HISTOLOGY DRAWINGS. created by Dr Carol Lazer during the period INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Sims
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HISTOLOGY DRAWINGS created by Dr Carol Lazer during the period INTRODUCTION The first pages illustrate introductory concepts for those new to microscopy as well as definitions of commonly used histology terms. The drawings of histology images were originally designed to complement the histology component of the first year Medical course run prior to They are sketches from selected slides used in class from the teaching slide set. These labelled diagrams should closely follow the current Science courses in histology, anatomy and embryology and complement the virtual microscopy used in the current Medical course. Dr Carol Lazer, April 2005
2 STEREOLOGY: SLICING A 3-D OBJECT SIMPLE TUBE CROSS SECTION = TRANSVERSE SECTION (XS) (TS) OBLIQUE SECTION 3-D LONGITUDINAL SECTION (LS) 2-D BENDING AND BRANCHING TUBE 3-D 2-D branch off a tube 2 sections from 2 tubes cut at different angles section at the beginning of a branch 3 sections from one tube en face view = as seen from above 1 section and the grazed wall of a tube COMPLEX STRUCTURE (gland) COMPOUND ( = branched ducts) ACINAR ( = bunches of secretory cells) GLAND duct (XS =TS) acinus (cluster of cells) (TS) 3-D duct and acinus 2-D (LS) Do microscope images of 2-D slices represent a single plane of section of a 3-D structure? No, 2-D slices have a thickness which can vary from a sliver of one cell to several cells deep. With the limited depth of field of high power lenses it is possible to focus through the various levels within a slice. Do all microscope slides show 2-D slices of 3-D structures? No, slides can also be smears, where entire cells lie on the surface of the slide, or whole tissue mounts of very thin structures, such as mesentery. Dr Carol Lazer, April 2005
3 LININGS, COVERINGS & TERMINOLOGY KEY lamina propria lumen epithelium connective tissue beneath epithelium connective tissue, muscle, glands, etc mesothelium (simple squamous epithelium) ORIGIN: mesoderm lining epithelium ORIGIN: endoderm or mesoderm MUCOSA or MUCOUS MEMBRANE has a wet surface (mucus). Lines organs that open to the outside. SEROSA or SEROUS MEMBRANE has a wet surface (watery). Lines body cavities. Covers organs in body cavities. GENERALISED SECTION OF THE BODY epidermis (keratinised stratified squamous epithelium) ORIGIN: ectoderm dermis mesentery SKIN Covers the external surface. ADVENTITIA Connective tissue of one structure meets connective tissue of another structure. blood vessel lined by endothelium (simple squamous epithelium) ORIGIN: mesoderm Dr Carol Lazer, September 2000 April 2005
4 EPITHELIUM: non-keratinised stratified squamous TISSUE / ORGAN: oesophagus COVERING AND LINING EPITHELIA STRATIFIED EPITHELIA STRATA: squamous spinosum germinativum mitotic figure lamina propria EPITHELIUM: keratinised stratified squamous TISSUE / ORGAN: skin (epidermis) squames STRATA: corneum granulosum spinosum germinativum mitotic figure dermis vacuoles (folded plasma membrane) binucleate cell adluminal or facet cell EPITHELIUM: transitional TISSUE / ORGAN: bladder (relaxed) TISSUE / ORGAN: bladder (stretched) Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
5 SIMPLE EPITHELIA EPITHELIUM: simple cuboidal colloid TISSUE / ORGAN: thyroid lamina propria EPITHELIUM: simple columnar TISSUE / ORGAN: gall bladder lamina propria blood vessel 2 EPITHELIUM: simple squamous TISSUES / ORGANS: 1 1 endothelium lining blood vessel 2 mesothelium of serosa covering lung edge on terminal bar above ciliated columnar cell cilia columnar goblet cell EPITHELIUM: simple columnar or pseudostratified columnar TISSUE / ORGAN: seminal vesicle (ox) EPITHELIUM: basal cell pseudostratified columnar (respiratory epithelium) basement membrane MORE FULLY: pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells TISSUE / ORGAN: trachea Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
6 EXOCRINE GLANDS & DUCTS SIMPLE GLANDS hair epidermis dying inner large cells outer small basal cells (dividing) FEATURE: sebaceous gland TISSUE / ORGAN: around hair follicle in dermis of skin coiled duct portion hair follicle branched alveolar (acinar) gland sebaceous gland opening into hair follicle coiled tube secretory portion (TS) FEATURE: eccrine sweat gland TISSUE / ORGAN: dermis of skin (also in hypodermis) arrector pili muscle duct secretory portion duct portion with dark staining stratified cuboidal epithelium (bi-layer) secretory portion with thicker, pale staining bi-layer of cells basement membrane dermis coiled tubular eccrine sweat gland with duct twisting to open on the skin surface myoepithelial cells (TS) within basement membrane myoepithelial cells wrapped in a spiral around the coiled tube FEATURE: duct and secretory portions, myoepithelial cells TISSUE / ORGAN: eccrine sweat gland palisade of myoepithelial cells (LS) Are myoepithelial cells only present around sweat glands and what is their function? They are found around the secretory acini and some ducts of many glands. They contract under autonomic nervous control to expel the glandular secretions. Dr Carol Lazer, November 2001 April 2005
7 GLAND STRUCTURE lobe lobule layers of connective tissue connective tissue septum (between lobules) secretory tube and acinus COMPOUND GLAND DUCT ORGANISATION interlobar duct = excretory duct [drains the lobes of a gland] interlobular duct = intralobar duct [drains many lobules in a lobe] intralobular duct (e.g. striated duct) [drains many acini in a lobule] acinus = alveolus = adenomere FEATURE: lobe, lobules and ducts TISSUE / ORGAN: compound tubulo-alveolar (tubulo-acinar) gland intercalated duct [drains each acinus] part of lobe lobule connective tissue septum FEATURE: lobe, lobules and ducts (TS) TISSUE / ORGAN: part of a lobe of salivary gland mucous secretory tube intercalated ducts small lumen interlobular duct = intralobar duct intralobular duct (striated duct in salivary gland) blood vessels artery & vein interlobar duct striated duct large lumen and simple columnar epithelium with basal striations serous demilune mucous acinus wedge-shaped cells filled with pale staining remnant of mucous secretion and flattened basal nuclei serous acinus wedge-shaped cells packed with zymogen granules and round FEATURE: serous and mucous acini and ducts TISSUE / ORGAN: submandibular salivary gland (LS) (TS) intercalated ducts Do all compound glands have striated ducts? No, they all have intralobular ducts but these have a characteristic appearance in the salivary gland and so have a different name. Dr Carol Lazer, November 2001 April 2005
8 DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE CONNECTIVE TISSUE collagen fibre (LS) fibrocyte (LS) CLASSIFICATION: dense regular connective tissue (showing crimp pattern) TISSUE / ORGAN: tendon or ligament fascicle ground substance collagen fibre in the plane of section (LS) collagen fibre perpendicular to the plane of section (TS) fibroblast (TS) fibroblast (LS) CLASSIFICATION: dense irregular connective tissue TISSUE / ORGAN: dermis of skin ground substance collagen fibre in the plane of section (LS) collagen fibre perpendicular to the plane of section (TS) elastic fibre (LS) elastic fibre (TS) fibroblast (TS) fibroblast (LS) CLASSIFICATION: dense irregular connective tissue TISSUE / ORGAN: dermis of skin What is the difference between this specimen and the one before? It is stained to show elastic fibres. These were always present but not seen without the special stain. Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
9 SPECIFIC TISSUES & FIBRES brown fat cell (brown adipocyte) centrally located round lipid droplet (one of many -- multilocular) collagenous septum separating fat lobules fibroblast white fat cell (white adipocyte) flattened single large lipid droplet (unilocular) blood vessel CLASSIFICATION: brown and white adipose tissue TISSUE / ORGAN: fat stored in body collagen fibre anastomosing elastic fibre macrophage mast cell fibroblast CLASSIFICATION: loose connective tissue TISSUE / ORGAN: mesentery endothelium myofibroblast collagen fibre elastic fibres lymphocyte capsule with collagen and reticular fibres reticular fibre trabecula CLASSIFICATION: reticular fibres TISSUE / ORGAN: lymph node CLASSIFICATION: elastic fibres TISSUE / ORGAN: elastic artery (brachial artery) fenestration elastic fibre (TS) crenated elastic fibre (LS) Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
10 BLOOD CELLS (SMEAR) FEATURE: blood cell types TISSUE / ORGAN: peripheral blood MONONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES or AGRANULOCYTES POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES or GRANULOCYTES erythrocyte biconcave disc with pale centre small lymphocyte with a large, round and blue cytoplasmic rim neutrophil with multilobed and many small granules rouleaux formation stack of erythrocytes platelets cytoplasmic fragments with a dark chromomere and pale hyalomere monocyte with a single that may be irregular or bean shaped and blue cytoplasm which may have tiny granules or vacuoles Indentation of the (monocyte or lymphocyte) is caused by proximity to the Golgi apparatus. eosinophil with bi-lobed and many large red granules of similar size basophil with many blue granules of different size that obscure the BLOOD-RELATED CELLS (SECTION) numerous red granules in cytoplasm overlapping lobes of FEATURE: tissue eosinophil (and plasma cells) TISSUE / ORGAN: lamina propria of glands of stomach mucosa adipocyte marrow cells single, large, lobulated eosinophilic cytoplasm FEATURE: megakaryocyte TISSUE / ORGAN: bone marrow not to be confused with basophilic cytoplasm (rer) eosinophilic (or pale) perinuclear region (Golgi apparatus) eccentric (clock-faced) FEATURE: plasma cell TISSUE / ORGAN: lamina propria of salivary gland secretory acini bone trabecula osteocyte multiple nuclei in osteoclast eosinophilic cytoplasm shrinkage Schwann cell artefact FEATURE: osteoclast TISSUE / ORGAN: bone trabecula Dr Carol Lazer, November 2001 April 2005
11 CARTILAGE CARTILAGE AND BONE thick perichondrium adventitia with adipose tissue blood vessels peripheral nerve fold artefact fibrous layer (with fibroblasts) cellular layer ( chondroblasts) territorial matrix (dark staining / recent) interterritorial matrix (pale staining / older) interstitial growth (from the middle) appositional growth (from the edge) thin perichondrium lamina propria with glands cell nests (recently divided chondrocytes) lacuna (space in the matrix once occupied by a cell) chondrocyte chondroblast adventitia = loose connective tissue fibroblast chondroblast chondrocyte lacuna thick perichondrium epithelium -- respiratory (pseudostratified ciliated columnar) FEATURE: hyaline cartilage TISSUE / ORGAN: trachea attachment side cell nests (recently divided chondrocytes) territorial matrix (dark staining / recent) interterritorial matrix (pale staining / older) interstitial growth fibrous layer cellular layer elastic fibres appositional growth thin perichondrium FEATURE: elastic cartilage TISSUE / ORGAN: pinna of ear blood vessels peripheral nerve dermis and hypodermis of skin epithelium = epidermis of skin (keratinised stratified squamous) external ear side Dr Carol Lazer, July 2002 April 2005
12 COMPACT BONE skeletal muscle fibrous periosteum (with fibroblasts) tendon or ligament (TS) (LS) cellular periosteum ( osteoblasts) outer circumferential lamellae interstitial lamellae Volkmann s canal concentric lamellae of osteon cement line (outermost layer of osteon) Haversian canal (centre of osteon) osteocyte in lacuna (or empty lacuna) inner circumferential lamellae (absent in young bone) endosteum (osteoblasts) shrinkage artefact blood vessels in Haversian canal bone marrow cells adipocyte FEATURE: Haversian systems ( = osteons) with lamellae (TS) TISSUE / ORGAN: diaphysis (shaft) of femur canaliculus (channel in matrix) osteocyte in lacuna (or empty lacuna) concentric lamellae cement line Volkmann s canals (link Haversian canals) Haversian canal (centre of osteon) FEATURE: Haversian systems ( = osteons) with lamellae (LS) TISSUE / ORGAN: diaphysis of femur Dr Carol Lazer, August 2002 April 2005
13 BONE / MUSCLE FORMATION & JOINTS } } } } mesenchyme dura arachnoid pia brain osteoblast Howship s lacuna Meckel s cartilage perichondrium 1a FEATURE: intramembranous ossification examples TISSUE / ORGAN: 1 dura mater and calvaria 2 Meckel s cartilage and mandible YOUNG FETAL RAT HEAD (sagittal section) 1a 2 dura marrow precursor osteoclast 1b bone matrix in trabecula dura brain eye cartilage region of bone growth teeth tongue osteocyte osteoblasts osteoprogenitor cell INTRAMEMBRANOUS OSSIFICATION 1b OLDER FETAL RAT HEAD (coronal section) 2 MYOBLASTS MYOTUBES MYOFIBRES (LS) (TS) (LS) (TS) (LS) elongated cells (central nuclei) aligned in one direction mesenchyme (undifferentiated mesoderm) multiple central nuclei perinuclear cytoplasm peripheral myofibrils peripheral cytoplasm stellate-shaped cells central myofibrils spindle-shaped cell syncytium of cells (fused multiple cells) STRIATED MUSCLE DEVELOPMENT FEATURE: spindle- and stellate-shaped cells FEATURE: myoblasts and myotubes TISSUE / ORGAN: (developing striated muscle cells) TISSUE / ORGAN: fetal tongue multiple peripheral nuclei Dr Carol Lazer, September 2002 April 2005
14 OSSIFICATION & JOINTS DISTAL hyaline cartilage model of bone intervertebral disc FEATURE: stages in long bone development TISSUE / ORGAN: fetal rat tail endochondral ossification marrow cavity PROXIMAL collar of intramembranous bone in perichondrium pulposus JOINTS annulus fibrosus swelling, dying chondrocytes collagen fibres and matrix chondrocytes and cartilage matrix ingrowth of blood vessels, marrow cells and periosteal osteoprogenitor cells fibrous periosteum cellular periosteum with osteoprogenitor cells trabecula marrow cell forming Haversian canal marrow osteoblast osteocyte Howship s lacuna osteoclast ligament synovial membrane and villi 1 - epiphysis 2 - metaphysis 3 - diaphysis perichondrium periosteum FEATURE: developing symphysis joint TISSUE / ORGAN: intervertebral disc perichondriallined perforating channels with blood vessels (cartilage canals) pericondrium periosteum aponeurosis tendon or striated muscle lamina propria (loose c.t. or adipose tissue) joint capsule (ligament ) secondary ossification cancellous (spongy) bone compact bone FEATURE: generalised synovial joint TISSUE / ORGAN: knee (or elbow) FEATURE: bone growth and remodelling TISSUE / ORGAN: periosteal collar of vertebra ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION joint internal ligament fibrocartilage meniscus synovial cavity articular cartilage 1 marrow 2 ZONES 3 fornix resting chondrocytes advancing marrow cell proliferating chondrocytes calcified cartilage matrix chondrocyte hypertrophy calcifying matrix resorption bone trabeculae bone growth bone matrix FEATURE: epiphyseal disc (growth plate) TISSUE / ORGAN: growth zone of long bone Dr Carol Lazer, October 2002 April 2005
15 MUSCLE CLASSIFICATION: fascicle of skeletal or striated muscle (LS) fibroblast muscle fibre (myofibre) A band I band H band Z line endomysium perimysium CLASSIFICATION: fascicle of skeletal or striated muscle (TS) epimysium perimysium endomysium blood vessel endothelium muscle fibre cytoplasm muscle fibre nuclei perimysium endomysium blood vessel endothelium muscle fibre (TS) myofibrils (TS) muscle fibre nuclei fibroblast smooth muscle fascicle (LS) corkscrew smooth muscle cells (LS) blood vessel endothelium fibroblast smooth muscle fascicle (TS) smooth muscle cell nuclei CLASSIFICATION: smooth muscle in fascicles (LS & TS) and arteriole wall Why is there a large variation in smooth muscle nuclei (TS) from absent to small to large? The cells are so long that sections cut the ovoid from centre to edge or even miss it. Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
16 CLASSIFICATION: single smooth muscle cells TISSUE / ORGAN: intestinal villus simple columnar epithelium columnar cell goblet cell smooth muscle cell (myofibroblast) blood vessel endothelium lamina propria cardiac muscle fascicle (TS) cardiac muscle fascicle (LS) cardiac muscle cell (LS) intercalated disc A and I bands myofibril clear perinuclear region (TS) (LS) Purkinje fibres connective tissue septa (perimysium) fibroblast endothelium cardiac muscle cell (TS) myofibrils clear perinuclear region CLASSIFICATION: cardiac muscle fascicles TISSUE / ORGAN: heart (interventricular septum) interwoven muscle fibres endocardium (endothelium + lamina propria) Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
17 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) dura mater arachnoid pia mater septum of pia mater grey matter NERVOUS TISSUE dorsal nerve rootlet small neuron of dorsal horn ependymal cells around central canal motor neuron of ventral horn white matter myelinated axons (TS) myelinated axons (LS) blood vessels ventral nerve rootlet FEATURE: white matter and cells of grey matter TISSUE / ORGAN: spinal cord and meninges PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (PNS) neuropil oligodendrocyte astrocyte axon axon hillock Nissl granules dendrite FEATURE: myelin sheath TISSUE / ORGAN: peripheral nerve (TS) blood vessel (vasa nervorum) myelinated nerve fibre endoneurium perineurium epineurium epineurium perineurium endoneurium paranodal swelling node of Ranvier FEATURE: Nodes of Ranvier TISSUE / ORGAN: peripheral nerve (LS) Schmidt-Lanterman cleft myelin sheath axoplasm white adipocyte internode Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
18 epineurium perineurium around nerve fascicle (LS) perineurium around nerve fascicle (TS) FEATURE: Schwann cells TISSUE / ORGAN: sciatic nerve blood vessel (vasa nervorum) white fat cell (white adipocyte) septum of perineurium endoneurium axoplasm neurokeratin remnant of myelin sheath Schwann cell fibroblast axon Ranvier s cross Schmidt-Lanterman cleft neurokeratin of myelin sheath Nissl granules axon hillock ganglion cell ganglion cell satellite cell FEATURE: pseudounipolar neurons and myelin TISSUE / ORGAN: trigeminal sensory ganglion perineurium around nerve fascicle (LS) endoneurium myelinated axon Schwann cell blood vessel endothelium smooth muscle (TS) FEATURE: peripheral nerve fascicles TISSUE / ORGAN: connective tissue (tongue) perineurium around nerve fascicle (TS) endoneurium myelinated axon Schwann cell fibroblast Dr Carol Lazer, August 2000 April 2005
19 FETAL MEMBRANES PLACENTA FEATURE: chorionic plate, villi, uterine wall TISSUE / ORGAN: placenta (3 months) branch of umbilical blood vessel chorionic plate chorionic villi with trophoblast covering and a mesoblast (extraembryonic mesoderm) core maternal blood spaces (lacunae) syncytiotrophoblast sprout (primary villus) FETAL SIDE MATERNAL SIDE stratum basale of endometrium with darker peripheral region, glands and small vessels cytotrophoblastic anchoring column smooth muscle of myometrium large vessels in the myometrium SECONDARY VILLUS trophoblast + mesoblast PRIMARY VILLUS trophoblast only syncytiotrophoblast cytotrophoblast mesoblast rami of umbilical vessels TERTIARY VILLUS trophoblast + mesoblast + blood vessels columnar epithelium of tubular uterine (endometrial) gland blood vessel UMBILICAL CORD FEATURE: vessels and Wharton s jelly TISSUE / ORGAN: umbilical cord (TS) mucoid connective tissue (Wharton s jelly) umbilical vein Warton s jelly is an artefact of dead umbilical cord. What should living cord look like and why is this different? Before birth the cord has three large vessels and very little connective tissue. After birth the blood flow stops and without blood pressure the vessels collapse. The connective tissue swells with fluid that leaks from the vessels. collapsed lumen umbilical arteries Dr Carol Lazer, November 2001 April 2005
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY
 SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
CHAPTER 5: TISSUES. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
Function of Bones. Bone Tissue and Bones BONE CLASSIFICATION. Long Bones Gross Anatomy. Lab Activity 1 - Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
 Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
Laboratory 3 Histology
 Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Location: air sacs of lungs; nephrons of kidney; lining of circulatory system, lymphatic vessels, & ventral body cavity
 Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
E. Blood cells production. Blood cells are produced within the cavities of bones.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
BONES AND BONE TISSUE
 BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE. Chapter 6. Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY
 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system
 組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :[email protected]
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :[email protected]
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
Human Anatomy & Physiology: Fall Final Exam Review
 Chapter 1: 1. Anatomy is a term which means the study of. A. physiology B. morphology C. cell functions D. human functions 2. The study dealing with the explanations of how an organ works would be an example
Chapter 1: 1. Anatomy is a term which means the study of. A. physiology B. morphology C. cell functions D. human functions 2. The study dealing with the explanations of how an organ works would be an example
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit
 R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
Digestive System Digestive Tract
 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510
 Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
OBJECTIVE: List and describe the functions of the skeletal system. D. Storage depot for minerals and homeostasis
 Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System. What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system?
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE. BIOL 207 Human Anatomy
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 207 Human Anatomy Prepared By: Ron Tavernier, PhD School of Science, Health and Criminal Justice Science Department
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 207 Human Anatomy Prepared By: Ron Tavernier, PhD School of Science, Health and Criminal Justice Science Department
DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE
 2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Secondary dentition permanent teeth - 32. Primary dentition deciduous teeth - 20
 Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice DEVELOPMENT OF TEETH: Sylabus for foreign students Dental medicine Author: doc. MVDr. Iveta Domoráková, PhD. Primary
Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice DEVELOPMENT OF TEETH: Sylabus for foreign students Dental medicine Author: doc. MVDr. Iveta Domoráková, PhD. Primary
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012
 Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Protective Functions. Functions in Sensation. Functions in Excretion. Functions in Temperature Regulation
 Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Bone Tissue Chapter 7
 Bone Tissue Chapter 7 Tissues and organs of the skeletal system Histology of osseous tissue Bone development Physiology of osseous tissue Bone disorders Bone Tissue Bone is alive and continuously changing.
Bone Tissue Chapter 7 Tissues and organs of the skeletal system Histology of osseous tissue Bone development Physiology of osseous tissue Bone disorders Bone Tissue Bone is alive and continuously changing.
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Introduction and Overview During a 24-hour period, more than 9000 liters of air enter the interior of the body to participate in gas exchange. This air must be warmed, cleansed,
The Respiratory System Introduction and Overview During a 24-hour period, more than 9000 liters of air enter the interior of the body to participate in gas exchange. This air must be warmed, cleansed,
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Small & Large Intestines
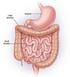 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
PCB 4023 Cell Biology. Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs
 PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
Visit www.ncerthelp.com For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-7
 Chapter-7 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS POINTS TO REMEMBER Tissue : A group of similar cells along with intercellular substances which perform a specific function. Simple epithelium : is composed
Chapter-7 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS POINTS TO REMEMBER Tissue : A group of similar cells along with intercellular substances which perform a specific function. Simple epithelium : is composed
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises
 1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Structural Organisation in Animals
 Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals Introduction Life activities are done by cells, tissues, organs and organ systems in animals. Tissues are a group of similar cells which perform a particular
Chapter 3 Structural Organisation in Animals Introduction Life activities are done by cells, tissues, organs and organ systems in animals. Tissues are a group of similar cells which perform a particular
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE BIOL 2401 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS:
 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE BIOL 2401 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Semester Hours Credit: 4 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: I. INTRODUCTION A. Anatomy and Physiology I is the study of the parts of the living organisms
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE BIOL 2401 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Semester Hours Credit: 4 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: I. INTRODUCTION A. Anatomy and Physiology I is the study of the parts of the living organisms
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture
 The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
