Integrating DNA Motif Discovery and Genome-Wide Expression Analysis. Erin M. Conlon
|
|
|
- Florence Harmon
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integrating DNA Motif Discovery and Genome-Wide Expression Analysis Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Massachusetts Amherst Statistics in Functional Genomics Workshop Ascona, Switzerland June 30, 2004 test
2 Motif Discovery Identify short patterns in DNA sequence Patterns play role in control of gene expression Finding sites will help: develop disease treatments understand disease susceptibility
3 Motif Discovery Whole genome sequence ATTTACCGATGGCTGCACTATGCCCTATCGATCGACCTC TCATCTTCACATCGCATCACCAGTTCAGGATAGACACGG ACGGCCTCGATTGACGGTGGTACAATTTACCGATGGCTG CACTATGCCCTATCGATCGACCTCTCATGCTTCACATCG CATCACCAGTTCAGGATAGACACGGTCACATCGCATCAC Microarray information Regulatory sequence upstream from genes GATGGCTGCACCTCATCGTATGCCCTACGACCTCTCGC CACATCGCATCTCATCGACCAGTTCAGACACGGACGGC GCCTCGCTCATCGGTGGTACAGTTCAAACCTGACTAAA TCTCGTTAGGACCATCTCATCGACCCACATCGAGAGCG CGCTAGCCCTCATCGGATCTTGTTCGAGAATTGCCTAT
4 Gene Expression Control transcription factor gene expression CTCATCG upstream DNA sequence gene
5 Transcription Factor Binding Sites Upstream Sequence Co-expressed Genes GATGGGGGCTCATCGACGTGTATGC...ACGATGTCTC Gene 1 CACACCCCCTCTCATCGCGTCCCTT...CGCCCCCCCG Gene 2 GCCTCCTCATCGGTGGTACTCCAGT...TACATGACTA Gene 3 TCTCATGCTCATCGCATCACGTGTA...GCAATGAGAG CGCCTCATCGTGGATCTTGCGAATT...AGAATGGCCT Gene 100 Transcription Start
6 1) Motif Matrix 2) Sequence Logo 3) Consensus Sequence CTCATCG
7 MDscan Motif Finding Algorithm Uses 100 highest expressed genes, finds 30 candidate motifs for each width [5,15] Confirms motifs using 500 highest expressed genes Repeat for lowest expressed genes
8 Motifs Correlated with Expression Goal: relate global gene expression to motif matrices For each motif: calculate sequence score for each gene. score number of copies of a motif in each gene s upstream sequence regress gene expression to motif scores, determine significant motifs
9 Single Motif Regression Expression Sequence score # motif copies
10 Linear Regression Model For each motif: where Y = α + β S + g m mg e g Y g = log 2 -ratio of expression β S mg e m g = = = regression coefficient sequence score error
11 Over-expression of a Transcription Factor Rox1p is a transcription factor in yeast that binds to the 10-mer: TCTATTGTTT (from SCPD database of transcription factor binding sites)
12 Rox1p Over-expression Yeast expression data for Rox1p over-expression for 5,838 genes 800 basepair upstream sequence for each gene Use genes most repressed to find and refine 330 candidate motifs width [5,15] Regression with global gene expression to calculate p-values and rank motifs
13 Overexpressing a Transcription Factor Known binding site: TCTATTGTTT
14 Comparison to Other Motif-Finding Algorithms Statistically-based algorithms 1) AlignAce (Roth et al. 1998): Gibbs sampling approach 2) MEME (Grundy et al. 1996): expectation maximization (EM) Both use iterative procedures to update random initial probability matrices Drawback may be trapped in local maxima
15 Over-expressing a Transcription Factor Known binding site: TCTATTGTTT
16 Combinatorial Effects of Motifs Identify motifs that work together to control gene expression Method: MDscan generates 660 motifs width [5,15] that both enhance and inhibit expression Remove non-significant motifs Stepwise regression to determine final additive model
17 Multiple Regression Model to Determine Motifs Working Together where S Y β g m mg M e g = = = = = log 2 -ratio of regression coefficient sequence score subset of error M Y = α + β S + g m mg m=1 expression e significant motifs g
18 Yeast Amino Acid Starvation Experiment Expression for 5,970 genes Find motifs both enhancing and inhibiting expression 235 significant motifs Stepwise regression yields 25 final motifs
19 Multiple Motifs Influencing Expression
20 Known Motifs Positive Coefficients: STRE, URS1: respond to stress PHO4, MET4: nutrient scavenging GCN4: amino acid production Negative Coefficients: M3A, M3B, RAP1: slow cell growth
21 Motifs Influencing Expression over Time Yeast cell cycle information (Spellman et al. 1998): 2 cell cycles 18 time points 7-minute intervals Examine expression patterns over time
22 Time Series Expression Use Motif Regressor to find multiple motifs at each time point 273 motifs total Each motif is regressed with the expression at all other 17 time points
23 Motif: ACGCGTCGCG Phase Test M/G1 G1 S G2 M M/G1 G1 S G2 M
24 Motif: GCTCATCGC Phase Test M/G1 G1 S G2 M M/G1 G1 S G2 M
25 Motif Clustering Method: Hierarchically cluster motif patterns Euclidean distance 20 clusters Plot average coefficients for each cluster
26 Cluster 1: Known Motif SCB (6 motifs) Regression Coefficient Test Phase M/G1 G1 S G2 M M/G1 G1 S G2 M
27 Known Cell Cycle Motifs Regression Coefficient Phase Test Cell Cycle Time Points M/G1 G1 S G2 M M/G1 G1 S G2 M
28 Other Cell Cycle Motifs Regression Coefficient Phase Test Cell Cycle Time Points M/G1 G1 S G2 M M/G1 G1 S G2 M
29 Non Cell Cycle Motifs Regression Coefficient Phase Test Cell Cycle Time Points M/G1 G1 S G2 M M/G1 G1 S G2 M
30 Simulation Study Randomly assign yeast cell cycle expression to 5,838 genes Use MDscan to find candidate motifs Use simple linear regression to determine p-values of motifs Repeat 100 times to generate 40,324 motifs
31 Simulation Results Motifs From Real Sequences Motifs From Random Sequences
32 Summary Microarray and sequence information are combined to find transcription factor binding sites Stepwise regression identifies motifs working together to control expression We find known motifs, and new putative motifs in single experiments and time course experiments
33 Acknowledgements X. Shirley Liu Jun Liu Departments of Biostatistics and Statistics, Harvard University Jason Lieb Department of Biology University of North Carolina This work was partially supported by NIH National Library of Medicine grant 1F37LM
34 Reference Conlon, E.M., Liu, X.S., Lieb, J.D., Liu, J.S. (2003) Integrating regulatory motif discovery and genomewide expression analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:
Data Integration. Lectures 16 & 17. ECS289A, WQ03, Filkov
 Data Integration Lectures 16 & 17 Lectures Outline Goals for Data Integration Homogeneous data integration time series data (Filkov et al. 2002) Heterogeneous data integration microarray + sequence microarray
Data Integration Lectures 16 & 17 Lectures Outline Goals for Data Integration Homogeneous data integration time series data (Filkov et al. 2002) Heterogeneous data integration microarray + sequence microarray
NOVEL GENOME-SCALE CORRELATION BETWEEN DNA REPLICATION AND RNA TRANSCRIPTION DURING THE CELL CYCLE IN YEAST IS PREDICTED BY DATA-DRIVEN MODELS
 NOVEL GENOME-SCALE CORRELATION BETWEEN DNA REPLICATION AND RNA TRANSCRIPTION DURING THE CELL CYCLE IN YEAST IS PREDICTED BY DATA-DRIVEN MODELS Orly Alter (a) *, Gene H. Golub (b), Patrick O. Brown (c)
NOVEL GENOME-SCALE CORRELATION BETWEEN DNA REPLICATION AND RNA TRANSCRIPTION DURING THE CELL CYCLE IN YEAST IS PREDICTED BY DATA-DRIVEN MODELS Orly Alter (a) *, Gene H. Golub (b), Patrick O. Brown (c)
T cell Epitope Prediction
 Institute for Immunology and Informatics T cell Epitope Prediction EpiMatrix Eric Gustafson January 6, 2011 Overview Gathering raw data Popular sources Data Management Conservation Analysis Multiple Alignments
Institute for Immunology and Informatics T cell Epitope Prediction EpiMatrix Eric Gustafson January 6, 2011 Overview Gathering raw data Popular sources Data Management Conservation Analysis Multiple Alignments
Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 30 UTRs by comparison of several mammals
 Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 30 UTRs by comparison of several mammals Xiaohui Xie 1, Jun Lu 1, E. J. Kulbokas 1, Todd R. Golub 1, Vamsi Mootha 1, Kerstin Lindblad-Toh
Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 30 UTRs by comparison of several mammals Xiaohui Xie 1, Jun Lu 1, E. J. Kulbokas 1, Todd R. Golub 1, Vamsi Mootha 1, Kerstin Lindblad-Toh
Genetomic Promototypes
 Genetomic Promototypes Mirkó Palla and Dana Pe er Department of Mechanical Engineering Clarkson University Potsdam, New York and Department of Genetics Harvard Medical School 77 Avenue Louis Pasteur Boston,
Genetomic Promototypes Mirkó Palla and Dana Pe er Department of Mechanical Engineering Clarkson University Potsdam, New York and Department of Genetics Harvard Medical School 77 Avenue Louis Pasteur Boston,
Probabilistic methods for post-genomic data integration
 Probabilistic methods for post-genomic data integration Dirk Husmeier Biomathematics & Statistics Scotland (BioSS) JMB, The King s Buildings, Edinburgh EH9 3JZ United Kingdom http://wwwbiossacuk/ dirk
Probabilistic methods for post-genomic data integration Dirk Husmeier Biomathematics & Statistics Scotland (BioSS) JMB, The King s Buildings, Edinburgh EH9 3JZ United Kingdom http://wwwbiossacuk/ dirk
TOWARD BIG DATA ANALYSIS WORKSHOP
 TOWARD BIG DATA ANALYSIS WORKSHOP 邁 向 巨 量 資 料 分 析 研 討 會 摘 要 集 2015.06.05-06 巨 量 資 料 之 矩 陣 視 覺 化 陳 君 厚 中 央 研 究 院 統 計 科 學 研 究 所 摘 要 視 覺 化 (Visualization) 與 探 索 式 資 料 分 析 (Exploratory Data Analysis, EDA)
TOWARD BIG DATA ANALYSIS WORKSHOP 邁 向 巨 量 資 料 分 析 研 討 會 摘 要 集 2015.06.05-06 巨 量 資 料 之 矩 陣 視 覺 化 陳 君 厚 中 央 研 究 院 統 計 科 學 研 究 所 摘 要 視 覺 化 (Visualization) 與 探 索 式 資 料 分 析 (Exploratory Data Analysis, EDA)
Network Analysis. BCH 5101: Analysis of -Omics Data 1/34
 Network Analysis BCH 5101: Analysis of -Omics Data 1/34 Network Analysis Graphs as a representation of networks Examples of genome-scale graphs Statistical properties of genome-scale graphs The search
Network Analysis BCH 5101: Analysis of -Omics Data 1/34 Network Analysis Graphs as a representation of networks Examples of genome-scale graphs Statistical properties of genome-scale graphs The search
Statistics Graduate Courses
 Statistics Graduate Courses STAT 7002--Topics in Statistics-Biological/Physical/Mathematics (cr.arr.).organized study of selected topics. Subjects and earnable credit may vary from semester to semester.
Statistics Graduate Courses STAT 7002--Topics in Statistics-Biological/Physical/Mathematics (cr.arr.).organized study of selected topics. Subjects and earnable credit may vary from semester to semester.
Current Motif Discovery Tools and their Limitations
 Current Motif Discovery Tools and their Limitations Philipp Bucher SIB / CIG Workshop 3 October 2006 Trendy Concepts and Hypotheses Transcription regulatory elements act in a context-dependent manner.
Current Motif Discovery Tools and their Limitations Philipp Bucher SIB / CIG Workshop 3 October 2006 Trendy Concepts and Hypotheses Transcription regulatory elements act in a context-dependent manner.
MIC - Detecting Novel Associations in Large Data Sets. by Nico Güttler, Andreas Ströhlein and Matt Huska
 MIC - Detecting Novel Associations in Large Data Sets by Nico Güttler, Andreas Ströhlein and Matt Huska Outline Motivation Method Results Criticism Conclusions Motivation - Goal Determine important undiscovered
MIC - Detecting Novel Associations in Large Data Sets by Nico Güttler, Andreas Ströhlein and Matt Huska Outline Motivation Method Results Criticism Conclusions Motivation - Goal Determine important undiscovered
FlipFlop: Fast Lasso-based Isoform Prediction as a Flow Problem
 FlipFlop: Fast Lasso-based Isoform Prediction as a Flow Problem Elsa Bernard Laurent Jacob Julien Mairal Jean-Philippe Vert September 24, 2013 Abstract FlipFlop implements a fast method for de novo transcript
FlipFlop: Fast Lasso-based Isoform Prediction as a Flow Problem Elsa Bernard Laurent Jacob Julien Mairal Jean-Philippe Vert September 24, 2013 Abstract FlipFlop implements a fast method for de novo transcript
Service courses for graduate students in degree programs other than the MS or PhD programs in Biostatistics.
 Course Catalog In order to be assured that all prerequisites are met, students must acquire a permission number from the education coordinator prior to enrolling in any Biostatistics course. Courses are
Course Catalog In order to be assured that all prerequisites are met, students must acquire a permission number from the education coordinator prior to enrolling in any Biostatistics course. Courses are
How To Cluster
 Data Clustering Dec 2nd, 2013 Kyrylo Bessonov Talk outline Introduction to clustering Types of clustering Supervised Unsupervised Similarity measures Main clustering algorithms k-means Hierarchical Main
Data Clustering Dec 2nd, 2013 Kyrylo Bessonov Talk outline Introduction to clustering Types of clustering Supervised Unsupervised Similarity measures Main clustering algorithms k-means Hierarchical Main
Clustering. Adrian Groza. Department of Computer Science Technical University of Cluj-Napoca
 Clustering Adrian Groza Department of Computer Science Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Outline 1 Cluster Analysis What is Datamining? Cluster Analysis 2 K-means 3 Hierarchical Clustering What is Datamining?
Clustering Adrian Groza Department of Computer Science Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Outline 1 Cluster Analysis What is Datamining? Cluster Analysis 2 K-means 3 Hierarchical Clustering What is Datamining?
Statistical issues in the analysis of microarray data
 Statistical issues in the analysis of microarray data Daniel Gerhard Institute of Biostatistics Leibniz University of Hannover ESNATS Summerschool, Zermatt D. Gerhard (LUH) Analysis of microarray data
Statistical issues in the analysis of microarray data Daniel Gerhard Institute of Biostatistics Leibniz University of Hannover ESNATS Summerschool, Zermatt D. Gerhard (LUH) Analysis of microarray data
Protein Protein Interaction Networks
 Functional Pattern Mining from Genome Scale Protein Protein Interaction Networks Young-Rae Cho, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University it My Definition of Bioinformatics
Functional Pattern Mining from Genome Scale Protein Protein Interaction Networks Young-Rae Cho, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University it My Definition of Bioinformatics
Title: Lending Club Interest Rates are closely linked with FICO scores and Loan Length
 Title: Lending Club Interest Rates are closely linked with FICO scores and Loan Length Introduction: The Lending Club is a unique website that allows people to directly borrow money from other people [1].
Title: Lending Club Interest Rates are closely linked with FICO scores and Loan Length Introduction: The Lending Club is a unique website that allows people to directly borrow money from other people [1].
Exploratory data analysis for microarray data
 Eploratory data analysis for microarray data Anja von Heydebreck Ma Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics, Dept. Computational Molecular Biology, Berlin, Germany [email protected] Visualization
Eploratory data analysis for microarray data Anja von Heydebreck Ma Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics, Dept. Computational Molecular Biology, Berlin, Germany [email protected] Visualization
Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform
 Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry, LNBio, CNPEM Tutorial version 1.0, January 2014. Note: This tutorial was written based on the information
Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry, LNBio, CNPEM Tutorial version 1.0, January 2014. Note: This tutorial was written based on the information
Likelihood Approaches for Trial Designs in Early Phase Oncology
 Likelihood Approaches for Trial Designs in Early Phase Oncology Clinical Trials Elizabeth Garrett-Mayer, PhD Cody Chiuzan, PhD Hollings Cancer Center Department of Public Health Sciences Medical University
Likelihood Approaches for Trial Designs in Early Phase Oncology Clinical Trials Elizabeth Garrett-Mayer, PhD Cody Chiuzan, PhD Hollings Cancer Center Department of Public Health Sciences Medical University
D-optimal plans in observational studies
 D-optimal plans in observational studies Constanze Pumplün Stefan Rüping Katharina Morik Claus Weihs October 11, 2005 Abstract This paper investigates the use of Design of Experiments in observational
D-optimal plans in observational studies Constanze Pumplün Stefan Rüping Katharina Morik Claus Weihs October 11, 2005 Abstract This paper investigates the use of Design of Experiments in observational
RNA Structure and folding
 RNA Structure and folding Overview: The main functional biomolecules in cells are polymers DNA, RNA and proteins For RNA and Proteins, the specific sequence of the polymer dictates its final structure
RNA Structure and folding Overview: The main functional biomolecules in cells are polymers DNA, RNA and proteins For RNA and Proteins, the specific sequence of the polymer dictates its final structure
LOGISTIC REGRESSION ANALYSIS
 LOGISTIC REGRESSION ANALYSIS C. Mitchell Dayton Department of Measurement, Statistics & Evaluation Room 1230D Benjamin Building University of Maryland September 1992 1. Introduction and Model Logistic
LOGISTIC REGRESSION ANALYSIS C. Mitchell Dayton Department of Measurement, Statistics & Evaluation Room 1230D Benjamin Building University of Maryland September 1992 1. Introduction and Model Logistic
They can be obtained in HQJHQH format directly from the home page at: http://www.engene.cnb.uam.es/downloads/kobayashi.dat
 HQJHQH70 *XLGHG7RXU This document contains a Guided Tour through the HQJHQH platform and it was created for training purposes with respect to the system options and analysis possibilities. It is not intended
HQJHQH70 *XLGHG7RXU This document contains a Guided Tour through the HQJHQH platform and it was created for training purposes with respect to the system options and analysis possibilities. It is not intended
Heuristics for the Sorting by Length-Weighted Inversions Problem on Signed Permutations
 Heuristics for the Sorting by Length-Weighted Inversions Problem on Signed Permutations AlCoB 2014 First International Conference on Algorithms for Computational Biology Thiago da Silva Arruda Institute
Heuristics for the Sorting by Length-Weighted Inversions Problem on Signed Permutations AlCoB 2014 First International Conference on Algorithms for Computational Biology Thiago da Silva Arruda Institute
Pairwise Sequence Alignment
 Pairwise Sequence Alignment [email protected] SS 2013 Outline Pairwise sequence alignment global - Needleman Wunsch Gotoh algorithm local - Smith Waterman algorithm BLAST - heuristics What
Pairwise Sequence Alignment [email protected] SS 2013 Outline Pairwise sequence alignment global - Needleman Wunsch Gotoh algorithm local - Smith Waterman algorithm BLAST - heuristics What
Gene Expression Analysis
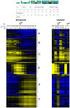 Gene Expression Analysis Jie Peng Department of Statistics University of California, Davis May 2012 RNA expression technologies High-throughput technologies to measure the expression levels of thousands
Gene Expression Analysis Jie Peng Department of Statistics University of California, Davis May 2012 RNA expression technologies High-throughput technologies to measure the expression levels of thousands
Univariate Regression
 Univariate Regression Correlation and Regression The regression line summarizes the linear relationship between 2 variables Correlation coefficient, r, measures strength of relationship: the closer r is
Univariate Regression Correlation and Regression The regression line summarizes the linear relationship between 2 variables Correlation coefficient, r, measures strength of relationship: the closer r is
BIOINF 525 Winter 2016 Foundations of Bioinformatics and Systems Biology http://tinyurl.com/bioinf525-w16
 Course Director: Dr. Barry Grant (DCM&B, [email protected]) Description: This is a three module course covering (1) Foundations of Bioinformatics, (2) Statistics in Bioinformatics, and (3) Systems
Course Director: Dr. Barry Grant (DCM&B, [email protected]) Description: This is a three module course covering (1) Foundations of Bioinformatics, (2) Statistics in Bioinformatics, and (3) Systems
Data Mining: Overview. What is Data Mining?
 Data Mining: Overview What is Data Mining? Recently * coined term for confluence of ideas from statistics and computer science (machine learning and database methods) applied to large databases in science,
Data Mining: Overview What is Data Mining? Recently * coined term for confluence of ideas from statistics and computer science (machine learning and database methods) applied to large databases in science,
Example: Credit card default, we may be more interested in predicting the probabilty of a default than classifying individuals as default or not.
 Statistical Learning: Chapter 4 Classification 4.1 Introduction Supervised learning with a categorical (Qualitative) response Notation: - Feature vector X, - qualitative response Y, taking values in C
Statistical Learning: Chapter 4 Classification 4.1 Introduction Supervised learning with a categorical (Qualitative) response Notation: - Feature vector X, - qualitative response Y, taking values in C
Comparing Methods for Identifying Transcription Factor Target Genes
 Comparing Methods for Identifying Transcription Factor Target Genes Alena van Bömmel (R 3.3.73) Matthew Huska (R 3.3.18) Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Folie 1 Transcriptional Regulation TF
Comparing Methods for Identifying Transcription Factor Target Genes Alena van Bömmel (R 3.3.73) Matthew Huska (R 3.3.18) Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Folie 1 Transcriptional Regulation TF
Feed Forward Loops in Biological Systems
 Feed Forward Loops in Biological Systems Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 7 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...
Feed Forward Loops in Biological Systems Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 7 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...
A Primer of Genome Science THIRD
 A Primer of Genome Science THIRD EDITION GREG GIBSON-SPENCER V. MUSE North Carolina State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts USA Contents Preface xi 1 Genome Projects:
A Primer of Genome Science THIRD EDITION GREG GIBSON-SPENCER V. MUSE North Carolina State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts USA Contents Preface xi 1 Genome Projects:
Logistic Regression (1/24/13)
 STA63/CBB540: Statistical methods in computational biology Logistic Regression (/24/3) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribe: Dinesh Manandhar Introduction Logistic regression is model for regression used
STA63/CBB540: Statistical methods in computational biology Logistic Regression (/24/3) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribe: Dinesh Manandhar Introduction Logistic regression is model for regression used
Core Facility Genomics
 Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture
 CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
How To Cluster Of Complex Systems
 Entropy based Graph Clustering: Application to Biological and Social Networks Edward C Kenley Young-Rae Cho Department of Computer Science Baylor University Complex Systems Definition Dynamically evolving
Entropy based Graph Clustering: Application to Biological and Social Networks Edward C Kenley Young-Rae Cho Department of Computer Science Baylor University Complex Systems Definition Dynamically evolving
STATISTICA Formula Guide: Logistic Regression. Table of Contents
 : Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
: Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
Lecture/Recitation Topic SMA 5303 L1 Sampling and statistical distributions
 SMA 50: Statistical Learning and Data Mining in Bioinformatics (also listed as 5.077: Statistical Learning and Data Mining ()) Spring Term (Feb May 200) Faculty: Professor Roy Welsch Wed 0 Feb 7:00-8:0
SMA 50: Statistical Learning and Data Mining in Bioinformatics (also listed as 5.077: Statistical Learning and Data Mining ()) Spring Term (Feb May 200) Faculty: Professor Roy Welsch Wed 0 Feb 7:00-8:0
Activity 7.21 Transcription factors
 Purpose To consolidate understanding of protein synthesis. To explain the role of transcription factors and hormones in switching genes on and off. Play the transcription initiation complex game Regulation
Purpose To consolidate understanding of protein synthesis. To explain the role of transcription factors and hormones in switching genes on and off. Play the transcription initiation complex game Regulation
Developing Risk Adjustment Techniques Using the SAS@ System for Assessing Health Care Quality in the lmsystem@
 Developing Risk Adjustment Techniques Using the SAS@ System for Assessing Health Care Quality in the lmsystem@ Yanchun Xu, Andrius Kubilius Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations,
Developing Risk Adjustment Techniques Using the SAS@ System for Assessing Health Care Quality in the lmsystem@ Yanchun Xu, Andrius Kubilius Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations,
Just the Facts: A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
 1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
Stepwise Regression. Chapter 311. Introduction. Variable Selection Procedures. Forward (Step-Up) Selection
 Chapter 311 Introduction Often, theory and experience give only general direction as to which of a pool of candidate variables (including transformed variables) should be included in the regression model.
Chapter 311 Introduction Often, theory and experience give only general direction as to which of a pool of candidate variables (including transformed variables) should be included in the regression model.
Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data
 Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data MICHAEL GREENACRE Professor of Statistics at the Pompeu Fabra University in Barcelona, Spain RAUL PRIMICERIO Associate Professor of Ecology, Evolutionary Biology
Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data MICHAEL GREENACRE Professor of Statistics at the Pompeu Fabra University in Barcelona, Spain RAUL PRIMICERIO Associate Professor of Ecology, Evolutionary Biology
How To Understand Multivariate Models
 Neil H. Timm Applied Multivariate Analysis With 42 Figures Springer Contents Preface Acknowledgments List of Tables List of Figures vii ix xix xxiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Multivariate Models
Neil H. Timm Applied Multivariate Analysis With 42 Figures Springer Contents Preface Acknowledgments List of Tables List of Figures vii ix xix xxiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Multivariate Models
Predictive Gene Signature Selection for Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
 Predictive Gene Signature Selection for Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients by Li Liu A practicum report submitted to the Department of Public Health Sciences in conformity with
Predictive Gene Signature Selection for Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients by Li Liu A practicum report submitted to the Department of Public Health Sciences in conformity with
Comparing Functional Data Analysis Approach and Nonparametric Mixed-Effects Modeling Approach for Longitudinal Data Analysis
 Comparing Functional Data Analysis Approach and Nonparametric Mixed-Effects Modeling Approach for Longitudinal Data Analysis Hulin Wu, PhD, Professor (with Dr. Shuang Wu) Department of Biostatistics &
Comparing Functional Data Analysis Approach and Nonparametric Mixed-Effects Modeling Approach for Longitudinal Data Analysis Hulin Wu, PhD, Professor (with Dr. Shuang Wu) Department of Biostatistics &
Lecture 11 Data storage and LIMS solutions. Stéphane LE CROM [email protected]
 Lecture 11 Data storage and LIMS solutions Stéphane LE CROM [email protected] Various steps of a DNA microarray experiment Experimental steps Data analysis Experimental design set up Chips on catalog
Lecture 11 Data storage and LIMS solutions Stéphane LE CROM [email protected] Various steps of a DNA microarray experiment Experimental steps Data analysis Experimental design set up Chips on catalog
Social Media Mining. Data Mining Essentials
 Introduction Data production rate has been increased dramatically (Big Data) and we are able store much more data than before E.g., purchase data, social media data, mobile phone data Businesses and customers
Introduction Data production rate has been increased dramatically (Big Data) and we are able store much more data than before E.g., purchase data, social media data, mobile phone data Businesses and customers
Please follow the directions once you locate the Stata software in your computer. Room 114 (Business Lab) has computers with Stata software
 STATA Tutorial Professor Erdinç Please follow the directions once you locate the Stata software in your computer. Room 114 (Business Lab) has computers with Stata software 1.Wald Test Wald Test is used
STATA Tutorial Professor Erdinç Please follow the directions once you locate the Stata software in your computer. Room 114 (Business Lab) has computers with Stata software 1.Wald Test Wald Test is used
Example: Document Clustering. Clustering: Definition. Notion of a Cluster can be Ambiguous. Types of Clusterings. Hierarchical Clustering
 Overview Prognostic Models and Data Mining in Medicine, part I Cluster Analsis What is Cluster Analsis? K-Means Clustering Hierarchical Clustering Cluster Validit Eample: Microarra data analsis 6 Summar
Overview Prognostic Models and Data Mining in Medicine, part I Cluster Analsis What is Cluster Analsis? K-Means Clustering Hierarchical Clustering Cluster Validit Eample: Microarra data analsis 6 Summar
Exercise with Gene Ontology - Cytoscape - BiNGO
 Exercise with Gene Ontology - Cytoscape - BiNGO This practical has material extracted from http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/chipcourse/exercises/ex_go/goexercise11.php In this exercise we will analyze microarray
Exercise with Gene Ontology - Cytoscape - BiNGO This practical has material extracted from http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/chipcourse/exercises/ex_go/goexercise11.php In this exercise we will analyze microarray
What is the difference between basal and activated transcription?
 What is the difference between basal and activated transcription? Regulation of Transcription I. Basal vs. activated transcription for mrna genes A. General transcription factor (TF) vs. promoterspecific
What is the difference between basal and activated transcription? Regulation of Transcription I. Basal vs. activated transcription for mrna genes A. General transcription factor (TF) vs. promoterspecific
Clustering & Visualization
 Chapter 5 Clustering & Visualization Clustering in high-dimensional databases is an important problem and there are a number of different clustering paradigms which are applicable to high-dimensional data.
Chapter 5 Clustering & Visualization Clustering in high-dimensional databases is an important problem and there are a number of different clustering paradigms which are applicable to high-dimensional data.
Building risk prediction models - with a focus on Genome-Wide Association Studies. Charles Kooperberg
 Building risk prediction models - with a focus on Genome-Wide Association Studies Risk prediction models Based on data: (D i, X i1,..., X ip ) i = 1,..., n we like to fit a model P(D = 1 X 1,..., X p )
Building risk prediction models - with a focus on Genome-Wide Association Studies Risk prediction models Based on data: (D i, X i1,..., X ip ) i = 1,..., n we like to fit a model P(D = 1 X 1,..., X p )
Metodi Numerici per la Bioinformatica
 Metodi Numerici per la Bioinformatica Biclustering A.A. 2008/2009 1 Outline Motivation What is Biclustering? Why Biclustering and not just Clustering? Bicluster Types Algorithms 2 Motivations Gene expression
Metodi Numerici per la Bioinformatica Biclustering A.A. 2008/2009 1 Outline Motivation What is Biclustering? Why Biclustering and not just Clustering? Bicluster Types Algorithms 2 Motivations Gene expression
Principle Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares: Two Dimension Reduction Techniques for Regression
 Principle Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares: Two Dimension Reduction Techniques for Regression Saikat Maitra and Jun Yan Abstract: Dimension reduction is one of the major tasks for multivariate
Principle Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares: Two Dimension Reduction Techniques for Regression Saikat Maitra and Jun Yan Abstract: Dimension reduction is one of the major tasks for multivariate
Statistical Analysis. NBAF-B Metabolomics Masterclass. Mark Viant
 Statistical Analysis NBAF-B Metabolomics Masterclass Mark Viant 1. Introduction 2. Univariate analysis Overview of lecture 3. Unsupervised multivariate analysis Principal components analysis (PCA) Interpreting
Statistical Analysis NBAF-B Metabolomics Masterclass Mark Viant 1. Introduction 2. Univariate analysis Overview of lecture 3. Unsupervised multivariate analysis Principal components analysis (PCA) Interpreting
Aiping Lu. Key Laboratory of System Biology Chinese Academic Society [email protected]
 Aiping Lu Key Laboratory of System Biology Chinese Academic Society [email protected] Proteome and Proteomics PROTEin complement expressed by genome Marc Wilkins Electrophoresis. 1995. 16(7):1090-4. proteomics
Aiping Lu Key Laboratory of System Biology Chinese Academic Society [email protected] Proteome and Proteomics PROTEin complement expressed by genome Marc Wilkins Electrophoresis. 1995. 16(7):1090-4. proteomics
Support Vector Machines with Clustering for Training with Very Large Datasets
 Support Vector Machines with Clustering for Training with Very Large Datasets Theodoros Evgeniou Technology Management INSEAD Bd de Constance, Fontainebleau 77300, France [email protected] Massimiliano
Support Vector Machines with Clustering for Training with Very Large Datasets Theodoros Evgeniou Technology Management INSEAD Bd de Constance, Fontainebleau 77300, France [email protected] Massimiliano
How To Understand How Gene Expression Is Regulated
 What makes cells different from each other? How do cells respond to information from environment? Regulation of: - Transcription - prokaryotes - eukaryotes - mrna splicing - mrna localisation and translation
What makes cells different from each other? How do cells respond to information from environment? Regulation of: - Transcription - prokaryotes - eukaryotes - mrna splicing - mrna localisation and translation
Performance Metrics for Graph Mining Tasks
 Performance Metrics for Graph Mining Tasks 1 Outline Introduction to Performance Metrics Supervised Learning Performance Metrics Unsupervised Learning Performance Metrics Optimizing Metrics Statistical
Performance Metrics for Graph Mining Tasks 1 Outline Introduction to Performance Metrics Supervised Learning Performance Metrics Unsupervised Learning Performance Metrics Optimizing Metrics Statistical
1 Solving LPs: The Simplex Algorithm of George Dantzig
 Solving LPs: The Simplex Algorithm of George Dantzig. Simplex Pivoting: Dictionary Format We illustrate a general solution procedure, called the simplex algorithm, by implementing it on a very simple example.
Solving LPs: The Simplex Algorithm of George Dantzig. Simplex Pivoting: Dictionary Format We illustrate a general solution procedure, called the simplex algorithm, by implementing it on a very simple example.
1. Introduction Gene regulation Genomics and genome analyses Hidden markov model (HMM)
 1. Introduction Gene regulation Genomics and genome analyses Hidden markov model (HMM) 2. Gene regulation tools and methods Regulatory sequences and motif discovery TF binding sites, microrna target prediction
1. Introduction Gene regulation Genomics and genome analyses Hidden markov model (HMM) 2. Gene regulation tools and methods Regulatory sequences and motif discovery TF binding sites, microrna target prediction
Paper D10 2009. Ranking Predictors in Logistic Regression. Doug Thompson, Assurant Health, Milwaukee, WI
 Paper D10 2009 Ranking Predictors in Logistic Regression Doug Thompson, Assurant Health, Milwaukee, WI ABSTRACT There is little consensus on how best to rank predictors in logistic regression. This paper
Paper D10 2009 Ranking Predictors in Logistic Regression Doug Thompson, Assurant Health, Milwaukee, WI ABSTRACT There is little consensus on how best to rank predictors in logistic regression. This paper
Cancer Biostatistics Workshop Science of Doing Science - Biostatistics
 Cancer Biostatistics Workshop Science of Doing Science - Biostatistics Yu Shyr, PhD Jan. 18, 2008 Cancer Biostatistics Center Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center [email protected] Aims Cancer Biostatistics
Cancer Biostatistics Workshop Science of Doing Science - Biostatistics Yu Shyr, PhD Jan. 18, 2008 Cancer Biostatistics Center Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center [email protected] Aims Cancer Biostatistics
Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis
 Microarray Data Analysis Workshop MedVetNet Workshop, DTU 2008 Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis Carsten Friis ( with several slides from
Microarray Data Analysis Workshop MedVetNet Workshop, DTU 2008 Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis Carsten Friis ( with several slides from
Healthcare Analytics. Aryya Gangopadhyay UMBC
 Healthcare Analytics Aryya Gangopadhyay UMBC Two of many projects Integrated network approach to personalized medicine Multidimensional and multimodal Dynamic Analyze interactions HealthMask Need for sharing
Healthcare Analytics Aryya Gangopadhyay UMBC Two of many projects Integrated network approach to personalized medicine Multidimensional and multimodal Dynamic Analyze interactions HealthMask Need for sharing
Polynomial Neural Network Discovery Client User Guide
 Polynomial Neural Network Discovery Client User Guide Version 1.3 Table of contents Table of contents...2 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Overview...3 1.2 PNN algorithm principles...3 1.3 Additional criteria...3
Polynomial Neural Network Discovery Client User Guide Version 1.3 Table of contents Table of contents...2 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Overview...3 1.2 PNN algorithm principles...3 1.3 Additional criteria...3
Gene Enrichment Analysis
 a Analysis of DNA Chips and Gene Networks Spring Semester, 2009 Lecture 14a: January 21, 2010 Lecturer: Ron Shamir Scribe: Roye Rozov Gene Enrichment Analysis 14.1 Introduction This lecture introduces
a Analysis of DNA Chips and Gene Networks Spring Semester, 2009 Lecture 14a: January 21, 2010 Lecturer: Ron Shamir Scribe: Roye Rozov Gene Enrichment Analysis 14.1 Introduction This lecture introduces
DATA MINING CLUSTER ANALYSIS: BASIC CONCEPTS
 DATA MINING CLUSTER ANALYSIS: BASIC CONCEPTS 1 AND ALGORITHMS Chiara Renso KDD-LAB ISTI- CNR, Pisa, Italy WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group will be similar
DATA MINING CLUSTER ANALYSIS: BASIC CONCEPTS 1 AND ALGORITHMS Chiara Renso KDD-LAB ISTI- CNR, Pisa, Italy WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group will be similar
Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) in Semi-supervised Learning Reducing Dimension and Maintaining Meaning
 Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) in Semi-supervised Learning Reducing Dimension and Maintaining Meaning SAMSI 10 May 2013 Outline Introduction to NMF Applications Motivations NMF as a middle step
Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) in Semi-supervised Learning Reducing Dimension and Maintaining Meaning SAMSI 10 May 2013 Outline Introduction to NMF Applications Motivations NMF as a middle step
7 Time series analysis
 7 Time series analysis In Chapters 16, 17, 33 36 in Zuur, Ieno and Smith (2007), various time series techniques are discussed. Applying these methods in Brodgar is straightforward, and most choices are
7 Time series analysis In Chapters 16, 17, 33 36 in Zuur, Ieno and Smith (2007), various time series techniques are discussed. Applying these methods in Brodgar is straightforward, and most choices are
