Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
|
|
|
- Shauna Brooks
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled Anatomy of the Blood Vessels. 1) In the first week you will look at blood vessel histology and complete the relevant portion of the Review Sheet for the exercise, As an alternate your instructor may have you submit a drawing of the blood vessels from the Virtual Microsocpe or other histology site. 2) In the second week you will study the vessels of the lower body and complete that portion of the Review Sheet. Also take the related quizzes on the upper and lower vessels. There are also video clips available of cadaver dissection of the blood vessels. Click on the sound icon for the audio file (mp3 format) for each slide. There is also a link to a dowloadable mp4 video which can be played on an ipod. 1
2 Vascular Histology 2 Both arteries and veins possess three layers: the outer tunica adventitia, made of connective tissue, the tunica media composed of smooth muscle and, in large arteries also elastic tissue, and the tunica interna, composed of a thin endothelium. Only the endothelium remains as the capillary wall. 2
3 Vascular Hierarchy Elastic arteries the aorta and its major branches. Muscular arteries distribute blood within the organs and tissues. Arterioles small arteries which lead to capillaries Capillaries thin-walled vessels which allow transport to and from tissues. Venules small veins which drain the capillaries Veins return blood to the heart. 3 Here is the hierarchy of vessels beginning with the largest arteries leaving the heart. 3
4 Tunica Media in a Large Elastic Artery Elastic fibers dominate the tunica media in the aorta and other elastic arteries. 4 Elastic tissue abounds in the tunica media of the aorta and other elastic arteries. It is this elastic tissue which provides the recoil one feels when taking the pulse, and this recoil helps to damp of the pulse pressure to keep blood flow continuous. 4
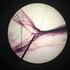
5 A Medium Size Artery Tunica adventitia: connective sheath Tunica media: smooth muscle Tunica interna: endothelial lining. Internal elastic membrane: a fenestrated elastic lamina, part of the tunica intima 5 As arteries get smaller along the hierarchy the elastic tissue diminishes, except for a prominent elastic membrane between the tunica media and the thin endothelium of the tunica interna. 5
6 Artery and Vein Comparison Artery-note the firmly open shape and the distinctive internal elastic membrane. Tunica media Vein - note the thin collapsed wall. 6 The internal elastic membrane can be clearly seen in this slide stained with PAS. This stain highlights the carbohydrate-containing connective tissues with blue, and other tissue red. Note how thin and collapsed the vein is, hardly thick enough to pick out the layers. 6
7 An Arteriole adventitia endothelium Smooth muscle 7 Arterioles have lost most of the adventitia and smooth muscle layers, and have no elastic tissue. The smooth muscle they do have is instrumental in regulating blood flow into subsequent capillaries. 7
8 Arterioles This is a venule, based on its size and thickness. Arterioles vary in size and amount of smooth muscle. Their smooth muscle functions in vasoconstriction. 8 Venules receive blood from the capillary beds on its way back to the heart. They are about the same thickness as arterioles, but a little larger in diameter. 8
9 Capillary Red blood cells work their way through the capillary in single file. 9 Capillaries are extremely small had have extremely thin walls. Red blood cells can only make their way through one at a time. Can you identify the tissue these capillaries are found in? 9
10 A Medium Vein Note the thin tunica media and absence of elastic lamina. 10 On the way back to the heart now, venules lead to small veins such as this one. Veins have little tunica media and are larger overall in diameter than arteries at the comparable level of branching. This provides for a lowresistance conduit back to the heart. 10
11 A Medium Vein in L.S. Note the elongated collapsed lumen. Tunica media cells are cut in cross section. 11 Veins continue to get larger in diameter as they approach the heart, but not much thicker. 11
12 Comparison of Artery and Vein 12 A comparison of a medium artery and vein illustrates the differences. Thicker wall for artery, more tunica media and an internal elastic membrane. 12
13 Artery, Vein, and Nerve 13 Another comparison, at low power, of artery and vein. Notice the nerve bundles in the upper right of slide. Nerves often travel along with arteries and veins, surrounded by a common connective tissue sheath, as a neurovascular bundle. 13
14 The Blood Vessels 14 The following slides illustrate the major vessels of the human body. Your lab manual contains tables of these vessels as well. Use ADAM according to the instructions in your lab manual to study the blood vessels. 14
15 15 This and the slides which follow illustrate the major arteries and veins. Use the terms list in the lab manual as a guide to the ones you will be responsible for. Use ADAM according to the directions in the lab manual to study the vessels, and view the cadaver videos. 15
16 16 16
17 17 17
18 18 18
19 19 19
20 20 20
21 21 21
22 22 22
23 First Week Lab Protocol 1) Complete the portion of the Review Sheet for this exercise which relates to vascular histology and the blood vessels of the upper body. 2) As an alternative your instructor may have you submit a drawing of blood vessel histology from the Virtual Microscope or other histology site. 3) Take the quiz on vascular histology and the upper body vessels. 4) Use ADAM identify vessels of the head, neck, arms. 5) View the cadaver videos on the upper blood vessels
24 ADAM Interactive Anatomy Atlas Anatomy, Region, Head and Neck, Arteries of Head and Neck (Lat), Veins of Head and Neck (Lat.), Cerebral Arterial Circle Dissectible Anatomy, Male, Anterior, Window centered on neck, Layer Indicator 246 Atlas Anatomy, Region, Upper Limb, Arteries of the Upper Limb (Ant) Dissectible Anatomy, Male, Anterior, Window centered on right arm, Layer Indicator, 5, superficial veins of the arm
25 25 25
26 26 26
27 27 27
28 28 28
29 Second Week Lab Protocol 1) Complete the portion of the Review Sheet for this exercise which relates to the blood vessels of the lower body. 2) Take the quiz on the lower body vessels. 3) Use ADAM to identify vessels of the abdomen and legs. 4) View the cadaver videos on the lower blood vessels
30 ADAM Interactive Anatomy Go to the following: Atlas Anatomy, Region, Lower Limb, Arteries of the Lower Limb (Ant). Atlas Anatomy, Region, Lower Limb, Arteries of the Lower Limb (Post). Dissectible Anatomy, Male, Anterior, Window centered on upper thigh, Layer Indicator 3, great spahenous vein 30 30
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
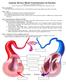 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
 Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
3. Tunica adventitia is the outermost layer; it is composed of loosely woven connective tissue infiltrated by nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics
 Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Introduction: Becoming Familiar with Anatomy and Physiology Revealed
 bro78143_01_1-32.qxd 8/31/07 11:10 PM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction: Becoming Familiar with Anatomy and Physiology Revealed Overview: Getting Started You have before you a workbook to accompany the most
bro78143_01_1-32.qxd 8/31/07 11:10 PM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction: Becoming Familiar with Anatomy and Physiology Revealed Overview: Getting Started You have before you a workbook to accompany the most
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Circulation Stations
 Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
OMONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 131 AW Human Anatomy and Physiology I (4 credits) Spring Semester, 2014
 OMONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 131 AW Human Anatomy and Physiology I (4 credits) Spring Semester, 2014 Instructor: Dr. Jay M. Templin Meeting Place: Rooms 220 and 244 Meeting Time: Telephone
OMONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 131 AW Human Anatomy and Physiology I (4 credits) Spring Semester, 2014 Instructor: Dr. Jay M. Templin Meeting Place: Rooms 220 and 244 Meeting Time: Telephone
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus
 Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Moravian College Department of Biological Sciences Anatomy and Physiology - BIO 103 Fall 2008
 Moravian College Department of Biological Sciences Anatomy and Physiology - BIO 103 Fall 2008 Instructors: Dr. Cecilia M. Fox Ms. Marie Hosier (lab instructor for laboratory section B) Phone: Fox: 610-861-1426
Moravian College Department of Biological Sciences Anatomy and Physiology - BIO 103 Fall 2008 Instructors: Dr. Cecilia M. Fox Ms. Marie Hosier (lab instructor for laboratory section B) Phone: Fox: 610-861-1426
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE BIOL 2401 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS:
 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE BIOL 2401 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Semester Hours Credit: 4 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: I. INTRODUCTION A. Anatomy and Physiology I is the study of the parts of the living organisms
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE BIOL 2401 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Semester Hours Credit: 4 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: I. INTRODUCTION A. Anatomy and Physiology I is the study of the parts of the living organisms
chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed
 1 Transport systems chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed Simple organisms Diffusion the free movement of particles in a liquid or a gas down a concentration
1 Transport systems chemicals > transported from outside to in > waste products created > they need to be removed Simple organisms Diffusion the free movement of particles in a liquid or a gas down a concentration
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
the Cardiovascular System
 5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
Living things: Cells Living things:
 unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment
 Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment 1a. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell 1b. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell c. an egg d. a phone 1c. The basic unit of all
Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment 1a. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell 1b. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell c. an egg d. a phone 1c. The basic unit of all
Exchange and transport
 Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology John Wojciakowski email: [email protected] phone ext: 28351 Room #1245 TEXTS: Text The Human Body Book author- Steve Parker copyright- 2007 Course Overview: Anatomy is a
Human Anatomy & Physiology John Wojciakowski email: [email protected] phone ext: 28351 Room #1245 TEXTS: Text The Human Body Book author- Steve Parker copyright- 2007 Course Overview: Anatomy is a
How To Make A Vascular Graft
 LCL-GRAFT TM - Innovative Large and Small Caliber Vascular Grafts for Coronary Bypass and Peripheral Vascular Surgery. A. Perets 1, M. Li 1, P. Uttayarat 1, P. Pimton 1, A. Wu 2, R. J. Levy 3, R. J. Composto
LCL-GRAFT TM - Innovative Large and Small Caliber Vascular Grafts for Coronary Bypass and Peripheral Vascular Surgery. A. Perets 1, M. Li 1, P. Uttayarat 1, P. Pimton 1, A. Wu 2, R. J. Levy 3, R. J. Composto
AgoraLink Agora for Life Science Technologies Linköpings Universitet Kurs i Fysiologisk mätteknik Biofluidflöden
 AgoraLink Agora for Life Science Technologies Linköpings Universitet Kurs i Fysiologisk mätteknik Biofluidflöden Fysiologisk mätteknik Anatomy of the heart The complex myocardium structure right ventricle
AgoraLink Agora for Life Science Technologies Linköpings Universitet Kurs i Fysiologisk mätteknik Biofluidflöden Fysiologisk mätteknik Anatomy of the heart The complex myocardium structure right ventricle
h. Large intestine 3
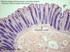 (1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
(1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
Additional information >>> HERE <<< ## 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology Course ø - User Experience
 Additional information >>> HERE
Additional information >>> HERE
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES
 SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Paper 1 Answer all questions. Each question is followed by four options, A, B, C and D. For each question, choose one answer only
 hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
Exploring Creation with Advanced Biology ~ Schedule for 2015-2016 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Date:
 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
BIOLOGY 203 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Karen K. McLellan, M. S., Course Coordinator Spring Semester, 2012
 BIOLOGY 203 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Karen K. McLellan, M. S., Course Coordinator Spring Semester, 2012 203 Lecture Times: T/R 9:00 10:15 AM in LA159 T/R 10:30-11:45 AM in LA 159 Textbook: Seeley s
BIOLOGY 203 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Karen K. McLellan, M. S., Course Coordinator Spring Semester, 2012 203 Lecture Times: T/R 9:00 10:15 AM in LA159 T/R 10:30-11:45 AM in LA 159 Textbook: Seeley s
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (BIOL. 213)
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (BIOL. 213) LECTURE SYLLABUS, Spring, 2011 Instructor: Dr. Vonnie D.C. Shields, Office- Smith 345, ext. (410-704-3130) [email protected] Office hours: Mond. 4-5 p.m (Smith
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I (BIOL. 213) LECTURE SYLLABUS, Spring, 2011 Instructor: Dr. Vonnie D.C. Shields, Office- Smith 345, ext. (410-704-3130) [email protected] Office hours: Mond. 4-5 p.m (Smith
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Milwaukee School of Engineering [email protected]. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
1. Anatomy & Physiology I, Biology 2401, Section 304 Lecture: MW 7:05-8:20 pm H-212 Lab: MW 8:30-9:45 pm H-123 Spring 2012
 1. Anatomy & Physiology I, Biology 2401, Section 304 Lecture: MW 7:05-8:20 pm H-212 Lab: MW 8:30-9:45 pm H-123 Spring 2012 2. Instructor: Teak Lee Office Hours: W 6:00 p.m.-7:00 p.m. Telephone: (979) 209-7571
1. Anatomy & Physiology I, Biology 2401, Section 304 Lecture: MW 7:05-8:20 pm H-212 Lab: MW 8:30-9:45 pm H-123 Spring 2012 2. Instructor: Teak Lee Office Hours: W 6:00 p.m.-7:00 p.m. Telephone: (979) 209-7571
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
LECTURE 3: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - BLOOD VESSELS
 LECTURE 3: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - BLOOD VESSELS INTRODUCTION To fully grasp the circulatory system and the processes that may progress to heart disease, it is vital that one comprehend the functioning
LECTURE 3: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - BLOOD VESSELS INTRODUCTION To fully grasp the circulatory system and the processes that may progress to heart disease, it is vital that one comprehend the functioning
3.1 Cells and cell function
 BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
SUMMARY A. GROSS ANATOMY OF SUPERFICIAL FASCIA AND
 SUMMARY A. GROSS ANATOMY OF SUPERFICIAL FASCIA AND SUBCUTANEOUS FAT 1. Anatomy of Superficial Fascia: In this study, we observed that the superficial fascia of the abdomen was multilayered in the midline.
SUMMARY A. GROSS ANATOMY OF SUPERFICIAL FASCIA AND SUBCUTANEOUS FAT 1. Anatomy of Superficial Fascia: In this study, we observed that the superficial fascia of the abdomen was multilayered in the midline.
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Transport in Plants. Lab Exercise 25. Introduction. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Transport in Plants Objectives - Become familiar and be able to recognize the different types of cells found in the plant s vascular tissue. - Be able to describe root pressure and transpiration
Lab Exercise Transport in Plants Objectives - Become familiar and be able to recognize the different types of cells found in the plant s vascular tissue. - Be able to describe root pressure and transpiration
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
BSCI 201 - HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Spring Semester, 2012 LECTURE SYLLABUS The prerequisite for BSCI 201 is BSCI 105 or its equivalent.
 BSCI 201 - HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Spring Semester, 2012 LECTURE SYLLABUS The prerequisite for BSCI 201 is BSCI 105 or its equivalent. Attendance: Lecture - Attendance is strongly recommended, since
BSCI 201 - HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Spring Semester, 2012 LECTURE SYLLABUS The prerequisite for BSCI 201 is BSCI 105 or its equivalent. Attendance: Lecture - Attendance is strongly recommended, since
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OBJECTIVES PROCEDURE. Lab 2- Bio 160. Name:
 Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
2.2.1 Pressure and flow rate along a pipe: a few fundamental concepts
 1.1 INTRODUCTION Single-cell organisms live in direct contact with the environment from where they derive nutrients and into where they dispose of their waste. For living systems containing multiple cells,
1.1 INTRODUCTION Single-cell organisms live in direct contact with the environment from where they derive nutrients and into where they dispose of their waste. For living systems containing multiple cells,
Lecture Syllabus Spring 2008
 Anatomy and Physiology Bio 222 Lecture Syllabus Spring 2008 Professor Marilyn Daly COURSE DESCRIPTION: TEXTBOOKS: BIO 222 Human Anatomy and Physiology II is a continuation of BIO 220 offered 1 st semester.
Anatomy and Physiology Bio 222 Lecture Syllabus Spring 2008 Professor Marilyn Daly COURSE DESCRIPTION: TEXTBOOKS: BIO 222 Human Anatomy and Physiology II is a continuation of BIO 220 offered 1 st semester.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
