ECE606: Solid State Devices Lecture 18. Bipolar Transistors a) Introduction b) Design (I)
|
|
|
- Felicia Payne
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 606: Solid State Devices Lecture 18 ipolar Trasistors a) Itroductio b) Desig (I) Gerhard Klimeck 1 ackgroud ase! Poit cotact Germaium trasistor Ralph ray from Purdue missed the ivetio of trasistors. Trasistor research was also i advaced stages i urope (radar).
2 Shockley s ipolar Trasistors + emitter Double Diffused JT + p base -collector + + emitter p base collector + Moder ipolar Juctio Trasistors (JTs) ase mitter + ollector P- - SiGe itrisic base P+ + Dielectric trech Why do we eed all these desig? Trasistor speed icreases as the electro's travel distace is reduced SiGe Layer 4
3 Symbols ad ovetio Symbols + P Poly emitter Low-doped base P ollector PP ollector ollector dopig optimizatio ase mitter ase mitter I +I +I 0 (D) V +V +V 0 5 Outlie 1) quilibrium ad forward bad-diagram ) urrets i bipolar juctio trasistors 3) ber s Moll model 4) Itermediate Summary 5) urret gai i JTs 6) osideratios for base dopig 7) osideratios for collector dopig 8) oclusios RF: SDF, hapter 10 6
4 Topic Map Diode quilibrium D Small sigal Large Sigal ircuit s Schottky JT/HT MOS 7 ad Diagram at quilibrium + ( D A ) D q p + 1 J r + g t q p 1 J r + g t q J J qµ + qd P P P qpµ qd p P P P quilibrium D d/dt0 Small sigal d/dt ~ jωt Trasiet --- harge cotrol model 8
5 ad Diagram at quilibrium P homojuctio JT mitter ase ollector Vacuum level F χ 1 χ 3 χ V 9 lectrostatics i quilibrium x p, ε q k s 0 ( + ) V bi x p, k s ε 0 ( + ) q V bi x, k s ε0 ( + ) q V bi x, ε q k s 0 ( + ) V bi mitter ase ollector Two back to back p- juctio 10
6 Outlie 1) quilibrium ad forward bad-diagram ) urrets i bipolar juctio trasistors 3) ber s Moll model 4) Itermediate Summary 5) urret gai i JTs 6) osideratios for base dopig 7) osideratios for collector dopig 8) oclusios RF: SDF, hapter Topic Map quilibriu m D Small sigal Large Sigal ircuit s Diode Schottk y JT/H T MOS 1
7 ad Diagram with ias + ( D A ) D q p + 1 J r + g t q p 1 J r + g t q J J qµ + qd P P P qpµ qd p P P P o-equilibrium D d/dt0 Small sigal d/dt ~ jωt Trasiet --- harge cotrol model 13 lectrostatics i quilibrium ε x V V k s 0 p, bi q ( ) ( ) + k s ε 0 p, bi q x V V ( ) ( ) + ε x V V k s 0, bi q ( ) ( ) + ε x V V k s 0, bi q ( ) ( ) + mitter ase ollector V Assume curret flow is small fermi level is flat V 14
8 urret flow with ias Iput small amout of holes results i large amout of electro output V -F, F p, - V -F, 15 Moder MOSFT - Fudametal Limit looks similar to JT S Metal Oxide p Vg D + + log I d Threshold Vg S 60 mv/dec 0 V dd V g x
9 Moder MOSFT - Fudametal Limit looks similar to JT Vg S D Metal Oxide p + + log I d Threshold DOS(), log f() f ` Vg 0 S 60 mv/dec V dd V g x oordiates ad ovetio mitter ase ollector + P X X X 0 W,...,... D, A, D, D D,... D D,... D D P P,... p p,... 0 p p 0 Dopig Miority carrier diffusio Majority carriers 18
10 arrier Distributio i ase x x ( x) Ax D W W D i, qv, ( ) ( x i qv 1) 1 ( x x e + e 1) W W + i, qv (0 ) ( e 1) i, qv ( ) ( x W e 1) Assume o recombiatio. Start from miority carrier V V 19 ollector ad mitter lectro urret i, qv, ( ) ( x i qv 1) 1 ( x x e + e 1) W W d qd i, qv qd i, qv J, qd ( e 1) + ( e 1 dx ) W W W V J p, dp qdp dx V D W p i D qv ( e 1) 0
11 urret-voltage haracteristics ormal, Active Regio : Forward biased : Reverse biased J qd i, qd i, qv J, e 1 + e 1 W W log 10 J qv ( ) ( ) High-level ijectio series resistace, etc. I > 60 mv/dec. V W is ot idepedet of bias > arly ffect V same physics of diode, rollover 1 Outlie 1) quilibrium ad forward bad-diagram ) urrets i bipolar juctio trasistors 3) ber s Moll model 4) Itermediate Summary 5) urret gai i JTs 6) osideratios for base dopig 7) osideratios for collector dopig 8) oclusios RF: SDF, hapter 10
12 Hole diffusio i collector bers Moll Model + qd + qd i, qd i, i, qv I A e A e W W W ( qv 1) p ( 1) ( qv 1) ( qv 1) α I e I e F F 0 R0 I I c, +I c,p I F I R I I, +I,p I I α R I R I F qdp i, qd i, qd i, qv A + e + A e W W W qv qv ( 1) α R R ( 1) I e I e F 0 0 α F I I qv ( 1) ( 1) F R F 0 R0 ( qv 1) ( qv 1) I I e I I e Temperature depedet 3 ommo ase ofiguratio I F I R V (i) I P I V (out) I Juctio capacitace ad diffusio capacitace How would the model chage if this was a Schottky barrier JT? I α R I R α F I F The origial trasistor was a metal/ semicod / metal device o miority carriers, o diffusio capacitace but the rest about the same. ommo base cofiguratio provides power gai, but o curret gai. > mitter ad collector curret are idetical > o curret gai > ollector curret I ca be drive through large resistor > power gai Is there aother cofiguratio that ca deliver curret gai? I 4
13 ommo mitter ofiguratio I µ I V (i) P P+ I V (out) I αrir αfif I IF IR α F I F α I α I α F ( 1 α ) I I 1 α F F F F F F π IR F α I α I F F R R F F This is a practice problem 5 Itermediate Summary The physics of JT is most easily uderstood with referece to the physics of juctio diodes. The equatios ca be ecapsulated i simple equivalet circuit appropriate for dc, ac, ad large sigal applicatios. Desig of trasistors is far more complicated tha this simple model suggests > the ext lecture elemets For a terrific ad iterestig history of ivetio of the bipolar trasistor, read the book rystal Fire. 6
14 Outlie 1) quilibrium ad forward bad-diagram ) urrets i bipolar juctio trasistors 3) ber s Moll model 4) Itermediate Summary 5) urret gai i JTs 6) osideratios for base dopig 7) osideratios for collector dopig 8) oclusios RF: SDF, hapter 10 7 qd qd i, p i, qd i, qv I A + e A W W + W F 0 qv qv ( e 1) α RI R0 ( e 1) I qv ( 1) ( e 1) bers Moll Model qdp i, qd i, qv I A e + A e W W qv p ( 1) ( 1) I I F I R I α R I R I α F I F F R F 0 R0 ( qv 1) ( qv 1) I I e I I e qd i, qd i, qd i, qv I A e + A + e W W W qv ( 1) ( 1) qv qv ( 1) ( 1) α I e I e F F 0 R0 8
15 bers Moll Model (asic defiitio) saturatio regio I active regio I 0 V The bers-moll model describes both the active ad the saturatio regios of JT operatio. 9 Gummel Plot ad Output haracteristics The simultaeous plot of collector ad base curret vs. the base-emitter voltage o a semi-logarithmic scale is kow as a Gummel Plot. This plot is extremely useful i device characterizatio because it reflects o the quality of the emitter-base juctio while the base-collector bias is kept at a costat. A umber of other device parameters ca be ascertaied either quatitatively or qualitatively directly from the Gummel plot because of its semi-logarithmic ature For example the d.c gai, base ad collector ideality factors, series resistaces ad leakage currets. 30
16 Gummel Plot ad Output haracteristics I qd i, qv / kt qd i, qv / kt ( e 1) + ( e 1) A W W I qdp i, qv / kt ( e 1) A W D I I D ommo emitter urret Gai V 31 urret Gai ommo mitter curret gai.. I D I qd W W i, qv / kt qd i, ( qv / kt ) ( e 1) + ( e 1) qd i, qv / kt W ( e 1) V (i) I P+ P i, p i, D W W D I Will examie ommo ase curret gai.. I α D D I I I I D trasfer gai I I α D 1 α D V (i) I P+ P Properties are related (trasistor did ot chage ) I 3 V (out)
17 urret Gai D D W W D i, p i, High ijectio collector curret >roll-off ase curret does ot roll off 33 How to make a Good Silico Trasistor For a give mitter legth D D W W D i, p i, ~1, same material primarily determied by badgap Make-ase short (few mm i 1950s, 00 A ow) Wat high gradiet of carrier desity mitter dopig higher tha ase dopig ase dopig hard to cotrol mitter dopig easier 34
18 Dopig for Gai D D W W D i, p i, + P 35 Outlie 1) quilibrium ad forward bad-diagram ) urrets i bipolar juctio trasistors 3) ber s Moll model 4) Itermediate Summary 5) urret gai i JTs 6) osideratios for base dopig what s wrog with the previous recipe? 7) osideratios for collector dopig 8) oclusios RF: SDF, hapter 10 36
19 Problem of Low ase Dopig: urret rowdig V qd I J ( x) dx W I J x dx W i, ( ) qd p i, + p base -collector + qv ' ( x) ( e 1) qv ' ( x) ( e 1) V dx dx Double diffused juctio cofiguratio: mitter dopig must compesate / overcome the base dopig Low dopig i base > resistace alog the curret path > potetial drop > Determies the ijectio > Spatially depedet > More curret i the corers 37 Low ase Dopig: o-uiform Tur-o Sketches from text book + p base -collector + o-uiform curret iefficiet High curret at the edge ca cause bur-out Iterdigitated desigs for almost all high power trasistors (- distace miimized) 38
20 Low ase Dopig: urret rowdig + p base V -collector + We talked about how low dopig for the base ehaces the curret gai. ut there is a potetial dowside to this approach If the base dopig is kept to small values, it will have a high resistace: Lesser ability to coduct meas higher resistace 39 Low ase Dopig: urret rowdig + p base V -collector + o-zero base resistace results i a lateral potetial differece uder the emitter regio For a -p- trasistor as show, the potetial decreases from edge of the emitter towards the cetre (the emitter is highly doped ad ca be cosidered a equipotetial regio) 40
21 Low ase Dopig: urret rowdig + p base V -collector + The umber of electros ijected from emitter to base is expoetially depedet o base-emitter voltage With the lateral drop i the voltage i the base betwee the edge ad cetre of emitter, more carriers will be ijected at the edge tha the emitter cetre. 41 Low ase Dopig: urret rowdig Key facts: 1. urret crowdig is due to D ature of JTs. It is a fuctio of the dopig cocetratio 3. As dopig cocetratio icreases, resistivity decreases osequece: urret gai goes smaller mitter curret ijectio efficiecy decreases The larger curret desity ear the emitter may cause localized heatig ad high ijectio effects Possible Solutio: mitter widths are fabricated with a iter-digitated desig May arrow emitters coected i parallel to achieve the required emitter area 4
22 Low ase Dopig: o-uiform Tur-o Sketches from text book + p base -collector + o-uiform curret iefficiet High curret at the edge ca cause bur-out Iterdigitated desigs for almost all high power trasistors (- distace miimized) 43 Problem of Low ase Dopig: Puch-through + k s ε0 p, bi q x V V ( ) ( ) + k s ε0 p, bi q x V V ( ) ( ) + Low base dopig is ot a good idea! 44
23 D Problem of low ase-dopig: ase Width Modulatio lectrical base regio is smaller tha the metallurgical regio! D W i, p, p, c p i, W x x D ε x V V k s 0 p, bi q ( ) ( ) + + P ε x V V k s 0 p, bi q ( ) ( ) + Gai depeds o collector voltage (bad) Depletio regio width modulatio 45 Problem of Low ase-dopig: arly Voltage D D W W x x D i, p. p. p i, qd i, ( qv / kt ) qd i, ( qv / kt ) I, ( e 1) ( e 1) W ' + W ' di I I dv V + V V A A V about 1V V A ideally ifiity Jim arly device pioeer V A I I practice Ideally V 46
24 The arly Voltage PS1 I I practice Ideally V V A The collector curret depeds o V : For a fixed value of V, as V icreases, the reverse bias o the collector-base juctio icreases, hece the width of the depletio regio icreases. The quasi-eutral base width decreases collector curret icreases. Due to the arly effect, collector curret icreases with icreasig V, for a fixed value of V. 47 The arly Voltage PS I I practice Ideally V V A The arly voltage is obtaied by drawig a lie tagetial to the trasistor I-V characteristic at the poit of iterest. The arly voltage equals the horizotal distace betwee the poit chose o the I-V characteristics ad the itersectio betwee the tagetial lie ad the horizotal axis. arly voltage is idicated o the figure by the horizotal dotted lie 48
25 Puch-through ad arly Voltage di I I dv V + V V A A di d di dv d q W dv ( ) ( q W ) 1 di dq q dw dv 1 I q W q W V I I A qw VA eed higher ad W or + qd i, qd i, qv I e e W W ξ qv ( 1) ( 1) W di d ξ ζ dw dw W W I W 49 Outlie 1) quilibrium ad forward bad-diagram ) urrets i bipolar juctio trasistors 3) ber s Moll model 4) Itermediate Summary 5) urret gai i JTs 6) osideratios for base dopig 7) osideratios for collector dopig 8) oclusios RF: SDF, hapter 10 50
26 ollector Dopig W x x D D W i, p, p, p i, + P V A qw ase-ollector i reverse bias Majority carriers oly o diffusio capacitace Reduce capacitace Icrease x x κ sε 0 + x, p, If you wat low base dopig the reduce collector dopig eve more to icrease ollector depletio.. 51 but (!) Kirk ffect ad ase Pushout Space-harge Desity x p-ase -ollector + W - c + x W q V V x + x bi κ sε 0 x Space-harge Desity p-ase -ollector + W c W x ( + ) x ' ( ) x ' q ( + ) ' + ( ) V V x x ' bi κ sε0 J ' qυ sat x x x J 1 1 qυ J sat qυ sat Additioal charge! a be large compared to low dopig 5
27 Kirk ffect ad ase Pushout + emitter p base collector + Space-harge Desity p-ase -ollector + c x W W Space-harge p-ase -ollector c W W + x Space-harge p-ase -ollector + W WI W x c-c WS Icrease bias & curret Juctio lost High curret domiates collector dopig 53 Kirk ffect ad ase Pushout x ' x J 1+ qυ sat J 1 qυ sat J qυ J, crit sat K a ot reduce collector dopig arbitrarily without causig base pushout 54
28 Kirk ffect The Kirk effect occurs at high curret desities i a bipolar trasistor. The effect is due to the charge desity associated with the curret passig through the base-collector regio. As this charge desity exceeds the charge desity i the depletio regio the depletio regio ceases to exist. Istead, there will be a build-up of majority carriers from the base i the base-collector depletio regio. The dipole formed by the positively ad egatively charged ioized doors ad acceptors is pushed ito the collector ad replaced by positively charged ioized doors ad a egatively charged electro accumulatio layer, which is referred to as base push out. This effect occurs if the charge desity associated with the curret is larger tha the ioized impurity desity i the base-collector depletio regio. Assumig full ioizatio, this traslates ito the followig coditio o the collector curret desity. Key poit : Uder high curret ad low collector dopig the depletio approximatio is ivalid i the - juctio! Perhaps High Dopig i mitter? ad-gap arrowig reduces gai sigificatly D W W i, Dp i, g, / kt W V e g, / kt p V D W D e e g / kt (aski-like) Tuelig cause loss of base cotrol 56
29 Summary While basic trasistor operatio is simple, its optimum desig is ot. I geeral, good trasistor gai requires that the emitter dopig be larger tha base dopig, which i tur should be larger tha collector dopig. If the base dopig is too low, however, the trasistor suffers from curret crowdig, arly effects. If the collector dopig is too low, the we have Kirk effect (base push out) with reduced high-frequecy operatio ad if the emitter dopig is too high the the gai is reduced. 57
Semiconductor Devices
 emicoductor evices Prof. Zbigiew Lisik epartmet of emicoductor ad Optoelectroics evices room: 116 e-mail: [email protected] Uipolar devices IFE T&C JFET Trasistor Uipolar evices - Trasistors asic
emicoductor evices Prof. Zbigiew Lisik epartmet of emicoductor ad Optoelectroics evices room: 116 e-mail: [email protected] Uipolar devices IFE T&C JFET Trasistor Uipolar evices - Trasistors asic
pn-junctions Semiconductor Metal Oxide Diode - The Simplest IC-device Advanced Digital IC-Design What is a MOS-transistor?
 Advaced Digital IC-Desig his lecture will he MOS-trasistor Refresh the MOS-trasistor fuctio ad models Especially, short chael effects Digital IC-Desig he Diode i a IC-device he Diode Diodes appears i all
Advaced Digital IC-Desig his lecture will he MOS-trasistor Refresh the MOS-trasistor fuctio ad models Especially, short chael effects Digital IC-Desig he Diode i a IC-device he Diode Diodes appears i all
CV-measurement basics
 V-measuremet basics M-capacitor V measuremet measuremet of differetial by small ac modulatio of the bias voltage (dc d d G G M j G M ω M j ω Y M G M G M M ualitative poit of view ad diagram i geeral (here
V-measuremet basics M-capacitor V measuremet measuremet of differetial by small ac modulatio of the bias voltage (dc d d G G M j G M ω M j ω Y M G M G M M ualitative poit of view ad diagram i geeral (here
Doped semiconductors: donor impurities
 Doed semicoductors: door imurities A silico lattice with a sigle imurity atom (Phoshorus, P) added. As comared to Si, the Phoshorus has oe extra valece electro which, after all bods are made, has very
Doed semicoductors: door imurities A silico lattice with a sigle imurity atom (Phoshorus, P) added. As comared to Si, the Phoshorus has oe extra valece electro which, after all bods are made, has very
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics. Distributions related to the normal distribution
 Uiversity of Califoria, Los Ageles Departmet of Statistics Statistics 100B Istructor: Nicolas Christou Three importat distributios: Distributios related to the ormal distributio Chi-square (χ ) distributio.
Uiversity of Califoria, Los Ageles Departmet of Statistics Statistics 100B Istructor: Nicolas Christou Three importat distributios: Distributios related to the ormal distributio Chi-square (χ ) distributio.
I. Chi-squared Distributions
 1 M 358K Supplemet to Chapter 23: CHI-SQUARED DISTRIBUTIONS, T-DISTRIBUTIONS, AND DEGREES OF FREEDOM To uderstad t-distributios, we first eed to look at aother family of distributios, the chi-squared distributios.
1 M 358K Supplemet to Chapter 23: CHI-SQUARED DISTRIBUTIONS, T-DISTRIBUTIONS, AND DEGREES OF FREEDOM To uderstad t-distributios, we first eed to look at aother family of distributios, the chi-squared distributios.
Chapter 4: Switch realization
 Chapter 4. Switch Realizatio 4.1. Switch applicatios Sigle-, two-, ad four-quadrat switches. Sychroous rectifiers 4.2. A brief survey of power semicoductor devices Power diodes, MOSFETs, BJTs, IGBTs, ad
Chapter 4. Switch Realizatio 4.1. Switch applicatios Sigle-, two-, ad four-quadrat switches. Sychroous rectifiers 4.2. A brief survey of power semicoductor devices Power diodes, MOSFETs, BJTs, IGBTs, ad
Heat (or Diffusion) equation in 1D*
 Heat (or Diffusio) equatio i D* Derivatio of the D heat equatio Separatio of variables (refresher) Worked eamples *Kreysig, 8 th Ed, Sectios.4b Physical assumptios We cosider temperature i a log thi wire
Heat (or Diffusio) equatio i D* Derivatio of the D heat equatio Separatio of variables (refresher) Worked eamples *Kreysig, 8 th Ed, Sectios.4b Physical assumptios We cosider temperature i a log thi wire
In nite Sequences. Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University. October 9, 2008
 I ite Sequeces Dr. Philippe B. Laval Keesaw State Uiversity October 9, 2008 Abstract This had out is a itroductio to i ite sequeces. mai de itios ad presets some elemetary results. It gives the I ite Sequeces
I ite Sequeces Dr. Philippe B. Laval Keesaw State Uiversity October 9, 2008 Abstract This had out is a itroductio to i ite sequeces. mai de itios ad presets some elemetary results. It gives the I ite Sequeces
GCSE STATISTICS. 4) How to calculate the range: The difference between the biggest number and the smallest number.
 GCSE STATISTICS You should kow: 1) How to draw a frequecy diagram: e.g. NUMBER TALLY FREQUENCY 1 3 5 ) How to draw a bar chart, a pictogram, ad a pie chart. 3) How to use averages: a) Mea - add up all
GCSE STATISTICS You should kow: 1) How to draw a frequecy diagram: e.g. NUMBER TALLY FREQUENCY 1 3 5 ) How to draw a bar chart, a pictogram, ad a pie chart. 3) How to use averages: a) Mea - add up all
Chapter 6: Variance, the law of large numbers and the Monte-Carlo method
 Chapter 6: Variace, the law of large umbers ad the Mote-Carlo method Expected value, variace, ad Chebyshev iequality. If X is a radom variable recall that the expected value of X, E[X] is the average value
Chapter 6: Variace, the law of large umbers ad the Mote-Carlo method Expected value, variace, ad Chebyshev iequality. If X is a radom variable recall that the expected value of X, E[X] is the average value
Properties of MLE: consistency, asymptotic normality. Fisher information.
 Lecture 3 Properties of MLE: cosistecy, asymptotic ormality. Fisher iformatio. I this sectio we will try to uderstad why MLEs are good. Let us recall two facts from probability that we be used ofte throughout
Lecture 3 Properties of MLE: cosistecy, asymptotic ormality. Fisher iformatio. I this sectio we will try to uderstad why MLEs are good. Let us recall two facts from probability that we be used ofte throughout
Approximating Area under a curve with rectangles. To find the area under a curve we approximate the area using rectangles and then use limits to find
 1.8 Approximatig Area uder a curve with rectagles 1.6 To fid the area uder a curve we approximate the area usig rectagles ad the use limits to fid 1.4 the area. Example 1 Suppose we wat to estimate 1.
1.8 Approximatig Area uder a curve with rectagles 1.6 To fid the area uder a curve we approximate the area usig rectagles ad the use limits to fid 1.4 the area. Example 1 Suppose we wat to estimate 1.
Diodes and Transistors
 Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
CS103X: Discrete Structures Homework 4 Solutions
 CS103X: Discrete Structures Homewor 4 Solutios Due February 22, 2008 Exercise 1 10 poits. Silico Valley questios: a How may possible six-figure salaries i whole dollar amouts are there that cotai at least
CS103X: Discrete Structures Homewor 4 Solutios Due February 22, 2008 Exercise 1 10 poits. Silico Valley questios: a How may possible six-figure salaries i whole dollar amouts are there that cotai at least
Chapter 5 Unit 1. IET 350 Engineering Economics. Learning Objectives Chapter 5. Learning Objectives Unit 1. Annual Amount and Gradient Functions
 Chapter 5 Uit Aual Amout ad Gradiet Fuctios IET 350 Egieerig Ecoomics Learig Objectives Chapter 5 Upo completio of this chapter you should uderstad: Calculatig future values from aual amouts. Calculatig
Chapter 5 Uit Aual Amout ad Gradiet Fuctios IET 350 Egieerig Ecoomics Learig Objectives Chapter 5 Upo completio of this chapter you should uderstad: Calculatig future values from aual amouts. Calculatig
0.7 0.6 0.2 0 0 96 96.5 97 97.5 98 98.5 99 99.5 100 100.5 96.5 97 97.5 98 98.5 99 99.5 100 100.5
 Sectio 13 Kolmogorov-Smirov test. Suppose that we have a i.i.d. sample X 1,..., X with some ukow distributio P ad we would like to test the hypothesis that P is equal to a particular distributio P 0, i.e.
Sectio 13 Kolmogorov-Smirov test. Suppose that we have a i.i.d. sample X 1,..., X with some ukow distributio P ad we would like to test the hypothesis that P is equal to a particular distributio P 0, i.e.
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
1 Correlation and Regression Analysis
 1 Correlatio ad Regressio Aalysis I this sectio we will be ivestigatig the relatioship betwee two cotiuous variable, such as height ad weight, the cocetratio of a ijected drug ad heart rate, or the cosumptio
1 Correlatio ad Regressio Aalysis I this sectio we will be ivestigatig the relatioship betwee two cotiuous variable, such as height ad weight, the cocetratio of a ijected drug ad heart rate, or the cosumptio
Bob York. Transistor Basics - BJTs
 ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
Confidence Intervals for One Mean
 Chapter 420 Cofidece Itervals for Oe Mea Itroductio This routie calculates the sample size ecessary to achieve a specified distace from the mea to the cofidece limit(s) at a stated cofidece level for a
Chapter 420 Cofidece Itervals for Oe Mea Itroductio This routie calculates the sample size ecessary to achieve a specified distace from the mea to the cofidece limit(s) at a stated cofidece level for a
Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about. µ when the population standard deviation is unknown
 Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about µ whe the populatio stadard deviatio is kow ad populatio distributio is ormal or sample size is large T-TEST / T-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about
Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about µ whe the populatio stadard deviatio is kow ad populatio distributio is ormal or sample size is large T-TEST / T-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE MATHEMATICS P EXEMPLAR 04 MARKS: 50 TIME: 3 hours This questio paper cosists of 8 pages ad iformatio sheet. Please tur over Mathematics/P DBE/04 NSC Grade Eemplar INSTRUCTIONS
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE MATHEMATICS P EXEMPLAR 04 MARKS: 50 TIME: 3 hours This questio paper cosists of 8 pages ad iformatio sheet. Please tur over Mathematics/P DBE/04 NSC Grade Eemplar INSTRUCTIONS
Lesson 17 Pearson s Correlation Coefficient
 Outlie Measures of Relatioships Pearso s Correlatio Coefficiet (r) -types of data -scatter plots -measure of directio -measure of stregth Computatio -covariatio of X ad Y -uique variatio i X ad Y -measurig
Outlie Measures of Relatioships Pearso s Correlatio Coefficiet (r) -types of data -scatter plots -measure of directio -measure of stregth Computatio -covariatio of X ad Y -uique variatio i X ad Y -measurig
Output Analysis (2, Chapters 10 &11 Law)
 B. Maddah ENMG 6 Simulatio 05/0/07 Output Aalysis (, Chapters 10 &11 Law) Comparig alterative system cofiguratio Sice the output of a simulatio is radom, the comparig differet systems via simulatio should
B. Maddah ENMG 6 Simulatio 05/0/07 Output Aalysis (, Chapters 10 &11 Law) Comparig alterative system cofiguratio Sice the output of a simulatio is radom, the comparig differet systems via simulatio should
Chapter 7 Methods of Finding Estimators
 Chapter 7 for BST 695: Special Topics i Statistical Theory. Kui Zhag, 011 Chapter 7 Methods of Fidig Estimators Sectio 7.1 Itroductio Defiitio 7.1.1 A poit estimator is ay fuctio W( X) W( X1, X,, X ) of
Chapter 7 for BST 695: Special Topics i Statistical Theory. Kui Zhag, 011 Chapter 7 Methods of Fidig Estimators Sectio 7.1 Itroductio Defiitio 7.1.1 A poit estimator is ay fuctio W( X) W( X1, X,, X ) of
1. C. The formula for the confidence interval for a population mean is: x t, which was
 s 1. C. The formula for the cofidece iterval for a populatio mea is: x t, which was based o the sample Mea. So, x is guarateed to be i the iterval you form.. D. Use the rule : p-value
s 1. C. The formula for the cofidece iterval for a populatio mea is: x t, which was based o the sample Mea. So, x is guarateed to be i the iterval you form.. D. Use the rule : p-value
Overview of some probability distributions.
 Lecture Overview of some probability distributios. I this lecture we will review several commo distributios that will be used ofte throughtout the class. Each distributio is usually described by its probability
Lecture Overview of some probability distributios. I this lecture we will review several commo distributios that will be used ofte throughtout the class. Each distributio is usually described by its probability
Chapter 5: Inner Product Spaces
 Chapter 5: Ier Product Spaces Chapter 5: Ier Product Spaces SECION A Itroductio to Ier Product Spaces By the ed of this sectio you will be able to uderstad what is meat by a ier product space give examples
Chapter 5: Ier Product Spaces Chapter 5: Ier Product Spaces SECION A Itroductio to Ier Product Spaces By the ed of this sectio you will be able to uderstad what is meat by a ier product space give examples
Non-life insurance mathematics. Nils F. Haavardsson, University of Oslo and DNB Skadeforsikring
 No-life isurace mathematics Nils F. Haavardsso, Uiversity of Oslo ad DNB Skadeforsikrig Mai issues so far Why does isurace work? How is risk premium defied ad why is it importat? How ca claim frequecy
No-life isurace mathematics Nils F. Haavardsso, Uiversity of Oslo ad DNB Skadeforsikrig Mai issues so far Why does isurace work? How is risk premium defied ad why is it importat? How ca claim frequecy
Ekkehart Schlicht: Economic Surplus and Derived Demand
 Ekkehart Schlicht: Ecoomic Surplus ad Derived Demad Muich Discussio Paper No. 2006-17 Departmet of Ecoomics Uiversity of Muich Volkswirtschaftliche Fakultät Ludwig-Maximilias-Uiversität Müche Olie at http://epub.ub.ui-mueche.de/940/
Ekkehart Schlicht: Ecoomic Surplus ad Derived Demad Muich Discussio Paper No. 2006-17 Departmet of Ecoomics Uiversity of Muich Volkswirtschaftliche Fakultät Ludwig-Maximilias-Uiversität Müche Olie at http://epub.ub.ui-mueche.de/940/
AMPLIFIERS BJT BJT TRANSISTOR. Types of BJT BJT. devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level
 AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
Queuing Systems: Lecture 1. Amedeo R. Odoni October 10, 2001
 Queuig Systems: Lecture Amedeo R. Odoi October, 2 Topics i Queuig Theory 9. Itroductio to Queues; Little s Law; M/M/. Markovia Birth-ad-Death Queues. The M/G/ Queue ad Extesios 2. riority Queues; State
Queuig Systems: Lecture Amedeo R. Odoi October, 2 Topics i Queuig Theory 9. Itroductio to Queues; Little s Law; M/M/. Markovia Birth-ad-Death Queues. The M/G/ Queue ad Extesios 2. riority Queues; State
Partial Di erential Equations
 Partial Di eretial Equatios Partial Di eretial Equatios Much of moder sciece, egieerig, ad mathematics is based o the study of partial di eretial equatios, where a partial di eretial equatio is a equatio
Partial Di eretial Equatios Partial Di eretial Equatios Much of moder sciece, egieerig, ad mathematics is based o the study of partial di eretial equatios, where a partial di eretial equatio is a equatio
Soving Recurrence Relations
 Sovig Recurrece Relatios Part 1. Homogeeous liear 2d degree relatios with costat coefficiets. Cosider the recurrece relatio ( ) T () + at ( 1) + bt ( 2) = 0 This is called a homogeeous liear 2d degree
Sovig Recurrece Relatios Part 1. Homogeeous liear 2d degree relatios with costat coefficiets. Cosider the recurrece relatio ( ) T () + at ( 1) + bt ( 2) = 0 This is called a homogeeous liear 2d degree
Solving Logarithms and Exponential Equations
 Solvig Logarithms ad Epoetial Equatios Logarithmic Equatios There are two major ideas required whe solvig Logarithmic Equatios. The first is the Defiitio of a Logarithm. You may recall from a earlier topic:
Solvig Logarithms ad Epoetial Equatios Logarithmic Equatios There are two major ideas required whe solvig Logarithmic Equatios. The first is the Defiitio of a Logarithm. You may recall from a earlier topic:
Swaps: Constant maturity swaps (CMS) and constant maturity. Treasury (CMT) swaps
 Swaps: Costat maturity swaps (CMS) ad costat maturity reasury (CM) swaps A Costat Maturity Swap (CMS) swap is a swap where oe of the legs pays (respectively receives) a swap rate of a fixed maturity, while
Swaps: Costat maturity swaps (CMS) ad costat maturity reasury (CM) swaps A Costat Maturity Swap (CMS) swap is a swap where oe of the legs pays (respectively receives) a swap rate of a fixed maturity, while
5: Introduction to Estimation
 5: Itroductio to Estimatio Cotets Acroyms ad symbols... 1 Statistical iferece... Estimatig µ with cofidece... 3 Samplig distributio of the mea... 3 Cofidece Iterval for μ whe σ is kow before had... 4 Sample
5: Itroductio to Estimatio Cotets Acroyms ad symbols... 1 Statistical iferece... Estimatig µ with cofidece... 3 Samplig distributio of the mea... 3 Cofidece Iterval for μ whe σ is kow before had... 4 Sample
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR FINAL EXAM. (1) (2) (3) (4) Find the following using the definition of the Riemann integral: (2x + 1)dx
 SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR FINAL EXAM REAL ANALYSIS I FALL 006 3 4 Fid the followig usig the defiitio of the Riema itegral: a 0 x + dx 3 Cosider the partitio P x 0 3, x 3 +, x 3 +,......, x 3 3 + 3 of the iterval
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR FINAL EXAM REAL ANALYSIS I FALL 006 3 4 Fid the followig usig the defiitio of the Riema itegral: a 0 x + dx 3 Cosider the partitio P x 0 3, x 3 +, x 3 +,......, x 3 3 + 3 of the iterval
GENERAL INFORMATION FOR PROXIMITY SWITCHES
 78 C wire proximity switch The devices operate exactly like mechaical switches, with the coected load beig switched i series. They ca be used ito PLC iputs like relays. Notice should be take o the ifluece
78 C wire proximity switch The devices operate exactly like mechaical switches, with the coected load beig switched i series. They ca be used ito PLC iputs like relays. Notice should be take o the ifluece
1. MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION
 1. MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION EXAMPLE 1: Prove that for ay iteger 1. Proof: 1 + 2 + 3 +... + ( + 1 2 (1.1 STEP 1: For 1 (1.1 is true, sice 1 1(1 + 1. 2 STEP 2: Suppose (1.1 is true for some k 1, that is 1
1. MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION EXAMPLE 1: Prove that for ay iteger 1. Proof: 1 + 2 + 3 +... + ( + 1 2 (1.1 STEP 1: For 1 (1.1 is true, sice 1 1(1 + 1. 2 STEP 2: Suppose (1.1 is true for some k 1, that is 1
AP Calculus AB 2006 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Calculus AB 6 Scorig Guidelies Form B The College Board: Coectig Studets to College Success The College Board is a ot-for-profit membership associatio whose missio is to coect studets to college success
AP Calculus AB 6 Scorig Guidelies Form B The College Board: Coectig Studets to College Success The College Board is a ot-for-profit membership associatio whose missio is to coect studets to college success
THE ARITHMETIC OF INTEGERS. - multiplication, exponentiation, division, addition, and subtraction
 THE ARITHMETIC OF INTEGERS - multiplicatio, expoetiatio, divisio, additio, ad subtractio What to do ad what ot to do. THE INTEGERS Recall that a iteger is oe of the whole umbers, which may be either positive,
THE ARITHMETIC OF INTEGERS - multiplicatio, expoetiatio, divisio, additio, ad subtractio What to do ad what ot to do. THE INTEGERS Recall that a iteger is oe of the whole umbers, which may be either positive,
Drift-Diffusion Model: Introduction
 Drift-Diffusio Model: Itroductio Preared by: Dragica Vasileska Associate Professor Arizoa State Uiversity The oular drift-diffusio curret equatios ca be easily derived from the oltzma trasort equatio by
Drift-Diffusio Model: Itroductio Preared by: Dragica Vasileska Associate Professor Arizoa State Uiversity The oular drift-diffusio curret equatios ca be easily derived from the oltzma trasort equatio by
Convexity, Inequalities, and Norms
 Covexity, Iequalities, ad Norms Covex Fuctios You are probably familiar with the otio of cocavity of fuctios. Give a twicedifferetiable fuctio ϕ: R R, We say that ϕ is covex (or cocave up) if ϕ (x) 0 for
Covexity, Iequalities, ad Norms Covex Fuctios You are probably familiar with the otio of cocavity of fuctios. Give a twicedifferetiable fuctio ϕ: R R, We say that ϕ is covex (or cocave up) if ϕ (x) 0 for
CHAPTER 3 THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY
 CHAPTER 3 THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY OVERVIEW A dollar i the had today is worth more tha a dollar to be received i the future because, if you had it ow, you could ivest that dollar ad ear iterest. Of all
CHAPTER 3 THE TIME VALUE OF MONEY OVERVIEW A dollar i the had today is worth more tha a dollar to be received i the future because, if you had it ow, you could ivest that dollar ad ear iterest. Of all
A probabilistic proof of a binomial identity
 A probabilistic proof of a biomial idetity Joatho Peterso Abstract We give a elemetary probabilistic proof of a biomial idetity. The proof is obtaied by computig the probability of a certai evet i two
A probabilistic proof of a biomial idetity Joatho Peterso Abstract We give a elemetary probabilistic proof of a biomial idetity. The proof is obtaied by computig the probability of a certai evet i two
Maximum Likelihood Estimators.
 Lecture 2 Maximum Likelihood Estimators. Matlab example. As a motivatio, let us look at oe Matlab example. Let us geerate a radom sample of size 00 from beta distributio Beta(5, 2). We will lear the defiitio
Lecture 2 Maximum Likelihood Estimators. Matlab example. As a motivatio, let us look at oe Matlab example. Let us geerate a radom sample of size 00 from beta distributio Beta(5, 2). We will lear the defiitio
Example 2 Find the square root of 0. The only square root of 0 is 0 (since 0 is not positive or negative, so those choices don t exist here).
 BEGINNING ALGEBRA Roots ad Radicals (revised summer, 00 Olso) Packet to Supplemet the Curret Textbook - Part Review of Square Roots & Irratioals (This portio ca be ay time before Part ad should mostly
BEGINNING ALGEBRA Roots ad Radicals (revised summer, 00 Olso) Packet to Supplemet the Curret Textbook - Part Review of Square Roots & Irratioals (This portio ca be ay time before Part ad should mostly
CHAPTER 7: Central Limit Theorem: CLT for Averages (Means)
 CHAPTER 7: Cetral Limit Theorem: CLT for Averages (Meas) X = the umber obtaied whe rollig oe six sided die oce. If we roll a six sided die oce, the mea of the probability distributio is X P(X = x) Simulatio:
CHAPTER 7: Cetral Limit Theorem: CLT for Averages (Meas) X = the umber obtaied whe rollig oe six sided die oce. If we roll a six sided die oce, the mea of the probability distributio is X P(X = x) Simulatio:
Infinite Sequences and Series
 CHAPTER 4 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 4.1. Sequeces A sequece is a ifiite ordered list of umbers, for example the sequece of odd positive itegers: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29...
CHAPTER 4 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 4.1. Sequeces A sequece is a ifiite ordered list of umbers, for example the sequece of odd positive itegers: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29...
Hypothesis testing. Null and alternative hypotheses
 Hypothesis testig Aother importat use of samplig distributios is to test hypotheses about populatio parameters, e.g. mea, proportio, regressio coefficiets, etc. For example, it is possible to stipulate
Hypothesis testig Aother importat use of samplig distributios is to test hypotheses about populatio parameters, e.g. mea, proportio, regressio coefficiets, etc. For example, it is possible to stipulate
Measuring Magneto Energy Output and Inductance Revision 1
 Measurig Mageto Eergy Output ad Iductace evisio Itroductio A mageto is fudametally a iductor that is mechaically charged with a iitial curret value. That iitial curret is produced by movemet of the rotor
Measurig Mageto Eergy Output ad Iductace evisio Itroductio A mageto is fudametally a iductor that is mechaically charged with a iitial curret value. That iitial curret is produced by movemet of the rotor
*The most important feature of MRP as compared with ordinary inventory control analysis is its time phasing feature.
 Itegrated Productio ad Ivetory Cotrol System MRP ad MRP II Framework of Maufacturig System Ivetory cotrol, productio schedulig, capacity plaig ad fiacial ad busiess decisios i a productio system are iterrelated.
Itegrated Productio ad Ivetory Cotrol System MRP ad MRP II Framework of Maufacturig System Ivetory cotrol, productio schedulig, capacity plaig ad fiacial ad busiess decisios i a productio system are iterrelated.
The Stable Marriage Problem
 The Stable Marriage Problem William Hut Lae Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Electrical Egieerig, West Virgiia Uiversity, Morgatow, WV [email protected] 1 Itroductio Imagie you are a matchmaker,
The Stable Marriage Problem William Hut Lae Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Electrical Egieerig, West Virgiia Uiversity, Morgatow, WV [email protected] 1 Itroductio Imagie you are a matchmaker,
Lecture 4: Cauchy sequences, Bolzano-Weierstrass, and the Squeeze theorem
 Lecture 4: Cauchy sequeces, Bolzao-Weierstrass, ad the Squeeze theorem The purpose of this lecture is more modest tha the previous oes. It is to state certai coditios uder which we are guarateed that limits
Lecture 4: Cauchy sequeces, Bolzao-Weierstrass, ad the Squeeze theorem The purpose of this lecture is more modest tha the previous oes. It is to state certai coditios uder which we are guarateed that limits
Basic Measurement Issues. Sampling Theory and Analog-to-Digital Conversion
 Theory ad Aalog-to-Digital Coversio Itroductio/Defiitios Aalog-to-digital coversio Rate Frequecy Aalysis Basic Measuremet Issues Reliability the extet to which a measuremet procedure yields the same results
Theory ad Aalog-to-Digital Coversio Itroductio/Defiitios Aalog-to-digital coversio Rate Frequecy Aalysis Basic Measuremet Issues Reliability the extet to which a measuremet procedure yields the same results
Trigonometric Form of a Complex Number. The Complex Plane. axis. ( 2, 1) or 2 i FIGURE 6.44. The absolute value of the complex number z a bi is
 0_0605.qxd /5/05 0:45 AM Page 470 470 Chapter 6 Additioal Topics i Trigoometry 6.5 Trigoometric Form of a Complex Number What you should lear Plot complex umbers i the complex plae ad fid absolute values
0_0605.qxd /5/05 0:45 AM Page 470 470 Chapter 6 Additioal Topics i Trigoometry 6.5 Trigoometric Form of a Complex Number What you should lear Plot complex umbers i the complex plae ad fid absolute values
Confidence Intervals. CI for a population mean (σ is known and n > 30 or the variable is normally distributed in the.
 Cofidece Itervals A cofidece iterval is a iterval whose purpose is to estimate a parameter (a umber that could, i theory, be calculated from the populatio, if measuremets were available for the whole populatio).
Cofidece Itervals A cofidece iterval is a iterval whose purpose is to estimate a parameter (a umber that could, i theory, be calculated from the populatio, if measuremets were available for the whole populatio).
Running Time ( 3.1) Analysis of Algorithms. Experimental Studies ( 3.1.1) Limitations of Experiments. Pseudocode ( 3.1.2) Theoretical Analysis
 Ruig Time ( 3.) Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects.
Ruig Time ( 3.) Aalysis of Algorithms Iput Algorithm Output A algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solvig a problem i a fiite amout of time. Most algorithms trasform iput objects ito output objects.
An integrated CMOS optical receiver with clock and data recovery circuit
 Uiversity of Pretoria etd Che, Y-J (5) A itegrated CMOS optical receiver with clock ad data recovery circuit by Yi-Ju Che Submitted i partial fulfillmet of the requiremet for the degree Master of Egieerig
Uiversity of Pretoria etd Che, Y-J (5) A itegrated CMOS optical receiver with clock ad data recovery circuit by Yi-Ju Che Submitted i partial fulfillmet of the requiremet for the degree Master of Egieerig
Sequences and Series
 CHAPTER 9 Sequeces ad Series 9.. Covergece: Defiitio ad Examples Sequeces The purpose of this chapter is to itroduce a particular way of geeratig algorithms for fidig the values of fuctios defied by their
CHAPTER 9 Sequeces ad Series 9.. Covergece: Defiitio ad Examples Sequeces The purpose of this chapter is to itroduce a particular way of geeratig algorithms for fidig the values of fuctios defied by their
Estimating Probability Distributions by Observing Betting Practices
 5th Iteratioal Symposium o Imprecise Probability: Theories ad Applicatios, Prague, Czech Republic, 007 Estimatig Probability Distributios by Observig Bettig Practices Dr C Lych Natioal Uiversity of Irelad,
5th Iteratioal Symposium o Imprecise Probability: Theories ad Applicatios, Prague, Czech Republic, 007 Estimatig Probability Distributios by Observig Bettig Practices Dr C Lych Natioal Uiversity of Irelad,
Case Study. Normal and t Distributions. Density Plot. Normal Distributions
 Case Study Normal ad t Distributios Bret Halo ad Bret Larget Departmet of Statistics Uiversity of Wiscosi Madiso October 11 13, 2011 Case Study Body temperature varies withi idividuals over time (it ca
Case Study Normal ad t Distributios Bret Halo ad Bret Larget Departmet of Statistics Uiversity of Wiscosi Madiso October 11 13, 2011 Case Study Body temperature varies withi idividuals over time (it ca
Math 113 HW #11 Solutions
 Math 3 HW # Solutios 5. 4. (a) Estimate the area uder the graph of f(x) = x from x = to x = 4 usig four approximatig rectagles ad right edpoits. Sketch the graph ad the rectagles. Is your estimate a uderestimate
Math 3 HW # Solutios 5. 4. (a) Estimate the area uder the graph of f(x) = x from x = to x = 4 usig four approximatig rectagles ad right edpoits. Sketch the graph ad the rectagles. Is your estimate a uderestimate
LECTURE 13: Cross-validation
 LECTURE 3: Cross-validatio Resampli methods Cross Validatio Bootstrap Bias ad variace estimatio with the Bootstrap Three-way data partitioi Itroductio to Patter Aalysis Ricardo Gutierrez-Osua Texas A&M
LECTURE 3: Cross-validatio Resampli methods Cross Validatio Bootstrap Bias ad variace estimatio with the Bootstrap Three-way data partitioi Itroductio to Patter Aalysis Ricardo Gutierrez-Osua Texas A&M
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime
 Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Modified Line Search Method for Global Optimization
 Modified Lie Search Method for Global Optimizatio Cria Grosa ad Ajith Abraham Ceter of Excellece for Quatifiable Quality of Service Norwegia Uiversity of Sciece ad Techology Trodheim, Norway {cria, ajith}@q2s.tu.o
Modified Lie Search Method for Global Optimizatio Cria Grosa ad Ajith Abraham Ceter of Excellece for Quatifiable Quality of Service Norwegia Uiversity of Sciece ad Techology Trodheim, Norway {cria, ajith}@q2s.tu.o
Listing terms of a finite sequence List all of the terms of each finite sequence. a) a n n 2 for 1 n 5 1 b) a n for 1 n 4 n 2
 74 (4 ) Chapter 4 Sequeces ad Series 4. SEQUENCES I this sectio Defiitio Fidig a Formula for the th Term The word sequece is a familiar word. We may speak of a sequece of evets or say that somethig is
74 (4 ) Chapter 4 Sequeces ad Series 4. SEQUENCES I this sectio Defiitio Fidig a Formula for the th Term The word sequece is a familiar word. We may speak of a sequece of evets or say that somethig is
Chapter 14 Nonparametric Statistics
 Chapter 14 Noparametric Statistics A.K.A. distributio-free statistics! Does ot deped o the populatio fittig ay particular type of distributio (e.g, ormal). Sice these methods make fewer assumptios, they
Chapter 14 Noparametric Statistics A.K.A. distributio-free statistics! Does ot deped o the populatio fittig ay particular type of distributio (e.g, ormal). Sice these methods make fewer assumptios, they
Vladimir N. Burkov, Dmitri A. Novikov MODELS AND METHODS OF MULTIPROJECTS MANAGEMENT
 Keywords: project maagemet, resource allocatio, etwork plaig Vladimir N Burkov, Dmitri A Novikov MODELS AND METHODS OF MULTIPROJECTS MANAGEMENT The paper deals with the problems of resource allocatio betwee
Keywords: project maagemet, resource allocatio, etwork plaig Vladimir N Burkov, Dmitri A Novikov MODELS AND METHODS OF MULTIPROJECTS MANAGEMENT The paper deals with the problems of resource allocatio betwee
NEW HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTATIONAL METHODS FOR MORTGAGES AND ANNUITIES. Yuri Shestopaloff,
 NEW HIGH PERFORMNCE COMPUTTIONL METHODS FOR MORTGGES ND NNUITIES Yuri Shestopaloff, Geerally, mortgage ad auity equatios do ot have aalytical solutios for ukow iterest rate, which has to be foud usig umerical
NEW HIGH PERFORMNCE COMPUTTIONL METHODS FOR MORTGGES ND NNUITIES Yuri Shestopaloff, Geerally, mortgage ad auity equatios do ot have aalytical solutios for ukow iterest rate, which has to be foud usig umerical
This document contains a collection of formulas and constants useful for SPC chart construction. It assumes you are already familiar with SPC.
 SPC Formulas ad Tables 1 This documet cotais a collectio of formulas ad costats useful for SPC chart costructio. It assumes you are already familiar with SPC. Termiology Geerally, a bar draw over a symbol
SPC Formulas ad Tables 1 This documet cotais a collectio of formulas ad costats useful for SPC chart costructio. It assumes you are already familiar with SPC. Termiology Geerally, a bar draw over a symbol
Determining the sample size
 Determiig the sample size Oe of the most commo questios ay statisticia gets asked is How large a sample size do I eed? Researchers are ofte surprised to fid out that the aswer depeds o a umber of factors
Determiig the sample size Oe of the most commo questios ay statisticia gets asked is How large a sample size do I eed? Researchers are ofte surprised to fid out that the aswer depeds o a umber of factors
AP Calculus BC 2003 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Calculus BC Scorig Guidelies Form B The materials icluded i these files are iteded for use by AP teachers for course ad exam preparatio; permissio for ay other use must be sought from the Advaced Placemet
AP Calculus BC Scorig Guidelies Form B The materials icluded i these files are iteded for use by AP teachers for course ad exam preparatio; permissio for ay other use must be sought from the Advaced Placemet
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES
 SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
Systems Design Project: Indoor Location of Wireless Devices
 Systems Desig Project: Idoor Locatio of Wireless Devices Prepared By: Bria Murphy Seior Systems Sciece ad Egieerig Washigto Uiversity i St. Louis Phoe: (805) 698-5295 Email: [email protected] Supervised
Systems Desig Project: Idoor Locatio of Wireless Devices Prepared By: Bria Murphy Seior Systems Sciece ad Egieerig Washigto Uiversity i St. Louis Phoe: (805) 698-5295 Email: [email protected] Supervised
3 Energy. 3.3. Non-Flow Energy Equation (NFEE) Internal Energy. MECH 225 Engineering Science 2
 MECH 5 Egieerig Sciece 3 Eergy 3.3. No-Flow Eergy Equatio (NFEE) You may have oticed that the term system kees croig u. It is ecessary, therefore, that before we start ay aalysis we defie the system that
MECH 5 Egieerig Sciece 3 Eergy 3.3. No-Flow Eergy Equatio (NFEE) You may have oticed that the term system kees croig u. It is ecessary, therefore, that before we start ay aalysis we defie the system that
HEXFET MOSFET TECHNOLOGY. n n n n n n
 PD - 90495G POWER MOSFET THRU-HOLE (TO-254) Product Summary Part Number RDS(o) ID IRFM9140 0.20Ω -18 IRFM9140 JNTX2N7236 JNTXV2N7236 JNS2N7236 REF:MIL-PRF-19500/595 100V, P-CHNNEL HEXFET MOSFET TECHNOLOGY
PD - 90495G POWER MOSFET THRU-HOLE (TO-254) Product Summary Part Number RDS(o) ID IRFM9140 0.20Ω -18 IRFM9140 JNTX2N7236 JNTXV2N7236 JNS2N7236 REF:MIL-PRF-19500/595 100V, P-CHNNEL HEXFET MOSFET TECHNOLOGY
Learning objectives. Duc K. Nguyen - Corporate Finance 21/10/2014
 1 Lecture 3 Time Value of Moey ad Project Valuatio The timelie Three rules of time travels NPV of a stream of cash flows Perpetuities, auities ad other special cases Learig objectives 2 Uderstad the time-value
1 Lecture 3 Time Value of Moey ad Project Valuatio The timelie Three rules of time travels NPV of a stream of cash flows Perpetuities, auities ad other special cases Learig objectives 2 Uderstad the time-value
3. Greatest Common Divisor - Least Common Multiple
 3 Greatest Commo Divisor - Least Commo Multiple Defiitio 31: The greatest commo divisor of two atural umbers a ad b is the largest atural umber c which divides both a ad b We deote the greatest commo gcd
3 Greatest Commo Divisor - Least Commo Multiple Defiitio 31: The greatest commo divisor of two atural umbers a ad b is the largest atural umber c which divides both a ad b We deote the greatest commo gcd
Research Article Sign Data Derivative Recovery
 Iteratioal Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 0, Article ID 63070, 7 pages doi:0.540/0/63070 Research Article Sig Data Derivative Recovery L. M. Housto, G. A. Glass, ad A. D. Dymikov
Iteratioal Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 0, Article ID 63070, 7 pages doi:0.540/0/63070 Research Article Sig Data Derivative Recovery L. M. Housto, G. A. Glass, ad A. D. Dymikov
The analysis of the Cournot oligopoly model considering the subjective motive in the strategy selection
 The aalysis of the Courot oligopoly model cosiderig the subjective motive i the strategy selectio Shigehito Furuyama Teruhisa Nakai Departmet of Systems Maagemet Egieerig Faculty of Egieerig Kasai Uiversity
The aalysis of the Courot oligopoly model cosiderig the subjective motive i the strategy selectio Shigehito Furuyama Teruhisa Nakai Departmet of Systems Maagemet Egieerig Faculty of Egieerig Kasai Uiversity
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT1 Financial Mathematics
 Istitute of Actuaries of Idia Subject CT1 Fiacial Mathematics For 2014 Examiatios Subject CT1 Fiacial Mathematics Core Techical Aim The aim of the Fiacial Mathematics subject is to provide a groudig i
Istitute of Actuaries of Idia Subject CT1 Fiacial Mathematics For 2014 Examiatios Subject CT1 Fiacial Mathematics Core Techical Aim The aim of the Fiacial Mathematics subject is to provide a groudig i
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 11
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE MATHEMATICS P NOVEMBER 007 MARKS: 50 TIME: 3 hours This questio paper cosists of 9 pages, diagram sheet ad a -page formula sheet. Please tur over Mathematics/P DoE/November
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE MATHEMATICS P NOVEMBER 007 MARKS: 50 TIME: 3 hours This questio paper cosists of 9 pages, diagram sheet ad a -page formula sheet. Please tur over Mathematics/P DoE/November
Building Blocks Problem Related to Harmonic Series
 TMME, vol3, o, p.76 Buildig Blocks Problem Related to Harmoic Series Yutaka Nishiyama Osaka Uiversity of Ecoomics, Japa Abstract: I this discussio I give a eplaatio of the divergece ad covergece of ifiite
TMME, vol3, o, p.76 Buildig Blocks Problem Related to Harmoic Series Yutaka Nishiyama Osaka Uiversity of Ecoomics, Japa Abstract: I this discussio I give a eplaatio of the divergece ad covergece of ifiite
BJT Circuit Configurations
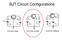 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
Finding the circle that best fits a set of points
 Fidig the circle that best fits a set of poits L. MAISONOBE October 5 th 007 Cotets 1 Itroductio Solvig the problem.1 Priciples............................... Iitializatio.............................
Fidig the circle that best fits a set of poits L. MAISONOBE October 5 th 007 Cotets 1 Itroductio Solvig the problem.1 Priciples............................... Iitializatio.............................
Domain 1: Designing a SQL Server Instance and a Database Solution
 Maual SQL Server 2008 Desig, Optimize ad Maitai (70-450) 1-800-418-6789 Domai 1: Desigig a SQL Server Istace ad a Database Solutio Desigig for CPU, Memory ad Storage Capacity Requiremets Whe desigig a
Maual SQL Server 2008 Desig, Optimize ad Maitai (70-450) 1-800-418-6789 Domai 1: Desigig a SQL Server Istace ad a Database Solutio Desigig for CPU, Memory ad Storage Capacity Requiremets Whe desigig a
Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Vol. 26, No.1, 2007. Sensitivity Analysis of Water Flooding Optimization by Dynamic Optimization
 Ira. J. Chem. Chem. Eg. Vol. 6, No., 007 Sesitivity Aalysis of Water Floodig Optimizatio by Dyamic Optimizatio Gharesheiklou, Ali Asghar* + ; Mousavi-Dehghai, Sayed Ali Research Istitute of Petroleum Idustry
Ira. J. Chem. Chem. Eg. Vol. 6, No., 007 Sesitivity Aalysis of Water Floodig Optimizatio by Dyamic Optimizatio Gharesheiklou, Ali Asghar* + ; Mousavi-Dehghai, Sayed Ali Research Istitute of Petroleum Idustry
Week 3 Conditional probabilities, Bayes formula, WEEK 3 page 1 Expected value of a random variable
 Week 3 Coditioal probabilities, Bayes formula, WEEK 3 page 1 Expected value of a radom variable We recall our discussio of 5 card poker hads. Example 13 : a) What is the probability of evet A that a 5
Week 3 Coditioal probabilities, Bayes formula, WEEK 3 page 1 Expected value of a radom variable We recall our discussio of 5 card poker hads. Example 13 : a) What is the probability of evet A that a 5
Current Carrying Capacity Analysis of TR42.7 update to IEEE802.3at
 IEEE80.3at Task Force Curret Carryig Capacity Aalysis of TR4.7 update to IEEE80.3at Ja 007, Moterey CA Yair Darsha Micro semi/powerdsie Curret Carryig Capacity Aalysis of TR4.7 update to IEEE80.3at Ja
IEEE80.3at Task Force Curret Carryig Capacity Aalysis of TR4.7 update to IEEE80.3at Ja 007, Moterey CA Yair Darsha Micro semi/powerdsie Curret Carryig Capacity Aalysis of TR4.7 update to IEEE80.3at Ja
Project Deliverables. CS 361, Lecture 28. Outline. Project Deliverables. Administrative. Project Comments
 Project Deliverables CS 361, Lecture 28 Jared Saia Uiversity of New Mexico Each Group should tur i oe group project cosistig of: About 6-12 pages of text (ca be loger with appedix) 6-12 figures (please
Project Deliverables CS 361, Lecture 28 Jared Saia Uiversity of New Mexico Each Group should tur i oe group project cosistig of: About 6-12 pages of text (ca be loger with appedix) 6-12 figures (please
Basic Elements of Arithmetic Sequences and Series
 MA40S PRE-CALCULUS UNIT G GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES CLASS NOTES (COMPLETED NO NEED TO COPY NOTES FROM OVERHEAD) Basic Elemets of Arithmetic Sequeces ad Series Objective: To establish basic elemets of arithmetic
MA40S PRE-CALCULUS UNIT G GEOMETRIC SEQUENCES CLASS NOTES (COMPLETED NO NEED TO COPY NOTES FROM OVERHEAD) Basic Elemets of Arithmetic Sequeces ad Series Objective: To establish basic elemets of arithmetic
Transistors. NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
 Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Department of Computer Science, University of Otago
 Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Otago Techical Report OUCS-2006-09 Permutatios Cotaiig May Patters Authors: M.H. Albert Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Otago Micah Colema, Rya Fly
Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Otago Techical Report OUCS-2006-09 Permutatios Cotaiig May Patters Authors: M.H. Albert Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Otago Micah Colema, Rya Fly
Lecture 17. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.
 Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
