Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
|
|
|
- Brent Jennings
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ( Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors: peripheral resistance vessel elasticity blood volume cardiac output As you go through this topic, keep in mind this flow chart, which outlines the factors affecting blood pressure: Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 2. Goals To understand the factors that affect peripheral resistance, and therefore blood pressure. To understand how vessel elasticity, blood volume, and cardiac output affect blood pressure. Page 3. Sources of One of the main factors that affects blood pressure is peripheral resistance. cells and plasma encounter resistance when they contact blood vessel walls. If resistance increases, then more pressure is needed to keep blood moving. Three main sources of peripheral resistance: 1. blood vessel diameter 2. blood viscosity 3. total vessel length Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 4. Analogy diameter affects peripheral resistance. As a the diameter of a tube gets smaller, a greater proportion of the fluid is in contact with the wall of the tube. Therefore resistance to flow is increased and pressure rises. Larger diameter, same volume, less pressure. Smaller diameter, same volume, more pressure. Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 5. Vasomotor Fibers Constriction of blood vessels raises blood pressure. diameter is actively regulated by vasomotor fibers, sympathetic nerve fibers that innervate the vessel's smooth muscle layer. Vasomotor fibers release norepinephrine, a powerful vasoconstrictor. A vasoconstrictor is a substance that causes blood vessels to constrict.
2 Page 6. Vasoconstrictors vessel diameter is also regulated by blood-borne vasoconstrictors. Record the effect of each of these chemicals on the blood vessel: Epinephrine Angiotensin II Vasopressin Page 7. Demonstration viscosity affects peripheral resistance. is related to the thickness of a fluid. The greater the viscosity, the less easily molecules slide past one another and the more difficult it is to get the fluid moving and keep it moving. Because of this greater resistance to flow, a greater pressure is required to pump the same volume of viscous fluid. Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 8. The hematocrit is the percentage of red blood cells in the total blood volume. The hematocrit affects blood viscosity and therefore resistance to flow. The more viscous the blood, the greater resistance it encounters and the higher the blood pressure. The hematocrit can increase when there are more red blood cells or less plasma in the blood. The hematocrit can decrease when there are fewer red blood cells or more plasma. Page 9. vessel length affects peripheral resistance. Increased fatty tissue requires more blood vessels to service it and adds to the total vessel length in the body. The longer the total vessel length, the greater the resistance encountered, and the greater the blood pressure. Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 10. Elasticity Besides peripheral resistance, blood vessel elasticity also affects blood pressure. A healthy elastic artery expands, absorbing the shock of systolic pressure. The elastic recoil of the vessel then maintains the continued flow of blood during diastole. When an individual has arteriosclerosis, arteries become calcified and rigid, so they can't expand when the pulse wave of systolic pressure passes through them. Thus the walls of the artery experience higher pressures and become weaker and weaker.
3 Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 11. Volume Analogy: Hoses volume affects blood pressure. When there is a greater volume of fluid, more fluid presses against the walls of the arteries resulting in a greater pressure. When there is less volume there is less pressure. Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 12. Volume Examples Reduced blood volume (for example due to excessive sweating) reduces blood pressure short term. Long term homeostatic mechanisms compensate, bringing blood volume and blood pressure back up to normal levels. Increased blood volume (for example due to water retention from excessive salt intake) increases blood pressure short term. Long term homeostatic mechanisms compensate, bringing blood volume and blood pressure back up to normal levels. Page 13. Cardiac Output: Heart Rate Anything that decreases cardiac output, also decreases blood pressure, because there is less pressure on the vessel walls. An increase in cardiac output results in increased blood pressure. Cardiac Output = Heart Rate X Stroke Volume Anything that affects heart rate or stroke volume affects cardiac output and thus blood pressure. What happens to heart rate, cardiac output, and blood pressure with parasympathetic stimulation (vagus nerve)? What happens to heart rate, cardiac output, and blood pressure with sympathetic stimulation? Factors Affecting Pressure Elasticity Volume Cardiac Output Page 14. Cardiac Output: Stroke Volume Affect of stroke volume on blood pressure.
4 If less blood is ejected from the heart with each beat, then blood pressure will be lower because there will be less blood pressing against the vessel walls. volume affects end diastolic volume and therefore stroke volume. With decreased stroke volume, due to decreased venous return, volume there is a decreased cardiac output and a decreased blood pressure. With increased stroke volume, due to increased venous return and/or increased contractility, there is an increased cardiac output and increased blood pressure. Page 15. Summary Increases in peripheral resistance, blood volume, and cardiac output result in higher blood pressure. Conversely decreases in any of these factors lead to lower blood pressure. Three main sources of peripheral resistance: vessel diameter, blood viscosity, and total vessel length. If arteries lose their elasticity and become more rigid, blood pressure increases. ** Now is a good time to go to quiz question 1: Click the Quiz button on the left side of the screen. Work through quiz question 1. Notes on Quiz Questions: Quiz Question #1: This question asks you to choose the factors that will decrease the blood pressure. Study Questions on Factors that Affect Pressure: 1. (Page 1.) What are the four main factors affecting blood pressure? 2. (Page 3.) cells and plasma encounter resistance when they contact blood vessel walls. What is this resistance called? 3. (Page 3.) Is more or less pressure needed to keep blood moving when resistance increases? 4. (Page 3.) What are the three main sources of peripheral resistance? 5. (Page 4.) What is the relationship between the diameter of a tube and the proportion of fluid that is in contact with the wall of the tube? 6. (Page 4.) What is the relationship between the diameter of a tube and resistance to flow? What effect does this have on pressure? 7. (Page 5.) Does constriction of blood vessels raise or lower blood pressure? 8. (Page 5.) What actively regulates the diameter of blood vessels? 9. (Page 5.) What chemical is released by vasomotor fibers that acts as a powerful vasoconstrictor? 10. (Page 6.) List three blood-borne vasoconstrictors? 11. (Page 7.) Explain viscosity. 12. (Page 7.) What is the relationship between viscosity and pressure required to pump a fluid? 13. (Page 8.) Define hematocrit. 14. (Page 8.) What is the effect of hematocrit on blood viscosity? 15. (Page 8.) When does hematocrit increase? 16. (Page 9.) What is the relationship between the total vessel length, resistance, and blood pressure? 17. (Page 10.) Why is expansion and recoil of the elastic arteries important?
5 18. (Page 10.) Why does blood pressure often increase in individuals with arteriosclerosis? 19 (Page 11.) What is the relationship between blood volume and blood pressure? 20. (Page 13.) What is the relationship between blood pressure and cardiac output? 21. (Page 13.) What is the relationship between heart rate, stroke volume and cardiac output? 22. (Page 13.) What happens to heart rate, cardiac output, and blood pressure with both parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation? 23. (Page 14.) What is the relationship between venous return and stroke volume?
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Milwaukee School of Engineering [email protected]. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
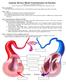 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
3. Tunica adventitia is the outermost layer; it is composed of loosely woven connective tissue infiltrated by nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics
 Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Pulmonary Ventilation
 Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
 Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction When there is an overwhelming threat to the
Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction When there is an overwhelming threat to the
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2. 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany
 Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Blood Pressure. Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls. Blood Pressure. Blood Pressure
 Blood Pressure Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls Systolic pressure exerted on arteries during systole Diastolic pressure in arteries during diastole 120/80 Borderline
Blood Pressure Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls Systolic pressure exerted on arteries during systole Diastolic pressure in arteries during diastole 120/80 Borderline
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly email [email protected]
 INTRODUCTION TO CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 125 16 TH MARCH 2009 Toby Elkington, Specialist Registrar Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Salford Royal NHS
INTRODUCTION TO CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 125 16 TH MARCH 2009 Toby Elkington, Specialist Registrar Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Salford Royal NHS
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise
 Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise Suggestions for Teachers Background Static exercise involves the contraction of skeletal muscle without a change in muscle length, hence the alternative term, isometric
Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise Suggestions for Teachers Background Static exercise involves the contraction of skeletal muscle without a change in muscle length, hence the alternative term, isometric
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
Gas Exchange. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
The EasySense unit can detect that the Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor is connected and the range it is set to.
 Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. For People With CKD Stages 1 4
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease
 High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Starling s Law Regulation of Myocardial Performance Intrinsic Regulation of Myocardial Performance
 Regulation of Myocardial Performance Intrinsic Regulation of Myocardial Performance Just as the heart can initiate its own beat in the absence of any nervous or hormonal control, so also can the myocardium
Regulation of Myocardial Performance Intrinsic Regulation of Myocardial Performance Just as the heart can initiate its own beat in the absence of any nervous or hormonal control, so also can the myocardium
AgoraLink Agora for Life Science Technologies Linköpings Universitet Kurs i Fysiologisk mätteknik Biofluidflöden
 AgoraLink Agora for Life Science Technologies Linköpings Universitet Kurs i Fysiologisk mätteknik Biofluidflöden Fysiologisk mätteknik Anatomy of the heart The complex myocardium structure right ventricle
AgoraLink Agora for Life Science Technologies Linköpings Universitet Kurs i Fysiologisk mätteknik Biofluidflöden Fysiologisk mätteknik Anatomy of the heart The complex myocardium structure right ventricle
Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop: Stimulus. Production Cell. Hormone. Target Cell. Target Cell Action
 Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Chapter 12. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation. Heat Balance. An Overview of Heat Balance. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Altitude. Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments. The Stress of Altitude. Reduced PO 2. O 2 Transport Cascade. Oxygen loading at altitude:
 Altitude Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments Reduced PO 2 The Stress of Altitude O 2 Transport Cascade Progressive change in environments oxygen pressure & various body areas Oxygen loading at altitude:
Altitude Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments Reduced PO 2 The Stress of Altitude O 2 Transport Cascade Progressive change in environments oxygen pressure & various body areas Oxygen loading at altitude:
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Circulation Stations
 Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION.
 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Modeling the Cardiovascular System using STELLA. A module for Computational Biology by Karl Romstedt
 Modeling the Cardiovascular System using STELLA A module for Computational Biology by Karl Romstedt Description This module teaches concepts regarding cardiovascular function and modeling. It is intended
Modeling the Cardiovascular System using STELLA A module for Computational Biology by Karl Romstedt Description This module teaches concepts regarding cardiovascular function and modeling. It is intended
Direct Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Angel M. Rivera CVT, VTS (ECC) Animal Emergency Center Glendale, WI March 2003
 Direct Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Angel M. Rivera CVT, VTS (ECC) Animal Emergency Center Glendale, WI March 2003 Introduction Direct measurement of arterial blood pressure is obtained via a peripheral
Direct Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Angel M. Rivera CVT, VTS (ECC) Animal Emergency Center Glendale, WI March 2003 Introduction Direct measurement of arterial blood pressure is obtained via a peripheral
To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes.
 Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Exchange and transport
 Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
Exchange and transport Examples of things which need to be interchanged between an organism and its environment include: Respiratory gases Nutrients Excretory products Heat This exchange can take place
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
High Blood Pressure (Essential Hypertension)
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Anatomy Review. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS
 Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Chapter 23. Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration
 Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
About High Blood Pressure
 About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
LABORATORY PROCEDURE MANUAL
 Exercise 2 Donor Physical Exam Textbook: Skills: 20 points Objectives 1. For each of the following state the acceptable values for blood donation using appropriate units: a. Pulse b. Temperature (Celsius
Exercise 2 Donor Physical Exam Textbook: Skills: 20 points Objectives 1. For each of the following state the acceptable values for blood donation using appropriate units: a. Pulse b. Temperature (Celsius
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering
 3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering Blood Pressure Estimation based on Pulse Transit Time and Compensation of Vertical Position Dipl.-Inform. Med. Christian Douniama Dipl.-Ing.
3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering Blood Pressure Estimation based on Pulse Transit Time and Compensation of Vertical Position Dipl.-Inform. Med. Christian Douniama Dipl.-Ing.
Hemodynamic Monitoring: Principles to Practice M. L. Cheatham, MD, FACS, FCCM
 SUMMARY HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING: FROM PRINCIPLES TO PRACTICE Michael L. Cheatham, MD, FACS, FCCM Director, Surgical Intensive Care Units Orlando Regional Medical Center Orlando, Florida Fluid-filled catheters
SUMMARY HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING: FROM PRINCIPLES TO PRACTICE Michael L. Cheatham, MD, FACS, FCCM Director, Surgical Intensive Care Units Orlando Regional Medical Center Orlando, Florida Fluid-filled catheters
Ion Channels. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** There are a number of ion channels introducted in this topic which you
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** There are a number of ion channels introducted in this topic which you
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate
 Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
A&P Basics. a. 1,6,3,4,5,2 b. 2,4,5,6,1,3 c. 1, 3,6,5,4,2 d. 3,1,5,6,4,2 e. 1,6,3,2,5,4
 1. Which of the following disciplines is MOST likely to concentrate on the structure and function of organelles? a. Gross anatomy b. Histology c. Cytology d. Embryology 2. Which of the following disciplines
1. Which of the following disciplines is MOST likely to concentrate on the structure and function of organelles? a. Gross anatomy b. Histology c. Cytology d. Embryology 2. Which of the following disciplines
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 2. Goals/ What You Need to Know Goals What You Need to Know
 Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness
 Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Edwards FloTrac Sensor & Edwards Vigileo Monitor. Measuring Continuous Cardiac Output with the FloTrac Sensor and Vigileo Monitor
 Edwards FloTrac Sensor & Edwards Vigileo Monitor Measuring Continuous Cardiac Output with the FloTrac Sensor and Vigileo Monitor 1 Topics System Configuration Physiological Principles Pulse pressure relationship
Edwards FloTrac Sensor & Edwards Vigileo Monitor Measuring Continuous Cardiac Output with the FloTrac Sensor and Vigileo Monitor 1 Topics System Configuration Physiological Principles Pulse pressure relationship
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4)
 Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 5. The newly formed bicarbonate moves into the plasma.
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 5. The newly formed bicarbonate moves into the plasma.
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
1. The potential sites of action for sympathomimetics and the difference between a direct and indirect acting agonist.
 1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
