EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Hodge
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude Easy to measure Empirical - except for M w, no direct tie to physics of faulting Note; not dimensionally correct
2 T s =D/V s T p = D/V p T s -T p = D/V s - D/V p = D (V p -V s ) / V s V p -> D = (T s - T p ) * V p V s /(V p - V s )
3
4
5
6 COMPARE EARTHQUAKES USING SEISMIC MOMENT M 0 Magnitudes, moments (dyncm), fault areas, and fault slips for several earthquakes Alaska & San Francisco differ much more than M s implies M 0 more useful measure Units: dyne-cm or Nt-M Directly tied to fault physics Doesnʼt saturate Stein & Wysession, 2003
7 the big one
8 EARTHQUAKE SOURCE PARAMETER ESTIMATES HAVE CONSIDERABLE UNCERTAINTIES FOR SEVERAL REASONS: - Uncertainties due to earth's variability and deviations from the mathematical simplifications used. Even with high-quality modern data, seismic moment estimates for the Loma Prieta earthquake vary by about 25%, and Ms values vary by about 0.2 units. - Uncertainties for historic earthquakes are large. Fault length estimates for the San Francisco earthquake vary from km, Ms was estimated at 8.3 but now thought to be ~7.8, and fault width is essentially unknown and inferred from the depths of more recent earthquakes and geodetic data. - Different techniques (body waves, surface waves, geodesy, geology) can yield different estimates. - Fault dimensions and dislocations shown are average values for quantities that can vary significantly along the fault Hence different studies yield varying and sometimes inconsistent values. Even so, data are sufficient to show effects of interest.
9 Moment magnitude M w Magnitudes saturate: No matter how big the earthquake m b never exceeds ~6.4 M s never exceeds ~8.4 M w defined from moment so never saturates
10 DIFFERENT MAGNITUDE SCALES REFLECT AMPLITUDE AT DIFFERENT PERIODS Body & surface wave magnitudes saturate - remain constant once earthquake exceeds a certain size - because added energy release in very large earthquakes is at periods > 20 s 20 s 1 s No matter how big an earthquake is, body and surface wave magnitudes do not exceed ~ 6.5 and 8.4, respectively. For very large earthquakes only low period moment magnitude reflects earthquakeʼs size. This issue is crucial for tsunami warning because long periods excite tsunami, but are harder to study in real time
11 THREE EARTHQUAKES IN NORTH AMERICA - PACIFIC PLATE BOUNDARY ZONE Tectonic setting affects earthquake size San Fernando earthquake on buried thrust fault in the Los Angeles area, similar to Northridge earthquake. Short faults are part of an oblique trend in the boundary zone, so fault areas are roughly rectangular. The down-dip width seems controlled by the fact that rocks deeper than ~20 km are weak and undergo stable sliding rather than accumulate strain for future earthquakes. San Francisco earthquake ruptured a long segment of the San Andreas with significantly larger slip, but because the fault is vertical, still had a narrow width. This earthquake illustrates approximately the maximum size of continental transform earthquakes. Stein & Wysession, 2003 Alaska earthquake had much larger rupture area because it occurred on shallow-dipping subduction thrust interface. The larger fault dimensions give rise to greater slip, so the combined effects of larger fault area and more slip cause largest earthquakes to occur at subduction zones rather than transforms.
12 LARGER EARTHQUAKES GENERALLY HAVE LONGER FAULTS AND LARGER SLIP Wells and Coppersmith, 1994 M7, ~ 100 km long, 1 m slip; M6, ~ 10 km long, ~ 20 cm slip Important for tectonics, earthquake source physics, hazard estimation
13 Earthquake Scaling Relations San Andreas Fault System log 10 A ~ M
14 ENERGY & MAGNITUDE ~ m b ~ M s 5 5
15 Earthquakes of a given magnitude are ~10 times less frequent than those one magnitude smaller. An M7 earthquake occurs approximately monthly, and an earthquake of M> 6 about every three days. Magnitude is proportional to the logarithm of the energy released, so most energy released seismically is in the largest earthquakes. An M 8.5 event releases more energy than all other earthquakes in a year combined. Hence the hazard from earthquakes is due primarily to large (typically magnitude > 6.5) earthquakes.
16 Working Group on California Earthquake Probabilities (2007) Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast (UCERF2) M 6.7: 97% M 7.0: 81% M 7.5: 39% Southern California 30-year probabilities M 8.0: 2% UCERF2 ratio of time-dependent to time-independent participation probabilities for M 6.7
17 Intensity scale Measures damage to structures Often used is Mercalli I-XII Can be used to examine historic earthquakes without seismic records For example, eastern US.
18
19 Intensity Observed Effects I Not felt at all II Felt only by a few individuals, indoors and at rest, usually on upper floors of tall buildings. III Felt indoors by many persons, but not necessarily recognized as an earthquake. Chandeliers and hanging plants swing. IV Felt both indoors and out. Feels like the vibration caused by a heavy truck or train passing. Windows rattle. V Strong enough to awaken sleeping persons. Small objects knocked off shelves. Beverages may splash out of cups or glasses on tables. VI Perceptible to everyone. May cause public fright. Pictures fall off walls. Weak masonry cracks. Some plaster may fall from ceilings. VII Difficult to stand upright. Ornamental masonry falls from buildings. Waves may be seen in ponds and swimming pools. VIII Mass panic may occur. Chimneys, smoke stacks and water towers may lean and fall. Unsecured frame houses slide off foundations. IX Panic is general. Heavy damage to masonry structures and to underground pipes. Large cracks open in ground. X Many buildings collapse. Water splashes over riverbanks. XI-XII Virtually total destruction.
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
How do scientists measure earthquakes?
 Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey
 The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION
 Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude
 Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Plotting Earthquakes LESSON
 13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
KCC Event Brief: 2014 La Habra Earthquake
 KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC Event Brief: 2014 La Habra Earthquake June 2014 2 COPLEY PLACE BOSTON, MA 02116 T: 617.423.2800 F: 617.423.2808 Overview On Friday, March 28, 2014 at 9:09pm, a magnitude 5.1 earthquake
KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC Event Brief: 2014 La Habra Earthquake June 2014 2 COPLEY PLACE BOSTON, MA 02116 T: 617.423.2800 F: 617.423.2808 Overview On Friday, March 28, 2014 at 9:09pm, a magnitude 5.1 earthquake
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake
 Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Economic Benefit Cost Analysis: CoreFirst vs. Standard Retrofit
 Economic Benefit Cost Analysis: CoreFirst vs. Standard Retrofit Kleinhenz & Associates 2602 Berkshire Road Cleveland, Ohio 44106 www.kleinhenzassociates.com June 2014 Introduction CoreFirst, llc. (CoreFirst)
Economic Benefit Cost Analysis: CoreFirst vs. Standard Retrofit Kleinhenz & Associates 2602 Berkshire Road Cleveland, Ohio 44106 www.kleinhenzassociates.com June 2014 Introduction CoreFirst, llc. (CoreFirst)
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
EARTHQUAKE. Definition of Hazard. History of Hazard as it Affects the City of Kent. Hazard Identification
 EARTHQUAKE Definition of Hazard Earthquakes are defined as the sudden release of energy occurring from the collision or shifting of crustal plates on the earth s surface or from the fracture of stressed
EARTHQUAKE Definition of Hazard Earthquakes are defined as the sudden release of energy occurring from the collision or shifting of crustal plates on the earth s surface or from the fracture of stressed
Earthquakes Natural and Induced. Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University
 Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES
 DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
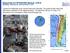 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet
 Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Locating the Epicenter and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake
 Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3
 Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates.
 Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Critical Facility Round Table
 Critical Facility Round Table October 16, 2003 San Francisco Seismic Risk for Data Centers David Bonneville Senior Principal Degenkolb Engineers San Francisco, California Presentation Outline Seismic Risk
Critical Facility Round Table October 16, 2003 San Francisco Seismic Risk for Data Centers David Bonneville Senior Principal Degenkolb Engineers San Francisco, California Presentation Outline Seismic Risk
Name Date Class. By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter.
 CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
Earthquakes: Risk and Insurance Issues
 Page 1 of 8 HOT TOPICS & INSURANCE ISSUES Earthquakes: Risk and Insurance Issues THE TOPIC JULY 2003 An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock
Page 1 of 8 HOT TOPICS & INSURANCE ISSUES Earthquakes: Risk and Insurance Issues THE TOPIC JULY 2003 An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk
 Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk. Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey
 Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest
 Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008
 Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra
 Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies
 Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy
 February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues
 Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock beneath the earth s surface. This shaking can sometimes trigger
Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock beneath the earth s surface. This shaking can sometimes trigger
Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE
 Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE To satisfy the performance goals of the NEHRP Recommended Seismic Provisions, a number of characteristics are important to the
Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE To satisfy the performance goals of the NEHRP Recommended Seismic Provisions, a number of characteristics are important to the
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #5 The Mercalli Scale
 EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #5 The Mercalli Scale All Grades 4 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness.
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #5 The Mercalli Scale All Grades 4 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness.
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013)
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
Earthquakes and Data Centers
 7x24 Exchange Fall Symposium September 11, 2013 Hilton Bellevue Andrew W. Taylor, Ph.D., S.E., FACI Earthquake Hazards 2 September 11, 2013 1 Cascadia Earthquake Sources Figure Credit: Craig Weaver, Pacific
7x24 Exchange Fall Symposium September 11, 2013 Hilton Bellevue Andrew W. Taylor, Ph.D., S.E., FACI Earthquake Hazards 2 September 11, 2013 1 Cascadia Earthquake Sources Figure Credit: Craig Weaver, Pacific
Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007
 Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007 1. Please fill in the missing labels. 2. Please fill in the missing labels. 3. How many large plates form the outer shell of the earth?
Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007 1. Please fill in the missing labels. 2. Please fill in the missing labels. 3. How many large plates form the outer shell of the earth?
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67)
 4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
When Things Go Wrong
 When Things Go Wrong When Things Go Wrong Our planet has many wondrous things. We plant a tiny sapling and it becomes a mighty tree. Water runs in rivers. Rainbows appear in the sky. But it is not always
When Things Go Wrong When Things Go Wrong Our planet has many wondrous things. We plant a tiny sapling and it becomes a mighty tree. Water runs in rivers. Rainbows appear in the sky. But it is not always
Project Report. Structural Investigations Hotel del Sol Yuma, Arizona
 Project Report Structural Investigations Yuma, Arizona Prepared by: 2619 Spruce Street Boulder, CO 80302 303-444-3620 Prepared for: Principle Engineering Group, Inc. 833 East Plaza Circle, Suite 100 Yuma,
Project Report Structural Investigations Yuma, Arizona Prepared by: 2619 Spruce Street Boulder, CO 80302 303-444-3620 Prepared for: Principle Engineering Group, Inc. 833 East Plaza Circle, Suite 100 Yuma,
Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks
 Vol. 1, 005 CSA Academic Perspective 0 Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks Lisa Yunxia Wang California State Polytechnic University Pomona ABSTRACT Practicing engineers face many
Vol. 1, 005 CSA Academic Perspective 0 Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks Lisa Yunxia Wang California State Polytechnic University Pomona ABSTRACT Practicing engineers face many
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q.
 Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Overview. NRC Regulations for Seismic. Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. NRC History. How we Regulate
 Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS
 EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS STEP 1. IDENTIFY POTENTIAL HAZARDS IN YOUR HOME AND BEGIN TO FIX THEM. Earthquake safety is more than minimizing damage to buildings. We must also secure the contents of our buildings
EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS STEP 1. IDENTIFY POTENTIAL HAZARDS IN YOUR HOME AND BEGIN TO FIX THEM. Earthquake safety is more than minimizing damage to buildings. We must also secure the contents of our buildings
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
Copyright 2011 Casa Software Ltd. www.casaxps.com. Centre of Mass
 Centre of Mass A central theme in mathematical modelling is that of reducing complex problems to simpler, and hopefully, equivalent problems for which mathematical analysis is possible. The concept of
Centre of Mass A central theme in mathematical modelling is that of reducing complex problems to simpler, and hopefully, equivalent problems for which mathematical analysis is possible. The concept of
AN ANALYSIS OF FIRE SPRINKLER SYSTEM FAILURES DURING THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE AND COMPARISON WITH THE SEISMIC DESIGN STANDARD FOR THESE SYSTEMS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2136 AN ANALYSIS OF FIRE SPRINKLER SYSTEM FAILURES DURING THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE AND COMPARISON WITH
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2136 AN ANALYSIS OF FIRE SPRINKLER SYSTEM FAILURES DURING THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE AND COMPARISON WITH
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Magnitude and Intensity
 Exercise 2 EXERCISE 2 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE AND INTENSITY Supplies Needed calculator metric ruler PURPOSE Exercise 1 introduced many of the fundamental concepts of earthquakes, and this exercise will add
Exercise 2 EXERCISE 2 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE AND INTENSITY Supplies Needed calculator metric ruler PURPOSE Exercise 1 introduced many of the fundamental concepts of earthquakes, and this exercise will add
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage
 Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Storms Assessment LESSON
 LESSON 8 Storms Assessment What will happen to the helix above a hot lamp? TERRY G. McCREA/SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION INTRODUCTION You have now completed Storms, the first part of Catastrophic Events. After
LESSON 8 Storms Assessment What will happen to the helix above a hot lamp? TERRY G. McCREA/SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION INTRODUCTION You have now completed Storms, the first part of Catastrophic Events. After
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
Tectonic plates push together at convergent boundaries.
 KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior
 Melissa Duran, Hoover Middle School, San Jose, CA 1/9/03 Bay Area Science Museum Collaboratory Project Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior Introduction Standards: 1.b, 7.e Objectives Students
Melissa Duran, Hoover Middle School, San Jose, CA 1/9/03 Bay Area Science Museum Collaboratory Project Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior Introduction Standards: 1.b, 7.e Objectives Students
1. You are about to begin a unit on geology. Can anyone tell me what geology is? The study of the physical earth I.
 PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
7.2.4 Seismic velocity, attenuation and rock properties
 7.2.4 Seismic velocity, attenuation and rock properties Rock properties that affect seismic velocity Porosity Lithification Pressure Fluid saturation Velocity in unconsolidated near surface soils (the
7.2.4 Seismic velocity, attenuation and rock properties Rock properties that affect seismic velocity Porosity Lithification Pressure Fluid saturation Velocity in unconsolidated near surface soils (the
Chapter 2. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics: Learning Goals
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
SMIP2000 Seminar Proceedings COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER. Ralph Archuleta
 COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER Ralph Archuleta Institute for Crustal Studies & Department of Geological Sciences University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT The COSMOS virtual data center
COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER Ralph Archuleta Institute for Crustal Studies & Department of Geological Sciences University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT The COSMOS virtual data center
Plate Tectonics Lab. Continental Drift. The Birth of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Lab Continental Drift Take a look at a globe sometime and observe the remarkable fit between South America and Africa. Could they have, in fact, been connected? During the 19th and early
Plate Tectonics Lab Continental Drift Take a look at a globe sometime and observe the remarkable fit between South America and Africa. Could they have, in fact, been connected? During the 19th and early
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones
 Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Earth Egg Model Teacher Notes
 Ancient Greeks tried to explain earthquakes and volcanic activity by saying that a massive bull lay underground and the land shook when it became angry. Modern theories rely on an understanding of what
Ancient Greeks tried to explain earthquakes and volcanic activity by saying that a massive bull lay underground and the land shook when it became angry. Modern theories rely on an understanding of what
NATHAN world map of natural hazards. 2011 version
 world map of natural hazards 2011 version World Map of Natural Hazards Geointelligence for your business A new name but the recipe for success is the same: In the 2011 version, we are offering both proven
world map of natural hazards 2011 version World Map of Natural Hazards Geointelligence for your business A new name but the recipe for success is the same: In the 2011 version, we are offering both proven
Practice Test SHM with Answers
 Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them
 Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them by Jeff White, AIA Published in Healthcare Design magazine There s a saying among seismologists: Earthquakes don t kill people. Buildings
Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them by Jeff White, AIA Published in Healthcare Design magazine There s a saying among seismologists: Earthquakes don t kill people. Buildings
CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS. Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2
 CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS Abstract Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2 With the impending Cascadia subduction zone event
CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS Abstract Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2 With the impending Cascadia subduction zone event
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Transform Boundaries
 Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT REPORT BOLINAS MARINE STATION - BOLINAS, CALIFORNIA
 STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT REPORT BOLINAS MARINE STATION - BOLINAS, CALIFORNIA College of Marin c/o Swinerton Management & Consulting P.O. Box 144003 835 College Avenue, Building MS-3 Kentfield, California
STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT REPORT BOLINAS MARINE STATION - BOLINAS, CALIFORNIA College of Marin c/o Swinerton Management & Consulting P.O. Box 144003 835 College Avenue, Building MS-3 Kentfield, California
SIESMIC SLOSHING IN CYLINDRICAL TANKS WITH FLEXIBLE BAFFLES
 SIESMIC SLOSHING IN CYLINDRICAL TANKS WITH FLEXIBLE BAFFLES Kayahan AKGUL 1, Yasin M. FAHJAN 2, Zuhal OZDEMIR 3 and Mhamed SOULI 4 ABSTRACT Sloshing has been one of the major concerns for engineers in
SIESMIC SLOSHING IN CYLINDRICAL TANKS WITH FLEXIBLE BAFFLES Kayahan AKGUL 1, Yasin M. FAHJAN 2, Zuhal OZDEMIR 3 and Mhamed SOULI 4 ABSTRACT Sloshing has been one of the major concerns for engineers in
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
APPLICATION OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING INFORMATION IN HOSPITAL EMERGENCY RESPONSE AND RECOVERY
 Workshop on Seismic Design and Retrofitting of Hospitals in Seismic Areas, October 21-22, 1999. APPLICATION OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING INFORMATION IN HOSPITAL EMERGENCY RESPONSE AND RECOVERY Robert Reitherman
Workshop on Seismic Design and Retrofitting of Hospitals in Seismic Areas, October 21-22, 1999. APPLICATION OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING INFORMATION IN HOSPITAL EMERGENCY RESPONSE AND RECOVERY Robert Reitherman
Geology 112 Earthquakes. Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake?
 Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
American Society of Civil Engineers
 American Society of Civil Engineers Technical Council on Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Earthquake Investigation Committee Lifelines Water and Wastewater Electric Power and Communication Gas and Liquid
American Society of Civil Engineers Technical Council on Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Earthquake Investigation Committee Lifelines Water and Wastewater Electric Power and Communication Gas and Liquid
NATURAL DISASTERS Vol. I - Earthquake Parameters Including Strong Earthquakes- S.L.Yunga EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES
 EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES S.L.Yunga United Institute of physics of the Earth, Russian academy of sciences. B. Gruzinskaya,10, Moscow, 123810, Russia Keywords earthquake, epicenter,
EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES S.L.Yunga United Institute of physics of the Earth, Russian academy of sciences. B. Gruzinskaya,10, Moscow, 123810, Russia Keywords earthquake, epicenter,
CH. 2 LOADS ON BUILDINGS
 CH. 2 LOADS ON BUILDINGS GRAVITY LOADS Dead loads Vertical loads due to weight of building and any permanent equipment Dead loads of structural elements cannot be readily determined b/c weight depends
CH. 2 LOADS ON BUILDINGS GRAVITY LOADS Dead loads Vertical loads due to weight of building and any permanent equipment Dead loads of structural elements cannot be readily determined b/c weight depends
Earthquakes in Hawaii:
 Earthquakes in Hawaii: What you need to know U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Prepared by: Janet L. Babb Hawaiian Volcano Observatory Hawaii Standard Time The State of Hawaii experiences
Earthquakes in Hawaii: What you need to know U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Prepared by: Janet L. Babb Hawaiian Volcano Observatory Hawaii Standard Time The State of Hawaii experiences
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics
 Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 [email protected] Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 [email protected] Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Section 1. Logarithms
 Worksheet 2.7 Logarithms and Exponentials Section 1 Logarithms The mathematics of logarithms and exponentials occurs naturally in many branches of science. It is very important in solving problems related
Worksheet 2.7 Logarithms and Exponentials Section 1 Logarithms The mathematics of logarithms and exponentials occurs naturally in many branches of science. It is very important in solving problems related
ABSG Consulting, Tokyo, Japan Email: [email protected] 2. Professor, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan 3
 Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
6.0 Results of Risk Analyses
 6. Results of Risk Analyses A risk analysis of the optimized embankment designs for the Salton Sea restoration project was conducted jointly by Kleinfelder and representatives from Reclamation. A risk
6. Results of Risk Analyses A risk analysis of the optimized embankment designs for the Salton Sea restoration project was conducted jointly by Kleinfelder and representatives from Reclamation. A risk
1 Exploring Earth s Interior
 1 Exploring Earth s Interior Crust Mantle Outer Core Crust-to-Mantle Inner Core Cross Section From Surface to Center SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Earth Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2 Evidence for Continental
1 Exploring Earth s Interior Crust Mantle Outer Core Crust-to-Mantle Inner Core Cross Section From Surface to Center SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Earth Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2 Evidence for Continental
