DIAGRAMS When bolted joints are subjected to external tensile loads, what forces and elastic deformation really exist? The majority of engineers in both the fastener manufacturing
AN EXPLANATION OF JOINT DIAGRAMS When bolted joints are subjected to external tensile loads, what forces and elastic deformation really exist? The majority of engineers in both the fastener manufacturing
Developing an ANSYS Creep Model for Polypropylene from Experimental Data
 Developing an ANSYS Creep Model for Polypropylene from Experimental Data Abstract Martin J. Dropik David H. Johnson, P.E. David E. Roth, P.E. Penn State-Erie, Erie, PA, USA This paper describes a procedure
Developing an ANSYS Creep Model for Polypropylene from Experimental Data Abstract Martin J. Dropik David H. Johnson, P.E. David E. Roth, P.E. Penn State-Erie, Erie, PA, USA This paper describes a procedure
Lecture 17. Last time we saw that the rotational analog of Newton s 2nd Law is
 Lecture 17 Rotational Dynamics Rotational Kinetic Energy Stress and Strain and Springs Cutnell+Johnson: 9.4-9.6, 10.1-10.2 Rotational Dynamics (some more) Last time we saw that the rotational analog of
Lecture 17 Rotational Dynamics Rotational Kinetic Energy Stress and Strain and Springs Cutnell+Johnson: 9.4-9.6, 10.1-10.2 Rotational Dynamics (some more) Last time we saw that the rotational analog of
Shelf Life Prediction Of Medical Gloves
 Shelf Life Prediction Of Medical Gloves Presented for the ASTM WG Committee for Medical Glove Expiration Dating Guidance By Uday Karmarkar Akron Rubber Development Laboratory, Inc. ardl@akron.infi.net
Shelf Life Prediction Of Medical Gloves Presented for the ASTM WG Committee for Medical Glove Expiration Dating Guidance By Uday Karmarkar Akron Rubber Development Laboratory, Inc. ardl@akron.infi.net
Scalars, Vectors and Tensors
 Scalars, Vectors and Tensors A scalar is a physical quantity that it represented by a dimensional number at a particular point in space and time. Examples are hydrostatic pressure and temperature. A vector
Scalars, Vectors and Tensors A scalar is a physical quantity that it represented by a dimensional number at a particular point in space and time. Examples are hydrostatic pressure and temperature. A vector
Prelab Exercises: Hooke's Law and the Behavior of Springs
 59 Prelab Exercises: Hooke's Law and the Behavior of Springs Study the description of the experiment that follows and answer the following questions.. (3 marks) Explain why a mass suspended vertically
59 Prelab Exercises: Hooke's Law and the Behavior of Springs Study the description of the experiment that follows and answer the following questions.. (3 marks) Explain why a mass suspended vertically
Bungee Constant per Unit Length & Bungees in Parallel. Skipping school to bungee jump will get you suspended.
 Name: Johanna Goergen Section: 05 Date: 10/28/14 Partner: Lydia Barit Introduction: Bungee Constant per Unit Length & Bungees in Parallel Skipping school to bungee jump will get you suspended. The purpose
Name: Johanna Goergen Section: 05 Date: 10/28/14 Partner: Lydia Barit Introduction: Bungee Constant per Unit Length & Bungees in Parallel Skipping school to bungee jump will get you suspended. The purpose
Solution for Homework #1
 Solution for Homework #1 Chapter 2: Multiple Choice Questions (2.5, 2.6, 2.8, 2.11) 2.5 Which of the following bond types are classified as primary bonds (more than one)? (a) covalent bonding, (b) hydrogen
Solution for Homework #1 Chapter 2: Multiple Choice Questions (2.5, 2.6, 2.8, 2.11) 2.5 Which of the following bond types are classified as primary bonds (more than one)? (a) covalent bonding, (b) hydrogen
Molar Mass of Polyvinyl Alcohol by Viscosity
 Molar Mass of Polyvinyl Alcohol by Viscosity Introduction Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVOH) is a linear polymer (i. e., it has little branching) of Ethanol monomer units: -CH 2 -CHOH- Unlike most high molar mass
Molar Mass of Polyvinyl Alcohol by Viscosity Introduction Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVOH) is a linear polymer (i. e., it has little branching) of Ethanol monomer units: -CH 2 -CHOH- Unlike most high molar mass
Fluid Mechanics: Static s Kinematics Dynamics Fluid
 Fluid Mechanics: Fluid mechanics may be defined as that branch of engineering science that deals with the behavior of fluid under the condition of rest and motion Fluid mechanics may be divided into three
Fluid Mechanics: Fluid mechanics may be defined as that branch of engineering science that deals with the behavior of fluid under the condition of rest and motion Fluid mechanics may be divided into three
Diffusion and Fluid Flow
 Diffusion and Fluid Flow What determines the diffusion coefficient? What determines fluid flow? 1. Diffusion: Diffusion refers to the transport of substance against a concentration gradient. ΔS>0 Mass
Diffusion and Fluid Flow What determines the diffusion coefficient? What determines fluid flow? 1. Diffusion: Diffusion refers to the transport of substance against a concentration gradient. ΔS>0 Mass
Gases. States of Matter. Molecular Arrangement Solid Small Small Ordered Liquid Unity Unity Local Order Gas High Large Chaotic (random)
 Gases States of Matter States of Matter Kinetic E (motion) Potential E(interaction) Distance Between (size) Molecular Arrangement Solid Small Small Ordered Liquid Unity Unity Local Order Gas High Large
Gases States of Matter States of Matter Kinetic E (motion) Potential E(interaction) Distance Between (size) Molecular Arrangement Solid Small Small Ordered Liquid Unity Unity Local Order Gas High Large
3.3. Rheological Behavior of Vinyl Ester Resins
 3.3. Rheological Behavior of Vinyl Ester Resins 3.3.1. Introduction Rheology is the study of the deformation and flow of matter 1. There has been significant appreciation of the importance of the rheological
3.3. Rheological Behavior of Vinyl Ester Resins 3.3.1. Introduction Rheology is the study of the deformation and flow of matter 1. There has been significant appreciation of the importance of the rheological
10.7 Kinetic Molecular Theory. 10.7 Kinetic Molecular Theory. Kinetic Molecular Theory. Kinetic Molecular Theory. Kinetic Molecular Theory
 The first scheduled quiz will be given next Tuesday during Lecture. It will last 5 minutes. Bring pencil, calculator, and your book. The coverage will be pp 364-44, i.e. Sections 0.0 through.4. 0.7 Theory
The first scheduled quiz will be given next Tuesday during Lecture. It will last 5 minutes. Bring pencil, calculator, and your book. The coverage will be pp 364-44, i.e. Sections 0.0 through.4. 0.7 Theory
Viscoelasticity of Polymer Fluids.
 Viscoelasticity of Polymer Fluids. Main Properties of Polymer Fluids. Entangled polymer fluids are polymer melts and concentrated or semidilute (above the concentration c) solutions. In these systems polymer
Viscoelasticity of Polymer Fluids. Main Properties of Polymer Fluids. Entangled polymer fluids are polymer melts and concentrated or semidilute (above the concentration c) solutions. In these systems polymer
Statistical Mechanics, Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas. 8.01t Nov 22, 2004
 Statistical Mechanics, Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas 8.01t Nov 22, 2004 Statistical Mechanics and Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Old & Fundamental Understanding of Heat (I.e. Steam) Engines Part of Physics Einstein
Statistical Mechanics, Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas 8.01t Nov 22, 2004 Statistical Mechanics and Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Old & Fundamental Understanding of Heat (I.e. Steam) Engines Part of Physics Einstein
Unified Lecture # 4 Vectors
 Fall 2005 Unified Lecture # 4 Vectors These notes were written by J. Peraire as a review of vectors for Dynamics 16.07. They have been adapted for Unified Engineering by R. Radovitzky. References [1] Feynmann,
Fall 2005 Unified Lecture # 4 Vectors These notes were written by J. Peraire as a review of vectors for Dynamics 16.07. They have been adapted for Unified Engineering by R. Radovitzky. References [1] Feynmann,
AP1 Electricity. 1. A student wearing shoes stands on a tile floor. The students shoes do not fall into the tile floor due to
 1. A student wearing shoes stands on a tile floor. The students shoes do not fall into the tile floor due to (A) a force of repulsion between the shoes and the floor due to macroscopic gravitational forces.
1. A student wearing shoes stands on a tile floor. The students shoes do not fall into the tile floor due to (A) a force of repulsion between the shoes and the floor due to macroscopic gravitational forces.
Section 1.4. Difference Equations
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 1.4 Difference Equations At this point almost all of our sequences have had explicit formulas for their terms. That is, we have looked mainly at sequences
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 1.4 Difference Equations At this point almost all of our sequences have had explicit formulas for their terms. That is, we have looked mainly at sequences
= 800 kg/m 3 (note that old units cancel out) 4.184 J 1000 g = 4184 J/kg o C
 Units and Dimensions Basic properties such as length, mass, time and temperature that can be measured are called dimensions. Any quantity that can be measured has a value and a unit associated with it.
Units and Dimensions Basic properties such as length, mass, time and temperature that can be measured are called dimensions. Any quantity that can be measured has a value and a unit associated with it.
Solid Mechanics. Stress. What you ll learn: Motivation
 Solid Mechanics Stress What you ll learn: What is stress? Why stress is important? What are normal and shear stresses? What is strain? Hooke s law (relationship between stress and strain) Stress strain
Solid Mechanics Stress What you ll learn: What is stress? Why stress is important? What are normal and shear stresses? What is strain? Hooke s law (relationship between stress and strain) Stress strain
Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products A B
 Reaction Rates: Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products A B change in number of moles of B Average rate = change in
Reaction Rates: Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products A B change in number of moles of B Average rate = change in
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1
 Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Nuclear Structure. particle relative charge relative mass proton +1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass
 Protons, neutrons and electrons Nuclear Structure particle relative charge relative mass proton 1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass Protons and neutrons make up
Protons, neutrons and electrons Nuclear Structure particle relative charge relative mass proton 1 1 atomic mass unit neutron 0 1 atomic mass unit electron -1 negligible mass Protons and neutrons make up
Spectrophotometry and the Beer-Lambert Law: An Important Analytical Technique in Chemistry
 Spectrophotometry and the Beer-Lambert Law: An Important Analytical Technique in Chemistry Jon H. Hardesty, PhD and Bassam Attili, PhD Collin College Department of Chemistry Introduction: In the last lab
Spectrophotometry and the Beer-Lambert Law: An Important Analytical Technique in Chemistry Jon H. Hardesty, PhD and Bassam Attili, PhD Collin College Department of Chemistry Introduction: In the last lab
Section 1.1 Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines
 Section. Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines Slope The measure of the steepness of a line is called the slope of the line. It is the amount of change in y, the rise, divided by the amount of
Section. Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines Slope The measure of the steepness of a line is called the slope of the line. It is the amount of change in y, the rise, divided by the amount of
CHEMISTRY. Matter and Change. Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3. The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
www.mathsbox.org.uk Displacement (x) Velocity (v) Acceleration (a) x = f(t) differentiate v = dx Acceleration Velocity (v) Displacement x
 Mechanics 2 : Revision Notes 1. Kinematics and variable acceleration Displacement (x) Velocity (v) Acceleration (a) x = f(t) differentiate v = dx differentiate a = dv = d2 x dt dt dt 2 Acceleration Velocity
Mechanics 2 : Revision Notes 1. Kinematics and variable acceleration Displacement (x) Velocity (v) Acceleration (a) x = f(t) differentiate v = dx differentiate a = dv = d2 x dt dt dt 2 Acceleration Velocity
Rheology of polymer systems/ Reologia dos sistemas poliméricos
 Rheology of polymer systems/ Reologia dos sistemas poliméricos 1. Viscosity/Viscosidade Jorge Morgado, IST Polymers Molecular materials in nature COMPLEX behaviour Viscosity of concentrated solu1ons and
Rheology of polymer systems/ Reologia dos sistemas poliméricos 1. Viscosity/Viscosidade Jorge Morgado, IST Polymers Molecular materials in nature COMPLEX behaviour Viscosity of concentrated solu1ons and
We know from the information given that we have an equal mass of each compound, but no real numbers to plug in and find moles. So what can we do?
 How do we figure this out? We know that: 1) the number of oxygen atoms can be found by using Avogadro s number, if we know the moles of oxygen atoms; 2) the number of moles of oxygen atoms can be found
How do we figure this out? We know that: 1) the number of oxygen atoms can be found by using Avogadro s number, if we know the moles of oxygen atoms; 2) the number of moles of oxygen atoms can be found
Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Fall 2005 Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation of Mechanical Energy D.1 Conservative and Non-conservative Force... 2 D.1.1 Introduction...
MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Fall 2005 Review D: Potential Energy and the Conservation of Mechanical Energy D.1 Conservative and Non-conservative Force... 2 D.1.1 Introduction...
Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm)
![Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm) Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm)](/thumbs/40/21435474.jpg) Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999 Equilibrium experiments study how the concentration of reaction products change as a function of reactant concentrations and/or reaction conditions. For
Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999 Equilibrium experiments study how the concentration of reaction products change as a function of reactant concentrations and/or reaction conditions. For
Tensile Testing of Steel
 C 265 Lab No. 2: Tensile Testing of Steel See web for typical report format including: TITL PAG, ABSTRACT, TABL OF CONTNTS, LIST OF TABL, LIST OF FIGURS 1.0 - INTRODUCTION See General Lab Report Format
C 265 Lab No. 2: Tensile Testing of Steel See web for typical report format including: TITL PAG, ABSTRACT, TABL OF CONTNTS, LIST OF TABL, LIST OF FIGURS 1.0 - INTRODUCTION See General Lab Report Format
Stress Relaxation Study of Paper and Plastic Film based Packaging Material
 Master's Degree Thesis ISRN: BTH-AMT-EX--2009/D-02--SE Stress Relaxation Study of Paper and Plastic Film based Packaging Material Rajdip Roy Lu Qi Department of Mechanical Engineering Blekinge Institute
Master's Degree Thesis ISRN: BTH-AMT-EX--2009/D-02--SE Stress Relaxation Study of Paper and Plastic Film based Packaging Material Rajdip Roy Lu Qi Department of Mechanical Engineering Blekinge Institute
2 A bank account for electricity II: flows and taxes
 PHYS 189 Lecture problems outline Feb 3, 2014 Resistors and Circuits Having introduced capacitors, we now expand our focus to another very important component of a circuit resistors. This entails more
PHYS 189 Lecture problems outline Feb 3, 2014 Resistors and Circuits Having introduced capacitors, we now expand our focus to another very important component of a circuit resistors. This entails more
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 1 STRESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following.
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
CHAPTER FIVE. Solutions for Section 5.1. Skill Refresher. Exercises
 CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 265 Solutions for Section 5.1 Skill Refresher S1. Since 1,000,000 = 10 6, we have x = 6. S2. Since 0.01 = 10 2, we have t = 2. S3. Since e 3 = ( e 3) 1/2 = e 3/2, we have z =
CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 265 Solutions for Section 5.1 Skill Refresher S1. Since 1,000,000 = 10 6, we have x = 6. S2. Since 0.01 = 10 2, we have t = 2. S3. Since e 3 = ( e 3) 1/2 = e 3/2, we have z =
The Method of Least Squares. Lectures INF2320 p. 1/80
 The Method of Least Squares Lectures INF2320 p. 1/80 Lectures INF2320 p. 2/80 The method of least squares We study the following problem: Given n points (t i,y i ) for i = 1,...,n in the (t,y)-plane. How
The Method of Least Squares Lectures INF2320 p. 1/80 Lectures INF2320 p. 2/80 The method of least squares We study the following problem: Given n points (t i,y i ) for i = 1,...,n in the (t,y)-plane. How
Mean Field Flory Huggins Lattice Theory
 Mean Field Flory Huggins Lattice Theory Mean field: the interactions between molecules are assumed to be due to the interaction of a given molecule and an average field due to all the other molecules in
Mean Field Flory Huggins Lattice Theory Mean field: the interactions between molecules are assumed to be due to the interaction of a given molecule and an average field due to all the other molecules in
4 Microscopic dynamics
 4 Microscopic dynamics In this section we will look at the first model that people came up with when they started to model polymers from the microscopic level. It s called the Oldroyd B model. We will
4 Microscopic dynamics In this section we will look at the first model that people came up with when they started to model polymers from the microscopic level. It s called the Oldroyd B model. We will
8.2 Elastic Strain Energy
 Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
vap H = RT 1T 2 = 30.850 kj mol 1 100 kpa = 341 K
 Thermodynamics: Examples for chapter 6. 1. The boiling point of hexane at 1 atm is 68.7 C. What is the boiling point at 1 bar? The vapor pressure of hexane at 49.6 C is 53.32 kpa. Assume that the vapor
Thermodynamics: Examples for chapter 6. 1. The boiling point of hexane at 1 atm is 68.7 C. What is the boiling point at 1 bar? The vapor pressure of hexane at 49.6 C is 53.32 kpa. Assume that the vapor
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME 2 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS
 ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
ENGINEERING COMPONENTS EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME ENGINEERING COMPONENTS TUTORIAL 1 STRUCTURAL MEMBERS Structural members: struts and ties; direct stress and strain,
AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations
 AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations Student Guide to Data Analysis New York, NY. College Board, Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks
AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations Student Guide to Data Analysis New York, NY. College Board, Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks
EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES
 Name Section EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to
Name Section EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to
"Essential Mathematics & Statistics for Science" by Dr G Currell & Dr A A Dowman (John Wiley & Sons) Answers to In-Text Questions
 "Essential Mathematics & Statistics for Science" by Dr G Currell & Dr A A Dowman (John Wiley & Sons) Answers to In-Text Questions 5 Logarithmic & Exponential Functions To navigate, use the Bookmarks in
"Essential Mathematics & Statistics for Science" by Dr G Currell & Dr A A Dowman (John Wiley & Sons) Answers to In-Text Questions 5 Logarithmic & Exponential Functions To navigate, use the Bookmarks in
1 Sufficient statistics
 1 Sufficient statistics A statistic is a function T = rx 1, X 2,, X n of the random sample X 1, X 2,, X n. Examples are X n = 1 n s 2 = = X i, 1 n 1 the sample mean X i X n 2, the sample variance T 1 =
1 Sufficient statistics A statistic is a function T = rx 1, X 2,, X n of the random sample X 1, X 2,, X n. Examples are X n = 1 n s 2 = = X i, 1 n 1 the sample mean X i X n 2, the sample variance T 1 =
Rotational Motion: Moment of Inertia
 Experiment 8 Rotational Motion: Moment of Inertia 8.1 Objectives Familiarize yourself with the concept of moment of inertia, I, which plays the same role in the description of the rotation of a rigid body
Experiment 8 Rotational Motion: Moment of Inertia 8.1 Objectives Familiarize yourself with the concept of moment of inertia, I, which plays the same role in the description of the rotation of a rigid body
THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND KINETIC THEORY
 Chapter 14 he Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic heory Chapter 14 HE IDEAL GAS LAW AND KINEIC HEORY REIEW Kinetic molecular theory involves the study of matter, particularly gases, as very small particles in constant
Chapter 14 he Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic heory Chapter 14 HE IDEAL GAS LAW AND KINEIC HEORY REIEW Kinetic molecular theory involves the study of matter, particularly gases, as very small particles in constant
Lesson 39: Kinetic Energy & Potential Energy
 Lesson 39: Kinetic Energy & Potential Energy Total Mechanical Energy We sometimes call the total energy of an object (potential and kinetic) the total mechanical energy of an object. Mechanical energy
Lesson 39: Kinetic Energy & Potential Energy Total Mechanical Energy We sometimes call the total energy of an object (potential and kinetic) the total mechanical energy of an object. Mechanical energy
Physics 1114: Unit 6 Homework: Answers
 Physics 1114: Unit 6 Homework: Answers Problem set 1 1. A rod 4.2 m long and 0.50 cm 2 in cross-sectional area is stretched 0.20 cm under a tension of 12,000 N. a) The stress is the Force (1.2 10 4 N)
Physics 1114: Unit 6 Homework: Answers Problem set 1 1. A rod 4.2 m long and 0.50 cm 2 in cross-sectional area is stretched 0.20 cm under a tension of 12,000 N. a) The stress is the Force (1.2 10 4 N)
Lecture 3: Models of Solutions
 Materials Science & Metallurgy Master of Philosophy, Materials Modelling, Course MP4, Thermodynamics and Phase Diagrams, H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 3: Models of Solutions List of Symbols Symbol G M
Materials Science & Metallurgy Master of Philosophy, Materials Modelling, Course MP4, Thermodynamics and Phase Diagrams, H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 3: Models of Solutions List of Symbols Symbol G M
1. Fluids Mechanics and Fluid Properties. 1.1 Objectives of this section. 1.2 Fluids
 1. Fluids Mechanics and Fluid Properties What is fluid mechanics? As its name suggests it is the branch of applied mechanics concerned with the statics and dynamics of fluids - both liquids and gases.
1. Fluids Mechanics and Fluid Properties What is fluid mechanics? As its name suggests it is the branch of applied mechanics concerned with the statics and dynamics of fluids - both liquids and gases.
FLUID DYNAMICS. Intrinsic properties of fluids. Fluids behavior under various conditions
 FLUID DYNAMICS Intrinsic properties of fluids Fluids behavior under various conditions Methods by which we can manipulate and utilize the fluids to produce desired results TYPES OF FLUID FLOW Laminar or
FLUID DYNAMICS Intrinsic properties of fluids Fluids behavior under various conditions Methods by which we can manipulate and utilize the fluids to produce desired results TYPES OF FLUID FLOW Laminar or
Weight The weight of an object is defined as the gravitational force acting on the object. Unit: Newton (N)
 Gravitational Field A gravitational field as a region in which an object experiences a force due to gravitational attraction Gravitational Field Strength The gravitational field strength at a point in
Gravitational Field A gravitational field as a region in which an object experiences a force due to gravitational attraction Gravitational Field Strength The gravitational field strength at a point in
Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalytic Processes Prof. K. K. Pant Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalytic Processes Prof. K. K. Pant Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module - 03 Lecture 10 Good morning. In my last lecture, I was
Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalytic Processes Prof. K. K. Pant Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module - 03 Lecture 10 Good morning. In my last lecture, I was
Lecture L3 - Vectors, Matrices and Coordinate Transformations
 S. Widnall 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2009 Lecture notes based on J. Peraire Version 2.0 Lecture L3 - Vectors, Matrices and Coordinate Transformations By using vectors and defining appropriate operations between
S. Widnall 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2009 Lecture notes based on J. Peraire Version 2.0 Lecture L3 - Vectors, Matrices and Coordinate Transformations By using vectors and defining appropriate operations between
A Question of Molecular Weight
 A Question of Molecular Weight Dr. Jack Cazes International Division Waters Associates, Inc. 34 Maple St., Milford, MA 01757 The molecular weight of benzene is 78. What is the molecular weight of a given
A Question of Molecular Weight Dr. Jack Cazes International Division Waters Associates, Inc. 34 Maple St., Milford, MA 01757 The molecular weight of benzene is 78. What is the molecular weight of a given
The Quantum Harmonic Oscillator Stephen Webb
 The Quantum Harmonic Oscillator Stephen Webb The Importance of the Harmonic Oscillator The quantum harmonic oscillator holds a unique importance in quantum mechanics, as it is both one of the few problems
The Quantum Harmonic Oscillator Stephen Webb The Importance of the Harmonic Oscillator The quantum harmonic oscillator holds a unique importance in quantum mechanics, as it is both one of the few problems
Ch 8 Potential energy and Conservation of Energy. Question: 2, 3, 8, 9 Problems: 3, 9, 15, 21, 24, 25, 31, 32, 35, 41, 43, 47, 49, 53, 55, 63
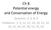 Ch 8 Potential energ and Conservation of Energ Question: 2, 3, 8, 9 Problems: 3, 9, 15, 21, 24, 25, 31, 32, 35, 41, 43, 47, 49, 53, 55, 63 Potential energ Kinetic energ energ due to motion Potential energ
Ch 8 Potential energ and Conservation of Energ Question: 2, 3, 8, 9 Problems: 3, 9, 15, 21, 24, 25, 31, 32, 35, 41, 43, 47, 49, 53, 55, 63 Potential energ Kinetic energ energ due to motion Potential energ
Section 5.0 : Horn Physics. By Martin J. King, 6/29/08 Copyright 2008 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved.
 Section 5. : Horn Physics Section 5. : Horn Physics By Martin J. King, 6/29/8 Copyright 28 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved. Before discussing the design of a horn loaded loudspeaker system, it is
Section 5. : Horn Physics Section 5. : Horn Physics By Martin J. King, 6/29/8 Copyright 28 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved. Before discussing the design of a horn loaded loudspeaker system, it is
Operation Count; Numerical Linear Algebra
 10 Operation Count; Numerical Linear Algebra 10.1 Introduction Many computations are limited simply by the sheer number of required additions, multiplications, or function evaluations. If floating-point
10 Operation Count; Numerical Linear Algebra 10.1 Introduction Many computations are limited simply by the sheer number of required additions, multiplications, or function evaluations. If floating-point
Mathematics 31 Pre-calculus and Limits
 Mathematics 31 Pre-calculus and Limits Overview After completing this section, students will be epected to have acquired reliability and fluency in the algebraic skills of factoring, operations with radicals
Mathematics 31 Pre-calculus and Limits Overview After completing this section, students will be epected to have acquired reliability and fluency in the algebraic skills of factoring, operations with radicals
Physics 1120: Simple Harmonic Motion Solutions
 Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Physics 1120: Simple Harmonic Motion Solutions 1. A 1.75 kg particle moves as function of time as follows: x = 4cos(1.33t+π/5) where distance is measured
Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Physics 1120: Simple Harmonic Motion Solutions 1. A 1.75 kg particle moves as function of time as follows: x = 4cos(1.33t+π/5) where distance is measured
Chapter NP-5. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Reactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 NUCLEAR REACTIONS 2.0 NEUTRON INTERACTIONS
 Chapter NP-5 Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 2.0 NEUTRON INTERACTIONS 2.1 ELASTIC SCATTERING 2.2 INELASTIC SCATTERING 2.3 RADIATIVE CAPTURE 2.4 PARTICLE
Chapter NP-5 Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 2.0 NEUTRON INTERACTIONS 2.1 ELASTIC SCATTERING 2.2 INELASTIC SCATTERING 2.3 RADIATIVE CAPTURE 2.4 PARTICLE
Stress Strain Relationships
 Stress Strain Relationships Tensile Testing One basic ingredient in the study of the mechanics of deformable bodies is the resistive properties of materials. These properties relate the stresses to the
Stress Strain Relationships Tensile Testing One basic ingredient in the study of the mechanics of deformable bodies is the resistive properties of materials. These properties relate the stresses to the
The Viscosity of Fluids
 Experiment #11 The Viscosity of Fluids References: 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. D. Tabor, Gases, Liquids and Solids: and Other States of Matter (Cambridge Press, 1991). 3. J.R. Van Wazer et
Experiment #11 The Viscosity of Fluids References: 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. D. Tabor, Gases, Liquids and Solids: and Other States of Matter (Cambridge Press, 1991). 3. J.R. Van Wazer et
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002
 CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid.
 Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading
 CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading Some machine elements are subjected to static loads and for such elements static failure theories are used to predict failure (yielding or fracture).
CH 6: Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading Some machine elements are subjected to static loads and for such elements static failure theories are used to predict failure (yielding or fracture).
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
F321 MOLES. Example If 1 atom has a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g 1 mole of atoms will have a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g x 6.02 x 10 23 = 7.
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Unit 6 Plane Stress and Plane Strain
 Unit 6 Plane Stress and Plane Strain Readings: T & G 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16 Paul A. Lagace, Ph.D. Professor of Aeronautics & Astronautics and Engineering Systems There are many structural configurations
Unit 6 Plane Stress and Plane Strain Readings: T & G 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16 Paul A. Lagace, Ph.D. Professor of Aeronautics & Astronautics and Engineering Systems There are many structural configurations
TIE-31: Mechanical and thermal properties of optical glass
 PAGE 1/10 1 Density The density of optical glass varies from 239 for N-BK10 to 603 for SF66 In most cases glasses with higher densities also have higher refractive indices (eg SF type glasses) The density
PAGE 1/10 1 Density The density of optical glass varies from 239 for N-BK10 to 603 for SF66 In most cases glasses with higher densities also have higher refractive indices (eg SF type glasses) The density
Element of same atomic number, but different atomic mass o Example: Hydrogen
 Atomic mass: p + = protons; e - = electrons; n 0 = neutrons p + + n 0 = atomic mass o For carbon-12, 6p + + 6n 0 = atomic mass of 12.0 o For chlorine-35, 17p + + 18n 0 = atomic mass of 35.0 atomic mass
Atomic mass: p + = protons; e - = electrons; n 0 = neutrons p + + n 0 = atomic mass o For carbon-12, 6p + + 6n 0 = atomic mass of 12.0 o For chlorine-35, 17p + + 18n 0 = atomic mass of 35.0 atomic mass
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS This is the second tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises.
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS This is the second tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises.
Gases. Macroscopic Properties. Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapter 6
 Gases Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapter 6 CHEM 1000A 3.0 Gases 1 We will be looking at Macroscopic and Microscopic properties: Macroscopic Properties of bulk gases Observable Pressure, volume, mass,
Gases Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapter 6 CHEM 1000A 3.0 Gases 1 We will be looking at Macroscopic and Microscopic properties: Macroscopic Properties of bulk gases Observable Pressure, volume, mass,
Section 1.3 P 1 = 1 2. = 1 4 2 8. P n = 1 P 3 = Continuing in this fashion, it should seem reasonable that, for any n = 1, 2, 3,..., = 1 2 4.
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section. The Sum of a Sequence This section considers the problem of adding together the terms of a sequence. Of course, this is a problem only if more than
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section. The Sum of a Sequence This section considers the problem of adding together the terms of a sequence. Of course, this is a problem only if more than
Reaction Rates and Chemical Kinetics. Factors Affecting Reaction Rate [O 2. CHAPTER 13 Page 1
 CHAPTER 13 Page 1 Reaction Rates and Chemical Kinetics Several factors affect the rate at which a reaction occurs. Some reactions are instantaneous while others are extremely slow. Whether a commercial
CHAPTER 13 Page 1 Reaction Rates and Chemical Kinetics Several factors affect the rate at which a reaction occurs. Some reactions are instantaneous while others are extremely slow. Whether a commercial
MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Vol. I Structure and Properties of Polymers - Pavel Kratochvíl STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS
 STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS Pavel Kratochvíl Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague, Czech Republic Keywords: Macromolecule, polymer, monomer,
STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS Pavel Kratochvíl Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague, Czech Republic Keywords: Macromolecule, polymer, monomer,
A) F = k x B) F = k C) F = x k D) F = x + k E) None of these.
 CT16-1 Which of the following is necessary to make an object oscillate? i. a stable equilibrium ii. little or no friction iii. a disturbance A: i only B: ii only C: iii only D: i and iii E: All three Answer:
CT16-1 Which of the following is necessary to make an object oscillate? i. a stable equilibrium ii. little or no friction iii. a disturbance A: i only B: ii only C: iii only D: i and iii E: All three Answer:
Measurement of Material Creep Parameters of Amorphous Selenium by Nanoindentation and the Relationship Between Indentation Creep and Uniaxial Creep
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-2004 Measurement of Material Creep Parameters of Amorphous Selenium by Nanoindentation
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-2004 Measurement of Material Creep Parameters of Amorphous Selenium by Nanoindentation
(Equation 1) to determine the cord s characteristics. Hooke s Law represents the
 Using Hooke s Law to Solve for Length of Bungee Cord Needed for Egg Drop Introduction This experiment is the second part of a three- part experiment. The first two lead up to the final in which we aim
Using Hooke s Law to Solve for Length of Bungee Cord Needed for Egg Drop Introduction This experiment is the second part of a three- part experiment. The first two lead up to the final in which we aim
Temperature Scales. The metric system that we are now using includes a unit that is specific for the representation of measured temperatures.
 Temperature Scales INTRODUCTION The metric system that we are now using includes a unit that is specific for the representation of measured temperatures. The unit of temperature in the metric system is
Temperature Scales INTRODUCTION The metric system that we are now using includes a unit that is specific for the representation of measured temperatures. The unit of temperature in the metric system is
Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 2 UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS
 1 P a g e Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 2 UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS The comparison of any physical quantity with its standard unit is called measurement. Physical Quantities All the quantities in terms of
1 P a g e Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 2 UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS The comparison of any physical quantity with its standard unit is called measurement. Physical Quantities All the quantities in terms of
= 16.00 amu. = 39.10 amu
 Using Chemical Formulas Objective 1: Calculate the formula mass or molar mass of any given compound. The Formula Mass of any molecule, formula unit, or ion is the sum of the average atomic masses of all
Using Chemical Formulas Objective 1: Calculate the formula mass or molar mass of any given compound. The Formula Mass of any molecule, formula unit, or ion is the sum of the average atomic masses of all
momentum change per impact The average rate of change of momentum = Time interval between successive impacts 2m x 2l / x m x m x 2 / l P = l 2 P = l 3
 Kinetic Molecular Theory This explains the Ideal Gas Pressure olume and Temperature behavior It s based on following ideas:. Any ordinary sized or macroscopic sample of gas contains large number of molecules.
Kinetic Molecular Theory This explains the Ideal Gas Pressure olume and Temperature behavior It s based on following ideas:. Any ordinary sized or macroscopic sample of gas contains large number of molecules.
