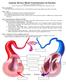
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
|
|
|
- Hortense Woods
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains waste materials, leucocytes and lymphocytes but not erythrocytes. The fluid moves via contraction of skeletal muscles, oncoming pressure from tissue fluids, movement towards thorax from inspiration and suction from negative pressure. Ducts empty into subclavian vein. Hot Stone Massage Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
2 The obstruction of lymphatic flow is known as oedema. Afferent vessels = arriving, Efferent vessels = exiting Lymph nodes made of lymph tissue: cells phagocytes (engulf and destroy waste and bacteria). Lymphocytes (produce antibodies). Cells divide to form lymphocytes. Lymphatic nodes are named submandibular, posterior, auricular, anterior auricular, occipital, deep and superficial cervical, axillery, supratrochlear, inguinal, popliteal and found throughout the body. Lymph tissue areas are the tonsils, thymus, peyer s patches(wall of small intestine),appendix, spleen(forms lymphocytes, kills erythrocytes and thromocytes, fights infection, stores blood). The Right Lymphatic duct drains lymph from right side, head, chest, neck, and arm. The Thoracic duct collects and drains lymph from left side head, neck, trunk, arm and lower limbs. Disorders Hodkins s disease and oedema. Summary Provides a channel for transporting excess tissue fluid away from tissues and back to the blood circulation. Collects and transports lymph from tissue walls. Nodes filter lymph of harmful materials before returning it to the blood circulation. Produces new lymphocytes. Produces antibodies. Lymphatic capillaries in lining of small intestine assist in the absorption of fat droplets. Hot Stone Massage Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 2
3 Effects of massage upon the Lymphatic System Massage is very useful in supporting the Lymphatic system as it assists with the movement of lymph fluid around the body. It helps reduce swelling (oedema) caused by too much fluid in the cells; it can help reduce cellulite and general body toxin overload. Diagram showing the Lymphatic circuit Hot Stone Massage Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 3
4 Diagram showing the Lymphatic Sites in the body The Muscular System This system consists of muscles of the body and their attachments tendons and fascia. A muscle is a group of specialised elastic tissues. Muscle tissue is bundled together in a sheath (fascia) the end of which attaches the muscle to other parts of the body via a tendon. Muscle is made up of 75% water, 20% proteins, 5%fats, mineral salts and glycogen. The Function of a muscle is to contract and start a movement in surrounding structures (tendons, ligaments and bones). Hot Stone Massage Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 4
5 Muscle contracts in reaction to a nerve stimulus sent by the brain through a motor nerve. The muscle then shortens becoming fatter at the centre. Other functions are to: Contract and produce movement, Stabilise joints, Maintain postural tone and aids in temperature control e.g.: shivering, dilation of capillaries. There are 3 types of muscle tissue. Voluntary/skeletal/striated muscles we consciously control arms/legs(look stripy). Involuntary/Smooth muscle non-conscious use walls of blood and lymphatic vessels, in respiratory, digestive and genito-urinary systems. Cardiac - to power pump action of heart only found in heart. How do muscles work? 2 types of muscle contraction. Isometric muscle contracts but produces no movement. Isotonic muscle contracts and moves and the tension remains unaltered in the muscle. Muscles usually work in pairs antagonist(opposing relaxing muscle) and agonist(contracting muscle) both must contract and relax equally to ensure a smooth and not jerky movement. When to contract? Stimulus to contract comes from nervous system through nerves. Motor nerves enter muscles. Muscle gets energy from adequate blood supply which comes from oxygen and nutrients from arterial capillaries which is converted into energy by chemical changes. Used by muscles and lactic acid (waste product) excreted into venous blood stream. Hot Stone Massage Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 5
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237)
 Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System
 The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
HOW TO CHECK YOUR LYMPH NODES
 HOW TO CHECK YOUR LYMPH NODES What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you to understand more about how to check your lymph nodes yourself. It tells you why you should be
HOW TO CHECK YOUR LYMPH NODES What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you to understand more about how to check your lymph nodes yourself. It tells you why you should be
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST. Part I: Cells. 1. The cell grows to its mature size during. a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d.
 7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 3 SOLVED PAPER Chapter PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION WARMING UP Warming up is a short time activity carried out prior to any severe or skilled activity. It is important to warm up before
3 SOLVED PAPER Chapter PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION WARMING UP Warming up is a short time activity carried out prior to any severe or skilled activity. It is important to warm up before
Sports, Remedial and Holistic Massage Therapist MISRM, DipThaiMast. Sports Massage Thai Yoga Massage Hot Stone Massage Seated Acupressure Massage
 Paul White Sports, Remedial and Holistic Massage Therapist MISRM, DipThaiMast Sports Massage Thai Yoga Massage Hot Stone Massage Seated Acupressure Massage Paul White Deep Tissue Massage improving YOUR
Paul White Sports, Remedial and Holistic Massage Therapist MISRM, DipThaiMast Sports Massage Thai Yoga Massage Hot Stone Massage Seated Acupressure Massage Paul White Deep Tissue Massage improving YOUR
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource
 CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
The lymphatic system and the immune system
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Immune System Memory Game
 Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Pre-requisites: Successful completion of 4th grade science and the 4th grade science assessment.
 Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system?
 Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Get It Right. Answers. Chapter 1: The Science of Life. A biologist studies all living things.
 Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
S.M.A.R.T.box. Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP. Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers
 CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema
 Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
CHAPTER 2 : CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 2 : CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Parts of microscope : An instrument that magnifies minute objects so they can be seen easily. It is one of the most important tools of science. Physicians and
CHAPTER 2 : CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Parts of microscope : An instrument that magnifies minute objects so they can be seen easily. It is one of the most important tools of science. Physicians and
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Paper 1 Answer all questions. Each question is followed by four options, A, B, C and D. For each question, choose one answer only
 hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Sit stand desks and musculo skeletal health. Katharine Metters
 Sit stand desks and musculo skeletal health Katharine Metters Topics Sitting Standing Movement and activity Work and human change Sitting uses less energy Sitting provides support for the body to reduce
Sit stand desks and musculo skeletal health Katharine Metters Topics Sitting Standing Movement and activity Work and human change Sitting uses less energy Sitting provides support for the body to reduce
