III. BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE
|
|
|
- Berniece Wright
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Top Five Body Shop Grade Level: Grade 1 Presented by: Linda Bruestle, Valleyview Elementary, Lakeland, FL Length of Unit: Eight days I. ABSTRACT This unit will take first graders on a journey through the human body. Join the teacher and her helper, who is dressed in a bodysuit designed to help the systems come alive. They lead the students through the skeletal basics of the skeletal, muscular, digestive, and nervous systems. Muscle in as we use hands-on activities, songs, and literature. Meet Healthy Harry as he helps us digest how to keep our body systems in top shape. Don t get nervous as the unit all comes together and the children have fun learning about the human body. II. OVERVIEW A. Concept Objectives 1. Explore and identify the basics of the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and digestive systems of the human body. 2. Demonstrate a basic knowledge of the importance of exercise and good nutrition. B. Core Knowledge Content 1. Exploring the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and digestive systems 2. Recognizing the importance of good nutrition and exercise C. Skills 1. Recognition of the major parts of the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and digestive systems of the human body 2. Measurement, patterning, greater than and less than, addition, number sense 3. Recognition of the basic food groups and food pyramid III. BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Hirsch, Jr., E. D. What Your First Grader Needs to Know. New York: Dell Publishing Company, 1991, ISBN X Hirsch, Jr. E.D. A First Dictionary of Cultural Literacy; What Our Children Need to Know. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1996, ISBN Parker, Steve. The Skeleton and Movement. London: Franklin Watts, 1989, ISBN Parker, Steve. Food and Digestion. London: Franklin Watts, 1990, ISBN X. Parker, Steve. The Brain and Nervous System. London: Franklin Watts, 1990, ISBN IV. RESOURCES Balestrino, Philip. The Skeleton Inside You. New York: Scholastic Inc., 1989, ISBN X. Cole, Joanna. Your Insides. New York: Putnam & Grosset, 1992, ISBN Learning About Your Body. California: Frank Schaffer Publications, Inc., Our Bodies. California: Teacher Created Materials, Inc., 1995, ISBN Sevaly, Karen. October. California: Teacher s Friend Publications, 1987,ISBN Showers, Paul. What Happens to a Hamburger. New York: Harper Collins, 1985, ISBN
2 Siepak, Karen. Keeping Healthy. North Carolina: Carson-Dellosa, What s Inside? My Body. London: A Dorling Kindersley, 1991, ISBN V. LESSONS A. Lesson One: Let s Talk Body 1. Objective/Goal a. The students will identify the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and digestive systems of the body. a. An adult in a black body suit with Velcro attachments that hold representations of the skeletal, muscular, nervous and digestive systems of the body (Frank Schaffer Pub., Learning About Your Body), chart, marker 3. Prior Knowledge for students a. The students will recognize and identify the body parts. a. Skeletal system, muscular system, nervous system, digestive system, nutrition a. Using a web, the students will relate their prior knowledge of the human body. b. The teacher will introduce the adult in the black body suit and discuss the body parts we see on the outside and ask about the inside. c. The teacher will read, What s Inside My Body. d. Use the adult in the black body suit and the representations of the skeletal, muscular, nervous and digestive systems to introduce the systems and give an overview of the function of each. f. Discuss the need for good nutrition to keep the body and all its functions strong and active. a. Use activity sheet (Appendix A) to label the four systems of the body that were introduced. a. The students will write and illustrate their ideas for the saying, An apple a day keeps the doctor away. This activity will be shared with the class before the nutrition lesson. B. Lesson Two: All About Bones 1. Objectives/Goals a. The students will know that the skeletal system has 206 bones. b. The students will know that joints connect the bones. c. The students will identify some of the main bones. a. Recording of the song, Dry Bones, book, The Skeleton Inside You, paper skeleton model (October, Teacher s Friend Publications, pages 60-64), scissors, rubber bands, poster model of the skeletal system, work sheet (Frank Schaffer, Learning About Your Body). a. The body has a skeletal system. a. Skeleton, skull, collar bone, pelvis, spine ribs, elbow, knee, wrist, ankle, joints, x-ray, ligaments 2
3 a. Play the recording of Dry Bones as the children assembly for the lesson. b. Reflect on the web created in Lesson One. c. Read The Skeleton Inside You. d. Discuss the knowledge in the book: 206 bones, bones give our body shape, bones break and show up on a picture called an x-ray, and bones fit together at joints held together by ligaments. e. Using the skeletal model, locate some of the main bones of the body: the skull, pelvis, ribs, spine, elbow, ankle, collar bone. f. Using the worksheet, construct a skeletal model. g. Put the model together with rubber bands that represent the joints. h. Discuss the make up of bones and the need for a healthy diet to keep bones strong. Also, that blood cells are made in the center of bones. a. The students will complete worksheet of the skeletal system for the What s Inside Me booklet (Frank Schaffer, Learning About Your Body). a. The students will take turns finding bones on the model. C. Lesson Three: Skeletal Math 1. Objectives/Goals a. The students will complete a pattern. b. The students will recognize greater than and less than. c. The students will be introduced to measurement using a ruler. d. The students will compare measurements. a Rulers, activity sheets (Appendix B, C, and D), candy bones a. The main bones of the skeletal system. a. Pattern, greater than / less than, ruler, graph, add a. The teacher will give each student a package of candy bones (Dem Bones by Brach & Brock Confections, Inc., Chicago, Illinois). b. The students will identify the bones. c. Using the bones, the students will create a pattern using worksheet B (Appendix B). d. Continue to use the bones and graph the bones on activity sheet C (Appendix C). e. Using the same bones, use addition to complete activity sheet D (Appendix D). f. The teacher will explain the basics of a ruler for standard measure, and review greater than / less than. g. The students will practice using standard measure with a ruler by measuring the hand, foot, and finger of a friend. a. The teacher will check the worksheets and pattern completed during the lesson. a. The students may put together a candy skeleton and then the students may eat the candy bones. D. Lesson Four: Muscles - Engines of the Body 3
4 1. Objectives/Goals a. The students will recognize the three kinds of muscles. b. The students will identify the number 650 with the number of muscles in an adult body. c. The students will recognize that muscles contract and relax. a. Worksheet, ruler, pipe cleaner, chart model of muscular system, small rubber balls, work sheet, (Frank Schaffer Pub, Learning About Your Body). a. The body has a muscular system. b. Our body moves. a. muscle, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, diaphragm a. While standing, the students will sing the song, Head, Shoulders, Knees, and Toes, and do the movements as they sing. They will vary the rhythm as they sing. b. The teacher will tell the students they can move because of the muscles in their bodies. There are 650 muscles. Some are large and some are small. The smallest is in the ear. c. The teacher will introduce the 3 kinds of muscles: 1) The skeletal muscles that attach to the bones so we can twist and bend. These muscles control every move we make. They are long and striped. To feel this muscle, put your finger inside of the elbow and raise your arm. 2) The smooth muscle controls the digestive and circulatory systems. These muscles work when active or still, when awake or asleep. When we are asleep they help our hearts beat and help us breathe. To feel a smooth muscle, put your hand on your stomach and breath. This is the diaphragm muscle. 3) The cardiac muscle is only in the heart. To feel this muscle, put your hand over your heart. You can feel the lub, dub, lub, dub. d. Muscles are either contracted or relaxed. e. The students will try some muscle activities. Stand up in front of your desk. Fold a pipe cleaner in half and place it over the end of a ruler. Hold the ruler in your hand; hold your arm straight out with the ruler over your desk without supporting your arm. Try to keep the pipe cleaner as close to the table and as steady as possible. In a few seconds, the tie will start to dance in time to your muscle contractions. The student will write their name on a sheet of paper. Then, squeeze a ball for four minutes. Last, try to write your name again. Next, the students will show expressions. As you look happy, sad, and angry you can feel the muscles in your fact move. f. To keep muscles healthy eat protein like in fish and vegetables. a. Complete the worksheet of the muscular system to the What s Inside Me booklet (Frank Schaffer Pub., Learning About Your Body). a. Have a whole class discussion on what happened during the muscle activities and share the names written before and after the activity with the ball. E. Lesson Five: You Are What You Eat - The Digestive System 4
5 1. Objective/Goal a. The students will recognize the parts of the digestive system. b. The students will be able to relate the basic steps in digestion. a. Book, What Happens to a Hamburger, paper plates, carrots, lemons, large charted model of the digestive system, separate parts of the digestive system, work sheet (Frank Schaffer Pub., Learning About Your Body). a. The food we eat goes through the digestive system. : a. digestion, saliva, stomach, esophagus, small intestine, large intestine. a. Read the book, What Happens to a Hamburger. b. Talk about the facts in the book. c. Digestion begins in the mouth. Try the carrot experiment. Give each child a bite of a carrot. Have the student chew it 10 times. Now, spit the chewed carrot on a paper plate. Observe the carrot. Next, give the students another piece of carrot and ask them to chew this piece 30 times. Then, spit the chewed carrot on the other side of the paper plate. Observe this carrot. Compare and contrast the two pieces of chewed carrot. d. Cut a lemon into parts. Walk around the room and let the students smell the lemon. Ask about what happens in their mouth when they smell the lemon. Explain that saliva helps break up the food in your mouth before you swallow it. e. Follow a model of food down the esophagus, into the stomach with the digestive fluids, on to the intestines --all 21 feet of them -- where digestive fluids enter from the pancreas and liver; finally, into the body through the blood to help build strong muscles, bones, and teeth, and to give you energy to grow and play. f. Look at the model of the digestive system. Discuss the parts and the function of each. At random have students place the model parts on the model and have them relate the function of the parts. a. The teacher will observe the students using the digestive system model to place the parts of the system and to relate the facts of digestion. a. The students will complete the digestion work sheet for the What s Inside Me booklet (Frank Schaffer Pub., Learning About Your Body). F. Lesson Six: The Boss -- The Brain 1. Objective/Goal a. The students will recognize that the brain has three parts. b. The students will recognize that the brain controls the other systems of the body. a. Poster model of a human body with the brain and nervous system highlighted, worksheets, (Frank Schaffer Publications and Teacher Created Materials, Inc., Our Bodies, 1995, pages 31-34), balloon filled with water to about 2 pounds a. The body has a brain and a nervous system that control the body. a. cerebellum, cerebrum, brain stem, brain, nerves 5
6 a. The teacher will ask the students if they know that the body has a boss. b. The teacher will relate the fact that the brain controls the functions of the rest of the body. It is like playing Simon Says only it is the Brain Says. c. Referring to the poster, the teacher will show the students the brain and nervous system. d. Still using the chart, the teacher will introduce the three main sections of the brain and relate the function of each. The cerebellum coordinates muscle movement, the cerebrum is the thought center, and the brain stem controls automatic and life sustaining functions like breathing. e. The brain also needs the five senses. They act like detectives for the brain as they gather information to send to the brain. f. The nervous system carries messages to the brain. To show how fast these messages travel, play a game of Slap Hand. The message gets to your brain quickly so your hands do not get slapped. a. The students will complete the worksheet for the brain and nervous system for the What s Inside Me booklet. (Frank Schaffer Pub., Learning About Your Body). a. The students will look at the fragile balloon filled with water and talk about the importance of wearing a helmet when riding a bicycle. G. Lesson Seven: Healthy Harry and Nutrition 1. Objective/Goal a. The students will recognize the food groups. b. The students will recognize the food pyramid. c. The students will construct a model for healthy food. a. Construction paper in yellow, green, brown, and orange, scissors, crayons, glue, a model of the food pyramid, book, Too Much Junk Food, Weekly Reader (Feb./Mar. 1998, Edition K, Week 3), worksheet (Appendix E) a. The students will know the four basic food groups. a. Nutrition, food groups, food pyramid, healthy a. Name the four food groups. b. Use the poster of the food pyramid and name the foods pictured in each group. c. Discuss how each food group benefits us. Use the Weekly Reader to add additional information. d. Read, Too Much Junk Food. Discuss healthy food habits of the characters. e. Make a Healthy Harry. Use the patterns (Appendix E ) to construct a fun model of the four food groups. f. The students will share the paper they wrote in Lesson One explaining the saying, An apple a day keeps the doctor away. a. The students will tell how one part of their Healthy Harry will keep them healthy. 6
7 a. The students will draw a Healthy Me picture to be used as the cover for the What s Inside Me booklet that they have been completing with each lesson. H. Lesson Eight: Shaping Up 1. Objectives/Goals a. To teach students the importance of exercise. b. To distinguish between good fitness habits and bad fitness habits. a. Worksheet (Carson Dellosa Publications, Keeping Healthy, K-5, 1994). a. Basic exercises a. flexible, maintain, muscles, fat, effort, health, beat, benefit, relaxed, strengthens a. Discuss the ways students exercise. b. Discuss the vocabulary words. c. Distinguish between good and bad fitness habits. d. The teacher will demonstrate proper stretching techniques. The students will model. e. The teacher and students will execute various aerobic exercises including warm up and cool down for twenty minutes. f. Discuss with the students how their hearts feel now that is different from when we started. g. Discuss different aerobic exercises that were performed. a. The students will complete the worksheet (Carson Dellosa from the Materials list). a. The students will take turns modeling healthy exercises. b. The students will take the unit assessment (Appendix F). 7
8 Appendix A Name Date Put the correct name under each picture. muscular system brain and nervous system skeletal system digestive system 8
9 Appendix B Name Date 1. Using your package of Dem Bones, make a pattern. 2. Draw the pattern. 3. Have a friend extend your pattern three more places. 9
10 Appendix C Name Date Graph Dem Bones Using your package of Dem Bones make a bar graph. 10
11 Appendix D Name Date Add Dem Bones + = + = + = + = + = 11
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
II. 2003 Core Knowledge National Conference, Amazing Body System, Grade 1 1
 Amazing Body Systems Grade Level or Special Area: First grade Technology, Science, Reading, and Writing Written by: Debbie DeFrancesco and Ivette Orama Length of Unit: 5 lessons + 12 days of Culminating
Amazing Body Systems Grade Level or Special Area: First grade Technology, Science, Reading, and Writing Written by: Debbie DeFrancesco and Ivette Orama Length of Unit: 5 lessons + 12 days of Culminating
Reader s Theater. I AM the Most Important. (A Script about the human body systems. By Amy Bowden) Characters
 Reader s Theater I AM the Most Important (A Script about the human body systems By Amy Bowden) Characters Judge (narrator) Digestive System Circulatory System Muscular System Respiratory System Nervous
Reader s Theater I AM the Most Important (A Script about the human body systems By Amy Bowden) Characters Judge (narrator) Digestive System Circulatory System Muscular System Respiratory System Nervous
First Grade The Human Body Assessment
 First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
Amazing AmMy Brain! DID YOU KNOW..
 My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
The Digestive System. The large intestine, or colon, holds waste products until elimination can occur. Its main function is to absorb.
 The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND
 Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND The Muscular System Muscle makes up most of everything underneath the skin. This is the tissue that makes up the heart, body organs, and skeletal muscles. Muscle accounts
Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND The Muscular System Muscle makes up most of everything underneath the skin. This is the tissue that makes up the heart, body organs, and skeletal muscles. Muscle accounts
TEACHING Body Systems
 TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Body Systems 3rd Grade Reading Level ISBN: 978-0-8225-2324-6 Green 2 TEACHING BODY SYSTEMS Standards Health Language Arts Writing Language Arts Reading Science Visual Arts Knows
TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Body Systems 3rd Grade Reading Level ISBN: 978-0-8225-2324-6 Green 2 TEACHING BODY SYSTEMS Standards Health Language Arts Writing Language Arts Reading Science Visual Arts Knows
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
Lapbooking through the Human Body
 Lapbooking through the Human Body 2 Lapbooking through the Human Body Second Edition 2014 Copyright @ Elemental Science, Inc. Email: [email protected] Digital Edition Cover Design by Paige Hudson
Lapbooking through the Human Body 2 Lapbooking through the Human Body Second Edition 2014 Copyright @ Elemental Science, Inc. Email: [email protected] Digital Edition Cover Design by Paige Hudson
2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment).
 2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment). Criteria Oral Presentation- Group project Poster Presentation display/ visual aids 1 - Attempts the standard use the
2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment). Criteria Oral Presentation- Group project Poster Presentation display/ visual aids 1 - Attempts the standard use the
Activity: Build Your Own Lung
 Activity: Build Your Own Lung Supplies per group: 2 liter pop bottle Scissors 2 straws 2 balloons 3 rubber bands clay piece of clear wrap paper binder clip Directions: 1. Carefully, cut the bottom off
Activity: Build Your Own Lung Supplies per group: 2 liter pop bottle Scissors 2 straws 2 balloons 3 rubber bands clay piece of clear wrap paper binder clip Directions: 1. Carefully, cut the bottom off
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Mini Medical School Lesson
 Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
I. ABSTRACT II. III. IV.
 Teaching About Magnets in Kindergarten Grade Level or Special Area: Kindergarten Written by: Lori Dawn Montanez, Swallows Charter Academy, Pueblo West, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately two
Teaching About Magnets in Kindergarten Grade Level or Special Area: Kindergarten Written by: Lori Dawn Montanez, Swallows Charter Academy, Pueblo West, CO Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately two
Preventing Falls. Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing
 Preventing Falls Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing Exercise should be comfortable and fun. To get the most out of your home exercise book, join a class for older people to check your exercises
Preventing Falls Strength and balance exercises for healthy ageing Exercise should be comfortable and fun. To get the most out of your home exercise book, join a class for older people to check your exercises
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Human Body Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Name: Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them out.
Name: Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them out.
My Family FREE SAMPLE. This unit focuses on sequencing. These extension
 Unit 5 This unit focuses on sequencing. These extension Unit Objectives activities give the children practice with sequencing beginning, middle, and end. As the learn to name family members and rooms children
Unit 5 This unit focuses on sequencing. These extension Unit Objectives activities give the children practice with sequencing beginning, middle, and end. As the learn to name family members and rooms children
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource
 CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
What is a Biomedical Engineer?
 A What is a Biomedical Engineer? Draw and label a picture of a biomedical engineer at work. Explain your drawing of a biomedical engineer: A-6 Student Post Assessment Lessons 1 and 2 What is a Biomedical
A What is a Biomedical Engineer? Draw and label a picture of a biomedical engineer at work. Explain your drawing of a biomedical engineer: A-6 Student Post Assessment Lessons 1 and 2 What is a Biomedical
II. 2007 Core Knowledge National Conference, First Graders Measure Up!, Grade 1 1
 First Graders Measure Up! Grade Level or Special Area: First Grade Written by: Cindy Todd and Nancy Sanchez, Roscoe Wilson Elementary Magnet School, Lubbock, TX Length of Unit: Ten Lessons (10 days) I.
First Graders Measure Up! Grade Level or Special Area: First Grade Written by: Cindy Todd and Nancy Sanchez, Roscoe Wilson Elementary Magnet School, Lubbock, TX Length of Unit: Ten Lessons (10 days) I.
Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear.
 Page 1 Safety Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear. Prepare a space and have your exercise band and a glass of water (for afterwards) ready
Page 1 Safety Ensure that the chair you use is sturdy and stable. Wear comfortable clothes and supportive footwear. Prepare a space and have your exercise band and a glass of water (for afterwards) ready
The Body Systems Lesson Plan
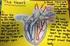 The Body Systems Lesson Plan Science Standards Addressed (From the Colorado Department of Education) http://www2.cde.state.co.us/scripts/allstandards/costandards.asp?stid=7&stid2=0&glid2=0 Standard 2-Life
The Body Systems Lesson Plan Science Standards Addressed (From the Colorado Department of Education) http://www2.cde.state.co.us/scripts/allstandards/costandards.asp?stid=7&stid2=0&glid2=0 Standard 2-Life
The Dance Lesson. A good dance lesson should contain some or all of the following:-
 The Dance Lesson The Primary School Curriculum says:- Dance in education involves the child in creating, performing and appreciating movement as a means of expression and communication. Dance differs from
The Dance Lesson The Primary School Curriculum says:- Dance in education involves the child in creating, performing and appreciating movement as a means of expression and communication. Dance differs from
Human Body Grade 3 Summative Assessment. Assessed Understandings
 Human Body Grade 3 Summative Assessment Students will understand: Assessed Understandings 1. Bones, muscles, and joints function as a system allowing vertebrates to move and survive. 2. Structures and
Human Body Grade 3 Summative Assessment Students will understand: Assessed Understandings 1. Bones, muscles, and joints function as a system allowing vertebrates to move and survive. 2. Structures and
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal. Index of Topics. You and Your Heart Activity 1: How Your Heart Functions.2 Activity 2: Break the Heart Code..
 This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3
 California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3 Words were selected using the following established frequency lists: (1) Dolch 220 (2) Fry 100 (3) American Heritage Top 150 Words in English
California Treasures High-Frequency Words Scope and Sequence K-3 Words were selected using the following established frequency lists: (1) Dolch 220 (2) Fry 100 (3) American Heritage Top 150 Words in English
Lesson Plan on Cells, Tissues, and Organs. Jay A. Haron, Ph.D.
 Cells, Tissues, and Organs 1 RUNNING TITLE: Cells, Tissues, and Organs Lesson Plans Lesson Plan on Cells, Tissues, and Organs Jay A. Haron, Ph.D. In partial fulfillment of requirements for TED 624 Professor
Cells, Tissues, and Organs 1 RUNNING TITLE: Cells, Tissues, and Organs Lesson Plans Lesson Plan on Cells, Tissues, and Organs Jay A. Haron, Ph.D. In partial fulfillment of requirements for TED 624 Professor
Do you have a. of what you want to be when you grow up? Do you look at your teacher and think you might want to have that job
 DREAM BIG Do you look at your teacher and think you might want to have that job when you are bigger, or have you passed the fire station and thought about helping others as a firefighter? What about a
DREAM BIG Do you look at your teacher and think you might want to have that job when you are bigger, or have you passed the fire station and thought about helping others as a firefighter? What about a
From Cells to Systems Grade Level: Second Grade Presented by: Jan Polzin and Mary Ann Mahoney Length of Unit: 10 Lessons
 From Cells to Systems Grade Level: Second Grade Presented by: Jan Polzin and Mary Ann Mahoney Length of Unit: 10 Lessons I. ABSTRACT This second grade science unit begins with the concept of cells as the
From Cells to Systems Grade Level: Second Grade Presented by: Jan Polzin and Mary Ann Mahoney Length of Unit: 10 Lessons I. ABSTRACT This second grade science unit begins with the concept of cells as the
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE?
 MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE? Grade Level: Kindergarten Presented by: Karen Davis and Tamara Young, Tate Elementary, Van Buren, AR Length of unit:5 lessons I. ABSTRACT A. This unit focuses
MAPS AND GLOBES: WHERE IN THE WORLD ARE WE? Grade Level: Kindergarten Presented by: Karen Davis and Tamara Young, Tate Elementary, Van Buren, AR Length of unit:5 lessons I. ABSTRACT A. This unit focuses
WHAT IS A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE?
 TEACHER NOTES WHAT IS A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE? A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE Indicators Reads information about a healthy lifestyle. Critically analyzes examples of lifestyles and suggests improvements. Teacher information
TEACHER NOTES WHAT IS A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE? A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE Indicators Reads information about a healthy lifestyle. Critically analyzes examples of lifestyles and suggests improvements. Teacher information
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
This is how quickly your brain forgets things
 Brain gym starters This is how quickly your brain forgets things Your brain is a muscle Like every other muscle it needs exercise Brain gym is one way to exercise your mind so that you can learn better.
Brain gym starters This is how quickly your brain forgets things Your brain is a muscle Like every other muscle it needs exercise Brain gym is one way to exercise your mind so that you can learn better.
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario)
 Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
II. Third Grade, Human Body 2004 Colorado Summer Writing Institute 1
 HUMAN BODY Grade Level or Special Area: Third Grade Written by: Vicki Menefee, Louisville Elementary School, Louisville, CO Length of Unit: Seven lessons (seven days, one day = 45 minutes) not including
HUMAN BODY Grade Level or Special Area: Third Grade Written by: Vicki Menefee, Louisville Elementary School, Louisville, CO Length of Unit: Seven lessons (seven days, one day = 45 minutes) not including
How To Stretch Your Body
 Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
Exercise Module A New Leaf Choices for Healthy Living University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 2007 Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Physical Activity Exercises for Keeping Active
5TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Session 1. Body Systems and Structures. Teacher Notes. Body Systems and Organs: Descriptions and Functions. Intermediate ENGLISH FOR YOUR HEALTH
 Session 1 Body Systems and Structures Teacher Notes Body Systems and Organs: Descriptions and Functions Heart The heart is a muscle that pumps blood to all parts of the body by contracting and releasing
Session 1 Body Systems and Structures Teacher Notes Body Systems and Organs: Descriptions and Functions Heart The heart is a muscle that pumps blood to all parts of the body by contracting and releasing
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
MINDING OUR BODIES. Healthy Eating and Physical Activity for Mental Health
 MINDING OUR BODIES Healthy Eating and Physical Activity for Mental Health Facilitators Guide: Background Information (note: tell participants to consult with their doctor before starting to exercise) What
MINDING OUR BODIES Healthy Eating and Physical Activity for Mental Health Facilitators Guide: Background Information (note: tell participants to consult with their doctor before starting to exercise) What
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Muscles and Bones. Lesson aim. Lesson objectives. Lesson Outcomes. Curriculum links. Suggested age group suitability.
 Muscles and Bones Lesson aim To familiarise students with the function of the skeleton and how muscles attached to the skeleton allow us to move. Lesson objectives Students will be expected to: Work effectively
Muscles and Bones Lesson aim To familiarise students with the function of the skeleton and how muscles attached to the skeleton allow us to move. Lesson objectives Students will be expected to: Work effectively
Get Moving! All About Muscles
 Get Moving! All About Muscles A Reading A Z Level U Quick Reader Word Count: 2,002 Q U I C K R E A D E R U Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
Get Moving! All About Muscles A Reading A Z Level U Quick Reader Word Count: 2,002 Q U I C K R E A D E R U Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
Digestive System Simulation
 Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
Systems of the Human Body
 . s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
. s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
Teaching Children to Praise
 Teaching Children to Praise Thinking About Praise Discuss one or two of the following questions with a partner. When did you last praise God in a heartfelt way? What were you doing at the time? What effect
Teaching Children to Praise Thinking About Praise Discuss one or two of the following questions with a partner. When did you last praise God in a heartfelt way? What were you doing at the time? What effect
From ead to oe. Developed and Published by. 2010 AIMS Education Foundation
 TM From H T ead to oe Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science)
TM From H T ead to oe Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science)
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
STREETSENSE. Gym Cards
 Teachers Notes The Scottish Road Safety Campaign have developed a series of Gym Cards to support activities at Level A in Streetsense. The Gym Cards can either be used in conjunction with specific Level
Teachers Notes The Scottish Road Safety Campaign have developed a series of Gym Cards to support activities at Level A in Streetsense. The Gym Cards can either be used in conjunction with specific Level
Fun ways to group students
 Fun ways to group students Tips for dividing into groups. Picture Cards: Hand out cards with images on such as strawberries, blueberries, blackberries and other such groups of things. Then get them to
Fun ways to group students Tips for dividing into groups. Picture Cards: Hand out cards with images on such as strawberries, blueberries, blackberries and other such groups of things. Then get them to
Week 4 Lesson Plan. Pre-K. Animals in the Wild. Macmillan /McGraw-Hill. Extend. the Unit
 Lesson Plan Extend Unit the Unit Pre-K Animals in the Wild Alphabet Time.....................2-3 Book Time.........................-5 Retelling Puppets................... 6 Content Area......................7-8
Lesson Plan Extend Unit the Unit Pre-K Animals in the Wild Alphabet Time.....................2-3 Book Time.........................-5 Retelling Puppets................... 6 Content Area......................7-8
Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle:
 Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle: Print out pages 3-7 on cardstock, then laminate with regular
Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle: Print out pages 3-7 on cardstock, then laminate with regular
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
"Plumkin's Choice" A Tobacco-Education Puppet Show Curriculum Guide Grades K to 3. Contents Activity #1 Tobacco is an Unhealthy Drug
 "Plumkin's Choice" A Tobacco-Education Puppet Show Curriculum Guide Grades K to 3 Contents Activity #1 Tobacco is an Unhealthy Drug Activity #2 Tobacco is Bad for Your Body Activity #3 Make a Healthy Choice
"Plumkin's Choice" A Tobacco-Education Puppet Show Curriculum Guide Grades K to 3 Contents Activity #1 Tobacco is an Unhealthy Drug Activity #2 Tobacco is Bad for Your Body Activity #3 Make a Healthy Choice
The Search for the Missing Bones
 The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises
 Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Aquatic Exercises: Upper Body Strengthening
 Aquatic Exercises: Upper Body Strengthening These exercises will strengthen your muscles in your arms, shoulders, chest and neck. Exercising in water allows you to have less stress on your joints. When
Aquatic Exercises: Upper Body Strengthening These exercises will strengthen your muscles in your arms, shoulders, chest and neck. Exercising in water allows you to have less stress on your joints. When
A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT
 PURDUE UNIVERSITY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Crawford County A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Developed by Carol Judd Description: Brain architecture is a process that begins early in life and continues
PURDUE UNIVERSITY COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE Crawford County A LIFESPAN OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Developed by Carol Judd Description: Brain architecture is a process that begins early in life and continues
stretches and exercises
 stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
Music and Food: How to Make Musical Instruments Out of Food. Lesson Overview
 Lesson Overview Lesson Participants: CACFP personnel and school-age child care staff Type of Lesson: Short face-to-face training session Time Needed to Conduct the Lesson: 20 minutes Lesson Description:
Lesson Overview Lesson Participants: CACFP personnel and school-age child care staff Type of Lesson: Short face-to-face training session Time Needed to Conduct the Lesson: 20 minutes Lesson Description:
WHAT S IN OUR SHOPPING CART?
 Theme: Me and My Choices WHAT S IN OUR SHOPPING CART? Overview: In this series of activities, students will set up an imaginary grocery store. They will discuss food choices and create a shopping list
Theme: Me and My Choices WHAT S IN OUR SHOPPING CART? Overview: In this series of activities, students will set up an imaginary grocery store. They will discuss food choices and create a shopping list
Creative Curriculum Developmental Continuum Checklist
 Social/Emotional Development: Prosocial Behavior Curriculum Objective: 13 Uses thinking skills to resolve conflicts Accepts adult solution to resolve a conflict Seeks adult assistance to resolve a conflict
Social/Emotional Development: Prosocial Behavior Curriculum Objective: 13 Uses thinking skills to resolve conflicts Accepts adult solution to resolve a conflict Seeks adult assistance to resolve a conflict
Float Your Feelings Away Activity Stop and Think Again Activity. KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS loss feelings worry fear
 FIRE PREVENTION Float Your Feelings Away Activity Stop and Think Again Activity KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS loss feelings worry fear PURPOSE To help the students understand how they can cope with feelings after
FIRE PREVENTION Float Your Feelings Away Activity Stop and Think Again Activity KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS loss feelings worry fear PURPOSE To help the students understand how they can cope with feelings after
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]
![[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]](/thumbs/40/20967878.jpg) [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version
 The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
Days. Day 1. Reflection Teacher Responsibilities. Lesson Plans
 Days Day 1 Lesson Plans Call the students to the carpet by the number of letters in their names. If your name has less than 5 letters, come to the carpet. If your name has more than 5 letters, come to
Days Day 1 Lesson Plans Call the students to the carpet by the number of letters in their names. If your name has less than 5 letters, come to the carpet. If your name has more than 5 letters, come to
Changes to Your Baby and Your Body During Pregnancy
 Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Changes to and Your Body During Pregnancy 1st Trimester: Conception to Week 16 Your baby s traits and sex are set when the sperm meets the egg. During this time: The brain, nerves, heart, lungs and bones
Safety Smart Ambassador Lesson Plan Safety Smart Healthy & Fit! A Lesson In Health And Safety For Children K 2
 INTRODUCTION LifeSmarts invites you to become a Safety Smart Ambassador! As a Safety Smart Ambassador, you will have the opportunity to share reassuring, clear and confidence-building messages to help
INTRODUCTION LifeSmarts invites you to become a Safety Smart Ambassador! As a Safety Smart Ambassador, you will have the opportunity to share reassuring, clear and confidence-building messages to help
EXTRA ACTIVITy pages
 EXTRA FUN ACTIVITIES This booklet contains extra activity pages for the student as well as the tests. See the next page for information about the activity pages. Go to page 7 to find the Alpha tests. EXTRA
EXTRA FUN ACTIVITIES This booklet contains extra activity pages for the student as well as the tests. See the next page for information about the activity pages. Go to page 7 to find the Alpha tests. EXTRA
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Last name: State/ Province: Home telephone number:
 54 Ages & Stages Questionnaires 51 months 0 days through 56 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this
54 Ages & Stages Questionnaires 51 months 0 days through 56 months 30 days Month Questionnaire Please provide the following information. Use black or blue ink only and print legibly when completing this
Transferring Safety: Prevent Back Injuries
 Transferring Safety: Prevent Back Injuries OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class you will be able to: 1. Describe the back and what it does. 2. List things that you can do everyday in your home and at work
Transferring Safety: Prevent Back Injuries OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class you will be able to: 1. Describe the back and what it does. 2. List things that you can do everyday in your home and at work
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines
 USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
What is Energy? 1 45 minutes Energy and You: Energy Picnic Science, Physical Education Engage
 Unit Grades K-3 Awareness Teacher Overview What is energy? Energy makes change; it does things for us. It moves cars along the road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen
Unit Grades K-3 Awareness Teacher Overview What is energy? Energy makes change; it does things for us. It moves cars along the road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen
Knowledge and Understanding of the World. Early Learning Goals. National Curriculum. (learning objectives) (level 1 descriptors)
 Knowledge and Understanding of the World Knowledge and Understanding of the world Science K&U4 Ask questions about why things happened and how things work To talk about what they see To make recordings
Knowledge and Understanding of the World Knowledge and Understanding of the world Science K&U4 Ask questions about why things happened and how things work To talk about what they see To make recordings
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
How does your heart pump blood in one direction?
 Have a Heart How does your heart pump blood in one direction? Description How does your heart move blood in one direction, around in a loop? In this activity, you will make a model of one of the heart
Have a Heart How does your heart pump blood in one direction? Description How does your heart move blood in one direction, around in a loop? In this activity, you will make a model of one of the heart
