Supplementary information
|
|
|
- Tyrone Clarke
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary information De novo mutations of SETBP1 cause Schinzel-Giedion syndrome Alexander Hoischen 1,*, Bregje WM van Bon 1,*, Christian Gilissen 1,*, Peer Arts 1, Bart van Lier 1, Marloes Steehouwer 1, Petra de Vries 1, Rick de Reuver 1, Nienke Wieskamp 1, Geert Mortier 2, Koen Devriendt 3, Marta Z Amorim 4, Nicole Revencu 5, Alexa Kidd 6, Mafalda Barbosa 7, Anne Turner 8, Janine Smith 9, Christina Oley 10, Alex Henderson 11, Ian M Hayes 12, Elizabeth M Thompson 13, Han G Brunner 1, Bert BA de Vries 1, Joris A Veltman 1 1 Department of Human Genetics, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, 6525GA Nijmegen, The Netherlands; 2 Centre for Medical Genetics, Antwerp University Hospital, Antwerp, Belgium; 3 Centre for Human Genetics, Leuven University Hospital, Leuven, Belgium; 4 Serviço de Genética de Coimbra, Hospital Pediátrico de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal; 5 Centre for Human Genetics, Cliniques Universitaires St Luc, Université Catholique de Louvain, Brussels, Belgium; 6 Canterbury Health Laboratories, Christchurch Hospital, New Zealand; 7 Centro de Genética Médica Doutor Jacinto Magalhães, Instituto Nacional de Saúde Doutor Ricardo Jorge, Porto, Portugal; 8 Department of Medical Genetics, Sydney Children's Hospital, Sydney, Australia; 9 Department of Clinical Genetics, The Children's Hospital at Westmead, Sydney, Australia; 10 Clinical Genetics Unit, Birmingham Women's Hospital, Birmingham, UK; 11 Institute of Human Genetics, Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK; 12 Northern Regional Genetics Service, Auckland, New Zealand; 13 SA Clinical Genetics Service, SA Pathology, Women's & Children's Hospital site, North Adelaide, South Australia. *These authors contributed equally to this work Correspondence to: Joris A Veltman, PhD Department of Human Genetics-855 Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Box 9101, 6500 HB Nijmegen; The Netherlands Phone: (+31) Fax: (+31) j.veltman@antrg.umcn.nl
2 Supplementary Table 1: Overview of exome-sequencing performance Patient Total reads Uniquely mapped reads Reads overlapping with targets Unique reads Mean coverage Number of called bases Patient 1 89,949,891 58,189,014 46,075,589 29,610, ,123,687 Patient 2 86,104,150 55,453,009 45,014,396 27,565, ,688,964 Patient 3 88,542,531 52,783,914 40,266,883 28,586, ,062,516 Patient 4 61,480,688 52,684,110 38,528,450 27,384, ,431,228
3 Supplementary Table 2: Overview of all variants identified by exome sequencing in 4 patients with Schinzel-Giedion syndrome Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Mean No. of genes with variants in all 4 samples Total variants called 22,916 22,602 22,152 19,528 21,800 4,735 Exonic + SpliceSites(SS) (+/- 2nts intronic) variants Non-synonymous (NS) + SS variants Unknown SNP variants (dbsnp130) Unknown variants (inhouse database) 12,196 12,255 11,796 10,498 11,686 3,331 5,556 5,618 5,427 4,802 5,351 1, Genes showing variants in at least 2 different genomic positions 2
4 Supplementary Table 3: Further clinical details of all 13 patients with Schinzel-Giedion syndrome Individuals ID Gender F M F M M F F F M F M M M Current Age yr 10m yr yrs - 3 yr 1 m - Age at death 4 yr 6 m 2 yr 3 m - 7 m 2 yr 6 m - 6 m 9 yr 3 m u - 3 m - 7 wks Craniofacial findings Head circumference <P3 u <P3 <P3 u P10 <P3 <P3 p25 P3 P10 <P3 P90 Large anterior fontanelle/sutures - + u Prominent forehead Bitemporal narrowing u Mid-face retraction Prominent eyes/shallow orbits Hypertelorism Deep groove under eyes u Abnormal helices and pinnae Low-set ears Short, upturned nose Macroglossia + u u Macrostomia - u u u - + Capillary malformation - u u Short neck Hypertrichosis - u Other upslanting palpebral fissures hyperconvex nails cutis marmorata upslanting palpebral fissures; cutis marmorata hypoplastic nipples; hyperconvex nails upslanting palpebral fissures hypoplastic toenails hypoplastic nipples Congenital anomalies Hydronephrosis/vesicoureteral reflux Genital abnormalities Cardiac defects Choanal stenosis u Post-axial polydactyly other hip dysplasia Laryngomala cia nodular growth in forearm of u origin club feet hydrocele pharyngeal incoordinati on; renal calculi Neurodevelopmental anomalies Developmental delay u* + u* Seizures Vision impairment u u u + - u Hearing impairment u u u + + u cleft palate tracheomalacia tracheomalacia; subglottic cysts; hydrocele
5 Brain MRI/CT Ventriculomegaly + u u u Underdeveloped corpus callosum/septum + + u u Cortical atrophy - + u - + u u + - u Choroid plexus cysts + u u + + u u - - u Other polymicrogyr ia cortical dysplasia dysmorphic ventricles Polymicrogyr ia Ophthalmological Abnormal fundoscopy u u - + u u u - - u + - u Alacrima with corneal hypoesthesia na u u u Progressive failure to thrive u u Radiological findings Skull Sclerotic base or mastoid u Wide occipital synchondrosis u u u u Steep base u u u u - u + u + + Wormian bones u u u - u - u - u Extremities Cortices: dense, thickened, undertubulated u u u u + u - u Hypoplastic distal phalanges u u u u + u + + Broad metaphyses u u u + - u + u Short first metacarpal u u u + u - + Chest Broad ribs u + - Abnormal (long/irregular) clavicles - u u + u + u - u Hypoplastic first rib(s) - u u u u u - u - + Pelvis Hypoplastic/underossified pubic bones + u - u + + u + u + u + u Other Tumors left kidney lesion of unknown origin u=unknown, PNET = primitive neuroectodermal tumor, * died shortly after birth Table adapted from Lehman et al. 1 bowed forearm bones; radio ulnar synostosis wide sutures Recurrent sacrococcyg eal PNET wide sutures; hydrocephaly congenital hip dislocation - accessory ribs cystic mass in spine PNET mild shortening humeri and femora
6 Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of fold coverage of the targeted exomes for all 4 samples. Figure legend: Comparison of fold coverage (x-axis) and percentage of covered targets (y-axis) for all 4 samples.
7 Supplementary Figure 2: Comparison of fold coverage of the SETBP1 gene for all 4 samples. Figure legend: a) Coverage histogram of read depth per basepair of exon 4 of SETBP1, displayed in hg18 version of the UCSC genome browser. b) SOLiD sequencing reads displayed for patient 1. Reads overlapping the mutation in exon 4 of SETBP1 (bp position g , hg18, NCBI36) show the heterozygous T>C change.
8 Supplementary Figure 3: Confirmation of de novo SETBP1 mutations by Sanger sequencing Figure legend: Confirmation and de novo proof by Sanger sequencing, shown for Patient 1-4 (A = affected), in comparison with their respective parents (M = mother, F = father).
9 Supplementary Note: Clinical samples All 13 Schinzel-Giedion syndrome patients fulfilled the diagnostic criteria suggested by Lehman et al. 1 (Table 1 and supplementary Table 3) and are from various parts of the world (Europe (n=7), New- Zealand (n=3), Australia (n=2) and the USA (n=1)). The DNA samples studied from 13 subjects and 94 normal control DNAs were isolated from peripheral blood leucocytes following standard techniques. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Center. Written informed consent to participate in the study was obtained for all patients as well as informed consent to publish clinical photos for cases 1, 3 and 4. Exome Sequencing DNA was obtained from peripheral blood of all patients. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre. For exome enrichment 3µg genomic DNA was required. We used a AB SOLiD optimized SureSelect human exome kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), which contained exonic sequences of ~ genes, covering a total of 37Mb genomic sequences, following the manufacturer's instructions. The enriched exome libraries were subsequently used for e-pcrs following manufacturer's instructions (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA), based on a library concentration of 0.5pM. For each sample one quad of a SOLiD sequencing slide (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used. Color space reads were mapped to the hg18 reference genome with the SOLiD bioscope software which utilizes an iterative mapping approach. Single nucleotide variants were subsequently called by the DiBayes algorithm 2 using the conservative default call stringency. Small insertions and deletions were detected using the SOLiD Small InDel Tool. Called SNP variants and indels were combined and annotated using a custom analysis pipeline. For prioritization we excluded known SNPs from dbsnp v1.30 and variants from our in-house database which consists of data from in-house targeted resequencing projects (6,595 variants), the 1000 genomes project ( as well as published data from various studies 3-5 (2,535,563 variants).
10 Sanger Sequencing validation Validation and de novo testing for the mutation hotspot was performed by classical Sanger sequencing using following primers. Additional 94 DNAs from normal controls were analyzed for the same amplicon. No. Name Sequence 1 SETBP1_exon4_F CTTCACCAGCAGCTATGCAC 2 SETBP1_exon4_R CGGTGGGAGATTCTGAACAC To exclude additional changes in all individuals with Schinzel-Giedion syndrome the following primers have been used to generate amplicons for all coding exons: No. Name Sequence 3 SETBP1_Exon1_Fw GGTAAGGAAAGGGGTGGG 4 SETBP1_Exon1_Rev CAAGAAAGAGACTCAAATCCATTG 5 SETBP1_Exon2.1_Fw GGGCCTCTGGAACTTAGATTG 6 SETBP1_Exon2.1_Rev CCGCCCTGAGCCTAGTTC 7 SETBP1_Exon2.2_Fw TTTGCTCTCCACTCCAGGAC 8 SETBP1_Exon2.2_Rev GACCCTAAGAAGTTGAGGATAAAATG 9 SETBP1_Exon3_Fw TGGTAAGTCCATTGCTGGTC 10 SETBP1_Exon3_Rev ATCCAAGGTTCGGGTTTCTG 11 SETBP1_Exon4.1_Fw CATGCTCATCTTTGTTTCTCTCTC 12 SETBP1_Exon4.1_Rev ATGCTTTCTGGGCATTCTTG 13 SETBP1_Exon4.2_Fw CCCCAGAACCACCTACGG 14 SETBP1_Exon4.2_Rev TTTGGATGCTGGATTTCTGG 15 SETBP1_Exon4.3_Fw CCCAGGAGGTGTGTCTAAGC 16 SETBP1_Exon4.3_Rev CTTTTGCCTTCAGAGCAACG 17 SETBP1_Exon4.4_Fw AGAAAGTTGGAAAGCTCGGC 18 SETBP1_Exon4.4_Rev GGACAGCGTGATTTCCTTTAG 19 SETBP1_Exon4.5_Fw ACACAGTGGAACCTGGAAGC 20 SETBP1_Exon4.5_Rev AGGCCTACCACGCTTCTTC
11 21 SETBP1_Exon4.6_Fw ACCACGAGAATCCATATCCC 22 SETBP1_Exon4.6_Rev CTTTGTCTGCGCTACTCAGC 23 SETBP1_Exon4.7_Fw CACAAGCATAAGCACAAGGAAG 24 SETBP1_Exon4.7_Rev ATGTGTCTGAGGTGCAAAGC 25 SETBP1_Exon5_Fw TGTTGTCTATCTTCCTGTTCCC 26 SETBP1_Exon5_Rev TCAACAGGCCATTCTCAGTG 27 SETBP1_Exon6.1_Fw TTGAAGGCACCTTGCATC 28 SETBP1_Exon6.1_Rev TTCACCTCCTCTTCCTGGG 29 SETBP1_Exon6.2_Fw GGTCATCCACATGGCCC 30 SETBP1_Exon6.2_Rev AATTTGCAGCTTTTCTCCCC 31 SETBP1_Exon6.1_Fw2 AATAATGCATCTTGGGCACG 32 SETBP1_Exon6.1_Rev2 TGTGTTTCCTCTTTCCGCC 33 SETBP1_Exon6.2_Fw2 CCACCCAGTTCGATGAGG 34 SETBP1_Exon6.2_Rev2 TCTGGAGAGAAGGGCGTG 35 SETBP1_Exon6.3_Fw GCACGGAGACATACCCATAGC 36 SETBP1_Exon6.3_Rev CTTCTGGAGAGAAGGGCGTG 37 SETBP1_Exon6.4_Fw AAAAGGAATAATGCATCTTGGG 38 SETBP1_Exon6.4_Rev AGAGAAGGGCGTGGGTGTC Parentage testing To confirm parentage in all 10 trios, 16 STR markers have been tested with the AmpFlSTR Identifiler PCR Amplification Kit (Applied Biosystems Inc., Foster City, CA, USA). Parentage was proven for all trios. Mutations interpretation The missense mutations have been tested for mutational effect by the amino acid substitution (AAS) prediction methods SIFT and PolyPhen prediction programs the prediction output is stated in Table 1. Amino acid conservation
12 Accession number of the SETBP1 protein sequences used for amino acid sequence comparison (Figure 1B) are as follows: Homo sapiens (NM_ ); Pan troglodytes (ENSPTRT ); Pongo pygmaeus (ENSPPYT ); Macaca mulatta (ENSMMUT ); Rattus norvegicus (ENSRNOT ); Mus musculus (ENSMUST ); Canis familiaris (ENSCAFT ); Felis catus (ENSFCAT ); Bos taurus (ENSBTAT ); Gallus gallus (ENSGALT ); Xenopus tropicalis (ENSXETT ). Web resources For variant visualization we used the IGV browser developed at: For in-house variant database: For genome browser annotations: For variant effect of identified mutations: Supplementary Reference List
13 1. Lehman,A.M. et al. Schinzel-Giedion syndrome: report of splenopancreatic fusion and proposed diagnostic criteria. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 146A, (2008). 2. Marth,G.T. et al. A general approach to single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery. Nat Genet. 23, (1999). 3. Ng,S.B. et al. Targeted capture and massively parallel sequencing of 12 human exomes. Nature 461, (2009). 4. Pushkarev,D., Neff,N.F., & Quake,S.R. Single-molecule sequencing of an individual human genome. Nat Biotechnol. 27, (2009). 5. Wang,J. et al. The diploid genome sequence of an Asian individual. Nature 456, (2008).
Disease gene identification with exome sequencing
 Disease gene identification with exome sequencing Christian Gilissen Dept. of Human Genetics Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre c.gilissen@antrg.umcn.nl Contents Infrastructure Exome sequencing
Disease gene identification with exome sequencing Christian Gilissen Dept. of Human Genetics Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre c.gilissen@antrg.umcn.nl Contents Infrastructure Exome sequencing
SeqScape Software Version 2.5 Comprehensive Analysis Solution for Resequencing Applications
 Product Bulletin Sequencing Software SeqScape Software Version 2.5 Comprehensive Analysis Solution for Resequencing Applications Comprehensive reference sequence handling Helps interpret the role of each
Product Bulletin Sequencing Software SeqScape Software Version 2.5 Comprehensive Analysis Solution for Resequencing Applications Comprehensive reference sequence handling Helps interpret the role of each
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing
 Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Next Generation Sequencing. mapping mutations in congenital heart disease
 Next Generation Sequencing mapping mutations in congenital heart disease AV Postma PhD Academic Medical Center Amsterdam, the Netherlands Overview talk Congenital heart disease and genetics Next generation
Next Generation Sequencing mapping mutations in congenital heart disease AV Postma PhD Academic Medical Center Amsterdam, the Netherlands Overview talk Congenital heart disease and genetics Next generation
Data Analysis for Ion Torrent Sequencing
 IFU022 v140202 Research Use Only Instructions For Use Part III Data Analysis for Ion Torrent Sequencing MANUFACTURER: Multiplicom N.V. Galileilaan 18 2845 Niel Belgium Revision date: August 21, 2014 Page
IFU022 v140202 Research Use Only Instructions For Use Part III Data Analysis for Ion Torrent Sequencing MANUFACTURER: Multiplicom N.V. Galileilaan 18 2845 Niel Belgium Revision date: August 21, 2014 Page
Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia
 Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia Introduction to Genome Browsing with Ensembl Ensembl The vast amount of information in biological databases today demands a way of organising and accessing
Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia Introduction to Genome Browsing with Ensembl Ensembl The vast amount of information in biological databases today demands a way of organising and accessing
Information leaflet. Centrum voor Medische Genetica. Version 1/20150504 Design by Ben Caljon, UZ Brussel. Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel
 Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Patient Information. Ordering Physician Information. Indication for Testing (REQUIRED)
 EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
Overview of Next Generation Sequencing platform technologies
 Overview of Next Generation Sequencing platform technologies Dr. Bernd Timmermann Next Generation Sequencing Core Facility Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Berlin, Germany Outline 1. Technologies
Overview of Next Generation Sequencing platform technologies Dr. Bernd Timmermann Next Generation Sequencing Core Facility Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Berlin, Germany Outline 1. Technologies
Targeted. sequencing solutions. Accurate, scalable, fast TARGETED
 Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
TWO NEW DNA BASED TESTS AVAILABLE FOR THE NSDTR
 TWO NEW DNA BASED TESTS AVAILABLE FOR THE NSDTR Written by Danika Bannasch DVM PhD; Professor Department of Population Health and Reproduction, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of California-Davis
TWO NEW DNA BASED TESTS AVAILABLE FOR THE NSDTR Written by Danika Bannasch DVM PhD; Professor Department of Population Health and Reproduction, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of California-Davis
The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics
 The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics The GS Junior System The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing on Your Benchtop Proven technology: Uses the same long
The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics The GS Junior System The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing on Your Benchtop Proven technology: Uses the same long
Nouvelles méthodes de diagnostic génétique des maladies mitochondriales
 Nouvelles méthodes de diagnostic génétique des maladies mitochondriales Mitochondrial disorders 1/8000 live birth Primary mitochondrial disorders Mutations in 80 nuclear genes Mutations in 13 mitochondrial
Nouvelles méthodes de diagnostic génétique des maladies mitochondriales Mitochondrial disorders 1/8000 live birth Primary mitochondrial disorders Mutations in 80 nuclear genes Mutations in 13 mitochondrial
LifeScope Genomic Analysis Software 2.5
 USER GUIDE LifeScope Genomic Analysis Software 2.5 Graphical User Interface DATA ANALYSIS METHODS AND INTERPRETATION Publication Part Number 4471877 Rev. A Revision Date November 2011 For Research Use
USER GUIDE LifeScope Genomic Analysis Software 2.5 Graphical User Interface DATA ANALYSIS METHODS AND INTERPRETATION Publication Part Number 4471877 Rev. A Revision Date November 2011 For Research Use
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
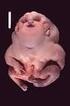 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Next generation DNA sequencing technologies. theory & prac-ce
 Next generation DNA sequencing technologies theory & prac-ce Outline Next- Genera-on sequencing (NGS) technologies overview NGS applica-ons NGS workflow: data collec-on and processing the exome sequencing
Next generation DNA sequencing technologies theory & prac-ce Outline Next- Genera-on sequencing (NGS) technologies overview NGS applica-ons NGS workflow: data collec-on and processing the exome sequencing
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA)
 Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
RETRIEVING SEQUENCE INFORMATION. Nucleotide sequence databases. Database search. Sequence alignment and comparison
 RETRIEVING SEQUENCE INFORMATION Nucleotide sequence databases Database search Sequence alignment and comparison Biological sequence databases Originally just a storage place for sequences. Currently the
RETRIEVING SEQUENCE INFORMATION Nucleotide sequence databases Database search Sequence alignment and comparison Biological sequence databases Originally just a storage place for sequences. Currently the
NGS and complex genetics
 NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
Breast cancer and the role of low penetrance alleles: a focus on ATM gene
 Modena 18-19 novembre 2010 Breast cancer and the role of low penetrance alleles: a focus on ATM gene Dr. Laura La Paglia Breast Cancer genetic Other BC susceptibility genes TP53 PTEN STK11 CHEK2 BRCA1
Modena 18-19 novembre 2010 Breast cancer and the role of low penetrance alleles: a focus on ATM gene Dr. Laura La Paglia Breast Cancer genetic Other BC susceptibility genes TP53 PTEN STK11 CHEK2 BRCA1
Leading Genomics. Diagnostic. Discove. Collab. harma. Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik
 Leading Genomics Diagnostic harma Discove Collab Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik Global leadership for using the genome to create better medicine WuXi NextCODE provides a uniquely proven and integrated
Leading Genomics Diagnostic harma Discove Collab Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik Global leadership for using the genome to create better medicine WuXi NextCODE provides a uniquely proven and integrated
Lecture 13: DNA Technology. DNA Sequencing. DNA Sequencing Genetic Markers - RFLPs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products of biotechnology
 Lecture 13: DNA Technology DNA Sequencing Genetic Markers - RFLPs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products of biotechnology DNA Sequencing determine order of nucleotides in a strand of DNA > bases = A,
Lecture 13: DNA Technology DNA Sequencing Genetic Markers - RFLPs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products of biotechnology DNA Sequencing determine order of nucleotides in a strand of DNA > bases = A,
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Chromosomal Abnormalities
 Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
IBGRL, NHSBT, Bristol
 IBGRL, NHSBT, Bristol Valuable to know D type of fetus Fetus D-positive: at risk pregnancy should be managed appropriately Fetus D-negative: not at risk no need for intervention RHD RHCE RHD* D 37 bp
IBGRL, NHSBT, Bristol Valuable to know D type of fetus Fetus D-positive: at risk pregnancy should be managed appropriately Fetus D-negative: not at risk no need for intervention RHD RHCE RHD* D 37 bp
Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform
 Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform NextCODE Health is bringing the full power of the world s largest and most successful genomics platform to everyday clinical care NextCODE
Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform NextCODE Health is bringing the full power of the world s largest and most successful genomics platform to everyday clinical care NextCODE
Tools for human molecular diagnosis. Joris Vermeesch
 Tools for human molecular diagnosis Joris Vermeesch Chromosome > DNA Genetic Code Effect of point mutations/polymorphisms Effect of deletions/insertions Effect of splicing mutations IVS2-2A>G Normal splice
Tools for human molecular diagnosis Joris Vermeesch Chromosome > DNA Genetic Code Effect of point mutations/polymorphisms Effect of deletions/insertions Effect of splicing mutations IVS2-2A>G Normal splice
Bioinformatics Resources at a Glance
 Bioinformatics Resources at a Glance A Note about FASTA Format There are MANY free bioinformatics tools available online. Bioinformaticists have developed a standard format for nucleotide and protein sequences
Bioinformatics Resources at a Glance A Note about FASTA Format There are MANY free bioinformatics tools available online. Bioinformaticists have developed a standard format for nucleotide and protein sequences
SOP 3 v2: web-based selection of oligonucleotide primer trios for genotyping of human and mouse polymorphisms
 W548 W552 Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, Vol. 33, Web Server issue doi:10.1093/nar/gki483 SOP 3 v2: web-based selection of oligonucleotide primer trios for genotyping of human and mouse polymorphisms Steven
W548 W552 Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, Vol. 33, Web Server issue doi:10.1093/nar/gki483 SOP 3 v2: web-based selection of oligonucleotide primer trios for genotyping of human and mouse polymorphisms Steven
IGV Hands-on Exercise: UI basics and data integration
 IGV Hands-on Exercise: UI basics and data integration Verhaak, R.G. et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA,
IGV Hands-on Exercise: UI basics and data integration Verhaak, R.G. et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA,
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
AS4.1 190509 Replaces 260806 Page 1 of 50 ATF. Software for. DNA Sequencing. Operators Manual. Assign-ATF is intended for Research Use Only (RUO):
 Replaces 260806 Page 1 of 50 ATF Software for DNA Sequencing Operators Manual Replaces 260806 Page 2 of 50 1 About ATF...5 1.1 Compatibility...5 1.1.1 Computer Operator Systems...5 1.1.2 DNA Sequencing
Replaces 260806 Page 1 of 50 ATF Software for DNA Sequencing Operators Manual Replaces 260806 Page 2 of 50 1 About ATF...5 1.1 Compatibility...5 1.1.1 Computer Operator Systems...5 1.1.2 DNA Sequencing
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
July 7th 2009 DNA sequencing
 July 7th 2009 DNA sequencing Overview Sequencing technologies Sequencing strategies Sample preparation Sequencing instruments at MPI EVA 2 x 5 x ABI 3730/3730xl 454 FLX Titanium Illumina Genome Analyzer
July 7th 2009 DNA sequencing Overview Sequencing technologies Sequencing strategies Sample preparation Sequencing instruments at MPI EVA 2 x 5 x ABI 3730/3730xl 454 FLX Titanium Illumina Genome Analyzer
BRCA1 / 2 testing by massive sequencing highlights, shadows or pitfalls?
 BRCA1 / 2 testing by massive sequencing highlights, shadows or pitfalls? Giovanni Luca Scaglione, PhD ------------------------ Laboratory of Clinical Molecular Diagnostics and Personalized Medicine, Institute
BRCA1 / 2 testing by massive sequencing highlights, shadows or pitfalls? Giovanni Luca Scaglione, PhD ------------------------ Laboratory of Clinical Molecular Diagnostics and Personalized Medicine, Institute
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
The NeurOmics team at a recent project meeting
 Introduction Welcome to the NeurOmics project newsletter. This is the second edition and comes after the project has been underway for just over a year. This means that whilst we still have lots of work
Introduction Welcome to the NeurOmics project newsletter. This is the second edition and comes after the project has been underway for just over a year. This means that whilst we still have lots of work
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
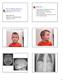 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Nazneen Aziz, PhD. Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation Program Office
 2013 Laboratory Accreditation Program Audioconferences and Webinars Implementing Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) as a Clinical Tool in the Laboratory Nazneen Aziz, PhD Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation
2013 Laboratory Accreditation Program Audioconferences and Webinars Implementing Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) as a Clinical Tool in the Laboratory Nazneen Aziz, PhD Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation
Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data
 Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data The Illumina TopHat Alignment and Cufflinks Assembly and Differential Expression apps make RNA data analysis accessible to any user, regardless
Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data The Illumina TopHat Alignment and Cufflinks Assembly and Differential Expression apps make RNA data analysis accessible to any user, regardless
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Just the Facts: A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
 1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
Automated DNA sequencing 20/12/2009. Next Generation Sequencing
 DNA sequencing the beginnings Ghent University (Fiers et al) pioneers sequencing first complete gene (1972) first complete genome (1976) Next Generation Sequencing Fred Sanger develops dideoxy sequencing
DNA sequencing the beginnings Ghent University (Fiers et al) pioneers sequencing first complete gene (1972) first complete genome (1976) Next Generation Sequencing Fred Sanger develops dideoxy sequencing
The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1
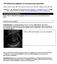 The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1 Werther Adrian Clavelli, MD 2, Silvia Susana Romaris de Clavelli, MD 2, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD 3 Adapted from The Ultrasound Detection of Chromosomal
The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies 1 Werther Adrian Clavelli, MD 2, Silvia Susana Romaris de Clavelli, MD 2, Philippe Jeanty, MD, PhD 3 Adapted from The Ultrasound Detection of Chromosomal
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS
 23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: wkc15@columbia.edu SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: wkc15@columbia.edu SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
Becker Muscular Dystrophy
 Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
 Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
 DIAGNOSIS, GENETICS AND PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS IN CHARGE Meg Hefner, M.S. Genetic Counselor and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Medical Genetics, St. Louis University School of Medicine, 1465
DIAGNOSIS, GENETICS AND PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS IN CHARGE Meg Hefner, M.S. Genetic Counselor and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Medical Genetics, St. Louis University School of Medicine, 1465
Plastic Surgery - Exceptional Referrals Patient Pathway April 2005
 Patient Presentation Patient seeks exceptional procedure Clinical assessment: Psychology criteria (see Appendix 1) Exceptional physical criteria (see Appendix 2) Patient meets criteria Patient does not
Patient Presentation Patient seeks exceptional procedure Clinical assessment: Psychology criteria (see Appendix 1) Exceptional physical criteria (see Appendix 2) Patient meets criteria Patient does not
Development of two Novel DNA Analysis methods to Improve Workflow Efficiency for Challenging Forensic Samples
 Development of two Novel DNA Analysis methods to Improve Workflow Efficiency for Challenging Forensic Samples Sudhir K. Sinha, Ph.D.*, Anne H. Montgomery, M.S., Gina Pineda, M.S., and Hiromi Brown, Ph.D.
Development of two Novel DNA Analysis methods to Improve Workflow Efficiency for Challenging Forensic Samples Sudhir K. Sinha, Ph.D.*, Anne H. Montgomery, M.S., Gina Pineda, M.S., and Hiromi Brown, Ph.D.
Core Facility Genomics
 Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation
 PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
Usher Syndrome Genetics
 Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
Exercises for the UCSC Genome Browser Introduction
 Exercises for the UCSC Genome Browser Introduction 1) Find out if the mouse Brca1 gene has non-synonymous SNPs, color them blue, and get external data about a codon-changing SNP. Skills: basic text search;
Exercises for the UCSC Genome Browser Introduction 1) Find out if the mouse Brca1 gene has non-synonymous SNPs, color them blue, and get external data about a codon-changing SNP. Skills: basic text search;
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Searching Nucleotide Databases
 Searching Nucleotide Databases 1 When we search a nucleic acid databases, Mascot always performs a 6 frame translation on the fly. That is, 3 reading frames from the forward strand and 3 reading frames
Searching Nucleotide Databases 1 When we search a nucleic acid databases, Mascot always performs a 6 frame translation on the fly. That is, 3 reading frames from the forward strand and 3 reading frames
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE
 AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
Milk protein genetic variation in Butana cattle
 Milk protein genetic variation in Butana cattle Ammar Said Ahmed Züchtungsbiologie und molekulare Genetik, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, Invalidenstraβe 42, 10115 Berlin, Deutschland 1 Outline Background
Milk protein genetic variation in Butana cattle Ammar Said Ahmed Züchtungsbiologie und molekulare Genetik, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, Invalidenstraβe 42, 10115 Berlin, Deutschland 1 Outline Background
Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research. March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage
 Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage Presentation Overview Core Technology Review Sequence Enrichment Application
Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage Presentation Overview Core Technology Review Sequence Enrichment Application
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING
 REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
All in a highly interactive, easy to use Windows environment.
 Database Providing: Accessibility Security Quality Control Review Variant Review Historical Library Variant Pathogenicity Prediction Laboratory Reporting Exportation to LIMS All in a highly interactive,
Database Providing: Accessibility Security Quality Control Review Variant Review Historical Library Variant Pathogenicity Prediction Laboratory Reporting Exportation to LIMS All in a highly interactive,
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis
 Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
Custom TaqMan Assays For New SNP Genotyping and Gene Expression Assays. Design and Ordering Guide
 Custom TaqMan Assays For New SNP Genotyping and Gene Expression Assays Design and Ordering Guide For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in
Custom TaqMan Assays For New SNP Genotyping and Gene Expression Assays Design and Ordering Guide For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in
Commonly Used STR Markers
 Commonly Used STR Markers Repeats Satellites 100 to 1000 bases repeated Minisatellites VNTR variable number tandem repeat 10 to 100 bases repeated Microsatellites STR short tandem repeat 2 to 6 bases repeated
Commonly Used STR Markers Repeats Satellites 100 to 1000 bases repeated Minisatellites VNTR variable number tandem repeat 10 to 100 bases repeated Microsatellites STR short tandem repeat 2 to 6 bases repeated
Human Genome Organization: An Update. Genome Organization: An Update
 Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice. Supplementary Guidelines
 Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice Next-generation Sequencing: Standardization of Clinical Testing (Nex-StoCT) Workgroup Principles and Guidelines Supplementary
Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice Next-generation Sequencing: Standardization of Clinical Testing (Nex-StoCT) Workgroup Principles and Guidelines Supplementary
G E N OM I C S S E RV I C ES
 GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology
 Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics
 G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
Please leave this space blank
 Please leave this space blank REQUEST FORM EXOME SEQUENCING Radboudumc 848 Human Genetics / Genome diagnostics Postbus 9101 6500 HB Nijmegen, The Netherlands Laboratory head: Dr. H. Yntema Tel : 0031-(0)24-3613799
Please leave this space blank REQUEST FORM EXOME SEQUENCING Radboudumc 848 Human Genetics / Genome diagnostics Postbus 9101 6500 HB Nijmegen, The Netherlands Laboratory head: Dr. H. Yntema Tel : 0031-(0)24-3613799
Development of a Workflow to Detect Sequence Variants in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes
 Your Innovative Research BRCA1 and BRCA2 Variant Detection Development of a Workflow to Detect Sequence Variants in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes The oncogenetics group in the DNA Diagnostics division of the
Your Innovative Research BRCA1 and BRCA2 Variant Detection Development of a Workflow to Detect Sequence Variants in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes The oncogenetics group in the DNA Diagnostics division of the
Services. Updated 05/31/2016
 Updated 05/31/2016 Services 1. Whole exome sequencing... 2 2. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)... 3 3. 16S rrna sequencing... 4 4. Customized gene panels... 5 5. RNA-Seq... 6 6. qpcr... 7 7. HLA typing...
Updated 05/31/2016 Services 1. Whole exome sequencing... 2 2. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)... 3 3. 16S rrna sequencing... 4 4. Customized gene panels... 5 5. RNA-Seq... 6 6. qpcr... 7 7. HLA typing...
Bioruptor NGS: Unbiased DNA shearing for Next-Generation Sequencing
 STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAAC GTGCAC GTGAAC Wouter Coppieters Head of the genomics core facility GIGA center, University of Liège Bioruptor NGS: Unbiased DNA
STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAAC GTGCAC GTGAAC Wouter Coppieters Head of the genomics core facility GIGA center, University of Liège Bioruptor NGS: Unbiased DNA
Innovations in Molecular Epidemiology
 Innovations in Molecular Epidemiology Molecular Epidemiology Measure current rates of active transmission Determine whether recurrent tuberculosis is attributable to exogenous reinfection Determine whether
Innovations in Molecular Epidemiology Molecular Epidemiology Measure current rates of active transmission Determine whether recurrent tuberculosis is attributable to exogenous reinfection Determine whether
A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing
 doi:1.138/nature9534 A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing The 1 Genomes Project Consortium* The 1 Genomes Project aims to provide a deep characterization of human genome sequence
doi:1.138/nature9534 A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing The 1 Genomes Project Consortium* The 1 Genomes Project aims to provide a deep characterization of human genome sequence
Human Genome and Human Genome Project. Louxin Zhang
 Human Genome and Human Genome Project Louxin Zhang A Primer to Genomics Cells are the fundamental working units of every living systems. DNA is made of 4 nucleotide bases. The DNA sequence is the particular
Human Genome and Human Genome Project Louxin Zhang A Primer to Genomics Cells are the fundamental working units of every living systems. DNA is made of 4 nucleotide bases. The DNA sequence is the particular
A Primer of Genome Science THIRD
 A Primer of Genome Science THIRD EDITION GREG GIBSON-SPENCER V. MUSE North Carolina State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts USA Contents Preface xi 1 Genome Projects:
A Primer of Genome Science THIRD EDITION GREG GIBSON-SPENCER V. MUSE North Carolina State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts USA Contents Preface xi 1 Genome Projects:
NOVEL FOXC2 MISSENSE MUTATION IDENTIFIED IN PATIENT WITH LYMPHEDEMA-DISTICHIASIS SYNDROME AND REVIEW
 98 Lymphology 41 (2008) 98-102 NOVEL FOXC2 MISSENSE MUTATION IDENTIFIED IN PATIENT WITH LYMPHEDEMA-DISTICHIASIS SYNDROME AND REVIEW M.T. Dellinger, K. Thome, M.J. Bernas, R.P. Erickson, M.H. Witte Departments
98 Lymphology 41 (2008) 98-102 NOVEL FOXC2 MISSENSE MUTATION IDENTIFIED IN PATIENT WITH LYMPHEDEMA-DISTICHIASIS SYNDROME AND REVIEW M.T. Dellinger, K. Thome, M.J. Bernas, R.P. Erickson, M.H. Witte Departments
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005
 Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle GmbH German Accreditation Body Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Period of validity: 26.03.2012 to 25.03.2017
Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle GmbH German Accreditation Body Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Period of validity: 26.03.2012 to 25.03.2017
Next Generation Mendelian Genetics by Exome Sequencing. Jay Shendure, MD, PhD Dept. of Genome Sciences University of Washington
 Next Generation Mendelian Genetics by Exome Sequencing Jay Shendure, MD, PhD Dept. of Genome Sciences University of Washington Second generation sequencing 10,000-fold drop in the cost of DNA sequencing
Next Generation Mendelian Genetics by Exome Sequencing Jay Shendure, MD, PhD Dept. of Genome Sciences University of Washington Second generation sequencing 10,000-fold drop in the cost of DNA sequencing
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing
 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics ACMG Practice Guidelines ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing Heidi L. Rehm, PhD 1,2, Sherri J. Bale, PhD 3, Pinar Bayrak-Toydemir,
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics ACMG Practice Guidelines ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing Heidi L. Rehm, PhD 1,2, Sherri J. Bale, PhD 3, Pinar Bayrak-Toydemir,
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making. Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina
 Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing?
 Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
New Technologies for Sensitive, Low-Input RNA-Seq. Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
 New Technologies for Sensitive, Low-Input RNA-Seq Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Outline Introduction Single-Cell-Capable mrna-seq Using SMART Technology SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for the Fluidigm C 1 System
New Technologies for Sensitive, Low-Input RNA-Seq Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Outline Introduction Single-Cell-Capable mrna-seq Using SMART Technology SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for the Fluidigm C 1 System
Submitting Data to ISCA and NCBI
 Submitting Data to ISCA and NCBI created by Tim Hefferon last updated August 28, 2012 Dear ISCA Submitter, This brief guide is intended to make the submission of your copy number variation and clinical
Submitting Data to ISCA and NCBI created by Tim Hefferon last updated August 28, 2012 Dear ISCA Submitter, This brief guide is intended to make the submission of your copy number variation and clinical
mygenomatix - secure cloud for NGS analysis
 mygenomatix Speed. Quality. Results. mygenomatix - secure cloud for NGS analysis background information & contents 2011 Genomatix Software GmbH Bayerstr. 85a 80335 Munich Germany info@genomatix.de www.genomatix.de
mygenomatix Speed. Quality. Results. mygenomatix - secure cloud for NGS analysis background information & contents 2011 Genomatix Software GmbH Bayerstr. 85a 80335 Munich Germany info@genomatix.de www.genomatix.de
Next Generation Sequencing
 Next Generation Sequencing Technology and applications 10/1/2015 Jeroen Van Houdt - Genomics Core - KU Leuven - UZ Leuven 1 Landmarks in DNA sequencing 1953 Discovery of DNA double helix structure 1977
Next Generation Sequencing Technology and applications 10/1/2015 Jeroen Van Houdt - Genomics Core - KU Leuven - UZ Leuven 1 Landmarks in DNA sequencing 1953 Discovery of DNA double helix structure 1977
Mitochondrial DNA Analysis
 Mitochondrial DNA Analysis Lineage Markers Lineage markers are passed down from generation to generation without changing Except for rare mutation events They can help determine the lineage (family tree)
Mitochondrial DNA Analysis Lineage Markers Lineage markers are passed down from generation to generation without changing Except for rare mutation events They can help determine the lineage (family tree)
Introduction to genetic testing and pharmacogenomics
 Introduction to genetic testing and pharmacogenomics Cecile Janssens Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, the Netherlands (a.janssens@erasmusmc.nl) Genetic prediction of monogenic diseases
Introduction to genetic testing and pharmacogenomics Cecile Janssens Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, the Netherlands (a.janssens@erasmusmc.nl) Genetic prediction of monogenic diseases
Developmental Disorders
 Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Introduction to NGS data analysis
 Introduction to NGS data analysis Jeroen F. J. Laros Leiden Genome Technology Center Department of Human Genetics Center for Human and Clinical Genetics Sequencing Illumina platforms Characteristics: High
Introduction to NGS data analysis Jeroen F. J. Laros Leiden Genome Technology Center Department of Human Genetics Center for Human and Clinical Genetics Sequencing Illumina platforms Characteristics: High
Why does my child have a hearing loss?
 Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Trisomies 13 and 18. -Maternal age. (Patau and Edward s syndrome)
 Trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edward s syndrome) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is the commonest chromosomal disorder at birth, and has been considered in detail in previous annual reports 23. Other relatively
Trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edward s syndrome) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is the commonest chromosomal disorder at birth, and has been considered in detail in previous annual reports 23. Other relatively
Introduction to Bioinformatics 3. DNA editing and contig assembly
 Introduction to Bioinformatics 3. DNA editing and contig assembly Benjamin F. Matthews United States Department of Agriculture Soybean Genomics and Improvement Laboratory Beltsville, MD 20708 matthewb@ba.ars.usda.gov
Introduction to Bioinformatics 3. DNA editing and contig assembly Benjamin F. Matthews United States Department of Agriculture Soybean Genomics and Improvement Laboratory Beltsville, MD 20708 matthewb@ba.ars.usda.gov
Go where the biology takes you. Genome Analyzer IIx Genome Analyzer IIe
 Go where the biology takes you. Genome Analyzer IIx Genome Analyzer IIe Go where the biology takes you. To published results faster With proven scalability To the forefront of discovery To limitless applications
Go where the biology takes you. Genome Analyzer IIx Genome Analyzer IIe Go where the biology takes you. To published results faster With proven scalability To the forefront of discovery To limitless applications
Frequently Asked Questions Next Generation Sequencing
 Frequently Asked Questions Next Generation Sequencing Import These Frequently Asked Questions for Next Generation Sequencing are some of the more common questions our customers ask. Questions are divided
Frequently Asked Questions Next Generation Sequencing Import These Frequently Asked Questions for Next Generation Sequencing are some of the more common questions our customers ask. Questions are divided
Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations Disclaimer Coding Information References Policy History
 Original Issue Date (Created): 4/1/2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 11/24/2015 Effective Date: 2/1/2016 Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations
Original Issue Date (Created): 4/1/2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 11/24/2015 Effective Date: 2/1/2016 Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations
Supplementary Appendix. Exome sequencing improves genetic diagnosis of structural fetal. abnormalities revealed by ultrasound
 Supplementary Appendix Exome sequencing improves genetic diagnosis of structural fetal abnormalities revealed by ultrasound Keren J. Carss 1, Sarah C. Hillman 2, Vijaya Parthiban 1, Dominic J. cullan 3,
Supplementary Appendix Exome sequencing improves genetic diagnosis of structural fetal abnormalities revealed by ultrasound Keren J. Carss 1, Sarah C. Hillman 2, Vijaya Parthiban 1, Dominic J. cullan 3,
