The Body s Transport System
|
|
|
- Clarence Mason
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete the cycle diagram below that shows the path that blood follows as it circulates through the body. Write each step of the pathway in a separate circle. Right side of heart Lungs The Cardiovascular System 1. Another name for the cardiovascular system is the system. 2. Complete this concept map to show what makes up the cardiovascular system. Cardiovascular system is made up of the heart
2 The Body s Transport System (continued) 3. What three things are carried throughout the body by the cardiovascular system? The Heart 4. Each time the heart beats, what does it do to blood? 5. Complete the table about the chambers of the heart. Chamber of the Hearts Questions Upper Chambers Lower Chambers What are these chambers called? How many are there? What is the function, or job, of these chambers? 6. A flap of tissue that prevents blood from flowing backward is a(n). 7. The group of cells that adjusts the speed of the heart beat is called the. The heart rate depends on how much the body needs. 8. What does an artificial pacemaker do?
3 Circulation Name Date Class Two Loops 9. Name the three kinds of blood vessels. 10. Describe the loop in which the blood picks up oxygen. 11. Draw arrows on the diagram below to show how blood circulates through the body. The first arrow should start in the right atrium. Blood vessels in lungs Artery to lungs Vein from lungs Right atrium Left atrium Vein from body Right ventricle Left ventricle Artery to body Blood vessels in body 12. The largest artery in the body is called the.
4 Circulation Review and Reinforce The Body s Transport System Understanding Main Ideas Use the diagram to answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. Lungs 1. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the path of the blood flow throughout the body. 2. What is the function of each atrium? What is the function of each ventricle? 3. Which of the large blood vessels labeled a, b, c, and d are arteries and which are veins? Explain how you know. b. c. a. d. Body Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence. aorta capillaries cardiovascular system heart pacemaker valve 4. The is a group of cells that adjusts the heart rate. 5. The muscular organ that pumps blood through the body is called the. 6. The is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. 7. A(n) is a flap of tissue that prevents blood from flowing backward. 8. The largest artery is called the. 9. Substances are exchanged between the blood and body cells in the.
5 A Closer Look at Blood Vessels This section describes the three kinds of blood vessels that are found in your body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, compare and contrast the three kinds of blood vessels by completing the table below. Comparing Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Function Structure of Wall Artery Carries blood away from heart Capillary Vein Arteries 1. Arteries carry blood away from the. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? The coronary arteries provide the stomach with its blood supply. 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about pulse. a. The faster your heart beats, the slower your pulse will be. b. Pulse is caused by the expanding and narrowing of artery walls. c. When you count pulse beats, you are also counting heartbeats. d. You can feel pulse in veins but not in arteries. 4. Is the following sentence true or false? Arteries control the amount of blood that different organs receive.
6 Circulation Name Date Class Capillaries 5. What important thing happens in the capillaries? 6. One process in which materials are exchanged between the blood and the body cells is. Veins 7. What job do veins carry out? 8. What three things help push blood through veins? a. b. c. Blood Pressure 9. What is blood pressure? 10. Circle the letter of the name of the instrument that measures blood pressure. a. stethoscope b. X-ray machine c. sphygmomanometer d. mercury
7 Circulation Review and Reinforce A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Understanding Main Ideas Answer the following questions. 1. Label the diagram with the names of the three kinds of blood vessels. Connective tissue Smooth muscle Epithelial tissue a. b. c. 2. After blood leaves the heart, through what kinds of vessels and in what order does blood move? 3. In which kind of blood vessel is blood pressure usually highest? 4. Which blood vessel allows diffusion through its walls? 5. What causes blood pressure? 6. What factors help blood move through veins? Building Vocabulary Match each term with its definition by writing the letter of the correct definition in the right column on the line beside the term in the left column. 7. blood pressure 8. pulse 9. diffusion 10. coronary artery a. the movement of molecules from an area in which they are highly concentrated to an area in which they have a low concentration b. the repetitious rise and fall of the artery in your wrist caused by the expansion and relaxation of the artery wall c. caused by the force with which the ventricles contract d. a vessel that supplies the heart itself with blood
8 Blood and Lymph This section explains the comonents of blood is and describes the jobs performed by the different parts of blood. This section also describes the lymphatic system. Use Target Reading Skills As you read the section Blood, write the main idea in the graphic organizer below. Then, write four supporting details that give examples of the main idea. Main Idea Blood is made up of four components. Detail Detail Detail Detail
9 Circulation Name Date Class Blood 1. What is the name for the liquid part of blood? 2. Complete the concept map below by naming the types of cells that are found in blood. Cells in blood Red blood cells include 3. What is plasma mostly made up of? 4. List three kinds of materials that are carried in plasma. a. b. c. 5. What job do red blood cells perform in the body? 6. What is hemoglobin, and where is it found? 7. What is the job of white blood cells?
10 Blood and Lymph (continued) 8. List four ways in which white blood cells are different from red blood cells. a. b. c. d. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Platelets are pieces of cells. 10. Describe how a blood clot forms. 11. What is a blood transfusion? 12. Why can't a person with blood type A safely receive a transfusion of blood type B? 13. What is the Rh factor? Blood Types Match the blood type with the kinds of clumping proteins in its plasma. Blood Type 14. A 15. B 16. AB 17. O Clumping Proteins in Its Plasma a. no clumping proteins b. anti-b proteins c. both anti-a and anti-b proteins d. anti-a proteins The Lymphatic System 18. What is the lymphatic system? 19. The fluid inside the lymphatic system is called. 20. How do lymph nodes help fight disease?
11 Circulation Name Date Class Circulation Review and Reinforce Blood and Lymph Understanding Main Ideas Complete the table. Then answer the questions. Blood Component Description Function Plasma Red Blood Cell White Blood Cell Platelet 1. If a person with type B blood needs a transfusion, which types of blood can he or she safely receive? Explain your answer. 2. How does fluid in the blood become lymph? How is it returned to your blood? Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence. plasma hemoglobin lymph node lymphatic system 3. A small knob of tissue that filters lymph is called a(n). 4. is the liquid part of the blood. 5. is an iron-containing protein that binds to oxygen molecules. 6. The is the network of vessels that returns fluid to the bloodstream.
12 Circulation Name Date Class Cardiovascular Health This section describes diseases of the cardiovascular system. The section also identifies steps that people can take to help prevent these diseases. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read, preview the red headings. In the graphic organizer below, ask a what or how question for each heading. As you read, write the answers to your questions. Asking Questions Question Answer What are some cardiovascular diseases? Cardiovascular Diseases 1. What is atherosclerosis? 2. What is cholesterol?
13 Cardiovascular Health (continued) 3. Complete the flowchart below, which describes what can happen when atherosclerosis develops in the coronary arteries. Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis develops in coronary arteries. Heart muscle receives less therefore its cells receive less, and. A(n) to part of the heart is cut off. occurs, which means that blood flow 4. What is hypertension? 5. Give two reasons why hypertension is a serious problem. 6. What is done to treat hypertension?
14 Circulation Name Date Class Keeping Healthy 7. To help maintain cardiovascular health, people should eat a diet that is low in these substances. a. b. c. 8. Is the following sentence true or false? Even if smokers quit, they cannot decrease their risk of death from cardiovascular disease. 9. In the table below, explain why each behavior is important for cardiovascular health. Cardiovascular Health Behavior Why It Is Important Getting a lot of exercise Eating healthy foods Not smoking
15 Circulation Review and Reinforce Cardiovascular Health Understanding Main Ideas Write each of the given behaviors in the appropriate column on the chart. Behaviors: eating foods high in saturated fat, running, smoking, eating lowsodium foods, playing basketball, eating salty foods, eating foods low in cholesterol, being overweight Behaviors That Affect Your Heart Healthy Harmful Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 9. Why is atherosclerosis dangerous? 10. Describe how hypertension affects your heart and blood vessels. Why is it called the silent killer? 11. Explain why hypertension is related to atherosclerosis. Building Vocabulary Write a definition for each of the following terms on the lines below. 12. atherosclerosis 13. cholesterol 14. heart attack 15. hypertension
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes.
 Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Blood Transfusion. There are three types of blood cells: Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets.
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Blood Transfusion. Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
This interchange is simple
 3 Circulation This interchange is simple compared to how blood travels within your body. In this chapter, you will discover how complex your circulatory system is. You ll learn what blood is made of and
3 Circulation This interchange is simple compared to how blood travels within your body. In this chapter, you will discover how complex your circulatory system is. You ll learn what blood is made of and
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
High Blood Pressure (Essential Hypertension)
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
3.5% 3.0% 3.0% 2.4% Prevalence 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% 0.0%
 S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
S What is Heart Failure? 1,2,3 Heart failure, sometimes called congestive heart failure, develops over many years and results when the heart muscle struggles to supply the required oxygen-rich blood to
Heart Diseases and their Complications
 Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Circulation. What does a highway have to do with circulation? 62 D Steve Allen/Getty Images
 Circulation sections 1 The Circulatory System Lab The Heart as a Pump 2 Blood 3 The Lymphatic System Lab Blood Type Reactions Virtual Lab What factors affect the likelihood of hypertension? What does a
Circulation sections 1 The Circulatory System Lab The Heart as a Pump 2 Blood 3 The Lymphatic System Lab Blood Type Reactions Virtual Lab What factors affect the likelihood of hypertension? What does a
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
 Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease
 High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Circulation Stations
 Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Immune System Memory Game
 Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness
 Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
S.M.A.R.T.box. Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP. Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers
 CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
In this exercise, you will name body organs and identify their position in the body.
 Humans and animals Exercise Body organs In this exercise, you will name ody organs and identify their position in the ody Some ody organs are shown Write the name of the ody organ elow each drawing Draw
Humans and animals Exercise Body organs In this exercise, you will name ody organs and identify their position in the ody Some ody organs are shown Write the name of the ody organ elow each drawing Draw
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision
 National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
Congestive Heart Failure
 Healthy People 2010 Conference Health Education on the Internet Welcome Mr. System Administrator Congestive Heart Failure What is congestive heart failure? How does it occur? What are the symptoms? How
Healthy People 2010 Conference Health Education on the Internet Welcome Mr. System Administrator Congestive Heart Failure What is congestive heart failure? How does it occur? What are the symptoms? How
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. For People With CKD Stages 1 4
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.)
 Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
Facts About Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.) One in every 20 Americans over the age of 50 has P.A.D., a condition that raises the risk for heart attack and stroke. Peripheral arterial disease, or P.A.D.,
Living with. Atrial Fibrillation
 Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
Living with Atrial Fibrillation U nderstanding Atrial Fibrillation An estimated 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation (AF). That makes it the most common heart rhythm abnormality in
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
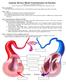 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
YOUR GUIDE TO. Managing and Understanding Your Cholesterol Levels
 YOUR GUIDE TO Managing and Understanding Your Cholesterol Levels Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
YOUR GUIDE TO Managing and Understanding Your Cholesterol Levels Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
About High Blood Pressure
 About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
What is a Heart Attack? 1,2,3
 S What is a Heart Attack? 1,2,3 Heart attacks, otherwise known as myocardial infarctions, are caused when the blood supply to a section of the heart is suddenly disrupted. Without the oxygen supplied by
S What is a Heart Attack? 1,2,3 Heart attacks, otherwise known as myocardial infarctions, are caused when the blood supply to a section of the heart is suddenly disrupted. Without the oxygen supplied by
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Milwaukee School of Engineering [email protected]. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
DIABETES. Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys. www.kidney.org
 DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys
 American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
American Kidney Fund reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys reaching out giving hope improving lives High Blood Pressure: The #2 Cause of Kidney Failure Your doctor
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
Name Date Class. This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread.
 Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Fighting Disease Name Date Class Infectious Disease This section explains what kinds of organisms cause infectious disease and how infectious diseases are spread. Use Target Reading Skills Before you read,
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Cardiovascular Disease and the Endothelium
 Cardiovascular Disease and the Endothelium by Jeffrey Porro A series of articles for general audiences This series of essays was developed as part of FASEB s efforts to educate the general public, and
Cardiovascular Disease and the Endothelium by Jeffrey Porro A series of articles for general audiences This series of essays was developed as part of FASEB s efforts to educate the general public, and
Cardioversion for. Atrial Fibrillation. Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation Your Heart s Electrical System Cardioversion Living with Atrial Fibrillation When You Have Atrial Fibrillation You ve been told you have a heart condition called atrial
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal. Index of Topics. You and Your Heart Activity 1: How Your Heart Functions.2 Activity 2: Break the Heart Code..
 This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
10 MINUTES TO CHANGE YOUR LIFE Lowering cholesterol
 10 MINUTES TO CHANGE YOUR LIFE Lowering cholesterol High cholesterol isn t something you can feel or notice, but if you have it you re more likely to have a heart attack or stroke. The good news is there
10 MINUTES TO CHANGE YOUR LIFE Lowering cholesterol High cholesterol isn t something you can feel or notice, but if you have it you re more likely to have a heart attack or stroke. The good news is there
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Blood Type Testing Lab Report Section 1101 Nattanit Trakullapphan (Nam) Chawalnrath Wongdeshanan (Kat)
 Blood Type Testing Lab Report Section 1101 Nattanit Trakullapphan (Nam) Chawalnrath Wongdeshanan (Kat) Introduction: figure 1.1 (Blood type n.d.) figure 1.2 (Blood type, Antigens-Antibodies n.d.) Multiple
Blood Type Testing Lab Report Section 1101 Nattanit Trakullapphan (Nam) Chawalnrath Wongdeshanan (Kat) Introduction: figure 1.1 (Blood type n.d.) figure 1.2 (Blood type, Antigens-Antibodies n.d.) Multiple
Paper 1 Answer all questions. Each question is followed by four options, A, B, C and D. For each question, choose one answer only
 hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Caring for the Client with Heart Failure
 Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the home health aide should be able to: 1. Define heart failure.
Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the home health aide should be able to: 1. Define heart failure.
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY. Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care
 TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care STAYING HEALTHY THE IMPORTANCE OF PROPER MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES Diabetes is
TYPE 2 DIABETES IN THE AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITY Understanding the Complications That May Happen Without Proper Care STAYING HEALTHY THE IMPORTANCE OF PROPER MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES Diabetes is
LABORATORY PROCEDURE MANUAL
 Exercise 2 Donor Physical Exam Textbook: Skills: 20 points Objectives 1. For each of the following state the acceptable values for blood donation using appropriate units: a. Pulse b. Temperature (Celsius
Exercise 2 Donor Physical Exam Textbook: Skills: 20 points Objectives 1. For each of the following state the acceptable values for blood donation using appropriate units: a. Pulse b. Temperature (Celsius
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource
 CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS AND FAMILIES A Patient s Guide to Living with Atrial Fibrillation 30 Bond Street, Toronto, ON M5B 1W8 Canada 416.864.6060 stmichaelshospital.com Form No. XXXXX Dev. XX/XXXX GOALS
